-
摘要
针对侧向激光雷达应用于气溶胶探测领域时,雷达回波信号易受噪声影响这一问题,本文提出了一种基于神经网络的激光雷达信号去噪算法。该算法在卷积神经网络基础上融合残差学习法和批量标准化,引入了注意力机制,改进激活函数,提升了网络性能和学习效率。采用本文提出的方法对噪声进行预测,实现了信号和噪声的有效分离,提高了侧向激光雷达CCD图像的信噪比。实验结果表明,使用本文提出的去噪算法对侧向激光雷达CCD图像进行去噪,图像的峰值信噪比提高了约5 dB,信号相对误差减小至9.62%,本文提出的去噪算法优于小波变换、维纳滤波等去噪方法,验证了该方法的可行性和实用性。
Abstract
A side-scatter lidar is known to have evident advantages over other types of lidar in atmosphere detection. However, the signal of the side-scatter lidar may suffer from the noise as all other lidars. It is noted that the original signal of the side-scatter lidar is an image captured by a CCD camera. Therefore, denoising the side-scatter lidar signal may need more efforts than ordinary radar signals. In the paper, a denoising algorithm based on convolution neutral network is proposed for the side-scatter lidar signal. We combine the residual learning with batch standardization in the network. Further, attention mechanism and activation function in the network are optimized in order to improve the learning efficiency and the network output performance. Using the proposed algorithm, we successfully identify the noise and separate the noise from the simulated lidar signal. The signal-to-noise ratio is hence increased. Simulation results show that the peak signal-to-noise ratio is increased by over 5 dB using the proposed denoising algorithm. The relative error of signal is reduced to 9.62%. The proposed denoising algorithm based on the convolution neutral network is shown to be efficient for improving the side-scatter lidar signal, compared with the possible denoising algorithms based on wavelet transform and Wiener filtering.
-
Key words:
- side-scatter lidar /
- signal processing /
- neural network /
- image denoising
-
Overview
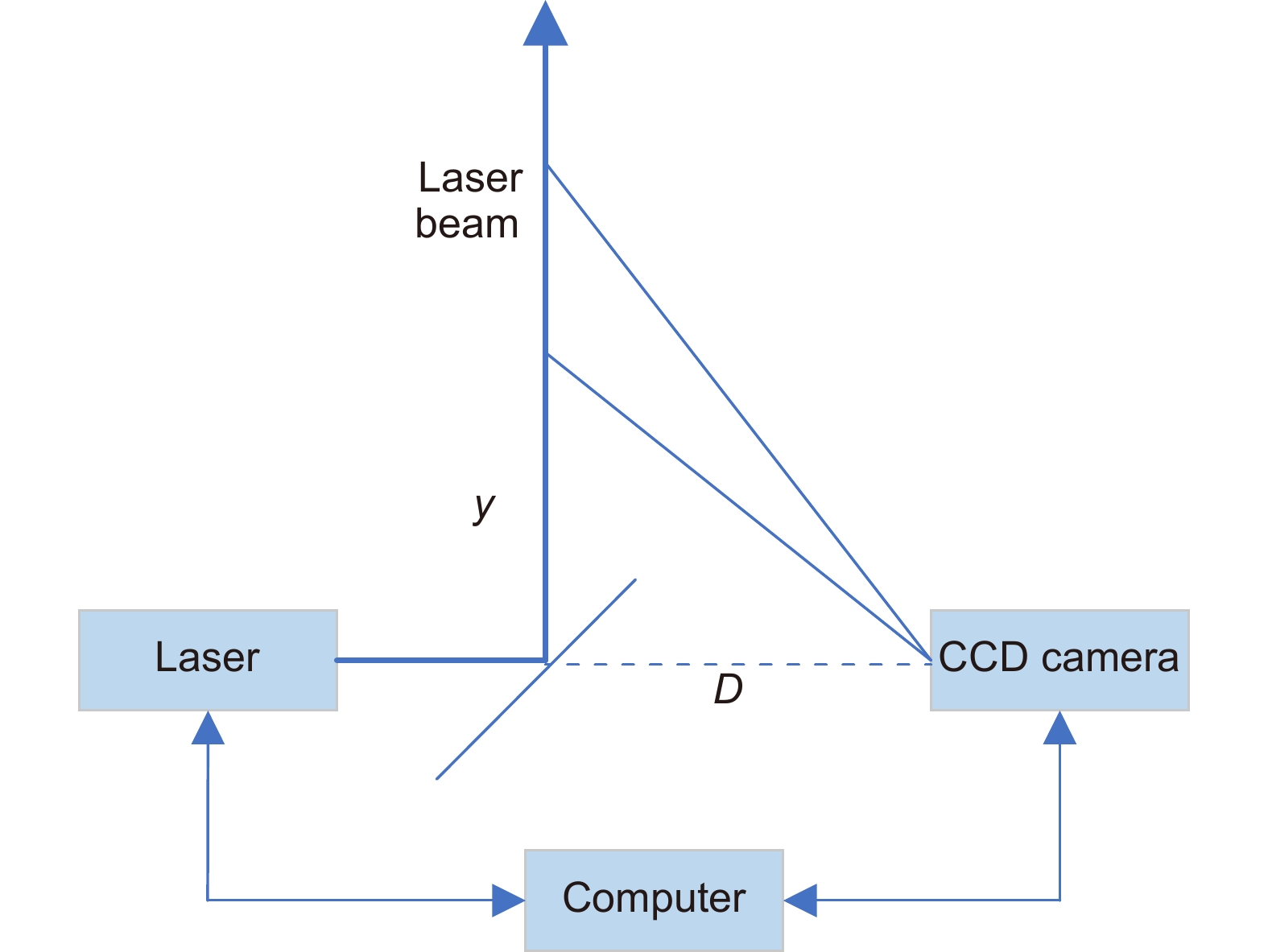
Overview: A side-scatter lidar is known to have evident advantages over other types of lidar in atmosphere detection, especially for lower atmosphere. For a side-scatter lidar, a high-power laser is normally used as the light source. As the charge coupled device (CCD) optoelectronic detector is used to capture the light backscattered by the atmosphere. Correspondingly, the original side-scatter lidar signal is depicted as a 2D CCD image. The 2D CCD image of the side-scatter lidar may suffer from the noise as all other lidars. Therefore, denoising the side-scatter lidar signal may need more efforts than ordinary lidar signals. The extinction coefficient profile can be derived from the CCD image. With the help of other auxiliary techniques, atmosphere features such as wind speed and meteorological optical range can be obtained.
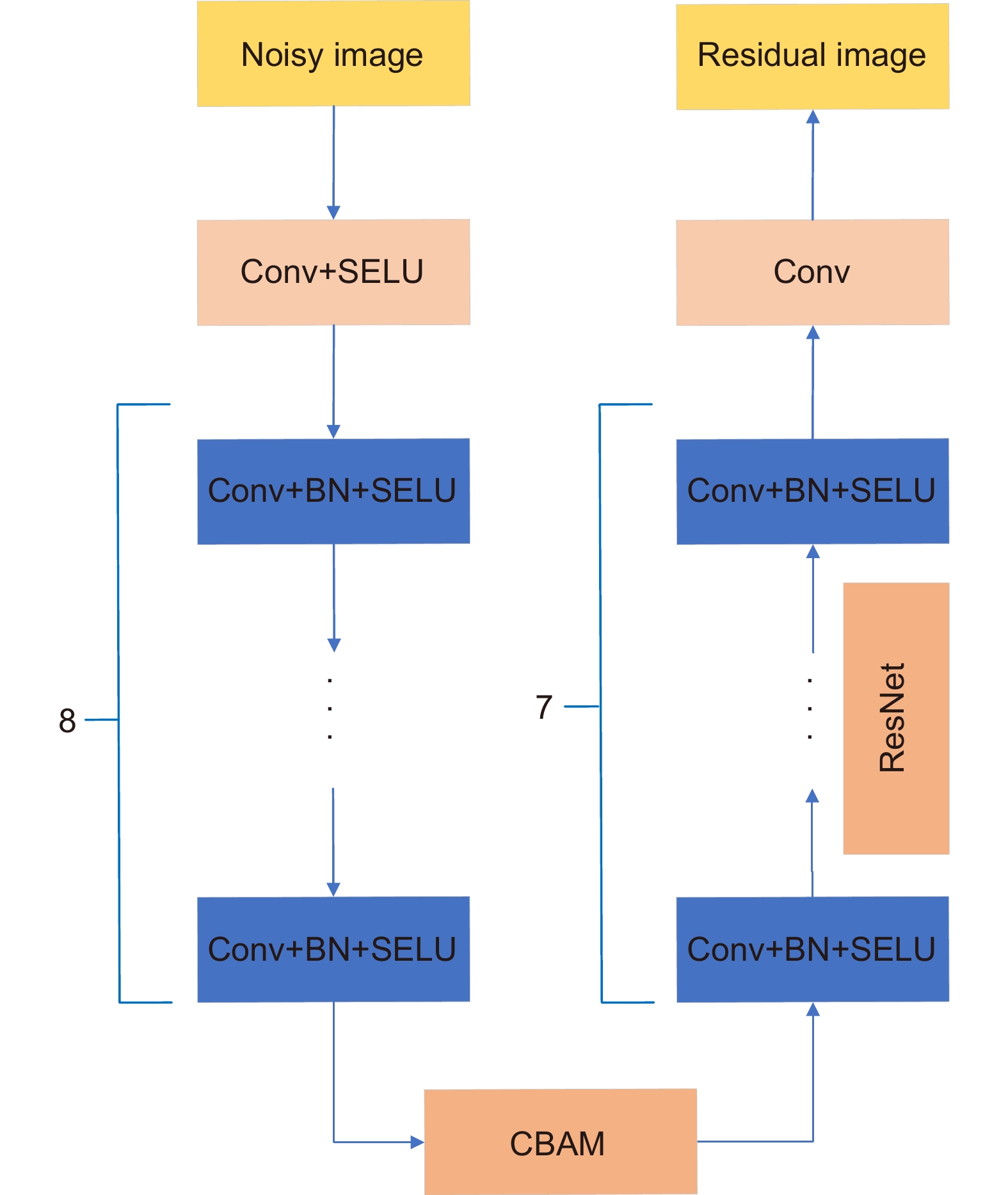
In the paper a denoising algorithm based on denoising convolution neutral network (DnCNN) is proposed for side-scatter lidar signal, called DnCNN+. The DnCNN+ uses scaled exponential linear units (SELU) as the activation function of the network in order to avoid the gradient explosion and gradient disappearance that might happen frequently in the traditional network. On the other hand, convolutional block attention module (CBAM) is used in the DnCNN+ to ensure the efficient allocation of the computation resources in the training process, hence increasing the learning efficiency. Furthermore, we introduce residual learning and batch standardization in the network to improve the network output performance.
For the denoising strategy, we identify the noise and separate the noise from the simulated lidar signal. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is hence increased. The denoising performances of five methods, including wavelet transform soft threshold, wavelet transform hard threshold, Visual Geometry Group (VGG16), DnCNN, and DnCNN+, are evaluated for the signals with SNR of 0.01-0.03 dB. VGG16 is one of the classic convolution neutral networks. Peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity (SSIM) are used to evaluate the denoising performance. Simulation results showe that the PSNR is increased by over 5 dB using the DnCNN+. The DnCNN+ has the best denoising performance in terms of PSNR and SSIM. Additionally, it is also seen that the DnCNN+ has smaller network loss than the methods using convolution neutral networks, VGG16, and DnCNN. Furthermore, the 1D signal photon number is retrieved from the CCD image. It is shown that the DnCNN+ has the smallest relative error of signal of 9.62%. The proposed denoising algorithm based on the convolution neutral network is shown to be efficient for improving the side-scatter lidar signal.
-

-
表 1 图像PSNR对比
Table 1. Comparison of the PSNR images
Denoising method PSNR /dB None
Wavelet (Soft)19.99
24.73Wavelet (Hard) 24.88 Wiener filtering
VGG16
DnCNN
DnCNN+23.54
25.19
25.26
25.87表 2 图像SSIM对比
Table 2. Comparison of the SSIM images
Denoising method SSIM None
Wavelet (Soft)0.05
0.22Wavelet (Hard) 0.27 Wiener filtering
VGG16
DnCNN
DnCNN+0.16
0.24
0.27
0.29表 3 不同噪声强度下图像PSNR对比
Table 3. Comparison of the PSNR imageses at different noise intensities
Noise intensity (variance)
Denoising method0.01
PSNR /dB0.02
PSNR /dB0.03
PSNR /dBNone
Wavelet (Soft)22.98
27.7919.96
24.5818.27
19.78Wavelet (Hard) 27.52 24.82 23.27 Wiener filtering
VGG16
DnCNN
DnCNN+26.69
27.84
28.20
28.6223.58
25.17
25.23
25.7521.79
23.09
23.26
23.64表 4 信号光子数平均偏离度对比
Table 4. Comparison of average deviation of the signal photon number
Denoising method S Wavelet (Soft) 0.35 Wavelet (Hard) 0.21 Wiener filtering
DnCNN+0.46
0.18 -
参考文献
[1] 马愈昭, 刘嘉琪, 王强强, 等. 基于Fernald-PSO法反演气溶胶激光雷达比及其对斜程能见度的影响[J]. 光子学报, 2019, 48(3): 201−210. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194803.0301001
Ma Y Z, Liu J Q, Wang Q Q, et al. Inversion of aerosol Lidar ratio and its effect on slant visibility based on Fernald-PSO method[J]. Acta Photonica Sin, 2019, 48(3): 201−210. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194803.0301001
[2] 陶宗明, 施奇兵, 谢晨波, 等. 利用CCD和后向散射激光雷达精确探测近地面气溶胶消光系数廓线[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2019, 48(S1): 49−55. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.S106007
Tao Z M, Shi Q B, Xie C B, et al. Precise detection of near ground aerosol extinction coefficient profile based on CCD and backscattering lidar[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2019, 48(S1): 49−55. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.S106007
[3] 陈海平, 李萌阳, 曹庭分, 等. 基于激光雷达数据的火星表面障碍物识别[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(2): 220240. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220240
Chen H P, Li M Y, Cao T F, et al. Obstacle recognition on Mars surface based on LiDAR data[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(2): 220240. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220240
[4] 黄思源, 刘利民, 董健, 等. 车载激光雷达点云数据地面滤波算法综述[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(12): 190688. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190688
Huang S Y, Liu L M, Dong J, et al. Review of ground filtering algorithms for vehicle LiDAR scans point cloud data[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(12): 190688. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190688
[5] 陈松, 胡淼, 曾然, 等. 基于侧向散射激光雷达的PM2.5浓度测量误差[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37(12): 1201003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.1201003
Chen S, Hu M, Zeng R, et al. Measurement error of PM2.5 concentration based on side scattering Lidar[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2017, 37(12): 1201003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.1201003
[6] 马愈昭, 刘逵, 张岩峰, 等. CEEMD结合改进小波阈值的激光雷达信号去噪算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(1): 93−100. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.01.12
Ma Y Z, Liu K, Zhang Y F, et al. Laser radar signal denoising algorithm based on CEEMD combined with improved wavelet threshold[J]. Syst Eng Electron, 2023, 45(1): 93−100. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.01.12
[7] Huan R H, Ge L Q, Yang P, et al. SAR multi-target interactive motion recognition based on convolutional neural networks[J]. IET Image Process, 2020, 14(11): 2567−2578. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2019.0861
[8] Zhu S J, Yu Z K. Self-guided filter for image denoising[J]. IET Image Process, 2020, 14(11): 2561−2566. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2019.1471
[9] Ma R J, Li S Y, Zhang B, et al. Meta PID attention network for flexible and efficient real-world noisy image denoising[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2022, 31: 2053−2066. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3150294
[10] 孙国栋, 秦来安, 程知, 等. 小波去噪在成像激光雷达仿真信号中的应用[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2017, 54(9): 090102. doi: 10.3788/LOP54.090102
Sun G D, Qin L A, Cheng Z, et al. Application of wavelet noise reduction for simulated signals of imaging Lidar[J]. Laser Optoelectron Prog, 2017, 54(9): 090102. doi: 10.3788/LOP54.090102
[11] 黄金, 周先春, 吴婷, 等. 混合维纳滤波与改进型TV的图像去噪模型[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2017, 31(10): 1659−1666. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.2017.10.020
Huang J, Zhou X C, Wu T, et al. Image denoising model based on mixing Wiener filtering and improved total variation[J]. J Electron Meas Instrum, 2017, 31(10): 1659−1666. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.2017.10.020
[12] Goel R K, Vishnoi S, Shrivastava S. Image denoising by hybridizing preprocessed discrete wavelet transformation and recurrent neural networks[J]. Int J Innovative Technol Explor Eng, 2019, 8(10): 3451−3457. doi: 10.35940/ijitee.J9718.0881019
[13] 钱满, 张向阳, 李仁昌. 改进卷积神经网络SAR图像去噪算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2020, 56(14): 176−182. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1911-0060
Qian M, Zhang X Y, Li R C. Improved convolutional neural network for SAR image despeckling algorithm[J]. Comput Eng Appl, 2020, 56(14): 176−182. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1911-0060
[14] 丁红波, 王珍珠, 刘东. 激光雷达信号去噪方法的对比研究[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41(24): 2401001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.2401001
Ding H B, Wang Z Z, Liu D. Comparison of de-noising methods of LiDAR signal[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2021, 41(24): 2401001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.2401001
[15] 李苏, 何大华, 李亚鹏. 散粒噪声对目标探测率的影响[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2021, 41(12): 196−199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2021.12.042
Li S, He D H, Li Y P. Effect of shot noise on target detection rate[J]. Ship Electron Eng, 2021, 41(12): 196−199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2021.12.042
[16] Jiang H L, Shen F H, Gao F, et al. Learning efficient, explainable and discriminative representations for pulmonary nodules classification[J]. Pattern Recognit, 2021, 113: 107825. doi: 10.1016/J.PATCOG.2021.107825
[17] Klambauer G, Unterthiner T, Mayr A, et al. Self-normalizing neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017: 972–981.
[18] Tian Q Y, Zaretskaya N, Fan Q Y, et al. Improved cortical surface reconstruction using sub-millimeter resolution MPRAGE by image denoising[J]. NeuroImage, 2021, 233: 117946. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.117946
[19] Zhang K, Zuo W M, Chen Y J, et al. Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2017, 26(7): 3142−3155. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2662206
[20] Yuan Z X, Xu T Y, Cai J, et al. Development and validation of an image-based deep learning algorithm for detection of synchronous peritoneal carcinomatosis in colorectal cancer[J]. Ann Surg, 2022, 275(4): e645−e651. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000004229
[21] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 770–778. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90.
[22] Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2018: 3–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1.
[23] 王红霞, 周家奇, 辜承昊, 等. 用于图像分类的卷积神经网络中激活函数的设计[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2019, 53(7): 1363−1373. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2019.07.016
Wang H X, Zhou J Q, Gu C H, et al. Design of activation function in CNN for image classification[J]. J Zhejiang Univ (Eng Sci), 2019, 53(7): 1363−1373. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2019.07.016
[24] Costas R, Figuero A, Peña E, et al. Integrated approach to assess resonance between basin eigenmodes and moored ship motions with wavelet transform analysis and proposal of operational thresholds[J]. Ocean Eng, 2022, 247: 110678. doi: 10.1016/J.OCEANENG.2022.110678
[25] 徐景秀, 张青. 改进小波软阈值函数在图像去噪中的研究应用[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2022, 44(1): 92−101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2022.01.011
Xu J X, Zhang Q. Research and application of an improved wavelet soft threshold function in image denoising[J]. Comput Eng Sci, 2022, 44(1): 92−101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2022.01.011
[26] 袁敏, 施佺, 许致火. 基于维纳滤波的汽车毫米波雷达干扰自适应抑制[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2021, 35(2): 194−201. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2003344
Yuan M, Shi Q, Xu Z H. Wiener filter based automotive millimeter wave radar interference adaptive reduction[J]. J Electron Meas Instrum, 2021, 35(2): 194−201. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2003344
[27] 王洪雁, 杨晓, 姜艳超, 等. 基于多通道GAN的图像去噪算法[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(3): 229−237. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021049
Wang H Y, Yang X, Jiang Y C, et al. Image denoising algorithm based on multi-channel GAN[J]. J Commun, 2021, 42(3): 229−237. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021049
[28] 麻晓敏, 陶宗明, 张璐璐, 等. 侧向散射激光雷达探测白天近地面气溶胶探测技术[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(4): 0401005. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0401005
Ma X M, Tao Z M, Zhang L L, et al. Ground layer aerosol detection technology during daytime based on side-scattering Lidar[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2018, 38(4): 0401005. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0401005
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: