-
摘要:
本文研究了一种基于贝塞尔光束的远距离激光三维成像系统,工作波长为532 nm,在激光出射端使用贝塞尔光束代替高斯光束,利用贝塞尔光束的中心光斑能量集中且束宽不随传输距离而变化的无衍射特性,降低激光光束的发散角,提高激光三维成像的角分辨率。结合Si-APD单光子探测器,搭建了远距离激光三维成像系统,并完成了远距离验证实验。在远距离目标成像中,实现了角分辨率为18.1 µrad的激光三维成像,为远距离高分辨率激光三维成像提供了一种有效的解决方案。
Abstract:We demonstrate a new laser detection and ranging (LiDAR) system for reconstructing remote targets in three dimensions (3D). In this system, a probe beam, of which wavelength is 532 nm, working at Bessel mode rather than Gaussian mode, exhibits a typical intensity distribution of a bright central spot and some surrounding rings, and takes advantage of non-diffraction character in long-distance ranging. It is an attractive way to improve the imaging resolution of the LiDAR system. Combined with the Si-APD, we built a long-distance LiDAR system and completed the verification experiment. The results indicate that we can achieve an 18.1-µrad angle resolution in long-range target imaging, which provides an effective solution for high-resolution remote imaging.
-
Key words:
- LiDAR /
- remote imaging /
- angular resolution /
- Bessel beam
-
Overview: Laser detection and ranging (LiDAR) technique has very important applications in many fields, including 3D terrain analysis, medical applications, object shape measurement, and surface defect detection. As one of the widely used LiDAR schemes, the time of flight (TOF) measurement technique can accurately measure the time interval between the target and the system, with the advantages of fast measurement and long working distance. With the help of highly sensitive photon detection techniques and high-precision time interval measurement methods, single-photon LiDAR can greatly expand its working range and distance accuracy. Angular resolution, as an important evaluation indicator for the LiDAR system, indicates its target recognition ability. The traditional LiDAR system usually contains a laser source that emits intense beams in Gaussian spatial mode to illuminate the target. The inherent diffraction property of the casting beam, however, sometimes hinders the performance improvement of the LiDAR, especially in angular resolution.
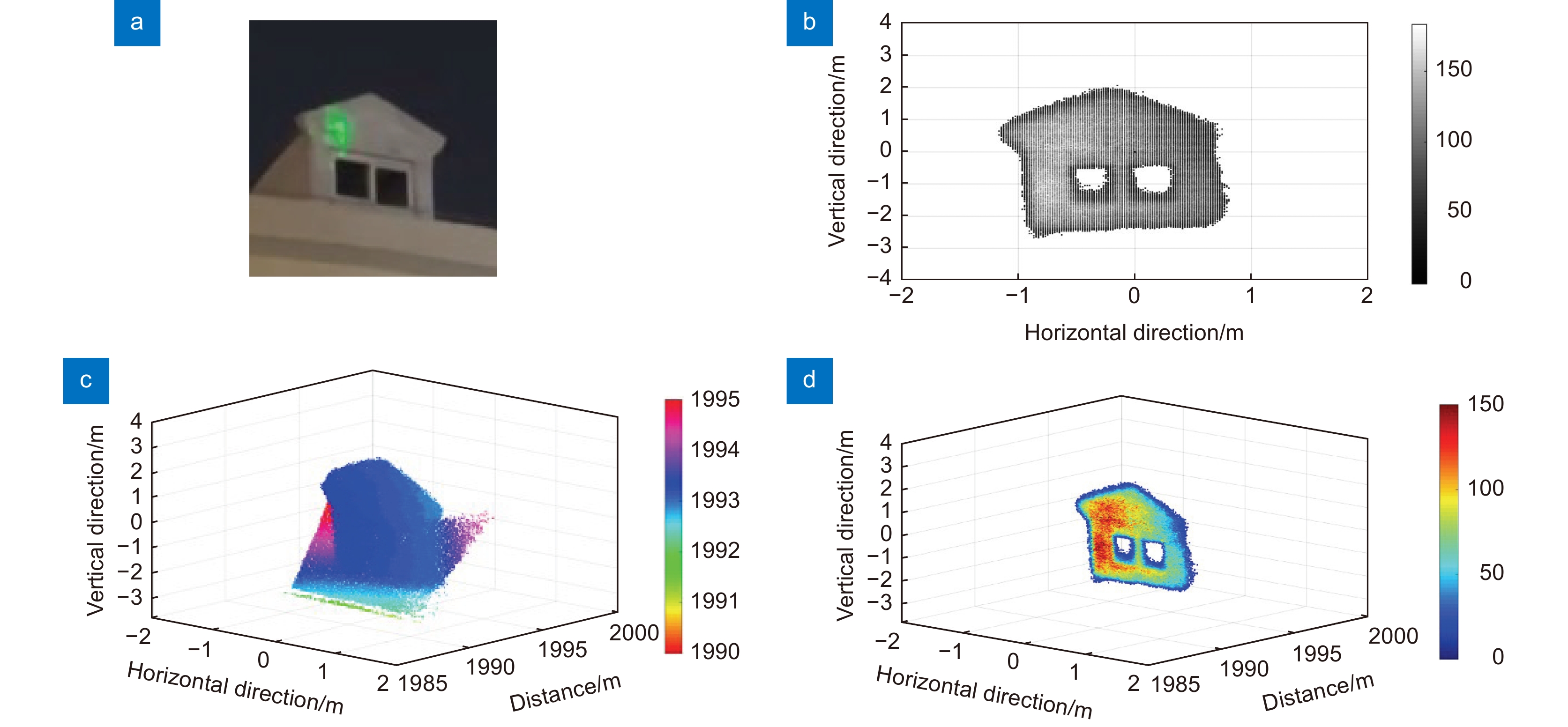
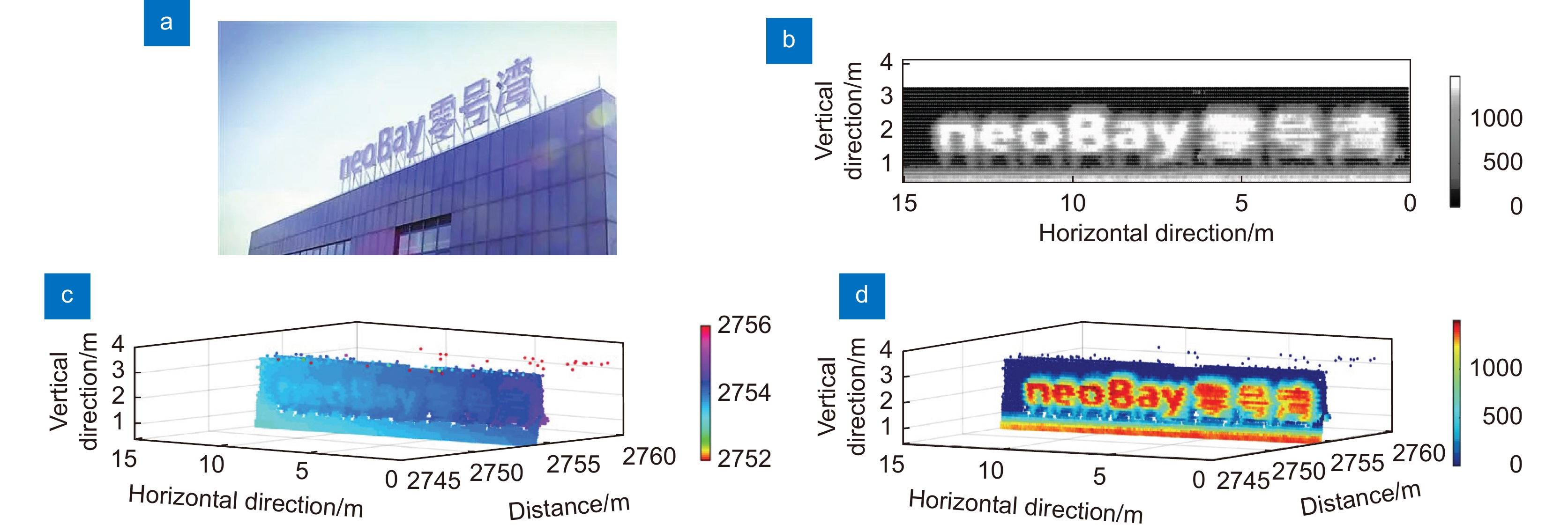
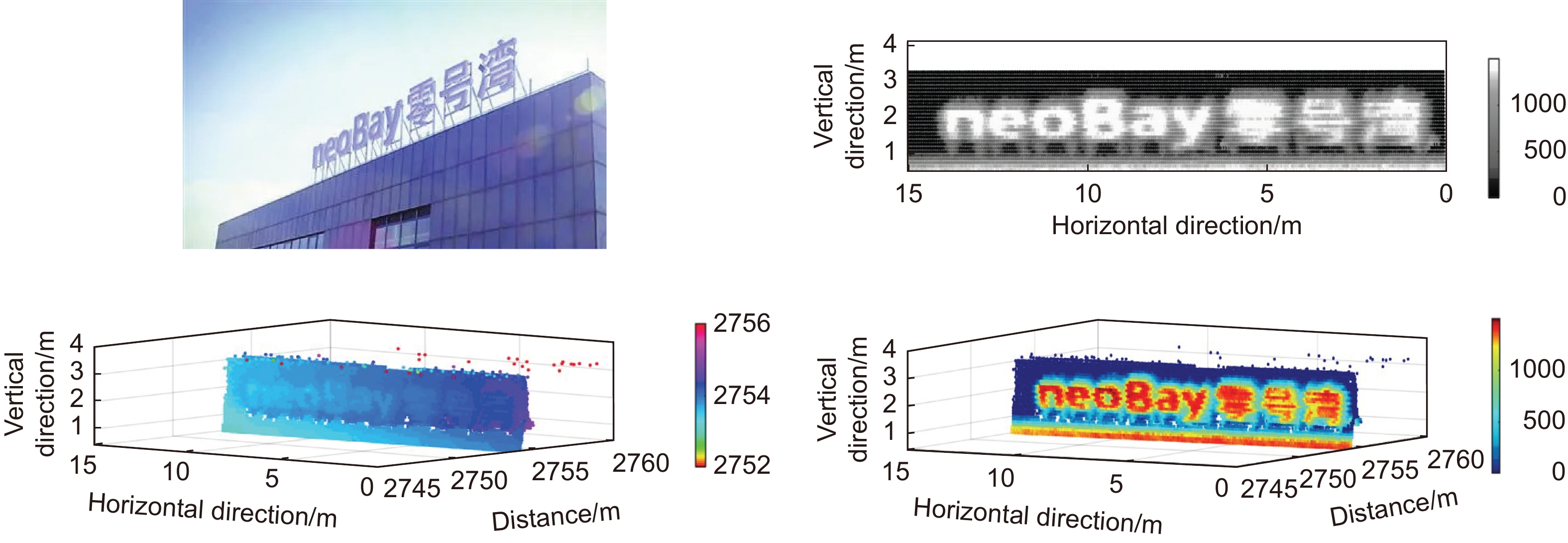
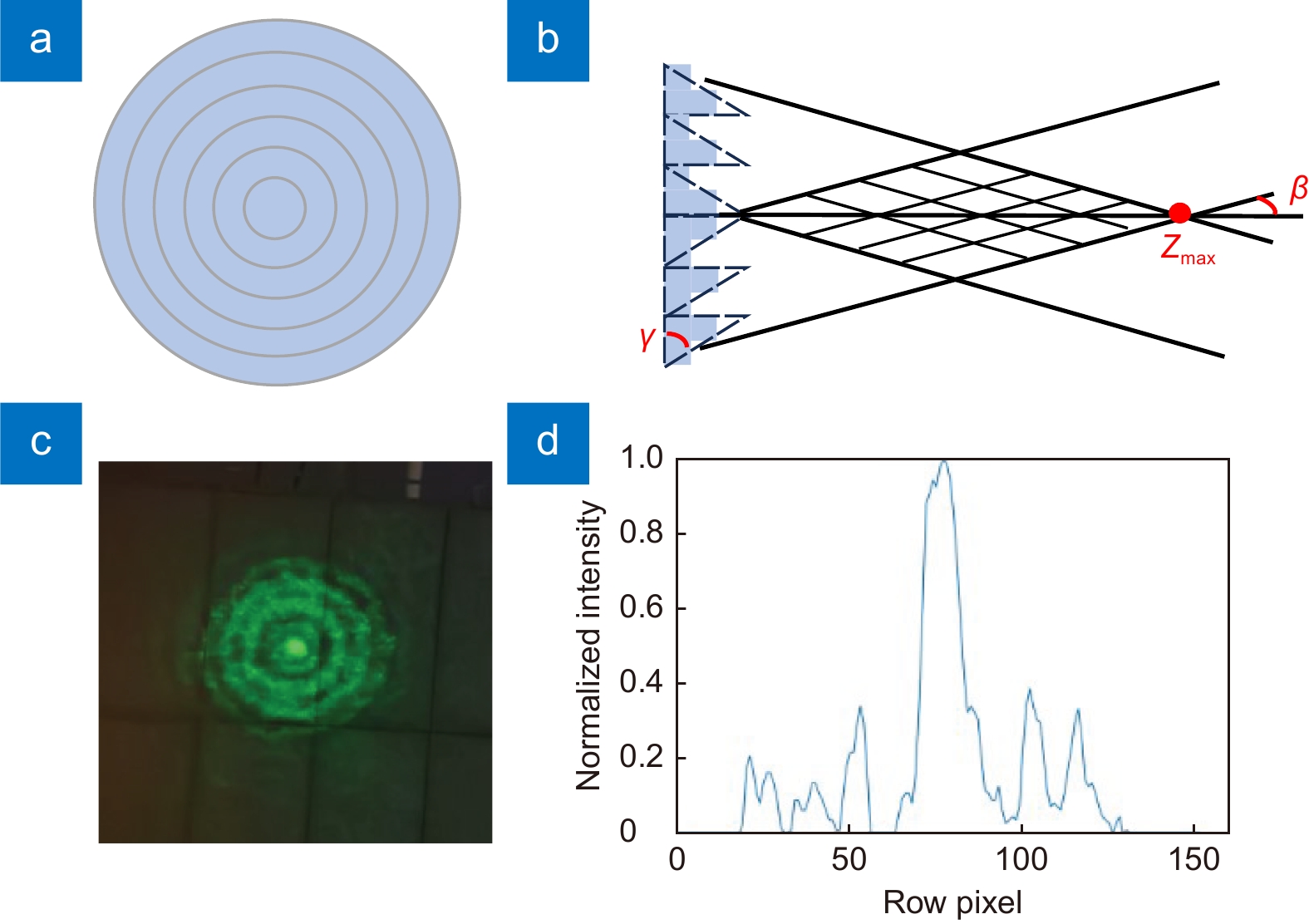
Based on the Si-APD single-photon detector, we demonstrate a new single-photon LiDAR at 532 nm for reconstructing remote targets. In this system, a probe beam, working at Bessel mode rather than Gaussian mode, exhibits a typical intensity distribution of a bright central spot and some surrounding rings. Taking advantage of the non-diffraction character in long-distance ranging, the employment of a Bessel beam could improve the imaging resolution of the LiDAR. To validate the angular resolution of the LiDAR system, we selected a billboard metal scaffold located 2.7 km away as the target. The billboard is supported by a scaffold at its base, with each scaffold beam approximately 5~6 cm wide. The system imaging result consists of 420×29 pixels. The distance point cloud is concentrated at a distance of 2755 m. Through the grayscale image, we can clearly observe the structure of the billboard message and supporting scaffold. The results indicate that the LiDAR system could achieve an 18.1-µrad angle resolution in long-range target imaging, which provides an effective solution for high-resolution remote imaging.
-

-
图 1 贝塞尔光束示意图。(a) 2阶DOE示意图;(b) 2阶DOE产生贝塞尔光束;(c) 2.7 km处贝塞尔光束照片;(d) 2.7 km处贝塞尔光束归一化强度曲线
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of Bessel beams. (a) Schematic diagram of the 2nd-order DOE; (b) Generation of Bessel beams by the 2nd-order DOE; (c) Photo of Bessel beams at the distance of 2.7 km; (d) Normalized intensity curve of Bessel beams at the distance of 2.7 km
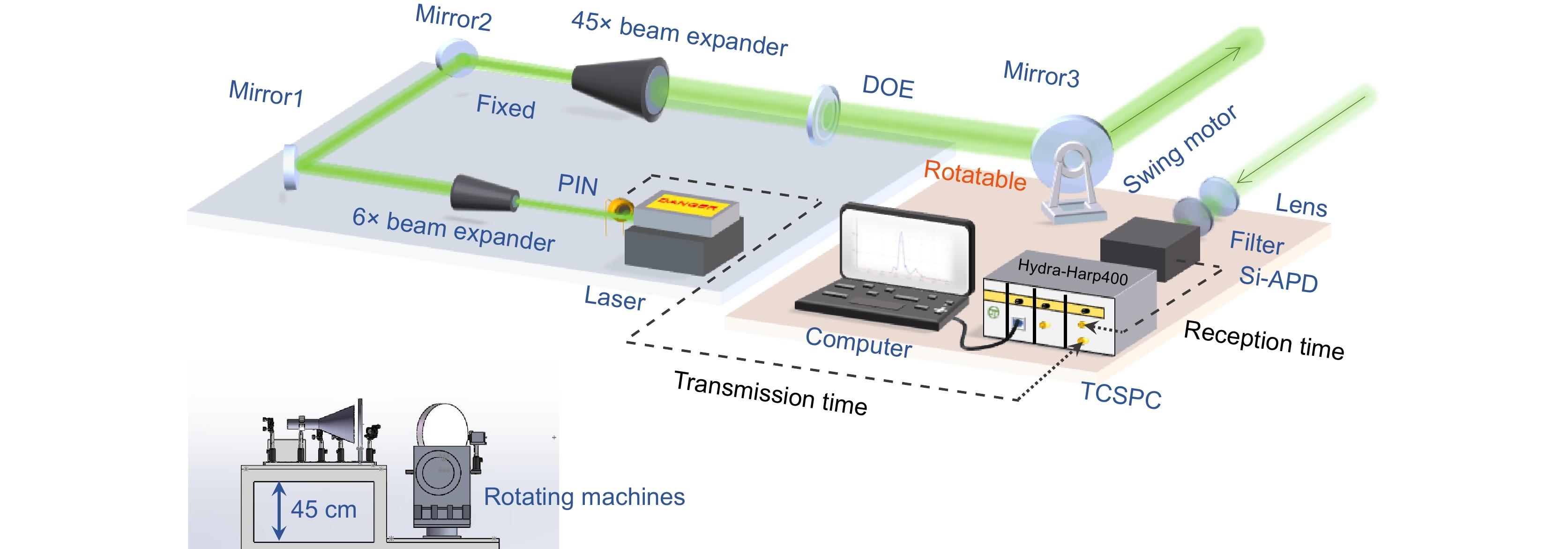
图 2 基于贝塞尔光束的高分辨率激光雷达系统装置图。Laser:532 nm脉冲激光器;PIN:高速光电二极管;6×beam expender:6×扩束镜,入瞳0.5 mm,出瞳孔径3 mm;Mirror1,Mirror2:介质膜高反镜;45×beam expender:45×扩束镜,入瞳3 mm,出瞳孔径135 mm;Mirror3:介质膜高反镜,直径200 mm、厚度10 mm,强反射角度为45°,有效通光孔径>90%;Lens:直径75 mm、焦距85 mm;Filter:532 nm±5 nm;SPAD:Si-APD单光子探测器;TCSPC:时间相关单光子计数器;Swing motor:一维偏摆台;Rotating machines:一维角位移平台
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of a high-resolution LiDAR system based on Bessel beams. Laser: 532 nm pulsed laser. PIN: PIN photodiode. 6× beam expender: the input pupil diameter is 0.5 mm and the output pupil diameter is 3 mm. Mirror1, Mirror2: dielectric mirror. 45× beam expender: the input pupil diameter of 3 mm and the output pupil diameter is 135 mm. Mirror3: 200 mm-diameter dielectric mirror, the thickness of the mirror is 10 mm, the strong reflection angle is 45°, and the effective aperture is greater than 90%. Lens: the diameter is 75 mm and the focal length is 85 mm. Filter: the bandwidth is 532 nm±5 nm. SPAD: Si-APD single-photon detector. TCSPC: time-correlated single-photon counter. Swing motor: one-dimensional tilt platform. Rotating machines: one-dimensional angular displacement platform
-
[1] Li Y, Ibanez-Guzman J. Lidar for autonomous driving: the principles, challenges, and trends for automotive Lidar and perception systems[J]. IEEE Signal Process Mag, 2020, 37(4): 50−61. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2020.2973615
[2] Li Y, Ma L F, Zhong Z L, et al. Deep learning for LiDAR point clouds in autonomous driving: a review[J]. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2021, 32(8): 3412−3432. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3015992
[3] 蔡怀宇, 陈延真, 卓励然, 等. 基于优化DBSCAN算法的激光雷达障碍物检测[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(7): 180514. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180514
Cai H Y, Chen Y Z, Zhuo L R, et al. LiDAR object detection based on optimized DBSCAN algorithm[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(7): 180514. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180514
[4] Li G, Huang Y, Zhang X L, et al. Hybrid maps enhanced localization system for mobile manipulator in harsh manufacturing workshop[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 10782−10795. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2965300
[5] Meng J, Wang S T, Xie Y L, et al. A safe and efficient LIDAR-based navigation system for 4WS4WD mobile manipulators in manufacturing plants[J]. Meas Sci Technol, 2021, 32(4): 045203. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/abce71
[6] Rollenbeck R, Bendix J. Rainfall distribution in the Andes of southern Ecuador derived from blending weather radar data and meteorological field observations[J]. Atmos Res, 2011, 99(2): 277−289. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2010.10.018
[7] Bates J S, Montzka C, Schmidt M, et al. Estimating canopy density parameters time-series for winter wheat using UAS mounted LiDAR[J]. Remote Sens, 2021, 13(4): 710. doi: 10.3390/rs13040710
[8] Miltiadou M, Campbell N D F, Cosker D, et al. A comparative study about data structures used for efficient management of voxelised full-waveform airborne LiDAR data during 3D polygonal model creation[J]. Remote Sens, 2021, 13(4): 559. doi: 10.3390/rs13040559
[9] 闫德立, 高尚, 李韶华, 等. 基于激光雷达的道路不平度及可行驶区域检测[J]. 激光技术, 2022, 46(5): 624−629. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2022.05.007
Yan D L, Gao S, Li S H, et al. Detection of road roughness and drivable area based on LiDAR[J]. Laser Technol, 2022, 46(5): 624−629. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2022.05.007
[10] 刘国栋, 刘佳, 刘浪. 一种基于机载LiDAR数据的山区道路提取方法[J]. 激光技术, 2022, 46(4): 466−473. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2022.04.005
Liu G D, Liu J, Liu L. A mountain road extraction method based on airborne LiDAR data[J]. Laser Technol, 2022, 46(4): 466−473. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2022.04.005
[11] 陈海平, 李萌阳, 曹庭分, 等. 基于激光雷达数据的火星表面障碍物识别[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(2): 220240. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220240
Chen H P, Li M Y, Cao T F, et al. Obstacle recognition on Mars surface based on LiDAR data[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(2): 220240. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220240
[12] Jaboyedoff M, Oppikofer T, Abellán A, et al. Use of LIDAR in landslide investigations: a review[J]. Nat Hazards, 2012, 61(1): 5−28. doi: 10.1007/s11069-010-9634-2
[13] Amzajerdian F, Vanek M, Petway L, et al. Utilization of 3D imaging flash lidar technology for autonomous safe landing on planetary bodies[J]. Proc SPIE, 2010, 7608: 760828. doi: 10.1117/12.843324
[14] Stettner R. Compact 3D flash lidar video cameras and applications[J]. Proc SPIE, 2010, 7684: 768405. doi: 10.1117/12.851831
[15] Patanwala S M, Gyongy I, Mai H N, et al. A high-throughput photon processing technique for range extension of SPAD-based LiDAR receivers[J]. IEEE Open J Solid-State Circuits Soc, 2022, 2: 12−25. doi: 10.1109/OJSSCS.2021.3118987
[16] David R, Allard B, Branca X, et al. Study and design of an integrated CMOS laser diode driver for an iToF-based 3D image sensor[C]//CIPS 2020; 11th International Conference on Integrated Power Electronics Systems, 2020: 1–6.
[17] Padmanabhan P, Zhang C, Cazzaniga M, et al. 7.4 A 256×128 3D-stacked (45 nm) SPAD FLASH LiDAR with 7-level coincidence detection and progressive gating for 100 m range and 10 klux background light[C]//2021 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), 2021: 111–113. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISSCC42613.2021.9366010.
[18] McCarthy A, Ren X M, Della Frera A, et al. Kilometer-range depth imaging at 1550 nm wavelength using an InGaAs/InP single-photon avalanche diode detector[J]. Opt Express, 2013, 21(19): 22098−22113. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.022098
[19] Pawlikowska A M, Halimi A, Lamb R A, et al. Single-photon three-dimensional imaging at up to 10 kilometers range[J]. Opt Express, 2017, 25(10): 11919−11931. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.011919
[20] Li Z P, Huang X, Cao Y, et al. Single-photon computational 3D imaging at 45 km[J]. Photonics Res, 2020, 8(9): 1532−1540. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.390091
[21] Halimi A, Maccarone A, Lamb R A, et al. Robust and guided Bayesian reconstruction of single-photon 3D Lidar data: application to multispectral and underwater imaging[J]. IEEE Trans Comput Imaging, 2021, 7: 961−974. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2021.3111572
[22] Henderson R K, Johnston N, Hutchings S W, et al. 5.7 A 256×256 40 nm/90 nm CMOS 3D-stacked 120dB dynamic-range reconfigurable time-resolved SPAD imager[C]//IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference - (ISSCC), 2019: 106–108. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISSCC.2019.8662355.
[23] Stettner R, Bailey H, Richmond R D. Eye-safe laser radar 3D imaging[J]. Proc SPIE, 2004, 5412: 111−116. doi: 10.1117/12.553992
[24] Marino R M, Davis W R, Jr. Jigsaw: a foliage-penetrating 3D imaging laser radar system[J]. Lincoln Lab J, 2005, 15(1): 23−36.
[25] Hutchings S W, Johnston N, Gyongy I, et al. A reconfigurable 3-D-stacked SPAD imager with in-pixel histogramming for flash LIDAR or high-speed time-of-flight imaging[J]. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2019, 54(11): 2947−2956. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2939083
[26] Gyongy I, Erdogan A T, Dutton N A W, et al. A direct time-of-flight image sensor with in-pixel surface detection and dynamic vision[J]. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2023.3238520.
[27] DeBeer D, Hartmann S R, Friedberg R. Comment on "Diffraction-free beams"[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1987, 59(22): 2611. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.59.2611
[28] 周莉萍, 赵斌, 李柱. 无衍射光束在激光三角测量系统中的应用研究[J]. 激光技术, 1998, 22(1): 22−25.
Zhou L P, Zhao B, Li Z. Research on laser triangulation measurement system with non-diffraction beam[J]. Laser Technol, 1998, 22(1): 22−25.
[29] Meng H F, Xiang B, Zhang J L, et al. The generation of Bessel beam and its application in millimeter wave imaging[J]. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves, 2014, 35(2): 208−217. doi: 10.1007/s10762-013-0037-9
[30] Scott G, McArdle N. Efficient generation of nearly diffraction-free beams using an axicon[J]. Opt Eng, 1992, 31(12): 2640−2643. doi: 10.1117/12.60017
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: