-
摘要
针对移动机器人在未知环境感知过程中对三维点云快速聚类分割的需求,提出一种基于图像信息约束的三维激光点云聚类方法。首先通过点云预处理获取有效的三维环境信息,采用RANSAC方法进行地面点云的分割剔除。其次传感器数据在完成时空配准后引入YOLOv5目标检测算法,对三维点云K-means聚类算法进行改进,利用二维图像目标物的检测框范围约束三维点云,减少非目标物的干扰;基于图像检测信息实现点云聚类算法的参数初始化;采用类内异点剔除法优化聚类结果。最后搭建移动机器人硬件平台,对箱体进行测试,实验结果表明,本文方法的聚类准确率和聚类时间分别为86.96%和23 ms,可用于移动机器人导航避障、自主搬运等领域。
Abstract
Aiming at the requirement of fast clustering and segmentation of 3D point clouds for mobile robots in the process of perception of unknown environments, a 3D laser point cloud clustering method based on image information constraints is proposed. Firstly, the effective 3D environment information is obtained through point cloud preprocessing, and the RANSAC method is used to segment and eliminate the ground point cloud. Secondly, the sensor data is introduced into the YOLOv5 target detection algorithm after completing the spatiotemporal registration, and the K-means clustering algorithm of the 3D point cloud is improved. The detection frame range of the 2D image target is used to constrain the 3D point cloud and reduce the interference of non-target objects. The parameter initialization of the point cloud clustering algorithm is realized based on the image detection information. The clustering results are optimized by the intra-class outlier elimination method. Finally, the mobile robot hardware platform is built, and the box is tested. The experimental results show that the clustering accuracy and clustering time of the method in this paper are 86.96% and 23 ms, respectively, which can be used in mobile robot navigation and obstacle avoidance, autonomous handling, and other fields.
-
Key words:
- moving robot /
- LiDAR /
- target detection /
- point cloud clustering
-
Overview
Overview: 3D laser point cloud clustering recognition is one of the important ways for mobile robots to perceive the environment. The main purpose is to obtain the semantics, position, size and attitude of the target in three-dimensional space. How to use sensor data to quickly and effectively extract target object information from complex environments containing ground point clouds is of great research significance.
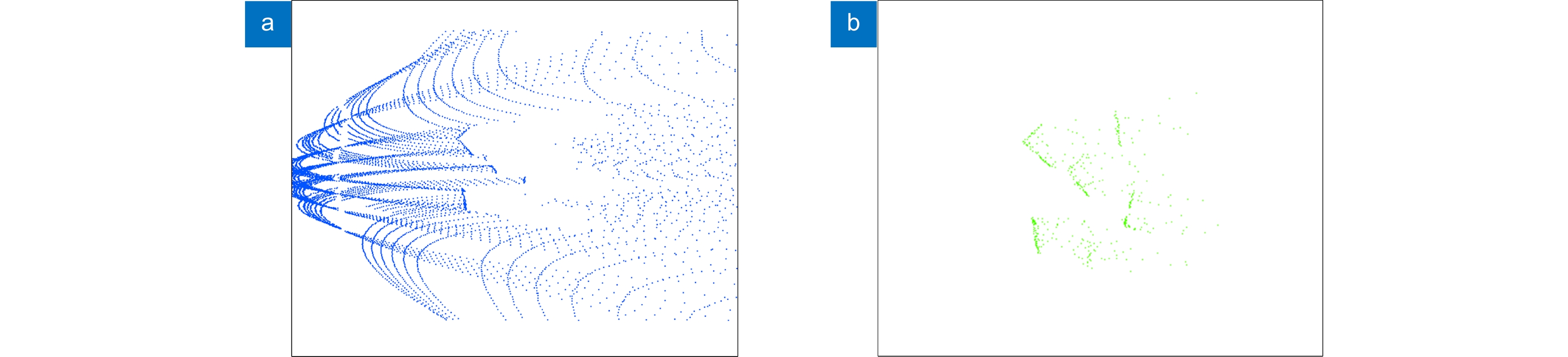
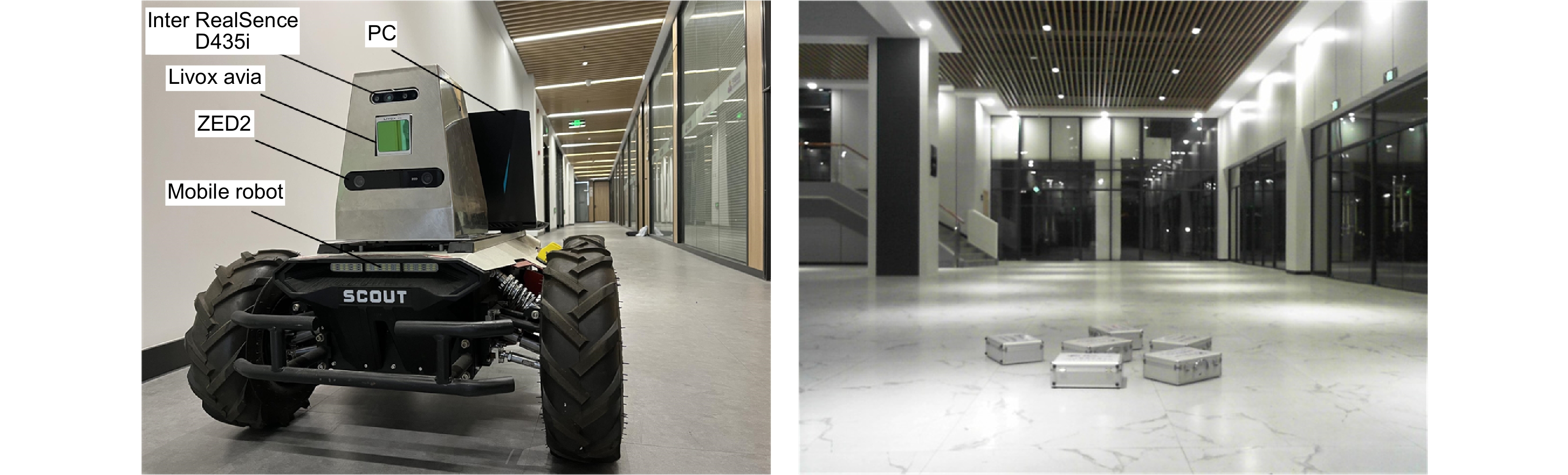
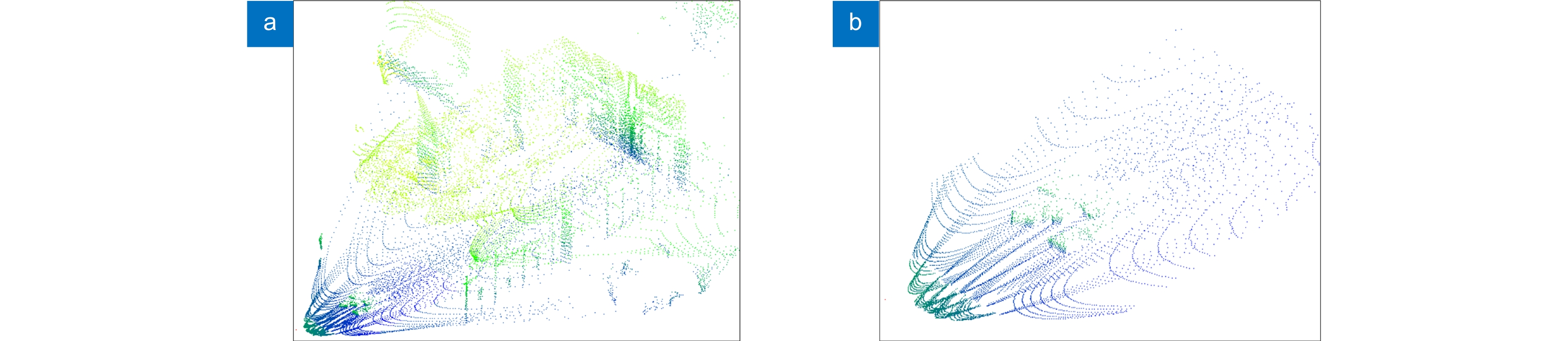
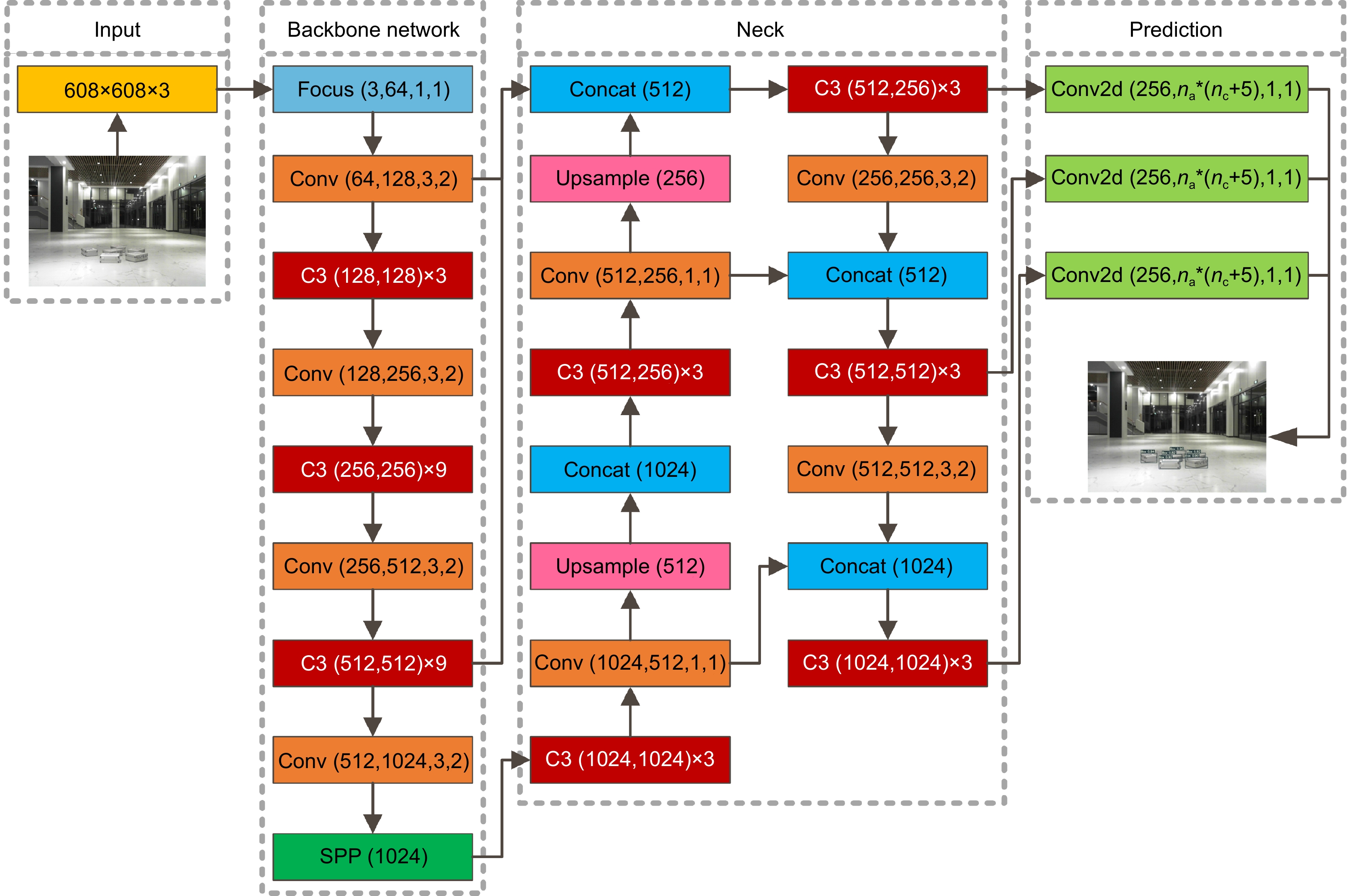
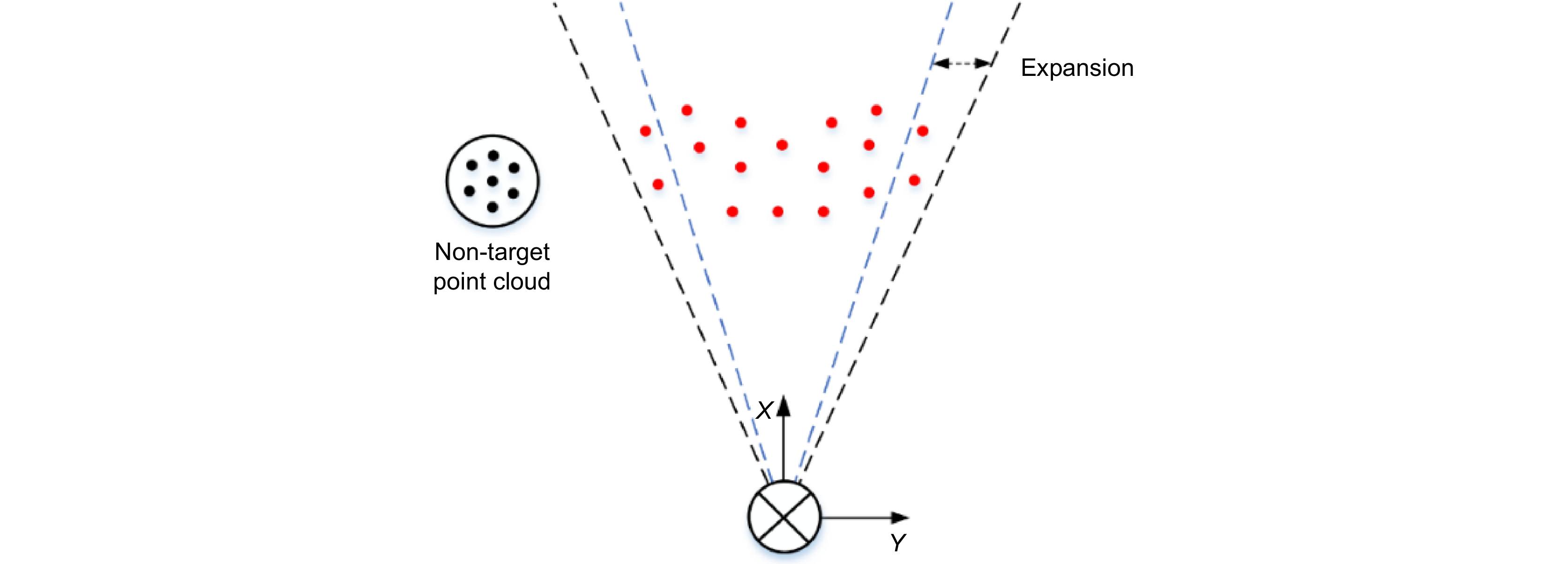
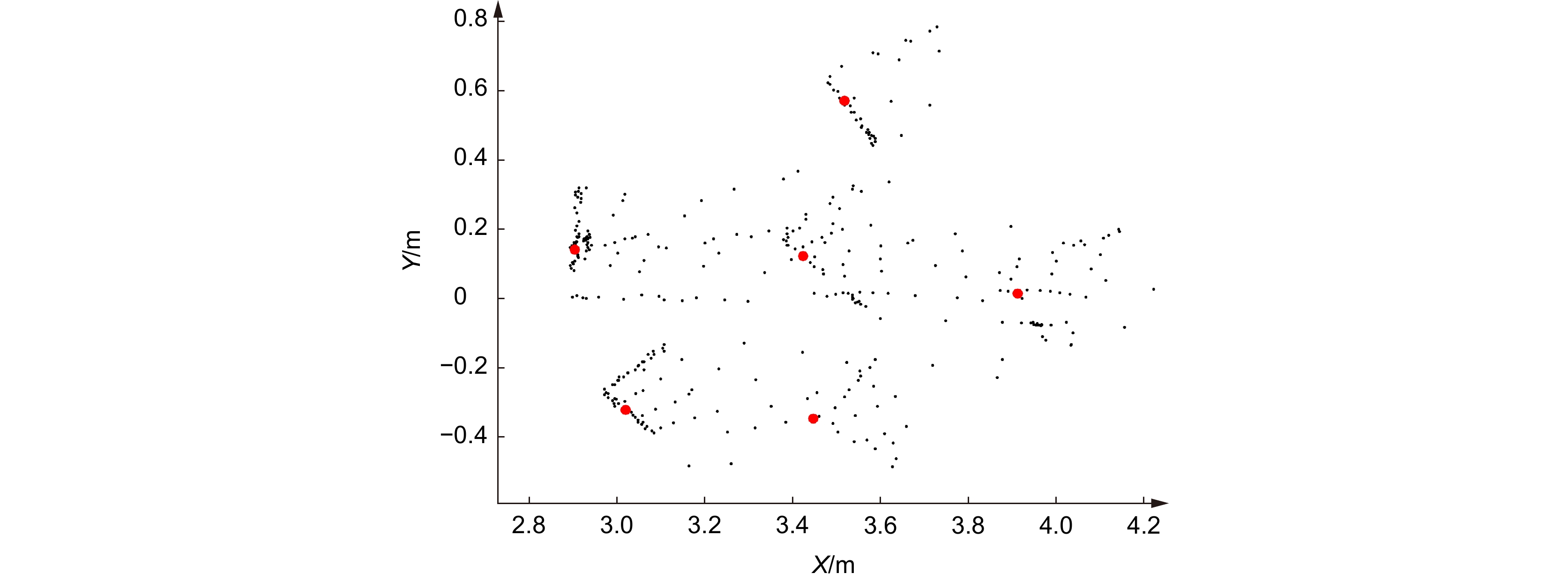
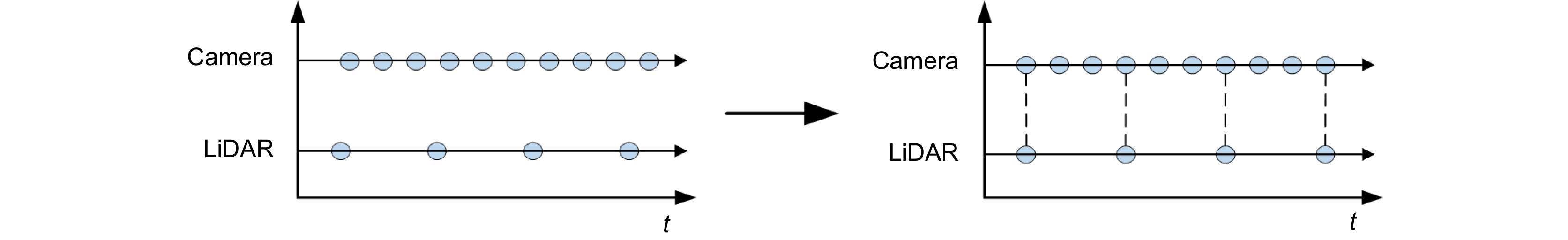
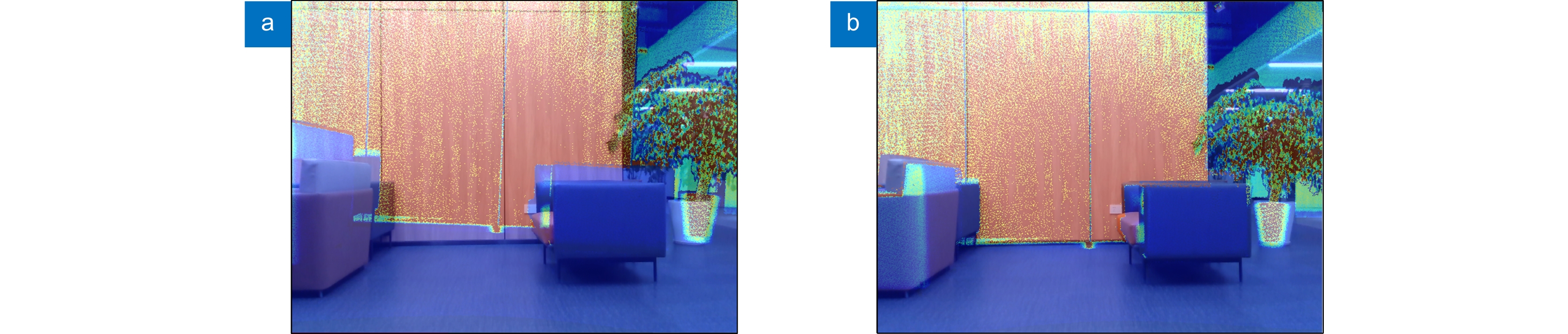
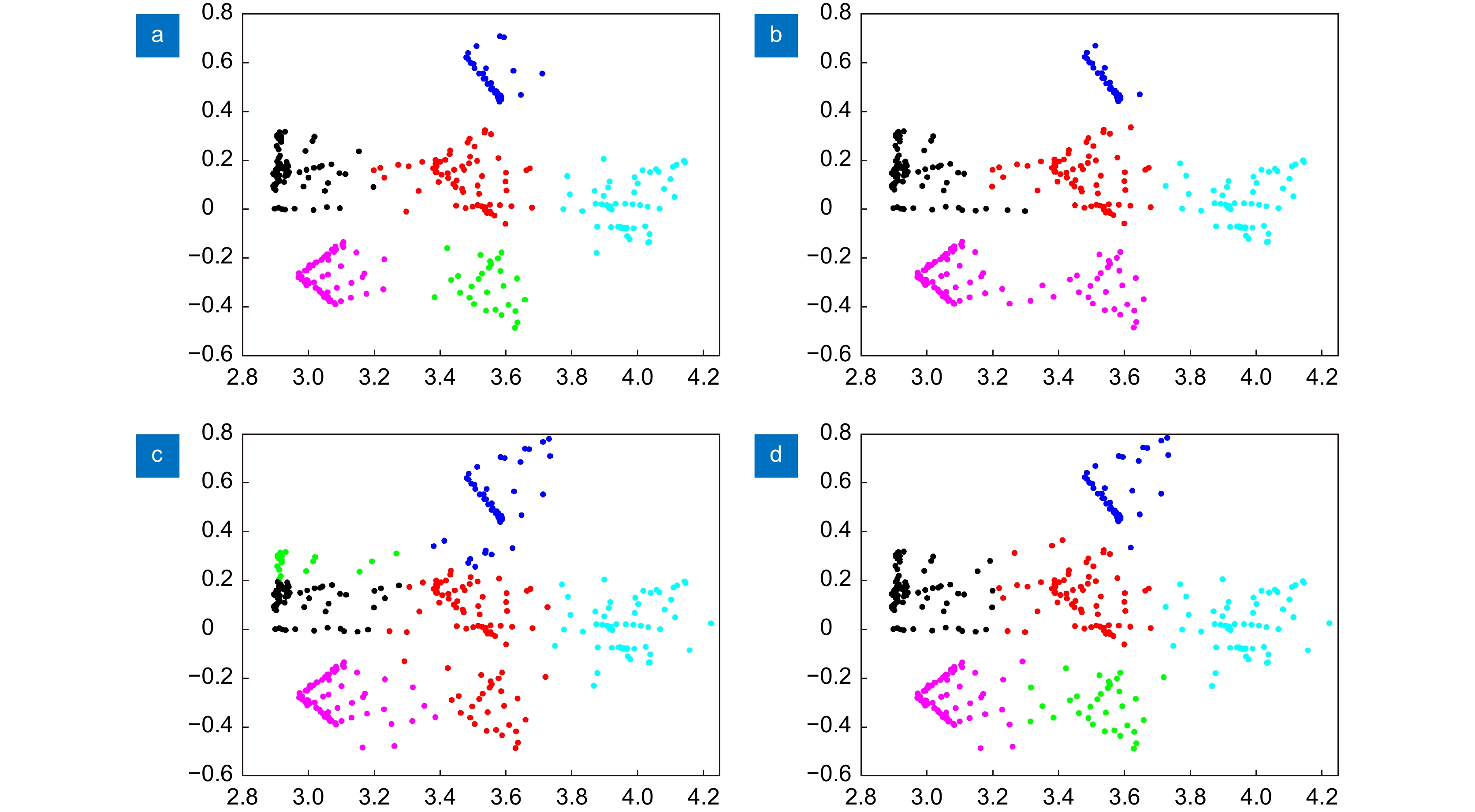
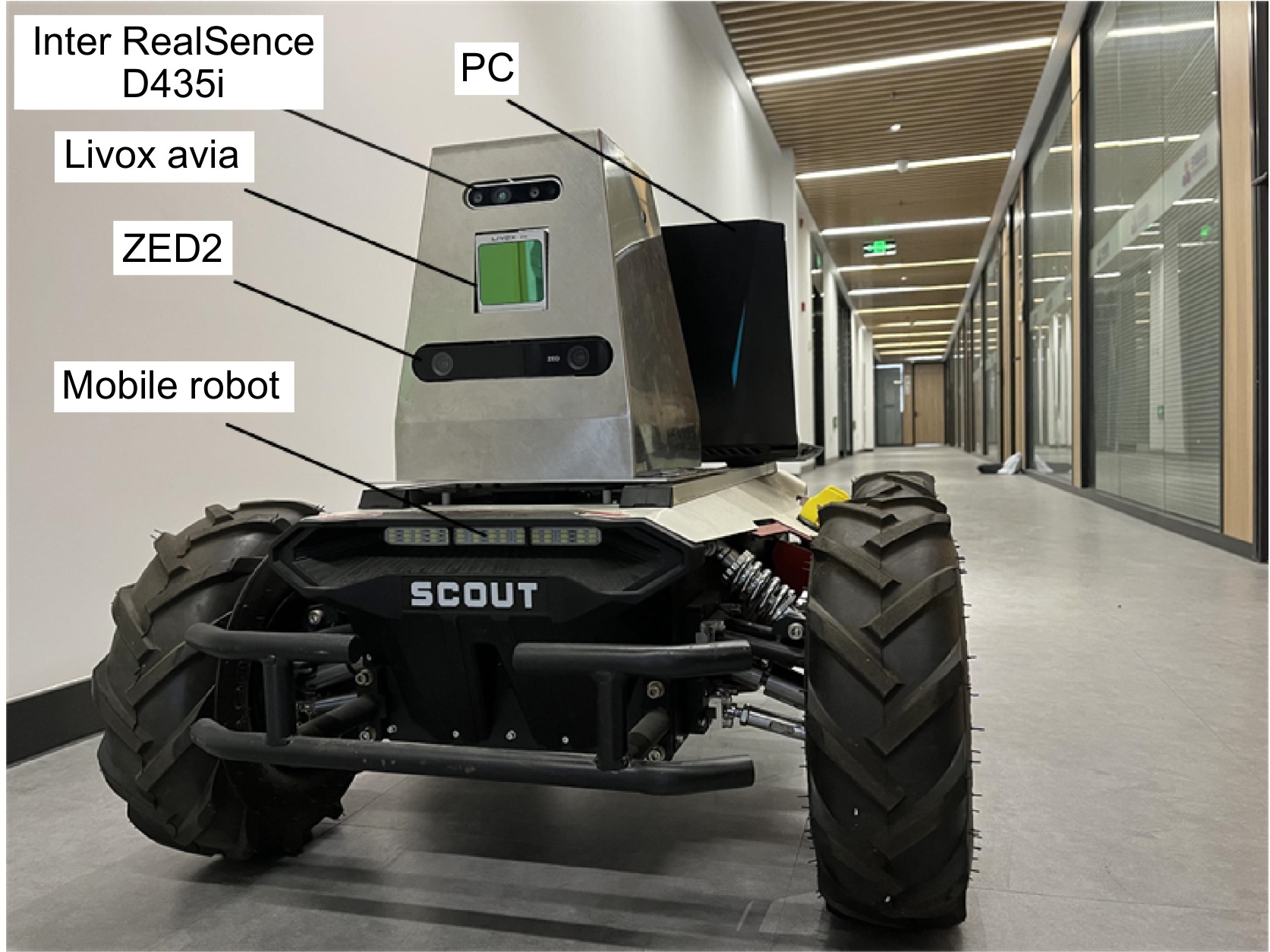
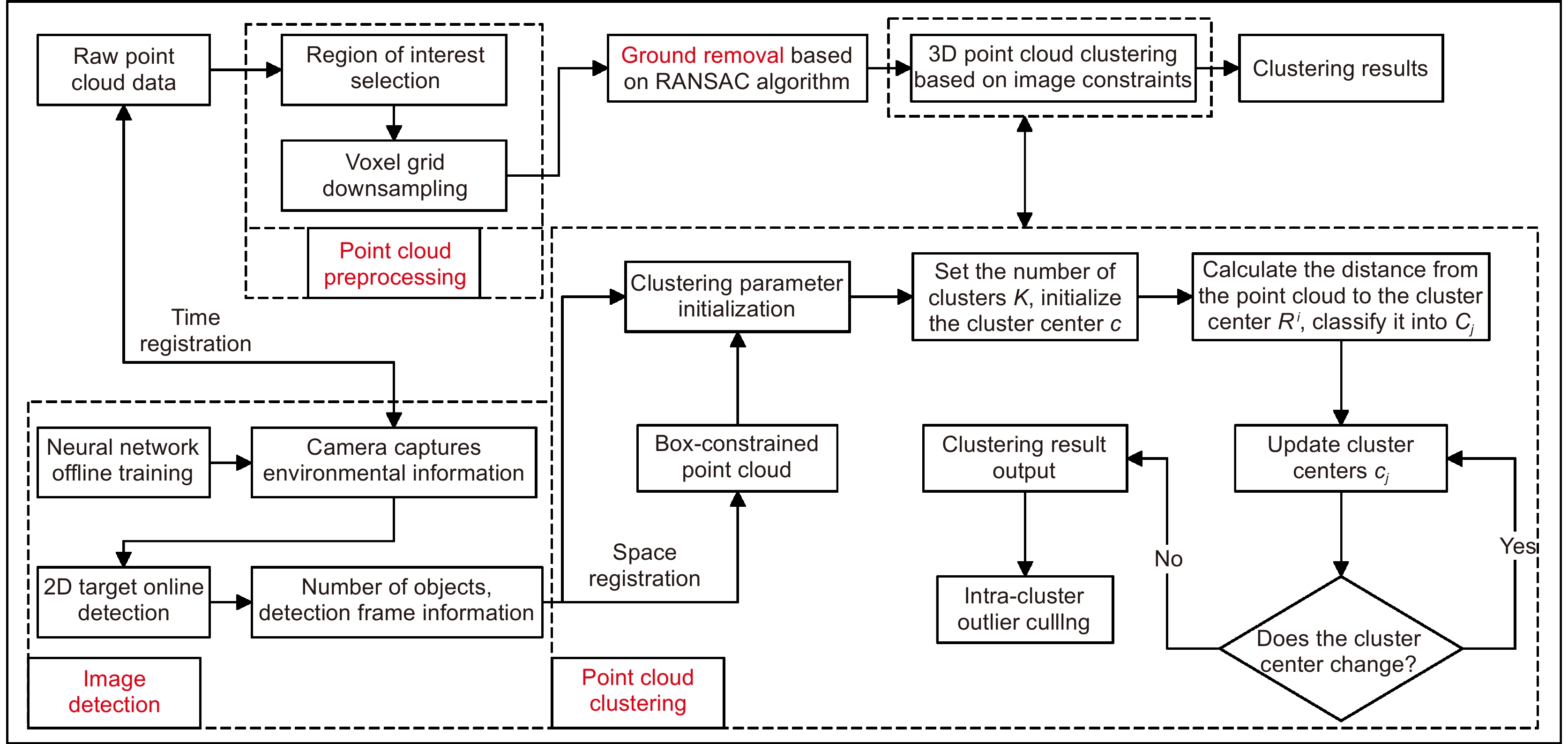
This paper proposes a 3D laser point cloud clustering method based on image information constraints to meet the needs of fast clustering and segmentation of 3D point clouds for mobile robots in the process of perception of unknown environments. First of all, considering the huge amount of laser point cloud data, point cloud preprocessing operations of the region of interest selection and voxel grid down sampling filtering are adopted. To prevent the ground point cloud from being falsely detected as valid data, the ground point cloud is segmented and culled by the RANSAC method. In order to construct the spatial mapping relationship of the lidar and camera, the internal and external parameters are obtained by Zhang’s calibration method and the pixel-level external parameter self-calibration method without a calibration board, and the calculated parameters enable spatial synchronization of point clouds and images. The time nearest neighbor matching method is adopted to complete the multi-sensor time registration based on the lidar timestamp. Secondly, the YOLOv5 target detection algorithm is introduced to improve the K-means clustering algorithm of the 3D point cloud. The detection frame range of the 2D image target is used to constrain the 3D point cloud to reduce the interference of non-target objects. The parameter initialization of the point cloud clustering algorithm is realized based on the image detection information, which effectively solves the problem of poor clustering effect caused by the difficulty in determining the initial parameter setting of the traditional 3D point cloud K-means clustering, and then uses the intra-class outlier elimination method to optimize the clustering results. Finally, we build a mobile robot hardware platform and test the box that are compared with DBSCAN, Euclidean Clustering, K-means, and K-means++ algorithms. In the case of densely arranged boxes, it has better detection robustness.
After testing with 50 frames of random data, the experimental results show that the clustering accuracy and clustering time of this method are 86.96% and 23 ms, respectively, which are better than other algorithms, and can be used in mobile robot navigation and obstacle avoidance, autonomous handling, and other fields.
-

-
表 1 内参标定结果
Table 1. Calibration results of internal parameters
fx fy cx cy k1 k2 p1 p2 K 657.58 660.12 296.12 246.35 — — — — D — — — — 0.238809 −0.643802 0.001786 −0.024125 表 2 外参标定结果
Table 2. Calibration results of external parameters
x/mm y/mm z/mm Roll/rad Pitch/rad Yaw/rad T 59.94 52.76 −14.46 −1.540 0.031 −1.581 表 3 分布间距对算法影响
Table 3. Affects of distribution spacing on the algorithm
Distribution spacing/cm My-method K-means K-means++ Euclidean Clustering DBSCAN $ \omega $ $ \eta $ $ \omega $ $ \eta $ $ \omega $ $ \eta $ $ \omega $ $ \eta $ $ \omega $ $ \eta $ 2 ✓ — ✓ 0.44 ✓ 0.72 ✗ — ✗ — 5 ✓ — ✓ 0.46 ✓ 0.70 ✗ — ✗ — 10 ✓ — ✓ 0.72 ✓ 0.88 ✗ — ✓ — 15 ✓ — ✓ 0.62 ✓ 0.74 ✓ — ✓ — 20 ✓ — ✓ 0.54 ✓ 0.70 ✓ — ✓ — 表 4 多种算法性能对比
Table 4. Performance comparison of multiple algorithms
Algorithm Number of correct
divisions/numberClustering
accuracy/%Average time
spent/msAverage number of
iterations/numberDBSCAN 258 70.11 3.625 — Euclidean Clustering 262 71.20 2.517 — K-means 210 57.07 1.951 12 K-means++ 222 60.33 3.373 10 My-method 320 86.96 1.106 6 -
参考文献
[1] 姬长英, 周俊. 农业机械导航技术发展分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2014, 45(9): 44−54. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2014.09.008
Ji C Y, Zhou J. Current situation of navigation technologies for agricultural machinery[J]. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach, 2014, 45(9): 44−54. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2014.09.008
[2] 赵佳琦, 周勇, 何欣, 等. 基于深度学习的点云分割研究进展分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(12): 4426−4440. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210972
Zhao J Q, Zhou Y, He X, et al. Research progress analysis of point cloud segmentation based on deep learning[J]. J Electron Inf Technol, 2022, 44(12): 4426−4440. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210972
[3] Su H, Maji S, Kalogerakis E, et al. Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2015: 945–953. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.114.
[4] Maturana D, Scherer S. VoxNet: a 3D convolutional neural network for real-time object recognition[C]//2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2015: 922–928. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2015.7353481.
[5] Qi C R, Su H, Mo K C, et al. PointNet: deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 77–85. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.16.
[6] Qi C R, Yi L, Su H, et al. PointNet++: deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017: 5105–5114.
[7] 金立生, 贺阳, 王欢欢, 等. 基于自适应阈值DBSCAN的路侧点云分割算法[J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(7): 987−996. doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2022.07.005
Jin L S, He Y, Wang H H, et al. Point cloud segmentation algorithm based on adaptive threshold DBSCAN for roadside LiDAR[J]. Automot Eng, 2022, 44(7): 987−996. doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2022.07.005
[8] 王子洋, 李琼琼, 张子蕴, 等. 应用于无人驾驶车辆的点云聚类算法研究进展[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 2021, 43(3): 274−285. doi: 10.16507/j.issn.1006-6055.2020.12.025.
Wang Z Y, Li Q Q, Zhang Z Y, et al. Research progress of unmanned vehicle point cloud clustering algorithm[J]. World Sci-Tech R& D, 2021, 43(3): 274−285. doi: 10.16507/j.issn.1006-6055.2020.12.025.
[9] 魏玉锋, 梁冬泰, 梁丹, 等. 基于多模态信息的机器人视觉识别与定位研究[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(2): 170650. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170650
Wei Y F, Liang D T, Liang D, et al. Visual identification and location algorithm for robot based on the multimodal information[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2018, 45(2): 170650. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170650
[10] 杨俊闯, 赵超. K-Means聚类算法研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2019, 55(23): 7−14,63. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1908-0347
Yang J C, Zhao C. Survey on K-means clustering algorithm[J]. Comput Eng Appl, 2019, 55(23): 7−14,63. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1908-0347
[11] 李沛婷, 赵庆展, 田文忠, 等. 结合无人机载LiDAR点云法向量的K-means++聚类精简[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2020, 32(2): 103−110. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2020.02.14
Li P T, Zhao Q Z, Tian W Z, et al. Point cloud simplification method combining K-means++ clustering with UAV LiDAR point cloud normal vectors[J]. Remote Sens Land Resour, 2020, 32(2): 103−110. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2020.02.14
[12] 刘亚坤, 李永强, 刘会云, 等. 基于改进RANSAC算法的复杂建筑物屋顶点云分割[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2021, 23(8): 1497−1507. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2021.200742
Liu Y K, Li Y Q, Liu H Y, et al. An improved RANSAC algorithm for point cloud segmentation of complex building roofs[J]. J Geo-Inf Sci, 2021, 23(8): 1497−1507. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2021.200742
[13] 潘济宇, 张水强, 苏志龙, 等. 基于数字图像相关的水下螺旋桨三维变形测量[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41(12): 1212001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1212001
Pan J Y, Zhang S Q, Su Z L, et al. Measuring three-dimensional deformation of underwater propellers based on digital image correlation[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2021, 41(12): 1212001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1212001
[14] Yuan C J, Liu X Y, Hong X P, et al. Pixel-level extrinsic self calibration of high resolution LiDAR and camera in targetless environments[J]. IEEE Robot Autom Lett, 2021, 6(4): 7517−7524. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3098923
[15] 许德刚, 王露, 李凡. 深度学习的典型目标检测算法研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(8): 10−25. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2012-0449
Li D G, Wang L, Li F. Review of typical object detection algorithms for deep learning[J]. Comput Eng Appl, 2021, 57(8): 10−25. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2012-0449
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: