-
摘要
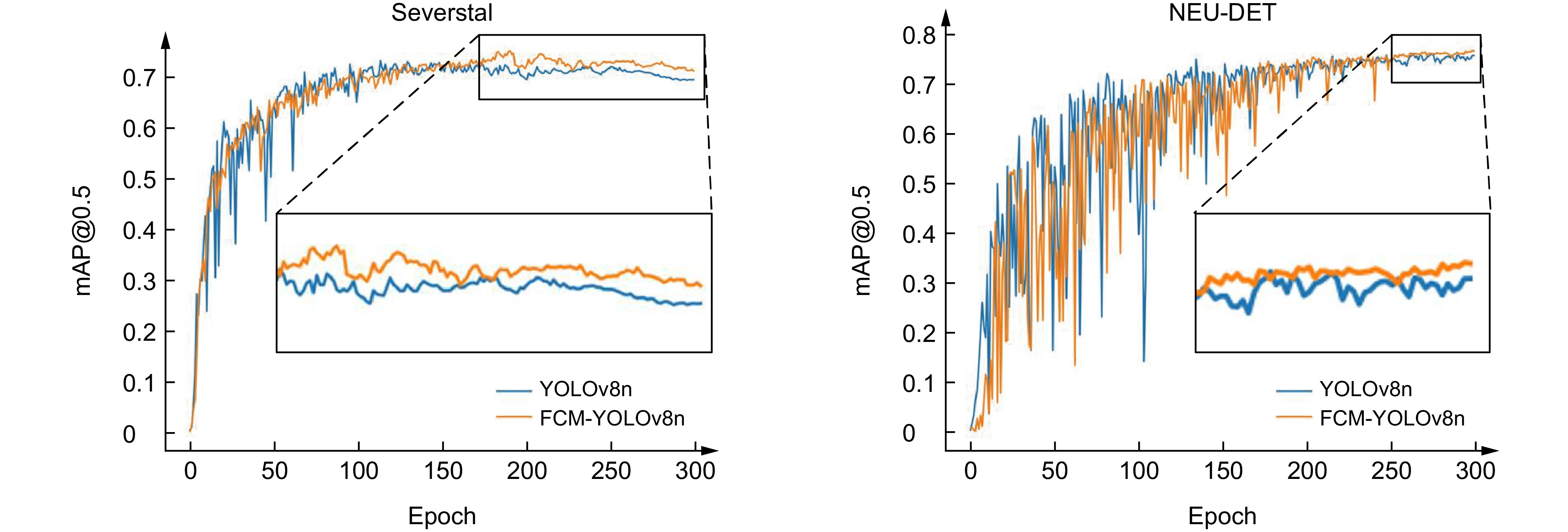
针对现有钢材表面缺陷检测算法在资源消耗、检测精度和效率等方面存在的不足,提出一种基于YOLOv8n的轻量级钢材缺陷检测算法(FCM-YOLOv8n)。该方法一是采用频率感知特征融合网络,高效提取并融合高频信息,以降低计算成本并提升检测速度;二是重构轻量化特征交互模块(Cc-C2f),有效保留空间和通道依赖关系,减少特征冗余,以降低模型参数量和计算复杂度;三是利用多谱注意力机制,从频域维度减少特征信息缺失,以提升复杂缺陷的识别准确度。在Severstal和NEU-DET钢材缺陷数据集上的实验结果表明,相较于YOLOv8n算法,FCM-YOLOv8n算法的mAP@0.5分别提高2.2%和1.5%;参数量和复杂度分别降低0.5 M和1.5 G;FPS分别达到143 f/s和154 f/s,展示优异的实时性。该算法在检测精度、计算成本和效率之间实现良好的平衡,为边缘终端设备应用提供有力的支持。在GC10-DET数据集上的进一步验证表明,FCM-YOLOv8n相较于基线模型mAP@0.5提升2.9%,充分佐证其卓越的泛化能力。
-
关键词:
- 缺陷检测 /
- YOLOv8n /
- 频率感知特征融合网络 /
- Cc-C2f /
- 多谱注意力
Abstract
In response to the deficiencies of existing steel surface defect detection algorithms in terms of resource consumption, detection accuracy, and efficiency, a lightweight steel defect detection algorithm based on YOLOv8n (FCM-YOLOv8n) is proposed. First, a frequency-aware feature fusion network is utilized to efficiently extract and integrate high-frequency information, reducing computational costs while enhancing detection speed. Second, a lightweight feature interaction module (Cc-C2f) is restructured to effectively preserve spatial and channel dependencies while reducing feature redundancy, thereby lowering model parameters and computational complexity. Finally, a multi-spectrum attention mechanism is applied to mitigate feature information loss in the frequency domain, improving the accuracy of detecting complex defects. Experimental results on the Severstal and NEU-DET steel defect datasets show that, compared to YOLOv8n, the FCM-YOLOv8n algorithm achieves a 2.2% and 1.5% improvement in mAP@0.5, respectively, with a 0.5 M and 1.5 G reduction in parameters and computational complexity. The FPS reaches 143 f/s and 154 f/s, respectively, demonstrating excellent real-time performance. The algorithm achieves an optimal balance between detection accuracy, computational cost, and efficiency, providing robust support for edge device applications. Further validation on the GC10-DET dataset shows a 2.9% improvement in mAP@0.5 compared to the baseline model, fully demonstrating the algorithm's exceptional generalization ability.
-
Key words:
- defect detection /
- YOLOv8n /
- frequency-aware feature fusion network /
- Cc-C2f /
- multi-spectral attention
-
Overview
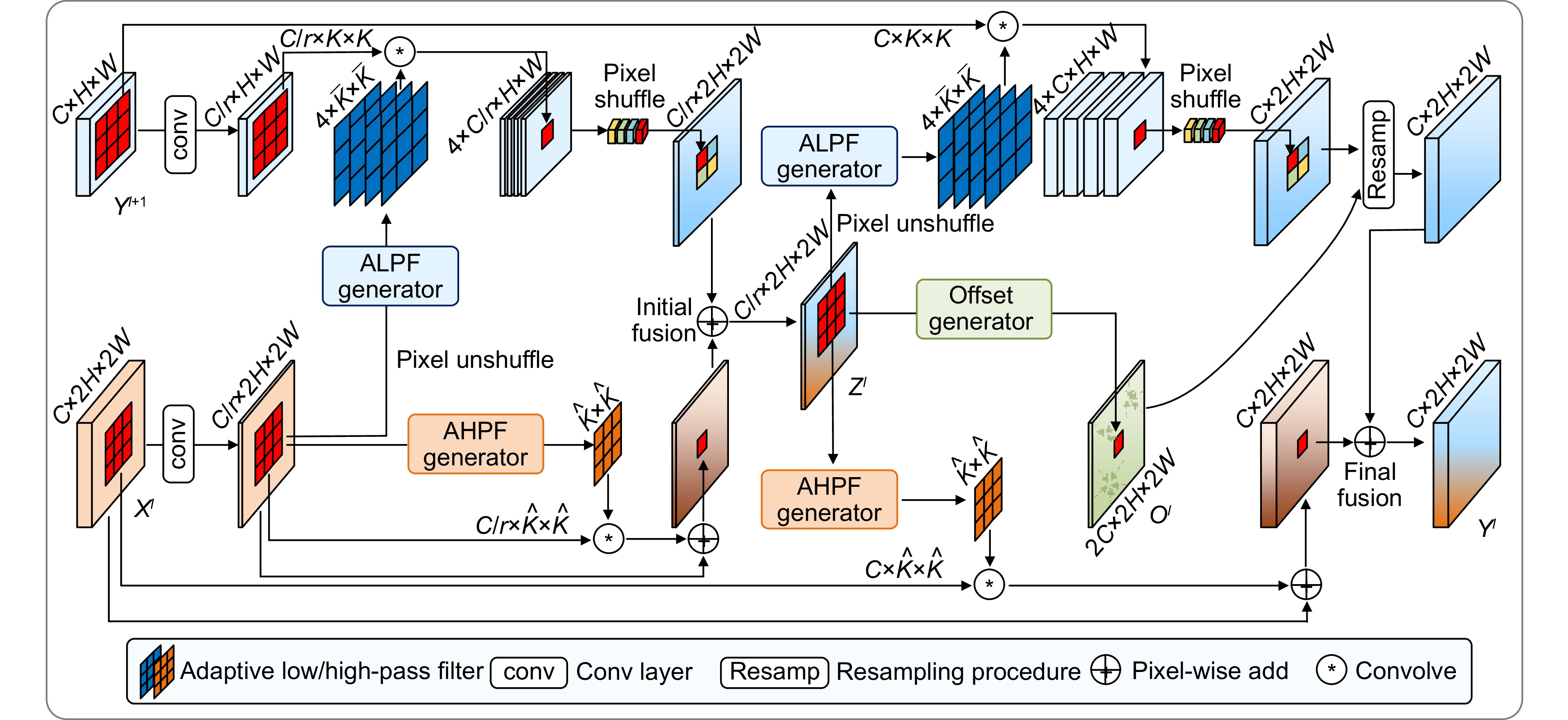
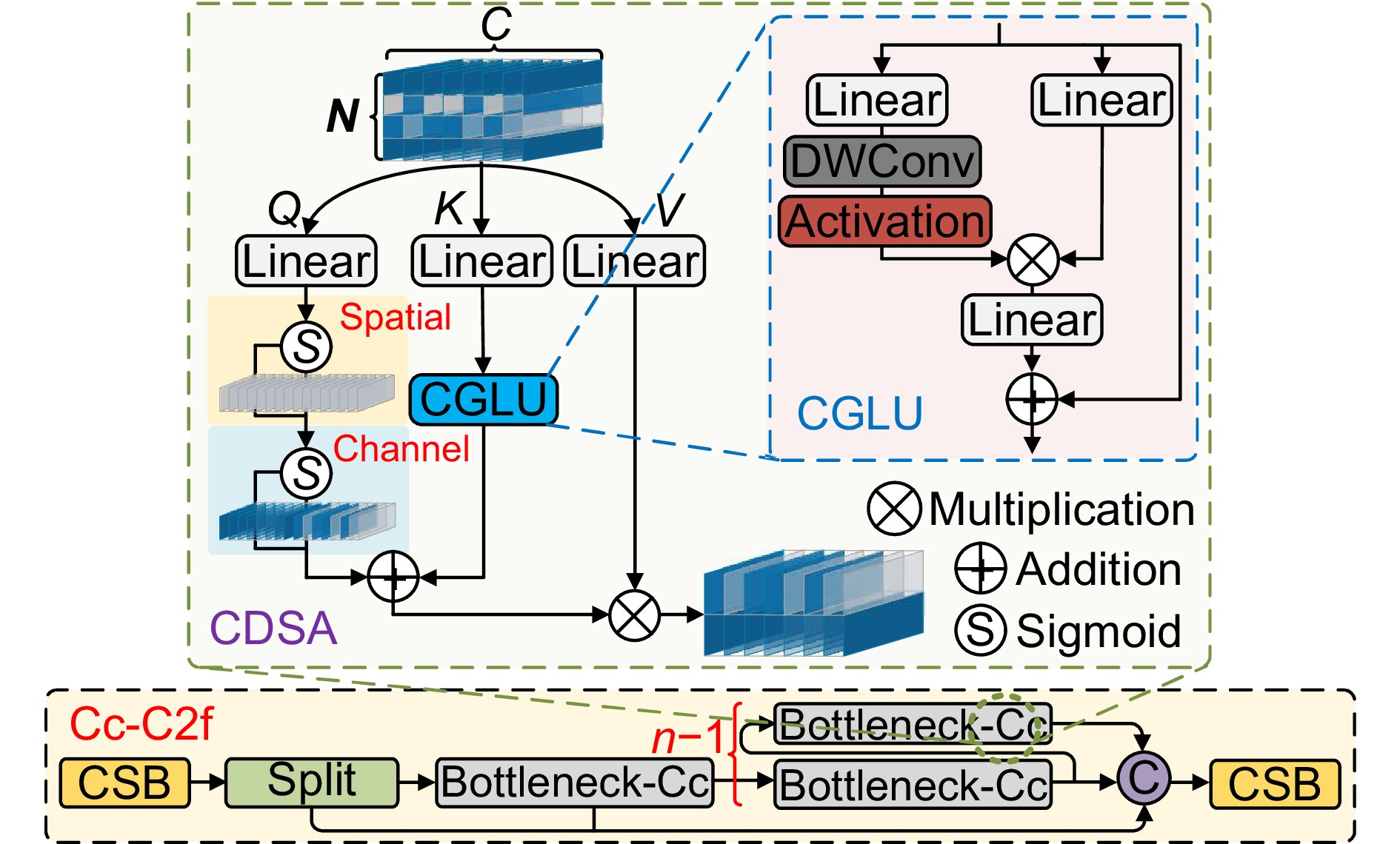
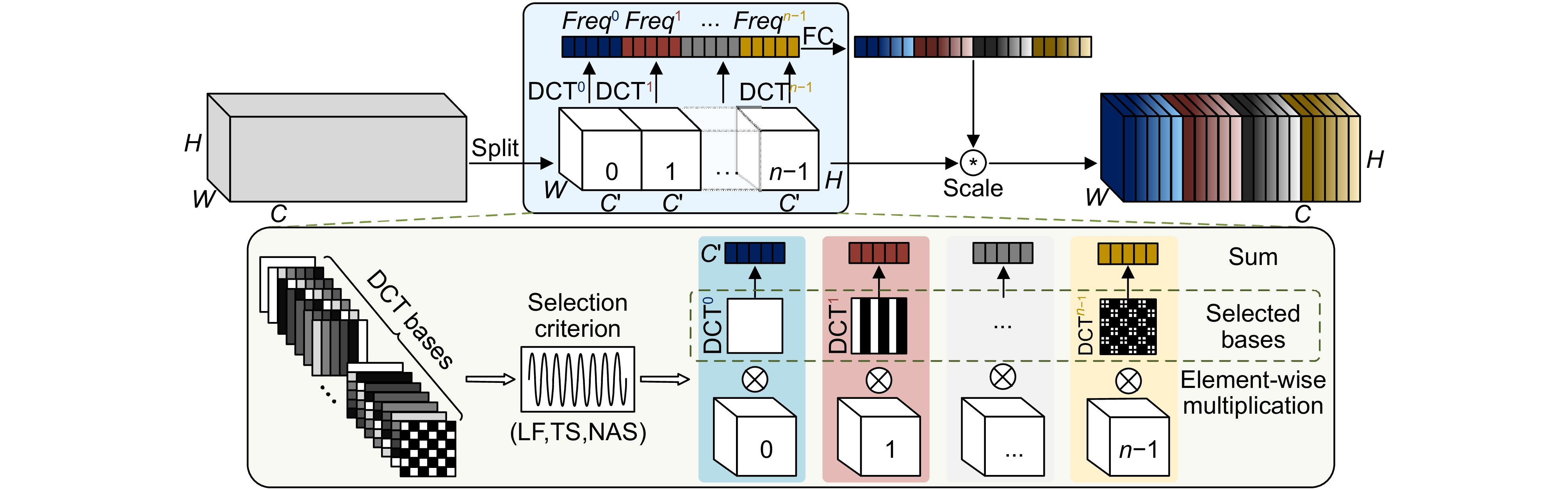
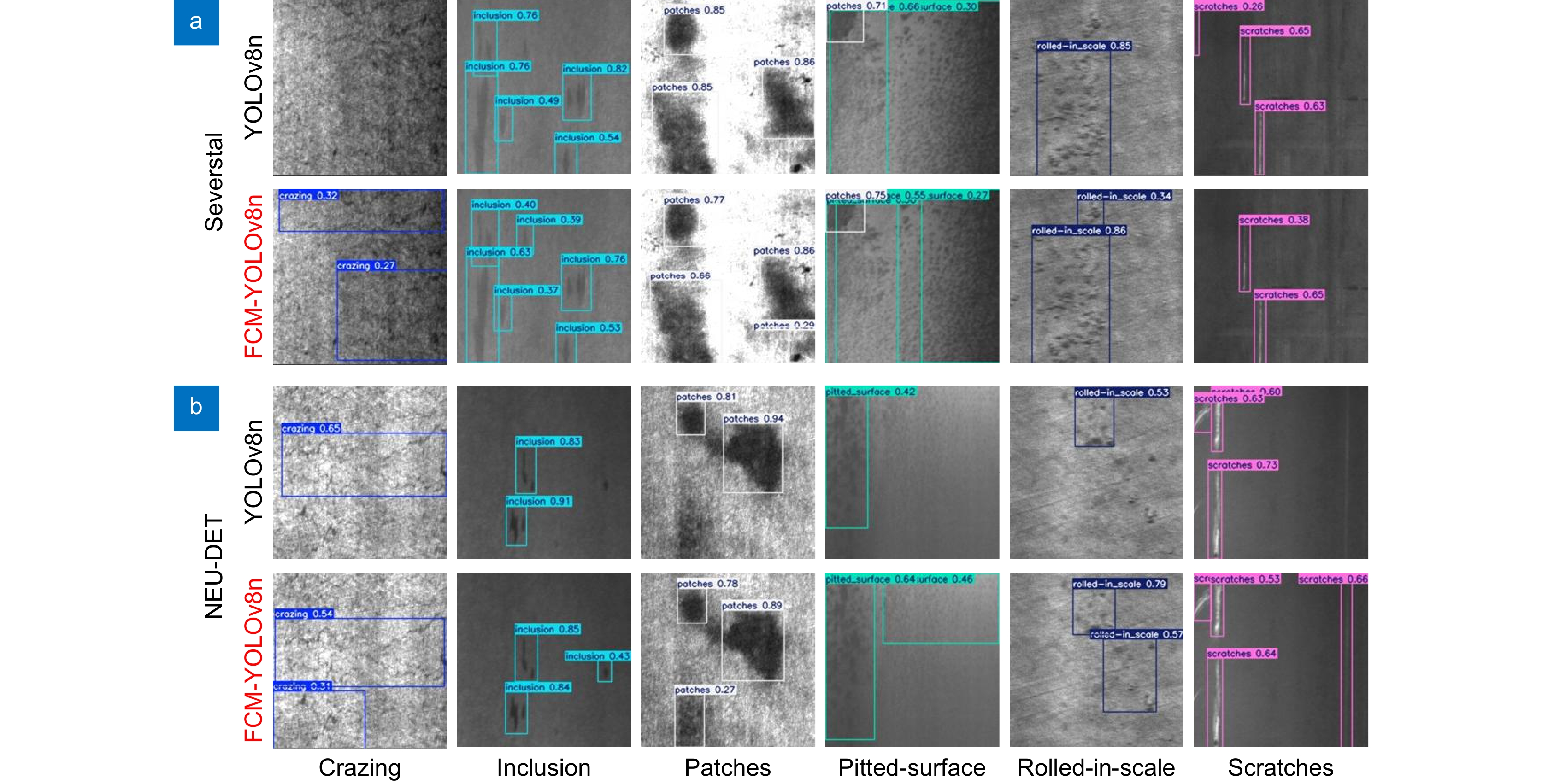
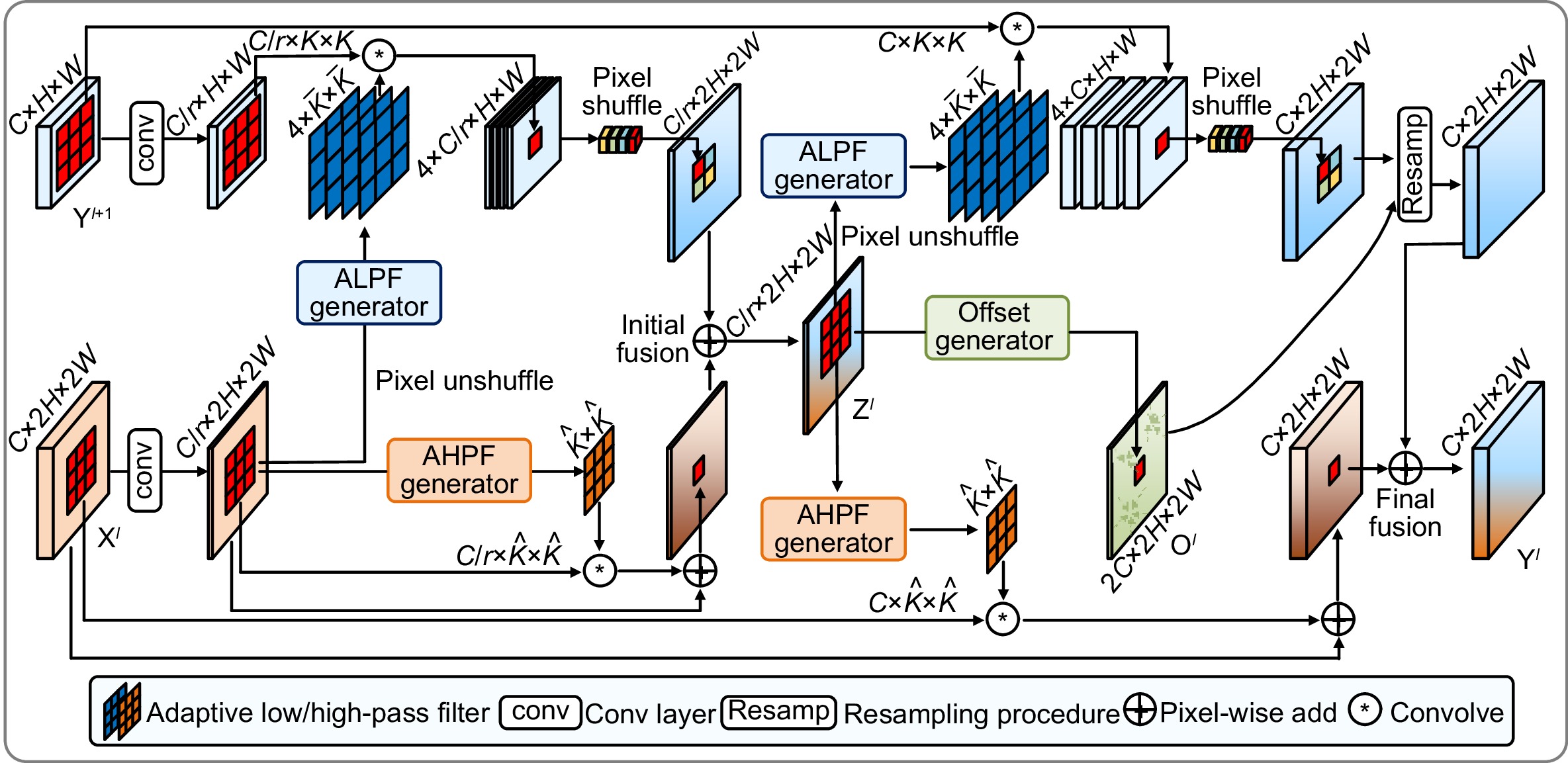
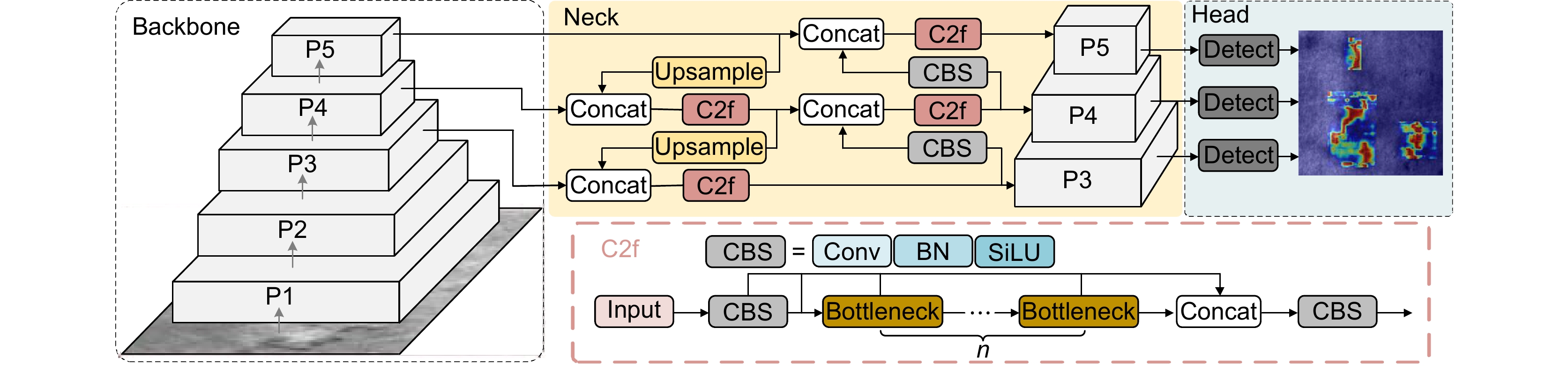
Overview: In response to the deficiencies of existing steel surface defect detection algorithms in terms of resource consumption, detection accuracy, and efficiency, a lightweight steel defect detection algorithm based on YOLOv8n (FCM-YOLOv8n) is proposed. This algorithm incorporates three principal innovative elements. First, a frequency-aware feature fusion network is utilized to efficiently extract and integrate high-frequency information, reducing computational costs while enhancing detection speed. This network ingeniously integrates an adaptive low-pass filter generator (ALPF), an offset generator, and an adaptive high-pass filter generator (AHPF). The ALPF generator forecasts spatially-variant low-pass filters, which serve to attenuate high-frequency constituents within objects, thereby diminishing intra-class disparities during the up-sampling procedure. The offset generator plays a pivotal role in refining pronounced inconsistent features and tenuous boundaries. It achieves this by substituting inconsistent elements with more congruous ones via resampling. Meanwhile, the AHPF generator functions to augment the high-frequency detailed boundary information that is otherwise lost during down-sampling. Collectively, this fusion paradigm substantially augments feature consistency and sharpens object boundaries. Secondly, a lightweight feature interaction module (Cc-C2f) is restructured to effectively preserve spatial and channel dependencies while reducing feature redundancy, lowering model parameters and computational complexity. The Cc-C2f module integrates the lightweight convolutional additive self-attention mechanism (CDSA) and the lightweight convolutional gated linear unit (CGLU). The CDSA module takes into account both channel and spatial information, and employs fast linear transformation to reduce the number of model parameters and computational complexity. The CGLU module combines local and global information to enhance the network's representational ability. Finally, a multi-spectrum attention mechanism is applied to mitigate feature information loss in the frequency domain, improving the accuracy of detecting complex defects. Experimental results on the Severstal and NEU-DET steel defect datasets show that, compared to YOLOv8n, the FCM-YOLOv8n algorithm achieves a 2.2% and 1.5% improvement in mAP@0.5, respectively, with a 0.5 M and 1.5 G reduction in parameters and computational complexity. The FPS reaches 143 f/s and 154 f/s, respectively, demonstrating excellent real-time performance. The algorithm achieves an optimal balance between detection accuracy, computational cost, and efficiency, providing robust support for edge device applications. Further validation on the GC10-DET dataset shows a 2.9% improvement in mAP@0.5 compared to the baseline model, demonstrating the algorithm's exceptional generalization ability. Through comparative analysis with disparate algorithms, the superiority of the proposed algorithm's performance is further accentuated.
-

-
表 1 Cc-C2f与C2f对比实验
Table 1. Comparison experiment between Cc-C2f and C2f
Module mAP@0.5/% Par/M FLOPs/G FPS C2f 75.2 3.0 8.1 181 Cc-C2f 75.9 2.6 6.9 161 表 2 消融实验数据
Table 2. Ablation experimental data
Dataset FreqFusion Cc-C2f MA mAP@0.5/% Par/M FLOPs/G FPS Severstal 72.9 3.0 8.1 153 √ 74.5 2.8 7.7 156 √ 73.0 2.6 6.9 141 √ 74.1 3.0 8.1 145 √ √ 74.0 2.5 6.6 145 √ √ √ 75.1 2.5 6.6 143 NEU-DET 75.2 3.0 8.1 181 √ 75.7 2.8 7.7 188 √ 75.9 2.6 6.9 161 √ 75.9 3.0 8.1 182 √ √ 76.0 2.5 6.6 154 √ √ √ 76.7 2.5 6.6 154 表 3 不同算法检测数据对比
Table 3. Comparison of detection data from different algorithms
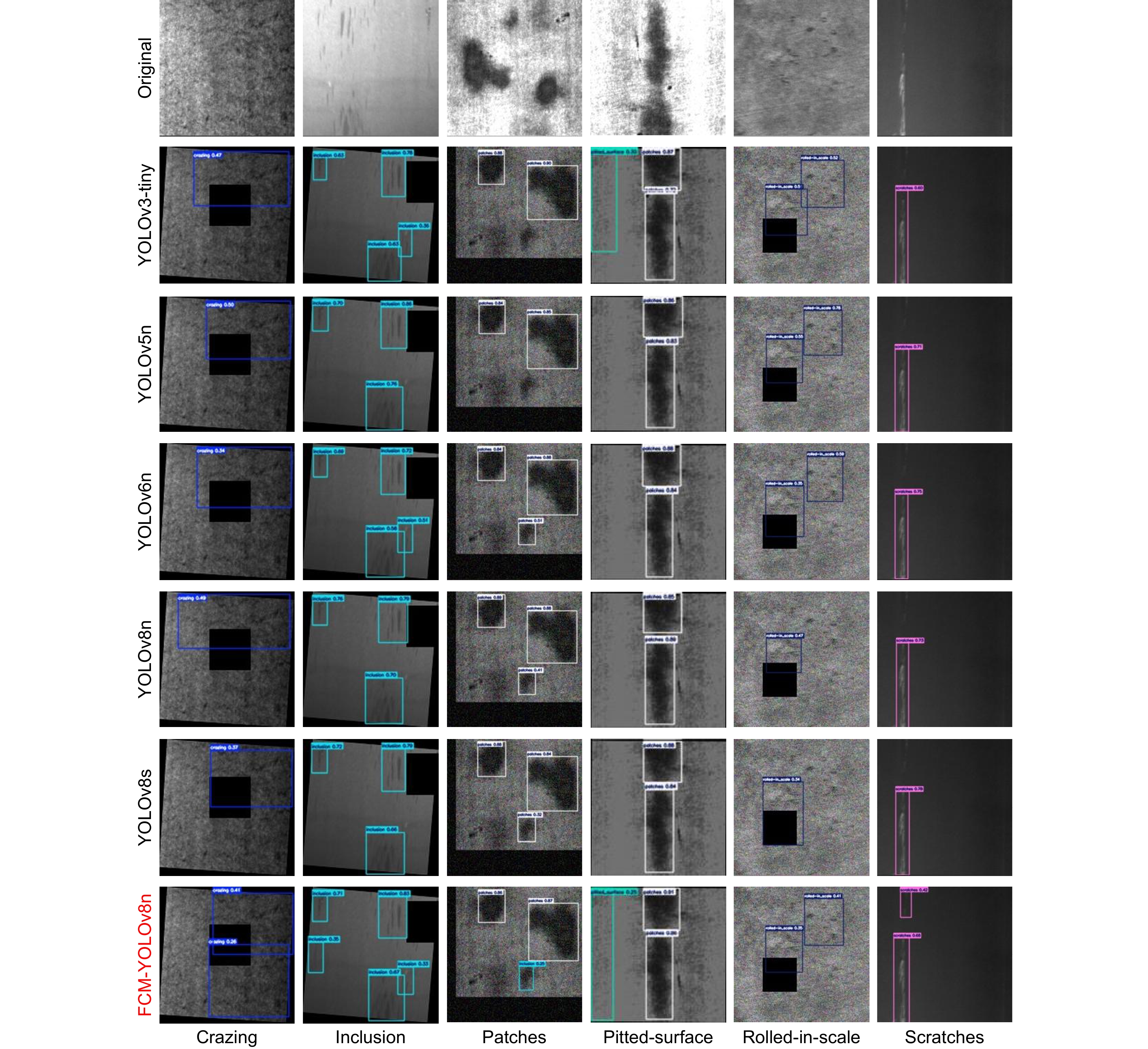
Dataset Model mAP@0.5/% Par/M FLOPs/G FPS Severstal YOLOv3-tiny 60.2 12.1 18.9 151 YOLOv4-tiny 55.5 5.9 16.1 97 YOLOv5n 72.6 2.5 7.1 175 YOLOv5s 72.1 9.1 23.8 120 YOLOv6n 74.5 4.2 11.8 153 YOLOv7-tiny 61.5 6.0 13.1 76 YOLOv8n 72.9 3.0 8.1 153 YOLOv8s 73.7 11.1 28.4 106 Ours 75.1 2.5 6.6 143 NEU-DET YOLOv3-tiny 64.4 12.1 18.9 156 YOLOv4-tiny 64.0 5.9 16.1 120 YOLOv5n 73.2 2.5 7.1 185 YOLOv5s 75.8 9.1 23.8 106 YOLOv6n 75.9 4.2 11.8 185 YOLOv7-tiny 68.6 6.0 13.1 89 Reference [3] 74.4 5.4 8.9 87 Reference [10] 75.1 2.3 9.0 - Reference [11] 75.7 14.4 - 109 Reference [12] 75.7 7.5 16.8 94 Reference [13] 76.0 3.0 - - YOLOv8n 75.2 3.0 8.1 181 YOLOv8s 75.2 11.1 28.4 108 Ours 76.7 2.5 6.6 154 表 4 GC10-DET数据集检测结果对比
Table 4. Comparison of GC10-DET dataset detection results
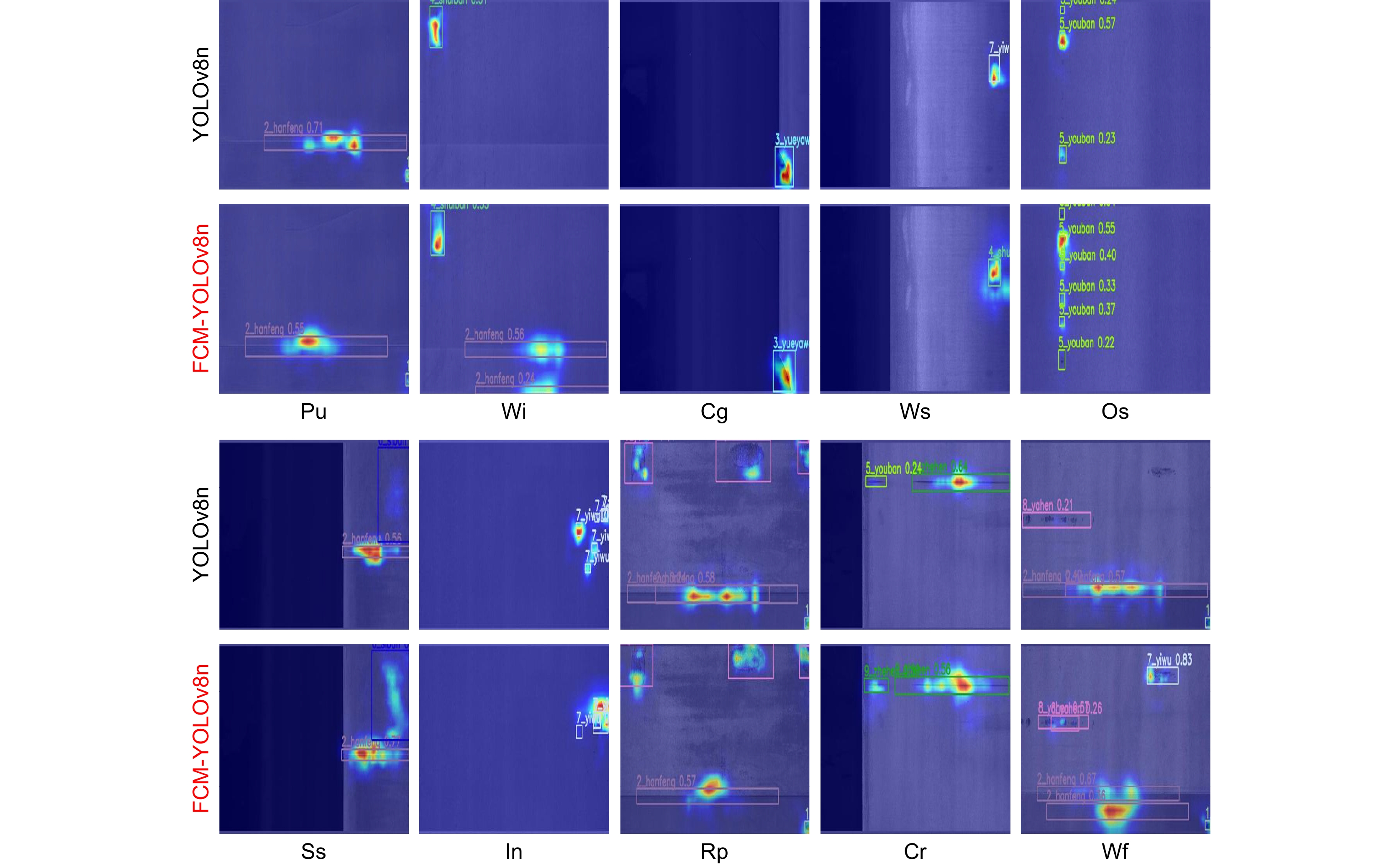
Model AP/% mAP@0.5/% Par/M FLOPs/G FPS Pu WI Cg Ws Os Ss In Rp Cr Wf YOLOv8n 97.9 89.2 96.0 77.9 68.2 63.0 37.5 28.1 44.7 85.6 68.8 3.0 8.1 303 FCM-YOLOv8n 98.6 89.3 96.5 78.4 69.7 67.3 29.1 36.6 60.8 90.4 71.7 2.5 6.6 270 -
参考文献
[1] 黄硕清, 黄金贵. 基于RFB和YOLOv5特征增强融合改进的钢材缺陷检测方法[J]. 计算机工程, 2024. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0068476
Huang S Q, Huang J G. Improved steel defect detection method based on enhanced fusion of RFB and YOLOv5 features[J]. Comput Eng, 2024. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0068476
[2] 梁礼明, 龙鹏威, 卢宝贺, 等. 改进GBS-YOLOv7t的钢材表面缺陷检测[J]. 光电工程, 2024, 51(5): 240044. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240044
Liang L M, Long P W, Lu B H, et al. Improvement of GBS-YOLOv7t for steel surface defect detection[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2024, 51(5): 240044. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240044
[3] 梁礼明, 龙鹏威, 冯耀, 等. 改进轻量化VTG-YOLOv7-tiny的钢材表面缺陷检测[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2024, 32(8): 1227−1240. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20243208.1227
Liang L M, Long P W, Feng Y, et al. Improving the lightweight VTG-YOLOv7-tiny for steel surface defect detection[J]. Opt Precis Eng, 2024, 32(8): 1227−1240. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20243208.1227
[4] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014: 580–587. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.81.
[5] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot multibox detector[C]//Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision–ECCV 2016, 2016: 21–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2.
[6] Reis D, Kupec J, Hong J, et al. Real-time flying object detection with YOLOv8[Z]. arXiv: 2305.09972, 2023. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.09972.
[7] Wang X Q, Gao H B, Jia Z M, et al. BL-YOLOv8: an improved road defect detection model based on YOLOv8[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(20): 8361. doi: 10.3390/s23208361
[8] Zeng S, Yang W Z, Jiao Y Y, et al. SCA-YOLO: a new small object detection model for UAV images[J]. Vis Comput, 2024, 40(3): 1787−1803. doi: 10.1007/s00371-023-02886-y
[9] 李刚, 邵瑞, 周鸣乐, 等. 基于注意力的轻量级工业产品缺陷检测网络[J]. 计算机工程, 2023, 49(11): 275−283. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0066270
Li G, Shao R, Zhou M L, et al. Lightweight industrial products defect detection network based on attention[J]. Comput Eng, 2023, 49(11): 275−283. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0066270
[10] 刘毅, 蒋三新. 基于改进YOLOX的钢材表面缺陷检测研究[J]. 现代电子技术, 2024, 47(9): 131−138. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2024.09.024
Liu Y, Jiang S X. Steel surface defect detection algorithm based on improved YOLOX[J]. Mod Electron Tech, 2024, 47(9): 131−138. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2024.09.024
[11] 马冬梅, 朱佳浩. 面向热轧带钢表面缺陷检测的YOLOv5算法优化分析[J]. 制造技术与机床, 2024, (6): 153−160. doi: 10.19287/j.mtmt.1005-2402.2024.06.023
Ma D M, Zhu J H. The optimization of YOLOv5 algorithm for detecting surface defects on hot rolled strips[J]. Manuf Technol Mach Tool, 2024, (6): 153−160. doi: 10.19287/j.mtmt.1005-2402.2024.06.023
[12] 徐薪羽, 沈通, 吕佳. 基于改进YOLOv8算法的钢材表面缺陷检测[J]. 自动化应用, 2024, 65(15): 6−10. doi: 10.19769/j.zdhy.2024.15.002
Xu X Y, Shen T, Lv J. Steel Surface Defect Detection Based On Improved YOLOv8 algorithm[J]. Autom Appl, 2024, 65(15): 6−10. doi: 10.19769/j.zdhy.2024.15.002
[13] Chen L W, Fu Y, Gu L, et al. Frequency-aware feature fusion for dense image prediction[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2024, 46(12): 10763−10780. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3449959
[14] Zhang T F, Li L, Zhou Y, et al. CAS-ViT: convolutional additive self-attention vision transformers for efficient mobile applications[Z]. arXiv: 2408.03703, 2024. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2408.03703.
[15] Shi D. TransNeXt: robust foveal visual perception for vision transformers[C]//Proceedings of 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024: 17773–17783. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.01683.
[16] Qin Z Q, Zhang P Y, Wu F, et al. FcaNet: frequency channel attention networks[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2021: 783–792. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00082.
[17] Yeung C C, Lam K M. Efficient fused-attention model for steel surface defect detection[J]. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas, 2022, 71: 2510011. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3176239
[18] Wang X, Zhuang K Y. An improved YOLOX method for surface defect detection of steel strips[C]//Proceedings of 2023 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Power, Electronics and Computer Applications, 2023: 152–157. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPECA56706.2023.10075827.
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: