-
摘要
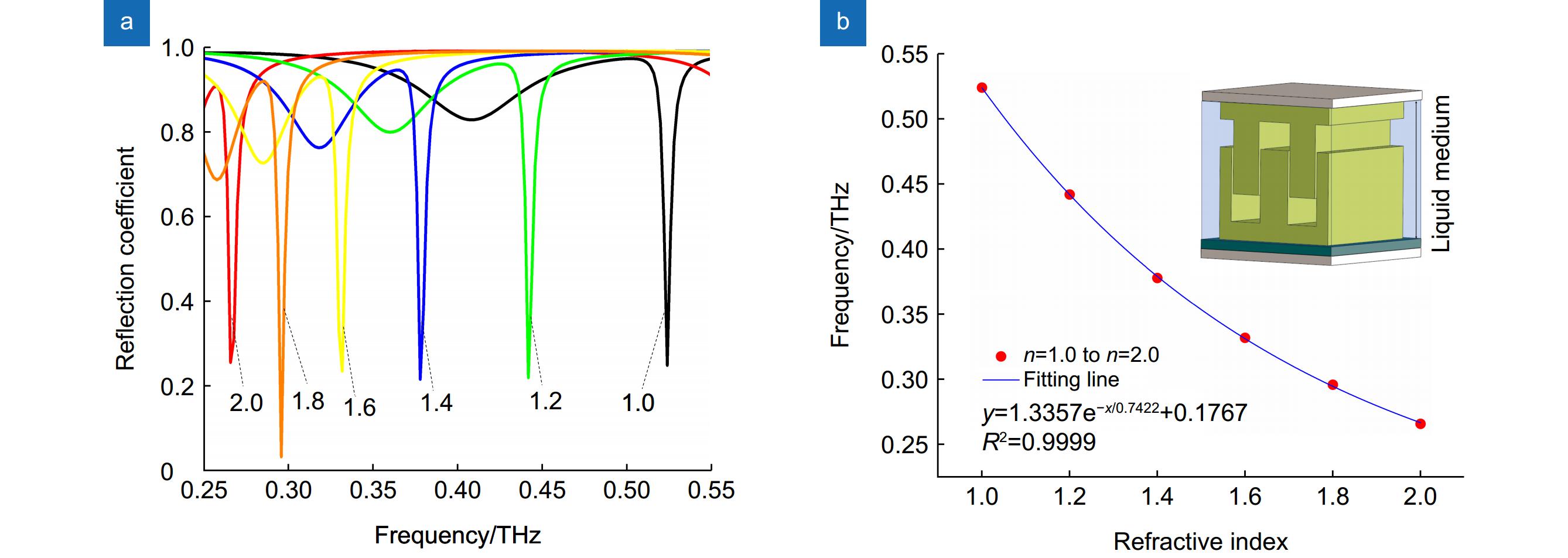
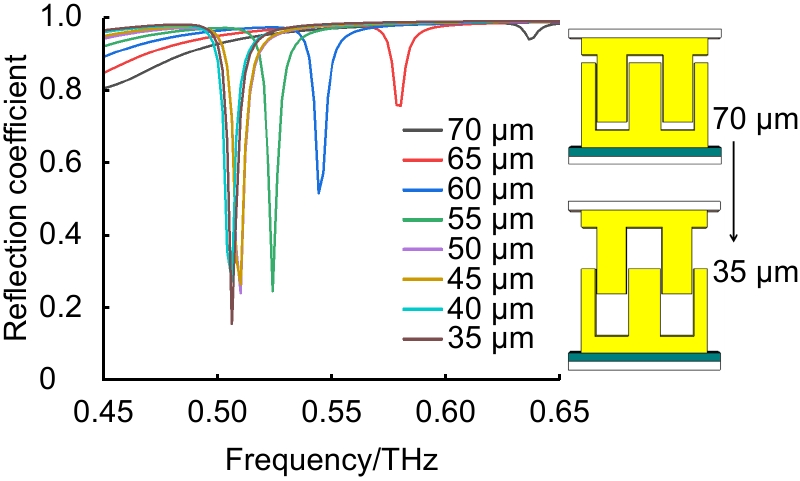
传感器作为集成化器件中至关重要的部分,其多功能性越来越受到重视。本文介绍了一种基于双层三维谐振结构耦合的太赫兹超材料多功能传感器。传感装置包括上下两层聚酰亚胺薄膜基底,附着在下层聚酰亚胺薄膜基底上的石墨层,以及在石墨层和上层聚酰亚胺薄膜基底之间的周期性双层三维齿形耦合谐振结构,此结构包括下层对称山形结构和上层对称凹形结构。该三维超材料结合多层结构可实现多功能测量:可通过谐振频率确定待测液体介质层的折射率变化,从而实现液体成分的高精度分辨;在一维方向的微位移传感方面,则可分别在
z 轴方向以及y 轴方向上实现微位移的高灵敏度测量。本文所提出的三维超材料传感器能为功能集成化传感在太赫兹领域的应用提供了新的思路。Abstract
The versatility of sensors, as a crucial part of integrated devices, is receiving increasing attention. Here, a terahertz metamaterial multifunctional sensor based on the coupling of a two-layer 3D resonant structure is introduced. The sensor consists of an upper and lower polyimide film substrate, a graphite layer attached to the lower polyimide film substrate, and a periodic double-layer 3D toothed coupling resonant structure between the graphite layer and the upper polyimide film substrate, which consists of a symmetric mountain-shaped structure in the lower layer and a symmetric concave structure in the upper layer. The three-dimensional metamaterial can achieve multifunctional measurements: the refractive index change of the liquid medium can be detected with high sensitivity by measuring the resonant frequency of the structure. Therefore, it is possible to detect the liquid medium with such a design. Meanwhile, in terms of micro displacement sensing, a high micro displacement measurement sensitivity can be realized in both the
z -axis andy -axis directions, respectively. The 3D metamaterial sensor proposed in this paper provides an idea for the design of a functionally integrated sensor in the terahertz region. -
Overview
Overview: Sensors are increasingly valued for their versatility as a crucial part of integrated devices. With the advancement of technology facing diverse environmental challenges, there is a growing need for multifunctional integration in the sensing field. Metamaterials are the combination of artificial periodic arrays with subwavelength resonant structures, and terahertz metamaterials sensors have a wide range of applications in biomacromolecule sensing and other trace precision detection fields due to their high penetration, specific fingerprint, low photon energy, high sensitivity and high resolution. At present, researchers in this field are increasingly demanding the highly sensitive performance of metamaterial sensors. Traditional metamaterial sensors have already enabled various sensing applications, but most of these sensors are designed for single detection targets and functions. Integrating sensors with multiple detection functions remains one of the challenges in the current research on metamaterial sensors. Moreover, the existing reported metamaterial sensors are primarily based on two-dimensional metasurfaces. A common issue with these sensors is their relatively low sensitivity and resolution, which limits the application of metamaterial sensors in high-precision detection.
In this paper, a terahertz metamaterial multifunctional sensor based on the coupling of a two-layer 3D resonant structure with high sensitivity is introduced. The sensor consists of an upper and lower polyimide film substrate, a graphite layer attached to the lower polyimide film substrate, and a periodic double-layer 3D toothed coupling resonant structure between the graphite layer and the upper polyimide film substrate, which consists of a symmetric mountain-shaped structure in the lower layer and a symmetric concave structure in the upper layer. The three-dimensional metamaterial can achieve multifunctional measurements with high sensitivity: the refractive index change of the liquid medium can be detected with a high sensitivity by measuring the resonant frequency of the structure. Therefore, it is possible to detect the liquid medium with such a design. Meanwhile, in terms of micro displacement sensing, a high micro displacement measurement sensitivity can be realized in both the z-axis and y-axis directions, respectively. Compared with other reported metamaterial sensors, the proposed design achieves multifunctional sensing ability. Moreover, it also outperforms metamaterial sensors based on two-dimensional metasurfaces in terms of sensitivity and resolution. The 3D metamaterial sensor proposed in this paper paves a new way for the design of functionally integrated sensor with high sensitivity at terahertz frequencies.
-

-
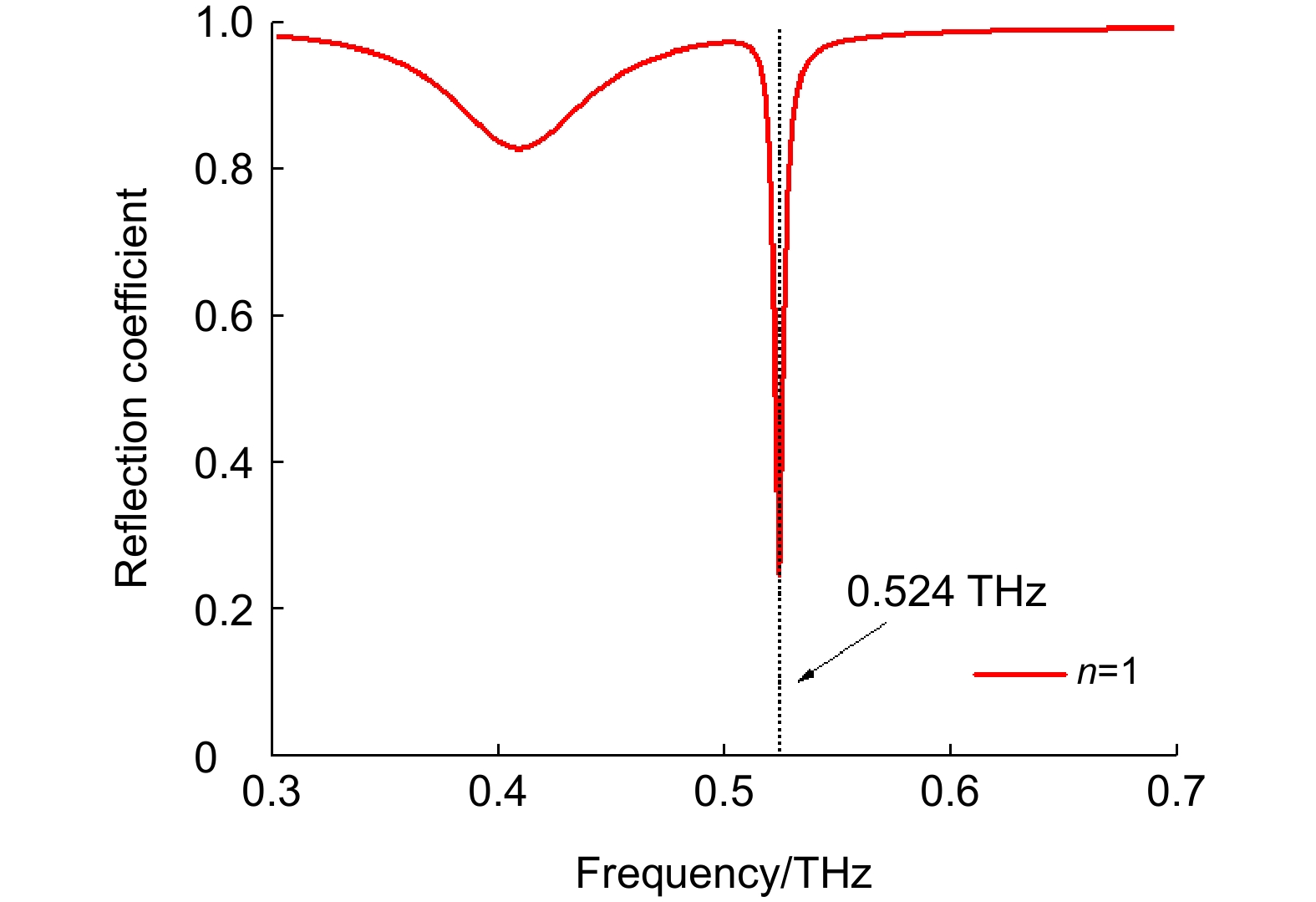
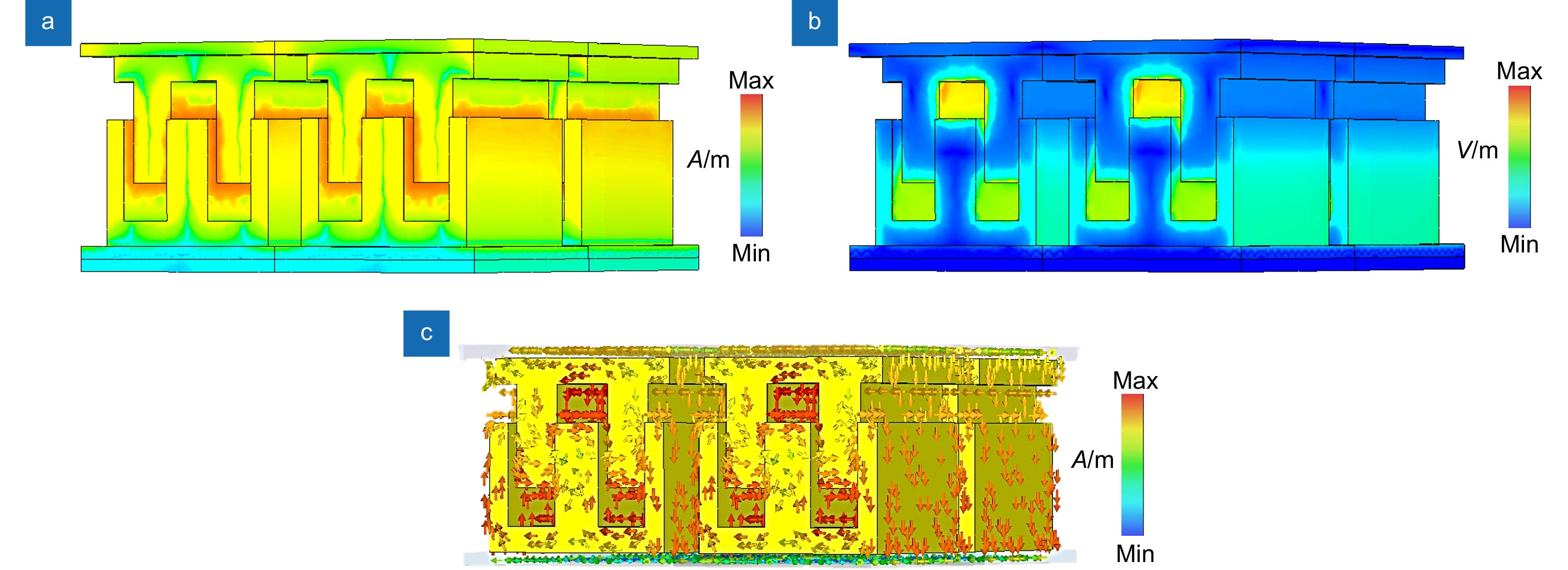
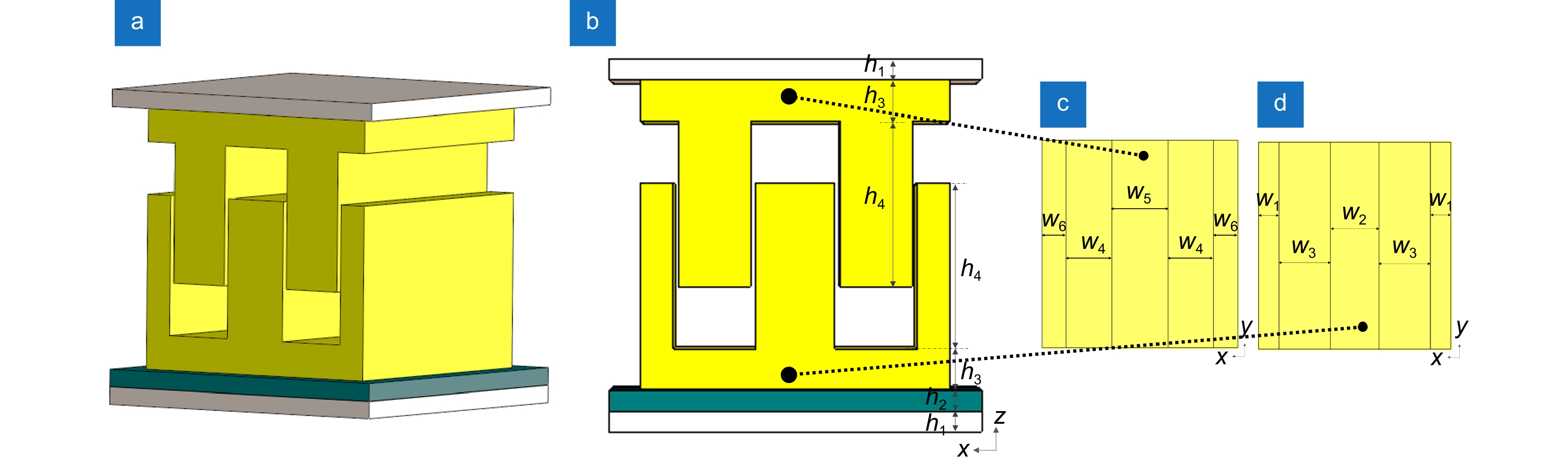
图 1 (a)双层三维超材料传感器的示意图;(b)传感器多层结构的侧视图;(c)下层山形立体结构平面俯视图;(d)上层凹形立体结构平面仰视图Fig.1 (a) Schematic diagram of a dual-layer stereo metamaterial sensor; (b) Side view of the multilayer structure of the sensor; (c) Plan view of the lower layer gabled stereo structure; (d) Plan view of the upper layer concave stereo structure
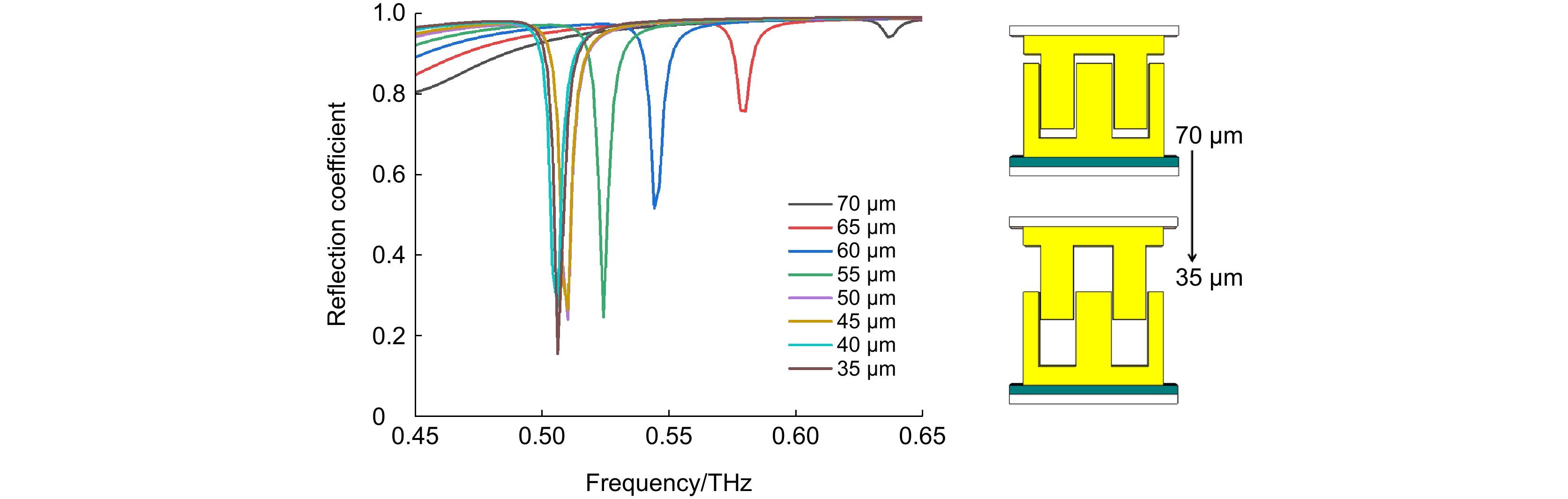
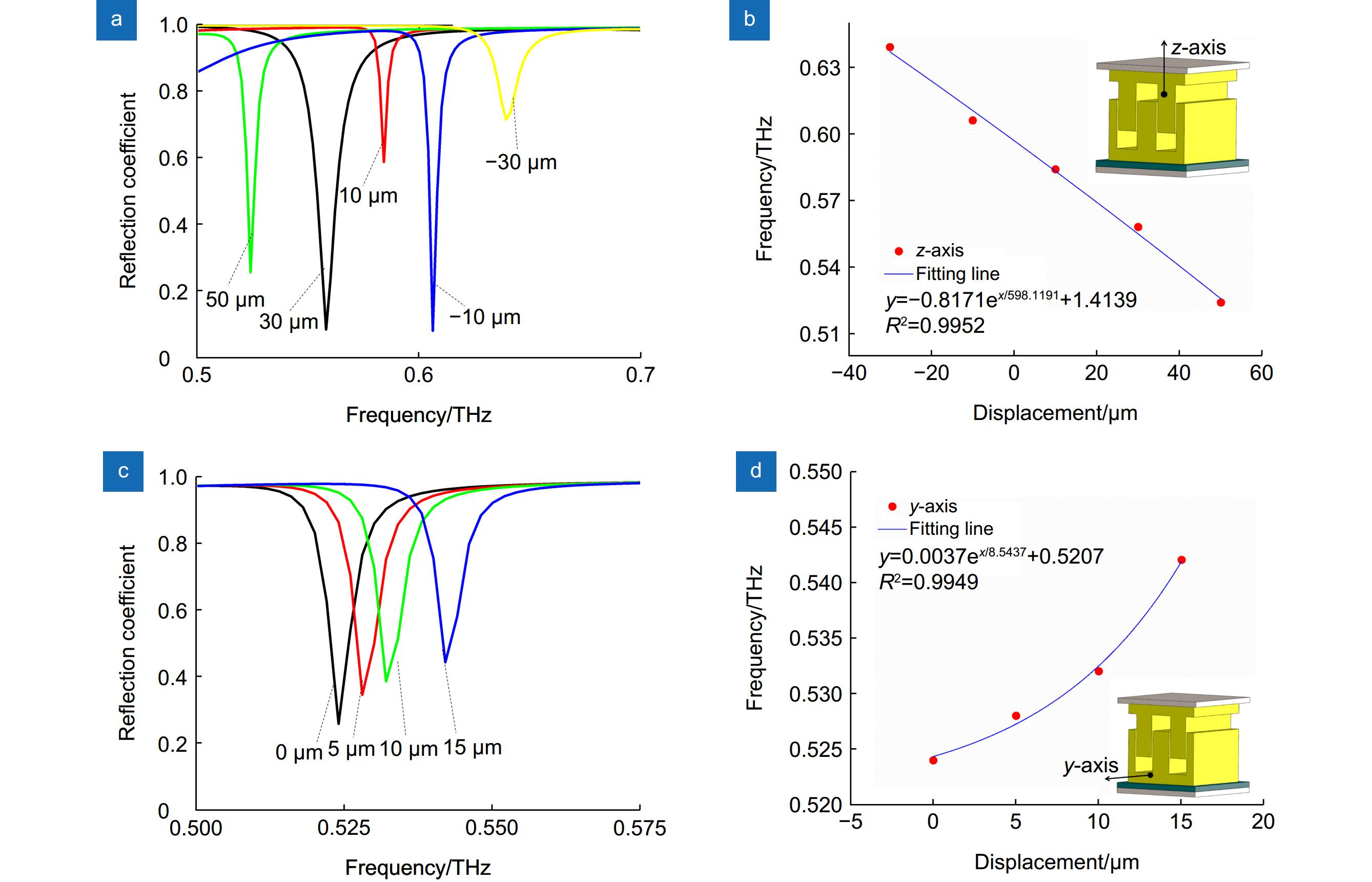
图 6 双层三维谐振结构用于(a) z轴向微位移传感的反射光谱及其(b)灵敏度拟合,(c) y轴向微位移传感的反射光谱及其(d)灵敏度拟合
Figure 6. Reflectance spectra of the dual-layer 3D structure for (a) the z-axis micro-displacement sensing and (b) its fitted sensitivity. (c) Reflectance spectra of the y-axis micro-displacement sensing and (d) its fitted sensitivity
表 1 传感器性能对比
Table 1. Comparison of sensor performance
Ref Structure Intended detection medium Resonance frequency
/THzSensitivity
/(GHz/RIU)Q-factor FOM [24] Single/2D Heavy metal ion 0.36 113.92 11.22 3.15 [25] Single/2D Glucose 0.40 23.30 — — [26] Dual/2D Ethanol oil sucrose 0.49 120.60 82.30 20.10 This work Dual/3D Liquid 0.52 258.00 118.70 58.90 Ref Structure Displacement Resonance frequency
/THzSensitivity
/(GHz/μm)Q-factor FOM [27] Dual/2D y-axis 0.27 0.30 40.10 0.045 This work Dual/3D y-axis 0.52 1.20* 118.70 0.27 z-axis 1.40* 0.12 *The results were obtained with linear fitting -
参考文献
[1] Shelby R A, Smith D R, Schultz S. Experimental verification of a negative index of refraction[J]. Science, 2001, 292(5514): 77−79. doi: 10.1126/science.1058847
[2] 朱潜, 田翰闱, 蒋卫祥. 电磁超表面对辐射波的调控与应用[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(9): 230115. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230115
Zhu Q, Tian H W, Jiang W X. Manipulations and applications of radiating waves using electromagnetic metasurfaces[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(9): 230115. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230115
[3] Baqir M A, Choudhury P K. Hyperbolic metamaterial-based optical biosensor for detecting cancer cells[J]. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2023, 35(4): 183−186. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2022.3228943
[4] 马长伟, 马文英, 谭毅, 等. 高Q值THz类EIT超材料及传感特性研究[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(11): 180298. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.180298
Ma C W, Ma W Y, Tan Y, et al. High Q-factor terahertz metamaterial based on analog of electromagnetically induced transparency and its sensing characteristics[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2018, 45(11): 180298. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.180298
[5] 胡维东, 杜响, 刘思玉, 等. 基于准连续域束缚态介质超表面的光微流折射率传感研究[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(9): 230124. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230124
Hu W D, Du X, Liu S Y, et al. Optofluidic refractometric sensor based on quasi-bound states in the continuum in all-dielectric metasurface[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(9): 230124. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230124
[6] Hu T Q, Pan T S, Guo D J, et al. Omnidirectional configuration of stretchable strain sensor enabled by the strain engineering with chiral Auxetic metamaterial[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(21): 22035−22045. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c08624
[7] Du X X, Mao H P, Yan Y T, et al. Study on the spectral characteristics of plant growth regulators based on the structure difference of terahertz metamaterial sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors J, 2022, 22(14): 14065−14074. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3180335
[8] Banerjee S, Dutta P, Basu S, et al. A new design of a terahertz metamaterial absorber for gas sensing applications[J]. Symmetry, 2023, 15(1): 24. doi: 10.3390/sym15010024
[9] Saadeldin A S, Hameed M F O, Elkaramany E M A, et al. Highly sensitive terahertz metamaterial sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors J, 2019, 19(18): 7993−7999. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2918214
[10] Federici J F, Schulkin B, Huang F, et al. THz imaging and sensing for security applications - explosives, weapons and drugs[J]. Semicond Sci Technol, 2005, 20(7): S266−S280. doi: 10.1088/0268-1242/20/7/018
[11] Li Z R, Zhong M, Zang L Y, et al. Dual-mode metamaterial absorber for independent sweat and temperature sensing[J]. J Electron Mater, 2023, 52(6): 4106−4116. doi: 10.1007/s11664-023-10388-9
[12] Cocker T L, Jelic V, Hillenbrand R, et al. Nanoscale terahertz scanning probe microscopy[J]. Nat Photonics, 2021, 15(8): 558−569. doi: 10.1038/s41566-021-00835-6
[13] He Z H, Li L Q, Ma H Q, et al. Graphene-based metasurface sensing applications in terahertz band[J]. Results Phys, 2021, 21: 103795. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2020.103795
[14] Ahmadivand A, Gerislioglu B, Ahuja R, et al. Terahertz plasmonics: the rise of toroidal metadevices towards immunobiosensings[J]. Mater Today, 2020, 32: 108−130. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2019.08.002
[15] Wang W J, Sun K X, Xue Y, et al. A review of terahertz metamaterial sensors and their applications[J]. Opt Commun, 2024, 556: 130266. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2024.130266,
[16] Vivek A, Shambavi K, Alex Z C. A review: metamaterial sensors for material characterization[J]. Sens Rev, 2019, 39(3): 417−432. doi: 10.1108/SR-06-2018-0152
[17] Deng X X, Shen Y C, Liu B W, et al. Terahertz metamaterial sensor for sensitive detection of citrate salt solutions[J]. Biosensors (Basel), 2022, 12(6): 408. doi: 10.3390/bios12060408
[18] Li J, Zhou Y D, Peng F W, et al. High-FOM temperature sensing based on Hg-EIT-like liquid metamaterial unit[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(9): 1395. doi: 10.3390/nano12091395
[19] 田小永, 尹丽仙, 李涤尘. 三维超材料制造技术现状与趋势[J]. 光电工程, 2017, 44(1): 69−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.01.006
Tian X Y, Yin L X, Li D C. Current situation and trend of fabrication technologies for three-dimensional metamaterials[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2017, 44(1): 69−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.01.006
[20] Zhang Y P, Li T T, Zeng B B, et al. A graphene based tunable terahertz sensor with double Fano resonances[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(29): 12682−12688. doi: 10.1039/C5NR03044G
[21] 王鑫, 王俊林. 基于三维开口谐振环阵列和微流通道的太赫兹超材料吸收体传感器[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(19): 1904001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.1904001
Wang X, Wang J L. Terahertz metamaterial absorber sensor based on three-dimensional split-ring resonator array and microfluidic channel[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2020, 40(19): 1904001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.1904001
[22] Fu Y P, Xu X C, Lin Y S. Actively programmable MEMS-based racetrack-shaped terahertz metamaterial[J]. J Appl Phys, 2022, 131(11): 115301. doi: 10.1063/5.0069625
[23] Lin Y S, Liao S Q, Liu X Y, et al. Tunable terahertz metamaterial by using three-dimensional double split-ring resonators[J]. Opt Laser Technol, 2019, 112: 215−221. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.11.020
[24] Almawgani A H M, Surve J, Parmar T, et al. A graphene-metasurface-inspired optical sensor for the heavy metals detection for efficient and rapid water treatment[J]. Photonics, 2023, 10(1): 56. doi: 10.3390/PHOTONICS10010056
[25] Yang J, Qi L M, Li B, et al. A terahertz metamaterial sensor used for distinguishing glucose concentration[J]. Results Phys, 2021, 26: 104332. doi: 10.1016/J.RINP.2021.104332
[26] Deng G S, Guo A R, Kou Z F, et al. High-sensitivity terahertz sensor for liquid medium detection using dual-layer metasurfaces[J]. IEEE Trans Terahertz Sci Technol, 2024, 14(1): 57−63. doi: 10.1109/TTHZ.2023.3318794
[27] Guo A R, Kou Z F, Yang J, et al. Electromagnetic anapole-inspired micro-displacement sensor using dual-layer terahertz metasurfaces with micrometer-level sensitivity and centimeter-level range[J]. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas, 2024, 73: 6006709. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2024.3398126
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: