Optimization of hand-eye calibration for blade repair robot based on anomalous sample detection
-
摘要
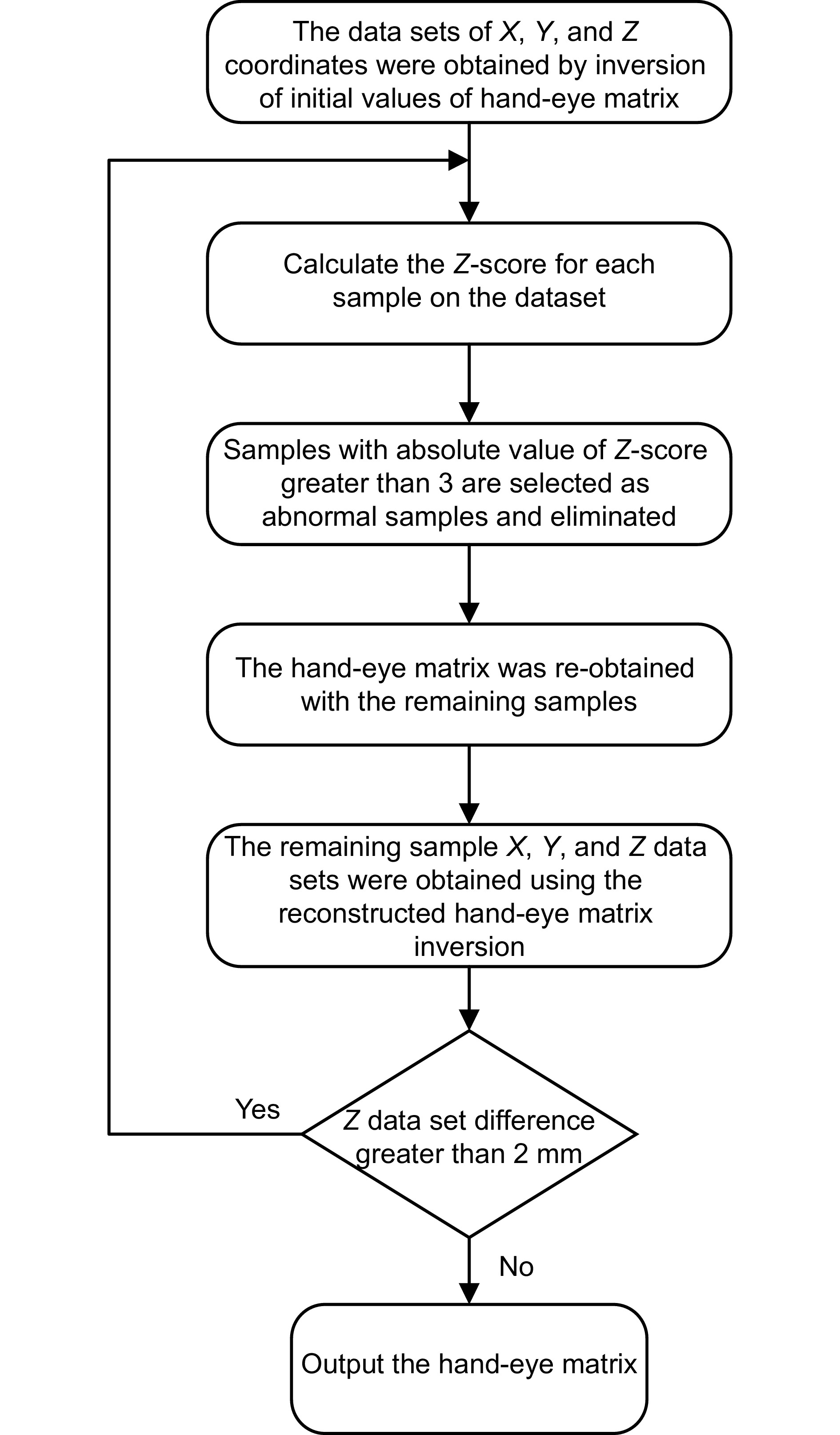
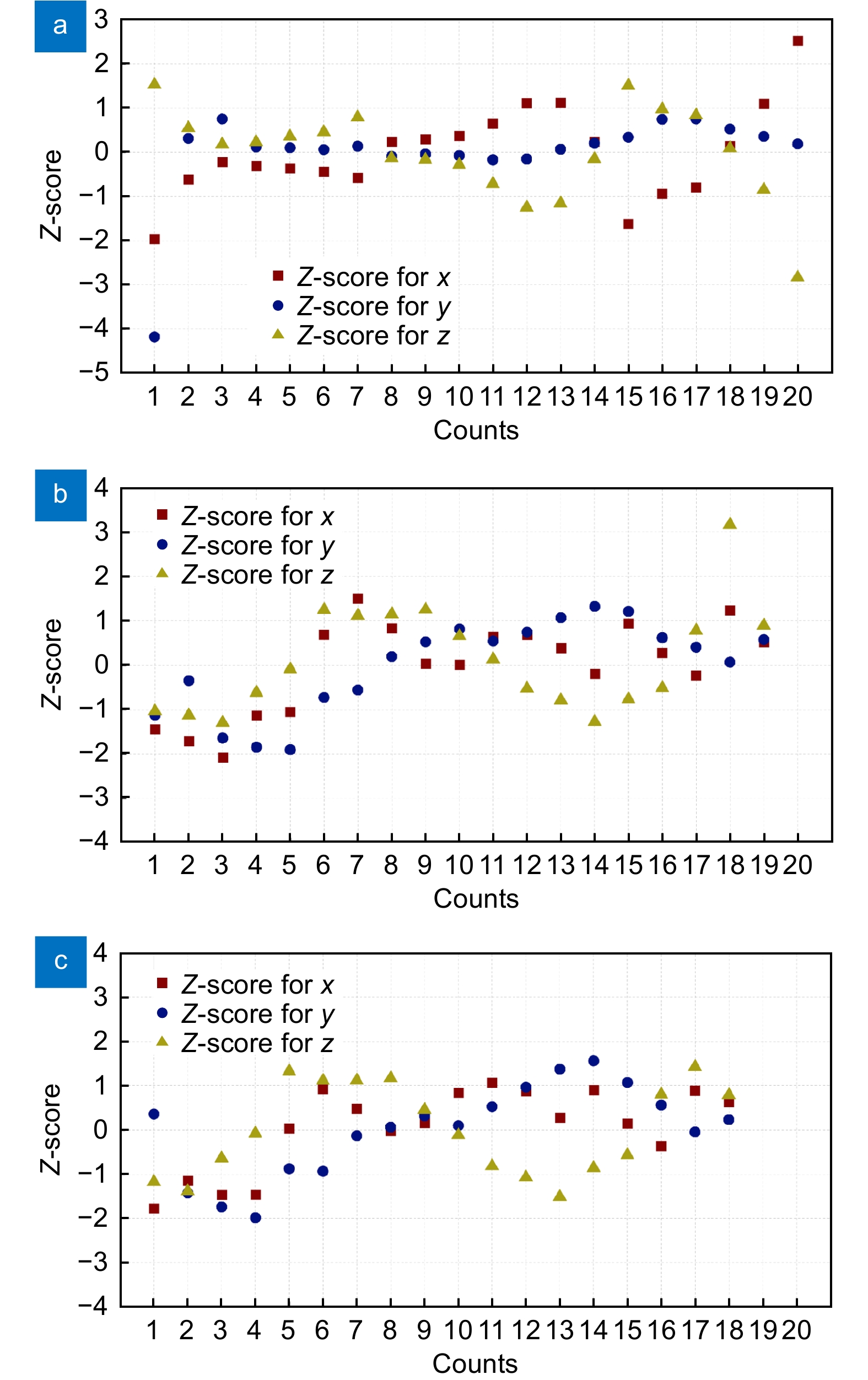
为了降低叶片修复机器人视觉系统中随机误差对手眼标定的影响,提出了一种基于异常样本检测的手眼标定优化方法。首先,建立手眼矩阵的线性方程,通过奇异值分解(SVD)求解手眼矩阵的初始值;随后,利用初始值对样本进行反演操作,并基于
Z -分数检测和剔除异常样本,以获取更高准确性的手眼矩阵;最后,将得到的手眼矩阵作为优化的初始值,采用单位四元数表示旋转,并使用Levenberg-Marquardt算法对初始值进一步优化,最终得到手眼矩阵。在搭载双目深度相机的叶片修复机器人上进行了手眼标定实验,通过TCP标定工具获取目标点的真实坐标,利用所提方法得到的手眼矩阵预测坐标与真实坐标的平均欧式距离为0.858 mm,且方差稳定在0.1以内。相比其他对比方法,本文方法有效减少了随机误差的影响,具有良好的稳定性与准确性。-
关键词:
- 奇异值分解 /
- Z-分数 /
- Levenberg-Marquardt /
- 手眼标定 /
- TCP标定
Abstract
To reduce the impact of random errors on hand-eye calibration in the visual system of a blade repair robot, an optimization method based on outlier detection is proposed. Firstly, a linear equation for the hand-eye matrix is established. The initial hand-eye matrix is solved using singular value decomposition (SVD). Secondly, the initial value is used to perform an inversion operation on the samples. Outlier samples are detected and removed based on
Z -scores, leading to a more accurate hand-eye matrix. Finally, the obtained hand-eye matrix is used as the initial value for optimization. The rotation is represented by unit quaternions, and the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm is applied to further optimize the initial value, yielding the final hand-eye matrix. Hand-eye calibration experiments were conducted on the blade repair robot equipped with a stereo depth camera. The real coordinates of the target points were obtained using a TCP calibration tool. The predicted coordinates from the hand-eye matrix, obtained by the proposed method, have an average Euclidean distance of 0.858 mm from the true coordinates, with a variance stabilizing below 0.1. Compared to other methods, the proposed approach effectively reduces the impact of random errors and demonstrates good stability and accuracy.-
Key words:
- singular value decomposition /
- Z-score /
- Levenberg-Marquardt /
- hand-eye calibration /
- TCP calibration
-
Overview
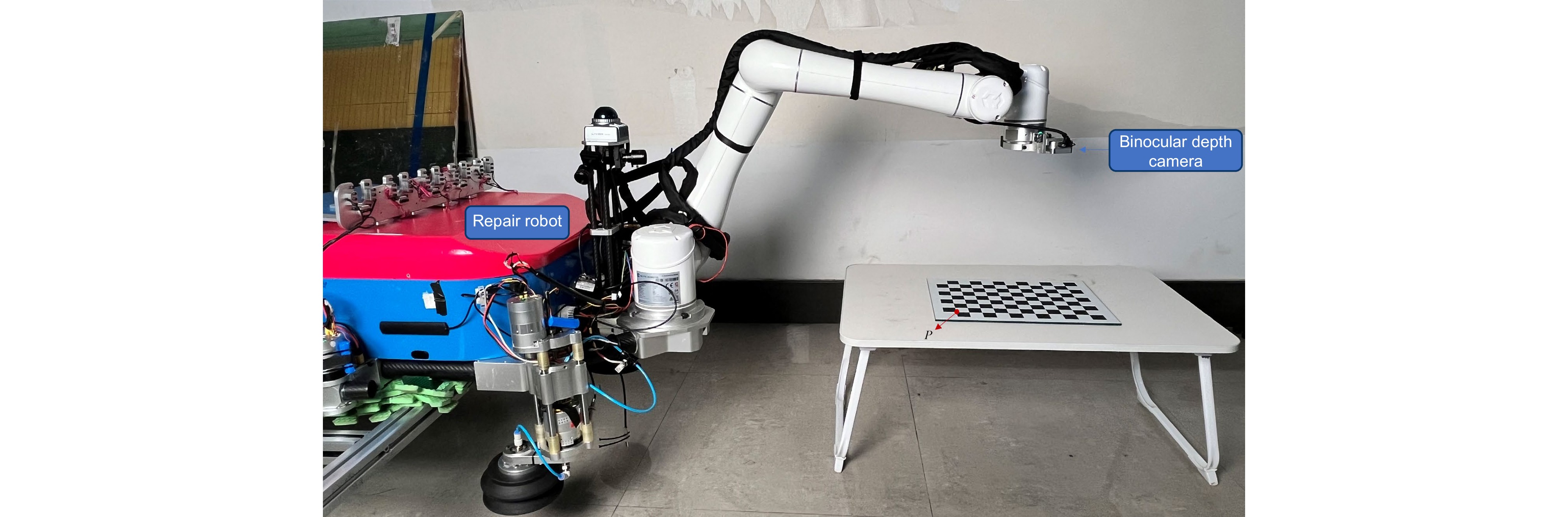
Overview: The surface defect repair of high-altitude wind turbine blades using repair robots is important. The vision system on the repair robot plays a crucial role in guiding the localization of defects on the blade surface, making stable and accurate hand-eye calibration of the repair robot key to successful repair. During the calibration process, various random errors, such as image distortion and inaccurate parameters, may occur, leading to unstable and inaccurate calibration results. This paper proposes an optimized hand-eye calibration method based on anomaly sample detection. Firstly, a linear equation for the hand-eye matrix is established, and its initial value is obtained by solving the equation using singular value decomposition (SVD). Next, the initial value is used to invert the samples, and anomaly samples are detected and removed based on the Z-score method, ensuring a higher accuracy hand-eye matrix. Finally, the obtained hand-eye matrix is used as the initial value for further optimization using the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm, where the rotation is represented by unit quaternions, and the hand-eye matrix is refined. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, hand-eye calibration experiments were conducted on a blade repair robot equipped with a binocular depth camera. The true coordinates of the target points were obtained through TCP calibration tools, and the hand-eye matrix's predicted coordinates yielded an average Euclidean distance of 0.858 mm from the true coordinates, with the variance remaining below 0.1. Compared with other calibration methods, the proposed method effectively reduces the influence of random errors, showing excellent stability and accuracy. Moreover, this method can be widely applied to hand-eye calibration tasks for other industrial robots.
-

-
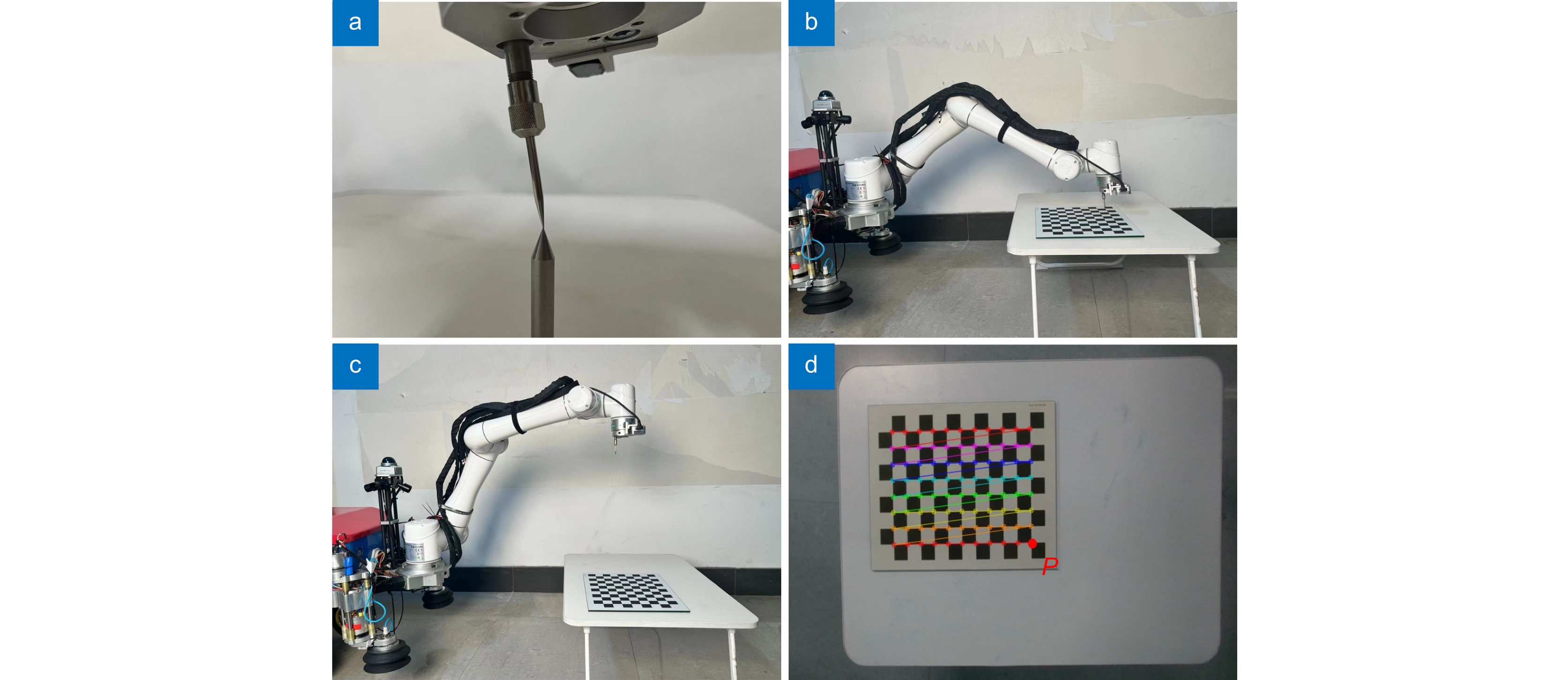
表 1 实验设备参数
Table 1. Experimental equipment parameters
Key equipment parameter Specific parameter Robot arm Aelite EC66 Collaborative Robot Depth camera model Intel RealSense D405 Depth measurement method Stereo Vision Depth measurement accuracy ±2% at 50 cm RGB image resolution 1280×720 RGB image frame rate Up to 90 f/s Checkerboard array 12×9 Checkerboard square size 25 mm Checkerboard accuracy ±0.01 mm 表 2 欧式距离对比结果
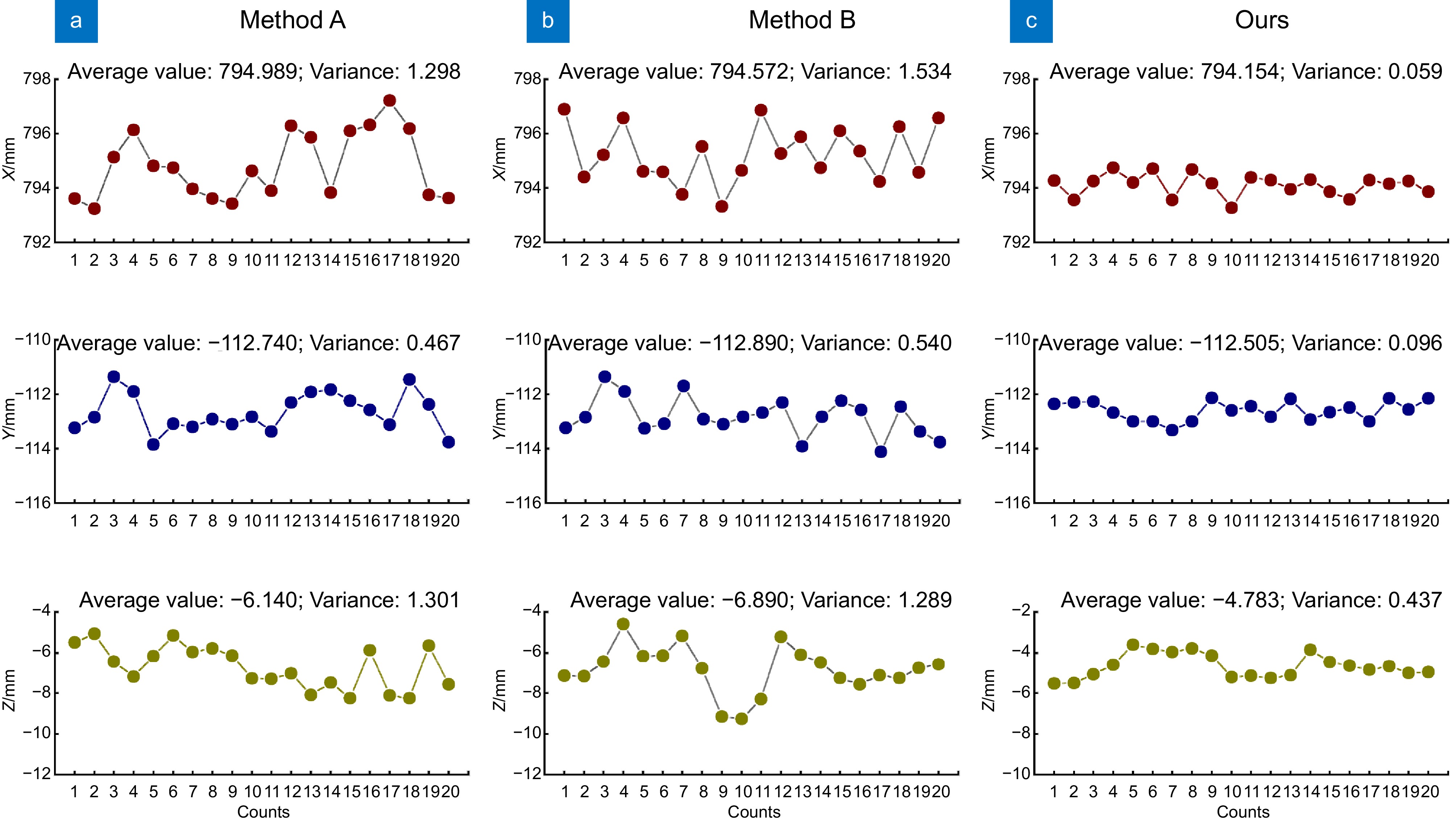
Table 2. Results of Euclidean distance comparison
Number of images Method A Method B Ours 1 1.371 4.197 1.202 2 0.980 2.845 1.132 3 2.635 2.678 0.799 4 3.654 2.810 0.986 5 2.482 2.110 1.069 6 1.372 2.028 1.231 7 1.748 1.033 1.050 8 1.483 2.969 1.211 9 1.916 4.815 0.524 10 2.996 4.945 0.989 11 3.047 4.939 0.937 12 3.588 1.664 1.058 13 4.239 3.060 0.750 14 3.129 2.309 0.903 15 4.467 3.650 0.267 16 2.895 3.512 0.352 17 5.083 3.235 0.875 18 4.605 3.742 0.477 19 1.246 2.639 0.759 20 3.438 3.744 0.596 Average 2.818 3.146 0.858 Variance 1.442 1.092 0.078 -
参考文献
[1] Cheng X H, Han Q G, Huang Y Z, et al. Bioinspired ultra-fine hybrid nanocoating for improving strength and damage tolerance of composite fan blades in flexible manufacturing[J]. Compos Sci Technol, 2025, 259: 110956. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2024.110956
[2] Feng X Z, Tian D Z, Wu H. A matrix-solving hand-eye calibration method considering robot kinematic errors[J]. J Manuf Process, 2023, 99: 618−635. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2023.05.073
[3] 邱垚. 基于3D目标识别的工业机器人无序分拣技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2019.
Qiu Y. Research on disordered sorting technology of industrial robot based on 3D target recognition[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2019.
[4] 孙阳, 翟雨农, 杨应科, 等. 视觉引导的大部件对接移载式定位器入位方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 1−18 doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2023.0591
Sun Y, Zhai Y N, Yang Y K, et al. Vision-based mobile positioner insertion method for pose alignment of large components[J]. J Beijing Univ Aeronaut Astronaut, 2024, 1−18 doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2023.0591
[5] 李光, 章晓峰, 杨加超, 等. 基于残差BP神经网络的6自由度机器人视觉标定[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(4): 366−374. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2021.04.040
Li G, Zhang X F, Yang J C, et al. Vision calibration of six degree of freedom robot based on residual BP neural network[J]. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach, 2021, 52(4): 366−374. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2021.04.040
[6] Tsai R Y, Lenz R K. A new technique for fully autonomous and efficient 3D robotics hand/eye calibration[J]. IEEE Trans Rob Autom, 1989, 5(3): 345−358. doi: 10.1109/70.34770
[7] 田鹏飞, 杨树明, 吴孜越, 等. 结合精度补偿的机器人优化手眼标定方法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2020, 54(8): 99−106. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202008013
Tian P F, Yang S M, Wu Z Y, et al. An optimal hand-eye calibration method for robots based on precision compensation[J]. J Xi'an Jiaotong Univ, 2020, 54(8): 99−106. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202008013
[8] 赵云涛, 谢万琪, 李维刚, 等. 基于协方差矩阵自适应进化策略的机器人手眼标定算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2023, 43(10): 3225−3229. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022081282
Zhao Y T, Xie W Q, Li W G, et al. Robot hand-eye calibration algorithm based on covariance matrix adaptation evolutionary strategy[J]. J Comput Appl, 2023, 43(10): 3225−3229. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022081282
[9] 毛成林, 于瑞强, 宋爱国. 一种结合TCP标定的深度相机手眼标定方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2023, 44(3): 280−286. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2210826
Mao C L, Yu R Q, Song A G. A hand-eye calibration method of depth camera combined with TCP calibration[J]. Chin J Sci Instrum, 2023, 44(3): 280−286. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2210826
[10] Shah M. Solving the robot-world/hand-eye calibration problem using the Kronecker product[J]. J Mechanisms Robotics 2013, 5 (3): 031007. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4024473.
[11] 郑震宇, 高健, 郑卓鋆, 等. 基于3D视觉点云配准的高精度手眼标定方法[J]. 机械设计, 2023, 40(S2): 51−56. doi: 10.13841/j.cnki.jxsj.2023.s2.018
Zheng Z Y, Gao J, Zheng Z J, et al. High precision hand-eye calibration method based on 3D visual point cloud registration[J]. J Mach Des, 2023, 40(S2): 51−56. doi: 10.13841/j.cnki.jxsj.2023.s2.018
[12] Daniilidis K. Hand-eye calibration using dual quaternions[J]. Int J Rob Res, 1999, 18(3): 286−298. doi: 10.1177/02783649922066213
[13] Horaud R, Dornaika F. Hand-eye calibration[J]. Int J Rob Res, 1995, 14(3): 195−210. doi: 10.1177/027836499501400301
[14] 付中涛, 饶书航, 潘嘉滨, 等. 基于LMI-SDP优化的机器人手眼关系精确求解[J]. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59(17): 109−115. doi: 10.3901/JME.2023.17.109
Fu Z T, Rao S H, Pan J B, et al. Towards accurate solution of robot hand-eye relationship based on the LMI-SDP optimization[J]. J Mech Eng, 2023, 59(17): 109−115. doi: 10.3901/JME.2023.17.109
[15] Chen L, Zhong G W, Wan Z H, et al. A novel binocular vision-robot hand-eye calibration method using dual nonlinear optimization and sample screening[J]. Mechatronics, 2023, 96: 103083. doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2023.103083
[16] 程麒, 潘丰, 袁瑜键. 基于3D视觉传感器的龙门架机器人手眼标定方法[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(4): 200239. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.200239
Cheng Q, Pan F, Yuan Y J. Hand-eye calibration method of gantry robot based on 3D vision sensor[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2021, 48(4): 200239. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.200239
[17] 徐呈艺, 刘英, 贾民平, 等. 木板抓取机器人手眼标定方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(12): 420−426. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.12.049
Xu C Y, Liu Y, Jia M P, et al. Method of hand-eye calibration for picking board robot[J]. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach, 2019, 50(12): 420−426. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.12.049
[18] 杨宏宇, 张豪豪, 成翔. 基于多尺度注意力特征增强的异常流量检测方法[J]. 通信学报, 2024, 45(11): 88−105. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2024262
Yang H Y, Zhang H H, Cheng X. Abnormal traffic detection method based on multi-scale attention feature enhancement[J]. J Commun, 2024, 45(11): 88−105. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2024262
[19] 杨海能, 唐杰, 邵武, 等. 基于规则库与PRRL模型的风电功率数据清洗方法[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45(12): 416−425.
Yang H N, Tang J, Shao W, et al. Wind power data cleaning method based on rule base and PRRL model[J]. Acta Energ Sol Sin, 2024, 45(12): 416−425.
[20] 李新春, 谭新欢, 李琳, 等. 基于深度元学习的工控系统异常检测方法[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2015. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2410047
Li X C, Tan X H, Li L, et al. Deep meta learning-based anomaly detection for industrial control systems[J]. J Front Comput Sci Technol, 2015. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2410047
[21] 张杰, 方浪森, 姚立明, 等. 基于图论及混合卷积神经网络的电力结算电量数据异常检测方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1643.tk.20241025.1656.012.html.
Zhang J, Fang L S, Yao L M, et al. Anomaly detection method for power settlement electricity data based on graph theory and hybrid convolutional neural network[J]. South Power Syst Technol, 2024. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1643.tk.20241025.1656.012.html.
[22] Zhang Z Y. Flexible camera calibration by viewing a plane from unknown orientations[C]//Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 1999: 666–673. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.1999.791289.
[23] Chen L, Han Z, Zhong G W, et al. A novel hand-eye calibration method using double-layer optimization and outlier sample screening for monocular vision robots[J]. Meas Sci Technol, 2023, 34(7): 075016. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/acc59f
[24] 班朝, 任国营, 王斌锐, 等. 融合加权SVD算法的工业机器人运动学标定[J]. 计量学报, 2021, 42(9): 1128−1135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158.2021.09.02
Ban Z, Ren Guo Y, Wang B R, et al. Kinematics calibration of industrial robot fusing weighted SVD algorithm[J]. Acta Metrol Sinica, 2021, 42(9): 1128−1135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158.2021.09.02
[25] 余承洋. 基于数据驱动的动力电池典型亚健康状态辨识[D]. 北京: 北方工业大学, 2022. https://doi.org/10.26926/d.cnki.gbfgu.2022.000681.
Yu C Y. Identification of typical sub-health state of power battery based on data drive[D]. Beijing: North China University of Technology, 2022. https://doi.org/10.26926/d.cnki.gbfgu.2022.000681.
[26] Fischer, Andreas and Izmailov, Alexey F, et al. The Levenberg–Marquardt method: an overview of modern convergence theories and more[J]. Comput Optim Appl, 2024, 89(1): 33−67 doi: 10.1007/s10589-024-00589-1
[27] 秦永元. 惯性导航[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.
Qin Y Y. Inertial Navigation [M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2014.
[28] 刘成业, 李文广, 马世国, 等. 一种机器人工具坐标系标定方法[J]. 山东科学, 2012, 25(1): 69−74. doi: 10.3976/j.issn.1002-4026.2012.01.015
Liu C Y, Li W G, Ma S G, et al. A robot tool frame calibration method[J]. Shandong Sci, 2012, 25(1): 69−74. doi: 10.3976/j.issn.1002-4026.2012.01.015
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: