-
摘要
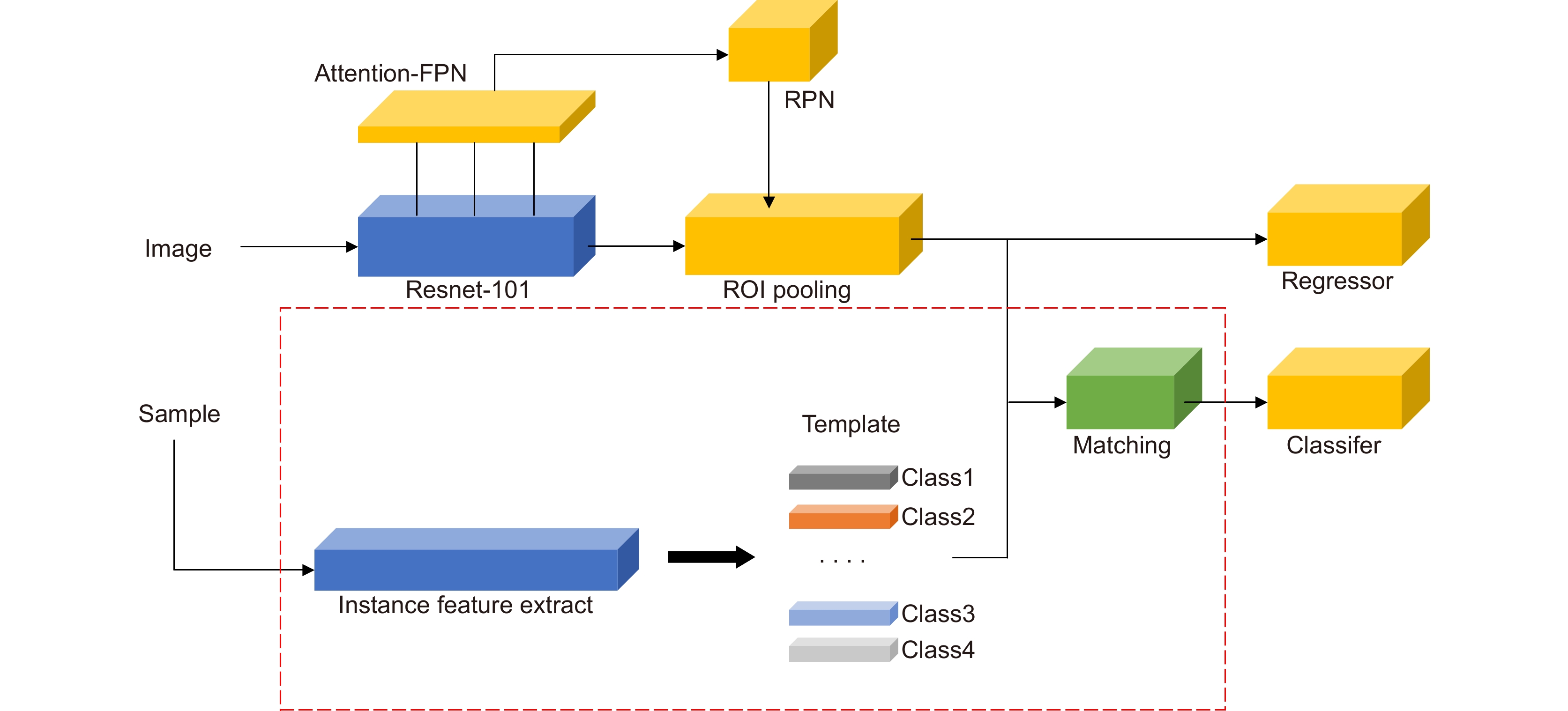
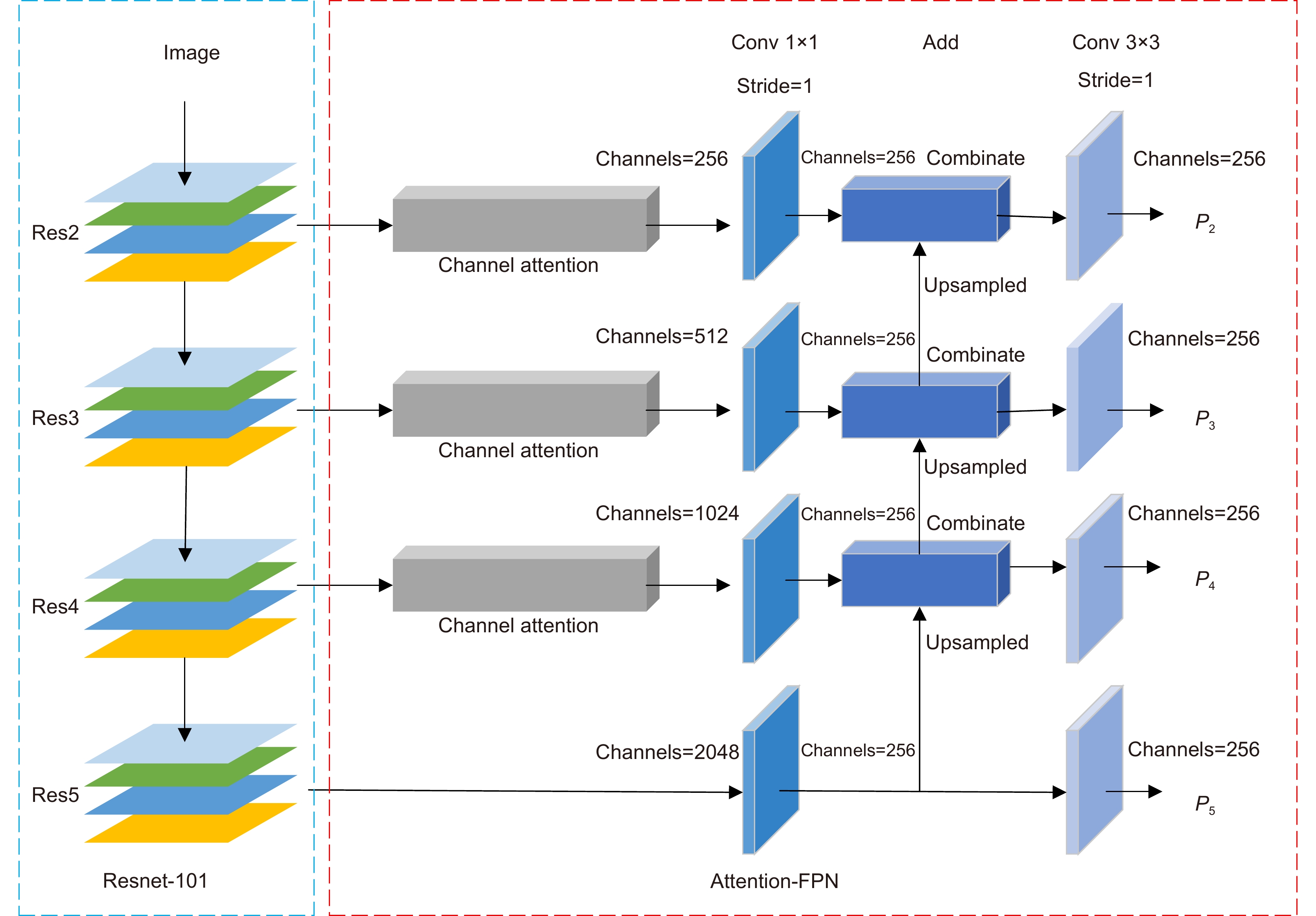
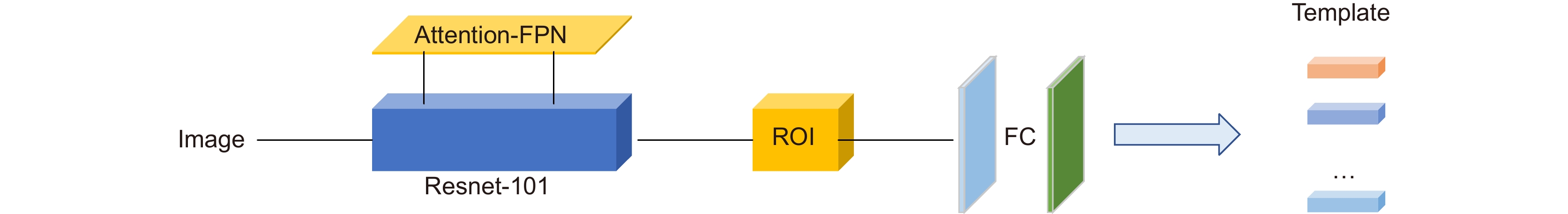
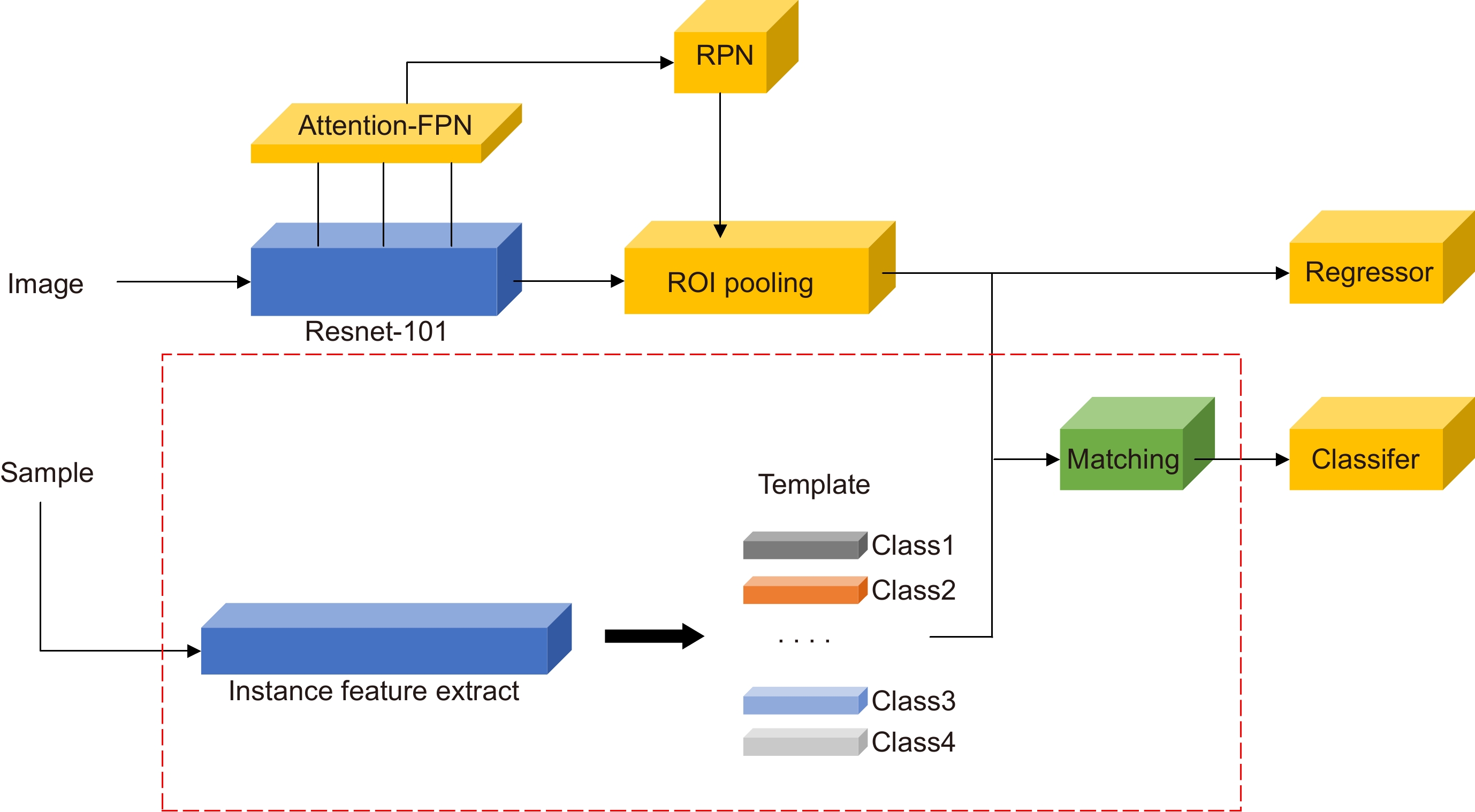
针对少量样本条件下模型易过拟合、目标错检与漏检问题,本文基于TFA (two-stage fine-tuning approach)提出了一种在线推断校准的小样本目标检测框架。该框架设计了一种全新的Attention-FPN网络,通过建模特征通道间的依赖关系选择性融合特征,结合分级冻结的学习机制引导RPN模块提取正确的新类前景目标;同时,构建了一种在线校准模块对样本进行实例分割编码,对众多候选目标进行评分重加权处理,纠正误检和漏检的预测目标。结果表明,所提算法在VOC数据集Novel Set1中,五个任务的平均nAP50提升10.16%,在性能上优于目前的主流算法。
Abstract
Considering that the model is easy to overfit and cause the target misdetection and missed detection under the condition of few samples, this paper propose the few-shot object detection via the online inferential calibration (FSOIC) based on the two-stage fine-tuning approach (TFA). In this framework, a novel Attention-FPN network is designed to selectively fuse the features by modeling the dependencies between the feature channels, and direct the RPN module to extract the correct novel classes of the foreground objects in combination with the hierarchical freezing learning mechanism. At the same time, the online calibration module is constructed to encode and segment the samples, reweight the scores of multiple candidate objects, and correct misclassifying and missing objects. The experimental results in the VOC Novel Set 1 show that the proposed method improves the average nAP50 of the five tasks by 10.16% and performs better than most comparisons.
-
Key words:
- few-shot object detection /
- attention-FPN /
- feature channels /
- hierarchical freezing /
- online calibration /
- RPN
-
Overview
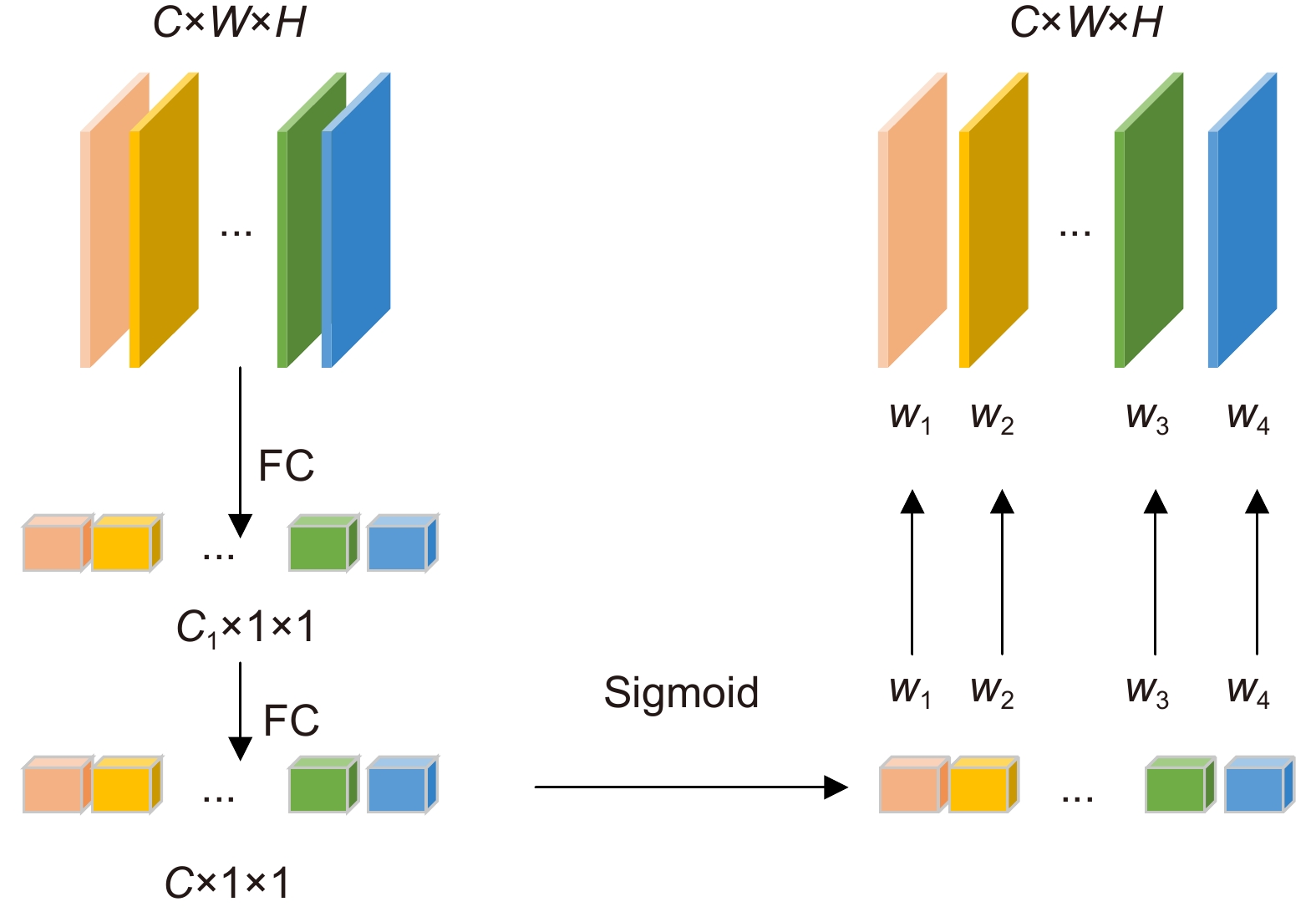
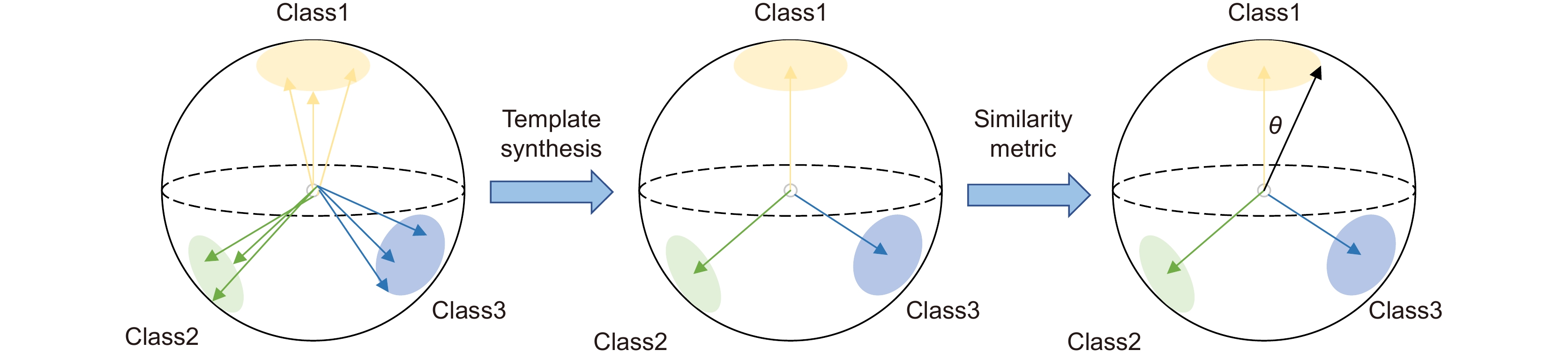
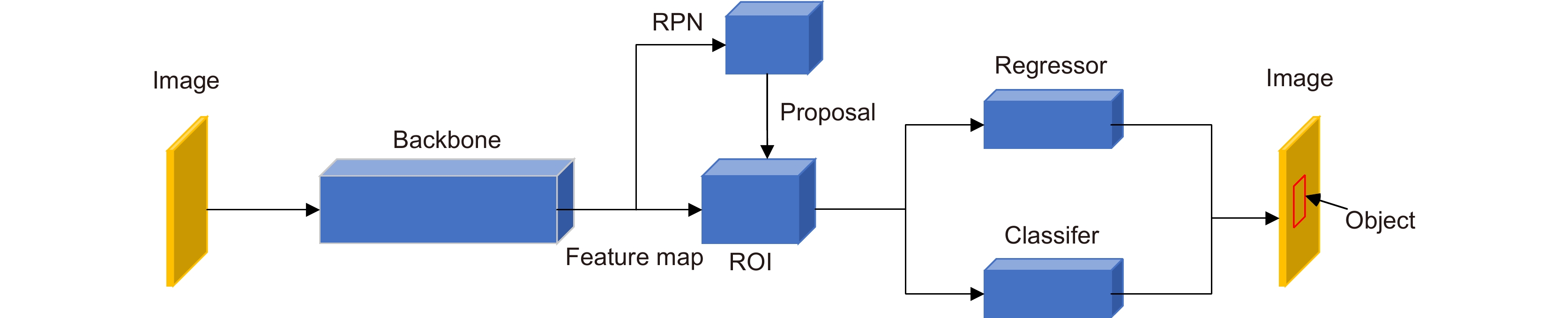
Overview: The success of the deep detection model largely requires a large amount of data for training. Under the condition of fewer training samples, the model is easy to overfit and the detection effect is unsatisfactory. In view of the model that is easy to overfit and cause the target misdetection and missed detection in the absence of training samples, we present the Few-Shot Object Detection via the Online Inferential Calibration (FSOIC) framework by using the Faster R-CNN as detector. Through its excellent detection performance and powerful ability to distinguish the foreground and background, it effectively solves the problem that the single-stage detector cannot locate the target when the training samples are scarce. The bottom-layer features have a larger size and stronger location information, but the lack of global vision leads to weak semantic information, while the top-layer features are the opposite. To make full use of the sample information, the framework is designed to possess a new Attention-FPN network, which selectively the fuses features through modeling the dependencies between the feature channels, and directs the RPN module to extract the correct novel classes of the foreground objects by combined with the hierarchical freezing learning mechanism. The channel attention mechanism compresses the feature map and spreads it into a one-dimensional vector for sigmoid through two fully connected layers. The weight is generated for each feature channel, and the correlation between each channel is established. The weight of the input features is allocated according to the category, and the dependence relationship between each channel is modeled. Due to the closed nature of the neural network, simple feature fusion is uncertain, and it is difficult to fuse the feature map in a satisfactory direction. To the imbalanced sample features, the candidate targets of the new class are scored too low and filtered in the selection of the prediction box, resulting in false detection and missed detection of the detector. We designed the online calibration module that segmentes and encodes the samples, scored the re-weighted the multiple candidate objects, and corrected the misdetected and missed predicted objects. The performance of our detection algorithm performs better than most comparisons. The experimental results in the VOC Novel Set 1 show that the proposed method improves the average nAP50 of the five tasks by 10.16% and performs better than most comparisons.
-

-
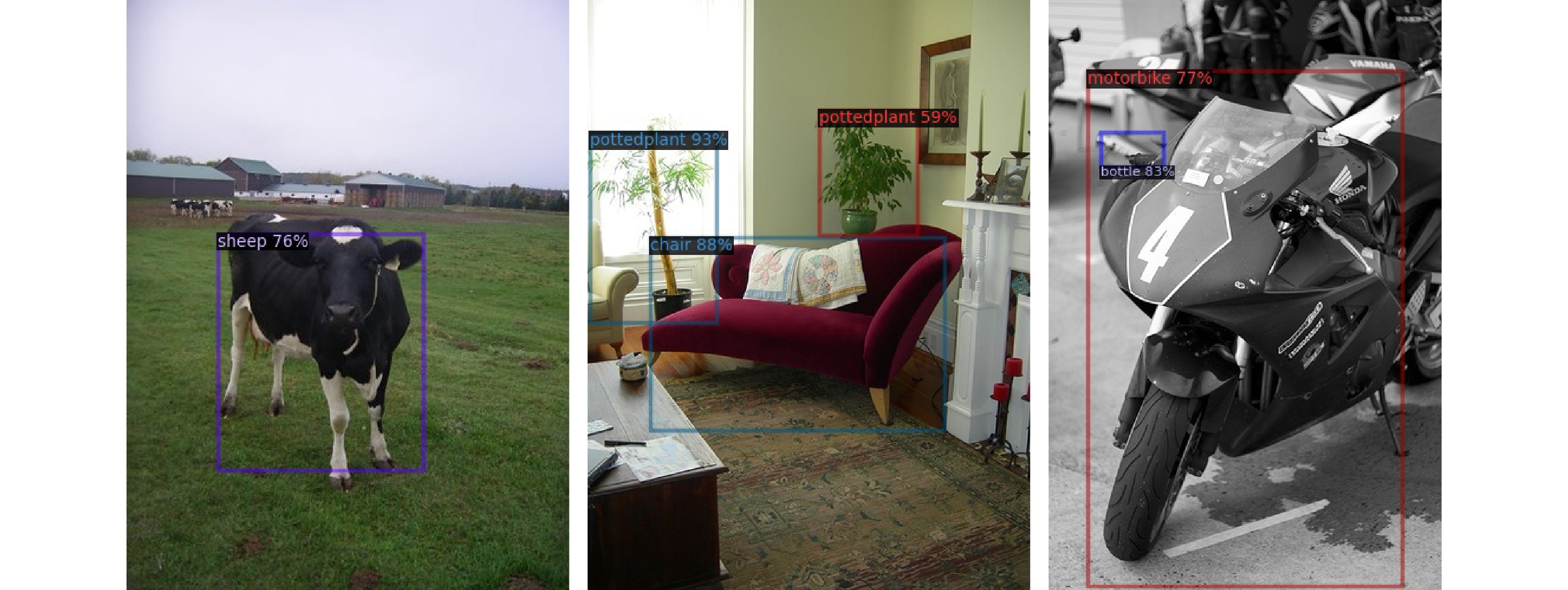
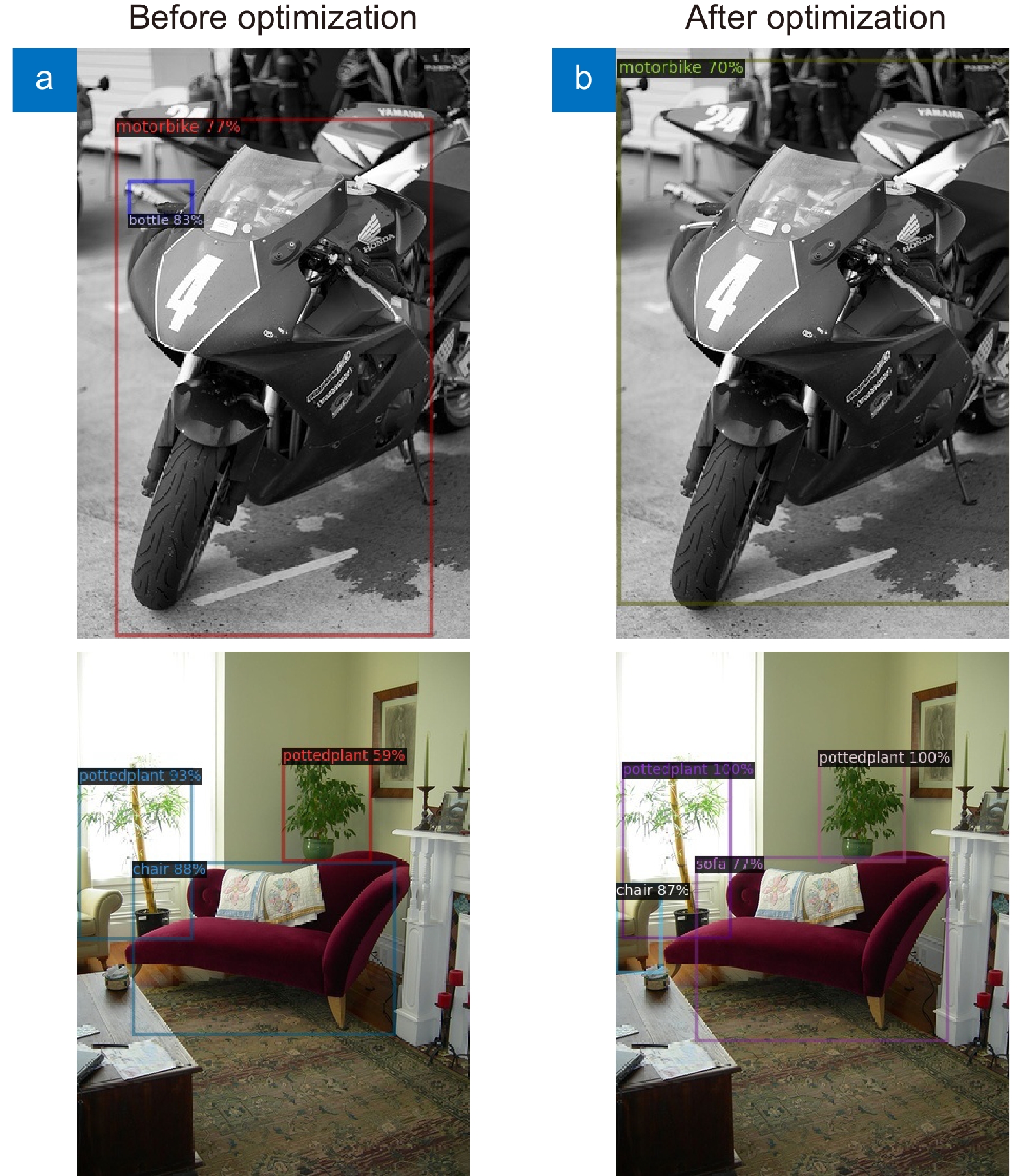
图 10 10 shot 任务下的检测结果。(a) 基于TFA的Faster R-CNN网络检测结果;(b) 使用在线推断校准模块的FasterR-CNN网络检测结果;(c) 使用在线推断校准模块并添加Attention-FPN网络的Faster R-CNN网络检测结果
Figure 10. 10 shot task detection results. (a) Detection results of the Faster R-CNN network based on TFA; (b) Detection results of the Faster R-CNN net work using the online inference calibration module; (c) Detection results of the Faster R-CNN network using the online inference calibration module and adding the Attention-FPN network
表 1 分级冻结机制
Table 1. Hierarchical freezing mechanism
Shot Backbone Regressor Classifer Attention-FPN RPN ROI 1 × √ √ × × × 2 × × × 3 √ × √ 5 √ √ √ 10 √ √ √ 表 2 数据集实验设置
Table 2. Experimental settings of the dataset
Dataset Shot Number of categories Initial learning rate Batch_size Decay ratio of learning rate Number of attenuation Iterations VOC 1 20 0.001 16 0.1 1 6000 2 0.1 1 7000 3 0.1 2 8000 5 0.5 2 9000 10 0.5 2 13000 COCO 10 80 0.001 16 0.3 1 30000 30 40000 表 3 小样本目标检测算法在VOC新类划分集的性能分析比较表
Table 3. Performance analysis and comparison of the few shot object detection algorithm in VOC new class partition sets
Method Year Novel Set 1 Novel Set 2 Novel Set 3 1 2 3 5 10 1 2 3 5 10 1 2 3 5 10 LSTD[26] AAAI 18 8.2 1.0 12.4 29.1 38.5 11.4 3.8 5.0 15.7 31.0 12.6 8.5 15.0 27.3 36.3 MetaDet[40] ICCV 19 18.9 20.6 30.2 36.8 49.6 21.8 23.1 27.8 31.7 43.0 20.6 23.9 29.4 43.9 44.1 Meta R-CNN[15] ICCV 19 19.9 25.5 35.0 45.7 51.5 10.4 19.4 29.6 34.8 45.4 14.3 18.2 27.5 41.2 48.1 RepMet[28] CVPR 19 26.1 32.9 34.4 38.6 41.3 17.2 22.1 23.4 28.3 35.8 27.5 31.1 31.5 34.4 37.2 FSRW[37] ICCV 19 14.8 15.5 26.7 33.9 47.2 15.7 15.3 22.7 30.1 40.5 21.3 25.6 28.4 42.8 45.9 FSDetView[42] ECCV 20 24.2 35.3 42.2 49.1 57.4 21.6 24.6 31.9 37.0 45.7 21.2 30.0 37.2 43.8 49.6 TFA w/cos[44] ICML 20 39.8 36.1 44.7 55.7 56.0 23.5 26.9 34.1 35.1 39.1 30.8 34.8 42.8 49.5 49.8 MPSR[51] ECCV 20 41.7 - 51.4 55.2 61.8 24.4 - 39.2 39.9 47.8 35.6 - 42.3 48.0 49.7 TFA w/cos+Halluc[18] CVPR 21 45.1 44.0 44.7 55.0 55.9 23.2 27.5 35.1 34.9 39.0 30.5 35.1 41.4 49.0 49.3 TIP[41] CVPR 21 27.7 36.5 43.3 50.2 59.6 22.7 30.1 33.8 40.9 46.9 21.7 30.6 38.1 44.5 50.9 FSCE[25] CVPR 21 44.2 43.8 51.4 61.9 63.4 27.3 29.5 43.5 44.2 50.2 37.2 41.9 47.5 54.6 58.5 Retentive R-CNN[45] CVPR 21 42.4 45.8 45.9 53.7 56.1 21.7 27.8 35.2 37.0 40.3 30.2 37.6 43.0 49.7 50.1 Meta-DETR[38] IEEE 22 35.1 49.0 53.2 57.4 62.0 27.9 32.3 38.4 43.2 51.8 34.9 41.8 47.1 54.1 58.2 AGCM[33] IEEE 22 40.3 - - 58.5 59.9 27.5 - - 49.3 50.6 42.1 - - 54.2 58.2 FSOIC(Ours) 46.6 53.4 56.6 62.0 64.5 25.7 30.5 43.8 45.9 53.3 42.4 44.9 49.5 56.6 58.8 表 4 小样本目标检测算法在COCO数据集的性能分析比较
Table 4. Performance analysis and comparison of few shot object detection algorithms in the COCO datasets
表 5 消融实验性能比较
Table 5. Comparison of the ablation experimental performance
Method FPN+4*ROI Finetune RPN Online calibration Attention of channel Novel Set1 1 3 10 TFA w/cos[44] - - - - 39.8 44.7 56.0 FSOIC(Ours) √ × × × 43.6 52.2 62.5 FSOIC(Ours) √ √ × × 44.1 53.0 63.2 FSOIC(Ours) √ √ √ × 45.7 54.2 64.2 FSOIC(Ours) √ × √ √ 46.2 54.9 62.8 FSOIC(Ours) √ √ × √ 44.7 54.0 61.7 FSOIC(Ours) √ √ √ √ 46.6 56.6 64.5 -
参考文献
[1] 陈旭, 彭冬亮, 谷雨. 基于改进YOLOv5s的无人机图像实时目标检测[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(3): 210372. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210372
Chen X, Peng D L, Gu Y. Real-time object detection for UAV images based on improved YOLOv5s[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2022, 49(3): 210372. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210372
[2] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014: 580−587. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.81.
[3] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2015, 37(9): 1904−1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824
[4] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2015: 1440–1448. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.169.
[5] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]//Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015, 91–99.
[6] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 779–788. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.91.
[7] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot MultiBox detector[C]//14th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2016: 21–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2.
[8] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 6517–6525. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.690.
[9] Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 2999−3007. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.324.
[10] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLOv3: an incremental improvement[Z]. arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02767.
[11] Bochkovskiy A, Wang C Y, Liao H Y M. YOLOv4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[Z]. arXiv: 2004.10934, 2020. https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934.
[12] 马梁, 苟于涛, 雷涛, 等. 基于多尺度特征融合的遥感图像小目标检测[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(4): 210363. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210363
Ma L, Gou Y T, Lei T, et al. Small object detection based on multi-scale feature fusion using remote sensing images[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2022, 49(4): 210363. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210363
[13] Bennequin E. Meta-learning algorithms for few-shot computer vision[Z]. arXiv: 1909.13579, 2019. https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.13579.
[14] Behl H S, Baydin A G, Torr P H S. Alpha MAML: adaptive model-agnostic meta-learning[Z]. arXiv: 1905.07435, 2019. https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.07435.
[15] Yan X P, Chen Z L, Xu A N, et al. Meta R-CNN: towards general solver for instance-level low-shot learning[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2019: 9576–9585. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00967.
[16] Wang Y Q, Yao Q M. Few-shot learning: a survey[Z]. arXiv: 1904.05046v1, 2019. https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.05046v1.
[17] Duan Y, Andrychowicz M, Stadie B, et al. One-shot imitation learning[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017: 1087–1098.
[18] Zhang W L, Wang Y X. Hallucination improves few-shot object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021: 13003–13012. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01281.
[19] Zhu J Y, Park T, Isola P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 2242–2251. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.244.
[20] Goodfellow I J, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014: 3672–2680.
[21] Li K, Zhang Y L, Li K P, et al. Adversarial feature hallucination networks for few-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 13467–13476. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01348.
[22] Hui B Y, Zhu P F, Hu Q H, et al. Self-attention relation network for few-shot learning[C]//2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), 2019: 198–203. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMEW.2019.00041.
[23] Hao F S, Cheng J, Wang L, et al. Instance-level embedding adaptation for few-shot learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 100501−100511. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2906665
[24] Schönfeld E, Ebrahimi S, Sinha S, et al. Generalized zero-and few-shot learning via aligned variational autoencoders[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019: 8239–8247. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00844.
[25] Sun B, Li B H, Cai S C, et al. FSCE: few-shot object detection via contrastive proposal encoding[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021: 7348–7358. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00727.
[26] Chen H, Wang Y L, Wang G Y, et al. LSTD: a low-shot transfer detector for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Thirtieth Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference and Eighth AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, 2018: 346.
[27] Hu H Z, Bai S, Li A X, et al. Dense relation distillation with context-aware aggregation for few-shot object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021: 10180–10189. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01005.
[28] Karlinsky L, Shtok J, Harary S, et al. RepMet: representative-based metric learning for classification and few-shot object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 5197–5206. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00534.
[29] Jiang W, Huang K, Geng J, et al. Multi-scale metric learning for few-shot learning[J]. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol, 2021, 31(3): 1091−1102. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.2995754
[30] Sung F, Yang Y X, Zhang L, et al. Learning to compare: relation network for few-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 1199–1208. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00131.
[31] Tao X Y, Hong X P, Chang X Y, et al. Few-shot class-incremental learning[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 12180–12189. .
[32] Wang Y, Wu X M, Li Q M, et al. Large margin few-shot learning[Z]. arXiv: 1807.02872, 2018. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1807.02872.
[33] Agarwal A, Majee A, Subramanian A, et al. Attention guided cosine margin to overcome class-imbalance in few-shot road object detection[C]//2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops (WACVW), 2022: 221–230. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACVW54805.2022.00028.
[34] Nichol A, Achiam J, Schulman J. On first-order meta-learning algorithms[Z]. arXiv: 1803.02999, 2018. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.02999.
[35] Li Z G, Zhou F W, Chen F, et al. Meta-SGD: learning to learn quickly for few-shot learning[Z]. arXiv: 1707.09835, 2017. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.09835.
[36] Ravi S, Larochelle H. Optimization as a model for few-shot learning[C]//5th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2016.
[37] Kang B Y, Liu Z, Wang X, et al. Few-shot object detection via feature reweighting[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019: 8419–8428. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00851.
[38] Zhang G J, Luo Z P, Cui K W, et al. Meta-DETR: image-level few-shot detection with inter-class correlation exploitation[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3195735.
[39] 马雯, 于炯, 王潇, 等. 基于改进Faster R-CNN的垃圾检测与分类方法[J]. 计算机工程, 2021, 47(8): 294−300. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0058258
Ma W, Yu J, Wang X, et al. Garbage detection and classification method based on improved faster R-CNN[J]. Comput Eng, 2021, 47(8): 294−300. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0058258
[40] Wang Y X, Ramanan D, Hebert M. Meta-learning to detect rare objects[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019: 9924–9933. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.01002.
[41] Li A X, Li Z G. Transformation invariant few-shot object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021: 3093–3101. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00311.
[42] Xiao Y, Marlet R. Few-shot object detection and viewpoint estimation for objects in the wild[C]//16th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2020: 192−210. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58520-4_12.
[43] Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 936−944. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.106.
[44] Wang X, Huang T, Gonzalez J, et al. Frustratingly simple few-shot object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2020: 9919–9928.
[45] Fan Z B, Ma Y C, Li Z M, et al. Generalized few-shot object detection without forgetting[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021: 4525−4534. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00450.
[46] Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Henriques J F, et al. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking[C]//14th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2016: 850–865. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48881-3_56.
[47] Li B, Yan J J, Wu W, et al. High performance visual tracking with Siamese region proposal network[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 8971−8980. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00935.
[48] Zhu Z, Wang Q, Li B, et al. Distractor-aware Siamese networks for visual object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2018: 103–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01240-3_7.
[49] 赵春梅, 陈忠碧, 张建林. 基于卷积网络的目标跟踪应用研究[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(1): 180668. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.180668
Zhao C M, Chen Z B, Zhang J L. Research on target tracking based on convolutional networks[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(1): 180668. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.180668
[50] 赵春梅, 陈忠碧, 张建林. 基于深度学习的飞机目标跟踪应用研究[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(9): 180261. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180261
Zhao C M, Chen Z B, Zhang J L. Application of aircraft target tracking based on deep learning[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(9): 180261. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180261
[51] Wu J X, Liu S T, Huang D, et al. Multi-scale positive sample refinement for few-shot object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2020: 456–472. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58517-4_27.
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: