-
摘要
Risley光栅跟瞄系统主要由两片旋转的偏振光栅组成,光源经过偏振光栅衍射后实现在圆锥形范围内的光束指向,进而对目标进行捕获、跟踪。而指向精度作为Risley光栅跟瞄系统的重要指标,不仅受伺服与光学系统影响,还受Risley光栅跟瞄系统中双光栅转台的天线安装位置精度以及轴系装配误差等系统误差影响。为此,本文主要对Risley光栅跟瞄系统中的各系统误差源及其造成的指向误差进行分析,首先建立系统误差数理模型并利用ZEMAX对数理模型进行验证,随后利用MATLAB分析各系统误差源对Risley光栅跟瞄系统指向误差的影响,最后根据分析结果及指标要求对某双光栅跟瞄系统误差源进行误差分配,指导双光栅转台的设计、装调。对双光栅转台指向误差进行实验测试,经多次实验测试后得到双光栅转台实际最大指向误差
δ e=7.2″,满足双光栅转台指向误差设计指标10″。Abstract
The Risley grating tracking system is mainly composed of two rotating polarization gratings. The light source is diffracted by the polarization grating to achieve beam pointing in the conical range, and then the target is captured and tracked. As an important index of the Risley grating tracking system, pointing accuracy is not only affected by servo and optical systems but also by system errors such as antenna installation accuracy and shafting assembly error of double grating turntable in the Risley grating tracking system. Therefore, this paper mainly analyzes the systematic error sources in the Risley grating tracking system and the pointing errors caused by them. First, a mathematical model of systematic error is established and verified by ZEMAX. Then, MATLAB is used to analyze the influence of each systematic error source on the pointing error of the Risley grating tracking system. Finally, according to the analysis results and index requirements, the error source of a double grating tracking system is assigned to guide the design and installation of the double grating turntable. The actual maximum pointing error of the double grating turntable
δ e=7.2" is obtained after several experimental tests, which satisfies the design index of pointing error of the double grating turntable 10".-
Key words:
- Risley grating /
- tracking system /
- pointing error /
- error distribution
-
Overview
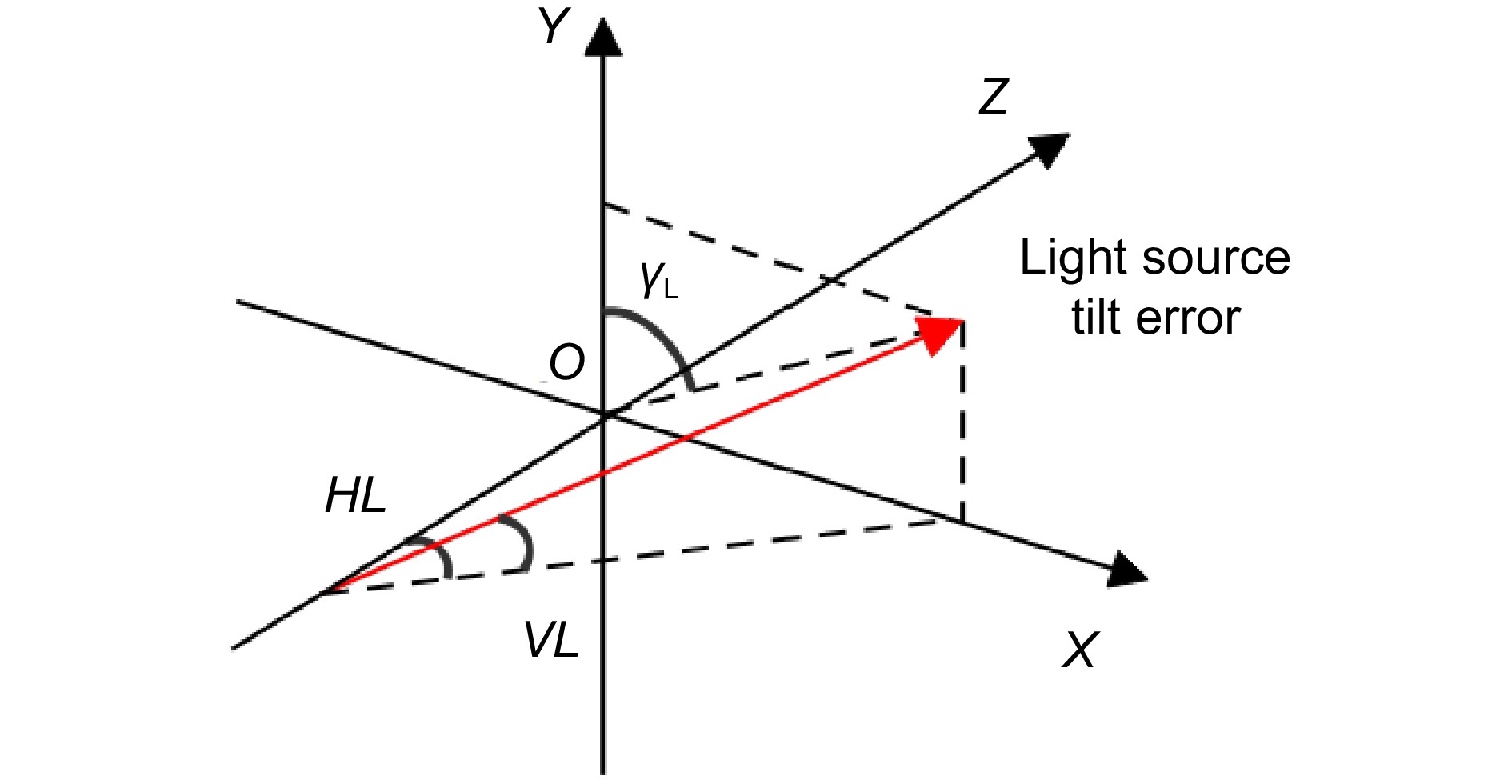
Overview: With the continuous progress of science and technology, laser application technologies such as space laser communication and photoelectric tracking continue to develop, and the requirements for tracking systems are becoming higher and higher. The Risley grating tracking system is small in size and light in weight, which can be used in some specific environments. The system is mainly composed of two rotating polarization gratings, through the diffraction of polarization gratings to achieve the direction of the beam in the conical range, so as to achieve the acquisition and tracking of the target. As an important index of the Risley grating tracking system, pointing accuracy is not only related to the servo system and optical system but also affected by system errors in the Risley grating turntable. Therefore, in this paper, systematic error sources in the Risley grating tracking system are classified and analyzed, and a systematic error source model is established, which mainly includes light source tilt error, grating axis tilt error, grating tilt error, and grating angle error.
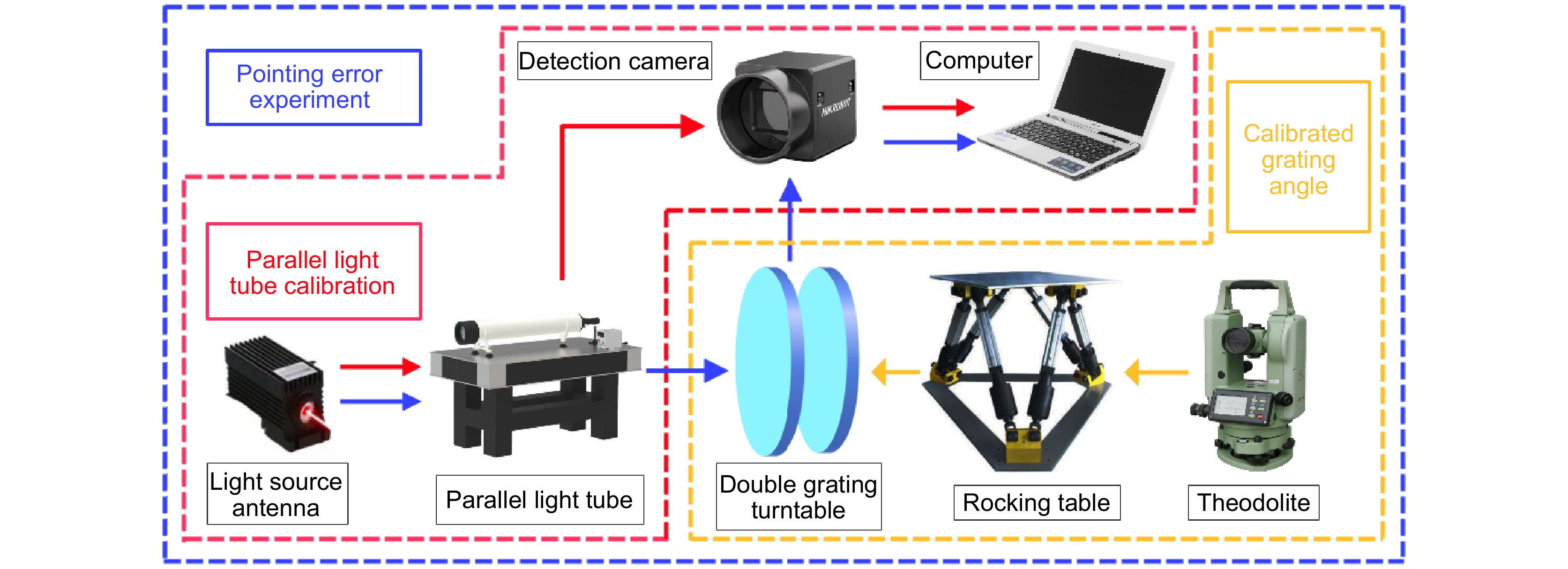
The polar angle and azimuth angle of the outgoing beam under the error model are obtained by introducing the error angle, and verified by ZEMAX optical software. The results show that the maximum difference between the polar angle and the azimuth angle is 0.00076 "and 0.0013", respectively. After verification, MATLAB software was used to simulate the influence of each error source on the pointing error of the Risley grating tracking system. When each system error was set to 0.1°, the influence of light source tilt error and grating angle error on pointing error was 0.1035° and 0.01305°, respectively. The grating axis tilt error and the grating tilt error are both 3.168". Finally, according to the sensitivity of each error source to the pointing error, the four errors are assigned and corresponding to the Risley grating turntable, which guides the design, processing, and installation of the turntable. After the Risley grating turntable is finished, the pointing accuracy of the Risley grating turntable is verified by experiments. Multiple experimental results show that the actual maximum pointing error of the Risley grating turntable δe=7.2", which meets the design index of 10".
-

-
图 9 光源倾斜误差造成的指向误差。(a) HL=0.1°时指向误差; (b) VL=0.1°时指向误差;(c)最大指向误差随γL的变化; (d)最大指向误差随光源倾斜误差的变化
Figure 9. Pointing error caused by the light source tilt error. (a) Pointing error at HL=0.1°; (b) Pointing error at VL=0.1°; (c) Maximum pointing error varies with γL; (d) Maximum pointing error varies with the tilt error of the light source
图 10 光栅轴倾斜误差造成的指向误差。(a) HR1=0.1°时指向误差;(b) VR1=0.1°时指向误差;(c) HR2=0.1°时指向误差; (d) VR2=0.1°时指向误差;(e)最大指向误差随γR1的变化;(f) 最大指向误差随γR2的变化;(g) 最大指向误差随光栅轴倾斜误差的变化
Figure 10. Pointing error caused by grating axis tilt error. (a) Pointing error at HR1=0.1°; (b) Pointing error at VR1=0.1°; (c) Pointing error at HR2=0.1°; (d) Pointing error at VR2=0.1°; (e) Maximum pointing error varies with γR1; (f) Maximum pointing error varies with γR2; (g) Change of the maximum pointing error with the tilt error of the grating axis
表 1 仿真使用的系统参数
Table 1. System parameters used in the simulation
System parameter Numerical value Grating period/μm 8.22 Incident wavelength/μm 1.064 Diffraction order ±1 表 2 各误差源引起指向误差大小
Table 2. Size of the pointing error under each error source
Error source (0.1°) ei/(°) Light tilt error 0.10350 Grating axis 1 tilt error 0.00088 Grating axis 2 tilt error 0.00250 Grating 1 tilt error 0.00088 Grating 2 tilt error 0.00250 Grating 1 angle error 0.01300 Grating 2 angle error 0.01300 表 3 误差源分配
Table 3. Error source allocation
Allocation of pointing errors The size of the allocation pointing error/(″) Corresponding source of error The corresponding error source assignment value/(″) Pointing error caused by the tilt of light δL 9.83841 Light tilt error YL 9.51 Pointing error caused by the tilt of grating axis 1 δR1 0.08365 Grating axis 1 tilt error YR1 9.55 Pointing error caused by the tilt of grating axis 2 δR1 0.23765 Grating axis 2 tilt error YR2 9.52 Pointing error caused by the tilt of grating 1 δP1 0.08365 Grating 1 tilt error YP1 9.55 Pointing error caused by the tilt of grating 2 δP2 0.23765 Grating 2 tilt error YP2 9.52 Pointing error caused by the error of grating angle δQ1 1.24050 Grating 1 angle error YQ1 9.54 Pointing error caused by the error of grating angle δQ2 1.24050 Grating 2 angle error YQ2 9.54 表 4 系统误差源对应的双光栅转台误差
Table 4. Error of double grating turntable corresponding to the system error source
Systematic error source The corresponding double grating turntable error The design error of the corresponding
double grating turntable/(″)Light tilt error Antenna coaxial error 8 Grating axis tilt error Deflection error of grating axis (grating axis 1)
Deflection error of grating axis+ Parallelism of the two axes (grating axis 2)5 5+4 Grating tilt error Grating 1 installation error
Grating 2 installation error7
7Grating angle error Encoder error 3 表 5 双光栅转台误差检测
Table 5. Error detection of double grating turntable
Double grating turntable error Design value/(″) Measured value/(″) Antenna coaxial error ≤8 6.53 Deflection error of grating axis ≤5 (grating axis 1)
≤5 (grating axis 2)4.20
4.05Parallelism of the two axes ≤4 3.29 Grating installation error ≤7 (grating 1)
≤7 (grating 2)5.30
6.00Encoder error ≤3 2.50 -
参考文献
[1] 姜会林, 佟首峰. 空间激光通信技术与系统[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2010.
Jiang H L, Tong S F. The Technologies and Systems of Space Laser Communication[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2010.
[2] 谢木军, 马佳光, 傅承毓, 等. 空间光通信中的精密跟踪瞄准技术[J]. 光电工程, 2000, 27(1): 13−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2000.01.003
Xie M J, Ma J G, Fu C Y, et al. Precision tracking and pointing technologies in space optical communication[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2000, 27(1): 13−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2000.01.003
[3] Schwarze C R, Vaillancourt R, Carlson D, et al. Risley-prism based compact laser beam steering for IRCM, laser communications, and laser radar[J]. Critical Technology, 2005, 9: 1−9.
[4] Hakun C, Budinoff J, Brown G, et al. A boresight adjustment mechanism for use on laser altimeters[EB/OL]. [2023-03-01]. https://esmats.eu/amspapers/pastpapers/pdfs/2004/hakun.pdf.
[5] 余辉龙, 鲍智康, 王璇, 等. XY-2号卫星激光通信载荷PAT在轨测试[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(5): 20200327. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200327
Yu H L, Bao Z K, Wang X, et al. XY-2 satellite laser communication equipment PAT test in orbit[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2021, 50(5): 20200327. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200327
[6] 宋一诺. 基于旋转双棱镜的激光通信粗指向机构关键技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2023. https://doi.org/10.27522/d.cnki.gkcgs.2023.000004.
Song Y N. Key technology research of coarse pointing mechanism for laser communication based on Risley prisms[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanicsand Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2023. https://doi.org/10.27522/d.cnki.gkcgs.2023.000004.
[7] Wang J, Gao L, Jiang L, et al. Establishment and verification of formulas of target tracking based on dual liquid crystal polarization gratings[J]. Opt Express, 2022, 30(24): 43062−43077. doi: 10.1364/OE.473947
[8] Oh C, Kim J, Muth J F, et al. A new beam steering concept: Risley gratings[J]. Proc SPIE, 2009, 7466: 74660J. doi: 10.1117/12.828005
[9] Kim J, Miskiewicz M N, Serati S, et al. Nonmechanical laser beam steering based on polymer polarization gratings: design optimization and demonstration[J]. J Lightw Technol, 2015, 33(10): 2068−2077. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2015.2392694
[10] Zhou Y, Fan D P, Fan S X, et al. Laser scanning by rotating polarization gratings[J]. Appl Opt, 2016, 55(19): 5149−5157. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.005149
[11] 李小明, 朱国帅, 郭名航, 等. 基于光学自准直的旋转轴平行度测量与不确定度分析[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2023, 52(5): 20220794. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220794
Li X M, Zhu G S, Guo M H, et al. Coaxiality measurement and uncertainty analysis of rotating shafts based on autocollimation[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2023, 52(5): 20220794. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220794
[12] 符红, 吴琼, 林斌, 等. 基于双光栅的平行度检测[J]. 光电工程, 2012, 39(7): 61−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2012.07.010
Fu H, Wu Q, Lin B, et al. The measurement of parallelism based on diffraction grating[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2012, 39(7): 61−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2012.07.010
[13] 佀明华, 王伟明, 张勇, 等. 基于光电伺服平台的动态角度测量方法研究[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(10): 180445. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180445
Si M H, Wang W M, Zhang Y, et al. Research on dynamic angle measurement method based on electro-optical servo platform[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(10): 180445. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180445
[14] 奚玉鼎, 于涌, 丁媛媛, 等. 一种快速搜索空中低慢小目标的光电系统[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(4): 170654. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170654
Xi Y D, Yu Y, Ding Y Y, et al. An optoelectronic system for fast search of low slow small target in the air[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2018, 45(4): 170654. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170654
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: