-
摘要
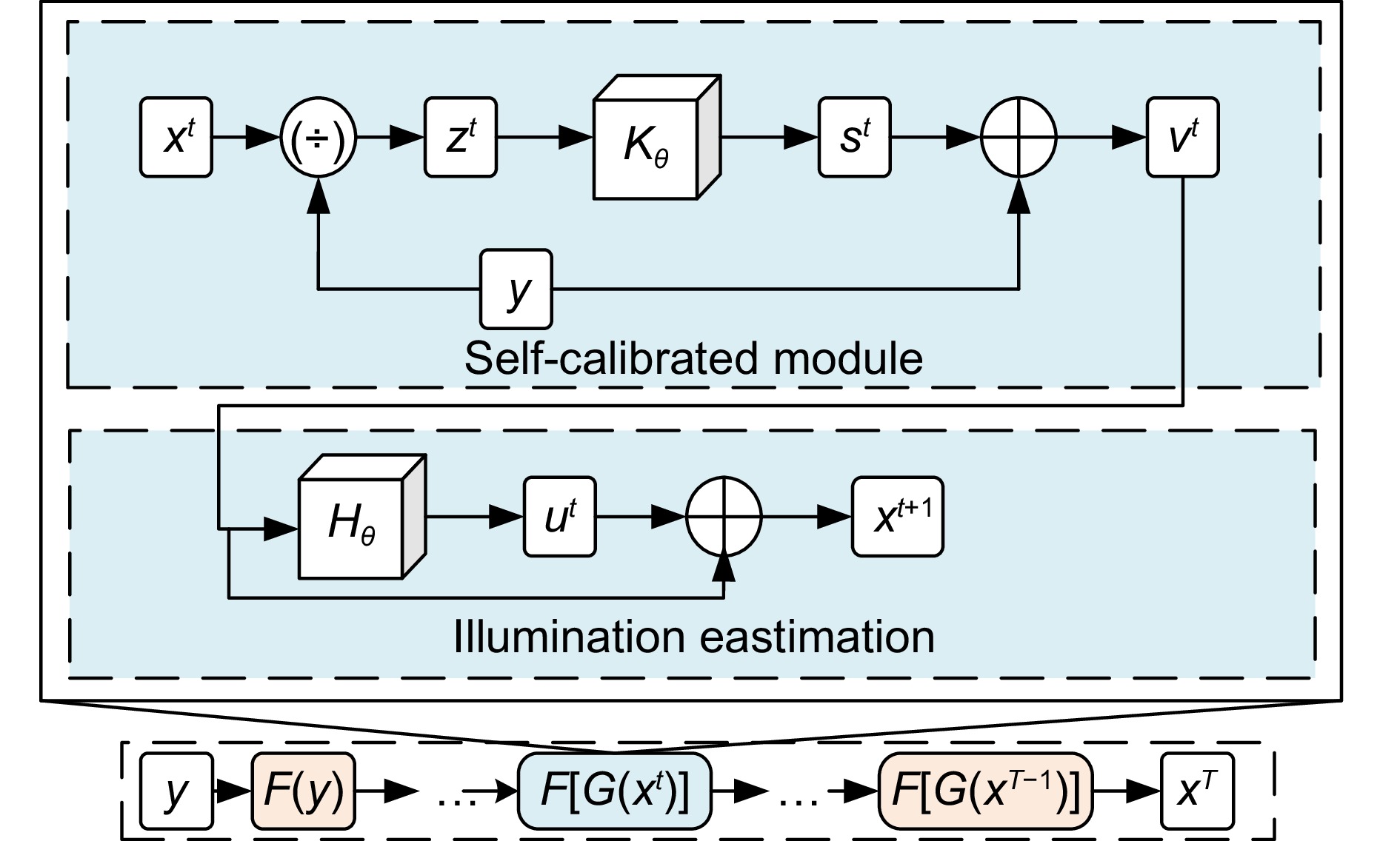
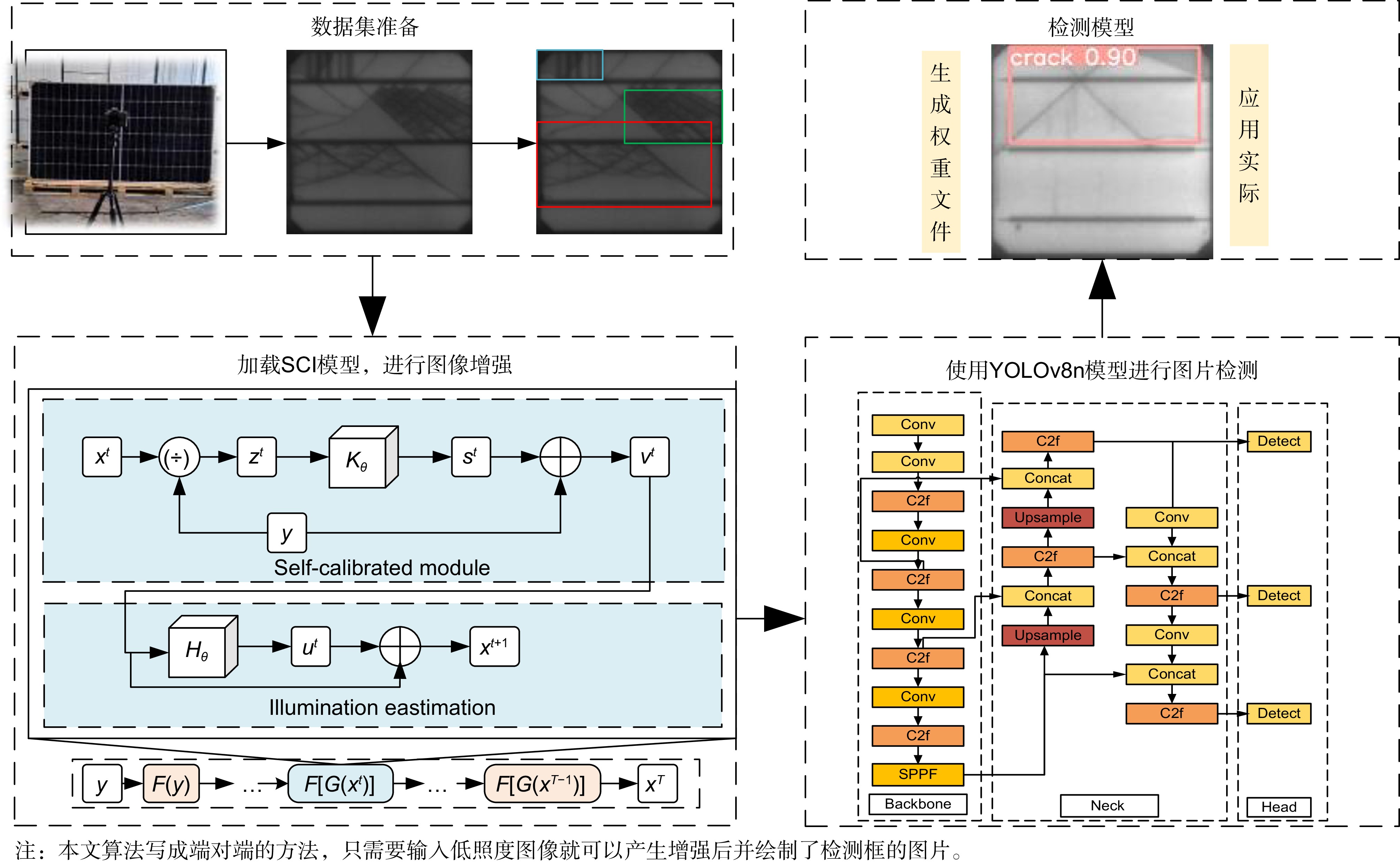
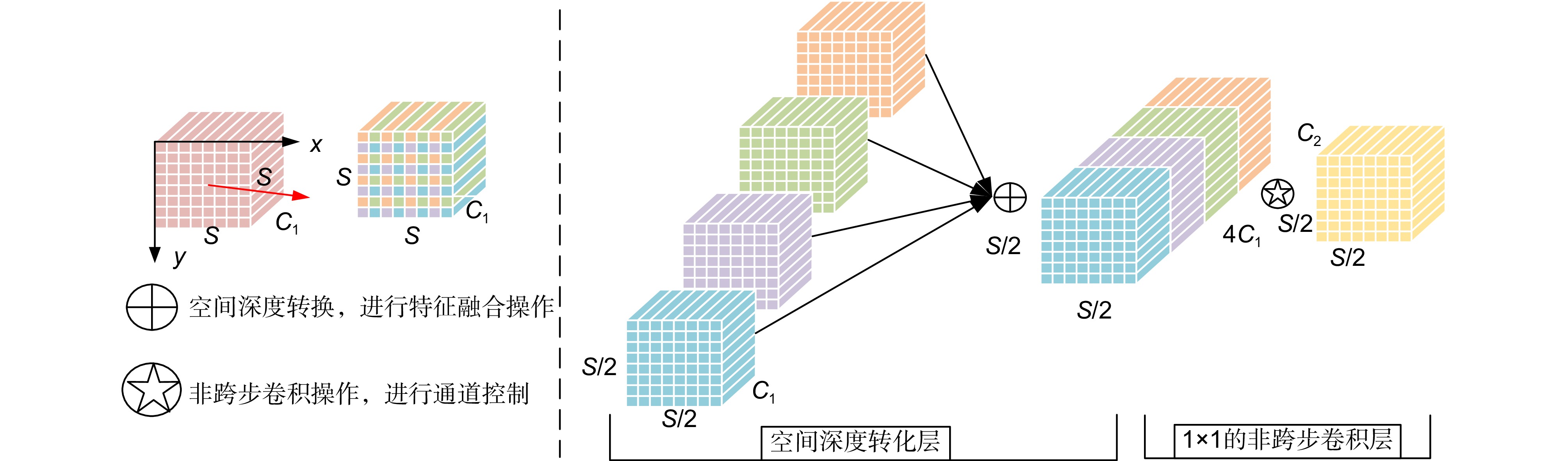
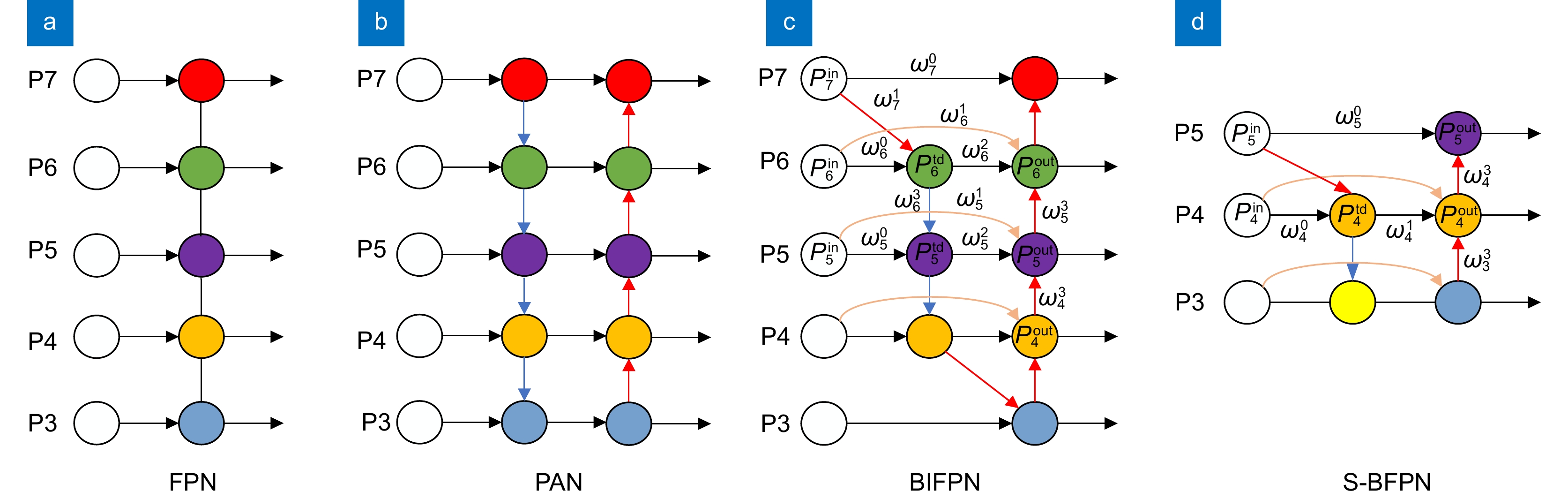
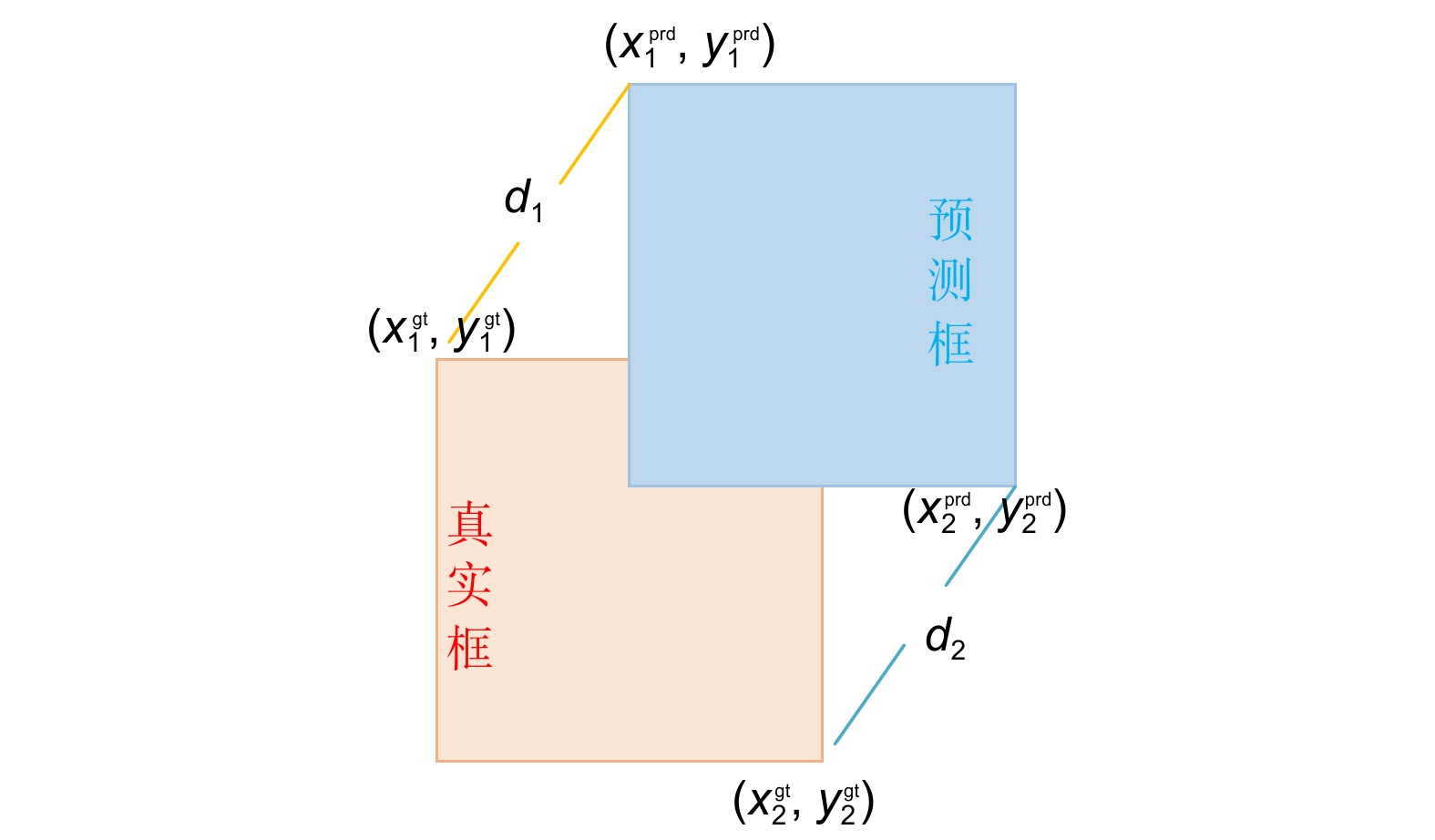
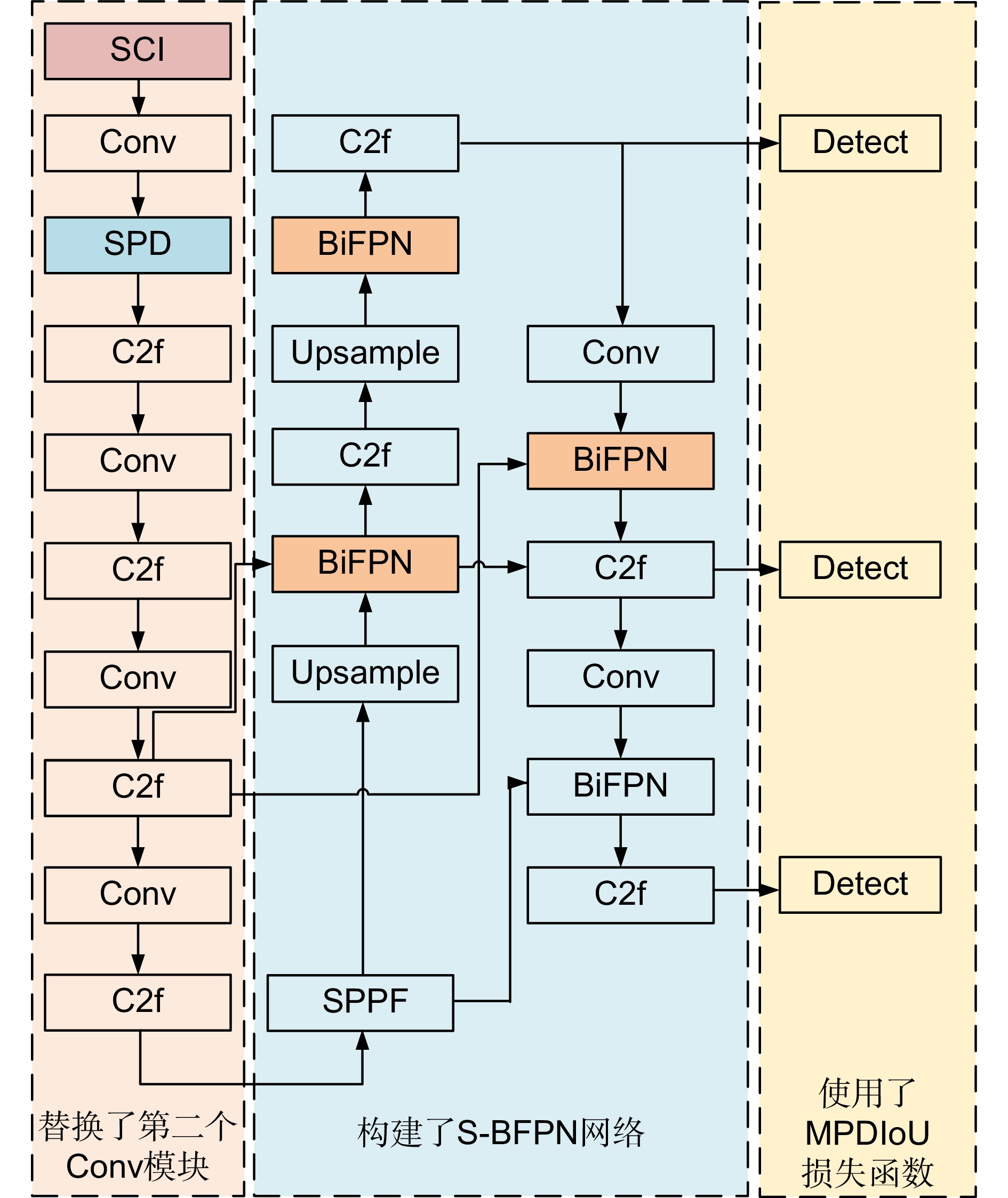
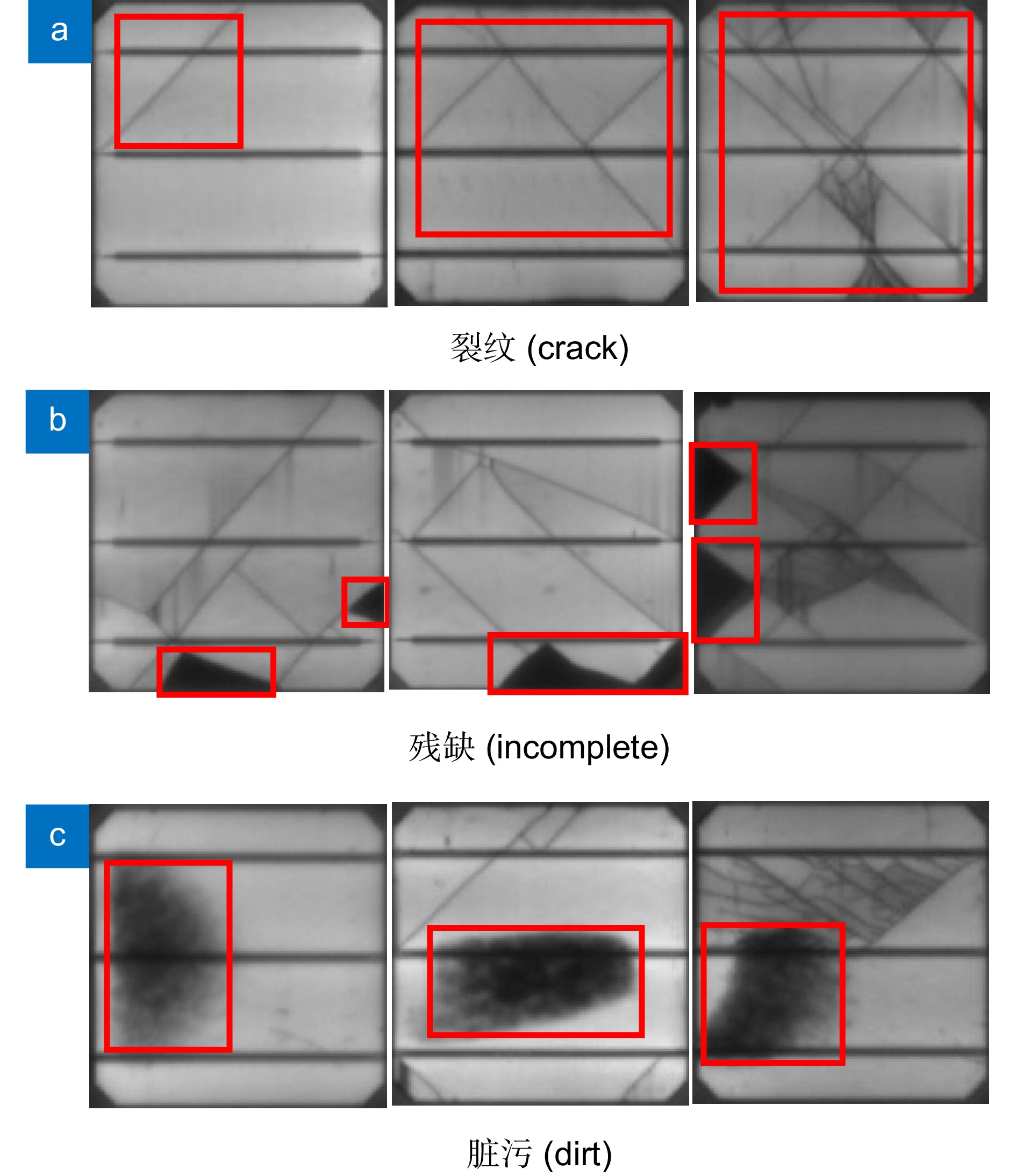
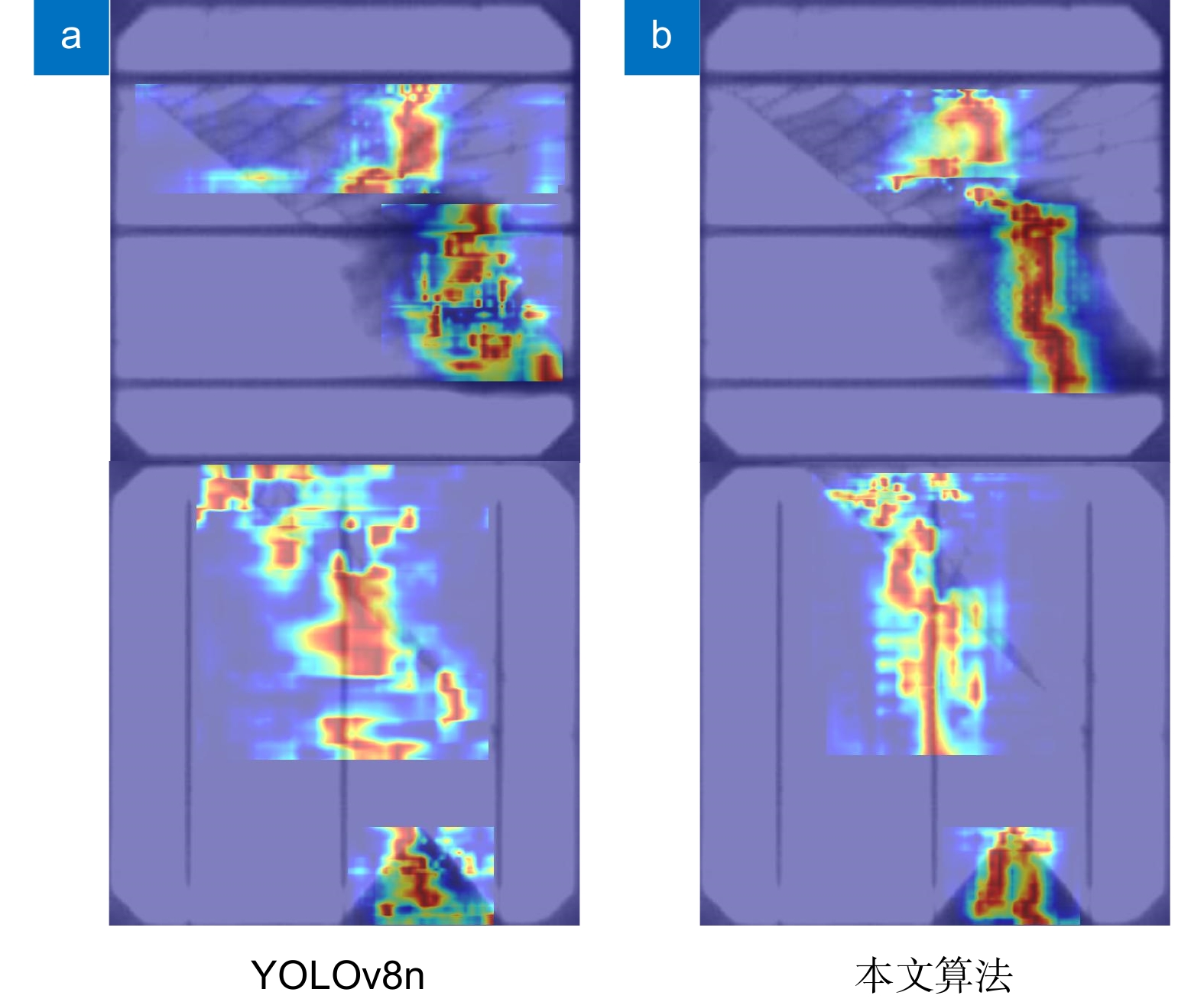
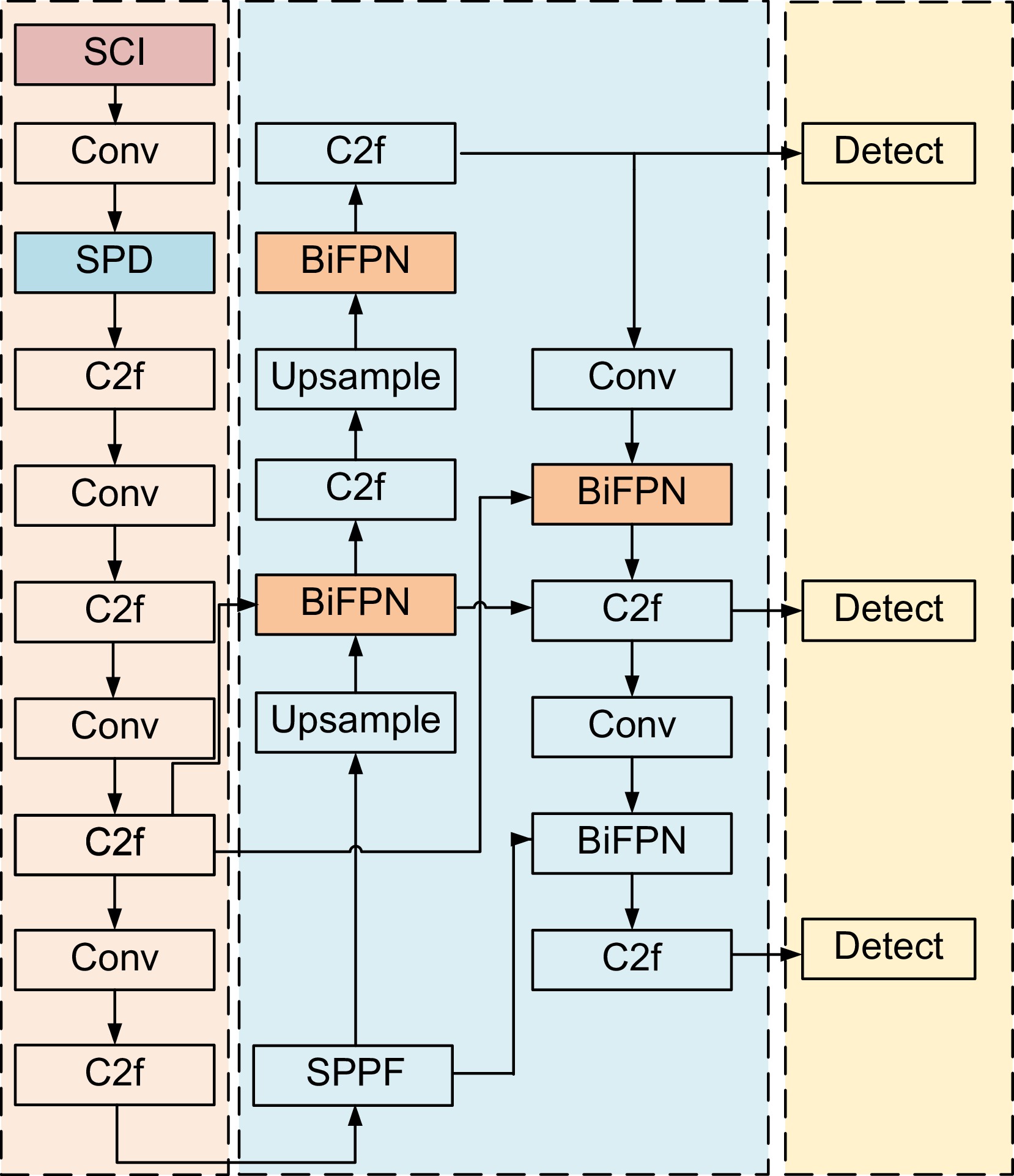
针对太阳能电池片缺陷检测中存在检测精度低、误检和漏检率高的问题,本文在深度学习模型YOLOv8的基础上进行优化与改进,提出了一种太阳能电池片电致成像(electroluminescent, EL)缺陷检测模型。首先,采用自校准光照学习(self-calibrated illumination, SCI)方法对低光照图像进行预处理,以增强太阳能电池片缺陷的有效特征信息。然后,引入一个空间到深度的注意力模块(space-to-depth, SPD),替换主干网络的第二个跨步卷积层,避免跨步卷积导致的信息丢失,扩大感受野,减少计算量,从而在特征提取时保留更多特征信息。其次,构建了空间双向要素金字塔网络(spatial-BiFPN, S-BFPN),通过多尺度特征融合,解决因太阳能电池片缺陷形状多样性而造成缺陷识别率不稳定的问题。最后,本文改进了损失函数,使用MPDIoU作为损失函数,解决了原有的CIoU损失函数中惩罚项失效的问题。实验结果显示,改进后的YOLOv8模型的mAP达到了96.9%,比原始YOLOv8提升了2.2%,计算量减少了0.2 GFlops,检测速度最高达155 f/s,实现了高精度与高实时性,更适合工业部署。
Abstract
To address issues of low detection accuracy and high false-positive and false-negative rates in solar cell defect detection, this paper proposes an optimized solar cell electroluminescent (EL) defect detection model based on the YOLOv8 deep learning framework. First, a self-calibrated illumination (SCI) method is applied to preprocess low-light images, enhancing effective feature information for solar cell defects. Then, a space-to-depth (SPD) attention module is introduced, replacing the second stride convolution layer in the backbone network. This substitution avoids information loss caused by stride convolution, expands the receptive field, and reduces computational load, preserving more feature information during extraction. Next, a spatial-BiFPN (S-BFPN) network is constructed to perform multi-scale feature fusion, stabilizing defect recognition rates by addressing the shape variability of solar cell defects. Lastly, the loss function is improved by adopting MPDIoU, which resolves the issue of ineffective penalties in the original CIoU loss function. The experimental results show that the improved YOLOv8 model achieved an mAP of 96.9%, a 2.2% increase compared to the original YOLOv8. The computational load was reduced by 0.2 GFlops, and the detection speed reached a maximum of 155 f/s, demonstrating high accuracy and real-time performance, making it more suitable for industrial deployment.
-
Key words:
- deep learning /
- solar cells /
- defect detection /
- YOLOv8
-
Overview
Overview: As the global demand for renewable energy grows, solar power has become an essential source of clean energy. However, solar cells often develop defects, such as microcracks, hotspots, and black spots, during production, which significantly impact their conversion efficiency and lifespan. Traditional manual inspection methods are inefficient and limited by lighting conditions, resulting in low detection accuracy with high false-positive and false-negative rates. To meet the need for efficient and precise automated inspection in industrial production, this study aims to develop a high-accuracy, real-time solar cell defect detection model suitable for practical industrial environments. In response, this paper proposes an optimized solar cell electroluminescent (EL) defect detection model based on the YOLOv8 deep learning framework. First, a self-calibrated illumination (SCI) method is applied to preprocess low-light images, enhancing the effective feature information for detecting solar cell defects. Next, a space-to-depth (SPD) attention module is introduced, replacing the second stride convolution layer in the backbone network to prevent information loss caused by stride convolution, expand the receptive field, and reduce computational load, ensuring more comprehensive feature retention. Additionally, a spatial-BiFPN (S-BFPN) network is constructed to perform multi-scale feature fusion, stabilizing recognition rates even when defect shapes vary. Finally, the loss function is improved with the adoption of MPDIoU, addressing the inadequate penalty issues in the original CIoU loss function. Experimental results show that the improved YOLOv8 model achieves an mAP of 96.9%, marking a 2.2% increase over the original YOLOv8, while reducing computational load by 0.2 GFlops. The detection speed reaches a maximum of 155 FPS, demonstrating high accuracy and real-time performance, making it more suitable for industrial applications.
-

-
表 1 多个位置添加注意力机制对比实验结果
Table 1. Comparative experimental results of adding attention mechanisms at multiple locations
替换位置 权重/MB 参数量/(106) GFlops mAP/% YOLOv8n 6.3 3.006 8.1 94.7 2,3,4,5 5.7 2.818 7.4 95.1 2,5 5.8 2.890 7.8 95.3 5 5.8 2.894 8.0 95 4 6.2 3.066 8.0 94.5 3 6.3 3.109 8.0 94.7 2 (本文) 6.2 3.002 7.9 96.0 表 2 增强算法对比实验
Table 2. Enhancement algorithm comparison experiment
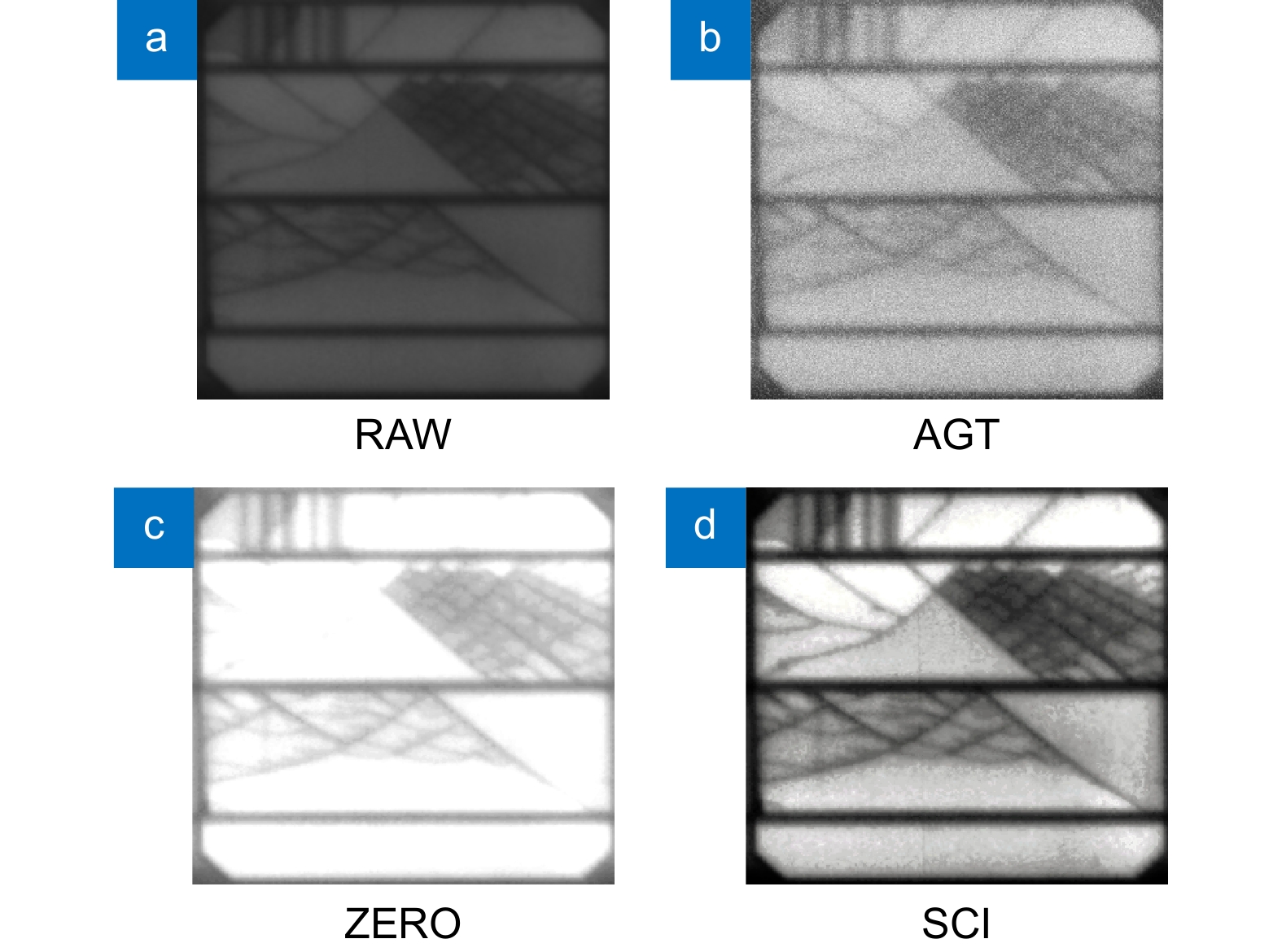
算法 准确率/% 召回率/% 平均精度/% RAW 93.1 91.0 91.0 AGT 93.5 90.4 91.8 ZERO-DCE 95.6 90.7 93.2 SCI (本文) 96.5 91.1 94.7 表 3 消融实验结果
Table 3. Results of the ablation experiment
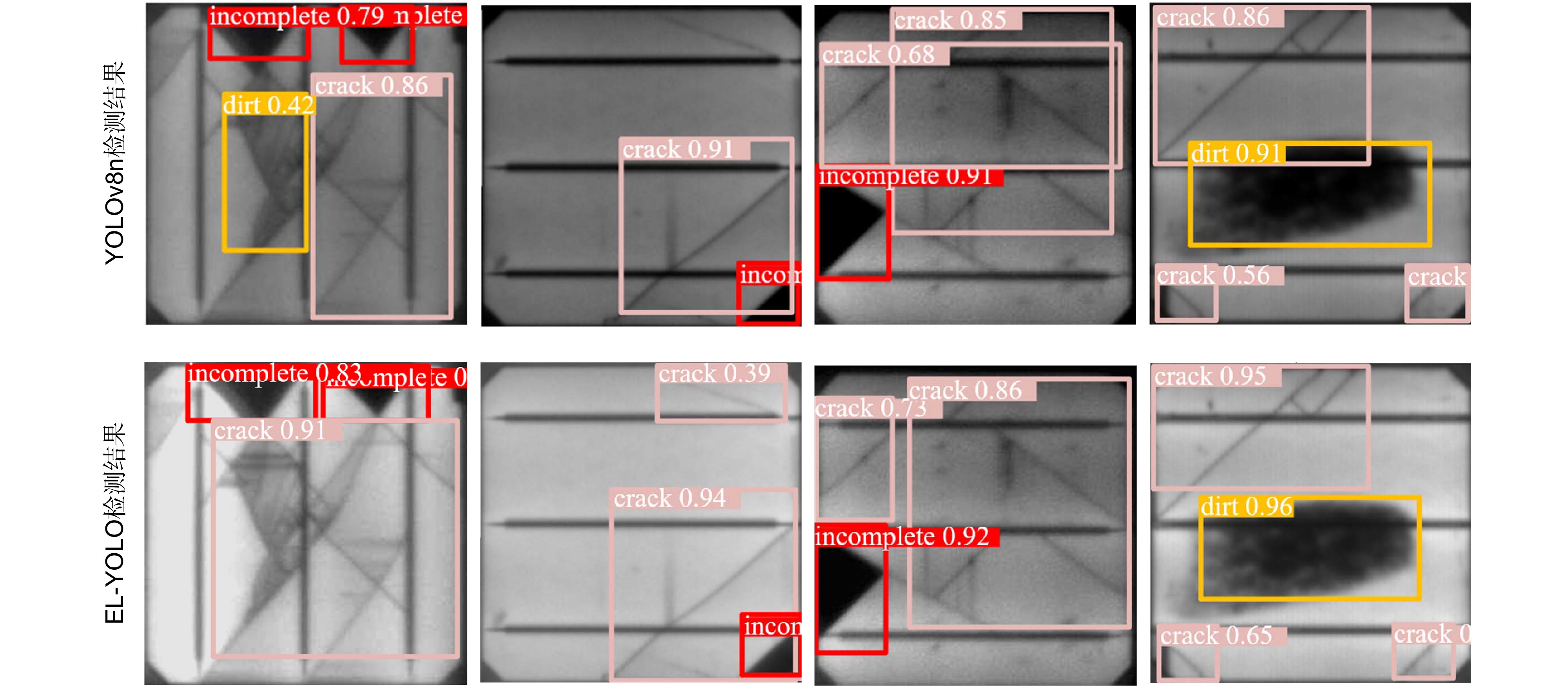
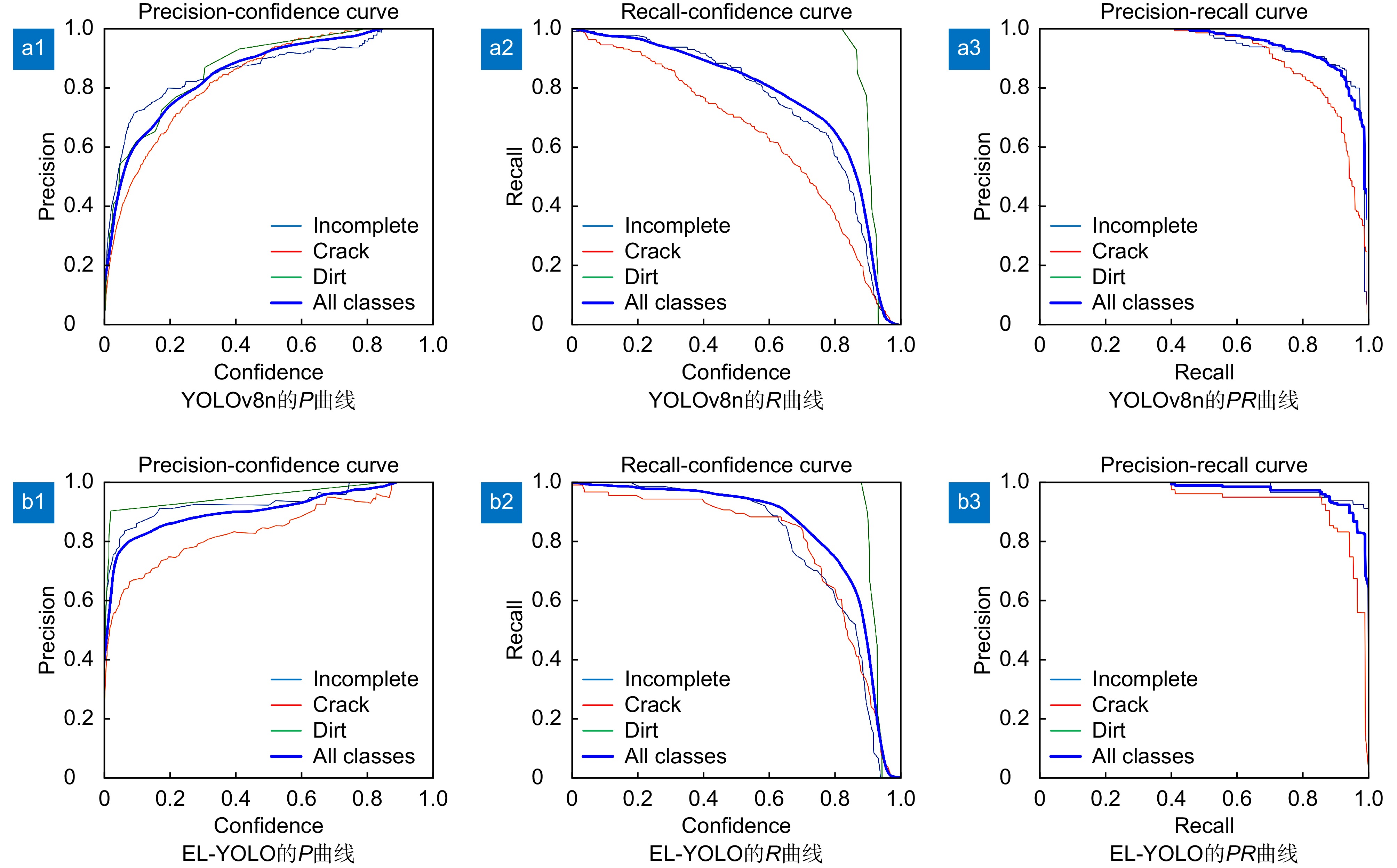
算法模型 S SB M 权重/MB 参数量/106 计算量/GFlops FPS mAP@(0.5)/% YOLOv8n 6.3 3.006 8.1 153 94.7 YOLOv8n-S √ 6.2 3.002 7.9 155 96.0 YOLOv8n-SB √ 6.3 3.006 8.1 147 95.4 YOLOv8n-M √ 6.3 3.006 8.1 154 95.5 YOLOv8n-S+SB √ √ 6.2 3.002 7.9 148 96.2 YOLOv8n-S+M √ √ 6.2 3.002 7.9 158 96.4 YOLOv8n-SB+M √ √ 6.3 3.006 8.1 150 96.0 EL-YOLO (本文) √ √ √ 6.2 3.002 7.9 155 96.9 表 4 多种检测算法结果对比
Table 4. Comparison of results of multiple detection algorithms
算法模型 权重/MB 参数量/106 计算量/GFlops FPS mAP@(0.5)/% YOLOv5s 14.5 7.018 15.8 118 89.8 YOLOv7 74.8 37.194 105.1 71 84.6 YOLOv8n 6.3 3.006 8.1 153 94.7 YOLOv8s 22.5 11.137 28.8 104 95.3 YOLOv8m 52.0 25.902 79.3 73 93.6 YOLOv10s 31.4 7.2 21.6 119 96.2 RT-DETR 63.1 32.8 108.2 46 96.0 Gold-YOLO 43.1 21.5 46.0 82 96.4 Faster-R-CNN 112.7 41.325 24.2 8 94.6 SSD 99.1 35.873 12.7 44 81.3 EL-YOLO(本文) 6.2 3.019 7.9 155 96.9 -
参考文献
[1] 彭自然, 许怀顺, 肖伸平. 一种基于CatBoost优化的光伏阵列故障诊断模型[J]. 电子学报, 2024, 52(7): 2418−2428. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20240236
Peng Z R, Xu H S, Xiao S P. A CatBoost optimization-based fault diagnosis model for photovoltaic arrays[J]. Acta Electron Sin, 2024, 52(7): 2418−2428. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20240236
[2] 时亚涛, 戴芳, 杨畅民. 太阳能光伏电池缺陷检测[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2020, 34(4): 157−164. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B1902656
Shi Y T, Dai F, Yang C M. Defect detection of solar photovoltaic cell[J]. J Electron Meas Instrum, 2020, 34(4): 157−164. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B1902656
[3] Bedrich K, Bokalič M, Bliss M, et al. Electroluminescence imaging of PV devices: advanced vignetting calibration[J]. IEEE J Photovoltaics, 2018, 8(5): 1297−1304. doi: 10.1109/JPHOTOV.2018.2848722
[4] Chen X, Karin T, Jain A. Automated defect identification in electroluminescence images of solar modules[J]. Solar Energy, 2022, 242: 20−29. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2022.06.031
[5] 彭自然, 张颖清, 肖伸平. 基于YOLOv5的太阳电池表面缺陷检测[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45(6): 368−375. doi: 10.19912/j.0254-0096.tynxb.2023-0335
Peng Z R, Zhang Y Q, Xiao S P. Research on surface defect detection of solar cell with improved YOLOv5 algorithm[J]. Acta Energ Sol Sin, 2024, 45(6): 368−375. doi: 10.19912/j.0254-0096.tynxb.2023-0335
[6] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2017, 39(6): 1137−1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
[7] 裴少通, 张行远, 胡晨龙, 等. 基于ER-YOLO算法的跨环境输电线路缺陷识别方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39(9): 2825−2840. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.232073
Pei S T, Zhang H Y, Hu C L, et al. The defect detection method for cross-environment power transmission line based on ER-YOLO algorithm[J]. Trans China Electrotech Soc, 2024, 39(9): 2825−2840. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.232073
[8] 钱晓亮, 张鹤庆, 张焕龙, 等. 基于视觉显著性的太阳能电池片表面缺陷检测[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(7): 1570−1578. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.07.002
Qian X L, Zhang H Q, Zhang H L, et al. Solar cell surface defect detection based on visual saliency[J]. Chin J Sci Instrum, 2017, 38(7): 1570−1578. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.07.002
[9] Tsai D M, Wu S C, Li W C. Defect detection of solar cells in electroluminescence images using Fourier image reconstruction[J]. Solar Energy Mater Solar Cells, 2012, 99: 250−262. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2011.12.007
[10] 刘磊, 王冲, 赵树旺, 等. 基于机器视觉的太阳能电池片缺陷检测技术的研究[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2018, 32(10): 47−52. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.2018.10.007
Liu L, Wang C, Zhao S W, et al. Research on solar cells defect detection technology based on machine vision[J]. J Electron Meas Instrum, 2018, 32(10): 47−52. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.2018.10.007
[11] Wei S Q, Li X X, Ding S H, et al. Hotspots infrared detection of photovoltaic modules based on Hough line transformation and Faster-RCNN approach[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 6th international conference on control, decision and information technologies, Paris, 2019: 1266–1271. https://doi.org/10.1109/CoDIT.2019.8820333.
[12] 张文彪, 马永华, 白晓静, 等. 基于改进Faster R-CNN的太阳能电池板缺陷识别[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46(7): 2593−2600. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2021.2373
Zhang W B, Ma Y H, Bai X J, et al. Defect identification of solar panels using improved Faster R-CNN[J]. Power Syst Technol, 2022, 46(7): 2593−2600. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2021.2373
[13] Lu S, Wu K X, Chen J X. Solar cell surface defect detection based on optimized YOLOv5[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 71026−71036. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3294344
[14] 周启宸, 王伯超. 基于改进YOLOv7的太阳能电池片表面缺陷检测[J]. 计算机应用, 2023, 43(S2): 223−228 doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2023020258
Zhou Q C, Wang B C. Solar cell surface defect detection based on improved YOLOv7[J]. J Comput Appl, 2023, 43(S2): 223−228 doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2023020258
[15] Fu H, Cheng G Q. Convolutional neural network based efficient detector for multicrystalline photovoltaic cells defect detection[J]. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util Environ Eff, 2023, 45(3): 8686−8702. doi: 10.1080/15567036.2023.2230935
[16] 张烨, 李博涛, 尚景浩, 等. 基于多尺度卷积注意力机制的输电线路防振锤缺陷检测[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39(11): 3522−3537. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.231155
Zhang Y, Li B T, Shang J H, et al. Defect detection of transmission line damper based on multi-scale convolutional attention mechanism[J]. Trans China Electrotech Soc, 2024, 39(11): 3522−3537. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.231155
[17] Wang Z, Hua Z X, Wen Y C, et al. E-YOLO: recognition of estrus cow based on improved YOLOv8n model[J]. Expert Syst Appl, 2024, 238: 122212. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122212
[18] Ma L, Ma T Y, Liu R S, et al. Toward fast, flexible, and robust low-light image enhancement[C]//Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, 2022: 5627–5636. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00555.
[19] 刘皓皎, 刘力双, 张明淳. 基于YOLOv5改进的红外目标检测算法[J]. 激光技术, 2024, 48(4): 534−541. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2024.04.011
Liu H J, Liu L S, Zhang M C. An improved infrared object detection algorithm based on YOLOv5[J]. Laser Technol, 2024, 48(4): 534−541. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2024.04.011
[20] 张润梅, 肖钰霏, 贾振楠, 等. 改进YOLOv7的无人机视角下复杂环境目标检测算法[J]. 光电工程, 2024, 51(5): 240051. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240051
Zhang R M, Xiao Y F, Jia Z N, et al. Improved YOLOv7 algorithm for target detection in complex environments from UAV perspective[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2024, 51(5): 240051. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240051
[21] 王鹏峰, 李运堂, 黄永勇, 等. 基于改进YOLOv5s网络的斜拉桥拉索表面缺陷检测[J]. 光电工程, 2024, 51(5): 240028. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240028
Wang P F, Li Y T, Huang Y Y, et al. Defects detection for cable surface of cable-stayed bridge based on improved YOLOv5s network[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2024, 51(5): 240028. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240028
[22] Zhao Y A, Lv W Y, Xu S L, et al. DETRs beat YOLOs on real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, 2024: 16965–16974. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.01605.
[23] Wang A, Chen H, Liu L H, et al YOLOv10: real-time end-to-end object detection[Z]. arXiv: 2405.14458, 2024. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2405.14458.
[24] Wang C C, He W, Nie Y, et al. Gold-YOLO: efficient object detector via gather-and-distribute mechanism[C]//Proceedings of the 37th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, 2023: 36.
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: