Lightweight remote sensing military aircraft target detection in complex backgrounds
-
摘要
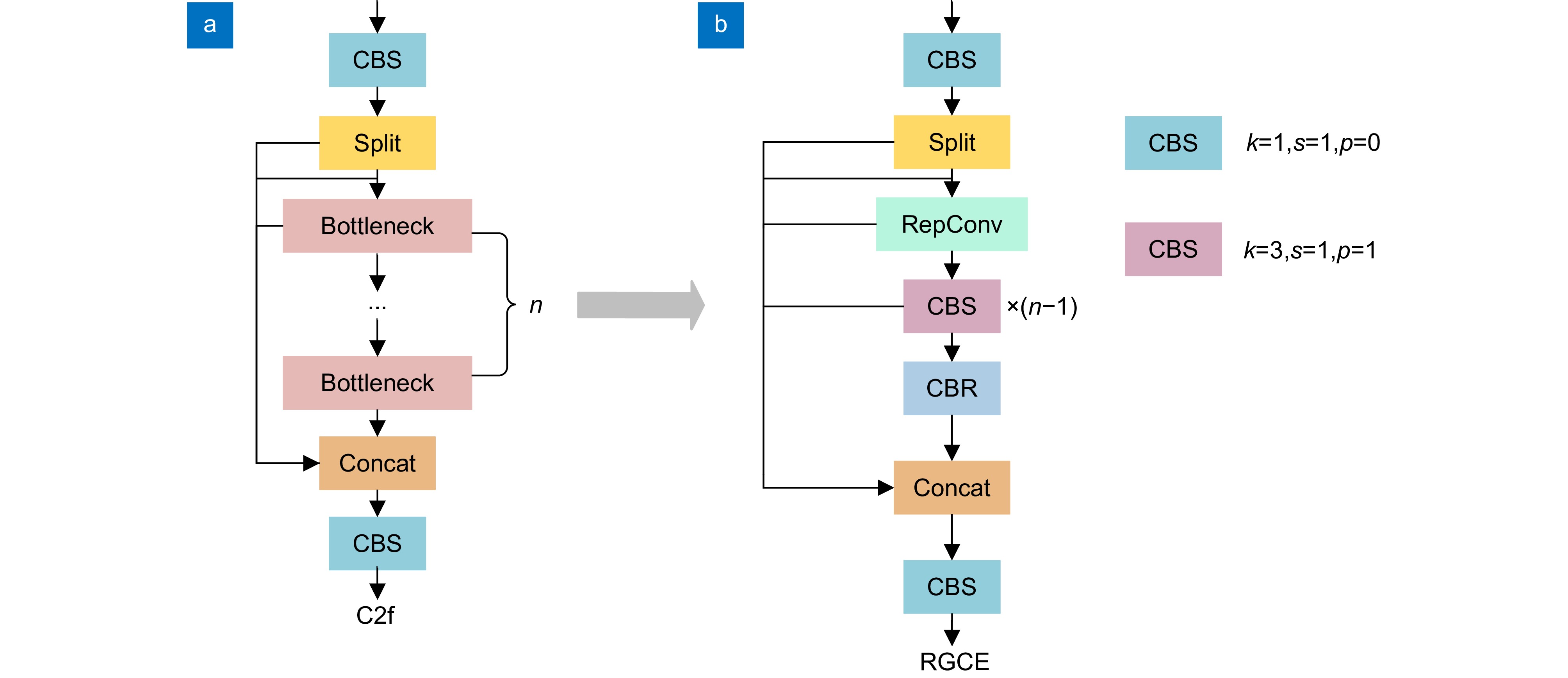
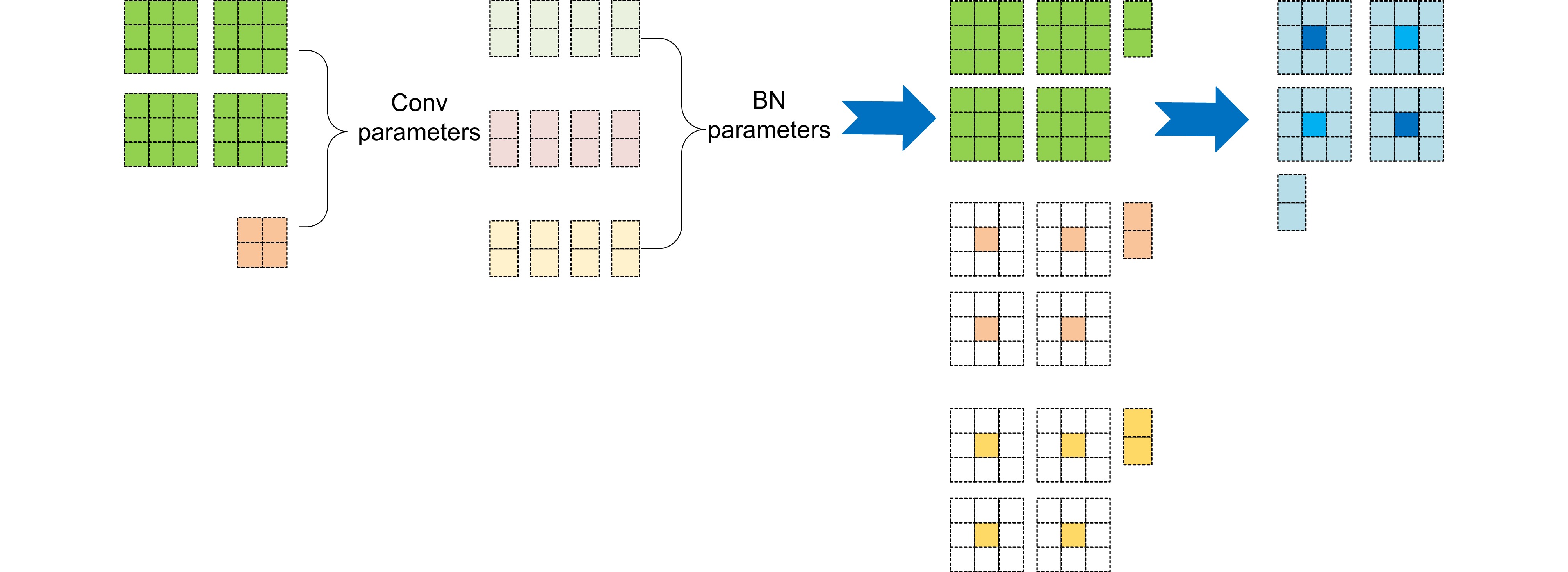
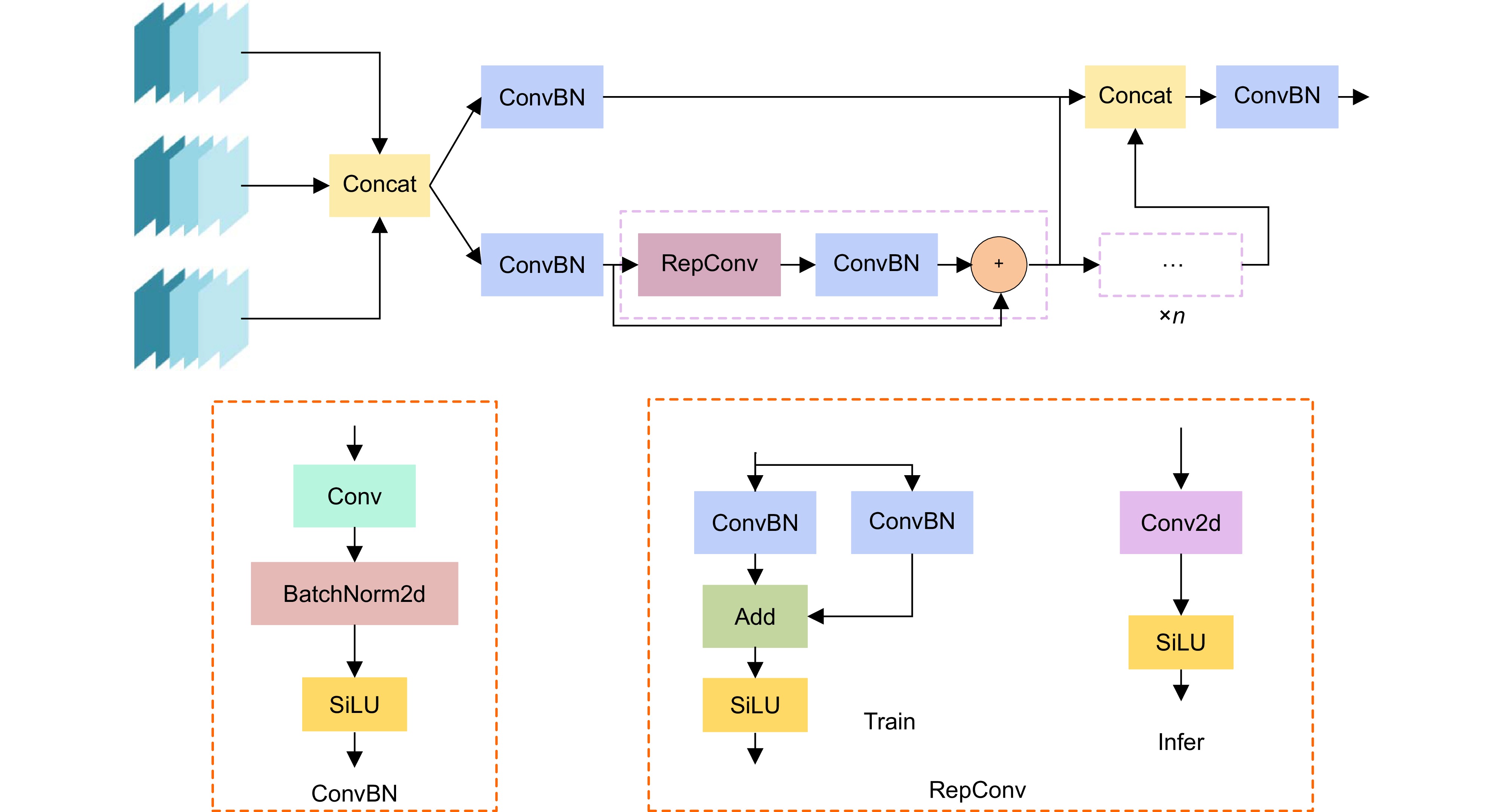
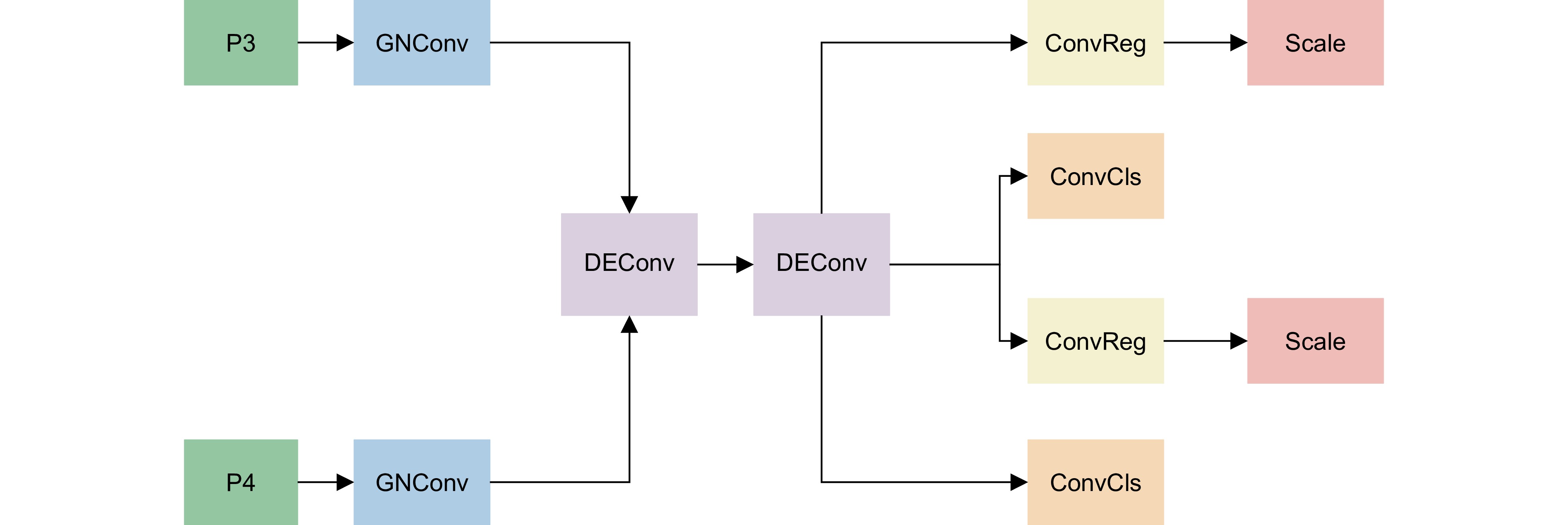
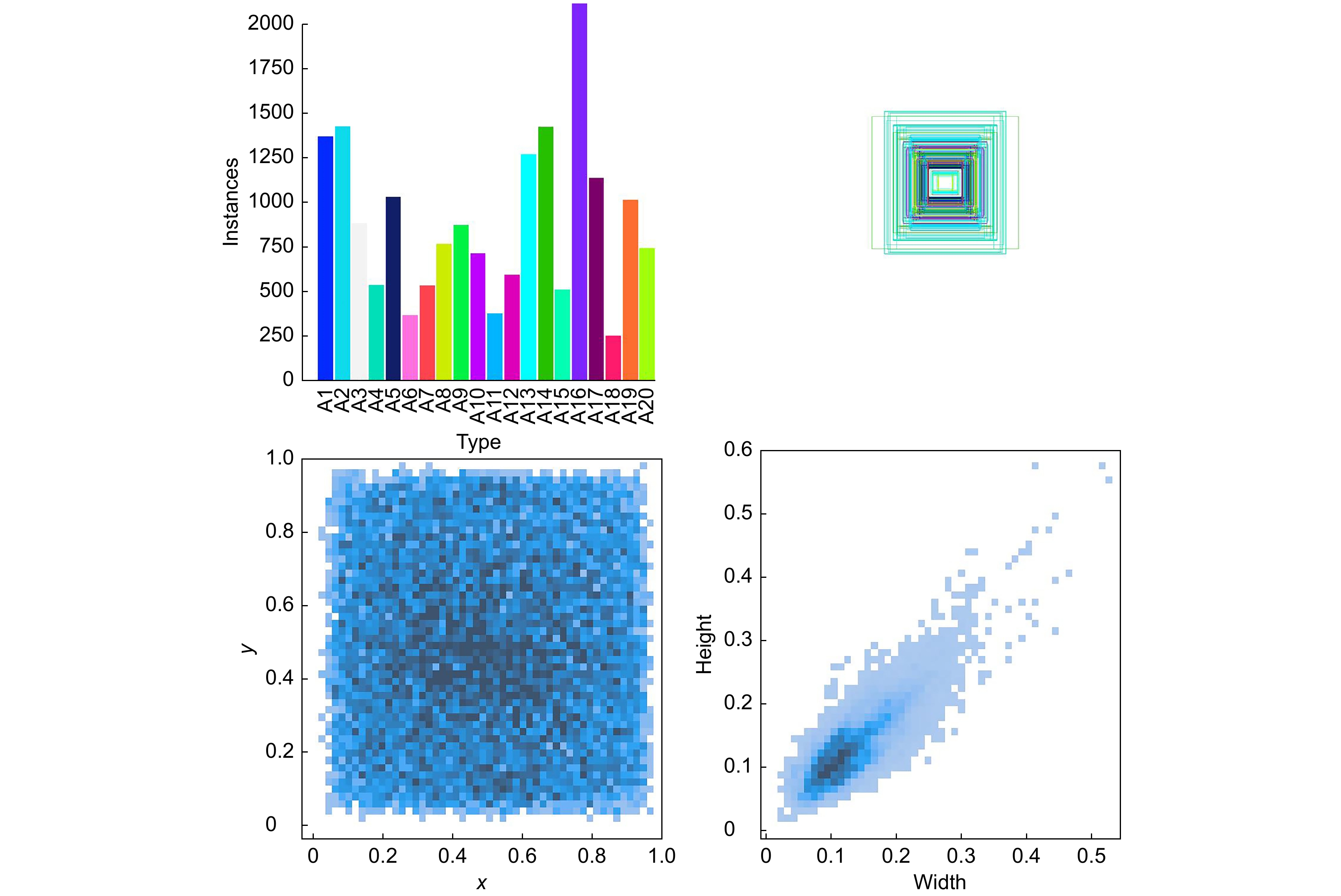
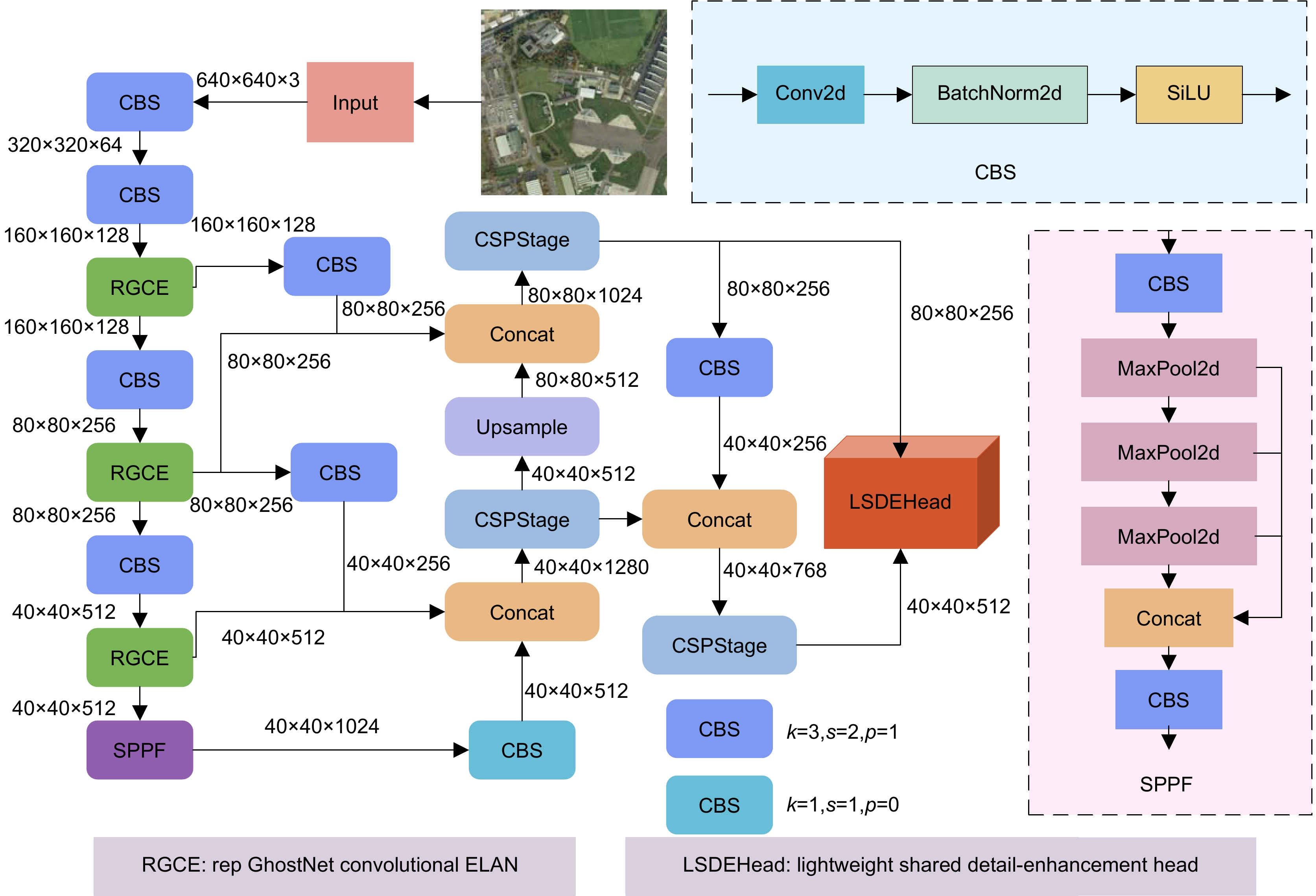
针对遥感图像军用飞机中背景复杂、目标尺度小所导致的识别精度低、计算成本高、模型体积大等问题,提出一种融合重参数化和细节增强的轻量级军用飞机目标检测算法YOLOv8-MA。首先,融合重参数化设计多分支梯度流通特征提取模块,提高模型推理速度;其次,结合Efficient RepGFPN舍弃冗余模型结构,融入P2层,构建多尺度特征融合网络,改善因过多下采样带来的小目标信息丢失问题;在此之上,结合群范卷积和细节增强提出轻量级检测头,减少模型参数量和计算量;最后,向Shape-IoU中引入聚焦系数融合成新的损失函数,提升模型检测性能。在公开军用飞机数据集MAR20上,该算法的mAP50高达97.9%,模型体积低至2.1 MB,相较于YOLOv8n参数量下降了74.7%,计算量下降了40.7%,FPS提高了14 f/s,证明其能够有效提升遥感图像中军用飞机的检测效果。
Abstract
Aiming at the issues of low recognition accuracy, high computational cost, and large model size caused by the complex background and small target scale in remote sensing images of military aircraft, a lightweight military aircraft target detection algorithm, namely YOLOv8-MA, integrating reparameterization and detail enhancement is proposed. Firstly, a multi-branch gradient flow feature extraction module is designed through reparameterization to enhance the model's inference speed. Secondly, in combination with efficient RepGFPN, redundant model structures are discarded and the P2 layer is incorporated to construct a multi-scale feature fusion network, mitigating the problem of small target information loss due to excessive downsampling. On this basis, a lightweight detection head is proposed by integrating GN convolution and detail enhancement to reduce the number of model parameters and the amount of computation. Finally, a focus coefficient is introduced into the Shape-IoU to form a new loss function, thereby improving the detection performance of the model. On the public military aircraft dataset MAR20, the mAP50 of this algorithm is as high as 97.9%, and the model size is as low as 2.1 MB. Compared with YOLOv8n, the number of parameters decreases by 74.7%, the amount of computation reduces by 40.7%, and the FPS increases by 14 f/s, demonstrating that it can effectively enhance the detection effect of military aircraft in remote sensing images.
-
Key words:
- remote sensing image /
- military aircraft /
- light weight /
- focusing coefficient
-

-
表 1 检测头参数对比
Table 1. Comparison of detector head parameters
Module Time/ms Params/M GFLOPs Detect 100.62 0.38 2.70 LSDEHead 58.98 0.28 0.17 表 2 实验参数设置
Table 2. Experimental parameter setting
Parameter Value Img-size 640×640 Batch-size 32 Epochs 200 Optimizer SGD lr 0.01 Momentum 0.937 Weight decay 0.0005 Workers 2 Pre-training pt no 表 3 消融实验结果
Table 3. Ablation experiment results
Group RGCE LRepGFPN P2 LSDEHead Wise-ShapeIoU P/% R/% mAP50/% mAP50-95/% Params/M GFLOPs Volume/MB FPS A 95.8 94.4 97.4 77.6 3.01 8.1 6.0 78 B √ 95.9 94.0 97.2 79.2 2.59 6.9 5.2 87 C √ √ 96.0 94.3 97.3 77.3 1.02 5.9 2.2 74 D √ √ √ 96.1 94.8 97.3 78.4 1.04 6.1 2.2 78 E √ √ √ √ 95.9 94.5 97.3 77.9 0.76 4.8 2.1 92 F √ √ √ √ √ 97.2 95.3 97.9 78.8 0.76 4.8 2.1 92 表 4 不同模块的对比
Table 4. Comparison of different modules
Module P/% R/% mAP50/% mAP50-95/% Params/M GFLOPs FPS C2f 95.8 94.4 97.4 77.6 3.01 8.1 78 C3 96.0 94.1 96.9 78.7 2.48 6.9 90 RepNCSPELAN4 96.4 95.3 97.7 79.5 2.20 6.1 91 RGCE 96.0 95.7 97.7 78.9 2.22 6.1 112 表 5 不同损失函数的对比实验结果
Table 5. Comparative experimental results of different loss functions
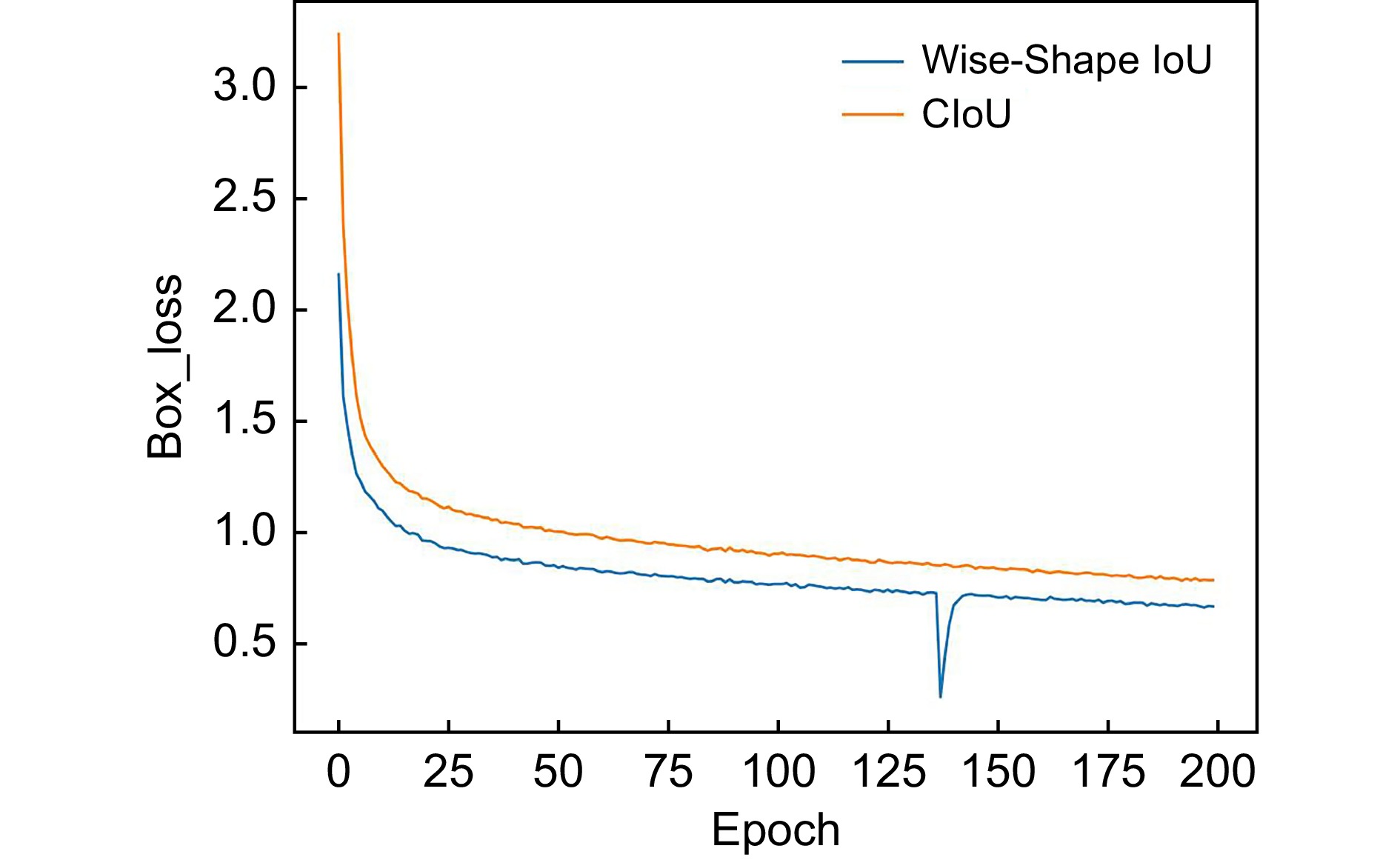
Loss function P/% R/% mAP50/% mAP50-95/% CIoU 95.9 94.5 97.3 77.9 SIoU 96.1 95.5 97.2 79 Inner-SIoU 95.1 94.5 97.4 78 WIoU V3 95.3 95.4 97.6 78.2 Shape-IoU 96.3 96.3 97.7 79.2 Wise-ShapeIoU 97.2 95.3 97.9 78.8 表 6 不同模型的性能对比
Table 6. Comparison of the performance of different models
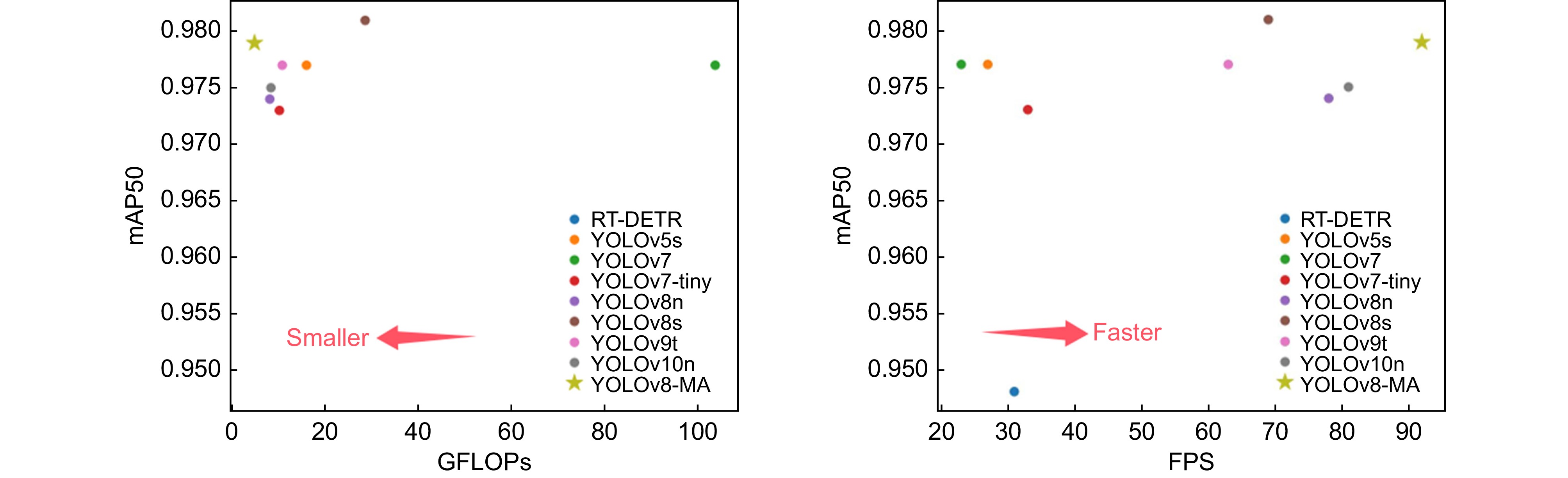
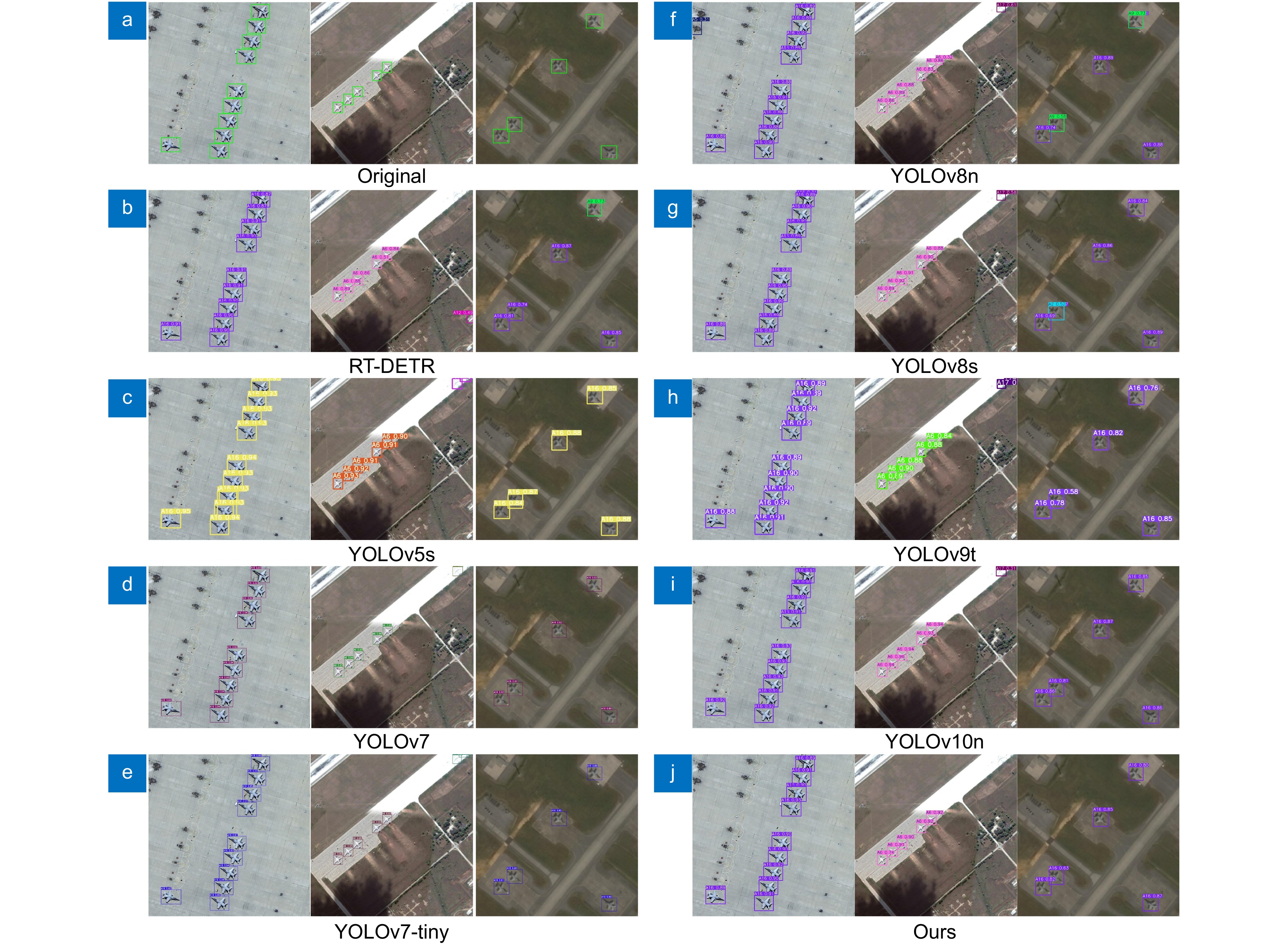
Module P/% R/% mAP50/% mAP50-95/% Params/M GFLOPs Volume/MB FPS RT-DETR 93.1 93.3 94.8 75.7 28.4 100.7 59.1 31 YOLOv5s 97.8 96.4 97.7 78.8 7.10 16.4 14.5 27 YOLOv7 96.3 95.6 97.7 77.8 36.58 103.5 75.0 23 YOLOv7-tiny 95.3 92.9 97.3 76.7 4.87 10.1 11.8 33 YOLOv8n 95.8 94.4 97.4 77.6 3.01 8.1 6.0 78 YOLOv8s 96.8 95.6 98.1 79.5 11.14 28.5 22.5 69 YOLO-MAR[14] — — 91.7 — — 11.3 3.9 — DTR R-CNN[4] — — 97.3 77.1 23.84 — — — FAS-YOLO[15] — — 97.2 77.3 0.89 5.6 1.9 — YOLOv9t 95.0 95.3 97.7 78.5 2.62 10.7 5.9 63 YOLOv10n 95.5 93.9 97.5 77.3 2.70 8.3 5.5 81 Ours 97.2 95.3 97.9 78.8 0.76 4.8 2.1 92 表 7 泛化实验结果
Table 7. Generalization experimental results
Dataset Module mAP50/% mAP50-95/% FPS MAR20 YOLOv8n 97.4 77.6 78 YOLOv8-MA 97.9 78.8 92 CASIA-S YOLOv8n 97.0 88.1 50 YOLOv8-MA 98.6 89.3 62 -
参考文献
[1] 禹文奇, 程塨, 王美君, 等. MAR20: 遥感图像军用飞机目标识别数据集[J]. 遥感学报, 2023, 27(12): 2688−2696. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20222139
Yu W Q, Cheng G, Wang M J, et al. MAR20: a benchmark for military aircraft recognition in remote sensing images[J]. Nat Remote Sens Bull, 2023, 27(12): 2688−2696. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20222139
[2] 梁礼明, 陈康泉, 王成斌, 等. 融合视觉中心机制和并行补丁感知的遥感图像检测算法[J]. 光电工程, 2024, 51(7): 240099. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240099
Liang L M, Chen K Q, Wang C B, et al. Remote sensing image detection algorithm integrating visual center mechanism and parallel patch perception[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2024, 51(7): 240099. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240099
[3] 肖振久, 张杰浩, 林渤翰. 特征协同与细粒度感知的遥感图像小目标检测[J]. 光电工程, 2024, 51(6): 240066. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240066
Xiao Z J, Zhang J H, Lin B H. Feature coordination and fine-grained perception of small targets in remote sensing images[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2024, 51(6): 240066. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240066
[4] 党玉龙, 叶成绪. 基于Faster R-CNN的轻量化遥感图像军用飞机检测模型[J]. 激光杂志, 2024, 45(7): 111−117. doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.jgzz.2024.07.111
Dang Y L, Ye C X. A lightweight remote sensing image military aircraft detection model based on Faster R-CNN[J]. Laser J, 2024, 45(7): 111−117. doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.jgzz.2024.07.111
[5] Ren S, He K, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2017, 39(6): 1137−1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
[6] 沙苗苗, 李宇, 李安. 改进Faster R-CNN的遥感图像多尺度飞机目标检测[J]. 遥感学报, 2022, 26(8): 1624−1635. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20219365
Sha M M, Li Y, Li A. Multiscale aircraft detection in optical remote sensing imagery based on advanced Faster R-CNN[J]. Nat Remote Sens Bull, 2022, 26(8): 1624−1635. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20219365
[7] 刘裕芸, 刘春阳, 周绍鸿, 等. 基于优化Faster-RCNN遥感影像飞机目标检测算法[J/OL]. 机电工程技术, 2024.
Liu Y Y, Liu C Y, Zhou S H, et al. Aircraft target detection algorithm based on optimized faster RCNN remote sensing images[J/OL]. Mech Electr Eng Technol, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1009-9492.2024.00127.
[8] Carion N, Massa F, Synnaeve G, et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers[C]//Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, 2020: 213–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58452-8_13.
[9] 党思航, 李晓哲, 夏召强, 等. 采用自适应预筛选的遥感图像目标开集检测研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(10): 3908−3917. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231426
Dang S H, Li X Z, Xia Z Q, et al. Research on open-set object detection in remote sensing images based on adaptive pre-screening[J]. J Electron Inf Technol, 2024, 46(10): 3908−3917. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231426
[10] Zhou X Y, Wang D Q, Krähenbühl P. Objects as points[Z]. arXiv: 1904.07850, 2019. https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.07850.
[11] 李婕, 周顺, 朱鑫潮, 等. 结合多通道注意力的遥感图像飞机目标检测[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(1): 209−217. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2107-0379
Li J, Zhou S, Zhu X C, et al. Remote sensing image aircraft target detection combined with multiple channel attention[J]. Comput Eng Appl, 2022, 58(1): 209−217. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2107-0379
[12] 黄子恒, 芮杰, 林雨准, 等. 基于改进的YOLOv5遥感影像飞机目标检测[J]. 测绘通报, 2024, (8): 73−78,89. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2024.0813
Huang Z H, Rui J, Lin Y Z, et al. Aircraft target detection based on improved YOLOv5 in remote sensing imagery[J]. Bull Surv Mapp, 2024, (8): 73−78,89. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2024.0813
[13] Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, 2018: 3–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1.
[14] 王杰, 张上, 张岳, 等. 改进YOLOv5的军事飞机检测算法[J]. 无线电工程, 2024, 54(3): 589−596. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2024.03.010
Wang J, Zhang S, Zhang Y, et al. Improved YOLOv5's military aircraft detection algorithm[J]. Radio Eng, 2024, 54(3): 589−596. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2024.03.010
[15] 刘丽, 张硕, 白宇昂, 等. 改进YOLOv8的轻量级军事飞机检测算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(18): 114−125. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2404-0058
Liu L, Zhang S, Bai Y A, et al. Improved lightweight military aircraft detection algorithm of YOLOv8[J]. Comput Eng Appl, 2024, 60(18): 114−125. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2404-0058
[16] Xu X Z, Jiang Y Q, Chen W H, et al. Damo-YOLO: a report on real-time object detection design[Z]. arXiv: 2211.15444, 2022. https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.15444.
[17] Wang C Y, Bochkovskiy A, Liao H Y M. YOLOv7: trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors[C]//Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, 2023: 7464–7475. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00721.
[18] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vega, 2015: 770–778. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90.
[19] Ding X H, Zhang X Y, Ma N N, et al. RepVGG: making VGG-style ConvNets great again[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, 2021: 13728–13737. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01352.
[20] Han K, Wang Y H, Tian Q, et al. GhostNet: more features from cheap operations[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, 2020: 1577–1586. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00165.
[21] Tian Z, Shen C H, Chen H, et al. FCOS: fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, 2019: 9626–9635. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00972.
[22] Chen Z X, He Z W, Lu Z M. DEA-Net: single image dehazing based on detail-enhanced convolution and content-guided attention[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2024, 33: 1002−1015. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2024.3354108
[23] Zheng Z H, Wang P, Liu W, et al. Distance-IoU loss: faster and better learning for bounding box regression[C]//Proceedings of the Thirty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, 2020: 12993–13000. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6999.
[24] Zhang H, Zhang S J. Shape-IoU: more accurate metric considering bounding box shape and scale[Z]. arXiv: 2312.17663, 2023. https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.17663.
[25] Tong Z J, Chen Y H, Xu Z W, et al. Wise-IoU: bounding box regression loss with dynamic focusing mechanism[Z]. arXiv: 2301.10051, 2023. https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10051.
[26] Wang C Y, Yeh I H, Liao H Y M. YOLOv9: learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information[C]//Proceedings of the18th European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, 2024: 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72751-1_1.
[27] Gevorgyan Z. SIoU loss: more powerful learning for bounding box regression[Z]. arXiv: 2205.12740, 2022. https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.12740.
[28] Wang A, Chen H, Liu L H, et al. YOLOv10: real-time end-to-end object detection[Z]. arXiv: 2405.14458, 2024. https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.14458.
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: