Research progress of acquisition, pointing and tracking in optical wireless communication system
-
摘要:
无线光通信是指以光波作为载体在自由空间中传递信息的技术,具有带宽高、成本低和安全性高等优点。捕获、瞄准和跟踪(acquisition, pointing and tracking, APT)系统是建立无线光通信系统的前提,简单、可靠、动态性能好的APT系统可以克服由机械平台震动及外界环境变化对无线光通信系统的影响。因此,需要对APT系统进行较为深入的理论和实验研究,从而设计出一种适合无线光通信的捕获、瞄准和跟踪方法。本文分析了国内外在捕获、瞄准、跟踪方面的研究成果,同时介绍了西安理工大学在自动瞄准方面所做的工作,主要包括初始捕获系统、非共视轴控制系统、光束检测系统等方面的进展,以及1.3 km、5.2 km、10.2 km、100 km距离链路的外场实验,验证了APT系统的有效性。最后展望了无线光通信中APT的发展。
Abstract:Optical wireless communication refers to the technology of transmitting information in free space using light waves as a carrier, which has the advantages of high bandwidth, low cost, and high security. The acquisition, pointing, and tracking (APT) system is the premise of establishing a wireless optical communication system. A simple, reliable, and dynamic APT system can overcome the impact of mechanical platform vibration and external environment changes on the wireless optical communication system. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct in-depth theoretical and experimental research on the APT system, so as to design a capture, aiming, and tracking method suitable for wireless optical communication. This paper analyzes the domestic and foreign research achievements in capturing, aiming, and tracking, and introduces the work done by Xi'an University of Technology in the field of automatic aiming. It mainly includes the progress of initial acquisition system, non-common visual axis control system, beam detection system, etc. At the same time, the field experiments of 1.3 km, 5.2 km, 10.2 km, and 100 km distance links are introduced to verify the effectiveness of the APT system. Finally, the development of APT in wireless optical communication is prospected.
-
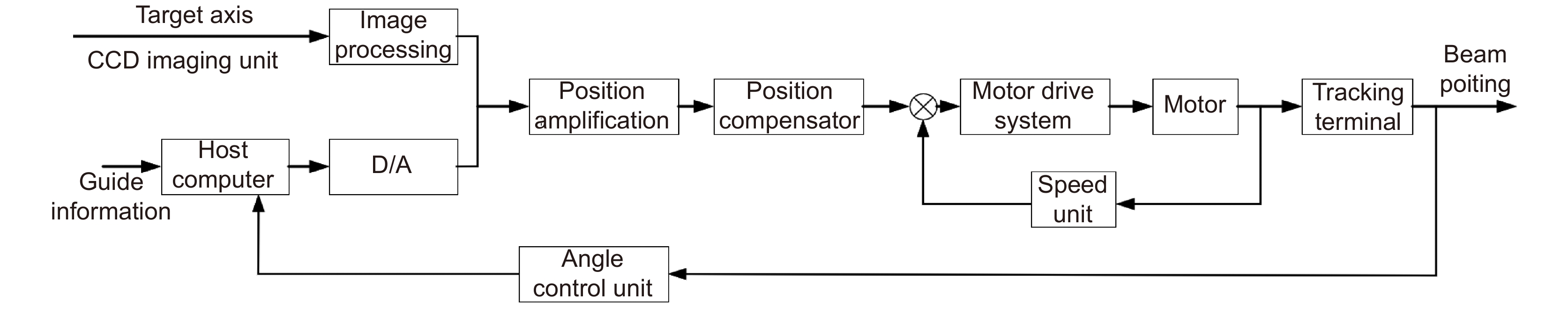
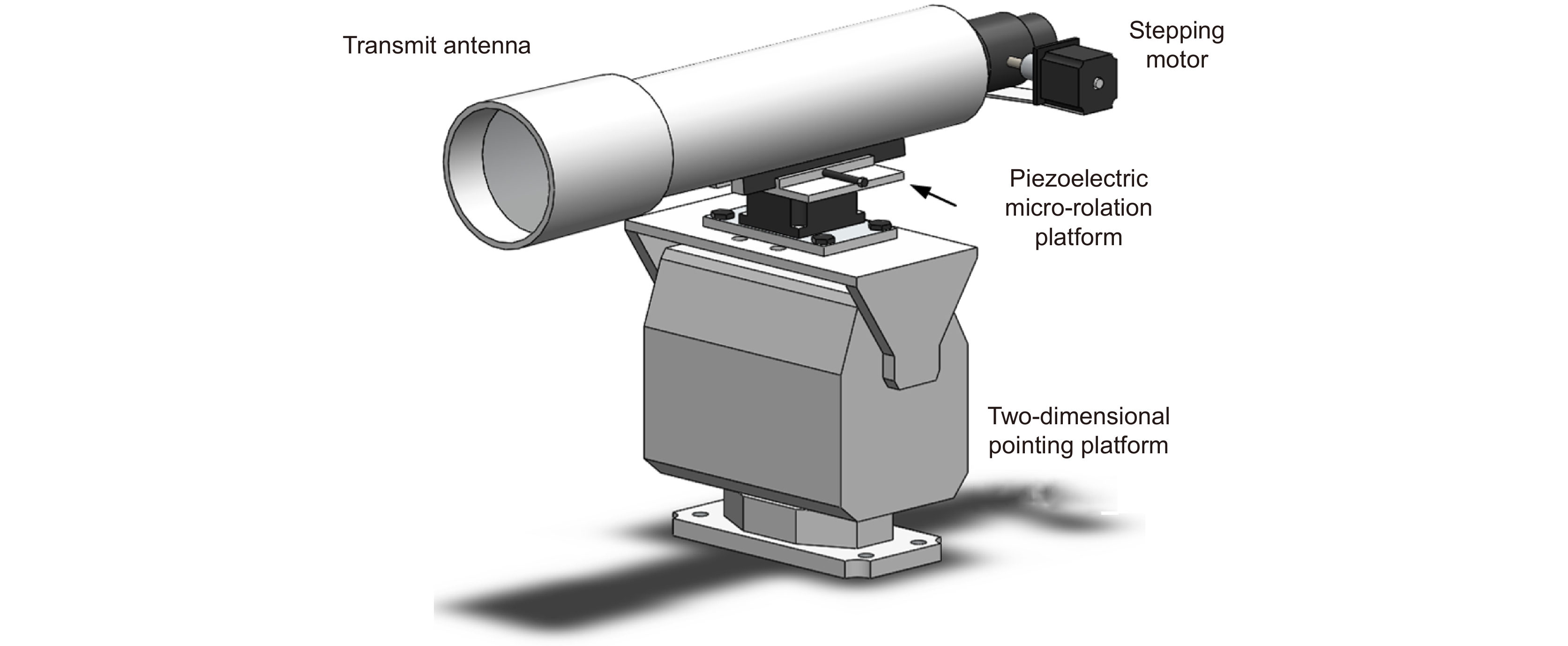
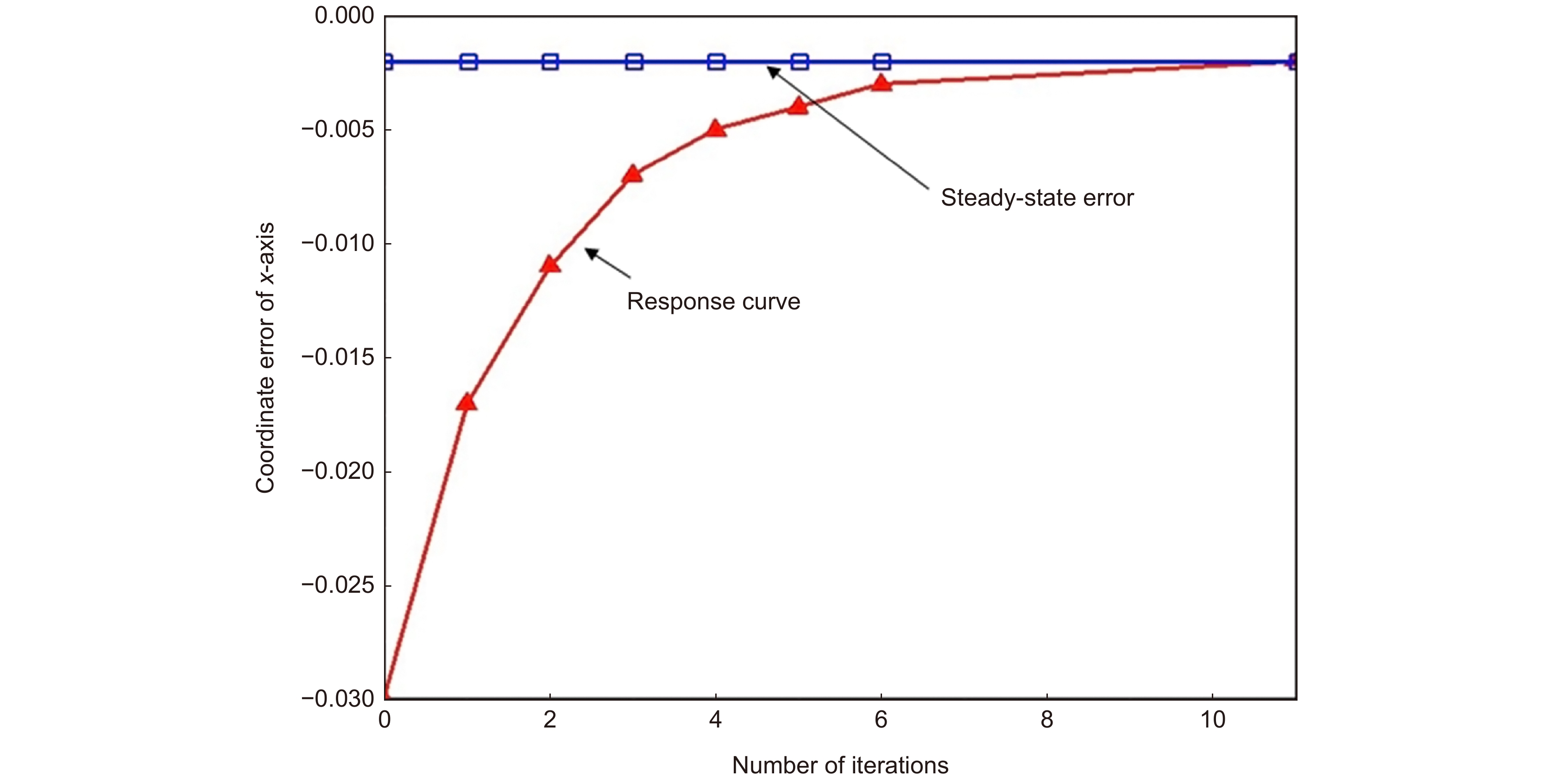
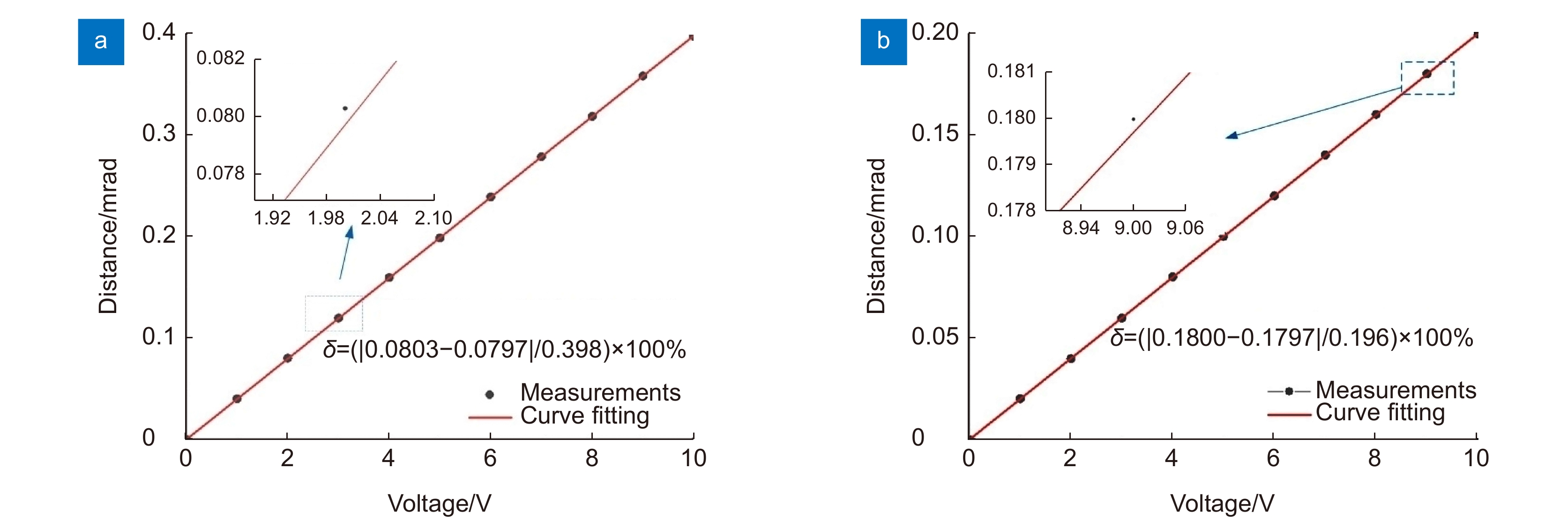
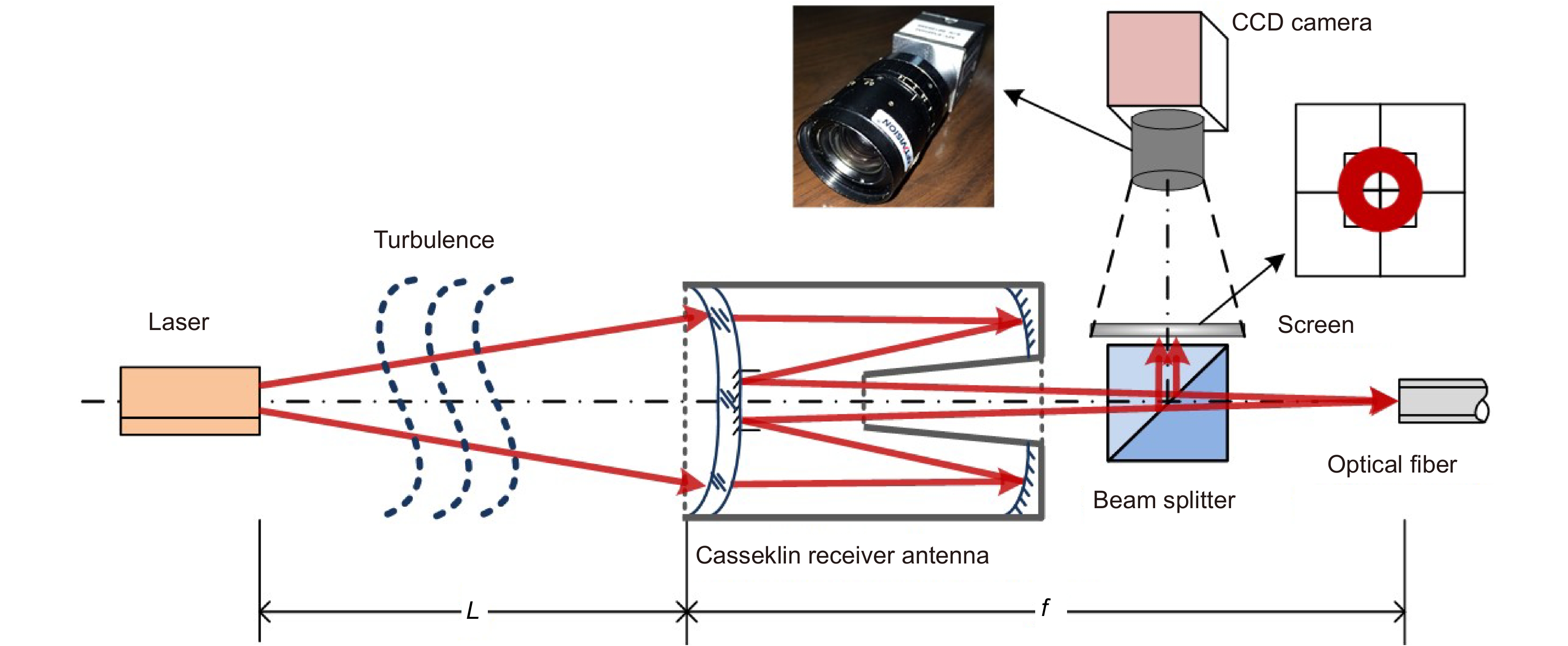
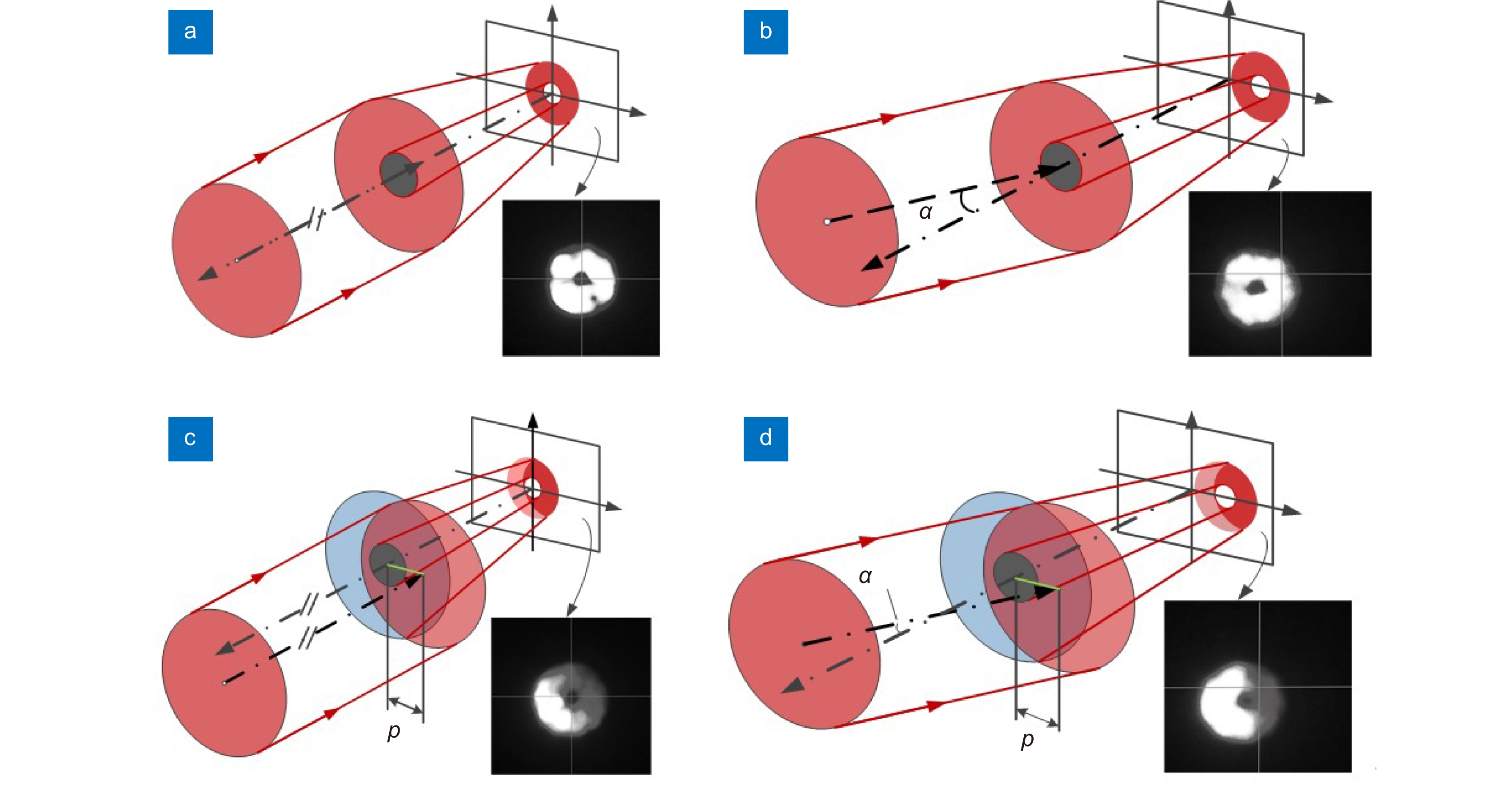
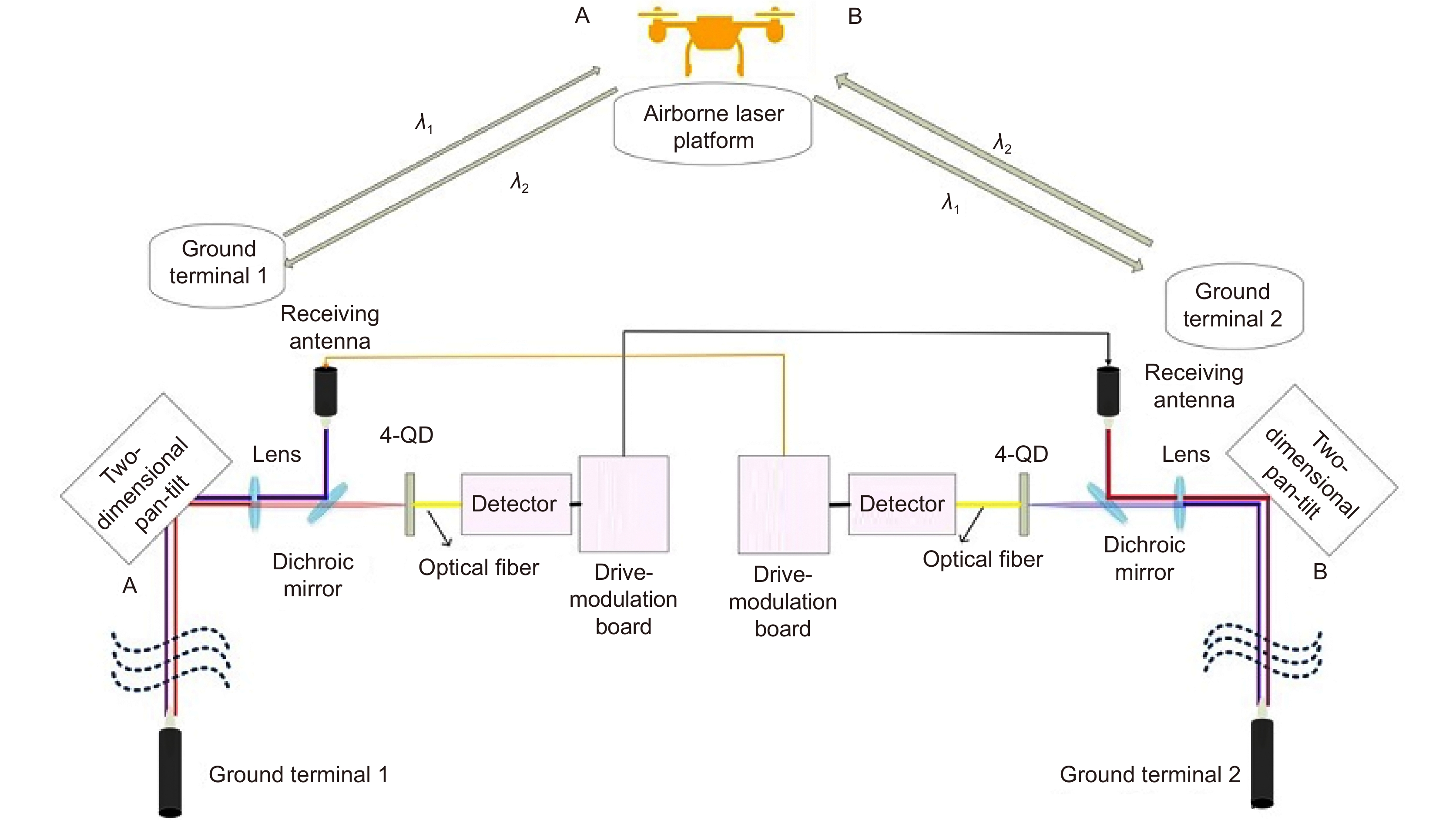
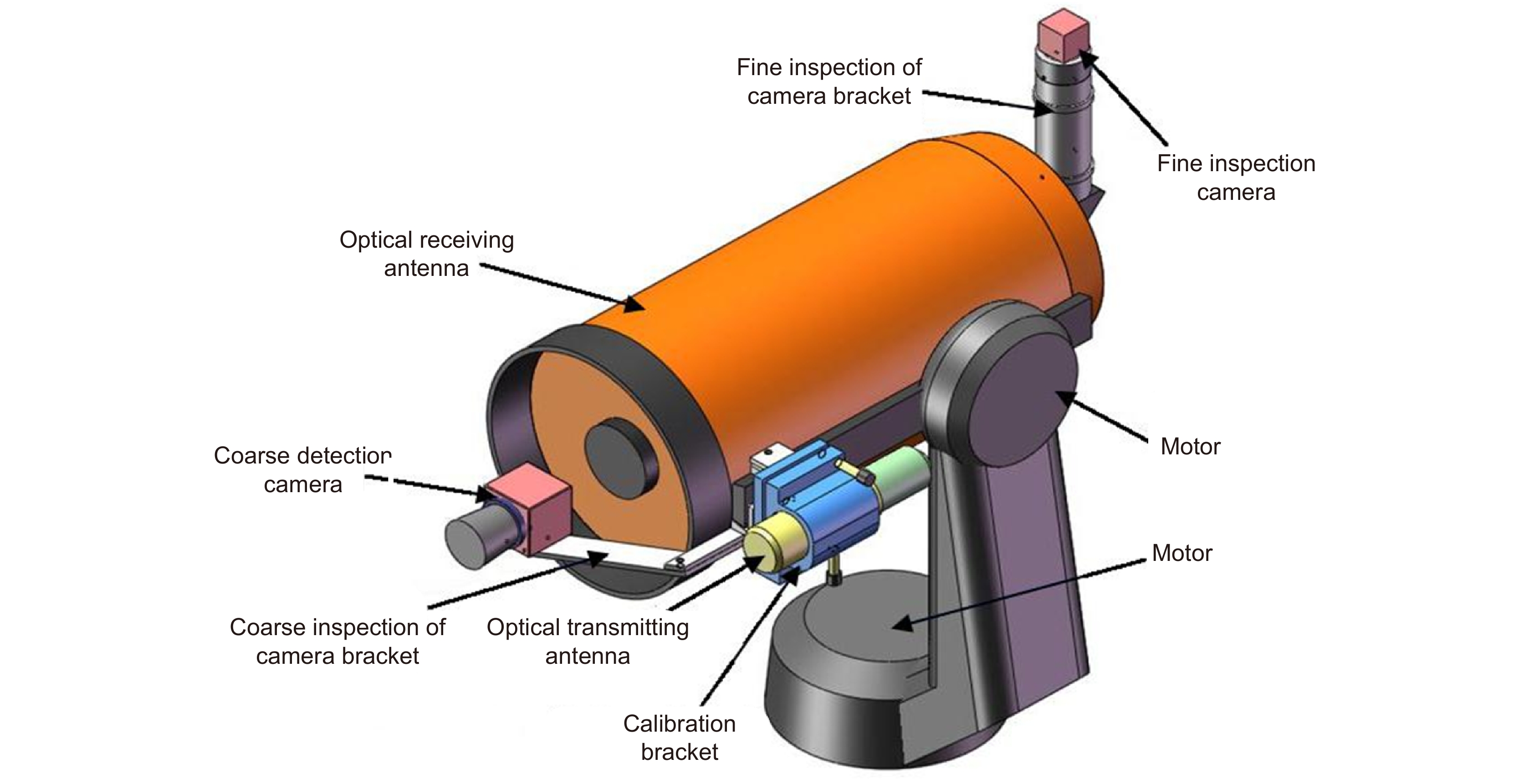
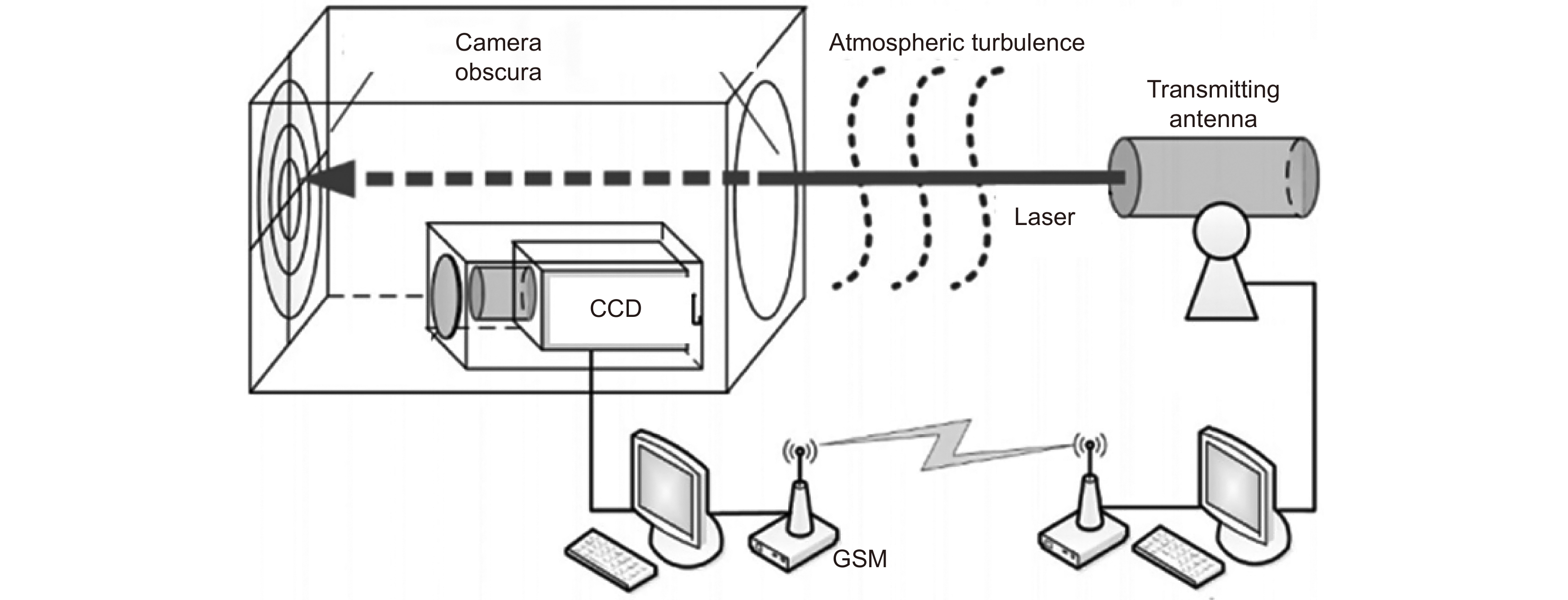
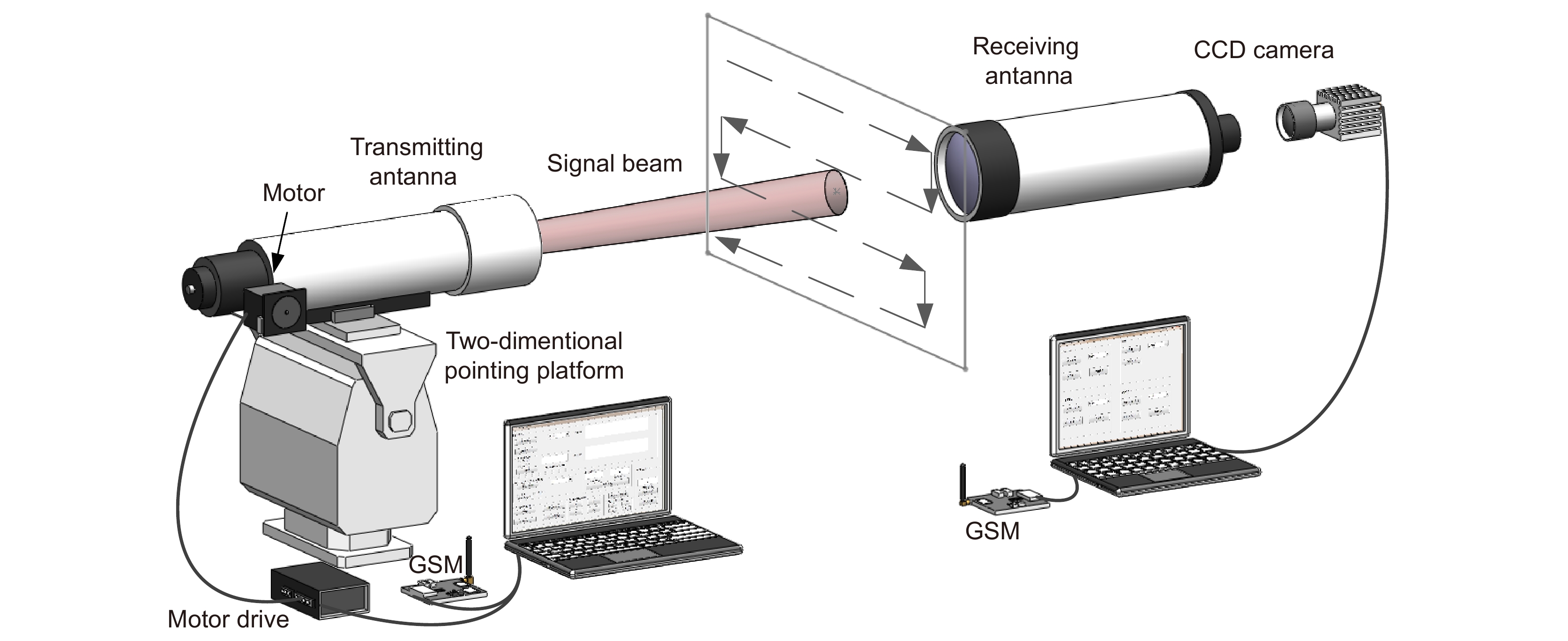
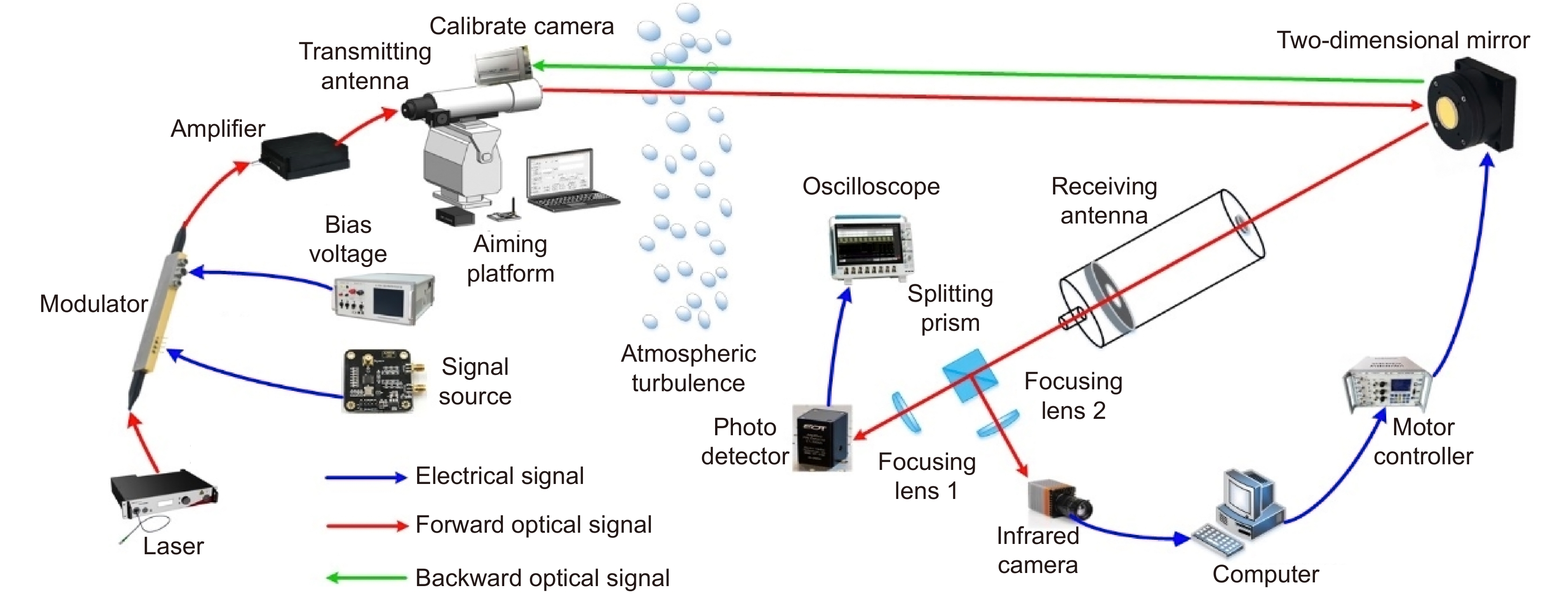
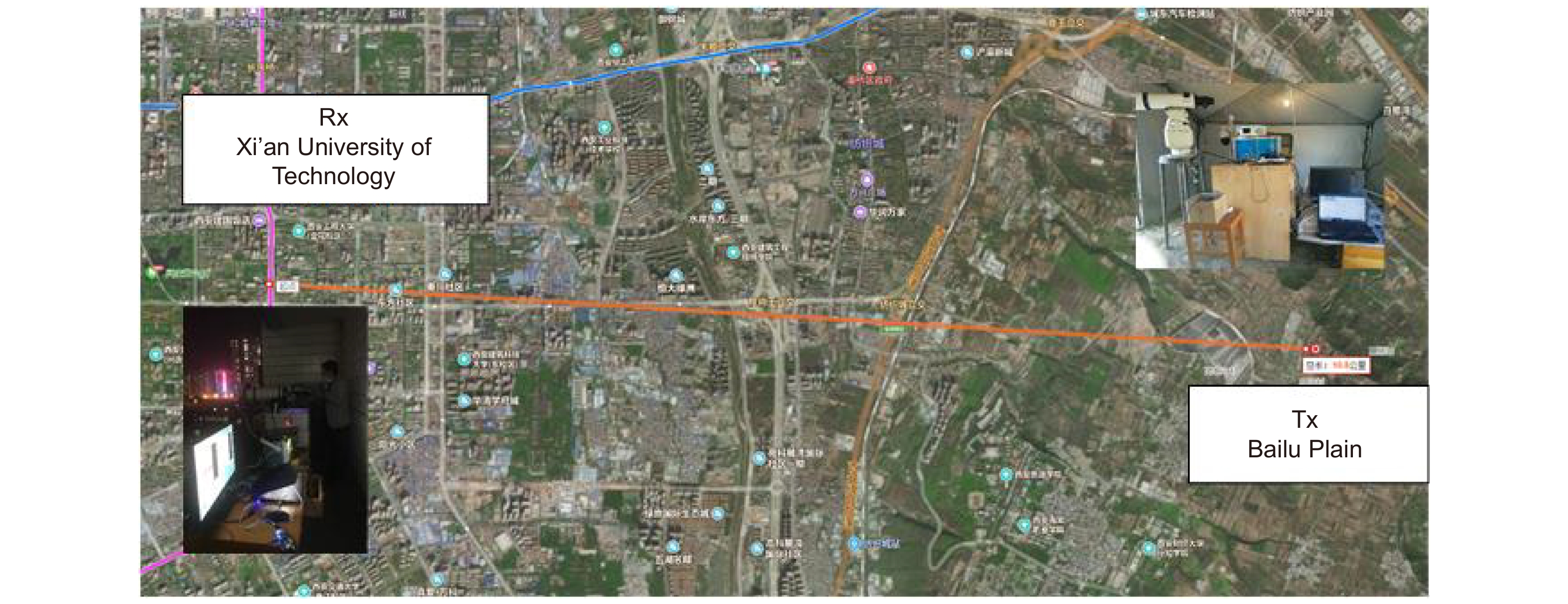
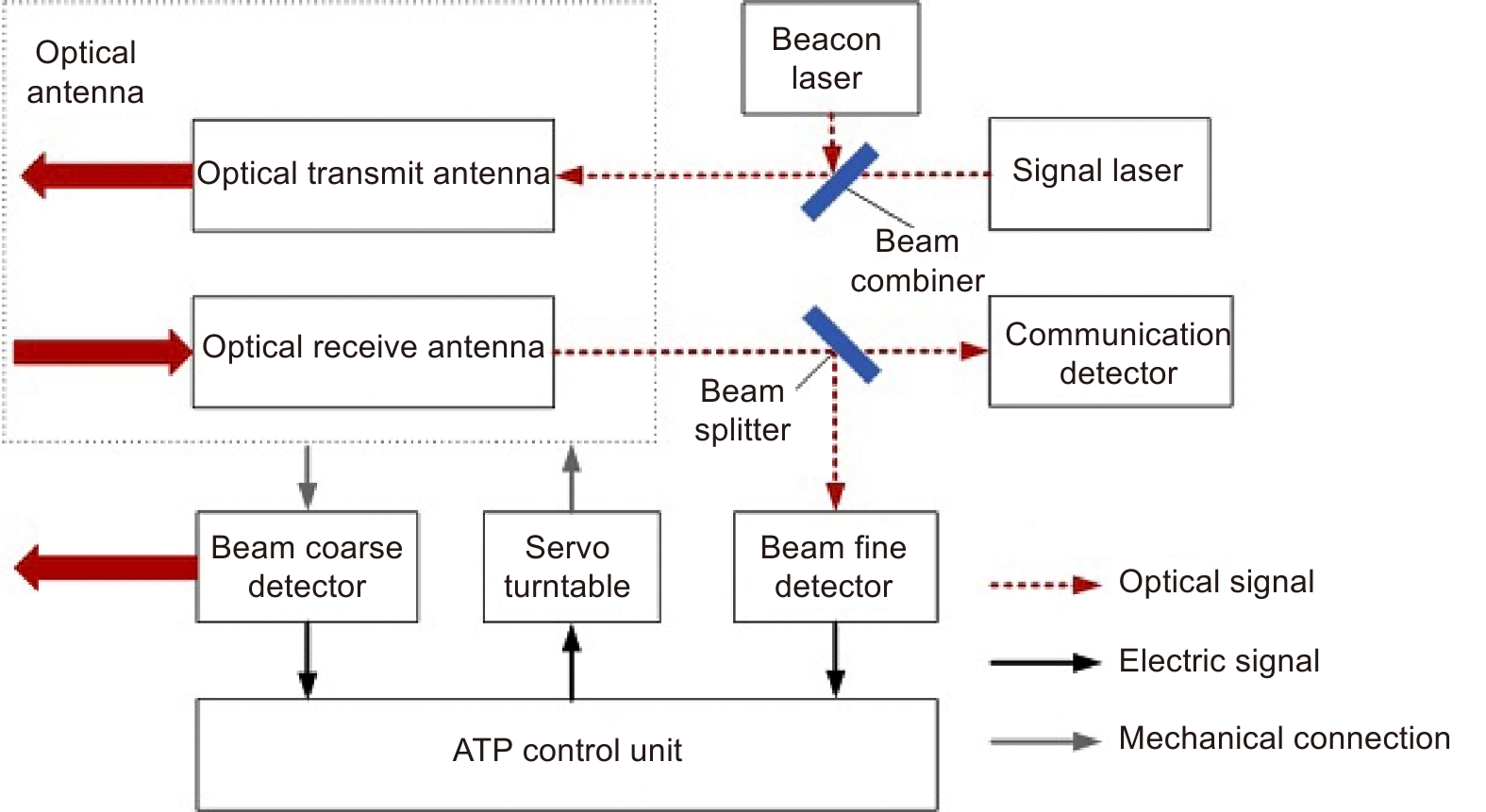
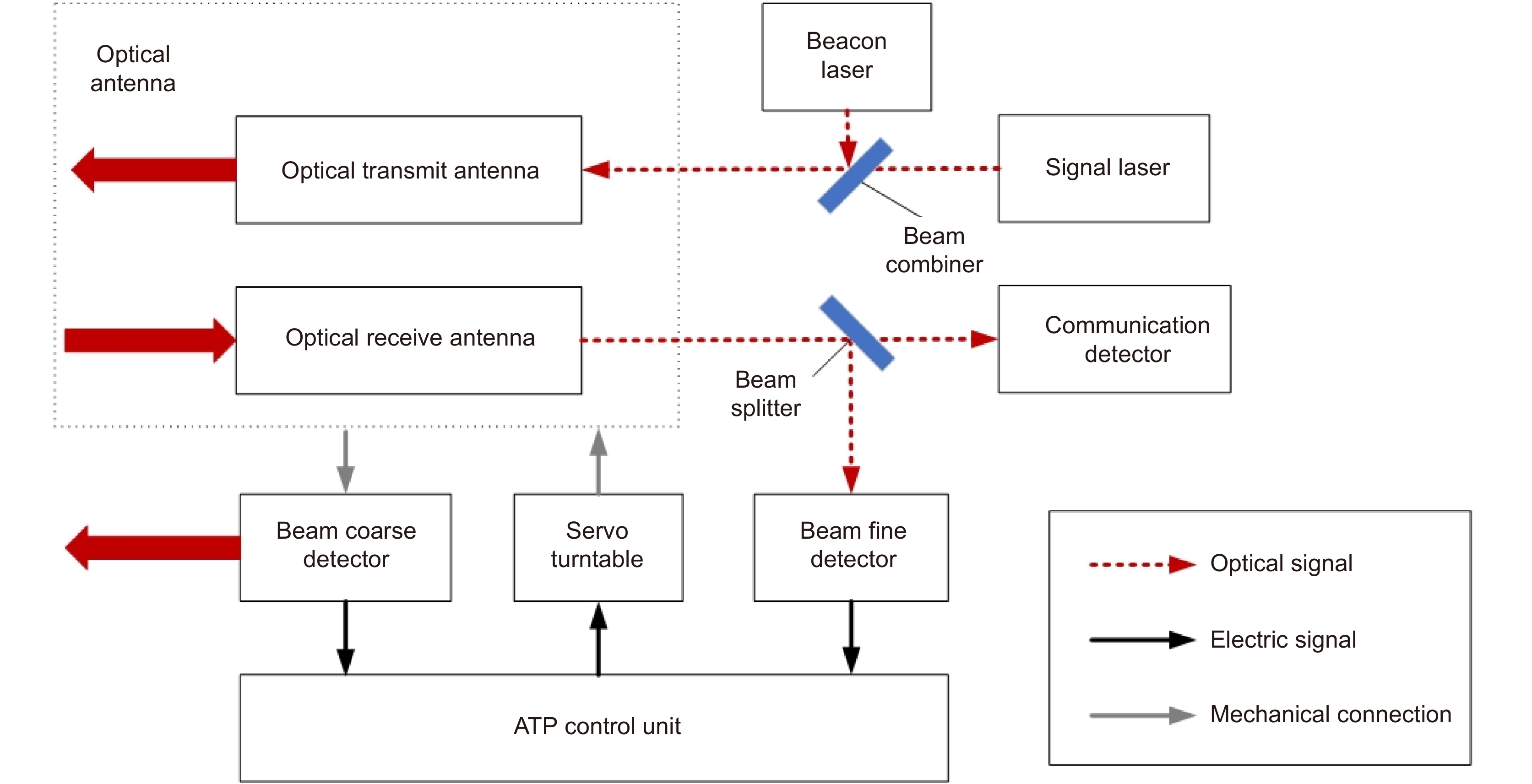
Overview: Wireless optical communication refers to the technology of transmitting information in free space using light beams as carriers, which has the advantages of high bandwidth, low cost, and high security. Due to factors such as narrow signal beam and long transmission distance, it is difficult to establish and maintain a wireless optical communication link. Therefore, an acquisition, targeting, and tracking system needs to be established to prevent the communication link from being interrupted. In the wireless optical communication system, the optical components on the two platforms carrying the transmitter and the receiver are required to be coaxial in real time, and this process is usually called automatic aiming. In order to maintain the real-time aiming of the transceiver boresight of both transceivers, it is necessary to design a fast and high-precision APT system. A typical wireless optical communication APT system is shown in Figure 1. Liu Changcheng established and analyzed the simulation model in the APT system in atmospheric laser communication, and designed an automatic beam capture system; Hu Qidi designed a beacon light spot detection scheme using CCD; Yang Peisong proposed a coaxial aiming detection method, and designed the aiming control system and tracking system according to the method, and carried out field experiments; Zhao Qi designed an initial capture system and conducted a 1.3 km field experiment; Xu Wei designed a light spot detection system and proposed a corresponding image processing algorithm; Li Shiyan proposed an optical axis aiming scheme, which can effectively improve the detection accuracy and aiming accuracy of the system; Yan Xi designed a spot tracking system and conducted a 5.2 km field tracking experiment. The experimental results show that the tracking accuracy of the system can reach 5.4 μrad; Jing Yongkang designed a light spot image detection method, and conducted a 100 km laser communication experiment on this basis; Zhang Pu embedded a high-precision actuator in the APT system to achieve high-precision aiming and tracking, designed a focusing system and conducted field experiments of 10.2 km and 100 km. Liang Hanli designed an APT system that can be mounted on UAVs and conducted an airborne laser communication experiment through a simulated airborne experimental platform, and its tracking accuracy can reach 2.42 μrad; Ke Xizheng, Yang Shangjun and others proposed a fast aiming method. The method does not need to feed back the control signal from the receiving end to the transmitting end, and can complete the establishment of the uplink and the downlink at the same time. And carried out 1.3 km and 10.3 km field experiments to verify the method. This paper systematically analyzes the development and application of the APT system in wireless optical communication and introduces the research progress and achievements of Xi'an University of Technology in this field. Including the experimental analysis and verification of the performance of the designed initial capture system, compound axis control system and beam detection system Improvements have increased the effectiveness and reliability of the APT system.
-

-
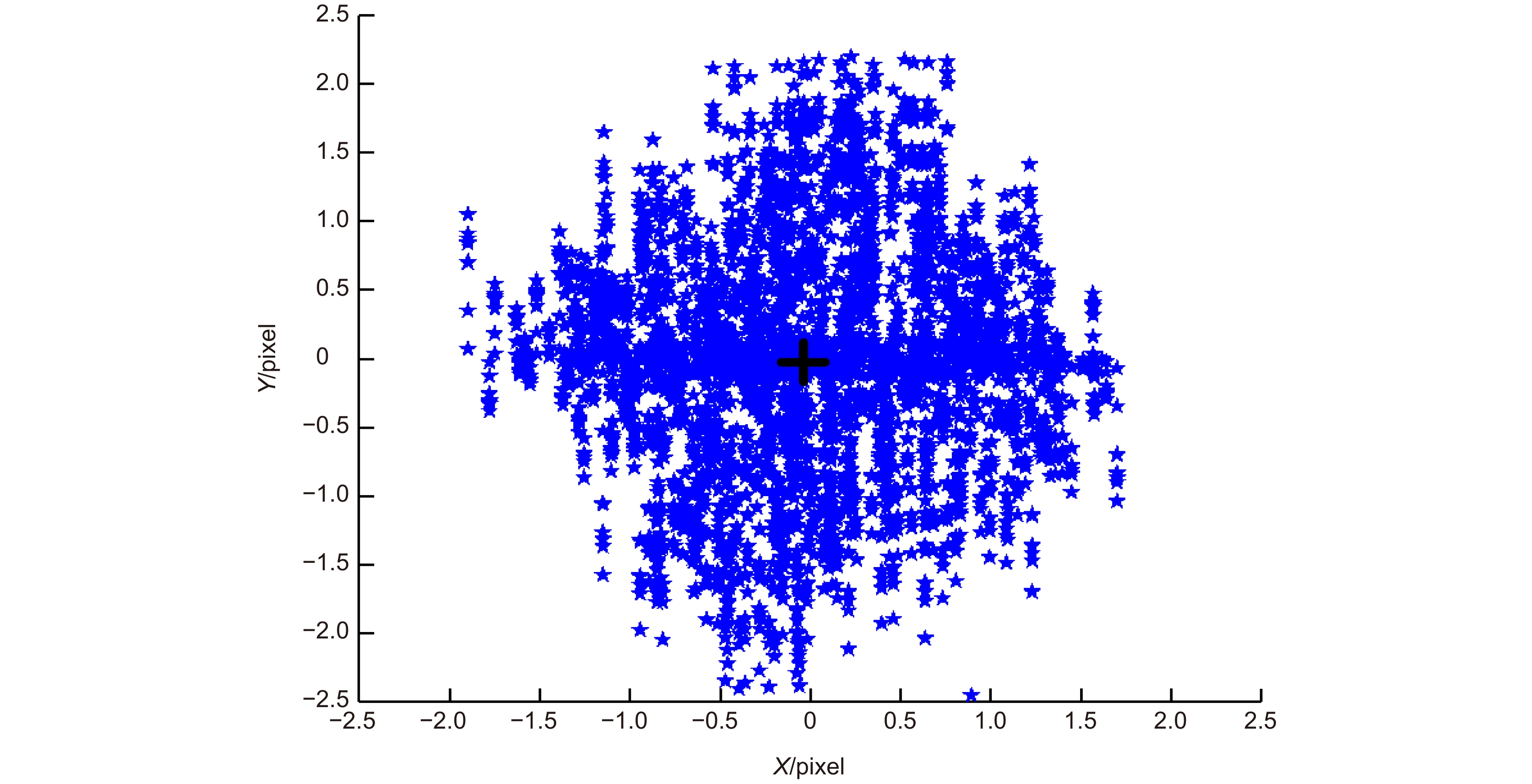
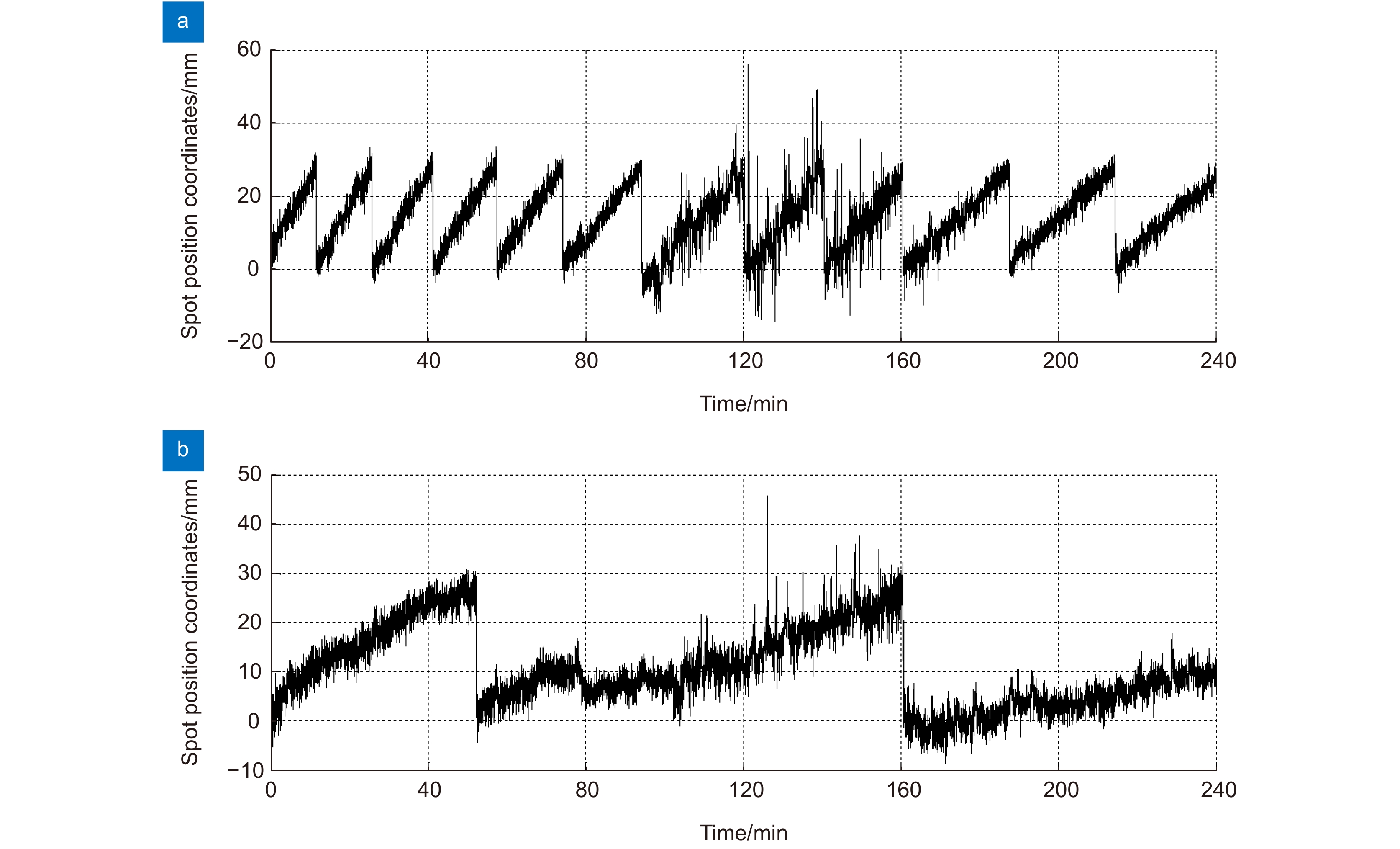
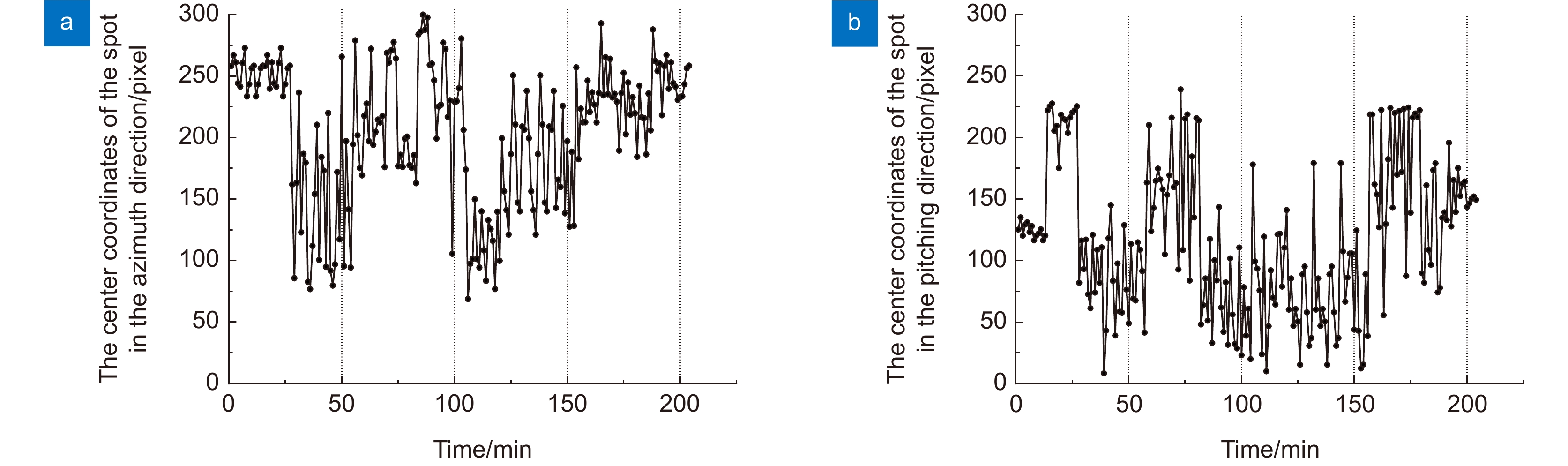
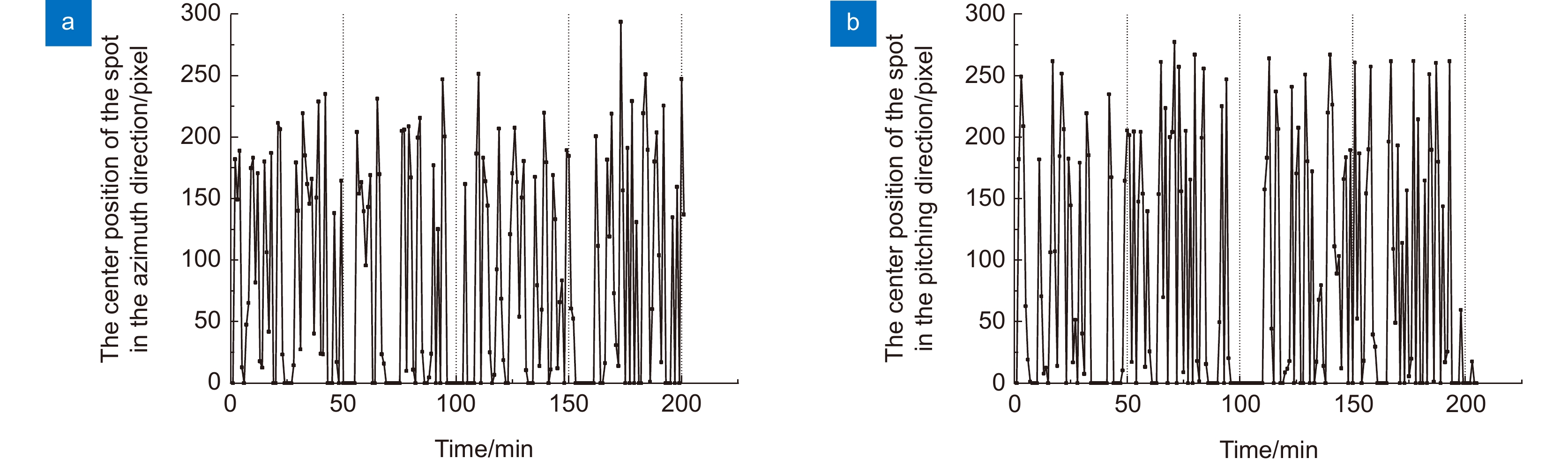
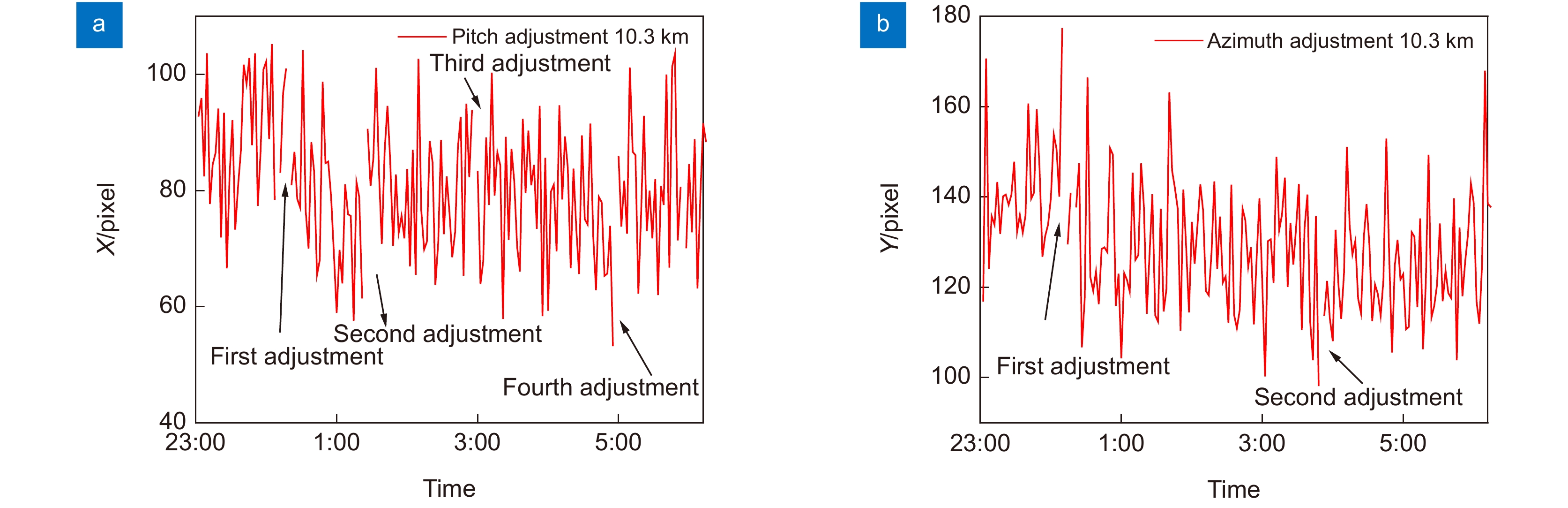
图 24 光斑中心坐标变化曲线(第一次实验)[48]。(a) 水平方向检测光斑中心坐标;(b) 俯仰方向检测光斑中心坐标(2019-08-18 23:00~2019-08-19 02:00,晴,14 ℃)
Figure 24. Spot center coordinate change curve (The first experiment) [48]. (a) Spot center coordinates in horizontal direction; (b) Spot center coordinates in pitch direction (2019-08-18 23:00~2019-08-19 02:00, sunny, 14 ℃)
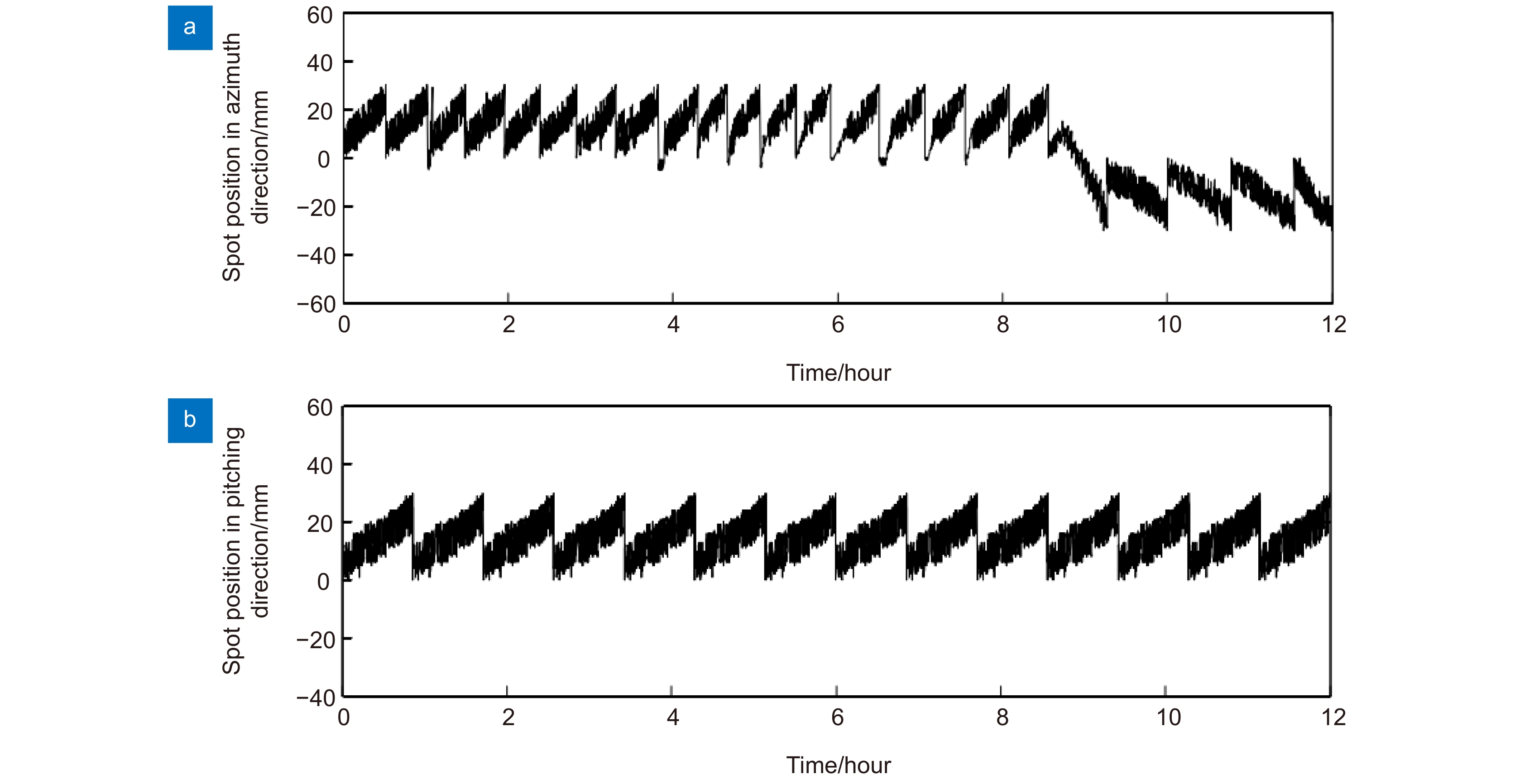
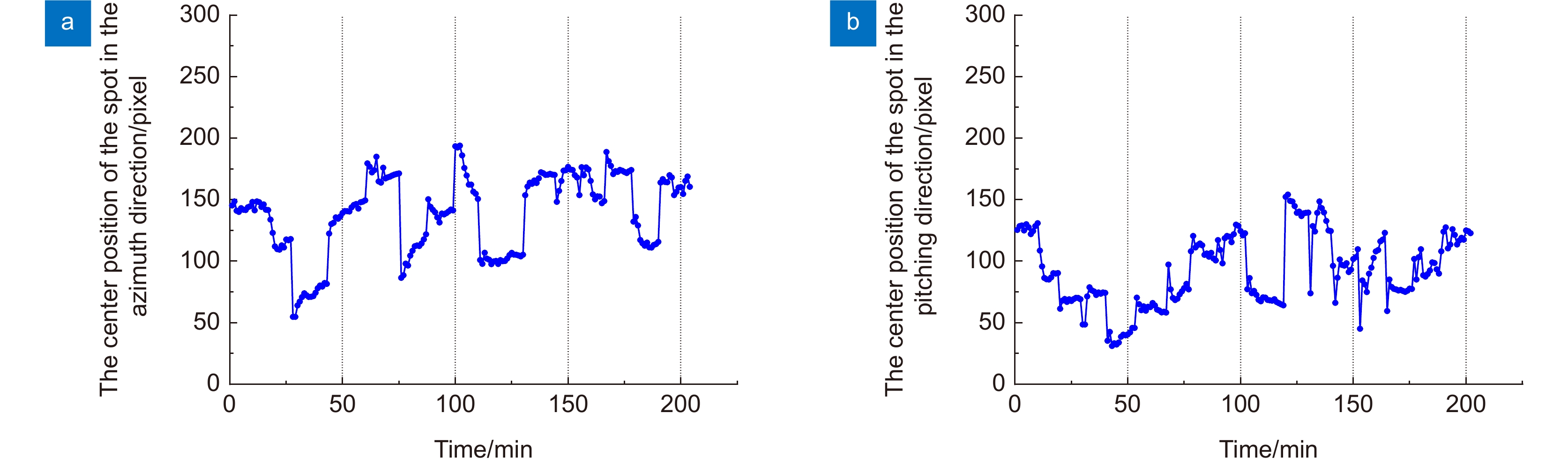
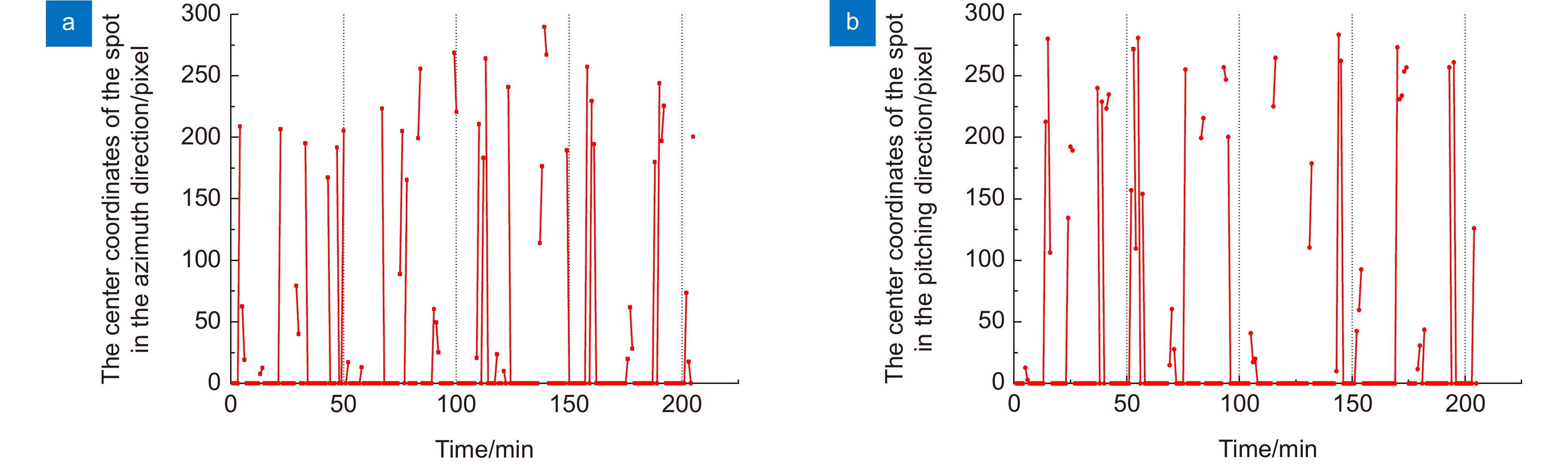
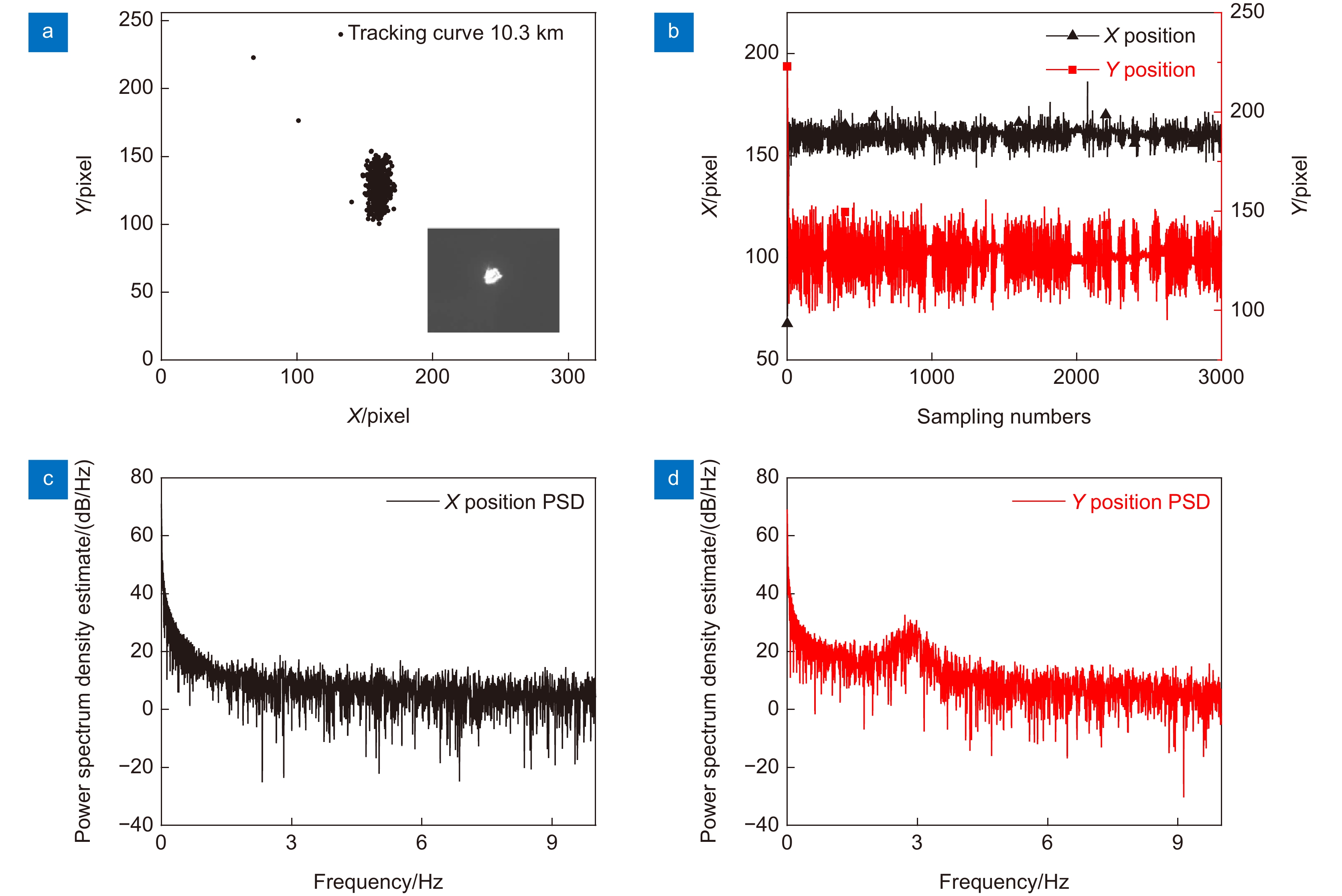
图 25 光斑中心坐标变化曲线(第二次实验) [48]。(a) 水平方向检测光斑中心坐标; (b) 俯仰方向检测光斑中心坐标(2019-08-20 23:00~2019-08-20 02:00,阴转小雨,9 ℃)
Figure 25. Spot center coordinate change curve (The second experiment) [48]. (a) Spot center coordinates in horizontal; (b) Spot center coordinates in pitch direction (2019-08-20 23:00~2019-08-20 02: 00, cloudy and rainy, 9 ℃)
表 1 国外研究进展
Table 1. Research progress abroad
文献 年份 人物/组织 研究进展 优点/参数 [6] 1985 NASDA 激光通信设备LUCE系统 跟瞄精度均优于1 mrad [7] 1994 JPL 激光通信演示终端OCD 通信速率250 Mb/s [8] 1994 MPT 激光通信设备LCE 粗、精跟踪精度优于32 μrad、2 μrad [9] 1999 A.Biswas 激光通信终端LCT系统 CCD工作帧频1.6 kHz [10] 2001 ESA 复合轴瞄准系统应用于SILEX系统 跟踪精度可达2 μrad [11] 2001 M.Guelman 利用复合轴APT系统进行激光通信实验 首次采用复合轴APT系统 [12] 2004 MIT NASA 火星激光通信演示OLCD系统 通信速率可达10 Mb/s [13] 2008 DLR 激光通信终端LCT 平均跟踪误差226 μrad [14] 2012 S.Christopher 能够实现宽视场捕获和瞄准的小型激光终端 捕获视场46° [15] 2013 DLR “狂风”战斗机实现地对空激光通信实验 链路距离79 km、数据传输速率1.25 Gb/s [17] 2016 C.Quintana 应用于机载激光通信的粗精跟踪系统 空对地通信速率可达2 Mb/s [18] 2020 A.Riccardo 应用于卫星通信的小型化高精度瞄准终端 瞄准误差小于10 μrad 表 2 国内研究进展
Table 2. Domestic research progress
文献 年份 人物/组织 研究进展 特点/参数 [4] 1999 刘泽金、舒柏宏 高能激光束自动瞄准系统 稳定有效带宽为50 Hz [30] 2005 柯熙政、刘长城 光束自动捕获系统 建立ATP系统仿真模型 [19] 2005 艾勇、周亚霖 空间光APT系统 角度测量相对误差约为1.3% [20] 2007 姜会林、佟首峰 复合轴粗跟踪伺服带宽优化设计 粗、精跟踪精度分别为60 μrad和4 μrad [21] 2008 潘高峰、张景旭 共光路自动瞄准系统 瞄准精度可达20.52 μrad [31] 2011 柯熙政、胡启迪 信标光光斑检测系统 利用PSD和CCD两种探测器设计APT子系统 [22] 2011 宋延嵩、常帅 空空机载激光通信实验 通信速率1.5 Gb/s [23] 2013 钱锋、贾建军 新型光斑探测相机 噪声对定位误差的影响降低至0.007 pixel [24] 2015 孟立新、赵丁选 粗、精复合跟踪系统 粗、精跟踪精度分别优于23.97 μrad和 7.0 μrad [32] 2016 柯熙政、杨沛松 同轴瞄准检测方法 角度跟踪精度为34.6 μrad [33] 2016 柯熙政、赵奇 初始捕获系统 采用位置校准点方法,减少系统设计成本 [25] 2017 张元生、仇振安 应用于机载激光通信的APT系统 跟踪精度可达10 μrad [36] 2019 柯熙政、严希 光斑跟踪系统 跟踪精度可达5.4 μrad [26] 2019 蔡美华、孔德聪 单探测型复合轴粗精瞄准系统 跟踪精度可达9.69 μrad [35] 2020 柯熙政、景永康 光斑图像检测算法 100 km实验中实现无信标光瞄准 [38] 2020 柯熙政、张璞 捕获、瞄准及调焦系统 10.2 km实验跟瞄精度为27.12 μrad [27] 2020 任斌、鲁倩 四象限探测器跟踪系统 跟踪精度优于3 μrad [39] 2021 柯熙政、杨尚君 二位反射镜快速对准系统 发射端采用相机标定,无需回传控制信息即可完成瞄准 [39] 2021 柯熙政、梁韩立 机载激光自动跟踪控制系统 跟踪精度可达2.42 μrad [28] 2021 李千、吴志勇 BP神经网络位置检测/多单元阵列探测位置检测 光斑位置检测系统角分辨率0.187 μrad/0.903 μrad 表 3 捕获不确定区域求解实验数据记录表[33]
Table 3. Capture uncertain region to solve the experimental data record table[33]
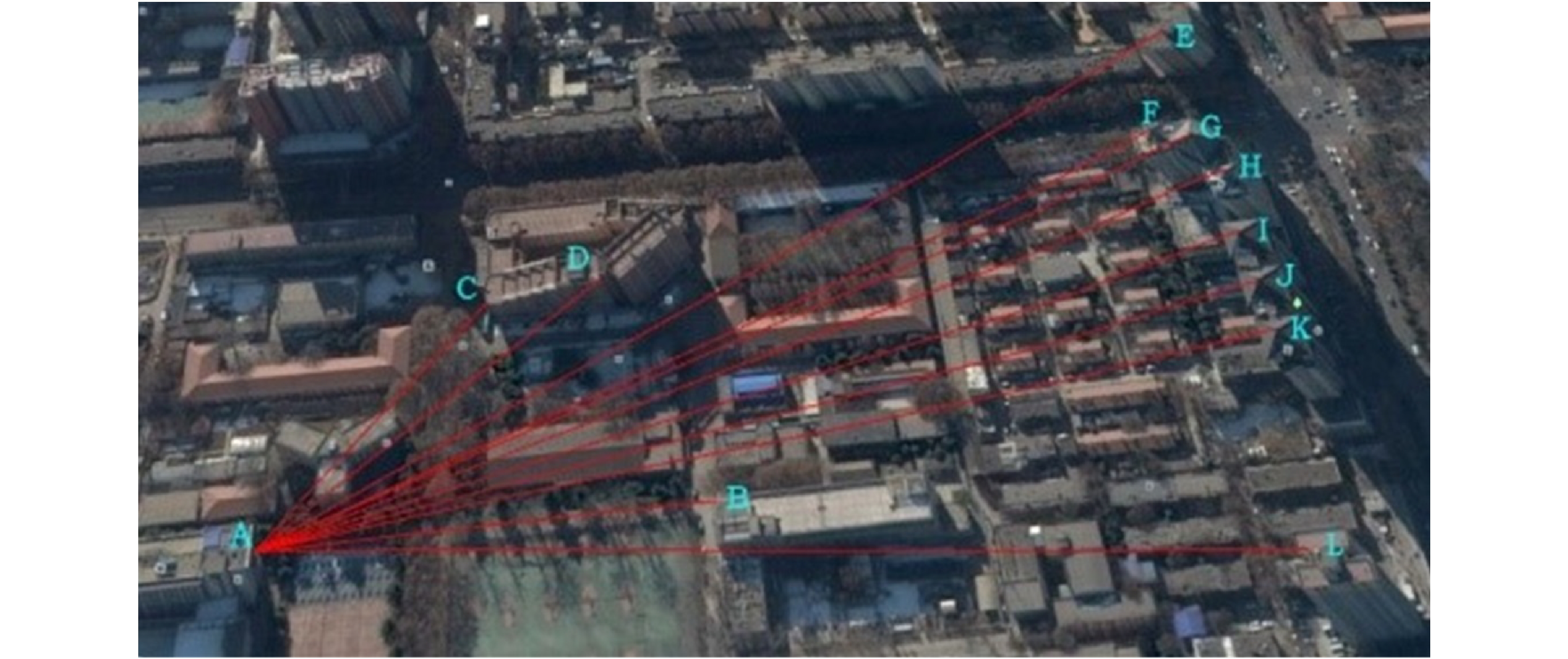
位置 精度/(°) 纬度/(°) 海拔高度/m 方位角(计算) 俯仰角(计算) 方位角(真实) 俯仰角(真实) A 108.989047 34.254260 424 B 108.986993 34.254459 421 C 108.988018 34.253207 422 41.371093 0.014749 41.100764 0.010549 D 108.987425 34.253136 421 30.354963 −0.031860 30.194587 −0.30598 E 108.984030 34.252024 425 19.403518 −0.036114 19.005784 −0.500756 F 108.984305 34.252335 425 17.402036 −0.039703 17.315786 −0.690475 G 108.984095 34.252387 425 15.973571 −0.029830 16.147860 −0.712659 H 108.983962 34.252302 424 13.204046 −0.018559 13.185405 −0.685246 I 108.984022 34.252950 425 9.599473 −0.009892 9.305784 −0.684959 J 108.984008 34.253207 424 6.655063 0.001487 6.512407 −0.685026 K 108.983992 34.253442 422 3.911638 0.014622 3.850078 −0.685104 L 108.983181 34.254314 417 −5.185554 0.056791 −4.990479 −0.571054 -
[1] 柯熙政, 邓莉君. 无线光通信[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.
Ke X Z, Deng L J. Optical Wireless Communication[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016.
[2] 闫鲁生, 王峰, 吴畏, 等. 无人机激光通信载荷发展现状与关键技术[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2016, 53(8): 080005. doi: 10.3788/LOP53.080005
Yan L S, Wang F, Wu W, et al. Current status and key technologies of unmanned aerial vehicle laser communication payloads[J]. Laser Optoelectron Prog, 2016, 53(8): 080005. doi: 10.3788/LOP53.080005
[3] 毛一聪, 王惠琴, 张悦, 等. 光空间调制技术的研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(3): 190712. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190712
Mao Y C, Wang H Q, Zhang Y, et al. Research status and development of optical spatial modulation technology[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(3): 190712. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190712
[4] 刘泽金, 舒柏宏, 王永仲, 等. 高能激光束自动对准和稳定系统的结构设计[J]. 光学技术, 1999(1): 19−20. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.1999.01.019
Liu Z J, Shu B H, Wang Y Z, et al. Design for automatically aligning and stabilizing high energy laser beam[J]. Opt Technol, 1999(1): 19−20. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.1999.01.019
[5] 杨沛松. 无线激光通信APT系统设计与实验研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2016.
Yang P S. Research and design of acquisition pointing tracking system for free-space optical communication[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2016.
[6] Nakagawa K, Yamamoto A, Toyoda M. Performance test result of LUCE (laser utilizing communications equipment) engineering model[J]. Proc SPIE, 2000, 3932: 68−76. doi: 10.1117/12.384314
[7] Chen C C, Lesh J R. Overview of the optical communications demonstrator[J]. Proc SPIE, 1994, 2123: 85−94. doi: 10.1117/12.184687
[8] Arimoto Y, Toyoshima M, Toyoda M, et al. Preliminary result on laser communication experiment using (ETS-VI)[J]. Proc SPIE, 1995, 2381: 151−158. doi: 10.1117/12.207423
[9] Biswas A, Williams G, Wilson K E, et al. Results of the STRV-2 lasercom terminal evaluation tests[J]. Proc SPIE, 1998, 3266: 2−13. doi: 10.1117/12.308694
[10] Tolker-Nielsen T, Oppenhauser G. In-orbit test result of an operational optical intersatellite link between ARTEMIS and SPOT4, SILEX[J]. Proc SPIE, 2002, 4635: 1−15. doi: 10.1117/12.464105
[11] Guelman M, Kogan A, Kazarian A, et al. Acquisition and pointing control for inter-satellite laser communications[J]. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst, 2004, 40(4): 1239−1248. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2004.1386877
[12] Boroson D M, Biswas A, Edwards B L. MLCD: overview of NASA's Mars laser communications demonstration system[J]. Proc SPIE, 2004, 5338: 16−28. doi: 10.1117/12.543014
[13] Walther F G, Michael S, Parenti R R, et al. Air-to-ground lasercom system demonstration design overview and results summary[J]. Proc SPIE, 2010, 7814: 78140Y. doi: 10.1117/12.864262
[14] Schmidt C, Horwath J. Wide-field-of-regard pointing, acquisition and tracking-system for small laser communication terminals[C]//Proceedings of ICSOS 2012, Ajaccio, 2012.
[15] Moll F, Mitzkus W, Horwath J, et al. Demonstration of high-rate laser communications from fast airborne platform: flight campaign and results[J]. Proc SPIE, 2014, 9248: 92480R. doi: 10.1117/12.2067248
[16] Moll F, Horwath J, Shrestha A, et al. Demonstration of high-rate laser communications from a fast airborne platform[J]. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun, 2015, 33(9): 1985−1995. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2015.2433054
[17] Quintana C, Erry G, Gomez A, et al. Design of a holographic tracking module for long-range retroreflector free-space systems[J]. Appl Opt, 2016, 55(25): 7173−7178. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.007173
[18] Antonello R, Branz F, Sansone F, et al. High-precision dual-stage pointing mechanism for miniature satellite laser communication terminals[J]. IEEE Trans Ind Electron, 2021, 68(1): 776−785. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.2972452
[19] 周亚霖, 艾勇, 左韬, 等. 空间光束实时捕获、跟踪实验与分析[J]. 光子学报, 2005, 34(6): 943−947.
Zhou Y L, Ai Y, Zuo T, et al. Experimentation of real-time acquisition and tracking of dree apace laser beam and analysis of the result[J]. Acta Photon Sin, 2005, 34(6): 943−947.
[20] 佟首峰, 姜会林, 刘云清, 等. 自由空间激光通信系统APT粗跟踪伺服带宽优化设计[J]. 光电工程, 2007, 34(9): 16−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2007.09.004
Tong S F, Jiang H L, Liu Y Q, et al. Optimum design of bandwidth for the APT coarse tracking assembly in free space laser communication[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2007, 34(9): 16−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2007.09.004
[21] 潘高峰, 张景旭, 陈娟. 一种共光路自动对准系统[J]. 中国激光, 2008, 35(10): 1500−1504. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2008.10.013
Pan G F, Zhang J X, Chen J. Common path auto-alignment system[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2008, 35(10): 1500−1504. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2008.10.013
[22] 宋延嵩, 常帅, 佟首峰, 等. 航空激光通信系统的特性分析及机载激光通信实验[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43(12): 1206004. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.1206004
Song Y S, Chang S, Tong S F, et al. Feature analysis of aeronautical laser communication system and airborne laser communication experiment[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2016, 43(12): 1206004. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.1206004
[23] 钱锋, 贾建军, 张亮, 等. 捕获、跟踪、瞄准系统中光斑探测相机的定位精度[J]. 中国激光, 2013, 40(2): 0205007. doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.0205007
Qian F, Jia J J, Zhang L, et al. Positioning accuracy of spot-detecting camera in acquisition, tracking, pointing system[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2013, 40(2): 0205007. doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.0205007
[24] 孟立新, 赵丁选, 张立中, 等. 机载激光通信稳瞄吊舱设计与跟踪精度测试[J]. 兵工学报, 2015, 36(10): 1916−1923. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.10.013
Meng L X, Zhao D X, Zhang L Z, et al. The test of tracking accuracy and design of airborne laser communication stabilized pod[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2015, 36(10): 1916−1923. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.10.013
[25] 张元生, 仇振安, 郭帅, 等. 机载激光通信系统关键技术分析与试验验证[J]. 电光与控制, 2017, 24(10): 80−84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2017.10.012
Zhang Y S, Qiu Z A, Guo S, et al. Key technology analysis of airborne laser communication system and its verification[J]. Electron Opt Control, 2017, 24(10): 80−84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2017.10.012
[26] 蔡美华, 孔德聪, 佟鑫刚. 单探测型复合轴系统粗精指向对准的研究与实现[J]. 光电技术应用, 2019, 34(1): 63−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2019.01.014
Cai M H, Kong D C, Tong X G. Research and implementation of coarse fine pointing alignment for single composite shaft detection system[J]. Electro-Opt Technol Appl, 2019, 34(1): 63−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2019.01.014
[27] 鲁倩, 任斌, 边晶莹. 四象限探测器的信号光捕获与跟踪技术研究[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(3): 190559. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190559
Lu Q, Ren B, Bian J Y. Research on acquisition and tracking technology for the four-quadrant detector[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(3): 190559. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190559
[28] 李千. 基于阵列探测器的空间激光通信光斑位置检测技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2020.
Li Q. Research on spot position detection technology of space laser communication based on array detector[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020.
[29] 柯熙政, 卢宁, 赵黎. 一种光束自动捕获装置及光束捕获方法: 201010185116.9[P]. 2010-10-06.
Ke X Z, Lu N, Zhao L. Automatic light beam capturing device and light beam capturing method: 201010185116.9[P]. 2010-10-06.
[30] 柯熙政, 席晓莉, 刘长城. 大气激光通信中一种新的光束自动捕获方法[J]. 光通信技术, 2004, 28(10): 39−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5561.2004.10.012
Ke X Z, Xi X L, Liu C C. A new auto beam acquiring method for laser communication in atmosphere[J]. Opt Commun Technol, 2004, 28(10): 39−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5561.2004.10.012
[31] 胡启迪. 大气激光通信信标光捕获过程中光斑检测技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2009.
Hu Q D. Research on spot detection technology in process of beacon acquisition of laser communication in atmosphere[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2009.
[32] 柯熙政, 雷思琛, 杨沛松. 大气激光通信光束同轴对准检测方法[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43(6): 0606003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0606003
Ke X Z, Lei S C, Yang P S. Beam coaxial alignment detection in atmospheric laser communication[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2016, 43(6): 0606003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0606003
[33] 赵奇. 无线激光通信初始捕获系统设计与实现[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2016.
Zhao Q. Design and implementation of initial acquisition system for wireless laser communication[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2016.
[34] 徐尉. 无线激光通信ATP系统光斑检测技术研究与实现[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2016.
Xu W. Research and implement of the laser spot detection in ATP system[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2016.
[35] 柯熙政, 李世艳. 光斑缺碎情形下光学天线光轴对准实验研究[J]. 光子学报, 2017, 46(4): 0406002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20174604.0406002
Ke X Z, Li S Y. Experimental study on optical axis alignment of the optical antenna under the spot broken[J]. Acta Photon Sin, 2017, 46(4): 0406002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20174604.0406002
[36] 柯熙政, 严希, 杨雅淇, 等. 5.2 km距离无线激光通信跟踪实验[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2018, 26(11): 233−237. doi: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2018.11.051
Ke X Z, Yan X, Yang Y Q, et al. 5.2 km distance wireless laser communication tracking experimen[J]. Comput Meas Control, 2018, 26(11): 233−237. doi: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2018.11.051
[37] Ke X Z, Jing Y K. Far-field laser spot image detection for use under atmospheric turbulence[J]. Opt Eng, 2020, 59(1): 016103.
[38] Ke X Z, Zhang P. Automatic focusing control in beaconless APT system[J]. J Russ Laser Res, 2020, 41(1): 61−71. doi: 10.1007/s10946-020-09848-y
[39] Ke X Z, Liang H L. Airborne laser communication system with automated tracking[J]. Int J Opt, 2021, 2021: 9920368.
[40] 杨尚君, 柯熙政, 吴加丽, 等. 利用二维反射镜实现无线光通信快速对准[J]. 中国激光, 2022, 49(11): 1106001. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1106001
Yang S J, Ke X Z, Wu J L, et al. Fast alignment of wireless optical communication using two-dimensional mirror[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2022, 49(11): 1106001. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1106001
[41] 赵雪. 空间激光通信APT初始捕获及误差分析[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2012.
Zhao X. The APT initial capture and error analysis of space laser communication[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Technology, 2012.
[42] 柯熙政, 张璞. 一种无线光通信的跟瞄控制系统及跟瞄控制方法: 201910339487.9[P]. 2021-07-20.
Ke X Z, Zhang P. Tracking and aiming control system and tracking and aiming control method for wireless optical communication: 201910339487.9[P]. 2021-07-20.
[43] 张璞. 无线激光通信捕获对准与调焦系统设计[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2020.
Zhang P. Design of acquisition pointing and focusing system for wireless laser communication[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2020.
[44] 柯熙政, 陈晓展, 吴加丽. 一种无人机中继激光通信系统: 201810919712.1[P]. 2018-08-14.
Ke X Z, Chen X Z, Wu J L. A relay laser communication system for an unmanned aerial vehicle: 201810919712.1[P]. 2018-08-14.
[45] 梁韩立. 机载激光通信自动跟踪控制系统设计与实现[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2021.
Liang H L. Design and realization of airborne laser communication automatic tracking control system[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2021.
[46] 柯熙政, 王姣. 一种基于四象限探测器的光斑对准方法: 201611244466.1[P]. 2017-05-31.
Ke X Z, Wang J. Light spot aligning method based on four-quadrant detector: 201611244466.1[P]. 2017-05-31.
[47] 严希. 无线激光通信APT系统中的光斑跟踪系统研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2019.
Yan X. Research on spot tracking system in APT system of wireless laser communication[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2019.
[48] 景永康. 无线光通信远场光斑图像检测实验研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2020. 西安市科技创新引导项目(NO: 201805030YD8CG14(12))、陕西省重点产业创新项目(2017ZDCXL-GY-06-01)
Jing Y K. Experimental study on far-field spot image detection for wireless optical communication[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2020.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: