-
摘要:
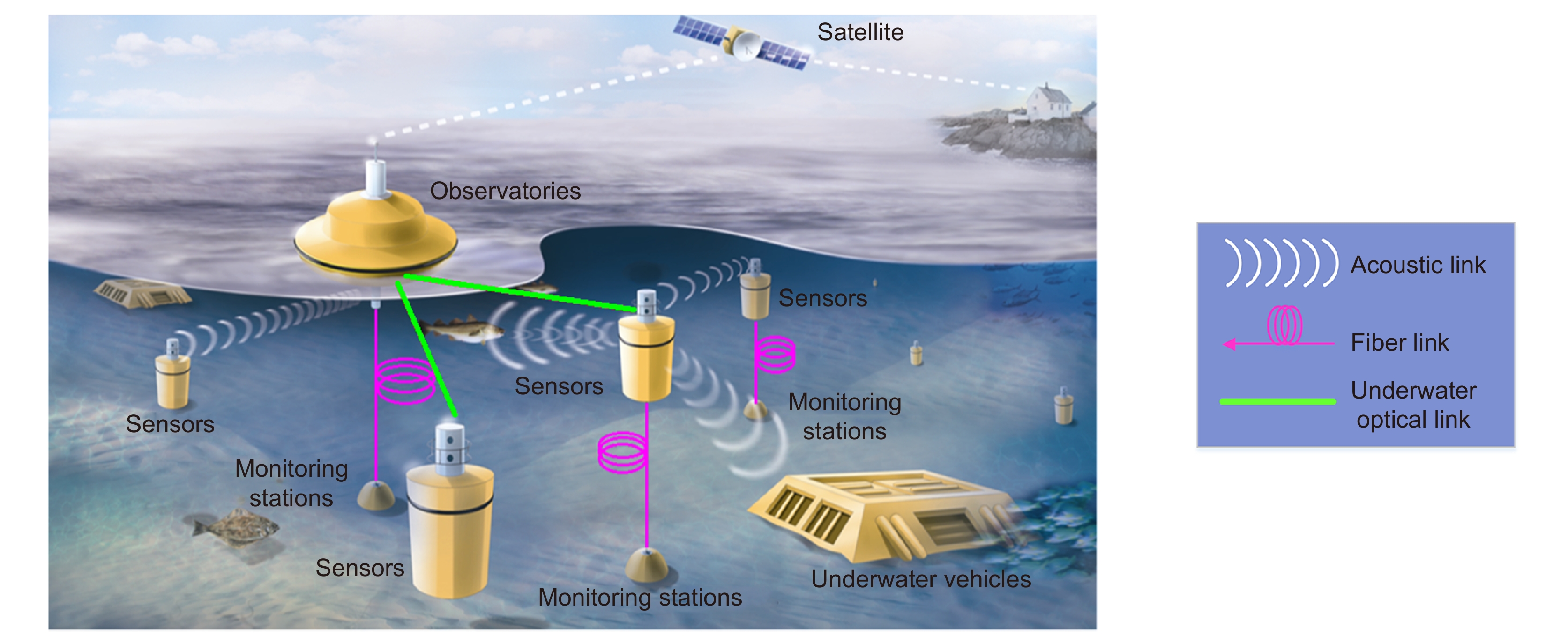
相比于传统基于声纳、光缆的水下频率传递技术,水下激光频率传递技术具有更高的灵活性。本文首先介绍了水下激光频率传递技术的背景与意义,同时简要展示了国内外科研机构在水下激光频率传递方面的成果。然后,从理论上描述了水下链路特性的时域和频域特性,前者基于水体折射率微扰,后者基于柯尔莫哥洛夫大气湍流模型。接着,重点报道了电子科技大学在该领域的研究进展,包括电学相位补偿技术、光学相位补偿技术和多址频率分发技术。最后总结了这三类水下频率传递实验,对课题组在水下激光频率传递方面将要进行的工作进行了展望。作为具有较大潜力的水下频率传递技术,未来水下激光频率传递技术将在相关应用中发挥重要作用。
Abstract:Inspired by underwater wireless optical communication, laser-based underwater frequency transfer technology extends frequency transfer and dissemination from fiber links and free-space links to underwater links and shows greater potential for applications. Compared with traditional underwater frequency transfer technologies (sonar, fiber links), laser-based underwater frequency transfer technology is more flexible and avoids the multipath effect and high latency. In the future, this technology is expected to contribute to the applications of underwater navigation and sensing, distributed observation networks, tracking and positioning systems, etc. This paper first introduces the background and significance of the underwater laser-based frequency transfer technique, and briefly shows the achievements of domestic and foreign scientific research institutions in underwater laser-based frequency transfer. Next, the paper presents the time domain and frequency domain descriptions of underwater link properties, in which the former is based on the refractive index perturbation of the water column and the latter is based on the Kolmogorov atmospheric turbulence model. Then, the research results of the University of Electronic Science and Technology in laser-based underwater frequency transfer are reported, including the electrical phase compensation technique, the optical phase compensation technique, and the multiple-access frequency dissemination technique. Finally, the three laser-based underwater frequency transfer experiments are summarized, and the future works of our group in laser-based underwater frequency transfer have been prospected. As a promising underwater frequency transfer technology, laser-based underwater frequency transfer technology will play a crucial role in relevant applications in the future.
-

-
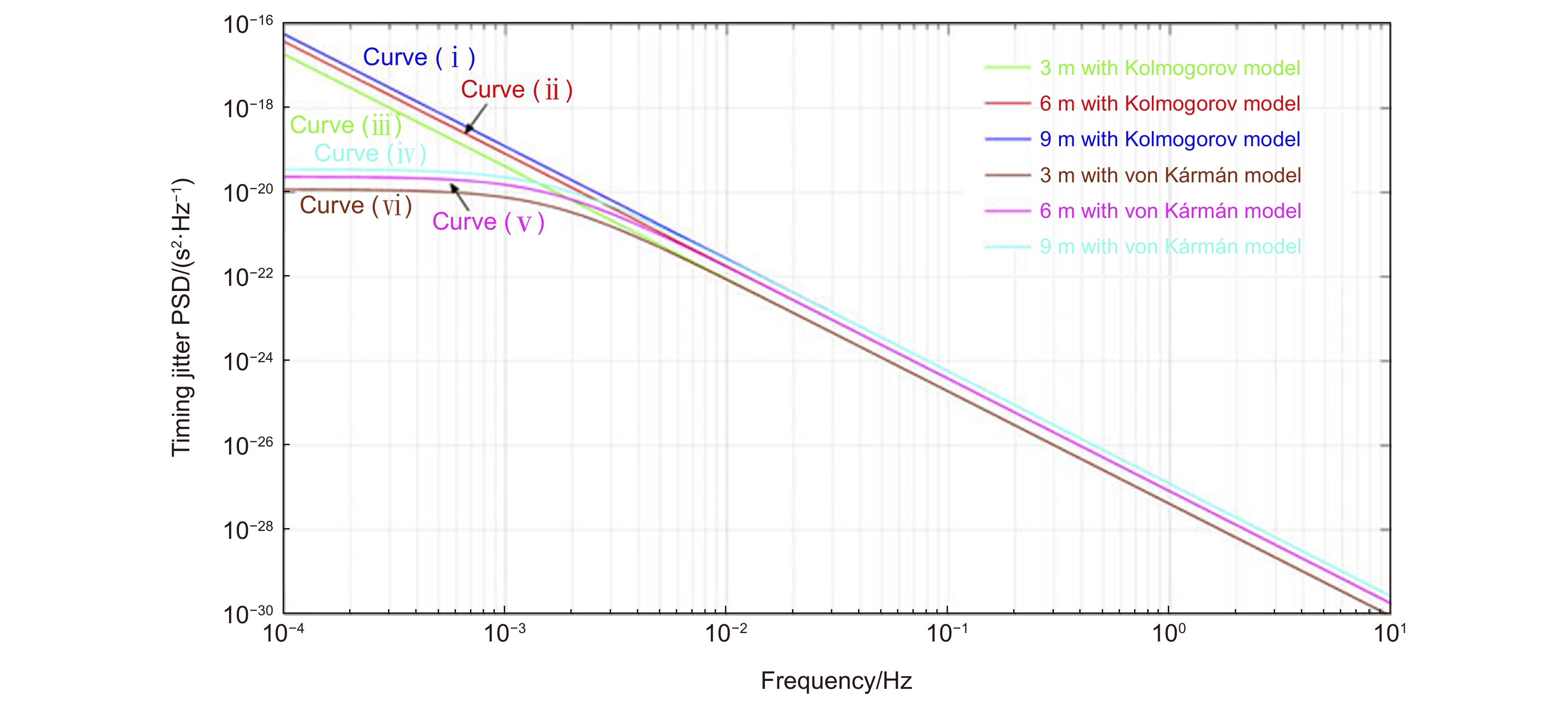
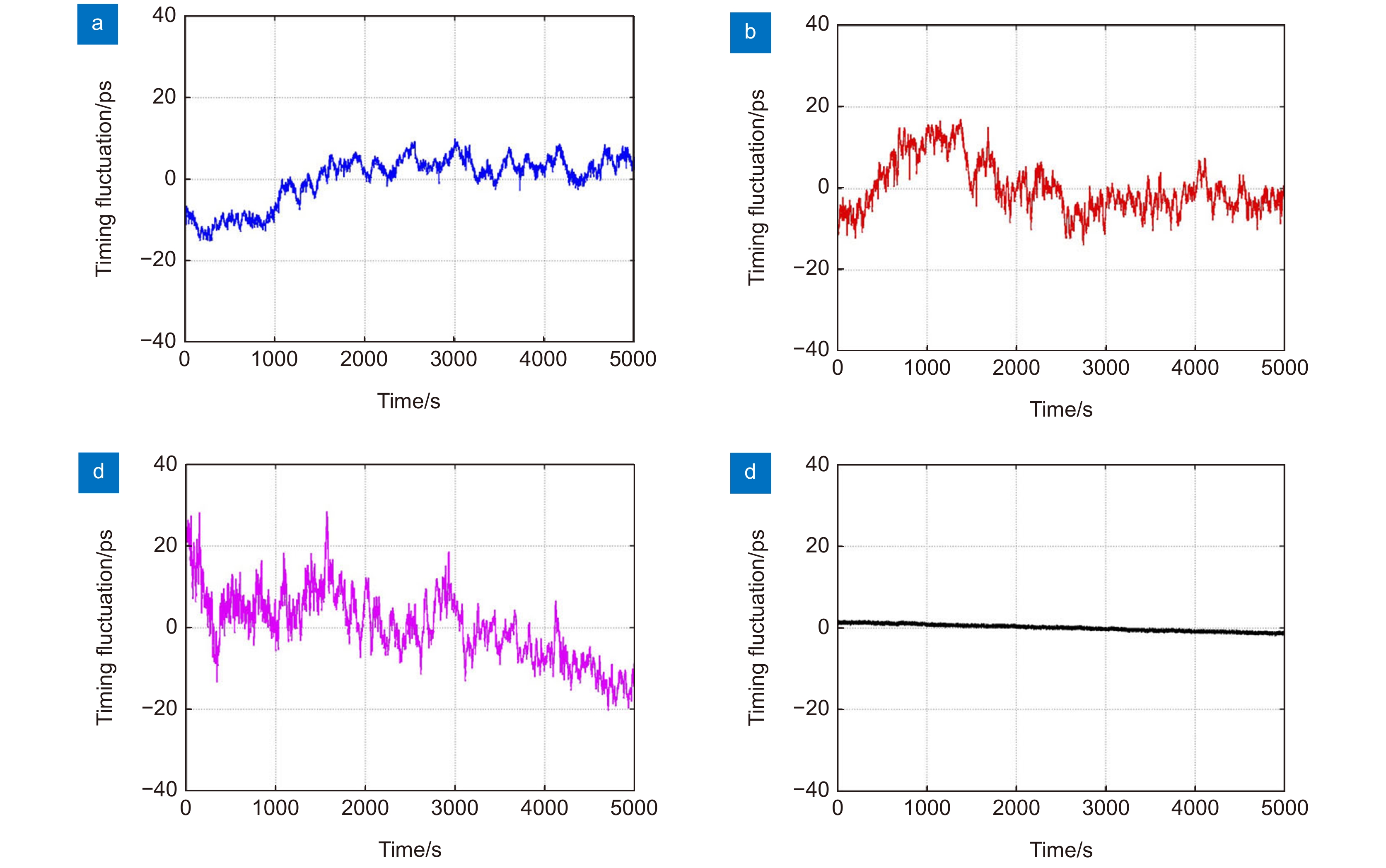
图 4 定时抖动曲线[49]。(a) 链路长度为3 m;(b) 链路长度为6 m;(c) 链路长度为9 m;(d) 测量本底
Figure 4. Timing fluctuation curves [49]. (a) Timing fluctuation of the underwater transmission link of 3 m; (b) Timing fluctuation of the underwater transmission link of 6 m; (c) Timing fluctuation of the underwater transmission link of 9 m; (d) Measurement floor for a short link
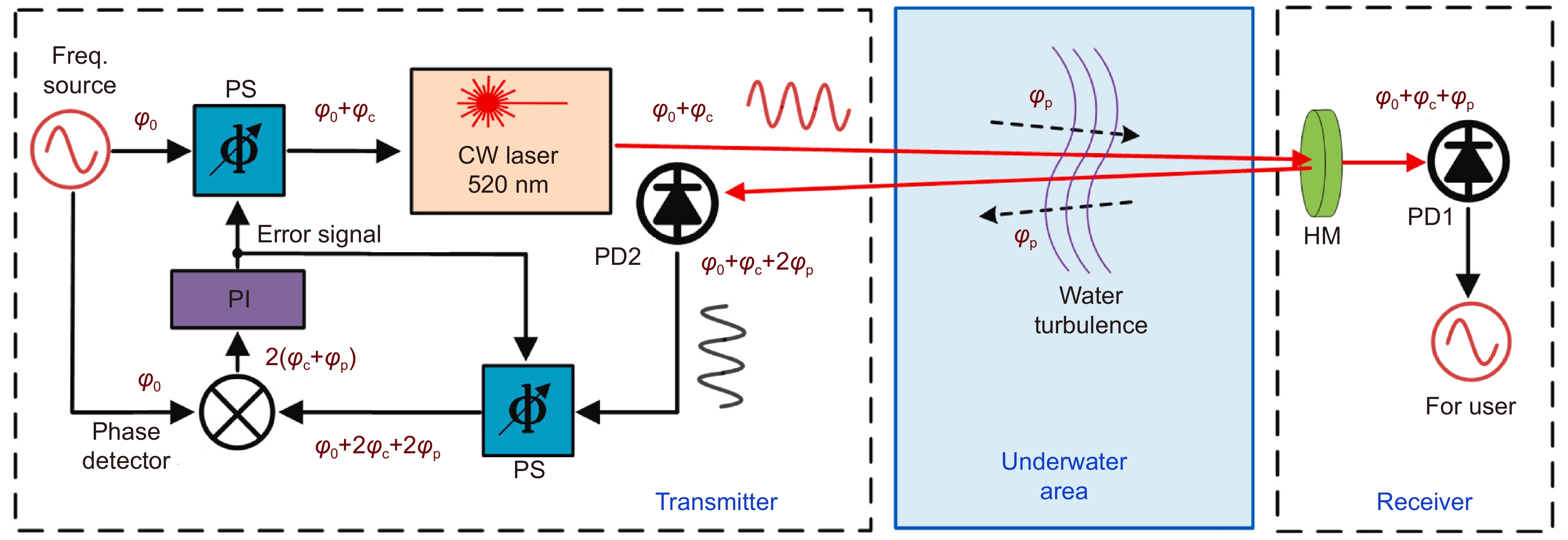
图 5 基于电学相位补偿技术的水下激光频率传递[50]。PS: 移相器;CW: 连续波;PD:光电探测器;PI:比例-积分控制器;HM:半反射镜
Figure 5. Laser-based underwater frequency transfer based on electronic phase compensation technique [50]. PS: phase shifter; CW: continuous wave; PD: photodetector; PI: proportion–integration controller; HM: half reflected mirror
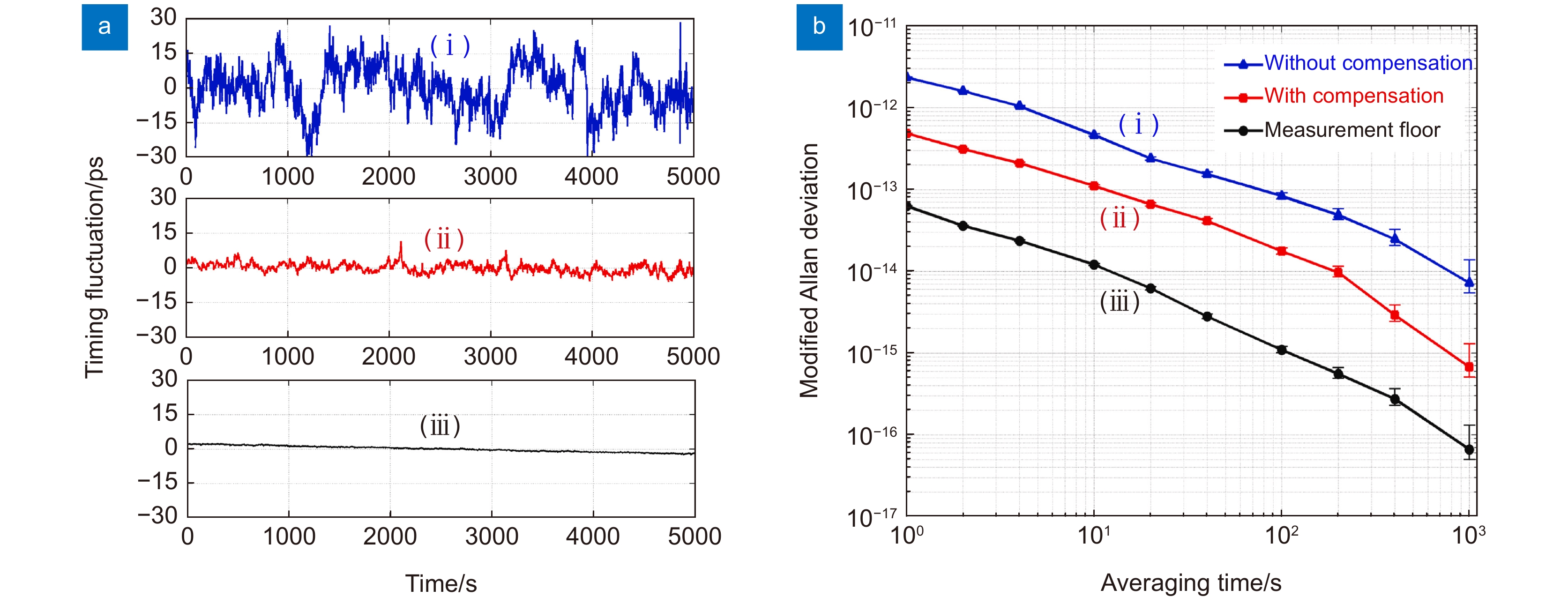
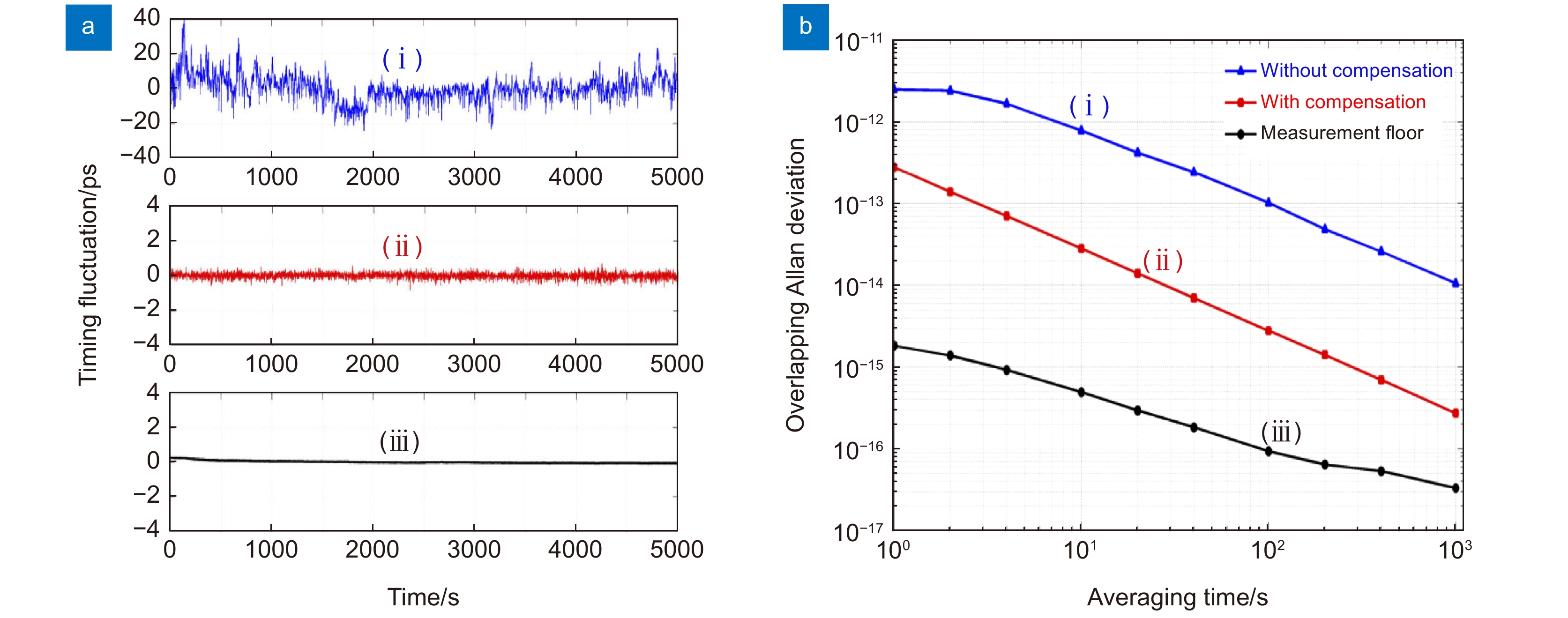
图 6 实验结果[50]。(a) 定时抖动曲线:(i)-无补偿;(ii)-有补偿;(iii)-测量本底;(b) 阿伦方差曲线:(i)-无补偿;(ii)-有补偿;(iii)-测量本底
Figure 6. Experimental results [50]. (a) Timing fluctuation curves: (i)-without compensation; (ii)-with compensation; (iii)-measurement floor; (b) Allan deviation curves: (i)-without compensation; (ii)-with compensation; (iii)-measurement floor
图 7 基于光学相位补偿技术的水下激光频率传递[51]。CW: 连续波;λ/2:半波片;PBS: 偏振分束器;λ/4:四分之一波片;PD:光电探测器;PI:比例-积分控制器;HM:半反射镜
Figure 7. Laser-based underwater frequency transfer based on optical phase compensation technique [51]. CW: continuous wave; λ/2: half-wave plate; PBS: polarization beam splitter; λ/4: quarter-wave plate; PD: photodetector; PI: proportion–integration controller; HM: half reflected mirror
图 8 实验结果[51]。(a) 定时抖动曲线:(i)-无补偿;(ii)-有补偿;(iii)-测量本底;(b) 阿伦方差曲线:(i)-无补偿;(ii)-有补偿;(iii)-测量本底
Figure 8. Experimental results [51]. (a) Timing fluctuation curves: (i)-without compensation; (ii)-with compensation; (iii)-measurement floor; (b) Allan deviation curves: (i)-without compensation; (ii)-with compensation; (iii)-measurement floor
图 9 基于终端相位补偿技术的水下多址激光频率传递[56]。TX: 发送端;RX: 接收端;VCO: 压控振荡器;λ/2:半波片;PBS: 偏振分束器;λ/4:四分之一波片;PD:光电探测器;PI:比例-积分控制器
Figure 9. Laser-based multiple-access underwater frequency transfer based on terminal phase compensation technique [56]. TX: transmitting site; RX: receiving site; VCO: voltage-controlled oscillator; M1: mirror 1; M2: mirror 2; Mn: mirror n; λ/2: half-wave plate; PBS: polarization beam splitter; λ/4: quarter-wave plate; PD: photodiode; PI: proportion–integration controller
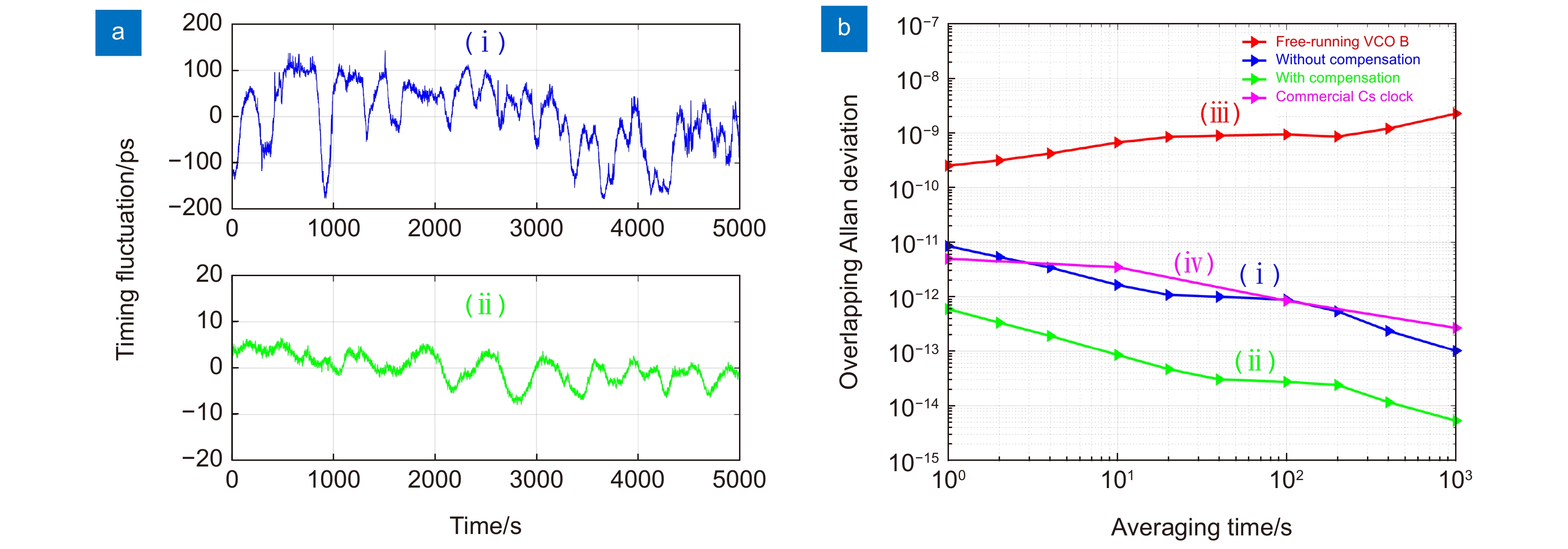
图 10 实验结果[56]。(a) 定时抖动曲线:(i)-无补偿;(ii)-有补偿;(b) 阿伦方差曲线:(i)-自由运转的VCO B;(ii)-无补偿;(iii)-有补偿;(iv)-商用铯原子钟Microsemi-5071A
Figure 10. Experimental results [56]. (a) Timing fluctuation curves: (i)-without compensation; (ii)-with compensation; (b) Allan deviation curves: (i)-free running VCO B; (ii)-without compensation; (iii)-with compensation; (iv)-commercial Cs clock Microsemi-5071A
-
[1] Kaushal H, Kaddoum G. Underwater optical wireless communication[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 1518−1547. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2552538
[2] Arnon S. Underwater optical wireless communication network[J]. Opt Eng, 2010, 49(1): 015001. doi: 10.1117/1.3280288
[3] Johnson L J, Jasman F, Green R J, et al. Recent advances in underwater optical wireless communications[J]. Underwater Technol, 2014, 32(3): 167−175. doi: 10.3723/ut.32.167
[4] Kojima N, Yabuta T, Negishi Y, et al. Submarine optical fiber cable: development and laying results[J]. Appl Opt, 1982, 21(5): 815−821. doi: 10.1364/AO.21.000815
[5] Nyman B. Flexibility in submarine fiber optic networks [Invited][J]. J Opt Commun Networking, 2015, 7(3): A553−A557. doi: 10.1364/JOCN.7.00A553
[6] Stojanovic M. Recent advances in high-speed underwater acoustic communications[J]. IEEE J Ocean Eng, 1996, 21(2): 125−136. doi: 10.1109/48.486787
[7] Stojanovic M, Preisig J. Underwater acoustic communication channels: propagation models and statistical characterization[J]. IEEE Commun Mag, 2009, 47(1): 84−89. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2009.4752682
[8] Al-Shamma’a A I, Shaw A, Saman S. Propagation of electromagnetic waves at MHz frequencies through seawater[J]. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag, 2004, 52(11): 2843−2849. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2004.834449
[9] Hale G M, Querry M R. Optical constants of water in the 200-nm to 200-μm wavelength region[J]. Appl Opt, 1973, 12(3): 555−563. doi: 10.1364/AO.12.000555
[10] Mullen L J, Vieira A J C, Herezfeld P R, et al. Application of RADAR technology to aerial LIDAR systems for enhancement of shallow underwater target detection[J]. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 1995, 43(9): 2370−2377. doi: 10.1109/22.414591
[11] 迟楠, 王超凡, 李韦萍, 等. 基于蓝绿光LED的水下可见光通信技术研究进展[J]. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 2019, 58(5): 537−548. doi: 10.15943/j.cnki.fdxb-jns.2019.05.001
Chi N, Wang C F, Li W P, et al. Research progress of underwater visible light communication technology based on blue/green LED[J]. J Fudan Univ Nat Sci, 2019, 58(5): 537−548. doi: 10.15943/j.cnki.fdxb-jns.2019.05.001
[12] Hanson F, Radic S. High bandwidth underwater optical communication[J]. Appl Opt, 2008, 47(2): 277−283. doi: 10.1364/AO.47.000277
[13] Cochenour B, Mullen L, Muth J. Modulated pulse laser with pseudorandom coding capabilities for underwater ranging, detection, and imaging[J]. Appl Opt, 2011, 50(33): 6168−6178. doi: 10.1364/AO.50.006168
[14] Pellen F, Jezequel V, Zion G, et al. Detection of an underwater target through modulated lidar experiments at grazing incidence in a deep wave basin[J]. Appl Opt, 2012, 51(31): 7690−7700. doi: 10.1364/AO.51.007690
[15] Cochenour B, Mullen L, Muth J. Temporal response of the underwater optical channel for high-bandwidth wireless laser communications[J]. IEEE J Ocean Eng, 2013, 38(4): 730−742. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2013.2255811
[16] 张雨凡, 李鑫, 吕伟超, 等. 水下无线光通信链路构成与性能优化进展[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(9): 190734. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190734
Zhang Y F, Li X, Lv W C, et al. Link structure of underwater wireless optical communication and progress on performance optimization[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(9): 190734. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190734
[17] 马春波, 王永辉, 敖珺, 等. 水下短距离高速激光通信系统的研究与实现[J]. 光通信技术, 2016, 40(4): 52−55. doi: 10.13921/j.cnki.issn1002-5561.2016.04.017
Ma C B, Wang Y H, Ao J, et al. Research and implementation of underwater short-distance high-speed laser communication system[J]. Opt Commun Technol, 2016, 40(4): 52−55. doi: 10.13921/j.cnki.issn1002-5561.2016.04.017
[18] Liu J, Zhou Z, Peng Z, et al. Mobi-sync: efficient time synchronization for mobile underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst, 2013, 24(2): 406−416. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2012.71
[19] Liu J, Wang Z H, Cui J H, et al. A joint time synchronization and localization design for mobile underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput, 2016, 15(3): 530−543. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2015.2410777
[20] Sprenger B, Zhang J, Lu Z H, et al. Atmospheric transfer of optical and radio frequency clock signals[J]. Opt Lett, 2009, 34(7): 965−967. doi: 10.1364/OL.34.000965
[21] Giorgetta F R, Swann W C, Sinclair L C, et al. Optical two-way time and frequency transfer over free space[J]. Nat Photonics, 2013, 7(6): 434−438. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.69
[22] Chen S J, Sun F Y, Bai Q S, et al. Sub-picosecond timing fluctuation suppression in laser-based atmospheric transfer of microwave signal using electronic phase compensation[J]. Opt Commun, 2017, 401: 18−22. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2017.05.029
[23] Sun F Y, Hou D, Zhang D N, et al. Femtosecond-level timing fluctuation suppression in atmospheric frequency transfer with passive phase conjunction correction[J]. Opt Express, 2017, 25(18): 21312−21320. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.021312
[24] Bergeron H, Sinclair L C, Swann W C, et al. Tight real-time synchronization of a microwave clock to an optical clock across a turbulent air path[J]. Optica, 2016, 3(4): 441−447. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.3.000441
[25] Sinclair L C, Bergeron H, Swann W C, et al. Comparing optical oscillators across the air to milliradians in phase and 10–17 in frequency[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2018, 120(5): 050801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.050801
[26] Caldwell E D, Swann W C, Ellis J L, et al. Optical timing jitter due to atmospheric turbulence: comparison of frequency comb measurements to predictions from micrometeorological sensors[J]. Opt Express, 2020, 28(18): 26661−26675. doi: 10.1364/OE.400434
[27] Bodine M I, Ellis J L, Swann W C, et al. Optical time-frequency transfer across a free-space, three-node network[J]. APL Photonics, 2020, 5(7): 076113. doi: 10.1063/5.0010704
[28] Dai H, Shen Q, Wang C Z, et al. Towards satellite-based quantum-secure time transfer[J]. Nat Phys, 2020, 16(8): 848−852. doi: 10.1038/s41567-020-0892-y
[29] Kang H J, Yang J, Chun B J, et al. Free-space transfer of comb-rooted optical frequencies over an 18 km open-air link[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 4438. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12443-8
[30] Dix-Matthews B P, Schediwy S W, Gozzard D R, et al. Point-to-point stabilized optical frequency transfer with active optics[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 515. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20591-5
[31] Gozzard D R, Howard L A, Dix-Matthews B P, et al. Ultrastable free-space laser links for a global network of optical atomic clocks[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2022, 128(2): 020801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.020801
[32] Mullen L, Laux A, Cochenour B. Propagation of modulated light in water: implications for imaging and communications systems[J]. Appl Opt, 2009, 48(14): 2607−2612. doi: 10.1364/AO.48.002607
[33] Mullen L, Alley D, Cochenour B. Investigation of the effect of scattering agent and scattering albedo on modulated light propagation in water[J]. Appl Opt, 2011, 50(10): 1396−1404. doi: 10.1364/AO.50.001396
[34] Cochenour B, Dunn K, Laux A, et al. Experimental measurements of the magnitude and phase response of high-frequency modulated light underwater[J]. Appl Opt, 2017, 56(14): 4019−4024. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.004019
[35] Lee R W, Laux A, Mullen L J. Hybrid technique for enhanced optical ranging in turbid water environments[J]. Opt Eng, 2013, 53(5): 051404. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.53.5.051404
[36] Luchinin A G, Kirillin M Y. Temporal and frequency characteristics of a narrow light beam in sea water[J]. Appl Opt, 2016, 55(27): 7756−7762. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.007756
[37] Nootz G, Matt S, Kanaev A, et al. Experimental and numerical study of underwater beam propagation in a Rayleigh-Bénard turbulence tank[J]. Appl Opt, 2017, 56(22): 6065−6072. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.006065.
[38] Nakamura K, Mizukoshi I, Hanawa M. Optical wireless transmission of 405 nm, 1.45 Gbit/s optical IM/DD-OFDM signals through a 4.8 m underwater channel[J]. Opt Express, 2015, 23(2): 1558−1566. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.001558
[39] Xu J, Kong M W, Lin A B, et al. OFDM-based broadband underwater wireless optical communication system using a compact blue LED[J]. Opt Commun, 2016, 369: 100−105. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.02.044
[40] Liu X Y, Yi S Y, Zhou X L, et al. 34.5 m underwater optical wireless communication with 2.70 Gbps data rate based on a green laser diode with NRZ-OOK modulation[J]. Opt Express, 2017, 25(22): 27937−27947. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.027937
[41] Liu X Y, Yi S Y, Zhou X L, et al. Laser-based white-light source for high-speed underwater wireless optical communication and high-efficiency underwater solid-state lighting[J]. Opt Express, 2018, 26(15): 19259−19274. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.019259.
[42] Nootz G, Jarosz E, Dalgleish F R, et al. Quantification of optical turbulence in the ocean and its effects on beam propagation[J]. Appl Opt, 2016, 55(31): 8813−8820. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.008813
[43] 俞雪平, 胡云安, 刘亮, 等. 基于多次散射和小散射角近似的水下激光传播特性[J]. 光子学报, 2015, 44(11): 1101002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20154411.1101002
Yu X P, Hu Y A, Liu L, et al. Propagation characteristics of underwater laser based on multiple scattering and small scattering angles approximation[J]. Acta Photonica Sin, 2015, 44(11): 1101002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20154411.1101002
[44] Liu W H, Xu Z Y, Yang L Q. SIMO detection schemes for underwater optical wireless communication under turbulence[J]. Photonics Res, 2015, 3(3): 48−53. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.3.000048
[45] Sinclair L C, Giorgetta F R, Swann W C, et al. Optical phase noise from atmospheric fluctuations and its impact on optical time-frequency transfer[J]. Phys Rev A, 2014, 89(2): 023805. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.89.023805
[46] Fante R L. Electromagnetic beam propagation in turbulent media[J]. Proc IEEE, 1975, 63(12): 1669−1692. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1975.10035
[47] Harvey A H, Gallagher J S, Sengers J M H L. Revised formulation for the refractive index of water and steam as a function of wavelength, temperature and density[J]. J Phys Chem Ref Data, 1998, 27(4): 761−774. doi: 10.1063/1.556029
[48] Quan X H, Fry E S. Empirical equation for the index of refraction of seawater[J]. Appl Opt, 1995, 34(18): 3477−3480. doi: 10.1364/AO.34.003477
[49] Hou D, Chen J Y, Guo G K. Analysis and experimental demonstration of underwater frequency transfer with diode green laser[J]. Rev Sci Instrum, 2020, 91(7): 075102. doi: 10.1063/5.0006328
[50] Hou D, Bai Q S, Guo G K, et al. Highly-stable laser-based underwater radio-frequency transfer with electronic phase compensation[J]. Opt Commun, 2019, 452: 247−251. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.07.012
[51] Hou D. Laser-based underwater frequency transfer with sub-picosecond timing fluctuation using optical phase compensation[J]. Opt Express, 2020, 28(22): 33298−33306. doi: 10.1364/OE.403189
[52] Hou D, Zhang D N, Sun F Y, et al. Free-space-based multiple-access frequency dissemination with optical frequency comb[J]. Opt Express, 2018, 26(15): 19199−19205. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.019199
[53] Wang B, Zhu X, Gao C, et al. Square kilometre array telescope—precision reference frequency synchronisation via 1f-2f dissemination[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5(1): 13851. doi: 10.1038/srep13851
[54] Grosche G. Eavesdropping time and frequency: phase noise cancellation along a time-varying path, such as an optical fiber[J]. Opt Lett, 2014, 39(9): 2545−2548. doi: 10.1364/OL.39.002545
[55] Bai Y, Wang B, Zhu X, et al. Fiber-based multiple-access optical frequency dissemination[J]. Opt Lett, 2013, 38(17): 3333−3335. doi: 10.1364/OL.38.003333
[56] Ren J W, Hou D, Gao Y F, et al. Highly stable multiple-access underwater frequency transfer with terminal phase compensation[J]. Opt Lett, 2021, 46(19): 4745−4748. doi: 10.1364/OL.435967
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: