A generative adversarial network incorporating dark channel prior loss used for single image defogging
-
摘要
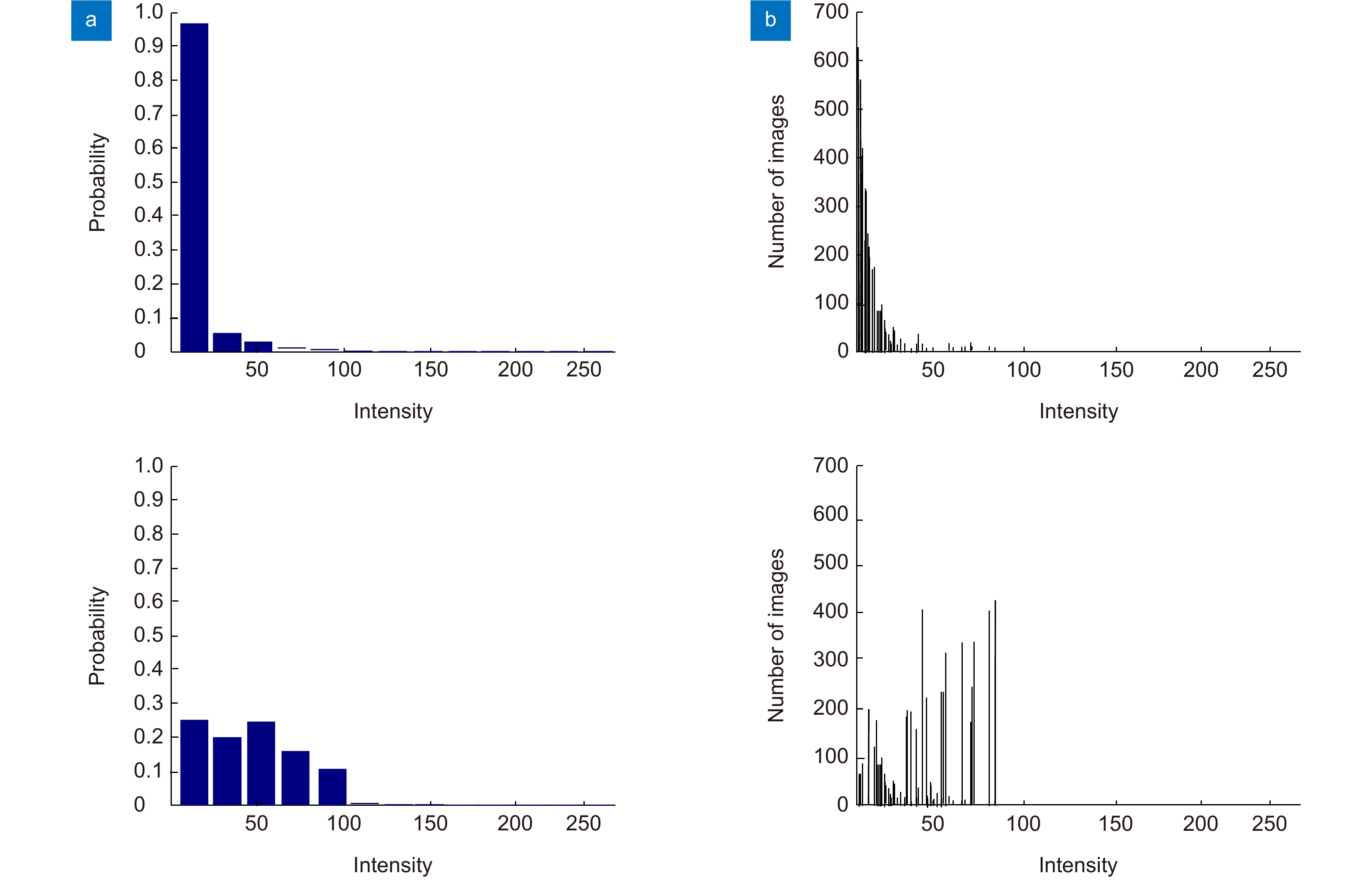
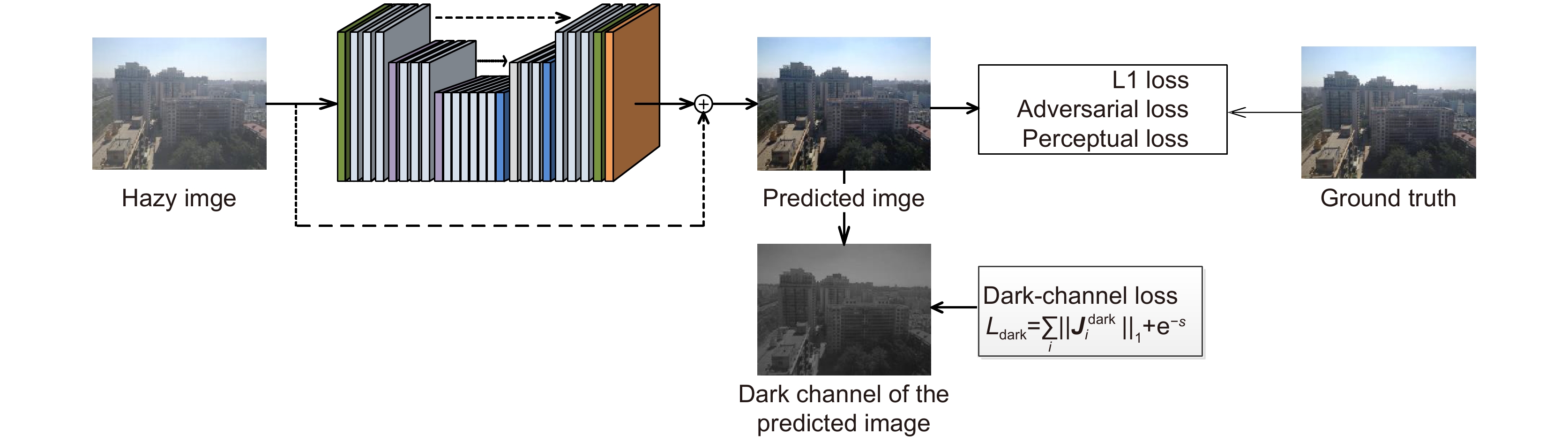
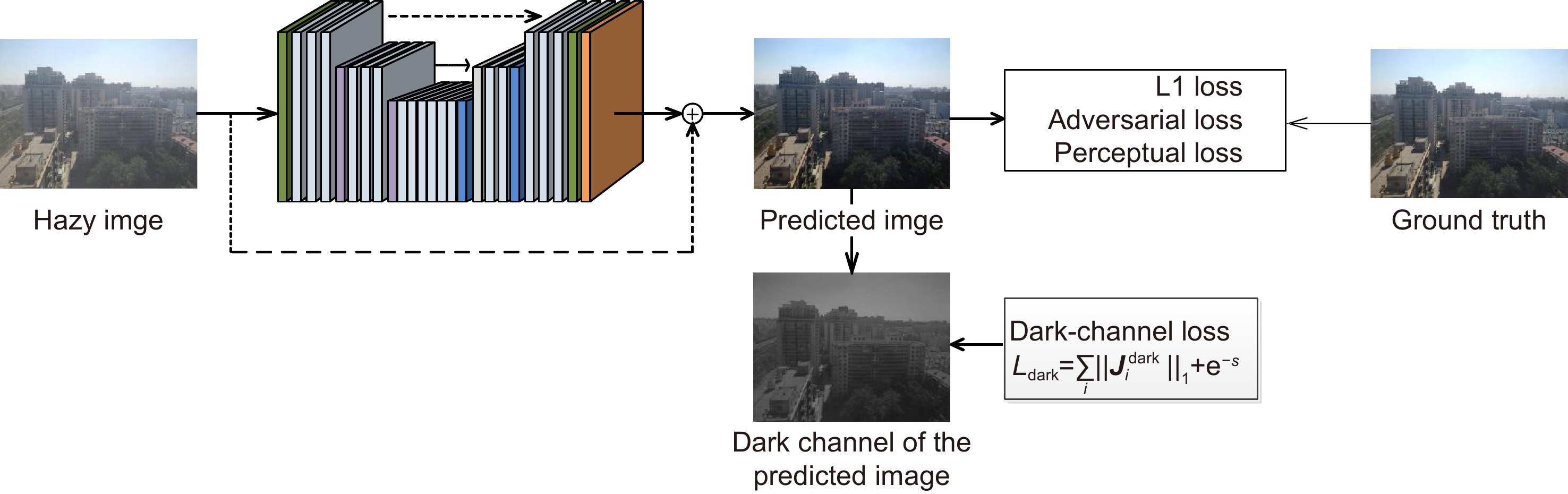
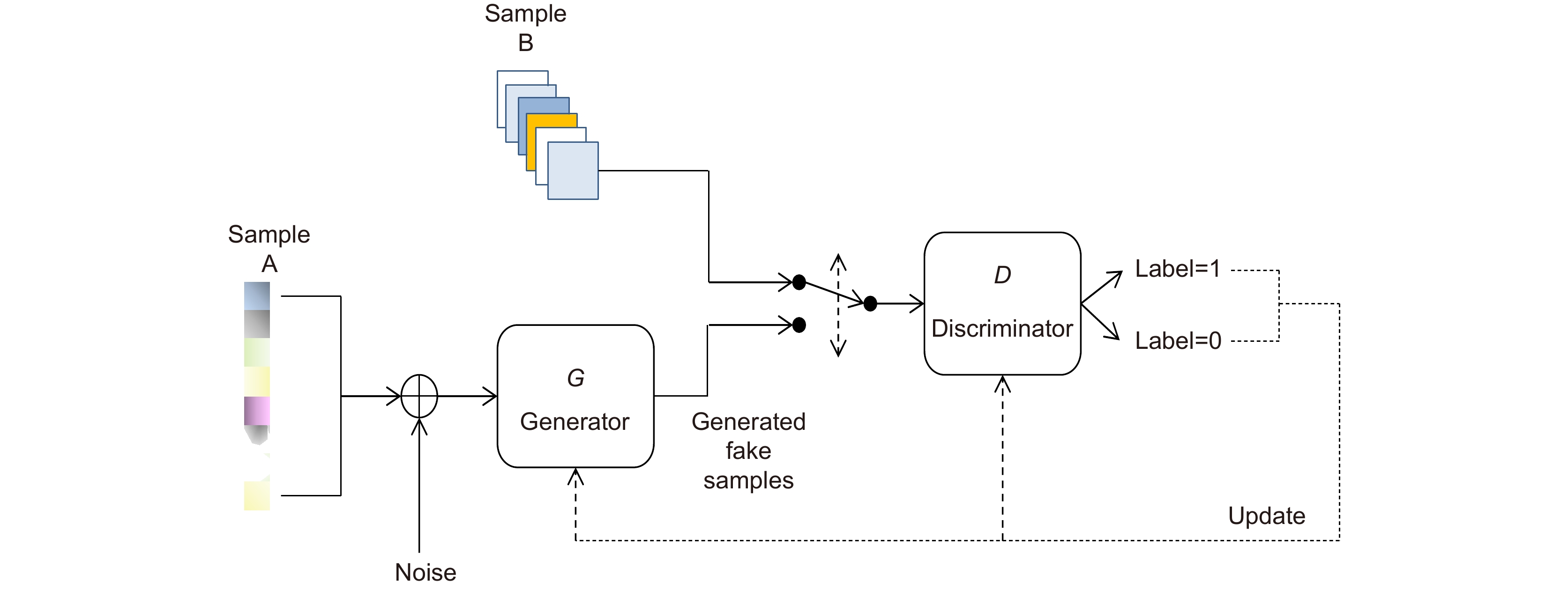
针对基于成对抗网络(GAN)的单幅图像去雾算法,其模型对样本真值过度拟合,而在自然图像上表现一般的问题,本文设计了一种融合暗通道先验损失的生成对抗网络来进行单幅图像去雾。该先验损失可以在网络训练中对模型预测结果产生影响,纠正暗通道特征图的稀疏性与偏度特性,提升去雾效果的同时阻止模型对样本真值过度拟合。另外,为了解决传统的暗通道特征图提取方法存在非凸函数,难以嵌入网络训练的问题,引入了一种基于像素值压缩的暗通道特征图提取策略。该策略将最小值滤波等效为对像素值压缩,其实现函数是一个凸函数,有利于嵌入网络训练,增强算法整体的鲁棒性。另外,基于像素值压缩的暗通道特征图提取策略不需要设置固定尺度提取暗通道特征图,对不同尺寸的图像均有良好的适应性。实验结果表明,相较于其它先进算法,本文算法在真实图像以及SOTS等合成测试集上均有良好的表现。
Abstract
Single image defogging using generative adversarial networks (GAN) relies on annotated datasets, which is easy to cause over-fitting of ground truth, and usually performs not well on natural images. To solve this problem, this paper designed a GAN network incorporating dark channel prior loss to defogging single image. This prior loss can influence the model prediction results in network training and correct the sparsity and skewness of the dark channel feature map. At the same time, it can definitely improve the actual defogging effect and prevent the model from over-fitting problem. In addition, in order to solve the problem that the extraction method of traditional dark channel feature has non-convex function and is difficult to be embedded into network training, this paper introduces a new extraction strategy which compresses pixel values instead of minimum filtering. The implementation function of this strategy is a convex function, which is conducive to embedded network training and enhances the overall robustness of the algorithm. Moreover, this strategy does not need to set a fixed scale to extract the dark channel feature map, and has good adaptability to images with different resolutions. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm performs better on real images and synthetic test-sets like SOTS when compared with other sota algorithms.
-
Key words:
- generative adversarial network /
- prior loss /
- sparsity /
- skewness
-
Overview
Overview: In the atmospheric environment, there are many fine particles in the air, which will lead to the absorption or refraction of light and affect the normal radiation of light. In this case, the color, contrast, saturation and detail of the image captured by the camera are often seriously affected. At present, computer vision needs to realize many high-level tasks such as pedestrian recognition, automatic driving, air navigation, remote sensing and telemetry, and these high-level tasks have a high demand for image quality. Therefore, it is of great significance to carry out single image defogging to obtain higher quality images before performing high-level tasks. In recent years, single image defogging using generative adversarial networks(GAN) has become a hot research aspect. However, the traditional GAN algorithms rely on annotated datasets, which is easy to cause over-fitting of ground truth, and usually performs not well on natural images. To solve this problem, this paper designed a GAN network incorporating dark channel prior loss to defogging single image. This prior loss can influence the model prediction results in network training and correct the sparsity and skewness of the dark channel feature map. At the same time, it can definitely improve the actual defogging effect and prevent the model from over-fitting problem. In addition, this paper introduced a new method to obtain dark channel feature map, which compresses pixel values instead of minimum filtering. This method does not need to set fixed scale to extract dark channel feature map, and has good adaptability to images with different resolutions. Moreover, the implementation function of this method is a convex function, which is conducive to embedded network training and enhances the overall robustness of the algorithm. The proposed algorithm is quantitatively analyzed in the comprehensive test set SOTS and the mixed subjective test set HSTS. The peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity SSIM and BCEA Metrics are used as the final evaluation indexes. The final result shows that our algorithm can raise PSNR up to 25.35 and raise SSIM up to 0.96 on HSTS test sets. While it comes to SOTS test sets, our method achieves the result of 24.44 PSNR and 0.89 SSIM. When we use BCEA metrics to evaluate our algorithm, we achieve the result of 0.8010 e,1.6672 r and 0.0123 p. In summary, Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm performs well on real images and synthetic test sets compared with other advanced algorithms.
-

-
表 1 生成器网络参数
Table 1. Parameters of generator network
卷积层 Conv Res Conv Res Conv Res Upconv Res Upconv Res Conv Tanh 输入通道数 3 64 64 128 128 256 256 128 128 64 64 3 输出通道数 64 64 128 128 256 256 128 128 64 64 3 3 卷积核尺寸 7 5 3 4 4 7 步长 1 2 2 2 2 1 边界填充 3 1 1 1 1 3 表 2 判别器网络参数
Table 2. Parameters of the discriminator network
卷积层 Conv1 Conv2 Conv3 Conv4 Conv5 输出通道数 64 128 256 512 1 卷积核大小 4 4 4 4 4 步长 2 2 2 1 1 表 3 各算法在SOTS测试集以及HSTS测试集合成图像上的定量结果
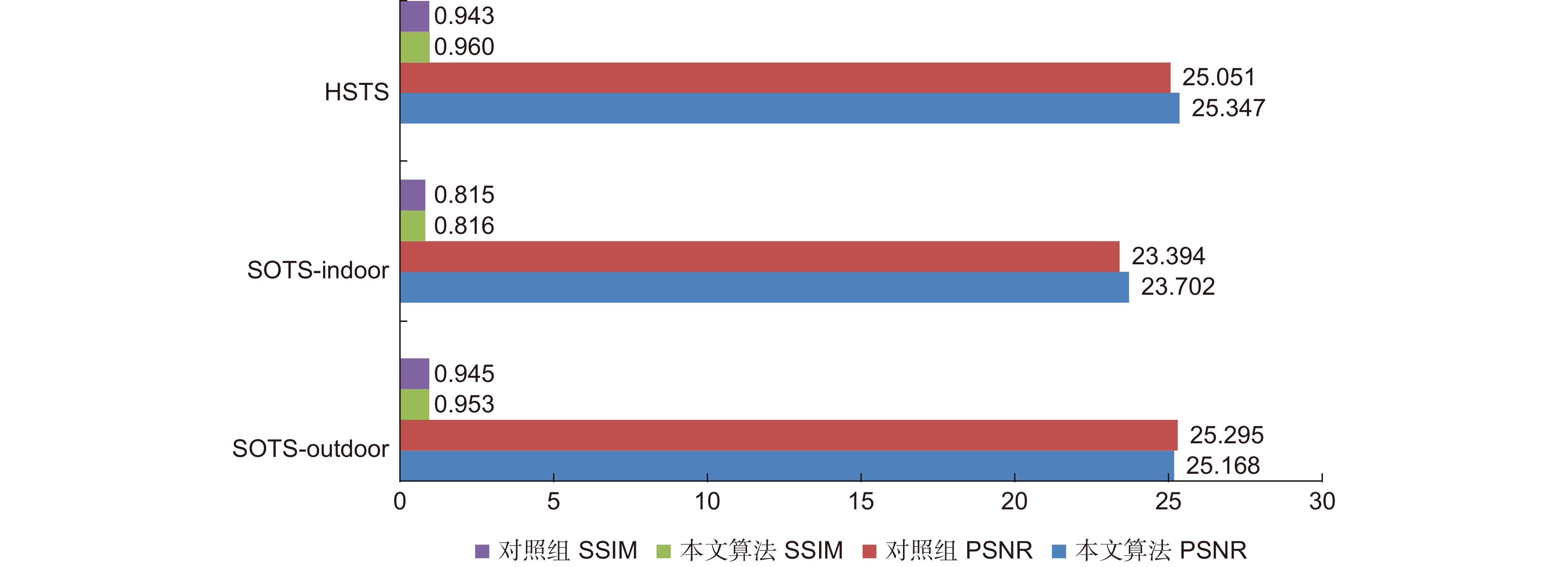
Table 3. Quantitative results of each algorithm on SOTS test-set & synthetic images of HSTS test-set
数据集 HSTS SOTS-outdoor SOTS-indoor 评价指标 PSNR SSIM PSNR SSIM PSNR SSIM DCP[7] 17.22 0.80 17.56 0.82 20.15 0.87 BCCR[9] 15.09 0.74 15.49 0.78 16.88 0.79 CAP[10] 21.54 0.87 22.30 0.91 19.05 0.84 MSCNN[15] 18.29 0.84 19.56 0.86 17.11 0.81 D-Net[16] 24.49 0.92 22.72 0.86 21.14 0.85 AOD-Net[17] 21.58 0.92 21.34 0.92 19.38 0.85 GFN[18] 22.94 0.87 21.49 0.84 22.32 0.88 DEnergy[26] 24.44 0.93 24.08 0.93 19.25 0.83 本文算法 25.35 0.96 25.17 0.96 23.70 0.82 表 4 各算法在D-HAZY、HazeRD以及BeDDE测试集上的定量结果
Table 4. Quantitative results of each algorithm on D-HAZY & HazeRD & BeDDE test-set
数据集 D-HAZY HazeRD BeDDE 评价指标 PSNR SSIM PSNR SSIM VSI VI RI DCP[7] 15.09 0.83 14.01 0.39 0.946 0.911 0.965 MSCNN[15] 13.57 0.80 15.58 0.42 0.947 0.892 0.972 D-Net[16] 13.76 0.81 15.53 0.41 0.952 0.890 0.972 AOD-Net[17] 13.13 0.79 15.63 0.45 0.954 0.896 0.970 CycleGAN[22] 13.55 0.77 15.64 0.44 0.942 0.866 0.961 RefineDNet[39] 15.44 0.83 15.61 0.43 0.960 0.907 0.971 SM-Net[24] 15.32 0.81 15.55 0.40 0.961 0.899 0.969 本文算法 15.39 0.82 15.59 0.44 0.967 0.899 0.967 表 5 对照组与本文算法在HSTS测试集真实图像上的定量结果
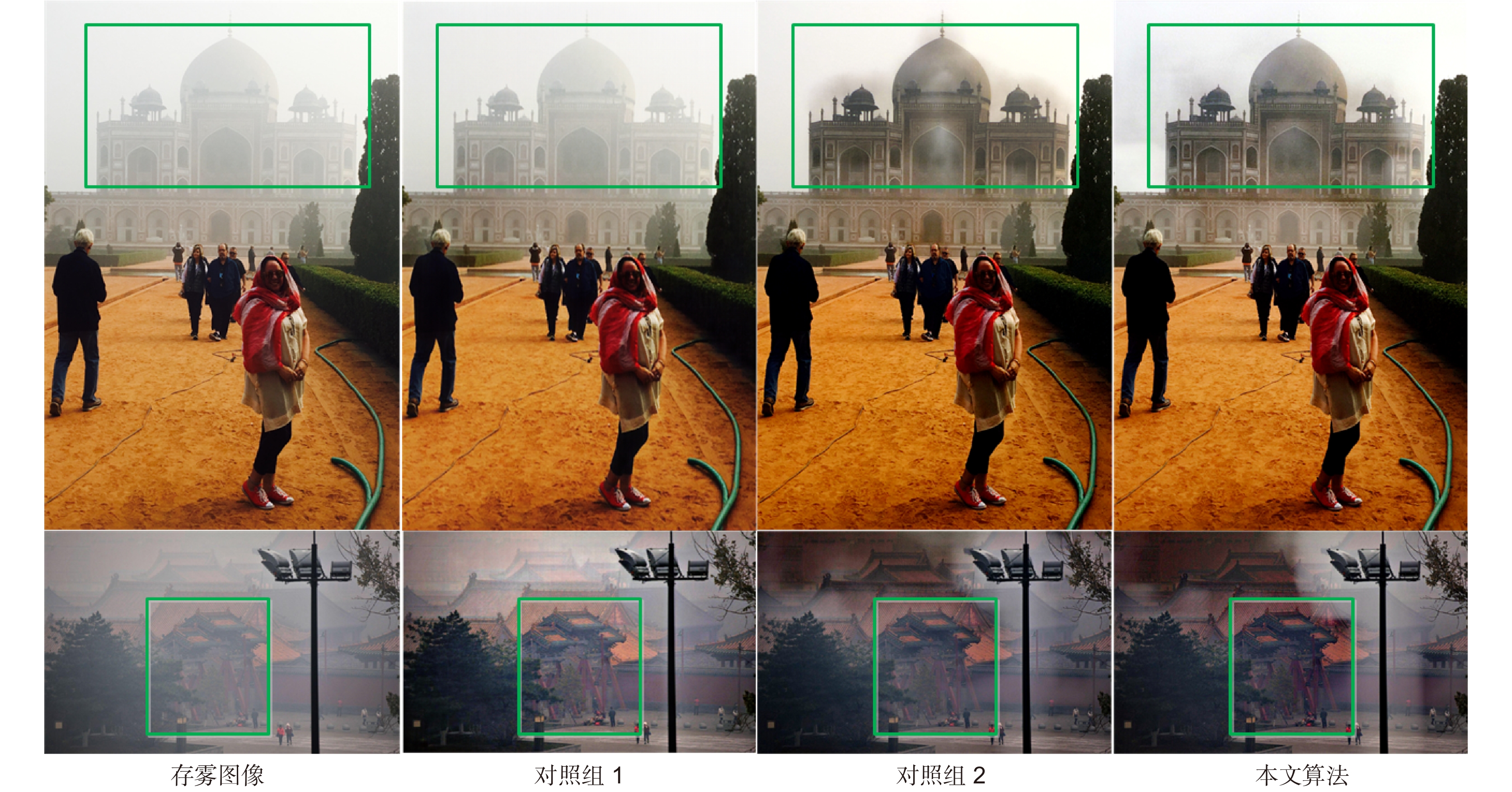
Table 5. Quantitative results of the control groups & proposed algorithm on real images of HSTS test-set
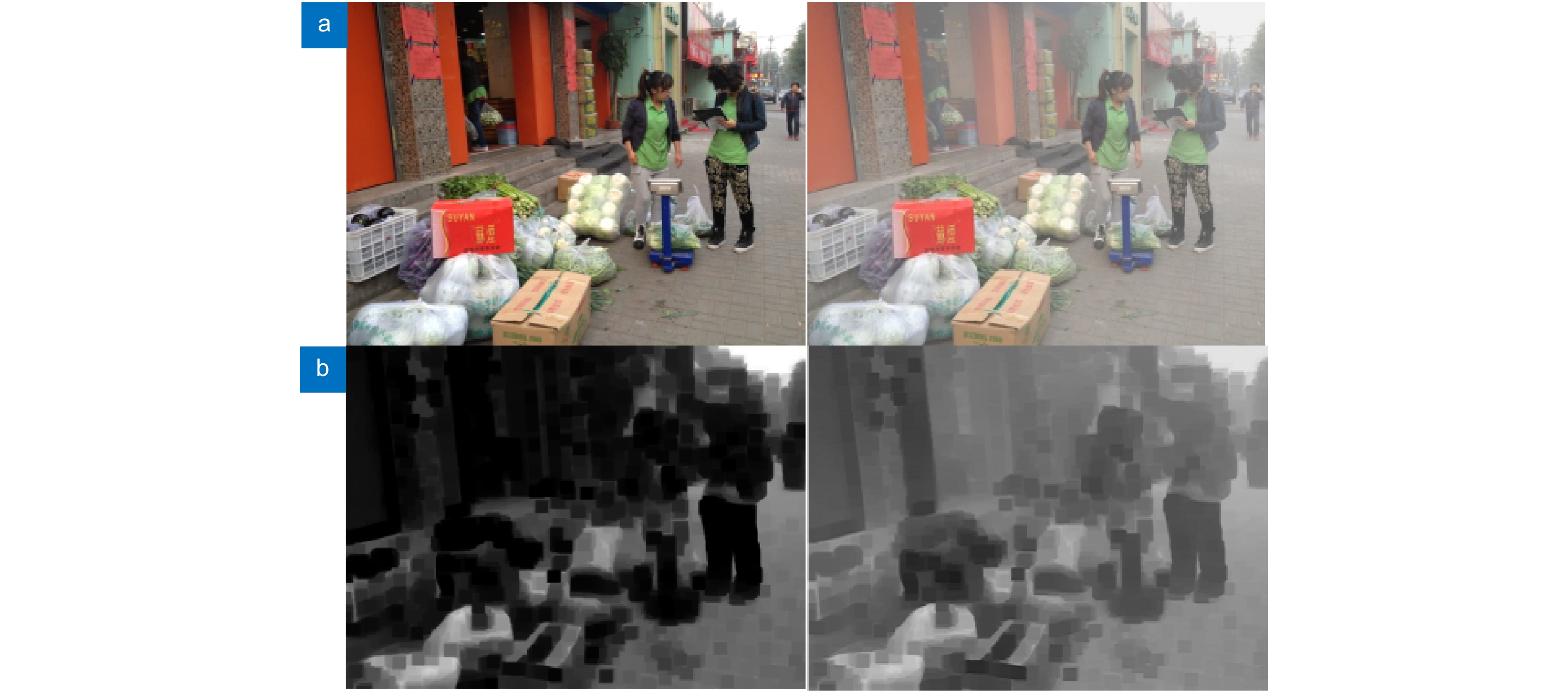
Pic1 Pic2 Pic3 Pic4 Pic5 Pic6 Pic7 Pic8 Pic9 Pic10 对照组1 e 0.0162 -0.0506 0.0868 0.1629 0.3869 0.3391 0.6262 1.0014 0.9579 0.0160 r 1.0100 1.0435 1.1291 1.0450 1.6743 1.4286 1.4641 1.4606 1.8278 1.0928 p 0.0000 0.0000 0 0.0019 0 0.0002 0 0.0002 0.0003 0.0000 对照组2 e 0.3360 0.6421 0.2709 0.0774 0.3833 0.4338 0.7845 1.8348 0.6207 0.4650 r 1.4605 1.4222 1.2640 1.2047 1.6926 1.4382 1.3379 1.5126 1.6021 1.1351 p 0.0102 0.1155 0.0001 0.0081 0 0.0072 0.0002 0.0081 0.0016 0.0286 本文算法 e 0.3534 0.6061 0.8870 0.1232 0.4504 0.6265 1.2378 2.0714 1.1443 0.5197 r 1.6284 1.5576 1.6631 1.3572 2.1599 1.6863 1.5793 1.7814 1.9561 1.3026 p 0.0082 0.1015 0.0001 0.0020 0 0.0079 0.0011 0.0108 0.0013 0.0153 -
参考文献
[1] 吕晨, 程德强, 寇旗旗, 等. 基于YOLOv3和ASMS的目标跟踪算法[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(2): 200175.
Lv C, Cheng D Q, Kou Q Q, et al. Target tracking algorithm based on YOLOv3 and ASMS[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2021, 48(2): 200175.
[2] 寇旗旗, 程德强, 于文洁, 等. 融合CLBP和局部几何特征的纹理目标分类[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(11): 180604.
Kou Q Q, Cheng D Q, Yu W J, et al. Texture target classification with CLBP and local geometric features[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(11): 180604.
[3] 江曼, 张皓翔, 程德强, 等. 融合HSV与方向梯度特征的多尺度图像检索[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(11): 210310.
Jiang M, Zhang H X, Cheng D Q, et al. Multi-scale image retrieval based on HSV and directional gradient features[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2021, 48(11): 210310.
[4] Kim T K, Paik J K, Kang B S. Contrast enhancement system using spatially adaptive histogram equalization with temporal filtering[J]. IEEE Trans Consum Electron, 1998, 44(1): 82−87. doi: 10.1109/30.663733
[5] Zhou J C, Zhang D H, Zou P Y, et al. Retinex-based laplacian pyramid method for image defogging[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 122459−122472. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2934981
[6] Nayar S K, Narasimhan S G. Vision in bad weather[C]//Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, 1999: 820–827.
[7] He K M, Sun J, Tang X O. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2011, 33(12): 2341−2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168
[8] He K M, Sun J, Tang X O. Guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2013, 35(6): 1397−1409. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.213
[9] Meng G F, Wang Y, Duan J Y, et al. Efficient image dehazing with boundary constraint and contextual regularization[C]//Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, 2013: 617–624.
[10] Zhu Q S, Mai J M, Shao L. A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2015, 24(11): 3522−3533. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2446191
[11] 王新, 张旭东, 张骏, 等. 结合光场多线索和大气散射模型的去雾算法[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(9): 190634.
Wang X, Zhang X D, Zhang J, et al. Image dehazing algorithm by combining light field multi-cues and atmospheric scattering model[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(9): 190634.
[12] Zhao D, Xu L, Yan Y H, et al. Multi-scale Optimal Fusion model for single image dehazing[J]. Signal Process Image Commun, 2019, 74: 253−265. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2019.02.004
[13] Yang Y, Wang Z W. Haze removal: push DCP at the edge[J]. IEEE Signal Process Lett, 2020, 27: 1405−1409. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.3013741
[14] Wang S, Chen J Y. Single image dehazing using dark channel fusion and dark channel confidence[C]//Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Big Data & Artificial Intelligence & Software Engineering, Bangkok, 2020: 439–444.
[15] Ren W Q, Liu S, Zhang H, et al. Single image dehazing via multi-scale convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, 2016: 154–169.
[16] Cai B L, Xu X M, Jia K, et al. DehazeNet: an end-to-end system for single image haze removal[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2016, 25(11): 5187−5198. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2598681
[17] Li B Y, Peng X L, Wang Z Y, et al. AOD-Net: all-in-one dehazing network[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, 2017: 4780–4788.
[18] Chen D D, He M M, Fan Q N, et al. Gated context aggregation network for image dehazing and deraining[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, 2019: 1375–1383.
[19] Goodfellow I J, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, 2014: 2672–2680.
[20] Li R D, Pan J S, Li Z H, et al. Single image dehazing via conditional generative adversarial network[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, 2018: 8202–8211.
[21] Johnson J, Alahi A, Fei-Fei L. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, 2016: 694–711.
[22] Engin D, Genc A, Ekenel H K. Cycle-dehaze: enhanced CycleGAN for single image dehazing[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, 2018: 939–946.
[23] Zhu J Y, Park T, Isola P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, 2017: 2242–2251.
[24] Li L R H, Dong Y L, Ren W Q, et al. Semi-supervised image dehazing[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2020, 29: 2766−2779. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2952690
[25] Pan J S, Sun D Q, Pfister H, et al. Blind image deblurring using dark channel prior[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, 2016: 1628–1636.
[26] Golts A, Freedman D, Elad M. Unsupervised single image dehazing using dark channel prior loss[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2020, 29: 2692−2701. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2952032
[27] Shen Z Y, Lai W S, Xu T F, et al. Deep semantic face deblurring[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, 2018: 8260–8269.
[28] Tao X, Gao H Y, Shen X Y, et al. Scale-recurrent network for deep image deblurring[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, 2018: 8174–8182.
[29] Nah S, Kim T H, Lee K M. Deep multi-scale convolutional neural network for dynamic scene deblurring[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, 2017: 257–265.
[30] Isola P, Zhu J Y, Zhou T H, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, 2017: 5967–5976.
[31] Ledig C, Theis L, Huszár F, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, 2017: 105–114.
[32] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, 2016: 770–778.
[33] Li B Y, Ren W Q, Fu D P, et al. Benchmarking single-image dehazing and beyond[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2019, 28(1): 492−505. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2867951
[34] Silberman N, Hoiem D, Kohli P, et al. Indoor segmentation and support inference from RGBD images[C]//Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, 2012.
[35] Scharstein D, Szeliski R. High-accuracy stereo depth maps using structured light[C]//Proceedings of 2003 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Madison, 2003: I-I.
[36] Beijing realtime weather photos[EB/OL]. (2022-06). https://www.tour-beijing.com/real_time_weather_photo/.
[37] Liu F Y, Shen C H, Lin G S, et al. Learning depth from single monocular images using deep convolutional neural fields[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2016, 38(10): 2024−2039. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2505283
[38] Hambarde P, Dudhane A, Patil P W, et al. Depth estimation from single image and semantic prior[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Abu Dhabi, 2020: 1441–1445.
[39] Zhao S Y, Zhang L, Shen Y, et al. RefineDNet: a weakly supervised refinement framework for single image dehazing[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2021, 30: 3391−3404. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3060873
[40] Ancuti C, Ancuti C O, De Vleeschouwer C, et al. D-HAZY: a dataset to evaluate quantitatively dehazing algorithms[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Phoenix, 2016: 2226–2230.
[41] Zhang Y F, Ding L, Sharma G. HazeRD: an outdoor scene dataset and benchmark for single image dehazing[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Beijing, 2017: 3205–3209.
[42] Zhang L, Shen Y, Li H Y. VSI: a visual saliency-induced index for perceptual image quality assessment[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2014, 23(10): 4270−4281. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2346028
[43] Zhao S Y, Zhang L, Huang S Y, et al. Dehazing evaluation: real-world benchmark datasets, criteria, and baselines[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2020, 29: 6947−6962. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2995264
[44] Hautière N, Tarel J P, Aubert D, et al. Blind contrast enhancement assessment by gradient ratioing at visible edges[J]. Image Anal Stereol, 2008, 27(2): 87−95.
[45] 崔光茫, 张克奇, 毛磊, 等. 结合多尺度分解和梯度绝对值算子的显微图像清晰度评价方法[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(6): 180531.
Cui G M, Zhang K Q, Mao L, et al. Micro-image definition evaluation using multi-scale decomposition and gradient absolute value[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(6): 180531.
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: