Boundary attention assisted dynamic graph convolution for retinal vascular segmentation
-
摘要
针对视网膜血管分割任务中存在的毛细血管分割遗漏和断连的问题,从最大限度地利用视网膜血管的特征信息的角度出发,添补视网膜血管的全局结构信息和边界信息,在U型网络的基础上,提出边界注意力辅助的动态图卷积视网膜血管分割网络。本模型先将动态图卷积嵌入到U型网络中形成多尺度结构,提升模型获取全局结构信息的能力,以提高分割质量,再利用边界注意力网络辅助模型,增加模型对边界信息的关注度,进一步提高分割性能。将模型在DRIVE、CHASEDB1和STARE三个视网膜图像数据集上进行实验,均取得了较好的分割效果。实验结果证明,该模型能较好地区分噪声和毛细血管,分割出结构较完整的视网膜血管,具有泛化性和鲁棒性。
Abstract
Aiming at the problem of missing and disconnected capillary segmentation in the retinal vascular segmentation task, from the perspective of maximizing the use of retinal vascular feature information, by adding the global structure information and retinal blood vessels boundary information, based on the U-shaped network, a dynamic graph convolution for retinal vascular segmentation model assisted by boundary attention is proposed. The dynamic graph convolution is first embedded into the U-shaped network to form a multi-scale structure, which improves the ability of the model to obtain the global structural information, and thus improving the segmentation quality. Then, the boundary attention network is utilized to assist the model to increase the attention to the boundary information, and further improve the segmentation performance. The proposed algorithm is tested on three retinal image datasets, DRIVE, CHASEDB1, and STARE, and good segmentation results are obtained. The experimental results show that the model can better distinguish the noise and capillary, and segment retinal blood vessels with more complete structure, which has generalization and robustness.
-
Overview
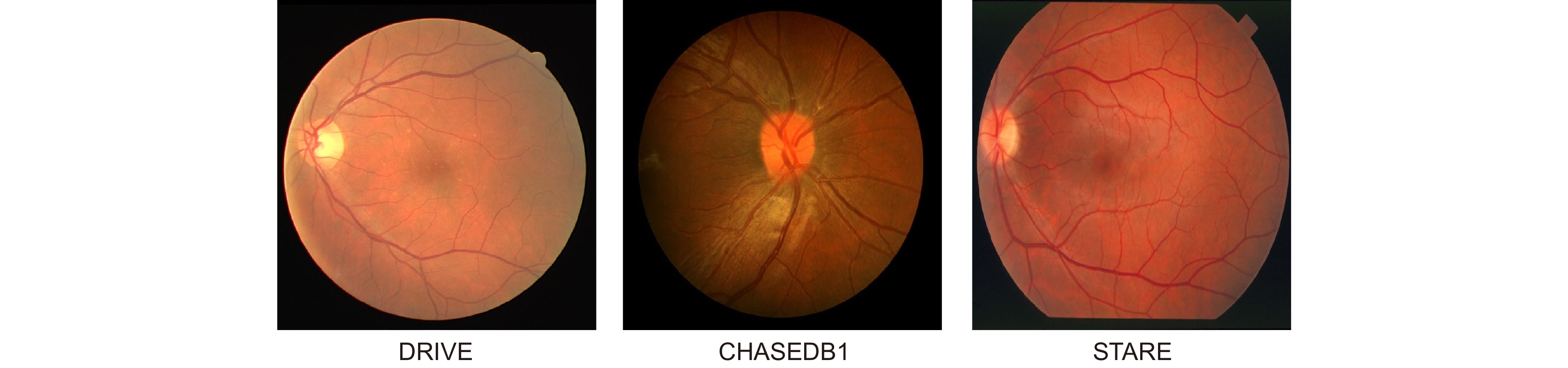
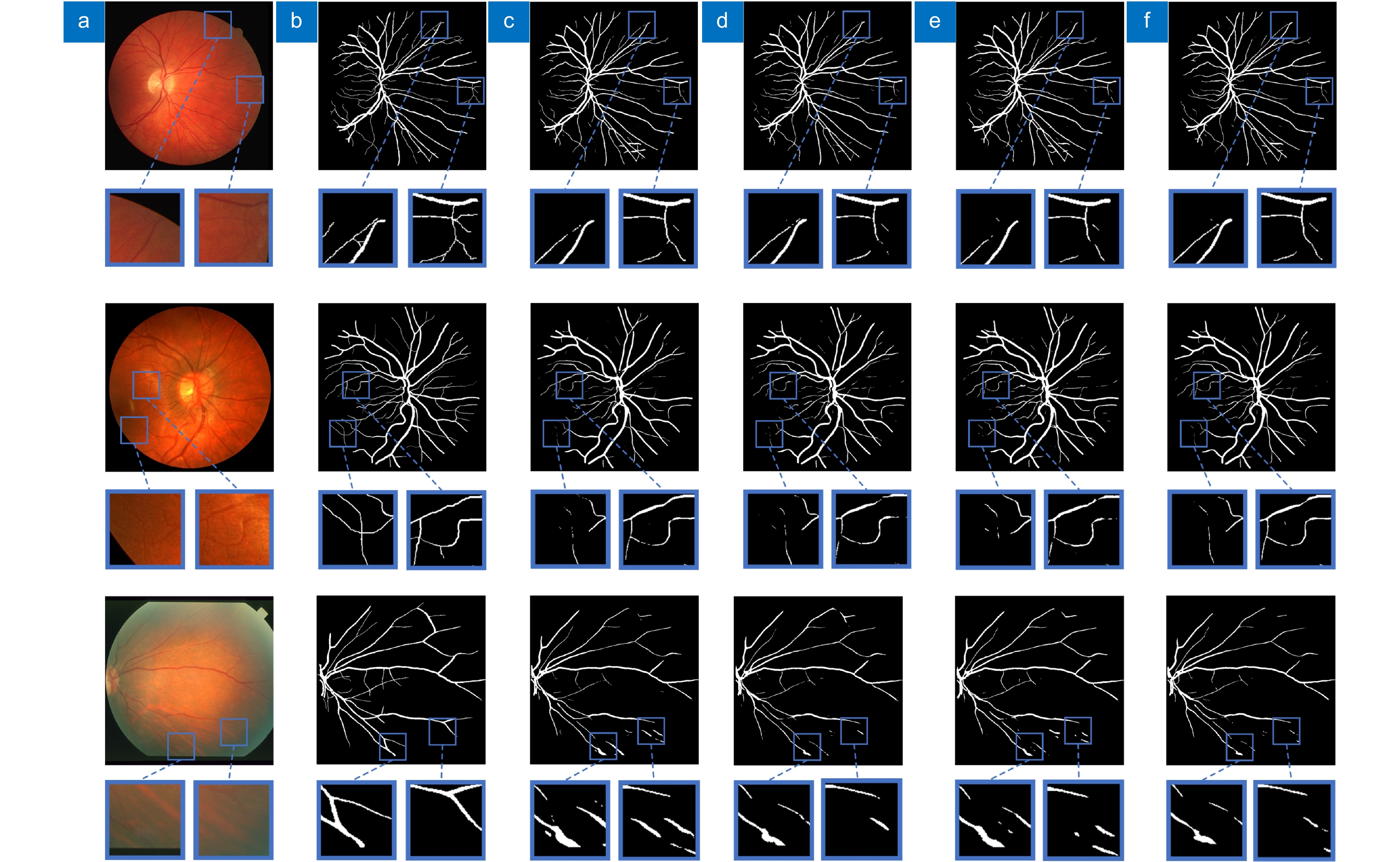
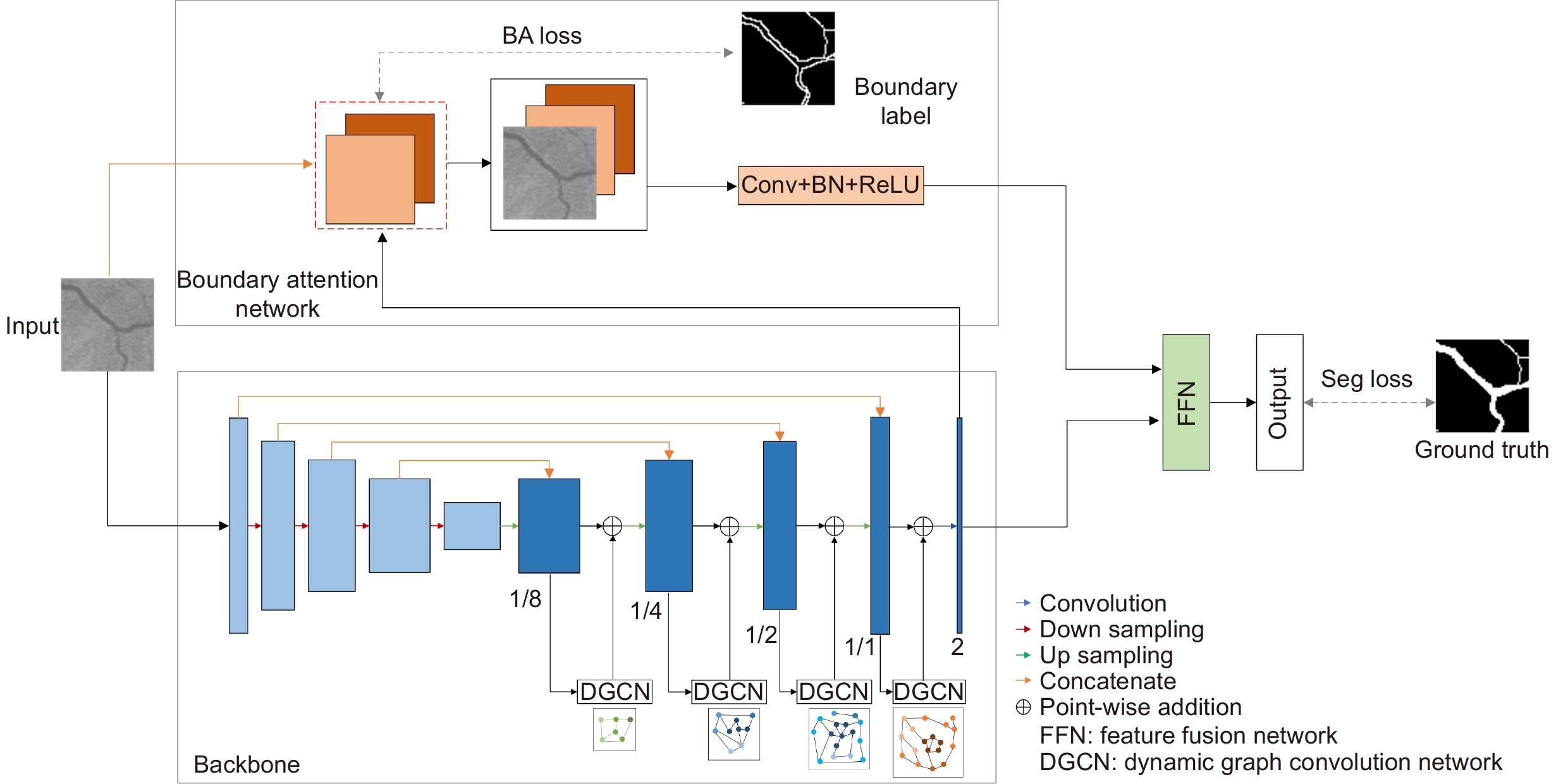
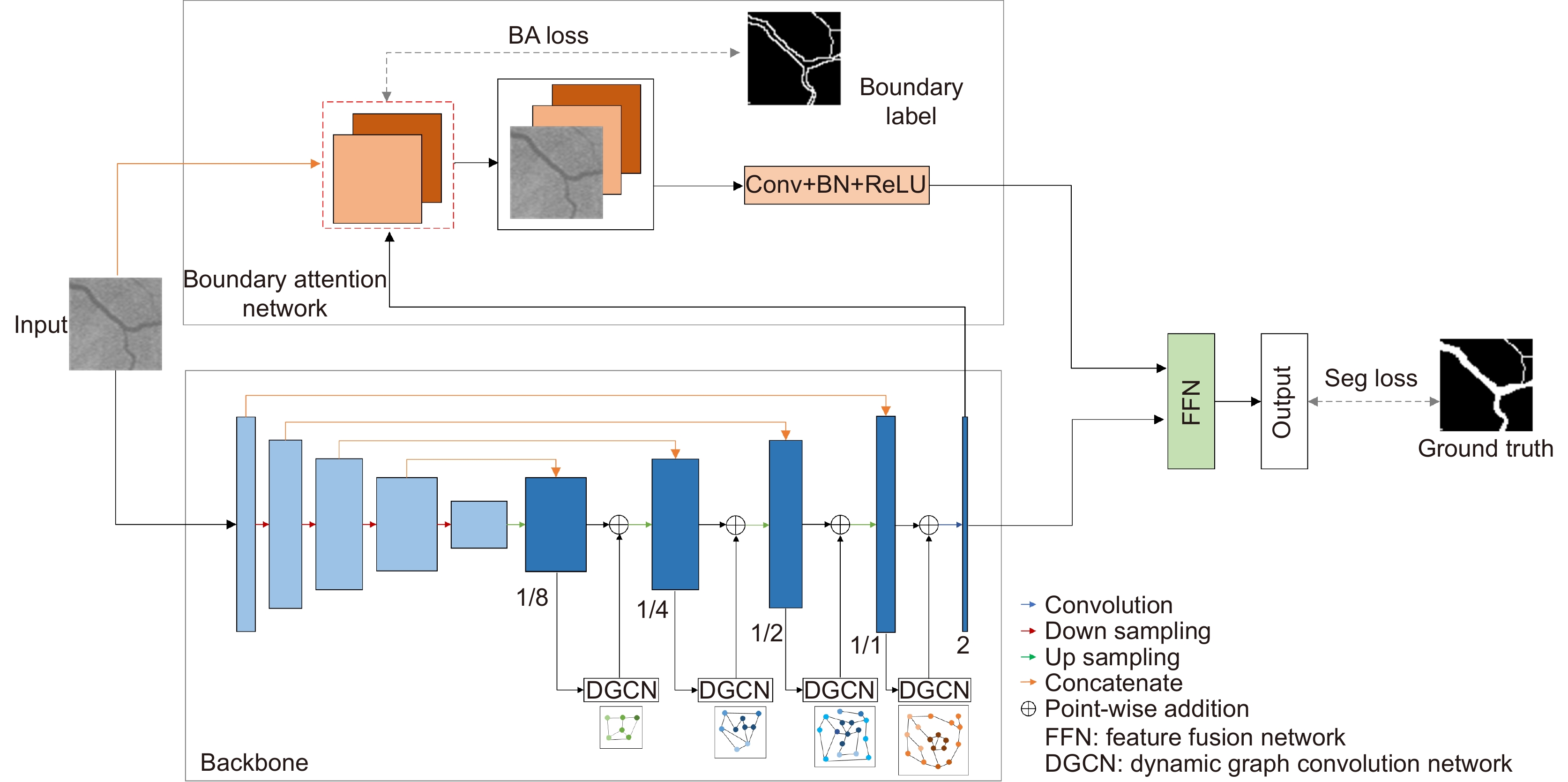
Overview: The state of retinal blood vessels is an important indicator for clinicians in the auxiliary diagnosis of eye diseases and systemic diseases. In particular, the degree of atrophy and pathological conditions of retinal blood vessels are the key indicators for judging the severity of the diseases. Automatic segmentation of retinal blood vessels is an indispensable step to obtain the key information. Good segmentation results are conducive to accurate diagnosis of the eye diseases. Due to the good characteristic of U-Net that can use skip connection to connect multi-scale feature maps, it performs well in segmentation tasks with small data volume, therefore, it could be applied to retinal vascular segmentation. However, U-Net ignores the features of retinal blood vessels in the training process, resulting in the inability to fully extract the feature information of blood vessels, while its segmentation results show that the vessel pixels are missing or the background noise is incorrectly segmented into blood vessels. Researchers have made various improvements on U-Net for the retinal vessel segmentation task, but the methods still ignore the global structure information and boundary information of retinal vessels. To solve the above problems, a boundary attention assisted dynamic graph convolution retinal vessel segmentation model based on U-Net is proposed in this paper, which supplements the model with more sufficient global structure information and blood vessel boundary information, and extracts more blood vessel feature information as much as possible. First, RGB image graying, contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization, and gamma correction were used to preprocess the retinal images, which can improve the contrast between the vascular pixels and background, and even improve the brightness of some vascular areas. Then, rotation and slice were adopted to enhance the data. The processed images were input into the model to obtain the segmentation result. In the model, dynamic graph convolution was embedded into the decoder of U-Net to form multi-scale structures to fuse the structural information of feature maps with different scales. The method not only can enhance the ability of dynamic graph convolution to obtain global structural information but also can reduce the interference degree of the noise and the segmenting incorrectly background on the vascular pixels. At the same time, in order to strengthen the diluted vascular boundary information in the process of up-down sampling, the boundary attention network was utilized to enhance the model’s attention to the boundary information for the sake of improving the segmentation performance. The presented model was tested on the retinal image datasets, DRIVE, CHASEDB1, and STARE. The experimental results show that the AUC of the algorithm on DRIVE, CHASEDB1 and STARE are 0.9851, 0.9856 and 0.9834, respectively. It is proved that the model is effective.
-

-
表 1 评价指标
Table 1. Evaluation indexes
F1 SE SP ACC $\dfrac{{2 \times PR \times SE}}{{PR + SE}}$ $\dfrac{{TP}}{{TP{\text{ + }}FN}}$ $\dfrac{{TN}}{{TN + FP}}$ $\dfrac{{TP + TN}}{{TP + TN + FP + FN}}$ 表 2 消融实验结果
Table 2. Ablation experiments results
Dataset Network F1 SE SP ACC AUC Time/s DRIVE U-Net 0.8353 0.8330 0.9777 0.9601 0.9848 1.00 DGU-Net 0.8357 0.8275 0.9789 0.9605 0.9850 1.22 BU-Net 0.8355 0.8352 0.9773 0.9600 0.9849 1.00 BDGU-Net 0.8359 0.8300 0.9785 0.9604 0.9851 1.24 CHASEDB1 U-Net 0.8108 0.8052 0.9820 0.9660 0.9854 1.31 DGU-Net 0.8053 0.7812 0.9842 0.9658 0.9846 1.73 BU-Net 0.8133 0.8210 0.9803 0.9659 0.9858 1.31 BDGU-Net 0.8136 0.8146 0.9813 0.9662 0.9856 1.76 STARE U-Net 0.7845 0.7380 0.9863 0.9648 0.9810 2.21 DGU-Net 0.7824 0.7045 0.9908 0.9660 0.9825 2.85 BU-Net 0.7845 0.7352 0.9868 0.9650 0.9806 2.21 BDGU-Net 0.7934 0.7273 0.9900 0.9672 0.9834 2.85 表 3 不同α和β系数取值分析
Table 3. Value analysis of different α and β coefficients
α β F1 SE SP ACC AUC 0.8 0.2 0.8348 0.8252 0.9790 0.9604 0.9848 0.7 0.3 0.8351 0.8230 0.9795 0.9605 0.9848 0.6 0.4 0.8359 0.8300 0.9785 0.9604 0.9851 0.5 0.5 0.8351 0.8284 0.9785 0.9603 0.9849 表 4 不同网络在DRIVE、CHASEDB1和STARE数据集的指标对比
Table 4. Index comparison of different networks in DRIVE, CHASEDB1 and STARE datasets
Dataset Network Year F1 SE SP ACC AUC Time/s DRIVE 2nd Human Observer[20] — — 0.7760 0.9724 0.9472 — — Iternet[21] 2020 0.8353 0.8370 0.9770 0.9600 0.9847 1.37 Yang[22] 2021 0.8297 0.8353 0.9751 0.9579 — — MLA-DU-Net[23] 2021 0.8352 0.8269 0.9788 0.9603 0.9849 1.64 Res2Unet[24] 2022 0.8292 0.8332 0.9756 0.9583 0.9782 1.21 Zhang[15] 2022 0.8349 0.8345 0.9773 0.9600 0.9850 1.20 BDGU-Net 2022 0.8359 0.8300 0.9785 0.9604 0.9851 1.24 CHASEDB1 2nd Human Observer[20] — — 0.8105 0.9711 0.9545 — — Iternet[21] 2020 0.8120 0.8144 0.9809 0.9658 0.9856 1.48 Yang[22] 2021 0.7997 0.8176 0.9776 0.9632 — — MLA-DU-Net[23] 2021 0.8063 0.8137 0.9796 0.9646 0.9841 2.13 Res2Unet[24] 2022 0.8071 0.8444 0.9753 0.9634 0.9794 1.47 Zhang[15] 2022 0.8050 0.8141 0.9792 0.9643 0.9841 1.72 BDGU-Net 2022 0.8136 0.8146 0.9813 0.9662 0.9856 1.76 STARE 2nd Human Observer[20] — — 0.8952 0.9384 0.9349 — — Iternet[21] 2020 0.7962 0.7490 0.9874 0.9667 0.9838 2.76 Yang[22] 2021 0.8155 0.7946 0.9821 0.9626 — — MLA-DU-Net[23] 2021 0.7965 0.7925 0.9812 0.9649 0.9826 3.95 Res2Unet[24] 2022 0.7858 0.7392 0.9865 0.9650 0.9709 2.77 Zhang[15] 2022 0.7878 0.7381 0.9871 0.9655 0.9823 3.07 BDGU-Net 2022 0.7934 0.7273 0.9900 0.9672 0.9834 2.85 -
参考文献
[1] Wu H S, Wang W, Zhong J F, et al. SCS-net: a scale and context sensitive network for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Med Image Anal, 2021, 70: 102025. doi: 10.1016/J.MEDIA.2021.102025
[2] 梁礼明, 周珑颂, 陈鑫, 等. 鬼影卷积自适应视网膜血管分割算法[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(10): 210291. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.210291
Liang L M, Zhou L S, Chen X, et al. Ghost convolution adaptive retinal vessel segmentation algorithm[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2021, 48(10): 210291. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.210291
[3] 李兰兰, 张孝辉, 牛得草, 等. 深度学习在视网膜血管分割上的研究进展[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2021, 15(11): 2063−2076. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2103099
Li L L, Zhang X H, Niu D C, et al. Research progress of deep learning in retinal vessel segmentation[J]. J Front Comput Sci Technol, 2021, 15(11): 2063−2076. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2103099
[4] Zhou Y Q, Yu H C, Shi H. Study group learning: improving retinal vessel segmentation trained with noisy labels[C]//Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, 2021: 57–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_6.
[5] Ummadi V. U-net and its variants for medical image segmentation: a short review[Z]. arXiv: 2204.08470, 2022. https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.08470v1.
[6] Jin Q G, Meng Z P, Pham T D, et al. DUNet: a deformable network for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Knowl-Based Syst, 2019, 178: 149−162. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.04.025
[7] Zhang T, Li J, Zhao Y, et al. MC-UNet multi-module concatenation based on u-shape network for retinal blood vessels segmentation[Z]. arXiv: 2204.03213, 2022. https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.03213v1.
[8] Zhu X F, Gan J Z, Lu G Q, et al. Spectral clustering via half-quadratic optimization[J]. World Wide Web, 2020, 23(3): 1969−1988. doi: 10.1007/s11280-019-00731-8
[9] Kipf T N, Welling M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks[Z]. arXiv: 1609.02907, 2016. https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.02907.
[10] Shin S Y, Lee S, Yun I D, et al. Deep vessel segmentation by learning graphical connectivity[J]. Med Image Anal, 2019, 58: 101556. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2019.101556
[11] Meng Y D, Wei M, Gao D X, et al. CNN-GCN aggregation enabled boundary regression for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Lima, 2020: 352–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59719-1_35.
[12] Zhu Y H, Ma J B, Yuan C A, et al. Interpretable learning based Dynamic Graph Convolutional Networks for Alzheimer’s Disease analysis[J]. Inf Fusion, 2022, 77: 53−61. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.07.013
[13] Li X, Yang Y B, Zhao Q J, et al. Spatial pyramid based graph reasoning for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, 2020: 8950–8959. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00897.
[14] Zhang Y S, Chung A C S. Deep supervision with additional labels for retinal vessel segmentation task[C]//Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Granada, 2018: 83–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00934-2_10.
[15] Zhang Y, Fang J, Chen Y, et al. Edge-aware U-net with gated convolution for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Biomed Signal Process Control, 2022, 73: 103472. doi: 10.1016/J.BSPC.2021.103472
[16] Yu F, Wang D Q, Shelhamer E, et al. Deep layer aggregation[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, 2018: 2403–2412. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00255.
[17] Jin X, Lai Z H, Jin Z. Learning dynamic relationships for facial expression recognition based on graph convolutional network[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2021, 30: 7143−7155. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3101820
[18] Chen X, Qi D L, Shen J X. Boundary-aware network for fast and high-accuracy portrait segmentation[Z]. arXiv: 1901.03814, 2019. https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.03814.
[19] Yu C Q, Wang J B, Peng C, et al. BiSeNet: bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, 2018: 325–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01261-8_20.
[20] Zhang Y, He M, Chen Z N, et al. Bridge-Net: context-involved U-net with patch-based loss weight mapping for retinal blood vessel segmentation[J]. Expert Syst Appl, 2022, 195: 116526. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.116526
[21] Li L Z, Verma M, Nakashima Y, et al. IterNet: retinal image segmentation utilizing structural redundancy in vessel networks[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Snowmass, 2020: 3656–3665. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV45572.2020.9093621.
[22] Yang L, Wang H X, Zeng Q S, et al. A hybrid deep segmentation network for fundus vessels via deep-learning framework[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 448: 168−178. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.03.085
[23] Yuan Y C, Zhang L, Wang L T, et al. Multi-level attention network for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2022, 26(1): 312−323. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3089201
[24] Li X J, Ding J Q, Tang J J, et al. Res2Unet: a multi-scale channel attention network for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Neural Comput Appl, 2022, 34(14): 12001−12015. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07086-8
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: