Improved YOLOv7 algorithm for target detection in complex environments from UAV perspective
-
摘要
针对无人机在航拍过程中容易受到恶劣环境的影响,导致航拍图像出现辨识度低、被障碍物遮挡、特征严重丢失等问题,提出了一种改进YOLOv7的无人机视角下复杂环境的目标检测算法(SSG-YOLOv7)。首先从VisDrone2019数据集和RSOD数据集中分别抽取图片进行五种环境的模拟,将VisDrone数据集扩充至12803张,RSOD数据集扩充至1320张。其次,聚类出更适合数据集的锚框尺寸。接着将3D无参注意力机制SimAM引入主干网络和特征提取模块中,增加模型的学习能力。然后重构特征提取模块SPPCSPC,融合不同尺寸池化通道提取的信息同时引入轻量级的卷积模块GhostConv,在不增加模型参数量的同时提高算法对密集多尺度目标检测精度。最后使用Soft NMS优化锚框的置信度,减少算法的误检、漏检率。实验结果表明,在复杂环境的检测任务中SSG-YOLOv7检测效果优良,性能指标VisDrone_mAP@0.5和RSOD_mAP@0.5较YOLOv7分别提高了10.45%和2.67%。
Abstract
To address the challenges faced by drones during UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) photography in adverse conditions, such as low image recognition, obstruction by obstacles, and significant feature loss, a novel algorithm named SSG-YOLOv7 was proposed to enhance object detection from the perspective of drones in complex environments. Firstly, 12803 images were augmented from the VisDrone2019 dataset, and 1320 images were augmented from the RSOD dataset to simulate five different environments. Subsequently, anchor box sizes suitable for the datasets were clustered. The 3D non-local attention mechanism SimAM was integrated into the backbone network and feature extraction module to enhance the model's learning capabilities. Furthermore, the feature extraction module SPPCSPC was restructured to integrate information extracted from channels with different pool sizes and introduce the lightweight convolution module GhostConv, thereby improving the precision of dense multi-scale object detection without increasing the model's parameter count. Finally, Soft NMS was employed to optimize the confidence of anchor boxes, reducing false positives and missed detections. Experimental results demonstrate that SSG-YOLOv7 exhibits superior detection performance in complex environments, with performance metrics VisDrone_mAP@0.5 and RSOD_mAP@0.5 showing improvements of 10.45% and 2.67%, respectively, compared to YOLOv7.
-
Key words:
- UAV /
- complex environment /
- YOLOv7 /
- simAM attention mechanism /
- SPPCSPC /
- data enhancement
-
Overview
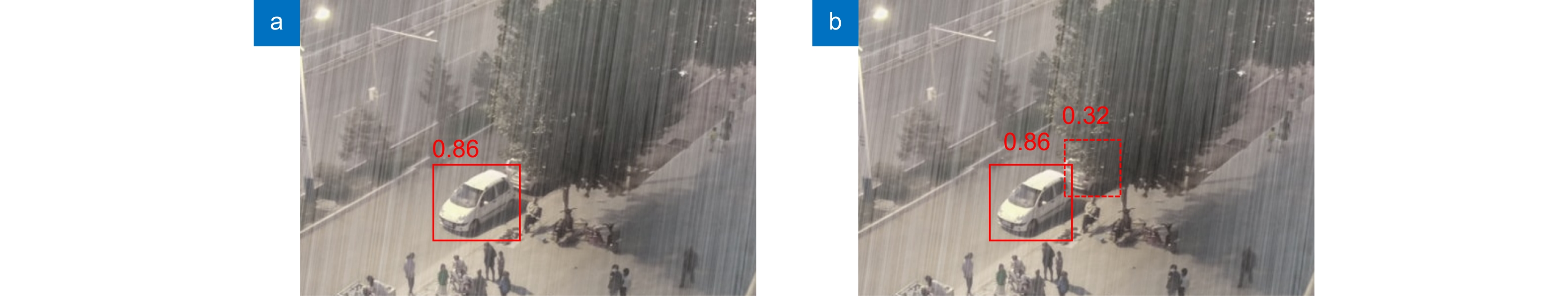
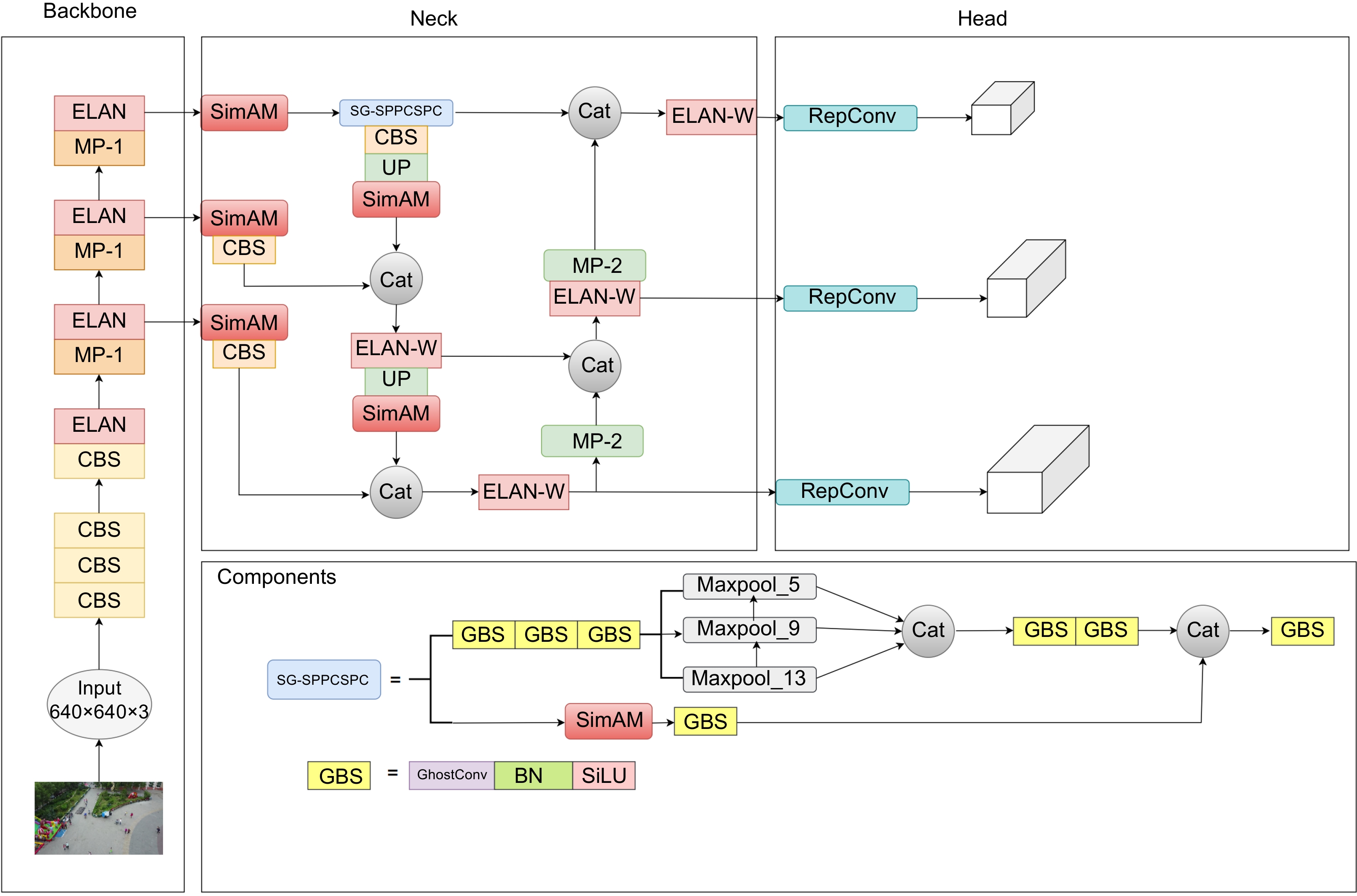
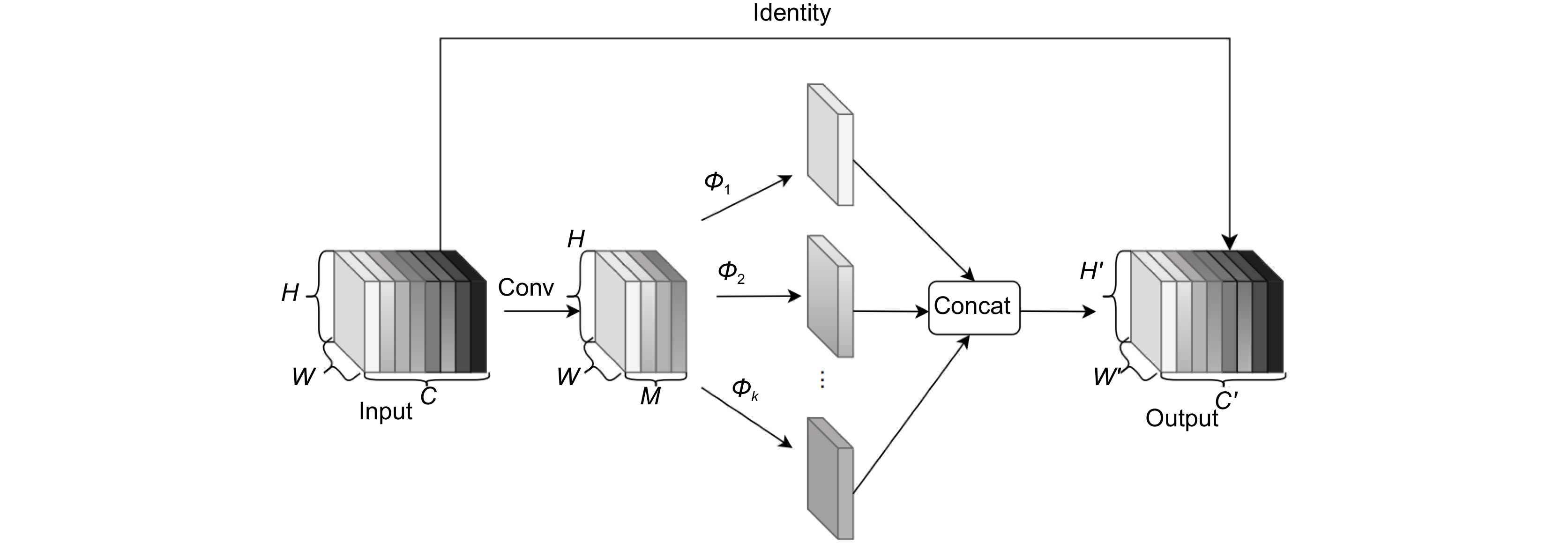
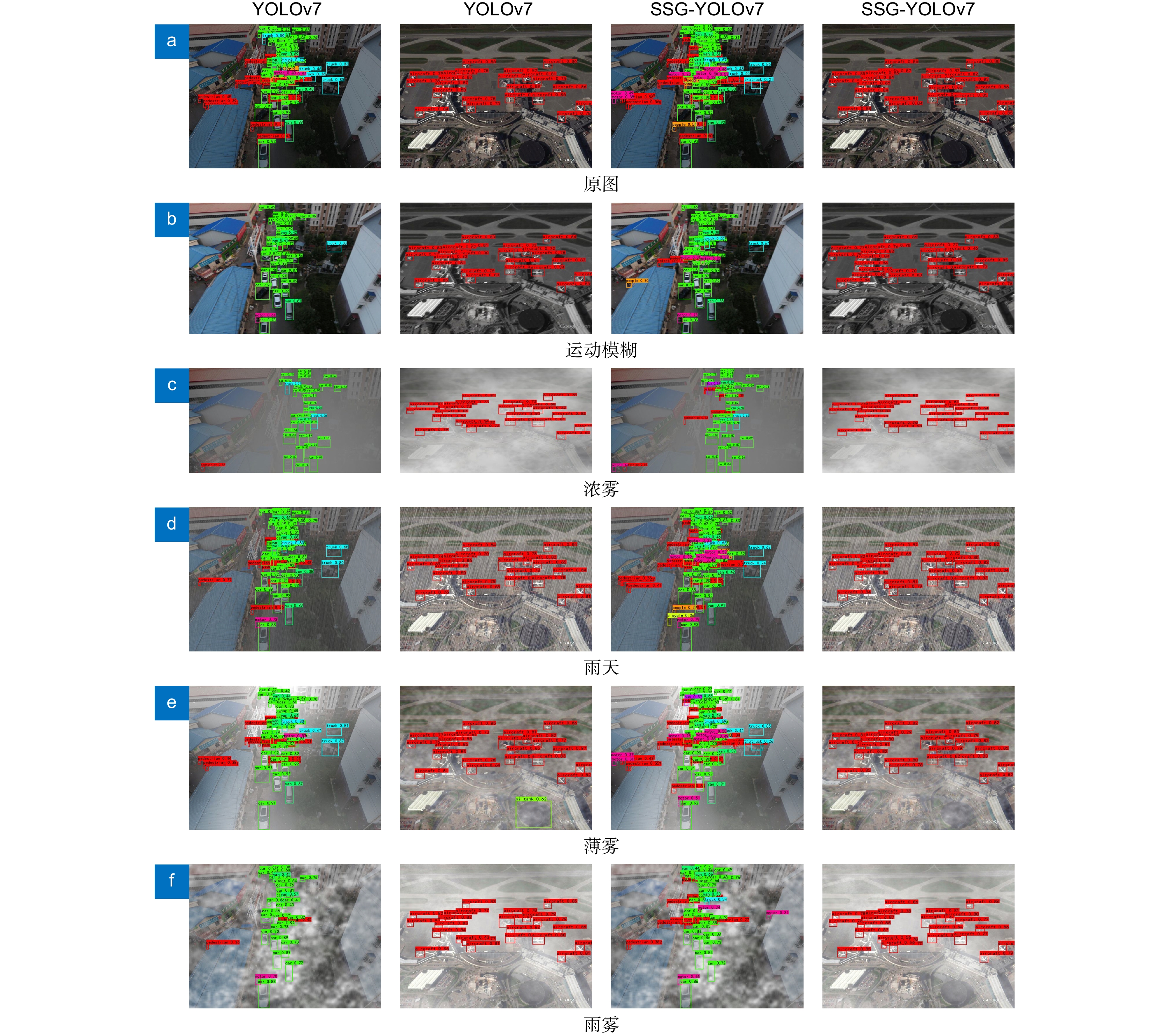
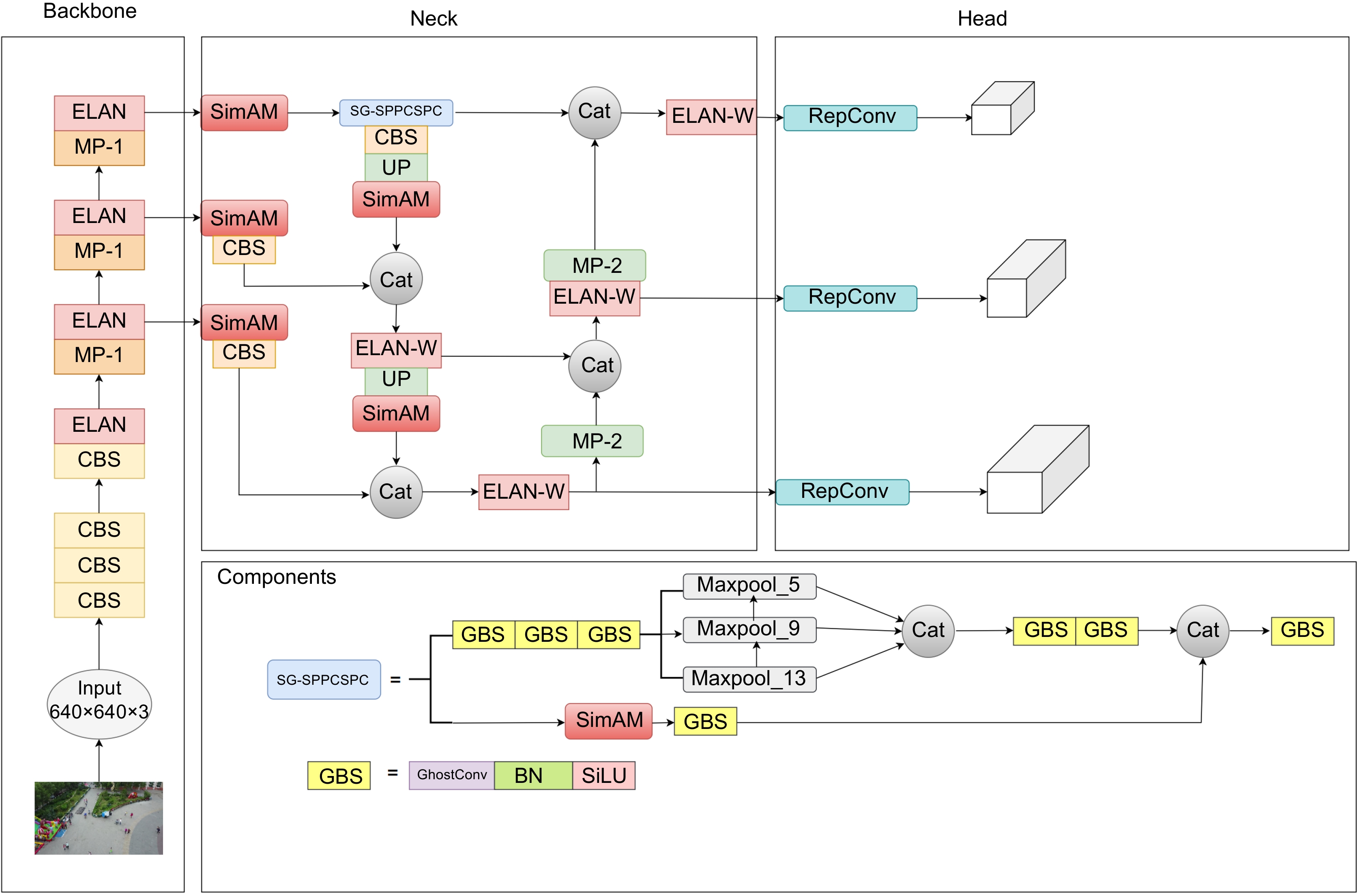
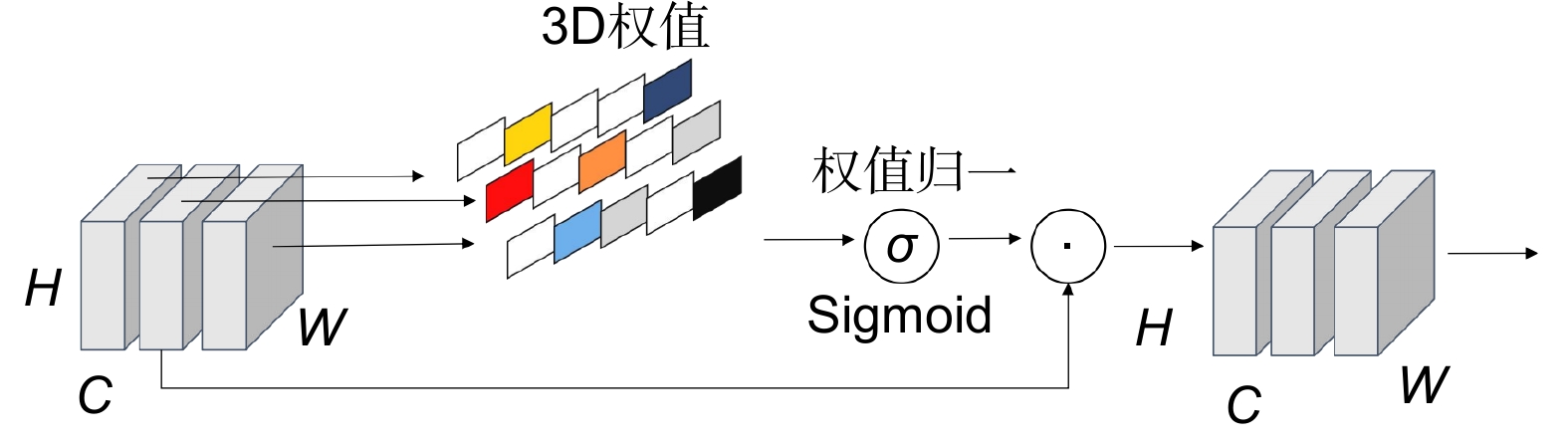
Overview: Using low-cost unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) photography technology combined with deep learning can create significant value in various fields. Targets captured from a UAV perspective often exhibit drastic scale variations, uneven distribution, and susceptibility to obstruction by obstacles. Moreover, UAVs typically fly at low altitudes and high speeds during the capture process, which can result in low-resolution aerial images affected by weather conditions or the drone's own vibrations. Maintaining high detection accuracy in such complex environments is a crucial challenge in UAV-based target detection tasks. Therefore, this paper proposes a new target detection algorithm, SSG-YOLOv7, based on YOLOv7. Firstly, the algorithm utilizes the K-means++ clustering algorithm to generate four different-scale anchor boxes suitable for the target dataset, effectively addressing the issue of large-scale variations in targets from the UAV perspective. Next, by introducing the SimAM attention mechanism into the neck network and feature extraction module, the model's detection accuracy is improved without increasing the model's parameter count. Subsequently, the pooling layers at different scales of the feature extraction module are fused to enable the model to learn richer target feature information in complex environments. Additionally, GhostConv is used to replace traditional convolutional modules to reduce the parameter count of the feature extraction module. Finally, Soft NMS is employed to reduce the false detection and missed detection rates of small-scale targets during the detection process, thereby enhancing target detection effectiveness from the UAV perspective. In the experimental process, the original VisDrone dataset and RSOD dataset are simulated under five complex environments using transformation functions from the Imgaug library. SSG-YOLOv7 is validated against the original algorithm. Compared to the original algorithm, the proposed algorithm improves the average precision (mAP@0.5) of the model by 10.45% in the VisDrone dataset and by 2.67% in the RSOD dataset, while reducing the model's parameter count by 24.2%. This effectively demonstrates that SSG-YOLOv7 is better suited for target detection tasks in complex environments from the UAV perspective. Additionally, the experiment compares the detection accuracy of YOLOv7 and SSG-YOLOv7 before and after data augmentation on both datasets. In the VisDrone dataset, YOLOv7 improves by 4.13%, while SSG-YOLOv7 improves by 8.71%. In the RSOD dataset, YOLOv7 improves by 3.59%, while SSG-YOLOv7 improves by 4.45%. This effectively proves that SSG-YOLOv7 can learn more target features from samples in complex environments, accurately locate the targets, and is suitable for multi-target detection tasks in complex environments from the UAV perspective.
-

-
表 1 K-means++生成的锚框尺寸
Table 1. Anchor frame size generated by K-means++
特征图尺寸 感受野 锚框 20x20 Big [33,49],[63,73] 40x40 Medium [14,35],[27,23] 80x80 Small [20,8,8,15,14] 160x160 Tiny [2,5,4,11] 表 2 SPPCSPC与SG-SPPCSPC模块参数量和GFLOPs对比结果
Table 2. Comparison of SPPCSPC and SG-SPPCSPC
模块类型 Parameters/M GFLOPS SPPCSPC模块 12.8 16.2 SG-SPPCSPC模块 3.69 4.9 表 3 消融实验结果
Table 3. Results of ablation experiments
Model K-means++ SimAM SG-SPPCSPC Soft NMS Vis_mAP@0.5/% RSOD_mAP@0.5/% Parameters/M FPS GFLOPs A 40.89 95.60 37.6 82 106.5 B √ 44.15 96.91 37.6 82 106.5 C √ √ 46.40 97.22 37.6 87 107.2 D √ √ √ 48.61 97.91 28.5 93 95.9 E √ √ √ √ 51.34(+10.45) 98.27(+2.67) 28.5 93 95.9 表 4 数据增强前后mAP(%)对比
Table 4. Comparison of mAP(%) before and after data enhancement
Model 原始VisDrone 增强后VisDrone 原始RSOD 增强后RSOD YOLOv7 36.76 40.89 92.01 95.60 SSG-YOLOv7 42.63 51.34 93.82 98.27 表 5 对比实验结果
Table 5. Comparison of experimental results
Method Visdrone_mAP@0.5 /% Visdrone_mAP@0.5:0.95 /% RSOD_mAP@0.5 /% RSOD_mAP@0.5:0.95 /% FPS Parameters/M Faster R-CNN[6] 20.0 8.91 85.6 54.1 43 137.10 SSD[23] 10.2 5.1 87.4 52.6 249 26.29 YOLOv5s 27.4 15.6 94.0 59.5 126 7.28 YOLOv5m 32.0 18.8 95.2 66.4 98 21.38 YOLOv5l 36.5 21.5 95.1 68.3 75 47.10 YOLOv7[13] 40.8 24.0 95.6 69.6 82 37.62 YOLOv8s 43.1 25.0 94.1 63.0 160 11.17 YOLOv8m 39.6 22.8 94.1 68.7 122 25.90 YOLOv8l 43.7 25.1 96.0 68.9 98 43.69 本文算法 51.3 29.2 98.3 70.0 93 28.49 -
参考文献
[1] 陈旭, 彭冬亮, 谷雨. 基于改进YOLOv5s的无人机图像实时目标检测[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(3): 210372. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210372
Chen X, Peng D L, Gu Y. Real-time object detection for UAV images based on improved YOLOv5s[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2022, 49(3): 210372. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210372
[2] 阳珊, 王建, 胡莉, 等. 改进RetinaNet的遮挡目标检测算法研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(11): 209−214. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2107-0277
Yang S, Wang J, Hu L, et al. Research on occluded object detection by improved RetinaNet[J]. Comput Eng Appl, 2022, 58(11): 209−214. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2107-0277
[3] Zhan W, Sun C F, Wang M C, et al. An improved Yolov5 real-time detection method for small objects captured by UAV[J]. Soft Comput, 2022, 26(6): 361−373. doi: 10.1007/s00500-021-06407-8
[4] Liu W, Quijano K, Crawford M M. YOLOv5-tassel: detecting tassels in RGB UAV imagery with improved YOLOv5 based on transfer learning[J]. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens, 2022, 15: 8085−8094. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3206399
[5] Purkait P, Zhao C, Zach C. SPP-Net: deep absolute pose regression with synthetic views[Z]. arXiv: 1712.03452, 2017. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1712.03452.
[6] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2015: 1440–1448. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.169.
[7] Uijlings J R R, van de Sande K E A, Gevers T, et al. Selective search for object recognition[J]. Int J Comput Vis, 2013, 104(2): 154−171. doi: 10.1007/s11263-013-0620-5
[8] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2017, 39(6): 1137−1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
[9] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.91.
[10] Yin R H, Zhao W, Fan X D, et al. AF-SSD: an accurate and fast single shot detector for high spatial remote sensing imagery[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(22): 6530. doi: 10.3390/s20226530
[11] 齐向明, 柴蕊, 高一萌. 重构SPPCSPC与优化下采样的小目标检测算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2023, 59(20): 158−166. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2305-0004
Qi X M, Chai R, Gao Y M. Algorithm of reconstructed SPPCSPC and optimized downsampling for small object detection[J]. Comput Eng Appl, 2023, 59(20): 158−166. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2305-0004
[12] Shang J C, Wang J S, Liu S B, et al. Small target detection algorithm for UAV aerial photography based on improved YOLOv5s[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(11): 2434. doi: 10.3390/electronics12112434
[13] WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, LIAO H Y M. YOLOv7: trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors[C]//Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2023: 7464–7475. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00721.
[14] Tang F, Yang F, Tian X Q. Long-distance person detection based on YOLOv7[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(6): 1502. doi: 10.3390/electronics12061502
[15] Huang T Y, Cheng M, Yang Y L, et al. Tiny object detection based on YOLOv5[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Image and Graphics Processing, 2022: 45–50. https://doi.org/10.1145/3512388.3512395.
[16] Ismkhan H. I-k-means-+: an iterative clustering algorithm based on an enhanced version of the k-means[J]. Pattern Recognit, 2018, 79: 402−413. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.02.015
[17] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017: 6000–6010. https://doi.org/10.5555/3295222.3295349.
[18] Yang L X, Zhang R Y, Li L D, et al. SimAM: a simple, parameter-free attention module for convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021: 11863–11874.
[19] Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 936–944. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.106.
[20] Han K, Wang Y H, Tian Q, et al. GhostNet: more features from cheap operations[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 1577–1586. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00165.
[21] Bodla N, Singh B, Chellappa R, et al. Soft-NMS - improving object detection with one line of code[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 5562–5570. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.593.
[22] Du D W, Zhu P F, Wen L Y, et al. VisDrone-DET2019: the vision meets drone object detection in image challenge results[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop, 2019: 213–226. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW.2019.00030.
[23] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot MultiBox detector[C]//Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2016: 21-37. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2.
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: