Image recognition of complex transmission lines based on lightweight encoder-decoder networks
-
摘要:
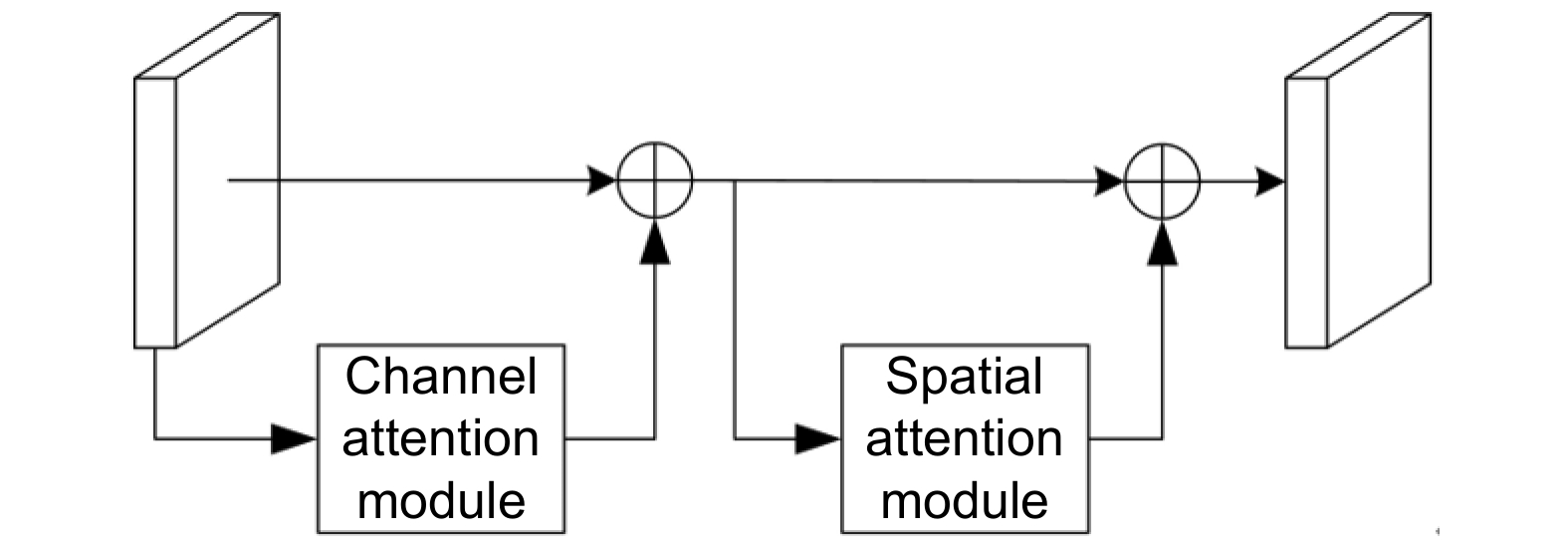
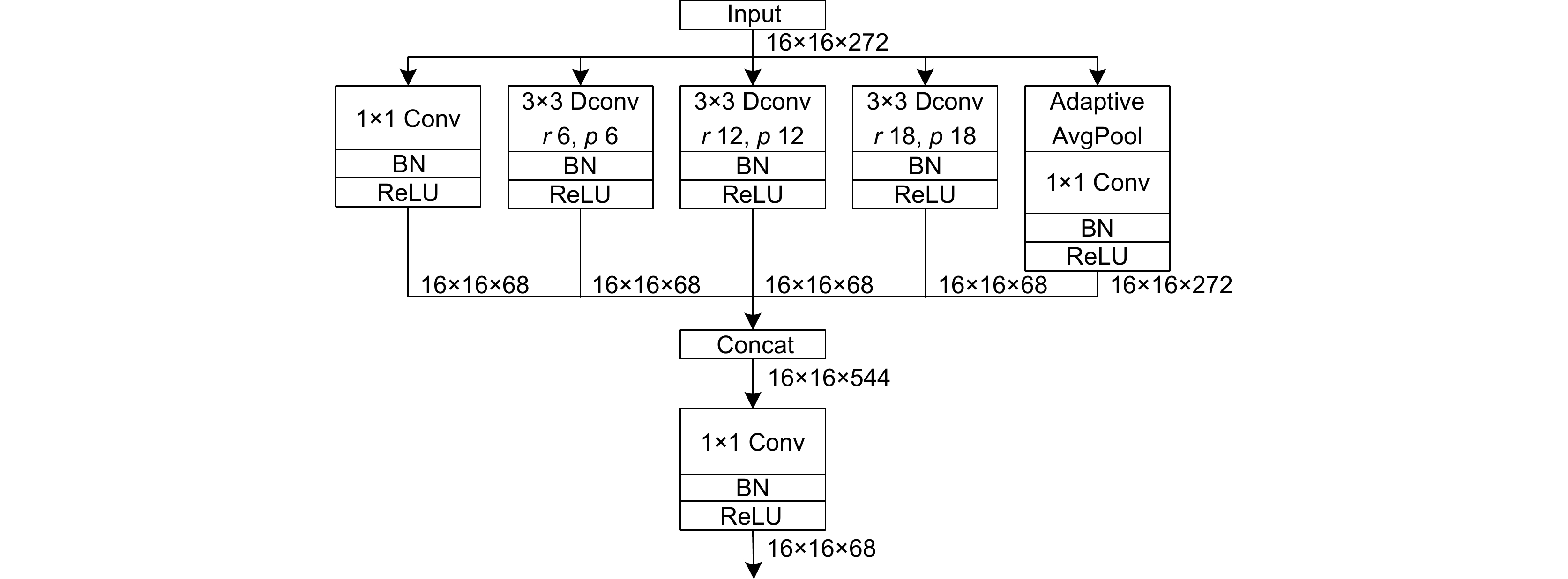
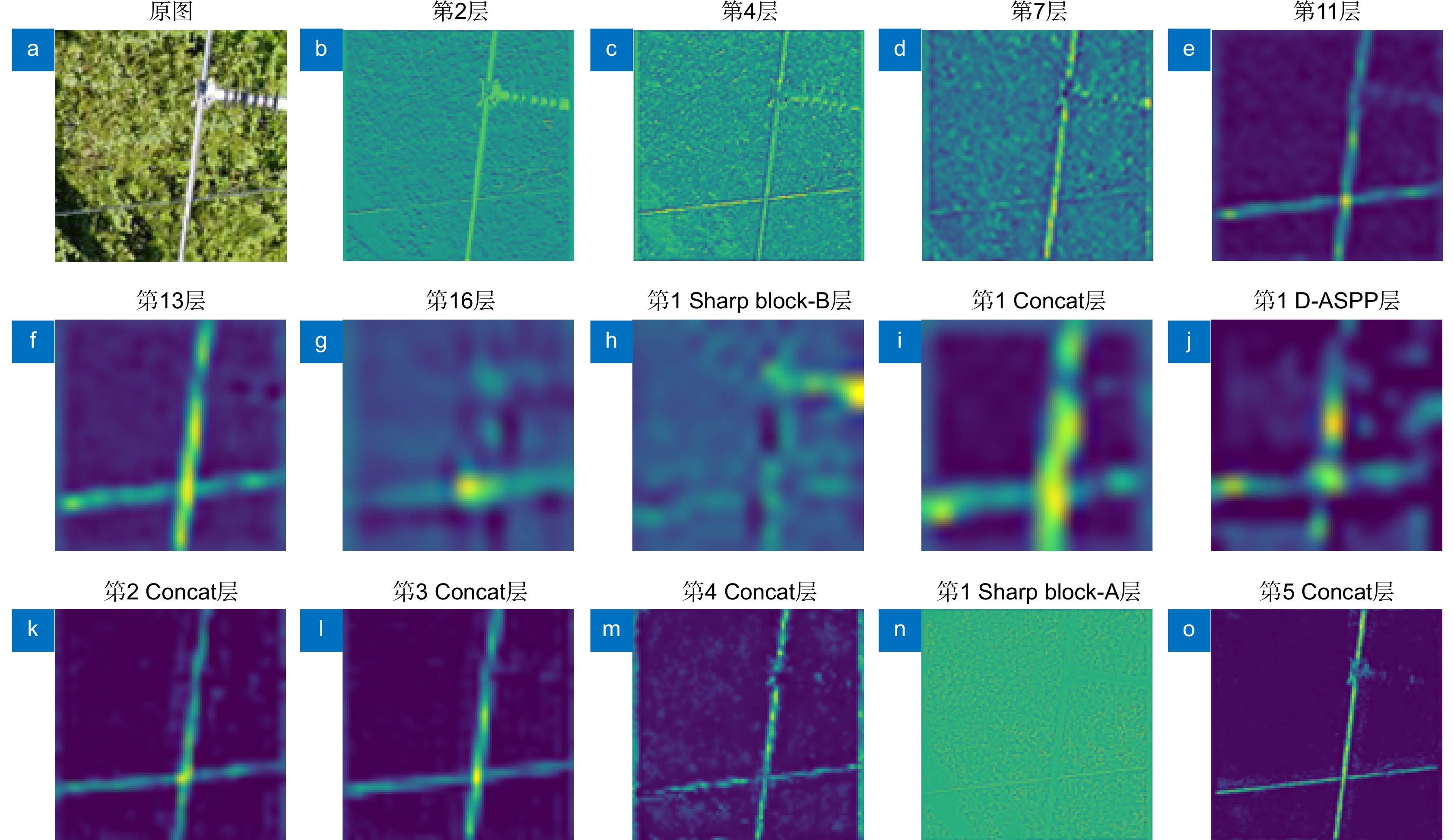
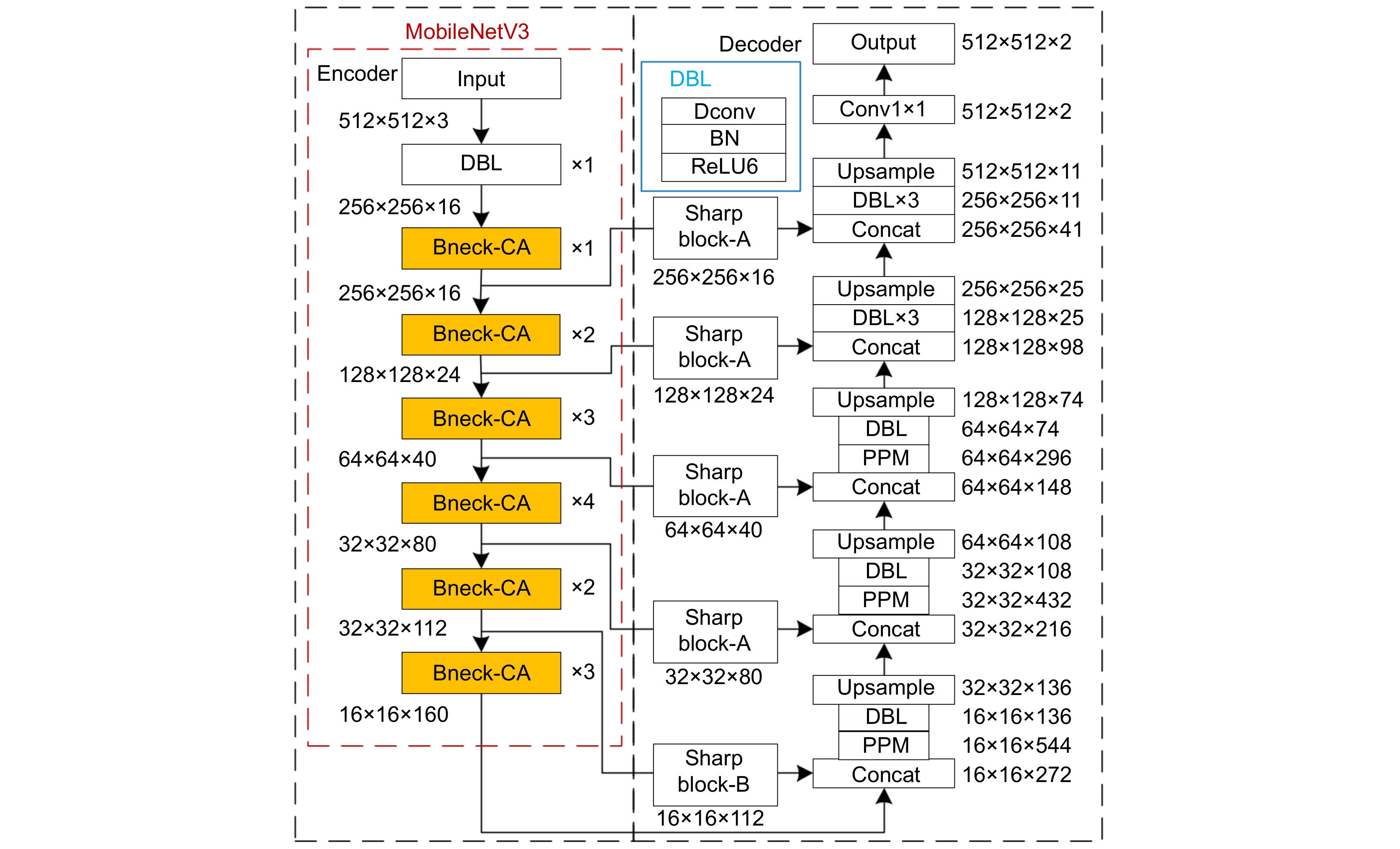
针对现有输电线图像识别网络参数多、耗时长等问题,本文构建了轻量型编解码网络,实现了多根交叉复杂输电线的快速准确识别。编码器以常规MobileNetV3前16层为基础,通过减少网络参数,采用卷积块注意力模块代替常规MobileNetV3网络的挤压和激励注意力模块,从而提高了网络的输电线特征信息提取能力。结合深度可分离卷积和深度空洞空间金字塔池化模块构建解码器,扩大感受野,提高网络聚合不同尺度上下文信息能力。利用L1正则方法稀疏训练网络,根据缩放因子与对应通道输出乘积的数值,设定剪枝阈值去除网络冗余通道,有效压缩网络体积,提高输电线识别速度。实验结果表明,轻量型编解码网络的平均像素精度(MPA)、平均交并比(MIoU)和识别速度分别达到了92.11%、84.19%和41 f/s,优于PSPNet、U2Net和已有改进的输电线识别网络。
-
关键词:
- 复杂输电线识别 /
- 轻量型编解码网络 /
- 注意力机制 /
- 深度空洞空间金字塔池化 /
- 网络剪枝
Abstract:To address the problems of too many parameters and much time consumption in existing recognition networks for transmission lines, a lightweight encoder-decoder network is constructed to discern complex transmission line images featured with multiple intersections quickly and accurately. The encoder is based on the first 16 layers of conventional MobileNetV3 to reduce network parameters. The convolutional block attention module is used to replace the squeeze and excitation attention module to improve the network's ability to extract the feature information of transmission lines. The decoder is constructed by combining deeply separable convolution and deep atrous spatial pyramid pooling to expand the receptive field and improve the network's ability to aggregate contextual information with different scales. Moreover, the training network is sparse by using the L1 regularization method. The pruning threshold is determined according to the product of the scaling factor and the corresponding output of each channel to remove redundant channels and compress the network effectively, which improves the recognition speed of transmission lines. Experimental results demonstrate that the mean pixel accuracy, mean intersection over union , and recognition speed of the lightweight encoder-decoder network are 92.11%, 84.19%, and 41 frames per second, respectively, which are better than PSPNet, U2Net, and existing improved transmission lines recognition networks.
-
Overview: Transmission line inspection is a key link in the regular maintenance of the power grid, which is very important to ensure the safe and stable operation of the power system. There are many problems with manual inspection, such as high cost, low efficiency, and high risk due to geographical influence. In contrast, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) intelligent inspection has advantages such as low cost, high efficiency, and good maneuverability, and has experienced rapid development in recent years. The important premise of realizing intelligent inspection of UAVs is to identify transmission lines quickly and accurately in complex backgrounds. At present, there are two main methods for transmission line recognition: conventional image processing and intelligent image processing based on deep learning. However, conventional image processing for identifying transmission lines is susceptible to background interference, which leads to low recognition accuracy of wrong detection or missed detection; Intelligent image recognition based on deep learning still has some problems, such as many network parameters, long time consumption and difficulty in deploying end devices. To solve these problems, a lightweight encoder-decoder network is constructed to realize fast and accurate identification of multiple intersecting complex transmission lines. The encoder is based on the first 16 layers of conventional MobileNetV3, reduces network parameters, and uses convolutional block attention modules to replace the squeezing and excitation attention modules of conventional MobileNetV3 networks, improving the network's ability to extract transmission line feature information. Combining deeply separable convolution and deep atrous spatial pyramid pooling, a decoder is constructed to expand the receptive field and improve the ability of the network to aggregate context information of different scales. Utilizing L1 regularization for sparse training of the network, setting pruning thresholds based on the product of scaling factors and corresponding channel outputs, effectively removes redundant channels from the network, compressing network volume and improving transmission line recognition speed. Experimental results show that the mean pixel accuracy, mean intersection over union, and the recognition speed of the lightweight encoder-decoder network are 92.11%, 84.19%, and 41 frames/sec, respectively, which are better than those of PSPNetU2Net and the improved transmission lines recognition network is helpful for the deployment of end equipment.
-

-
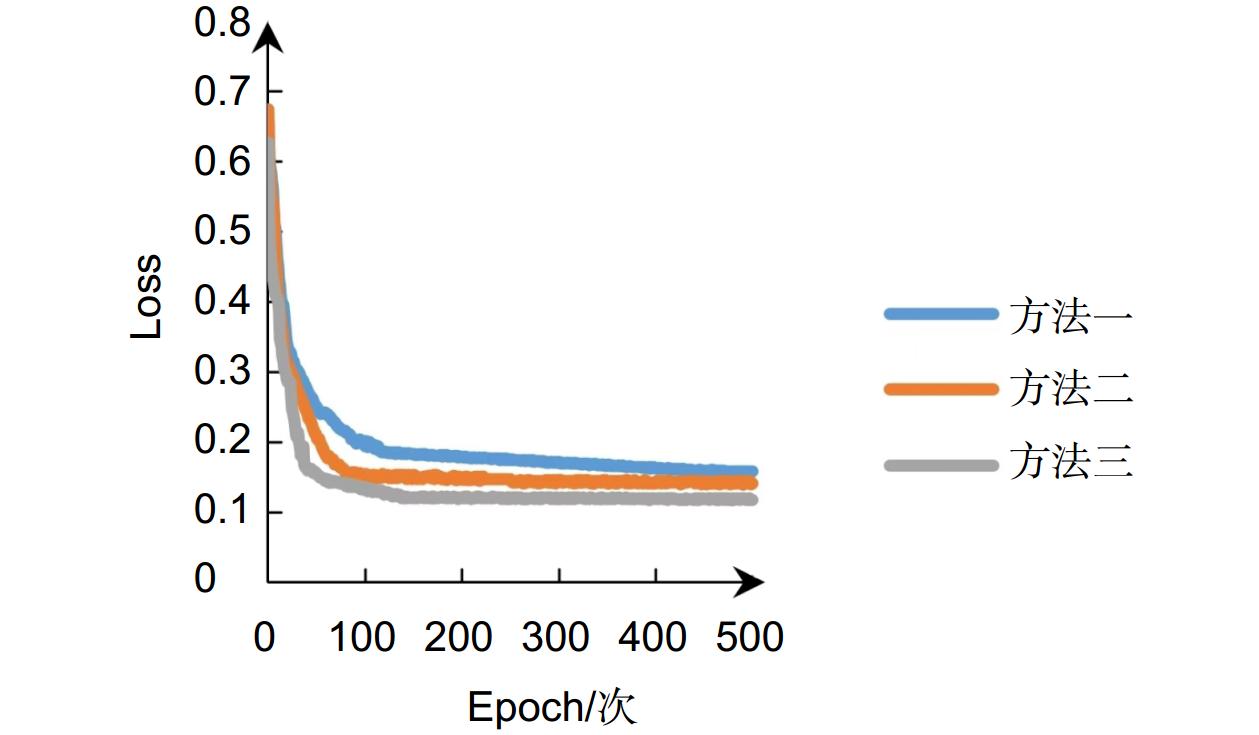
表 1 轻量型编解码网络训练参数
Table 1. Training parameters for lightweight encode-decoder network
训练参数 数值 Batch_size 8 Initial_lr 0.0001 Epoch 500 Cuda True 表 2 消融实验结果
Table 2. Results of ablation experiment
方法 MPA/% MIoU/% FPS 方法1 89.87 83.22 26 方法2 91.44 84.02 24 方法3 90.92 83.86 31 方法4 92.34 84.57 29 方法5 92.67 84.64 30 表 3 不同正则系数稀疏训练实验结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of sparse training experimental results with different regularization coefficients
λ MPA/% MIoU/% Epoch 0 92.67 84.64 500 0.01 91.52 83.77 500 0.001 92.07 84.12 500 0.0001 92.58 84.56 500 0.00001 92.56 84.55 500 表 4 不同剪枝率实验结果
Table 4. Comparison of experimental results with different pruning rates
剪枝率 MPA/% MIoU/% FPS 参数量/(106) 0 92.58 84.56 30 5.82 0.1 92.36 84.39 32 5.27 0.2 92.24 84.28 35 4.63 0.3 92.16 84.22 37 4.12 0.4 92.11 84.19 41 3.57 0.5 91.72 83.85 44 2.92 -
[1] 樊星, 李小彭, 彭健文, 等. 可变重心线路巡检机器人摆振分析及抑制[J]. 振动与冲击, 2024, 43(2): 323−333. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2024.02.035
Fan X, Li X P, Peng J W, et al. Pendulum vibration analysis and suppression of a power transmission line inspection robot with variable center of gravity[J]. J Vib Shock, 2024, 43(2): 323−333. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2024.02.035
[2] Xu B Y, Zhao Y L, Wang T, et al. Development of power transmission line detection technology based on unmanned aerial vehicle image vision[J]. SN Appl Sci, 2023, 5(3): 72. doi: 10.1007/S42452-023-05299-7
[3] 刘传洋, 吴一全. 基于深度学习的输电线路视觉检测方法研究进展[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(19): 7423−7445. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.221139
Liu C Y, Wu Y Q. Research progress of vision detection methods based on deep learning for transmission lines[J]. Proc CSEE, 2023, 43(19): 7423−7445. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.221139
[4] 赵延峰, 胡耀垓, 王先培, 等. 复杂场景下的电力线自动提取[J]. 测绘通报, 2021, (8): 1−6. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2021.0231
Zhao Y F, Hu Y G, Wang X P, et al. Automatic power line extraction algorithm in complex scene[J]. Bull Surv Mapp, 2021, (8): 1−6. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2021.0231
[5] 陈雪云, 夏瑾, 杜珂. 基于多线型特征增强网络的架空输电线检测[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2021, 55(12): 2382−2389. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2021.12.019
Chen X Y, Xia J, Du K. Overhead transmission line detection based on multiple linear-feature enhanced detector[J]. J Zhejiang Univ (Eng Sci), 2021, 55(12): 2382−2389. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2021.12.019
[6] 李运堂, 李恒杰, 张坤, 等. 基于新型编码解码网络的复杂输电线识别[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2024, 58(6): 1133−1141. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2024.06.004
Li Y T, Li H J, Zhang K, et al. Recognition of complex power lines based on novel encoder-decoder network[J]. J Zhejiang Univ (Eng Sci), 2024, 58(6): 1133−1141. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2024.06.004
[7] Jaffari R, Hashmani M A, Reyes-aldasoro C C. A novel focal phi loss for power line segmentation with auxiliary classifier U-Net[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(8): 2803. doi: 10.3390/S21082803
[8] Chen G K, Hao K, Wang B B, et al. A power line segmentation model in aerial images based on an efficient multibranch concatenation network[J]. Expert Syst Appl, 2023, 228: 120359. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120359
[9] Yang L, Fan J F, Huo B Y, et al. PLE-Net: automatic power line extraction method using deep learning from aerial images[J]. Expert Syst Appl, 2022, 198: 116771. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.116771
[10] 许刚, 李果. 轻量化航拍图像电力线语义分割[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2021, 26(11): 2605−2618. doi: 10.11834/jig.200690
Xu G, Li G. Research on lightweight neural network of aerial powerline image segmentation[J]. J Image Graphics, 2021, 26(11): 2605−2618. doi: 10.11834/jig.200690
[11] 陈梅林, 王逸舟, 戴彦, 等. SaSnet: 基于自监督学习的电力线实时分割网络[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(4): 1365−1374. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.210504
Chen M L, Wang Y Z, Dai Y, et al. Small and strong: power line segmentation network in real time based on self-supervised learning[J]. Proc CSEE, 2022, 42(4): 1365−1374. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.210504
[12] Gao Z S, Yang G D, Li E, et al. Efficient parallel branch network with multi-scale feature fusion for real-time overhead power line segmentation[J]. IEEE Sensors J, 2021, 21(10): 12220−12227. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3062660
[13] Zhu K J, Xu C H, Wei Y C, et al. Fast-PLDN: fast power line detection network[J]. J Real-Time Image Proc, 2022, 19(1): 3−13. doi: 10.1007/s11554-021-01154-3
[14] Han G J, Zhang M, Li Q, et al. A lightweight aerial power line segmentation algorithm based on attention mechanism[J]. Machines, 2022, 10(10): 881. doi: 10.3390/MACHINES10100881
[15] Zhu F W, Sun Y, Zhang Y Q, et al. An improved MobileNetV3 mushroom quality classification model using images with complex backgrounds[J]. Agronomy, 2023, 13(12): 2924. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13122924
[16] Yang K, Zhang Y, Zhang X, et al. YOLOX with CBAM for insulator detection in transmission lines[J]. Multimed Tools Appl, 2024, 83(14): 43419−43437. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-17245-1
[17] Tang G, Zhao H R, Claramunt C, et al. PPA-Net: pyramid pooling attention network for multi-scale ship detection in SAR images[J]. Remote Sens, 2023, 15(11): 2855. doi: 10.3390/rs15112855
[18] Saida S J, Sahoo S P, Ari S. Deep convolution neural network based semantic segmentation for ocean eddy detection[J]. Expert Syst Appl, 2023, 219: 119646. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119646
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: