-
摘要:
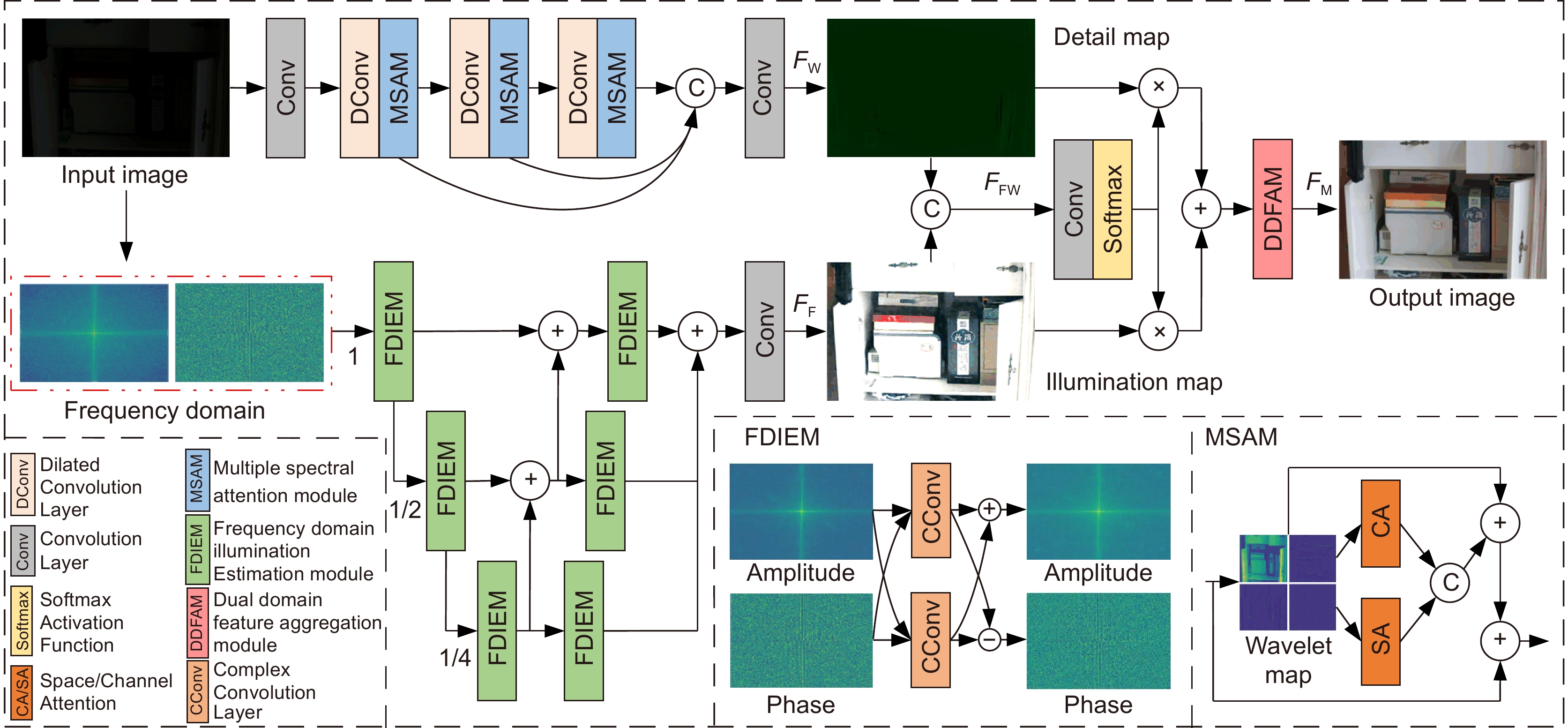
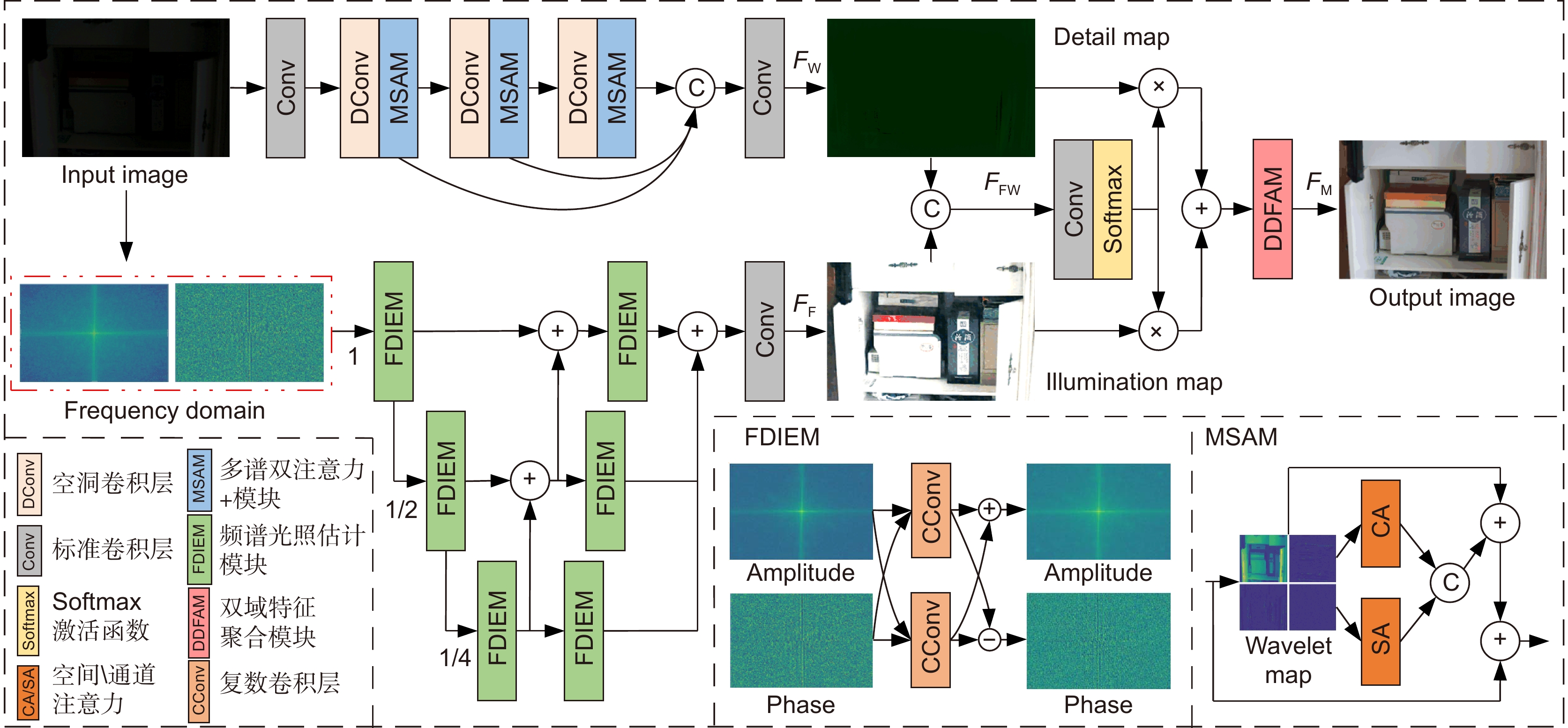
针对低照度图像质量较差、噪声多、纹理模糊等问题,提出一种基于双频域特征聚合的低照度增强网络(dual frequency-domain feature aggregation network, DF-DFANet)。首先,构建频谱光照估计模块(frequency domain illumination estimation module, FDIEM)实现跨域特征提取,通过共轭对称约束调整频域特征图抑制噪声信号,并采用逐层融合方式提高多尺度融合效率以扩大特征图感受野范围。其次,设计多谱双注意力模块(multiple spectral attention module, MSAM)聚焦图像局部频率特征,通过小波域空间、通道注意力机制关注图像细节信息。最后,提出双域特征聚合模块(dual domain feature aggregation module, DDFAM)融合傅里叶域和小波域特征信息,利用激活函数计算自适应调整权重实现像素级图像增强,并结合傅里叶域全局信息提高融合效果。实验结果表明,在LOL数据集上所提网络的PSNR达到24.3714,SSIM达到0.8937。与对比网络相比,所提网络增强效果更具自然性。
Abstract:Aiming at the problems of poor low-light image quality, noise, and blurred texture, a low-light enhancement network (DF-DFANet) based on dual-frequency domain feature aggregation is proposed. Firstly, a spectral illumination estimation module (FDIEM) is constructed to realize cross-domain feature extraction, which can adjust the frequency domain feature map to suppress noise signals through conjugate symmetric constraints and improve the multi-scale fusion efficiency by layer-by-layer fusion to expand the range of the feature map. Secondly, the multispectral dual attention module (MSAM) is designed to focus on the local frequency characteristics of the image, and pay attention to the detailed information of the image through the wavelet domain space and channel attention mechanism. Finally, the dual-domain feature aggregation module (DDFAM) is proposed to fuse the feature information of the Fourier domain and the wavelet domain, and use the activation function to calculate the adaptive adjustment weight to achieve pixel-level image enhancement and combine the Fourier domain global information to improve the fusion effect. The experimental results show that the PSNR of the proposed network on the LOL dataset reaches 24.3714 and the SSIM reaches 0.8937. Compared with the comparison network, the proposed network enhancement effect is more natural.
-
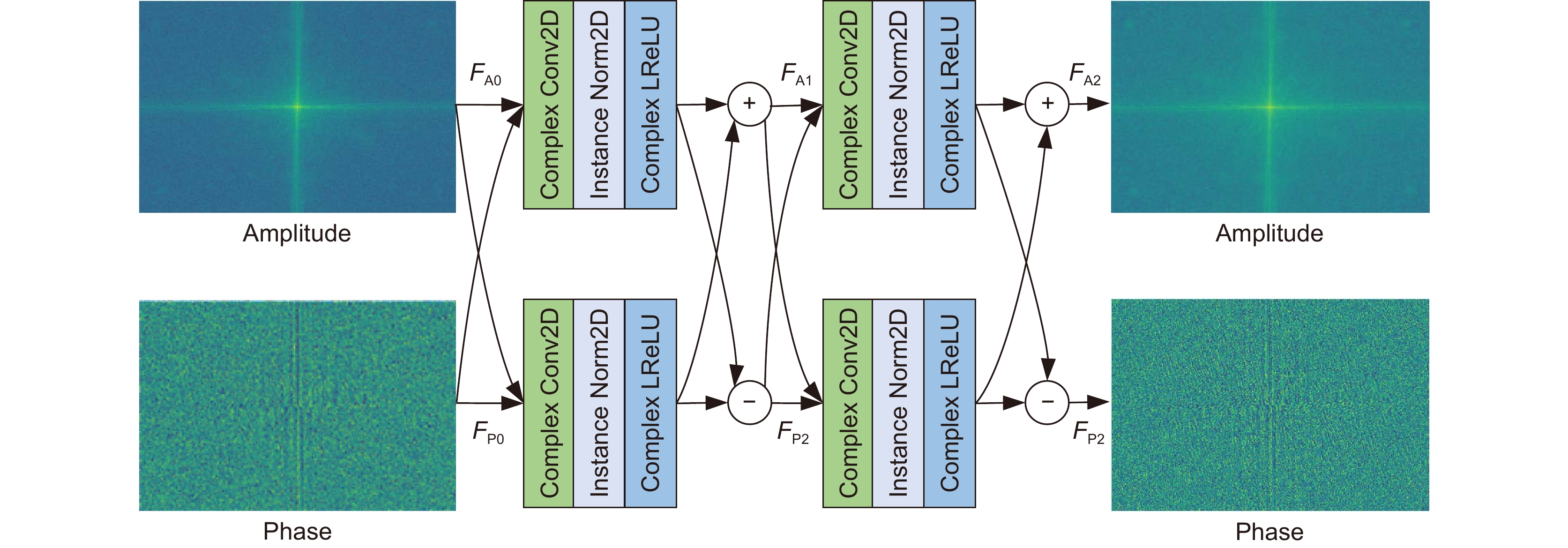
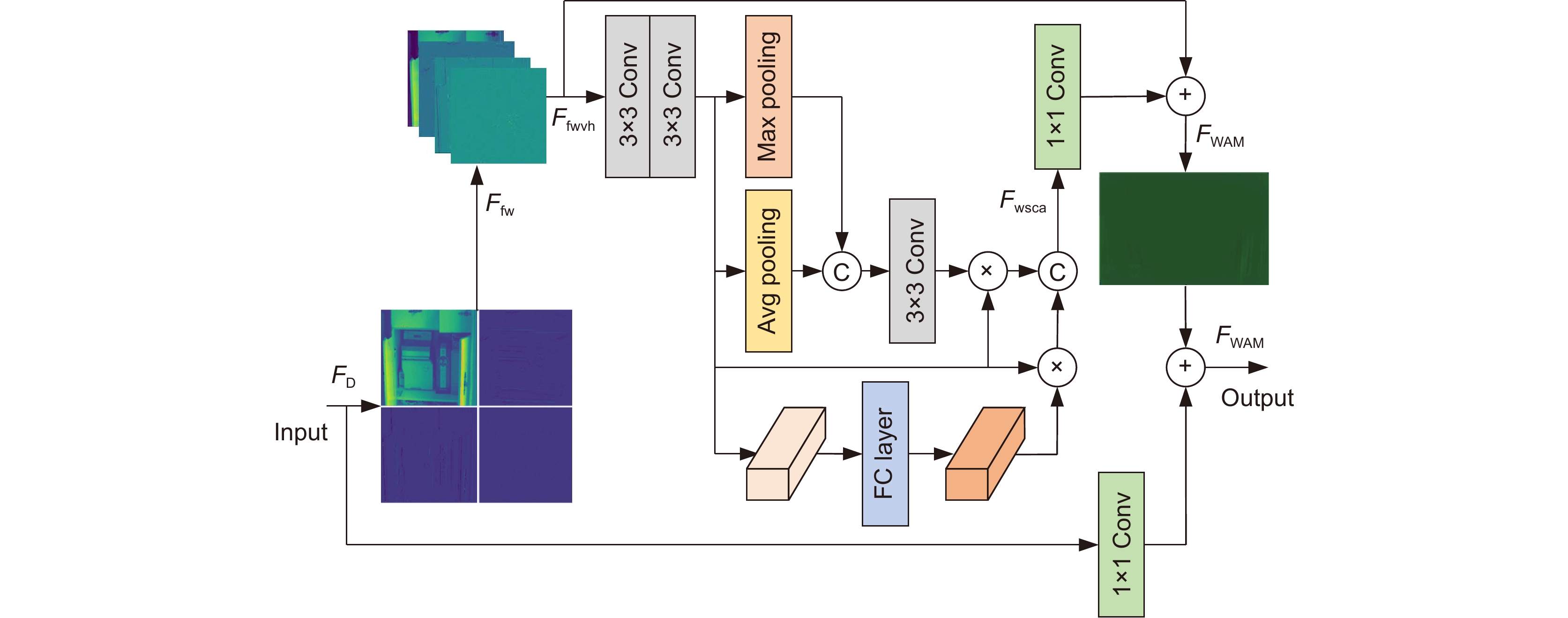
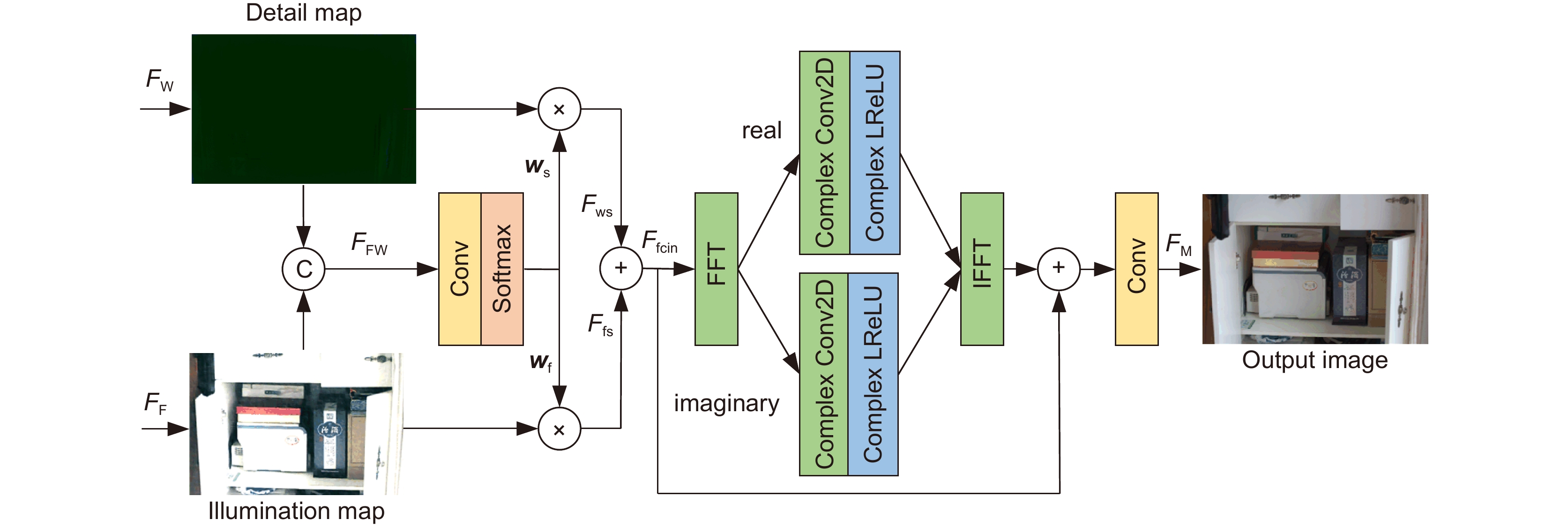
Overview: Road monitoring is an important part of the field of intelligent transportation. However, in the night scene under the condition of low illumination, the brightness and contrast of the images collected by the camera are low, and there are more noise particles, which brings difficulty to the visual tasks such as detection and recognition of important targets in the field of traffic supervision. Although deep learning has achieved certain results in the enhancement of low-light images, it is easy to amplify shadow noise while enhancing brightness and contrast. Unreasonable noise reduction strategies often lead to different degrees of detail blur in the image, especially for low-light images with poor picture quality, it is often difficult to restore the lost texture structure. To solve these problems, a dual-frequency domain based feature aggregation network (DF-DFANet) is proposed. Firstly, the spectral illumination estimation module (FDIEM) is designed to extract the global features of the image through the Fourier domain spectral feature map and reduce the response to the noise signal while pulling up the brightness of the image in the frequency domain. Secondly, a multispectral dual attention module (MSAM) is proposed, which uses the spatial and channel attention mechanism to make the network focus on the important features of the Baud sign subgraph and improves the ability of the network to recover image details. Finally, a dual-domain feature aggregation module (DDFAM) was constructed to learn the adaptive weight parameters of different pixel level features, and the complex domain convolution was used to promote the fusion of feature information, which enhanced the naturalness of image color performance and the richness of texture details. In the Fourier domain branch, the frequency domain feature map extracted by the spectral illumination estimation module is fused layer by layer, the range of the sensitivity field of the feature map is expanded, and the refined illumination map is obtained by combining rich contextual semantic information. The multi-spectral dual attention module is embedded in the branch of the wavelet domain, and the space and the channel attention are used to improve the ability of the network to pay attention to the high-frequency detail features of the image. Dual-domain feature aggregation module uses an activation function to obtain image pixel allocation weight, realizes more refined adjustment of the enhanced image, and improves the ability of the network to restore image color and texture. Comparative experiments on the LOL dataset show that the PSNR and SSIM of the proposed network reach 24.3714 and 0.8937. On the MIT-Adobe FiveK dataset, PSNR and SSIM reach 22.7214 and 0.8726, respectively. In addition, the proposed method has been tested in practical application scenarios, and the enhancement effect has good stability, robustness, and generalization ability.
-

-
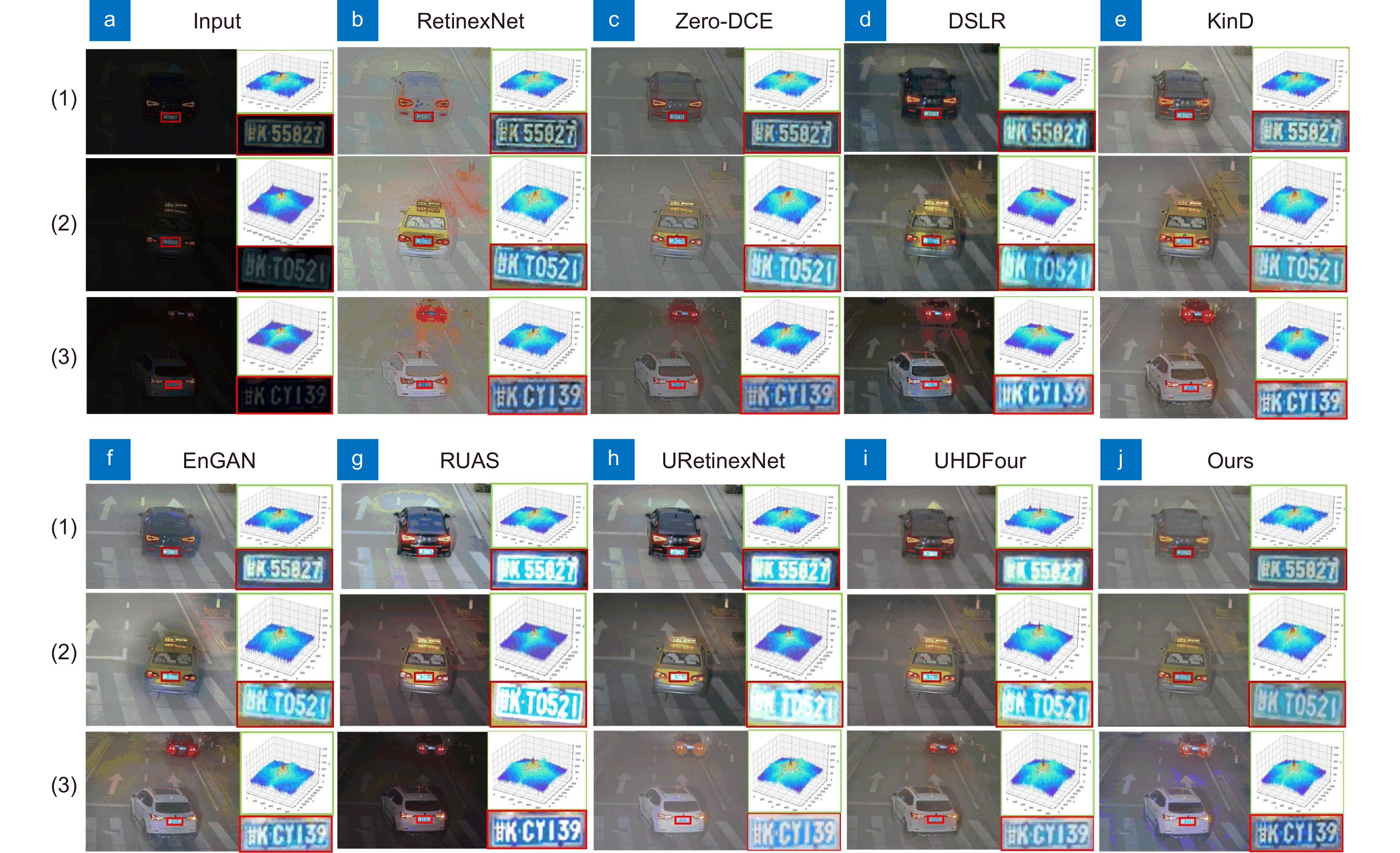
表 1 LOL真实低照度数据集测试结果
Table 1. LOL real-world dataset results
Method PSNR$ \uparrow $ SSIM$ \uparrow $ LPIPS$ \downarrow $ RetinexNet[26] 16.7740 0.4250 0.4739 Zero-DCE[27] 14.8607 0.5624 0.3352 DSLR[28] 14.9822 0.5964 0.3757 KinD[29] 17.6476 0.7715 0.1750 EnGAN[30] 17.4829 0.6515 0.3223 GLAD[32] 19.7182 0.6820 0.3994 RUAS[31] 16.4047 0.5034 0.2078 R2RNet[10] 20.2070 0.8160 - UHDFour[8] 23.0926 0.8720 - URetinexNet[6] 21.3282 0.8348 - Ours 24.3714 0.8937 0.1525 表 2 MIT-Adobe FiveK数据集测试结果
Table 2. MIT-Adobe FiveK dataset results
Method PSNR$ \uparrow $ SSIM$ \uparrow $ LPIPS$ \downarrow $ Exposure[33] 18.7412 0.8159 0.1674 CycleGAN[34] 19.3823 0.7852 0.1636 RetinexNet[26] 12.5146 0.6708 0.2535 DSLR[28] 20.2435 0.8289 0.1526 KinD[29] 16.2032 0.7841 0.1498 EnGAN[30] 17.9050 0.8361 0.1425 Zero-DCE[27] 15.9312 0.7668 0.1647 Zero-DCE++[35] 14.6111 0.4055 0.2309 RUAS[31] 15.9953 0.7863 0.1397 Ours 22.7214 0.8726 0.1153 表 3 模块注意力结构测试对比结果
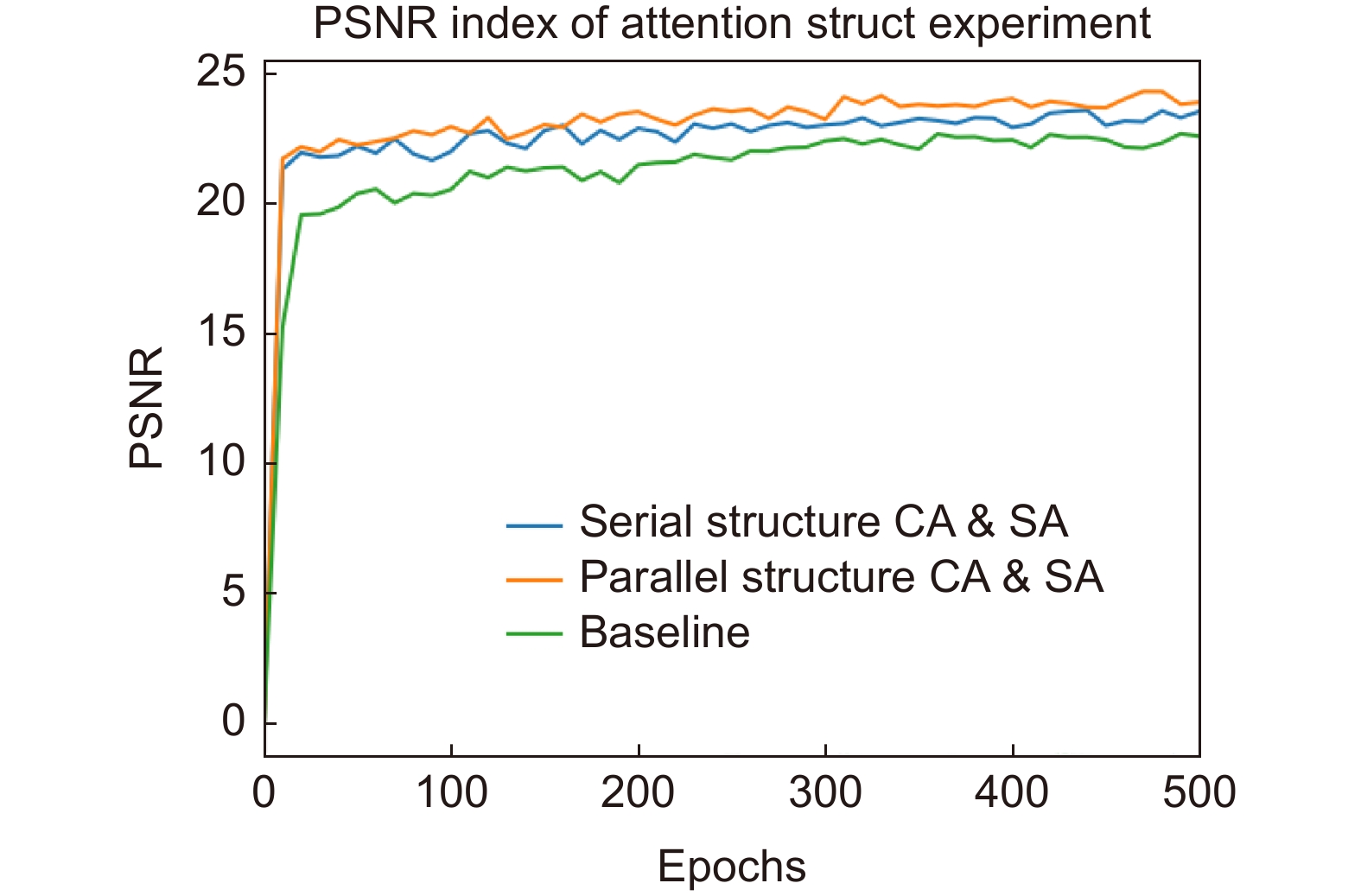
Table 3. Comparison results of module attention structure testing
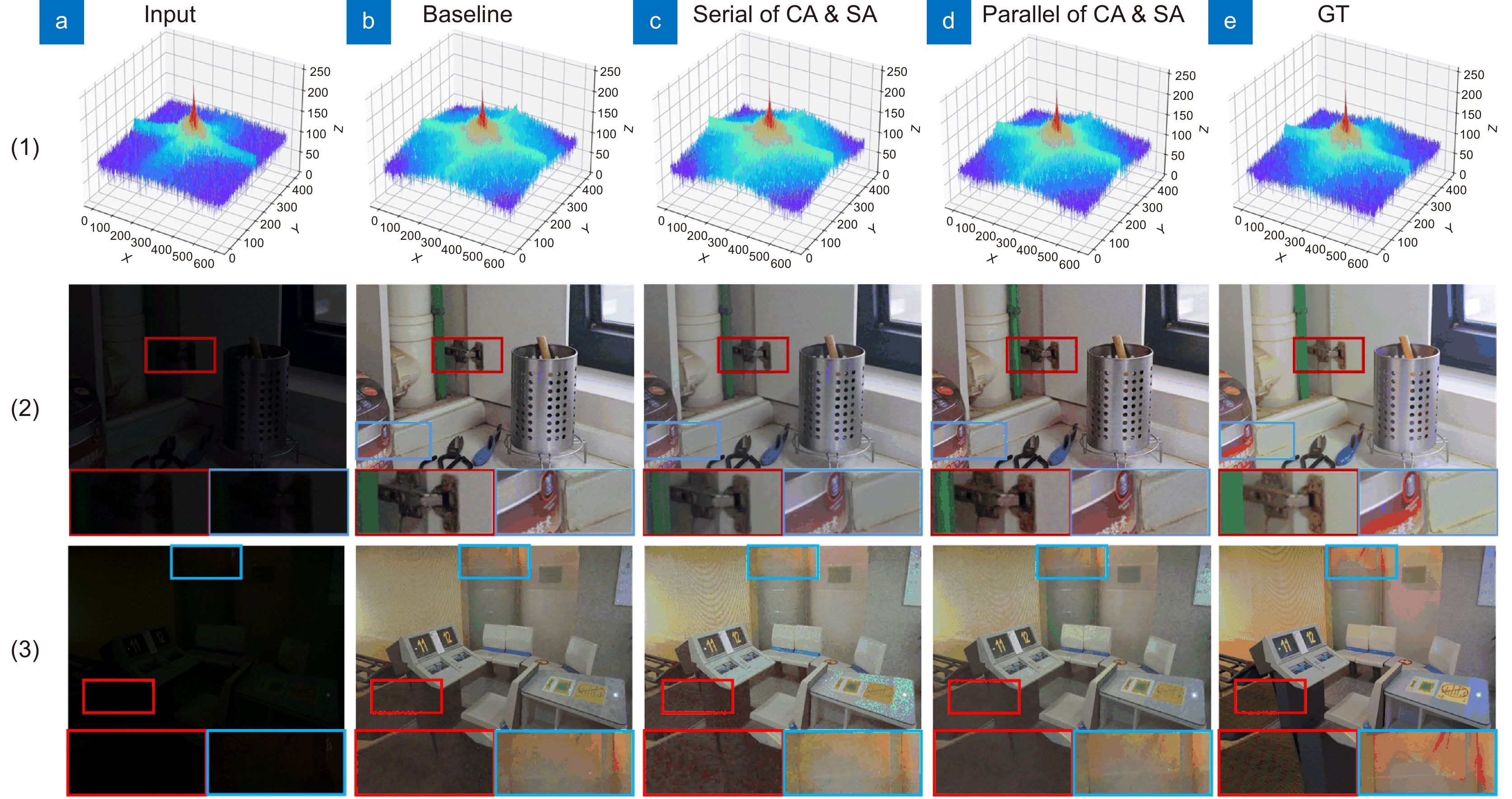
Method PSNR$ \uparrow $ SSIM$ \uparrow $ LPIPS$ \downarrow $ Baseline 22.7052 0.8147 0.2078 With serial of CA & SA 23.6042 0.8283 0.1837 With parallel of CA & SA 24.3714 0.8937 0.1525 表 4 网络模块消融实验结果
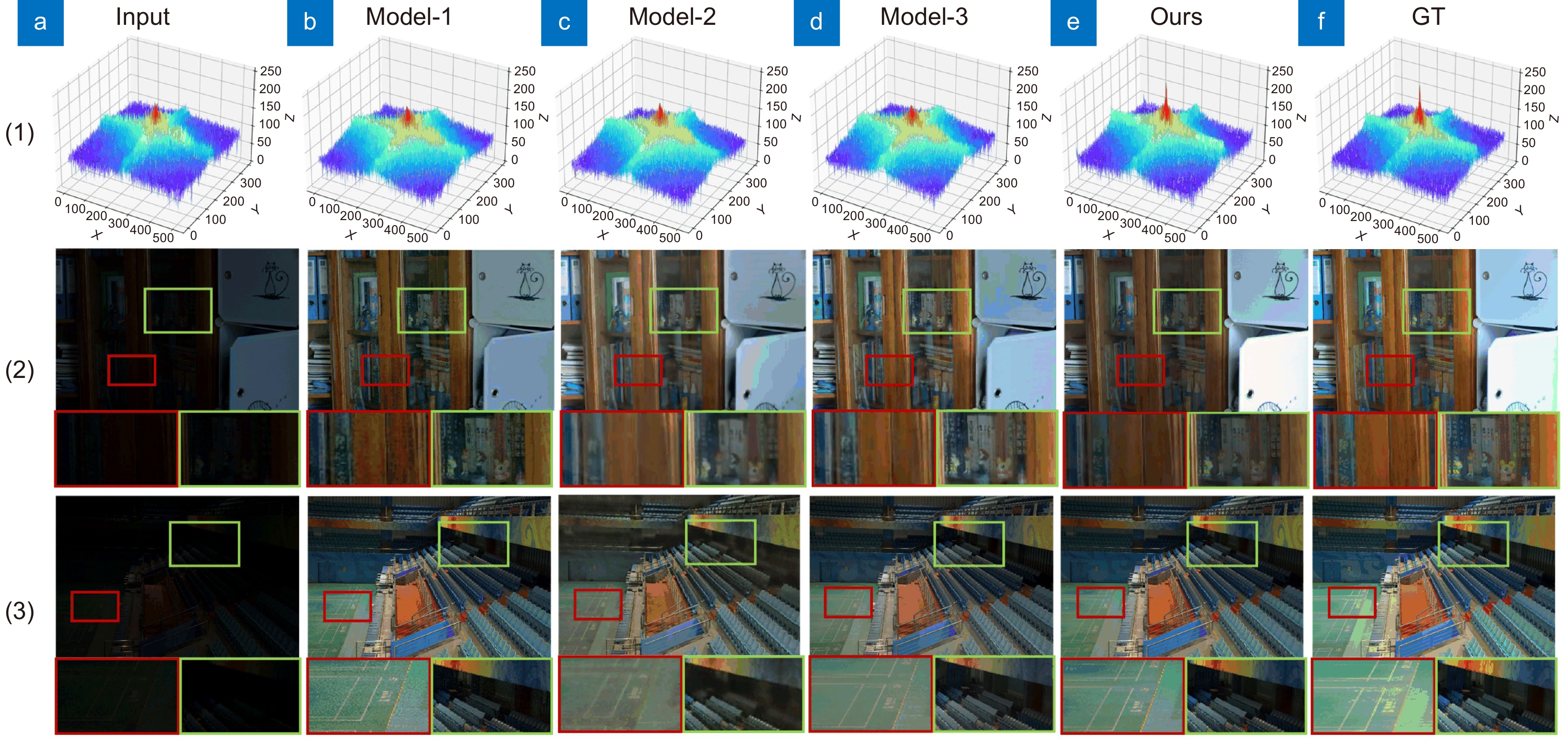
Table 4. Experimental results of network module ablation
Model FDIEM MSAM DDFAM PSNR SSIM Baseline × × × 20.8620 0.8515 Model-1 × √ √ 21.3582 0.8653 Model-2 √ × √ 22.0401 0.8878 Model-3 √ √ × 21.9068 0.8919 Ours √ √ √ 24.3714 0.8937 表 5 不同网络的PSNR和平均处理时间、模型大小和浮点运算量对比
Table 5. Comparison of different network average processing time, model size and floating-point operations
Model Time/ms Params/M FLOPs/G PSNR SSIM RetinexNet[26] 20 9.2 136.0151 16.7740 0.4250 Zero-DCE[27] 2 0.97 5.2112 14.8671 0.5624 KinD[29] 10 35 29.1303 20.3792 0.7715 EnGAN[30] 20 33 61.0102 17.4828 0.6515 GLAD[32] 25 11 252.1410 19.7182 0.6820 MBLLEN[36] 80 1.95 19.9560 17.8583 0.7247 LPNet[37] 18 0.15 0.7700 21.4612 0.8020 URetinexNet[6] 2.93 0.34 1801.4110 21.3282 0.8348 Ours 48 1.61 288.3776 24.3714 0.8937 -
[1] Zhu M F, Pan P B, Chen W, et al. EEMEFN: low-light image enhancement via edge-enhanced multi-exposure fusion network[C]//Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020: 13106–13113. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.7013
[2] Li C L, Tang S Q, Yan J W, et al. Low-light image enhancement based on quasi-symmetric correction functions by fusion[J]. Symmetry, 2020, 12(9): 1561. doi: 10.3390/sym12091561
[3] Pan X X, Li C L, Pan Z G, et al. Low-light image enhancement method based on retinex theory by improving illumination map[J]. Appl Sci, 2022, 12(10): 5257. doi: 10.3390/app12105257
[4] 李平, 梁丹, 梁冬泰, 等. 自适应图像增强的管道机器人缺陷检测方法[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(1): 190304. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190304
Li P, Liang D, Liang D T, et al. Research on defect inspection method of pipeline robot based on adaptive image enhancement[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(1): 190304. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190304
[5] Zhao R N, Han Y, Zhao J. End-to-end retinex-based illumination attention low-light enhancement network for autonomous driving at night[J]. Comput Intell Neurosci, 2022, 2022: 4942420. doi: 10.1155/2022/4942420
[6] Wu W H, Weng J, Zhang P P, et al. Uretinex-Net: retinex-based deep unfolding network for low-light image enhancement[C]//Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022: 5891–5900.https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00581.
[7] Jiang Q P, Mao Y D, Cong R M, et al. Unsupervised decomposition and correction network for low-light image enhancement[J]. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst, 2022, 23(10): 19440−19455. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3165176
[8] Li C Y, Guo C L, Zhou M, et al. Embedding fourier for ultra-high-definition low-light image enhancement[C]//The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, 2023.
[9] Zhang Y C, Liu H Y, Ding D D. A cross-scale framework for low-light image enhancement using spatial–spectral information[J]. Comput Electr Eng, 2023, 106: 108608. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2023.108608
[10] Hai J, Xuan Z, Yang R, et al. R2RNet: low-light image enhancement via real-low to real-normal network[J]. J Vis Commun Image Represent, 2023, 90: 103712. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2022.103712
[11] Lin X, Yue J T, Ren C, et al. Unlocking low-light-rainy image restoration by pairwise degradation feature vector guidance[Z]. arXiv: 2305.03997, 2023. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.03997
[12] Xu J Z, Yuan M K, Yan D M, et al. Illumination guided attentive wavelet network for low-light image enhancement[J]. IEEE Trans Multimedia, 2023, 25: 6258−6271. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2022.3207330
[13] Fan C M, Liu T J, Liu K H. Half wavelet attention on M-Net+ for low-light image enhancement[C]//2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2022: 3878–3882. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP46576.2022.9897503
[14] 胡聪, 陈绪君, 吴雨锴. 融合半波注意力机制的低光照图像增强算法研究[J]. 激光杂志, 2023.
Hu C, Chen X J, Wu Y K. Research on image enhancement algorithm of low illumination image based on half wave attention mechanism[J]. Laser J, 2023.
[15] Chen Z L, Liang Y L, Du M H. Attention-based broad self-guided network for low-light image enhancement[C]//2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2022: 31–38. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR56361.2022.9956143
[16] Chi L, Jiang B R, Mu Y D. Fast Fourier convolution[C]//Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020: 376.
[17] Suvorov R, Logacheva E, Mashikhin A, et al. Resolution-robust large mask inpainting with Fourier convolutions[C]//Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2022: 3172–3182. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV51458.2022.00323
[18] Zamir S W, Arora A, Khan S, et al. Learning enriched features for fast image restoration and enhancement[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2022, 45(2): 1934−1948. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3167175
[19] Zhang G, Li Z Y, Li J M, et al. CFNet: cascade fusion network for dense prediction[Z]. arXiv: 2302.06052, 2023. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2302.06052
[20] 刘光辉, 杨琦, 孟月波, 等. 一种并行混合注意力的渐进融合图像增强方法[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(4): 220231. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220231
Liu G H, Yang Q, Meng Y B, et al. A progressive fusion image enhancement method with parallel hybrid attention[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(4): 220231. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220231
[21] Li X, Wang W H, Hu X L, et al. Selective kernel networks[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 510–519. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00060
[22] Jiang J X, Ye T, Bai J B, et al. Five A+ network: you only need 9k parameters for underwater image enhancement[Z]. arXiv: 2305.08824, 2023. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.08824
[23] Starovoitov V V, Eldarova E E, Iskakov K T. Comparative analysis of the SSIM index and the Pearson coefficient as a criterion for image similarity[J]. Eurasian J Math Comput Appl, 2020, 8(1): 76−90. doi: 10.32523/2306-6172-2020-8-1-76-90
[24] 陶昕辰, 朱涛, 黄玉玲, 等. 基于DDR GAN的低质量图像增强算法[J]. 激光技术, 2023, 47(3): 322−328. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2023.03.006
Tao X C, Zhu T, Huang Y L, et al. Low-quality image enhancement algorithm based on DDR GAN[J]. Laser Technol, 2023, 47(3): 322−328. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2023.03.006
[25] Fuoli D, Van Gool L, Timofte R. Fourier space losses for efficient perceptual image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2021: 2340–2349. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00236
[26] Wei C, Wang W J, Yang W H, et al. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement[C]//British Machine Vision Conference 2018, 2018.
[27] Guo C L, Li C Y, Guo J C, et al. Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 1777–1786. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00185
[28] Lim S, Kim W. DSLR: deep stacked Laplacian restorer for low-light image enhancement[J]. IEEE Trans Multimedia, 2021, 23: 4272−4284. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2020.3039361
[29] Zhang Y H, Zhang J W, Guo X J. Kindling the darkness: a practical low-light image enhancer[C]//Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2019: 1632–1640. https://doi.org/10.1145/3343031.3350926
[30] Jiang Y F, Gong X Y, Liu D, et al. EnlightenGAN: deep light enhancement without paired supervision[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2021, 30: 2340−2349. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3051462
[31] Liu R S, Ma L, Zhang J A, et al. Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low-light image enhancement[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021: 10556–10565. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01042
[32] Jiao Y, Zheng X T, Lu X Q. Attention-based multi-branch network for low-light image enhancement[C]//2021 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things Engineering (ICBAIE), 2021: 401–407. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICBAIE52039.2021.9389960
[33] Hu Y M, He H, Xu C X, et al. Exposure: a white-box photo post-processing framework[J]. ACM Trans Graph, 2018, 37(2): 26. doi: 10.1145/3181974
[34] Zhu J Y, Park T, Isola P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 2242–2251. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017244
[35] Li C Y, Guo C L, Loy C C. Learning to enhance low-light image via zero-reference deep curve estimation[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2022, 44(8): 4225−4238. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3063604
[36] Lv F F, Lu F, Wu J H, et al. MBLLEN: low-light image/video enhancement using CNNs[C]//British Machine Vision Conference 2018, 2018.
[37] Li J, Li J, Fang F, et al. Luminance-aware pyramid network for low-light image enhancement[J]. IEEE Trans Multimedia, 2020, 23: 3153−3165.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: