-
摘要:
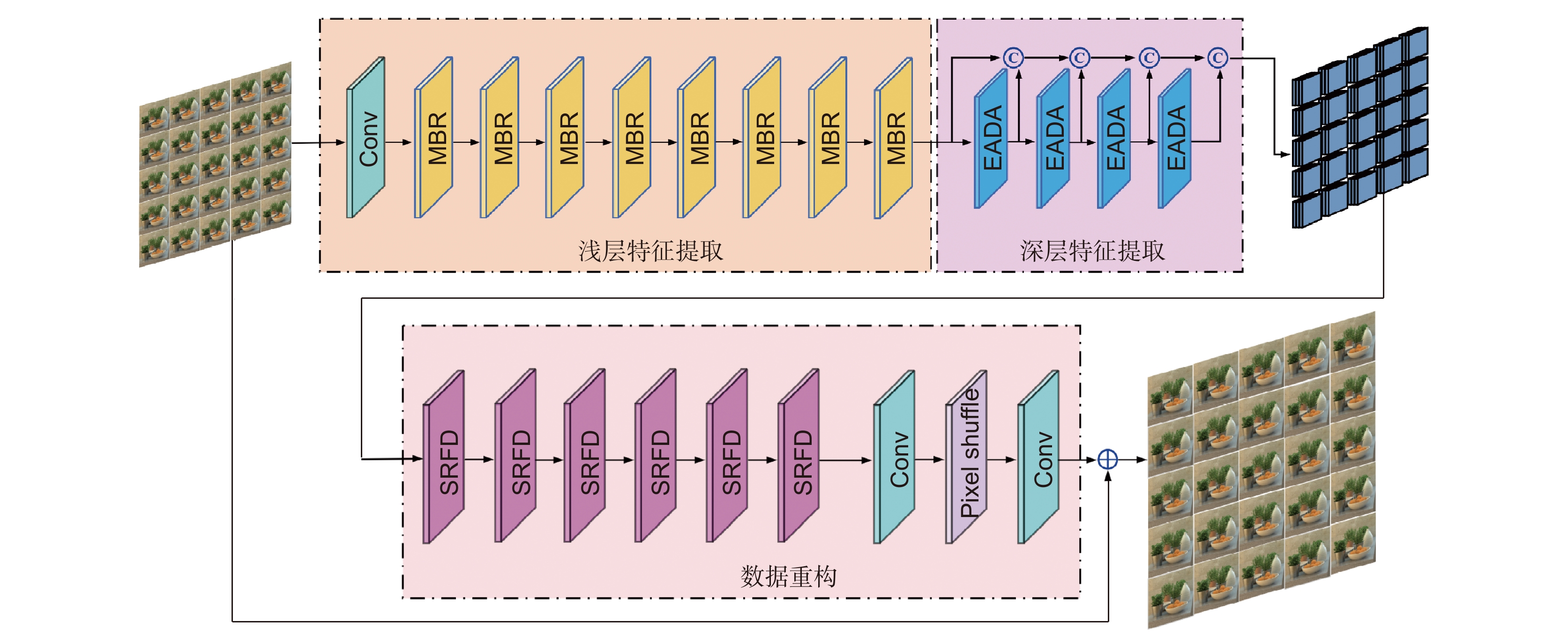
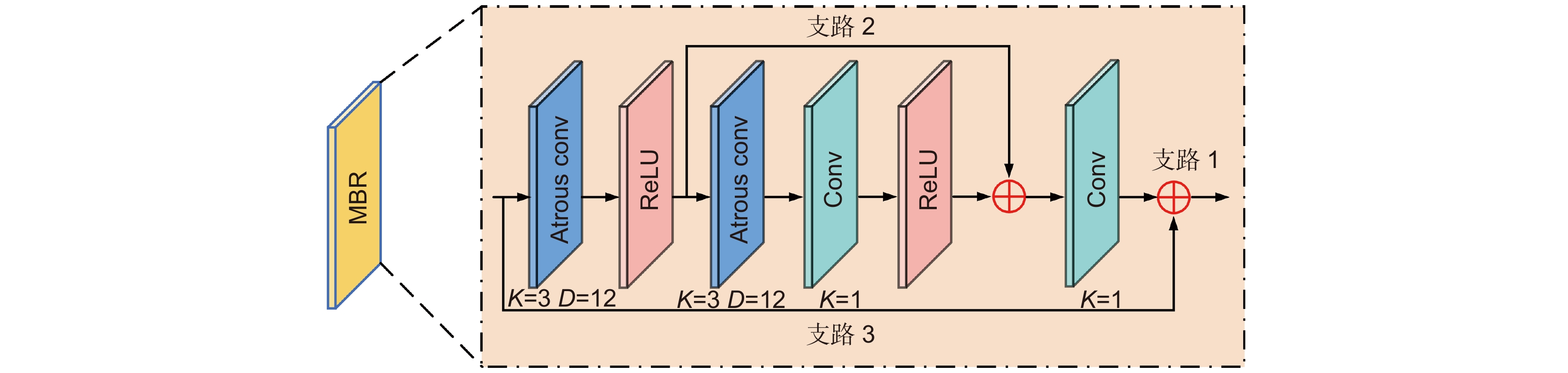
由于采用了更为先进的成像技术,光场相机可以同步获取场景的空间信息与角度信息。该技术以牺牲空间分辨率为代价,实现了更高维度的场景表示。为了提高光场相机拍摄场景的空间分辨率,本文搭建了角度差异强化的光场超分辨率重构网络。该网络先采用8个多分支残差块实现浅层特征提取,再采用4个强化的角度可变形对准模块实现深层特征提取,最后采用6个简化的残差特征蒸馏模块和像素洗牌模块完成数据重构。所提网络在利用光场角度差异完成空间信息超分时,更加强调视图自身特征的深入挖掘,以获得更加丰富的视图间差异特征。在5组公开的光场数据集上对本文所提网络的性能进行了验证,本文算法获得了PSNR、SSIM值更高的高分辨率光场子孔径图像。
Abstract:Based on the advanced imaging technology, light field camera can obtain the spatial information and the angular information of the scene synchronously. It achieves higher dimensional scene representation by sacrificing the spatial resolution. In order to improve the spatial resolution of the light field image, a light field super-resolution reconstruction network based on angle difference enhancement is built in this paper. In the proposed network, eight multi-branch residual blocks are used to extract shallow features. Then, four enhanced angular deformable alignment modules are used to extract deep features. Finally six simplified residual feature distillation modules and pixel shuffle modules are used to complete data reconstruction. The proposed network takes advantage of the angle difference of the light field to complete the spatial information super-resolution. In order to obtain more features difference between different views, the own feature of the single view is emphasized during the feature extraction. The performance of the proposed network is verified on five public light field data sets. The proposed algorithm obtains high-resolution light field sub-aperture images with higher PSNR and SSIM.
-

-
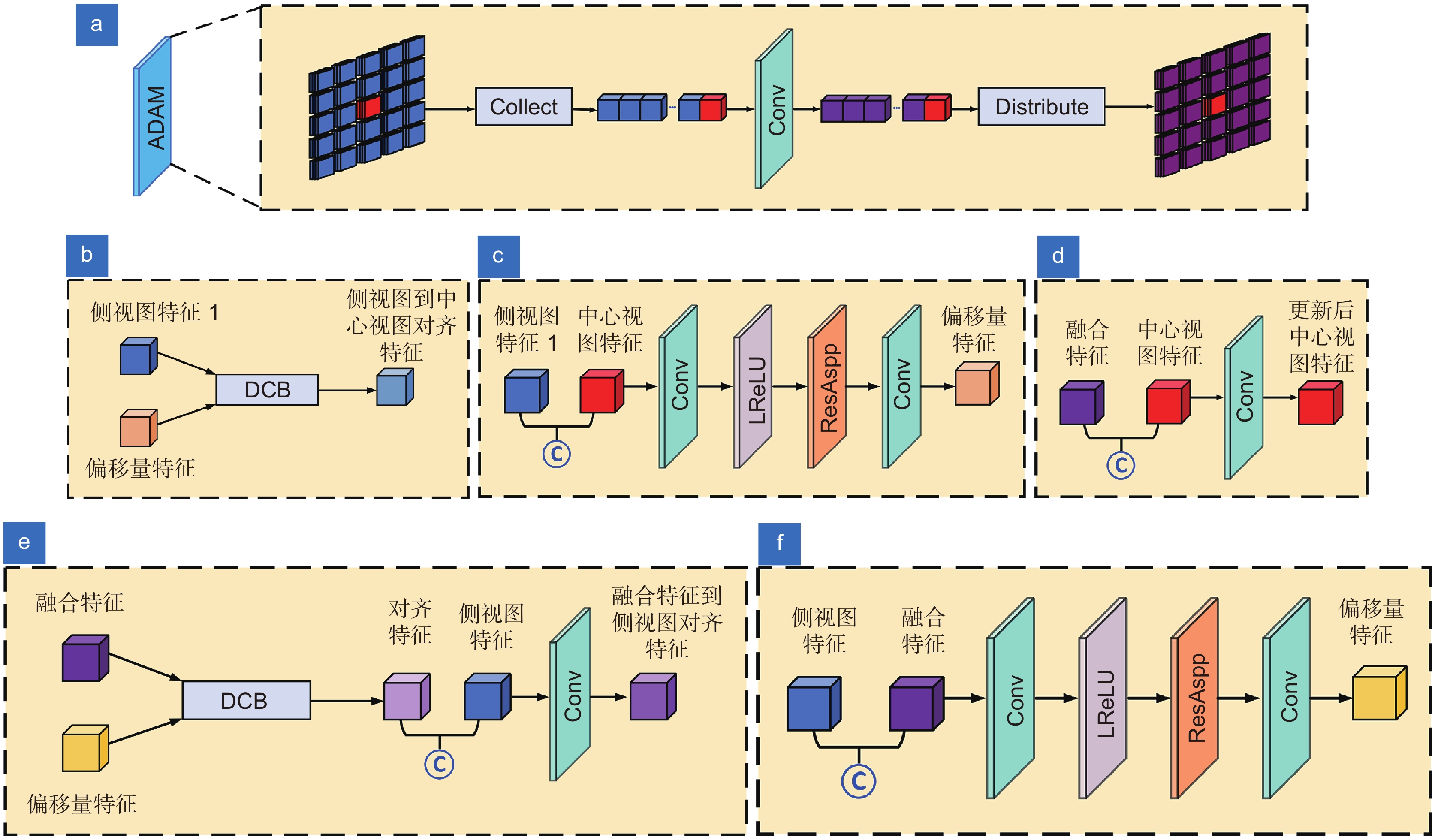
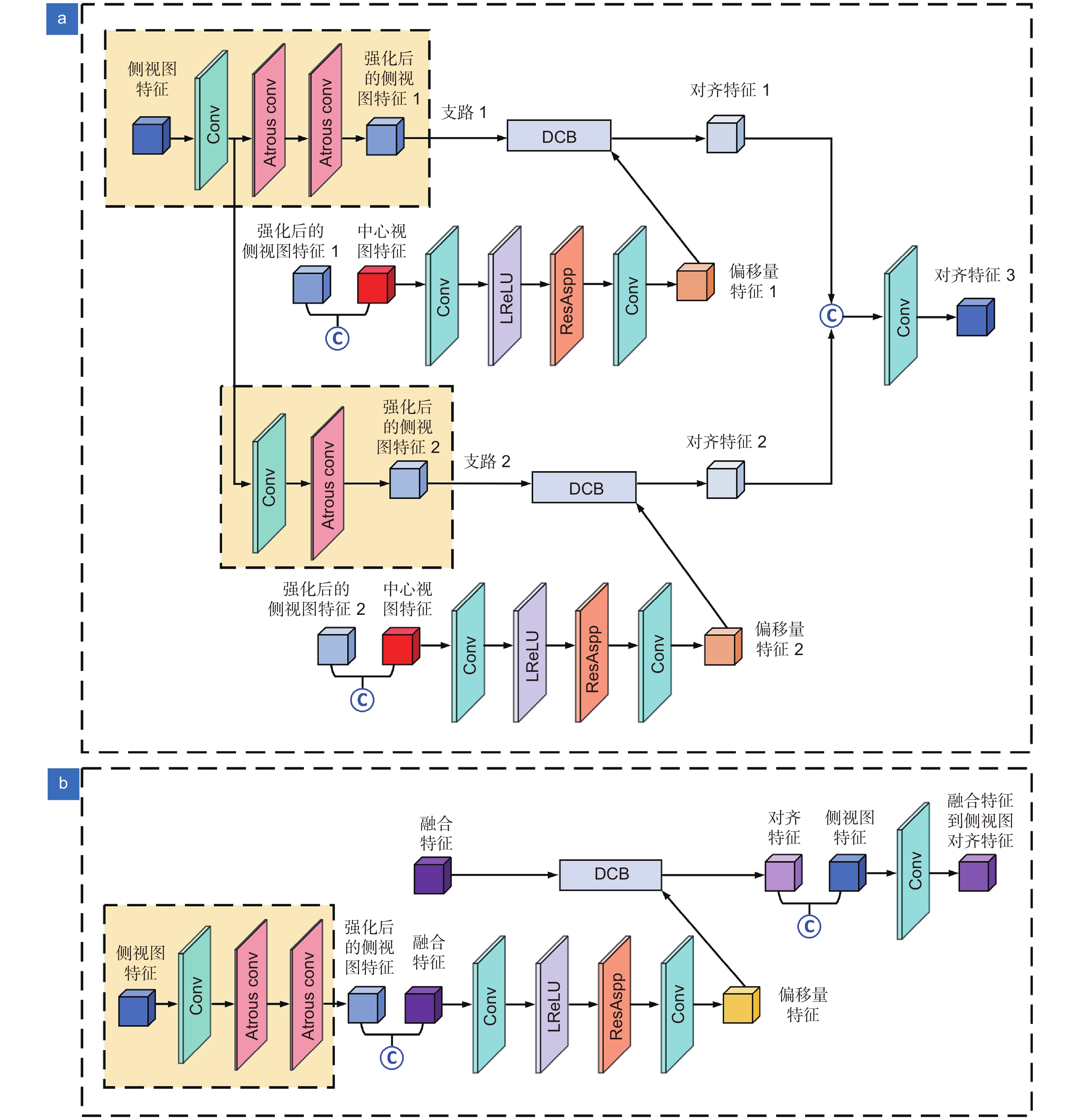
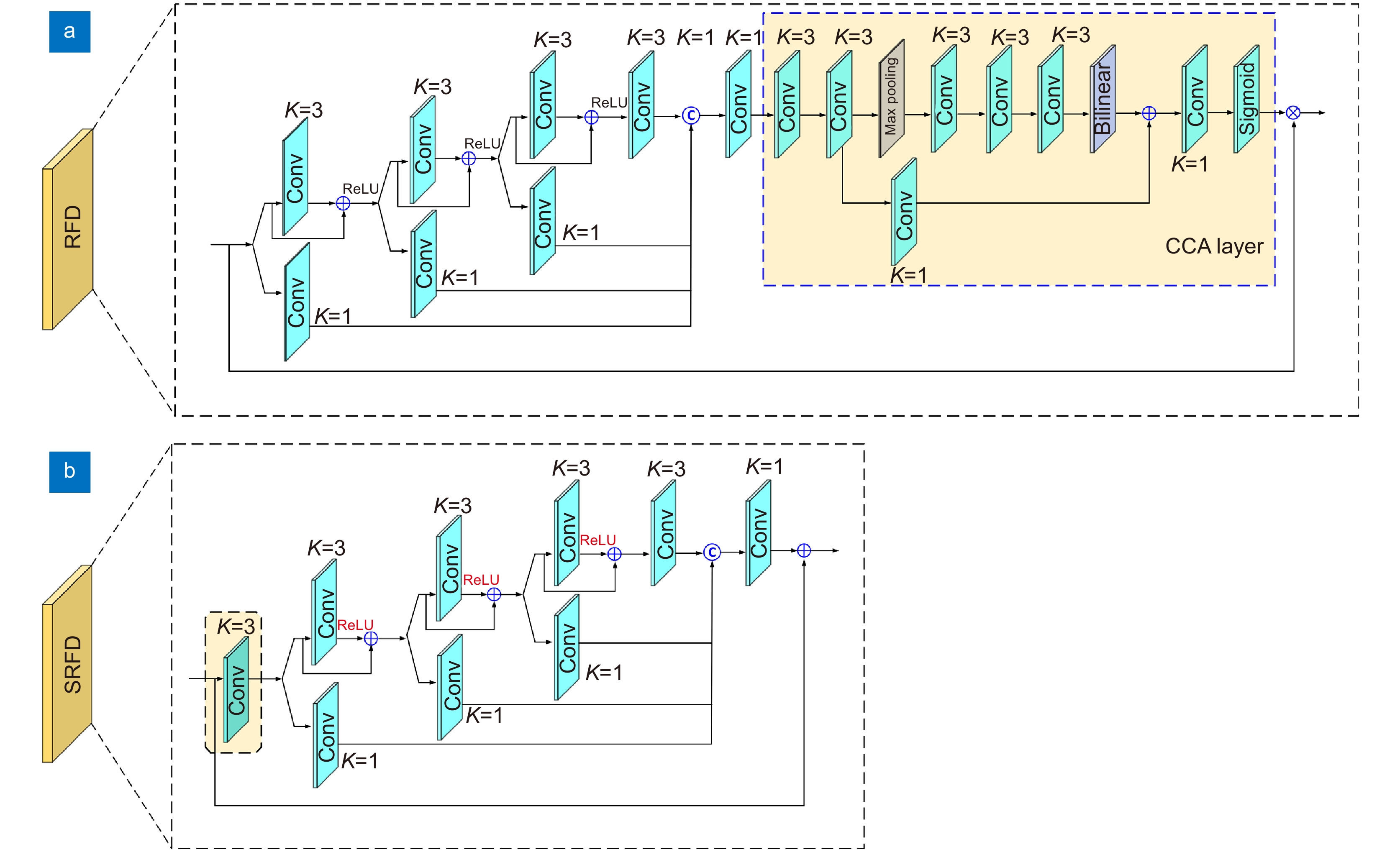
图 4 ADA 模块细节。(a) ADA 模块数据处理流程;(b) 特征收集(collect);(c) 特征收集中偏移 量的获取;(d)中心视图的更新;(e) 特征发散(distribute);(f) 特征发散中偏移量的获取
Figure 4. ADA module details. (a) ADA module data processing process; (b) Feature collection; (c) Offset acquisition in feature collection; (d) Update the central view; (e) Feature distribution; (f) Offset acquisition in feature distribution
表 1 实验使用的5个公共光场数据集
Table 1. Five public light field datasets used in our experiment
表 2 基于不同浅层特征提取模块的光场图像4倍超分PSNR/SSIM值
Table 2. PSNR/SSIM values achieved by different shallow feature extraction modules for 4× SR
表 3 基于不同深层特征提取模块的光场图像4倍超分PSNR/SSIM值
Table 3. PSNR/SSIM values achieved by different deep feature extraction modules for 4× SR
表 4 基于不同特征融合模块的光场图像4倍超分PSNR/SSIM值
Table 4. PSNR/SSIM values achieved by different feature fusion modules for 4× SR
表 5 不同算法对光场图像2倍超分PSNR/SSIM值
Table 5. PSNR/SSIM values achieved by different methods for 2× SR
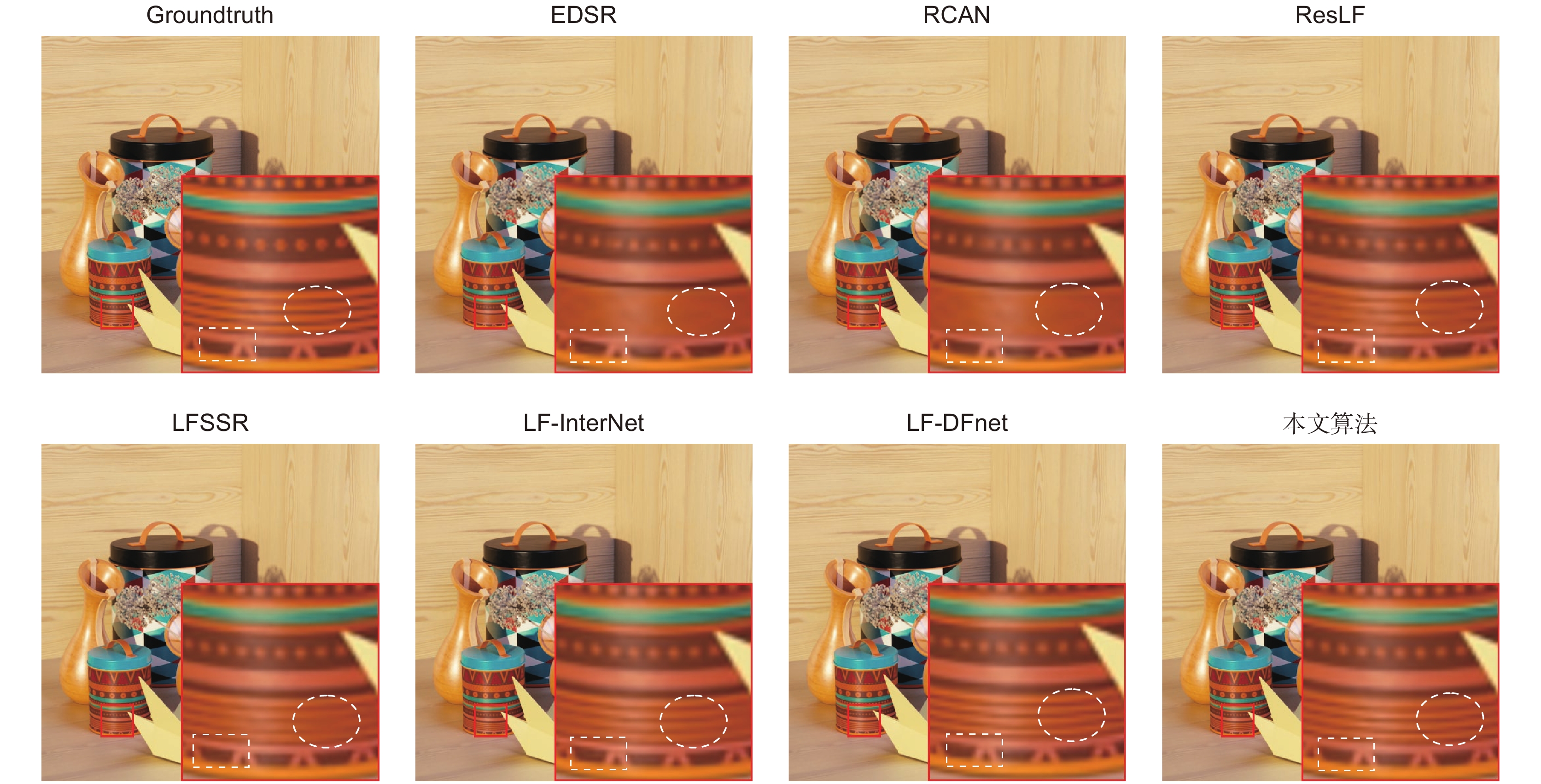
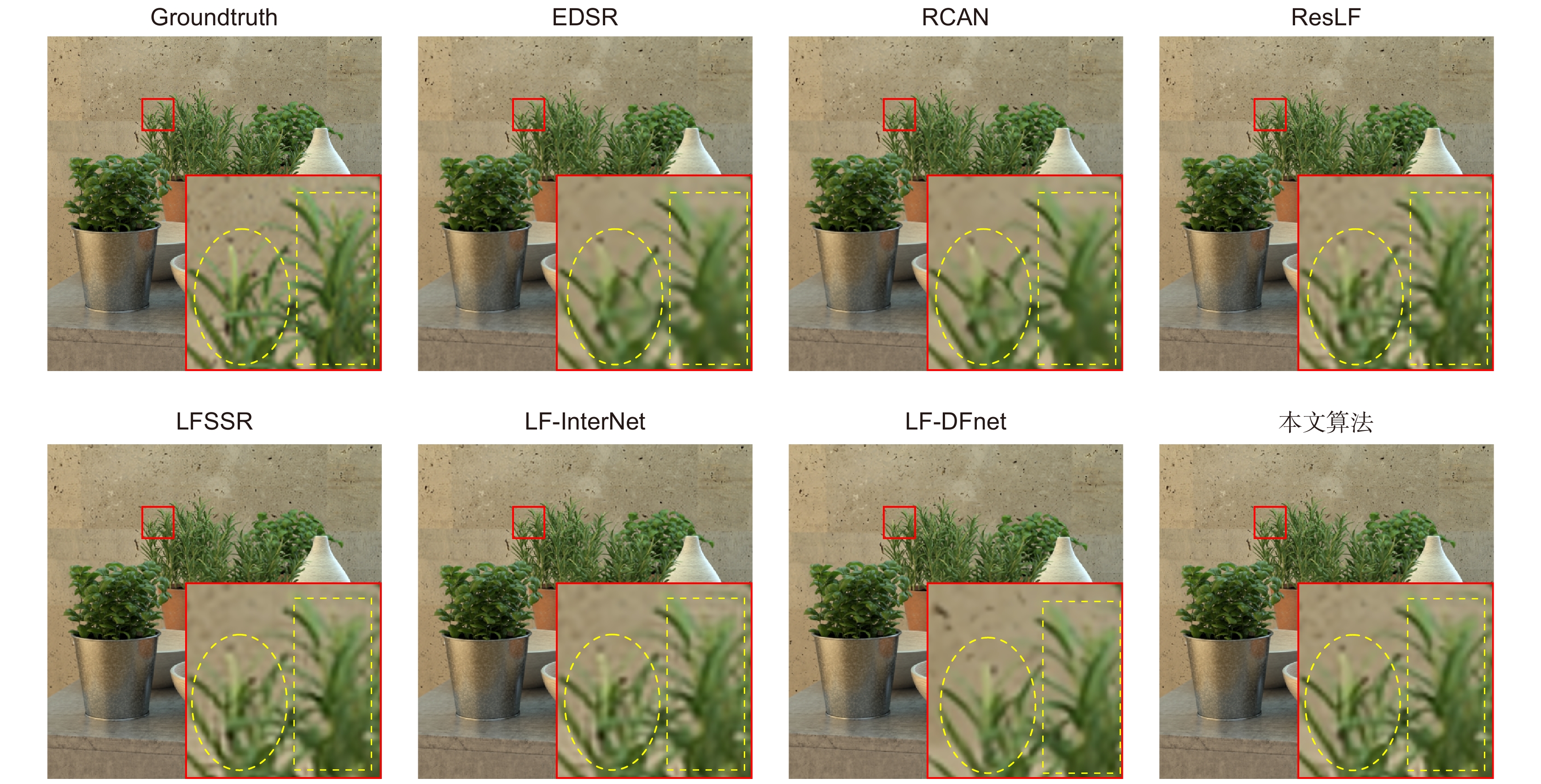
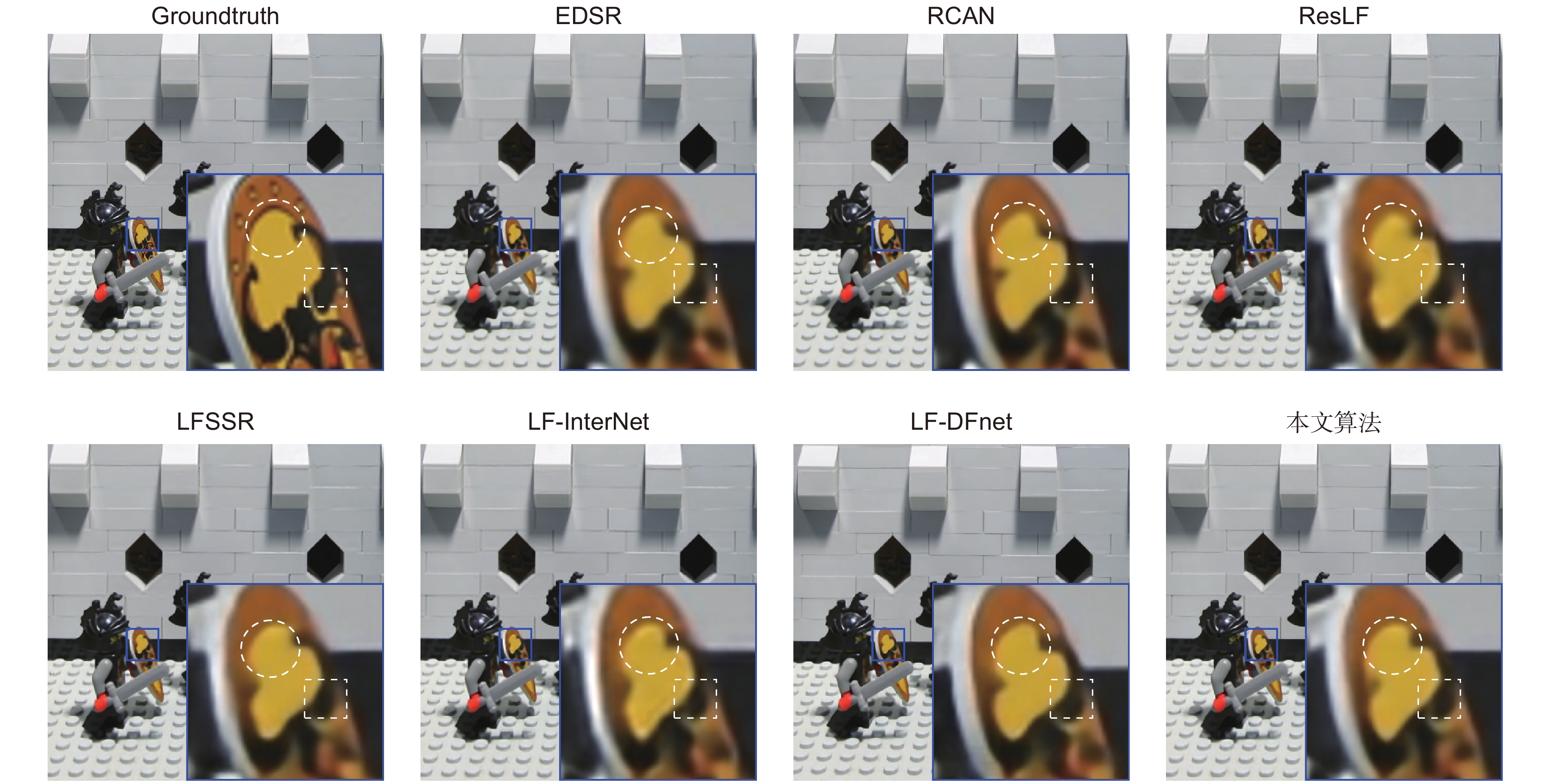
超分方法 EPFL[13] HCInew[14] HCIold[15] INRIA[16] STFgantry[17] Average EDSR[20] 33.09/0.9631 34.83/0.9594 41.01/0.9875 34.97/0.9765 36.29/0.9819 36.04/0.9728 RCAN[21] 33.16/0.9635 34.98/0.9602 41.05/0.9875 35.01/0.9769 36.33/0.9825 36.11/0.9741 ResLF[8] 32.75/0.9672 36.07/0.9715 42.61/0.9922 34.57/0.9784 36.89/0.9873 36.58/0.9793 LFSSR[7] 33.69/0.9748 36.86/0.9753 43.75/0.9939 35.27/0.9834 38.07/0.9902 37.53/0.9835 LF-InterNet[4] 34.14/0.9761 37.28/0.9769 44.45/0.9945 35.80/0.9846 38.72/0.9916 38.08/0.9847 LF-DFnet[5] 34.44/0.9766 37.44/0.9786 44.23/0.9943 36.36/0.9841 39.61/0.9935 38.42/0.9854 本文方法 34.58/0.9772 37.92/0.9796 44.84/0.9948 36.59/0.9854 40.11/0.9939 38.81/0.9862 表 6 不同算法对光场图像4倍超分PSNR/SSIM值
Table 6. PSNR/SSIM values achieved by different methods for 4× SR
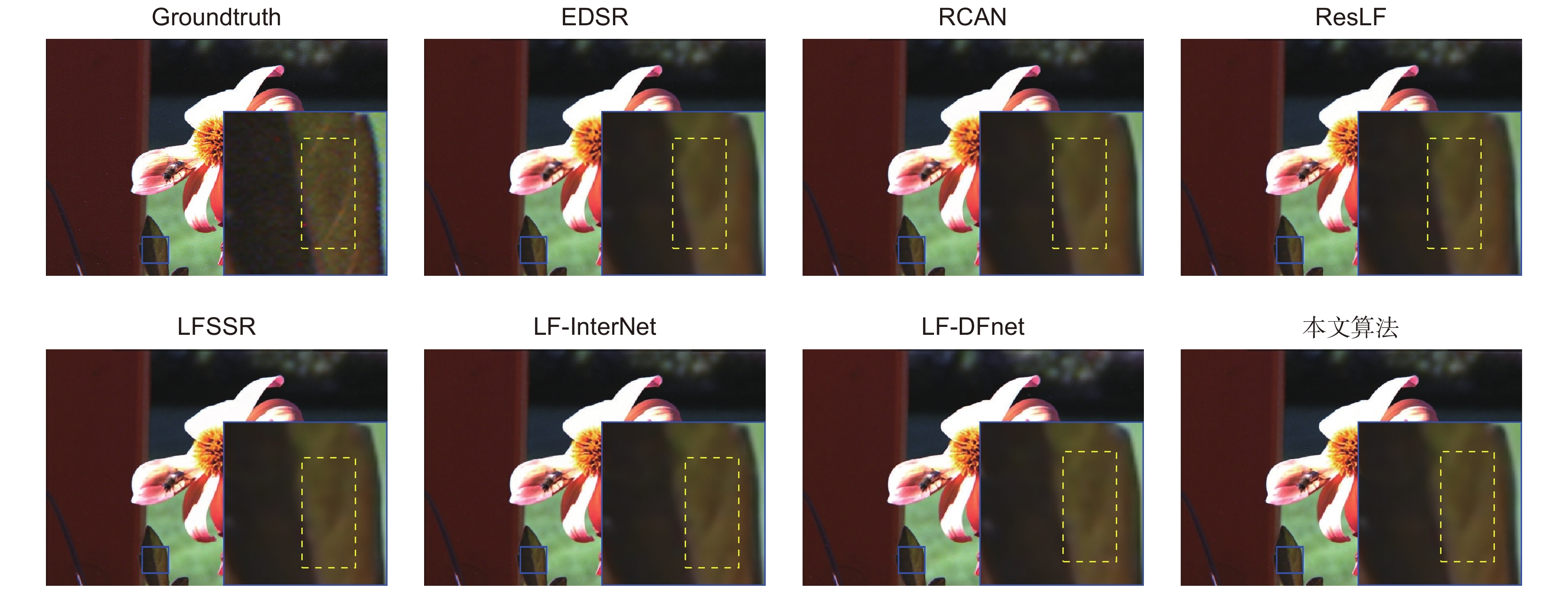
超分方法 EPFL[13] HCInew[14] HCIold[15] INRIA[16] STFgantry[17] Average EDSR[20] 27.84/0.8858 29.60/0.8874 35.18/0.9538 29.66/0.9259 28.70/0.9075 30.20/0.9121 RCAN[21] 27.88/0.8863 29.63/0.8880 35.20/0.9540 29.76/0.9273 28.90/0.9110 30.27/0.9133 ResLF[8] 27.46/0.8899 29.92/0.9011 36.12/0.9651 29.64/0.9339 28.99/0.9214 30.43/0.9223 LFSSR[7] 28.27/0.9080 30.72/0.9124 36.70/0.9690 30.31/0.9446 30.15/0.9385 31.23/0.9345 LF-InterNet[4] 28.67/0.9143 30.98/0.9165 37.11/0.9715 30.64/0.9486 30.53/0.9426 31.59/0.9387 LF-DFnet[5] 28.77/0.9165 31.23/0.9196 37.32/0.9718 30.83/0.9503 31.15/0.9494 31.86/0.9415 本文方法 28.81/0.9190 31.30/0.9206 37.39/0.9725 30.81/0.9513 31.29/0.9511 31.92/0.9429 表 7 不同算法(2倍超分/4倍超分)复杂度对比
Table 7. Comparisons of the number of parameters and FLOPs by different methods for 2× SR and 4× SR
-
[1] Ng R, Levoy M, Brédif M, et al. Light field photography with a hand-held plenoptic camera[J]. Comput Sci Tech Rep CSTR, 2005, 2(11): 1−11.
[2] Tao M W, Hadap S, Malik J, et al. Depth from combining defocus and correspondence using light-field Cameras[C]//Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, 2013: 673–680. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2013.89.
[3] Levoy M, Hanrahan P. Light field rendering[C]//Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, New York, 1996: 31–42. https://doi.org/10.1145/237170.237199.
[4] Wang Y Q, Wang L G, Yang J G, et al. Spatial-angular interaction for light field image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, 2020: 290–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58592-1_18.
[5] Wang Y Q, Yang J G, Wang L G, et al. Light field image super-resolution using deformable convolution[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2020, 30: 1057−1071. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3042059
[6] Mo Y, Wang Y Q, Xiao C, et al. Dense dual-attention network for light field image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol, 2022, 32(7): 4431−4443. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3121679
[7] Yeung H W F, Hou J H, Chen X M, et al. Light field spatial super-resolution using deep efficient spatial-angular separable convolution[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2019, 28(5): 2319−2330. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2885236
[8] Zhang S, Lin Y F, Sheng H. Residual networks for light field image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, 2019: 11046–11055. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.01130.
[9] Jin J, Hou J H, Chen J, et al. Light field spatial super-resolution via deep combinatorial geometry embedding and structural consistency regularization[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, 2020: 2260−2269. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00233.
[10] Liang Z Y, Wang Y Q, Wang L G, et al. Angular-flexible network for light field image super-resolution[J]. Electron Lett, 2021, 57(24): 921−924. doi: 10.1049/ell2.12312
[11] 赵圆圆, 施圣贤. 融合多尺度特征的光场图像超分辨率方法[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(12): 200007. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.200007
Zhao Y Y, Shi S X. Light-field image super-resolution based on multi-scale feature fusion[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(12): 200007. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.200007
[12] Liu J, Tang J, Wu G S. Residual feature distillation network for lightweight image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, 2020: 41–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67070-2_2.
[13] Rerabek M, Ebrahimi T. New light field image dataset[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience, Lisbon, 2016.
[14] Honauer K, Johannsen O, Kondermann D, et al. A dataset and evaluation methodology for depth estimation on 4D light fields[C]//Proceedings of the 13th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Cham, 2016: 19–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54187-7_2.
[15] Wanner S, Meister S, Goldluecke B. Datasets and benchmarks for densely sampled 4D light fields[M]//Bronstein M, Favre J, Hormann K. Vision, Modeling and Visualization. Eurographics Association, 2013: 225–226. https://doi.org/10.2312/PE.VMV.VMV13.225-226.
[16] Le Pendu M, Jiang X R, Guillemot C. Light field inpainting propagation via low rank matrix completion[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2018, 27(4): 1981−1993. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2791864
[17] Vaish V, Adams A. The (new) Stanford light field archive, computer graphics laboratory, Stanford University[EB/OL]. 2008. http://lightfield.stanford.edu
[18] Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, 2015.
[19] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification[C]//Proceedings of 2015 International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, 2015: 1026–1034. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.123.
[20] Lim B, Son S, Kim H, et al. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, 2017: 136−144. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2017.151.
[21] Zhang Y L, Li K P, Li K, et al. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, 2018: 294–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_18.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: