Research progress of pulse position modulation technology in optical wireless communication
-
摘要:
调制解调是提高无线光通信传输效率的关键技术,不同的调制方式其性能也有所不同。类脉冲位置调制是指脉冲位置调制(PPM)、差分脉冲位置调制(DPPM)及其组合以及由此演变而成的各种脉冲位置调制方式。本文总结了国内外类脉冲位置调制的研究进展,同时介绍了西安理工大学在类脉冲位置调制方面所做的工作,主要对开关键控、脉冲位置调制、多脉冲位置调制、差分脉冲位置调制、重叠脉冲位置调制、双宽脉冲位置调制、双幅度脉冲位置调制、数字脉冲间隔调制、双头脉冲间隔调制、双脉冲间隔调制、双幅度脉冲间隔调制、定长数字脉冲间隔调制、定长双幅度脉冲间隔调制、缩短脉冲位置调制和分离双脉冲位置调制等调制方式在符号结构、带宽需求、平均发射功率、误时隙率和平均信道容量等方面的性能做了分析比较。最后展望了无线光通信的发展方向。
Abstract:Modulation and demodulation are key technologies to improve the transmission efficiency of optical wireless communication. Different modulation methods have different performances. This paper summarizes the research progress of various types of pulse position modulation at home and abroad, and then introduces the research from the Xi’an University of Technology in the area of pulse position modulation. For on-off keying, pulse position modulation, multiple pulse position modulation, differential pulse position modulation, overlapping pulse position modulation, dual duration position modulation, dual-amplitude pulse position modulation, digital pulse interval modulation, double-headed pulse interval modulation, dual-pulse interval modulation, dual-amplitude pulse interval modulation, fixed-length digital pulse interval modulation, fixed-length dual-amplitude pulse interval modulation, shorten pulse position modulation and separated double pulse position modulation, the performance of the symbol structure, bandwidth requirement, average transmit power, time slot error rate and average channel capacity are analyzed and compared. Finally, the development direction of pulse-like position modulation is prospected.
-
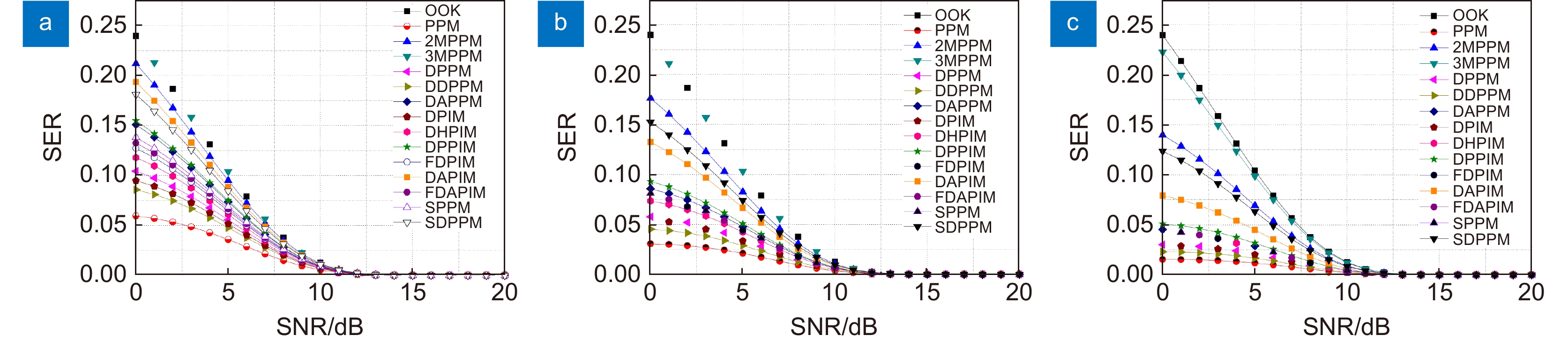
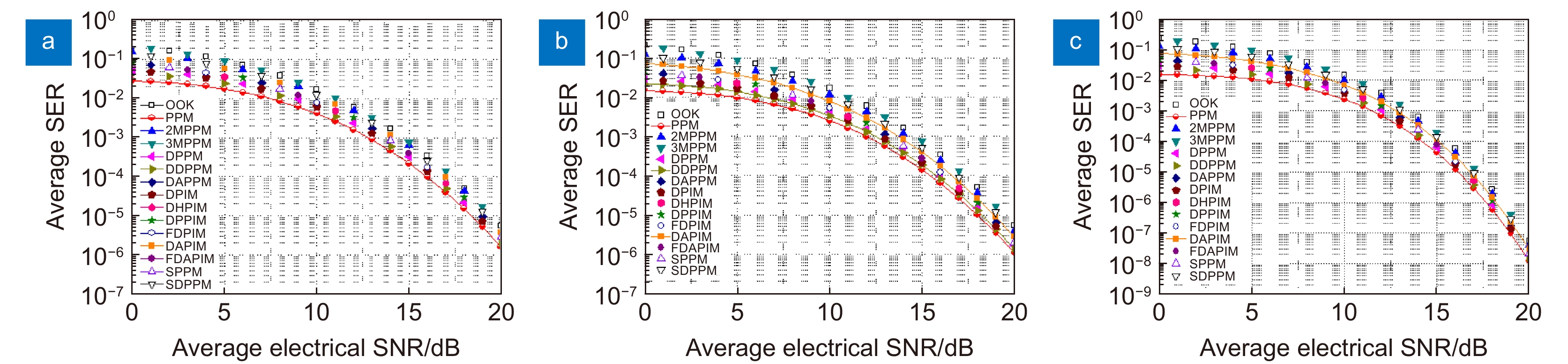
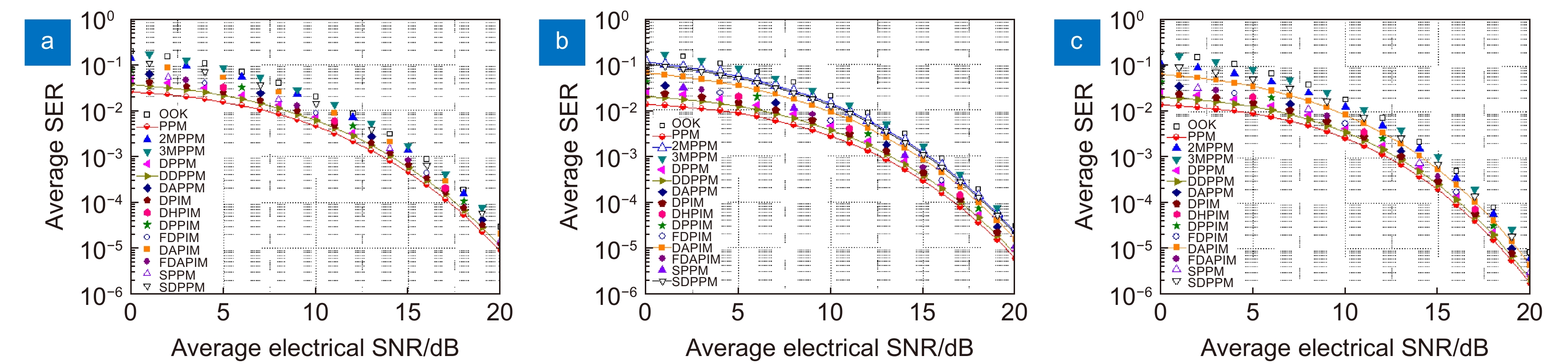
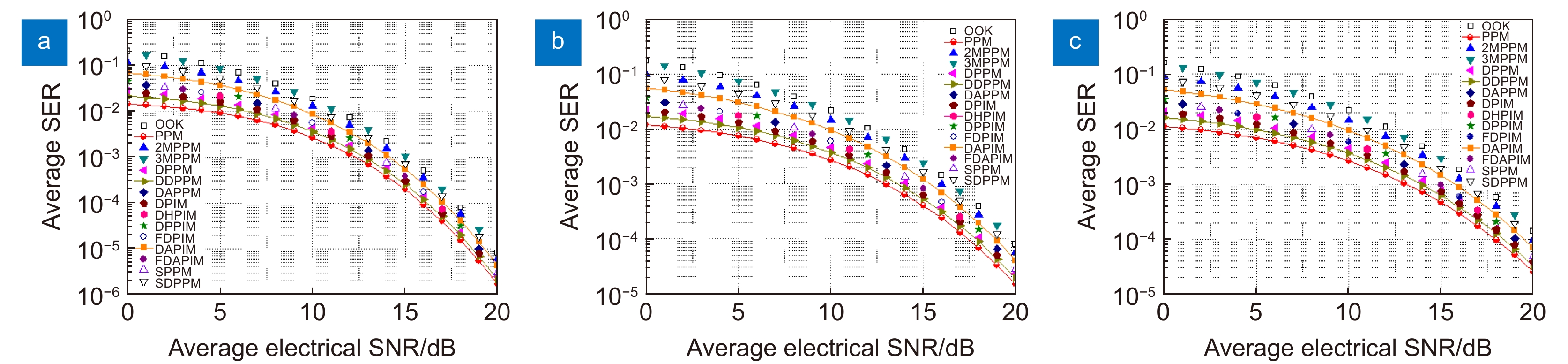
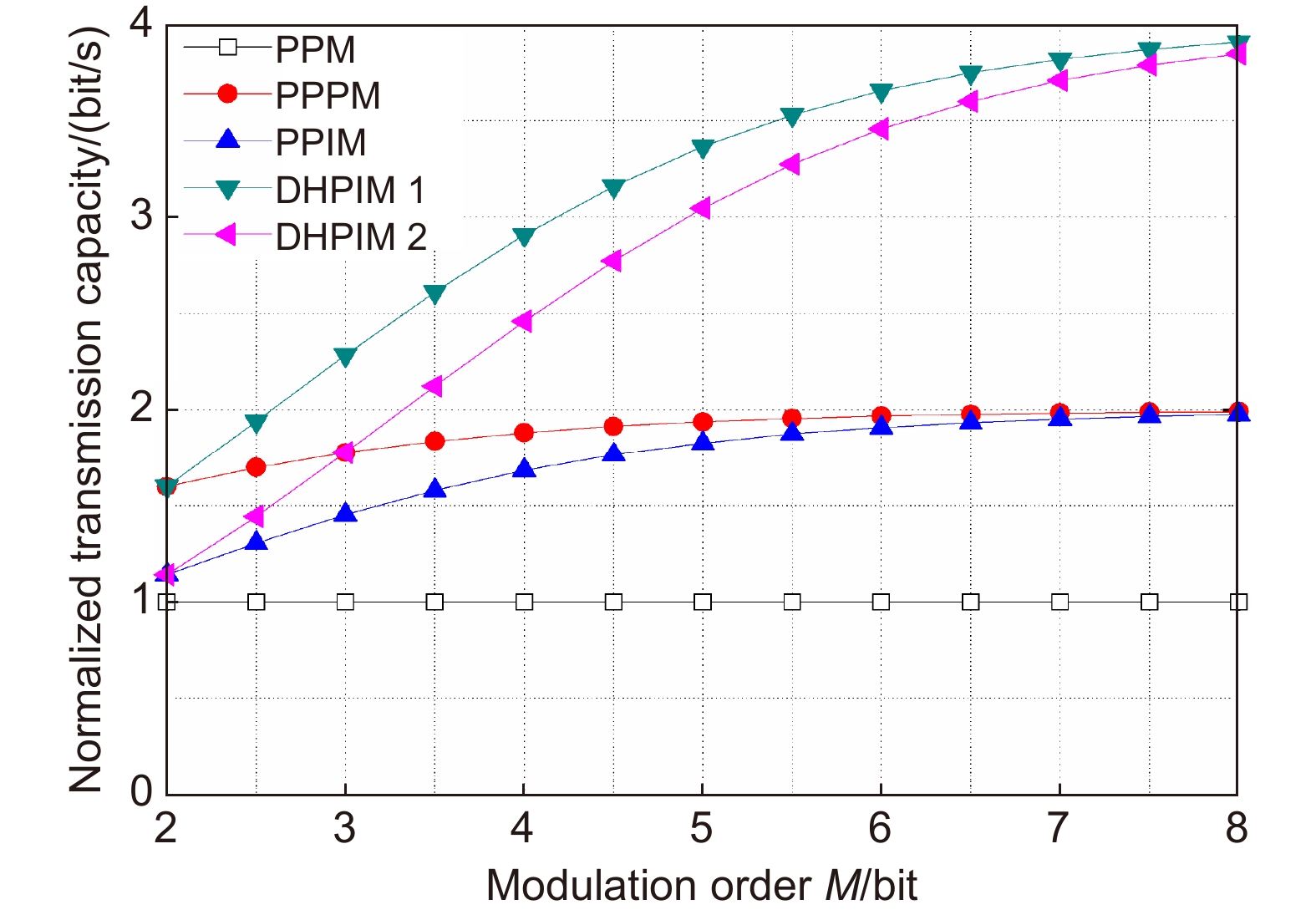
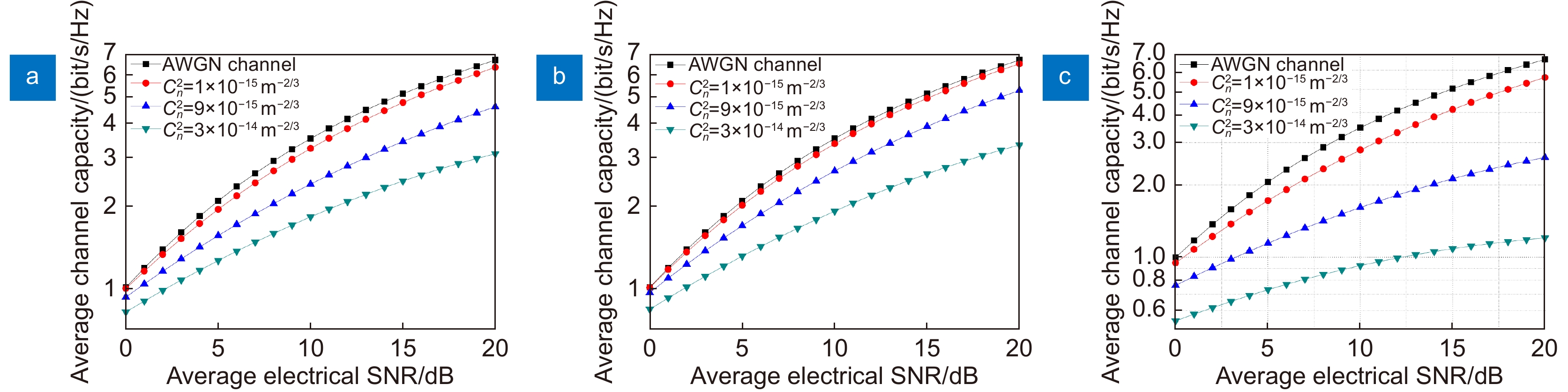
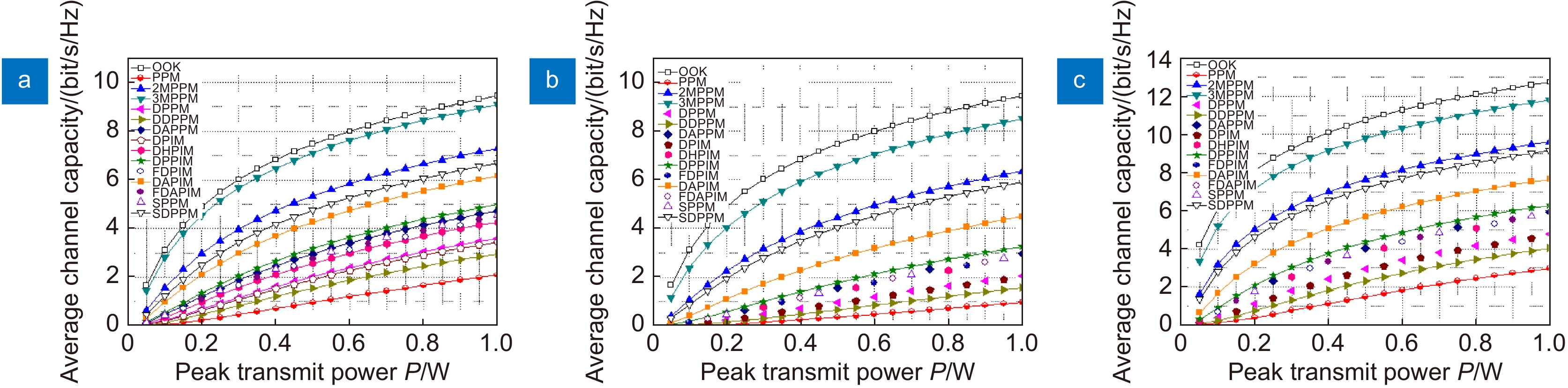
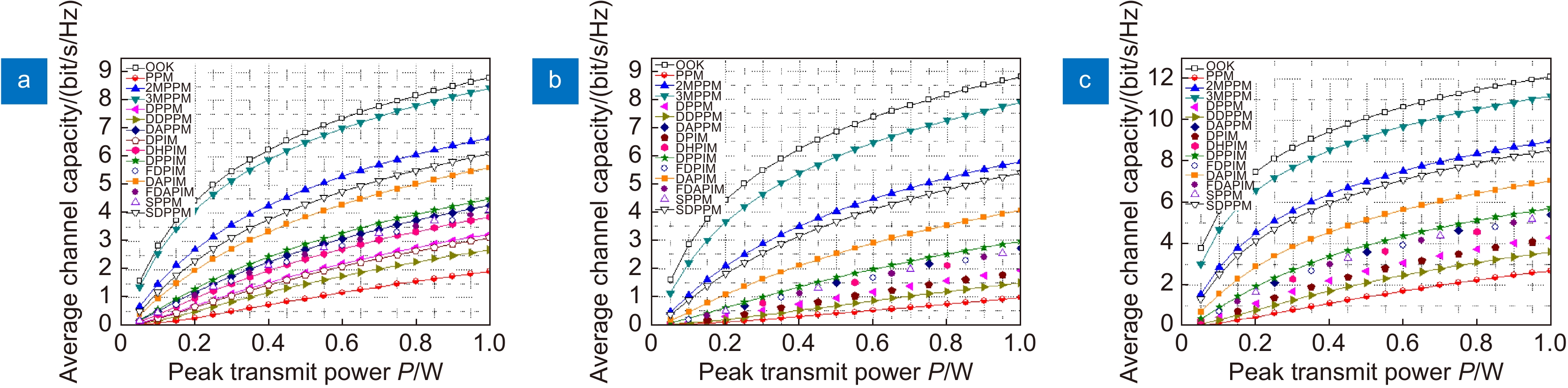
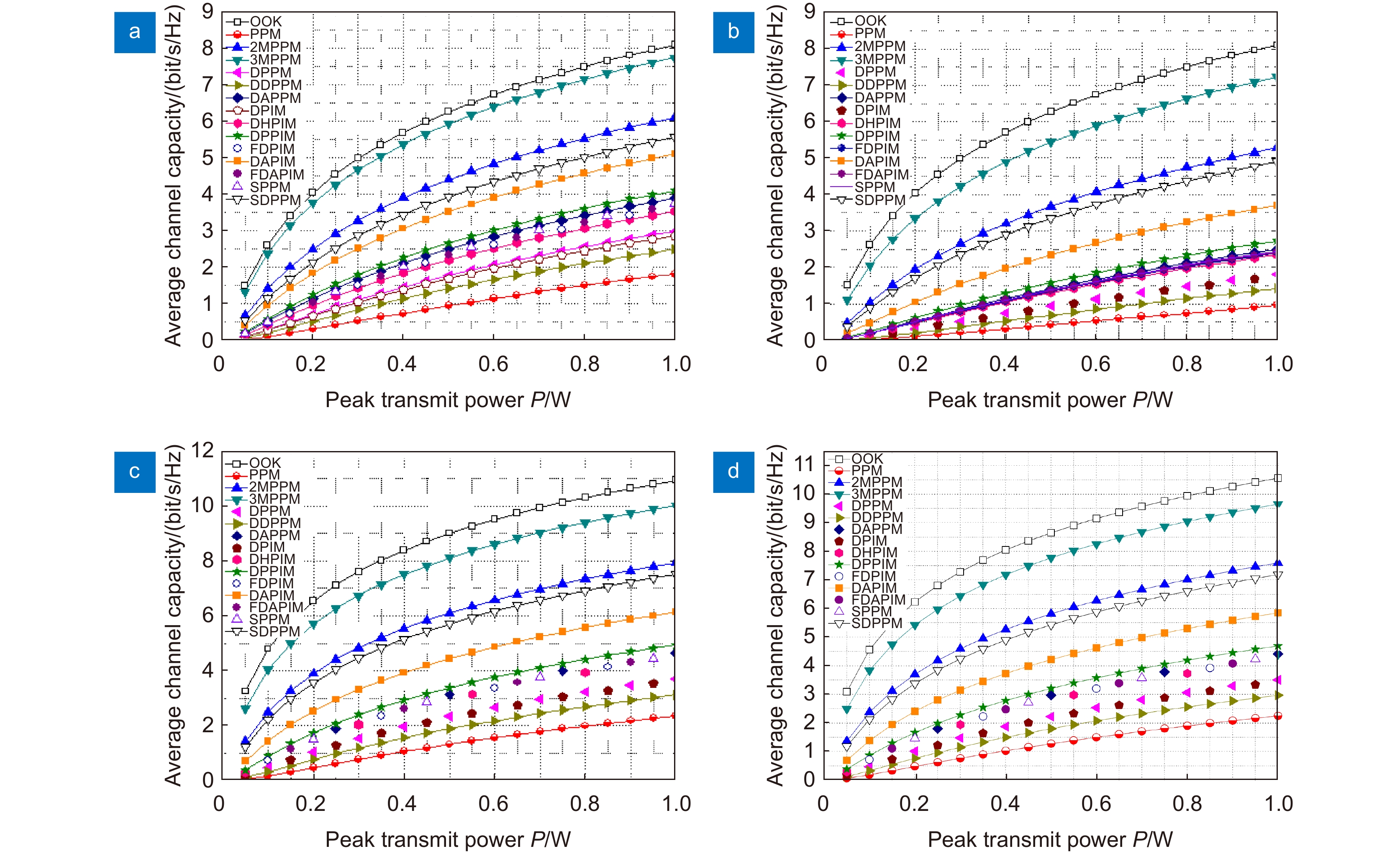
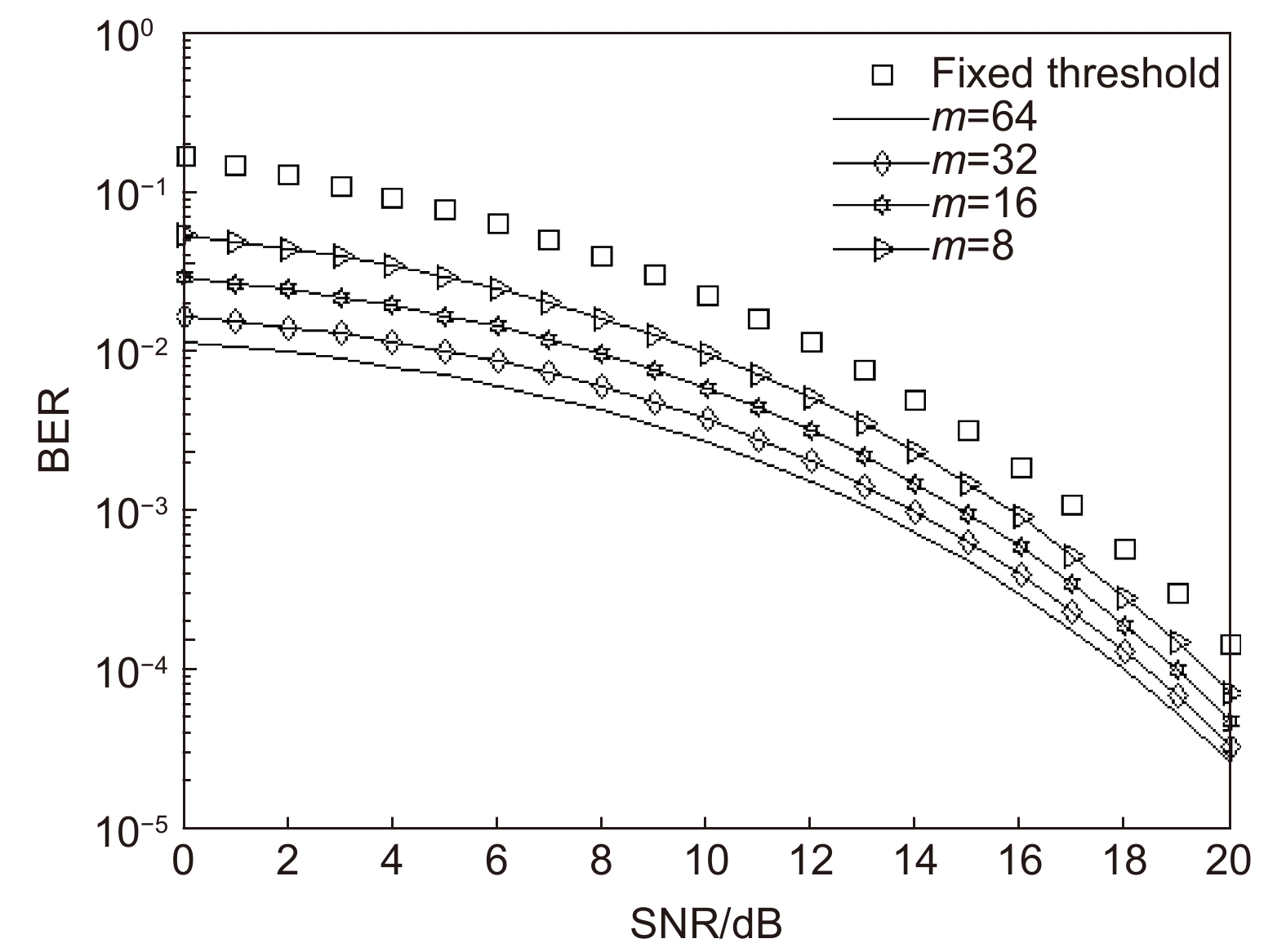
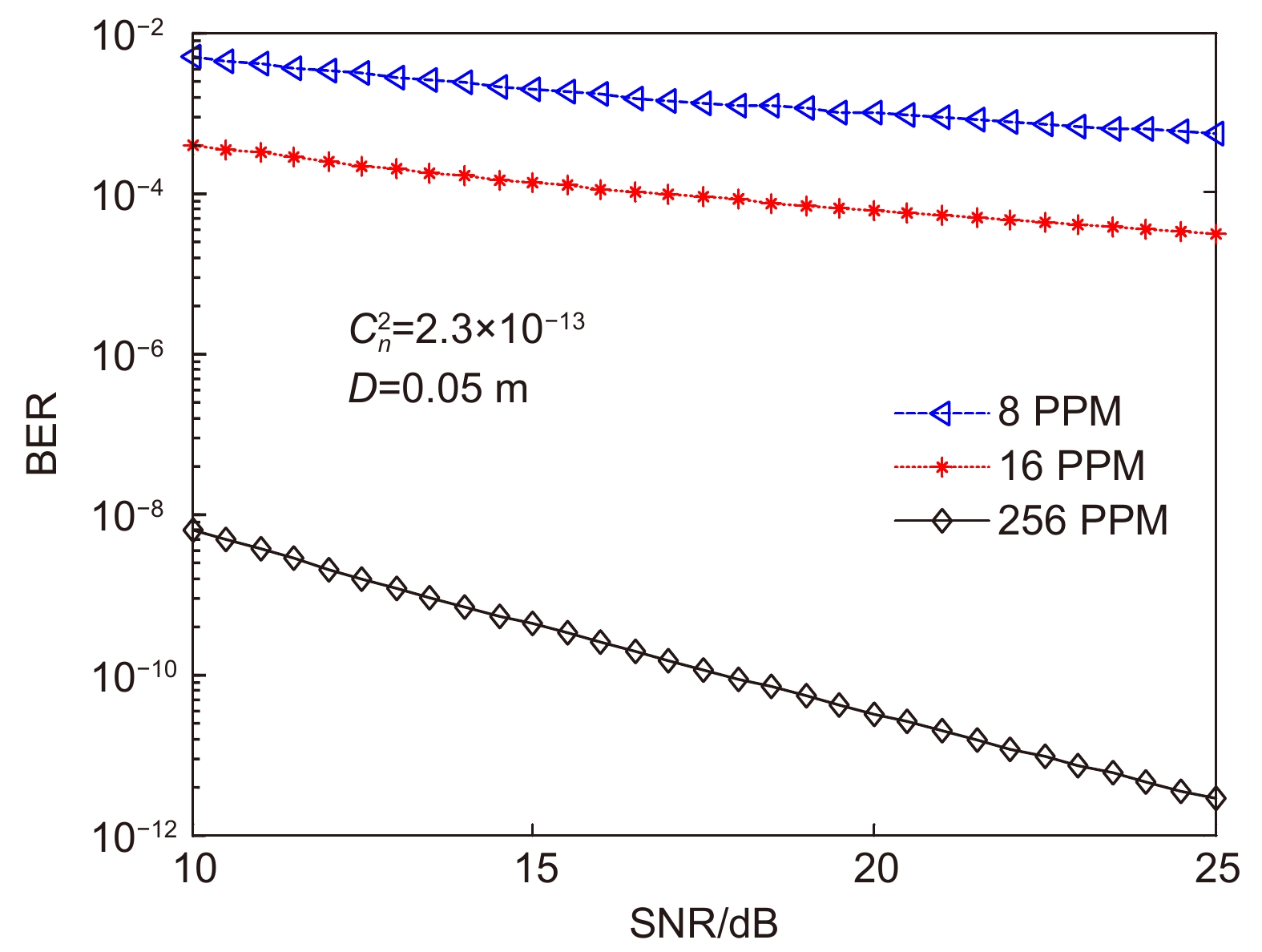
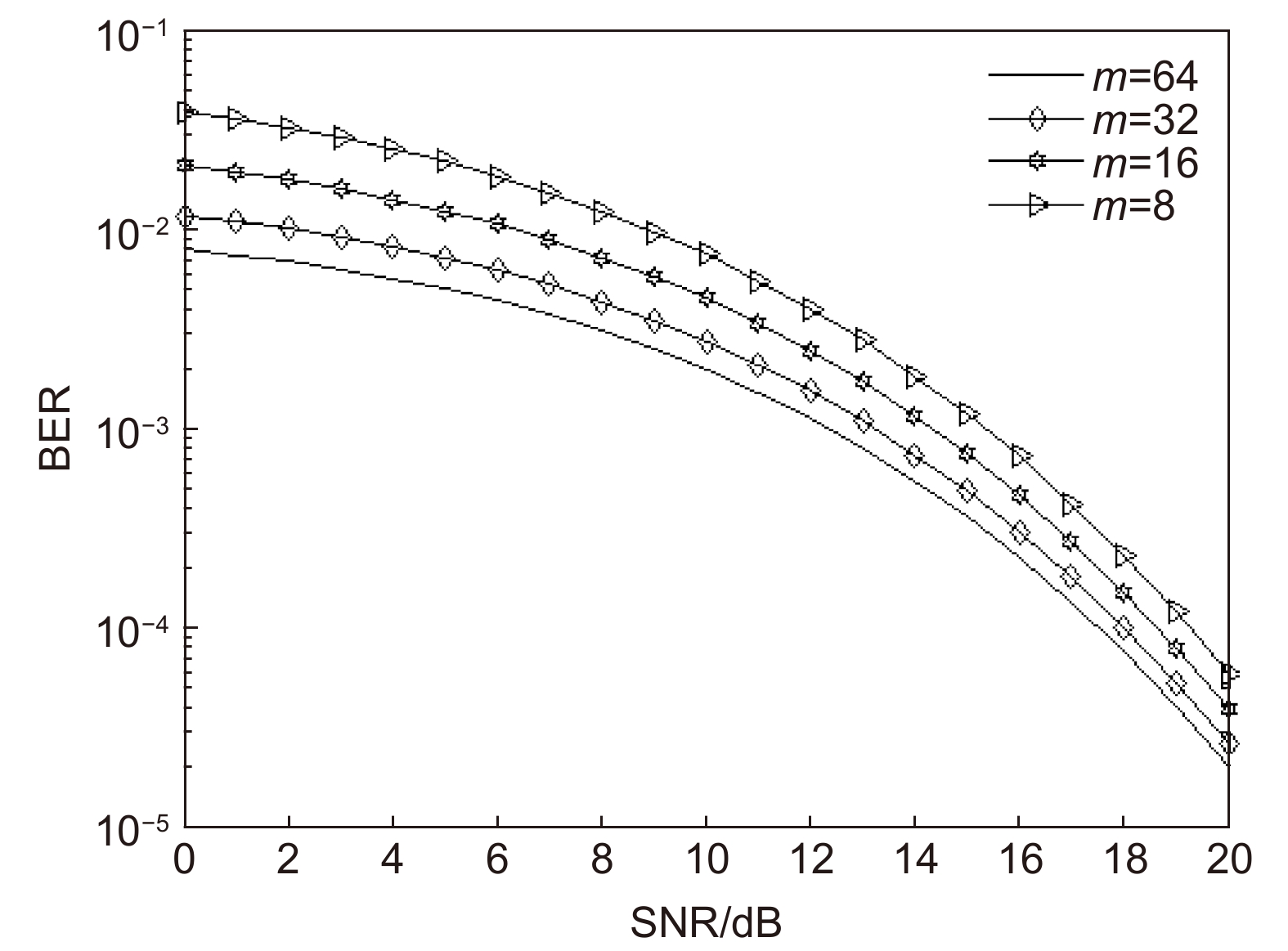
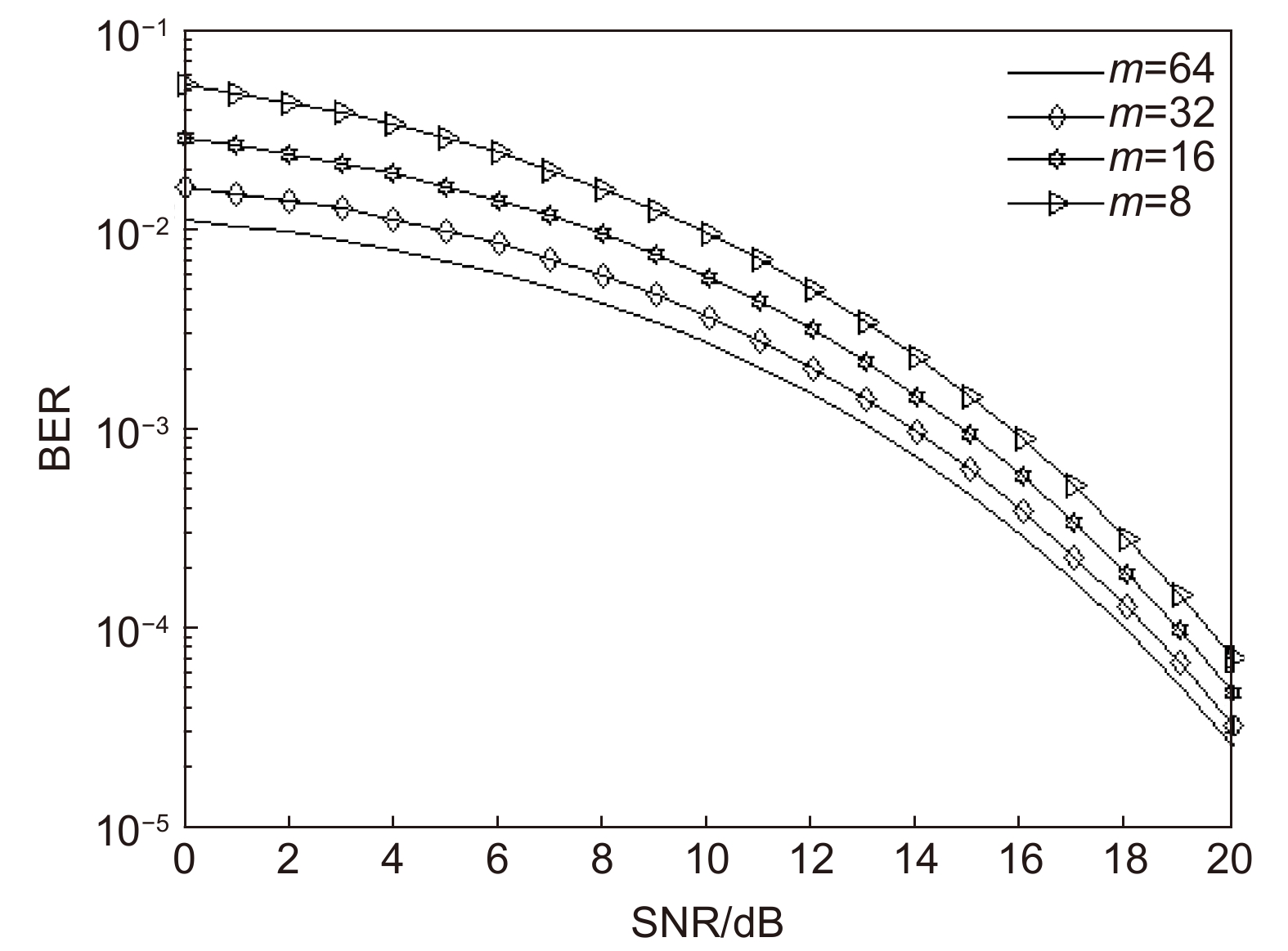
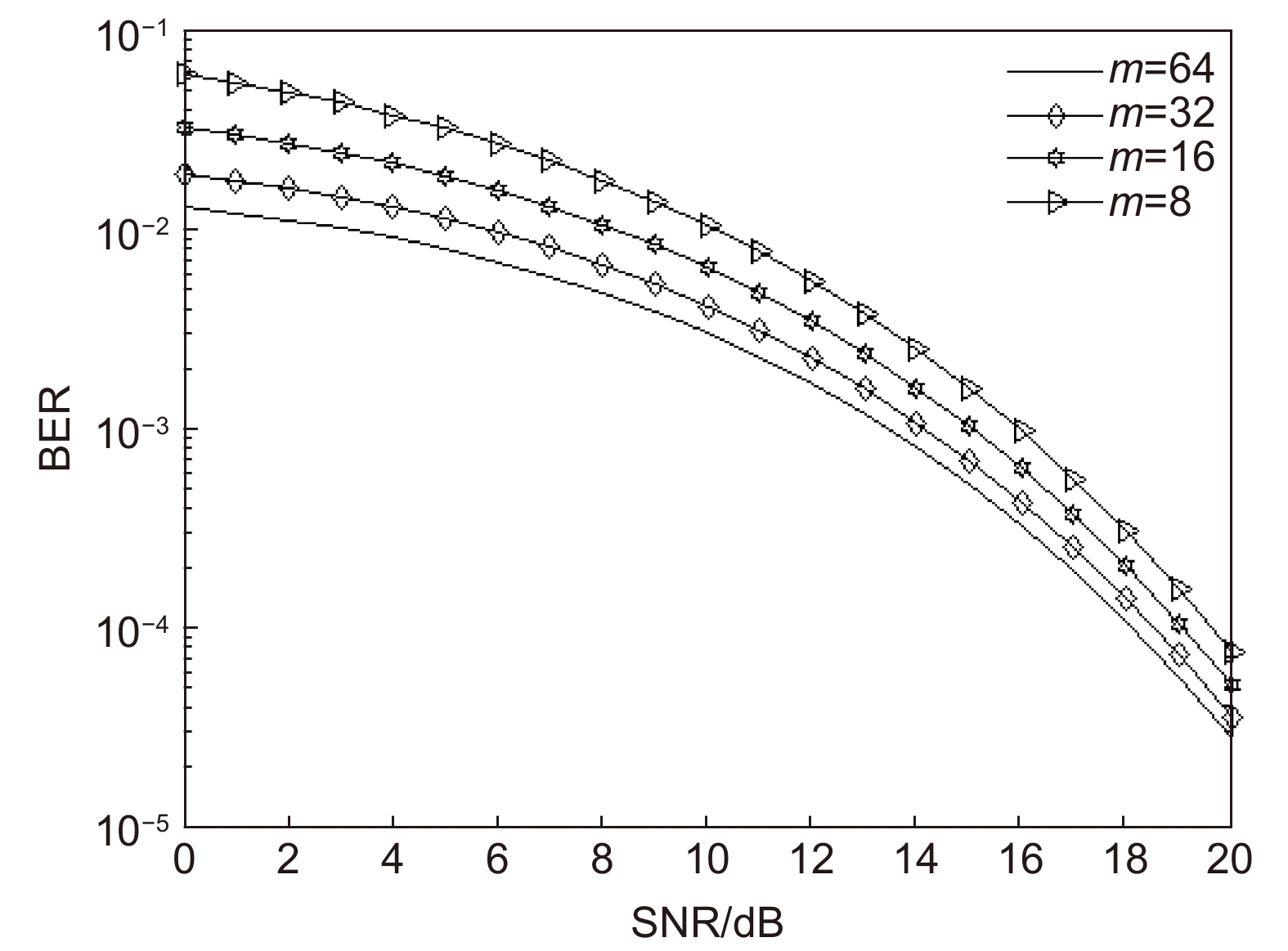
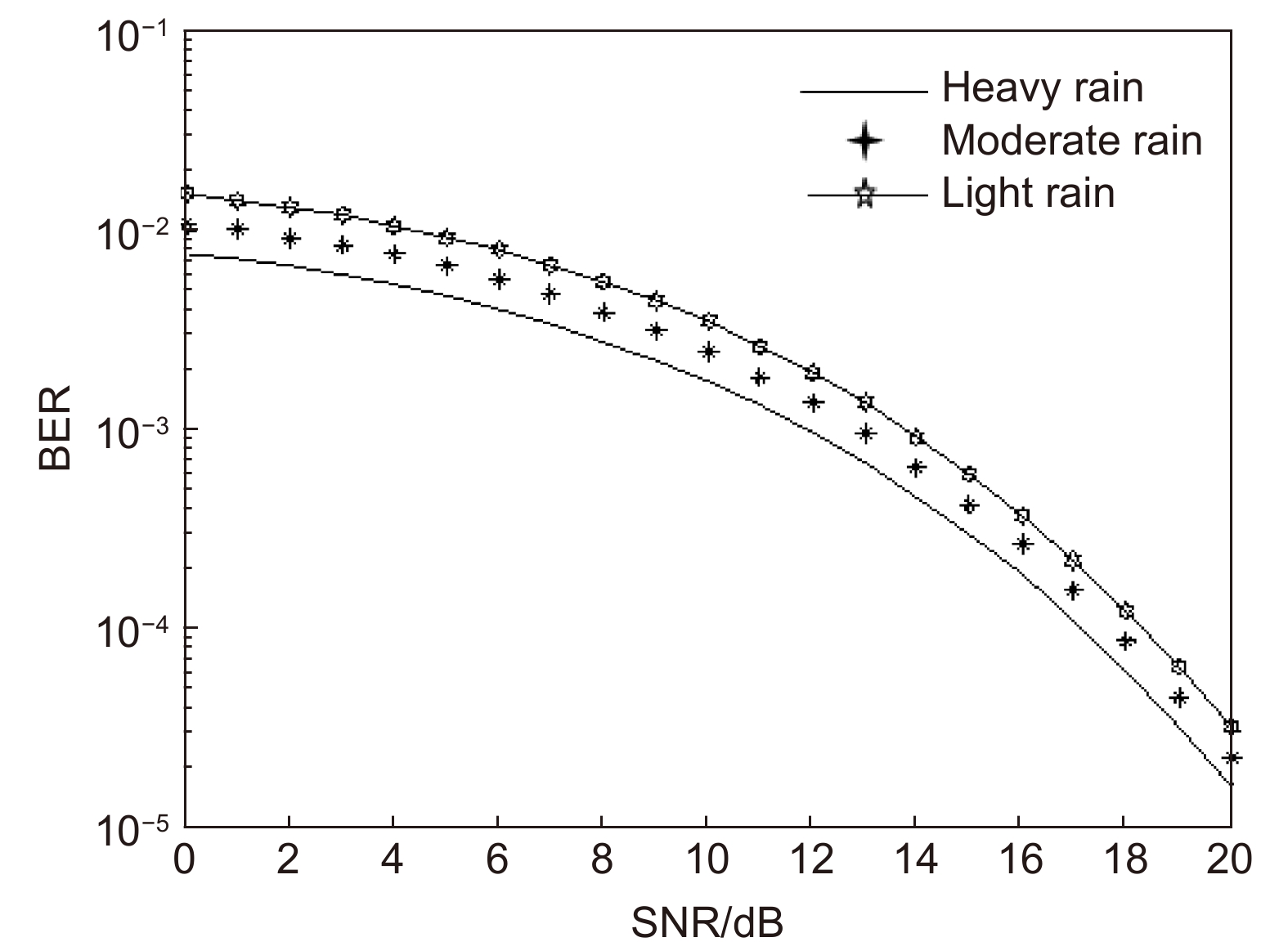
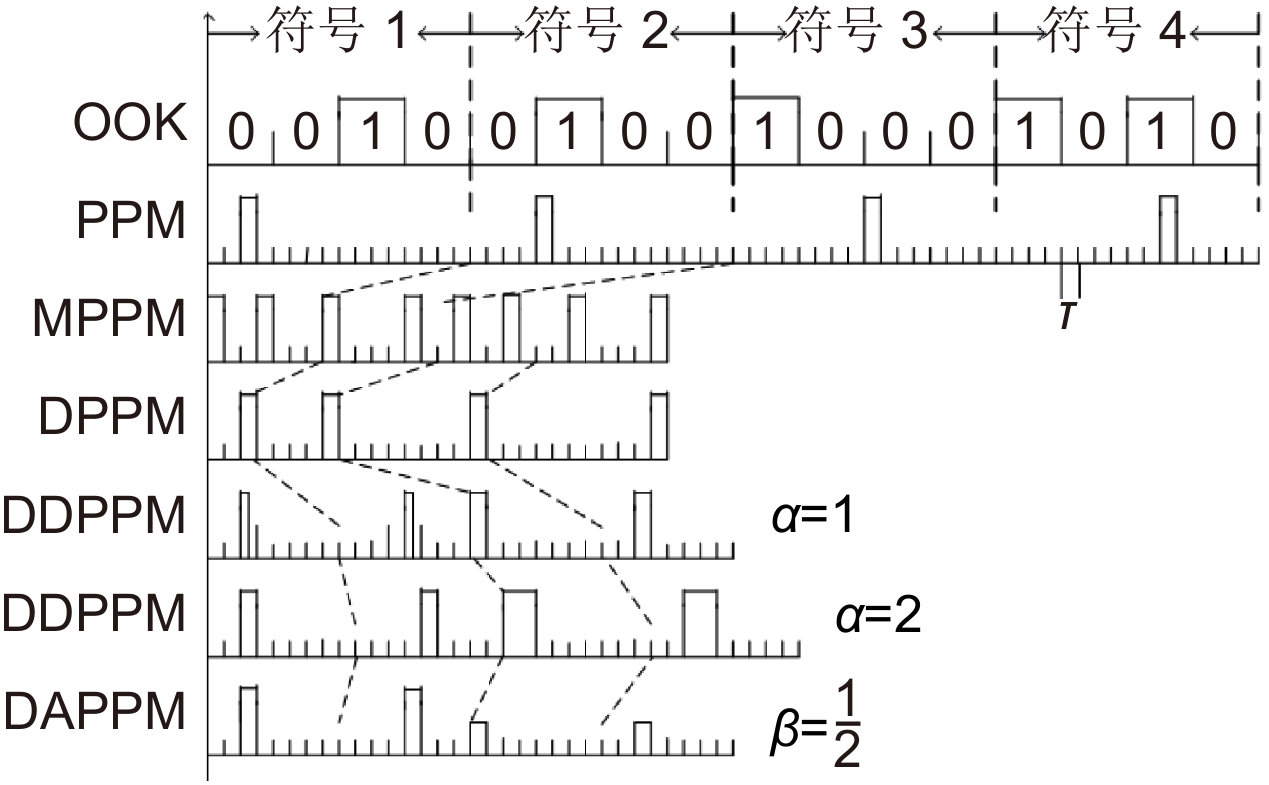
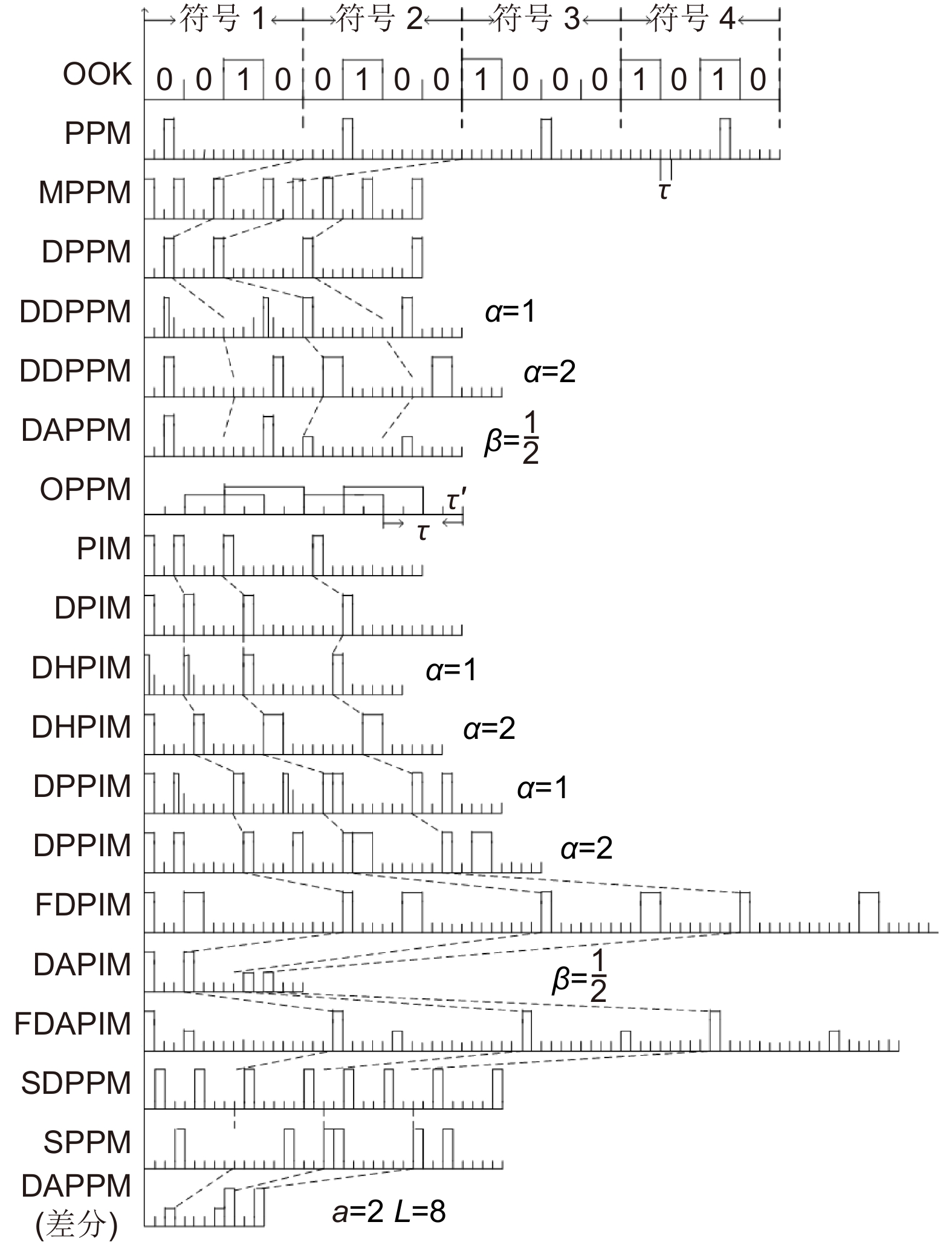
Overview: Optical wireless communication is using an optical carrier for information transmission. It has the advantages of high transmission rate, anti-electromagnetic interference, and high reliability. It has a good application prospect in solving the "last kilometer" problem, emergency communication, and satellite (satellite ground) communication. Quasi pulse position modulation refers to PPM, DPPM, their combinations and various pulse position modulation modes evolved from them. However, when the laser beam propagates through the atmospheric channel, the error control performance of the optical communication system will become worse due to various factors such as atmospheric attenuation and turbulence. In order to improve the efficiency of communication, a series of modulation technologies have been studied. Advanced modulation format and corresponding demodulation technology are selected to ensure high-efficiency transmission and low bit error rate, so as to reduce the interference of the atmospheric environment to the communication system. Therefore, the research on modulation is one of the important topics in the field of wireless optical communication. In order to select the appropriate modulation mode, Ke Xizheng made a systematic analysis of quasi pulse position modulation. Ding Deqiang analyzed the performance of PPM and realized it through hardware. Zhao Li studied DPPM and analyzed its performance. Qin Ling studied the symbol structure and constellation of MPPM and realized MPPM through hardware. Huang Lei analyzed the basic principle and performance of OPPM. Ma Lina organically combined PPM and polarization modulation. Sun Changmei analyzed the symbol structure, power spectral density and bandwidth requirements of DAPPM. Jia Chao analyzed the performance of DHPI. Liu Meiping systematically studied the symbol structure, power spectral density and bit error rate of pulse-like position modulation. Shi Biyao studied the quadrature amplitude modulation and demodulation program and analyzed the results. Tian Xiaochao discussed the adaptive threshold detection model and analyzed its performance. Pei Guoqiang studied multi-beam emission and multi-aperture reception methods to suppress turbulence and improve communication performance. Liu Zhaohui studied and optimized the response characteristics of semiconductor lasers and photodetectors to improve the modulation rate of the communication system. This paper makes a comprehensive analysis and comparison of the performance of more than ten modulation modes, obtains the best modulation mode in a certain performance, selects the matching modulation mode for different channels, and finds out the shortcomings of these modulation modes, so as to provide a theoretical basis for selecting the appropriate modulation mode in different occasions.
-

-
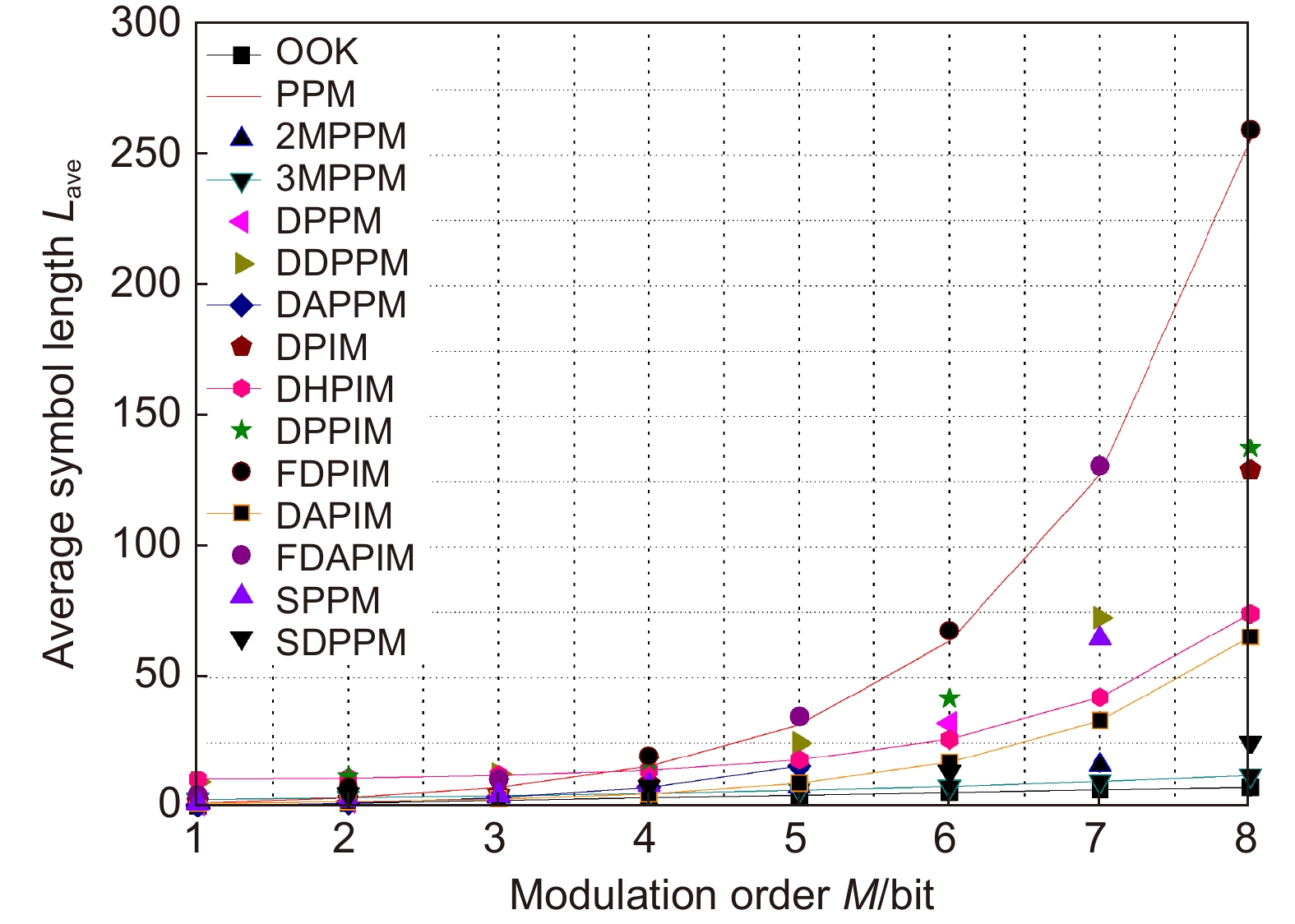
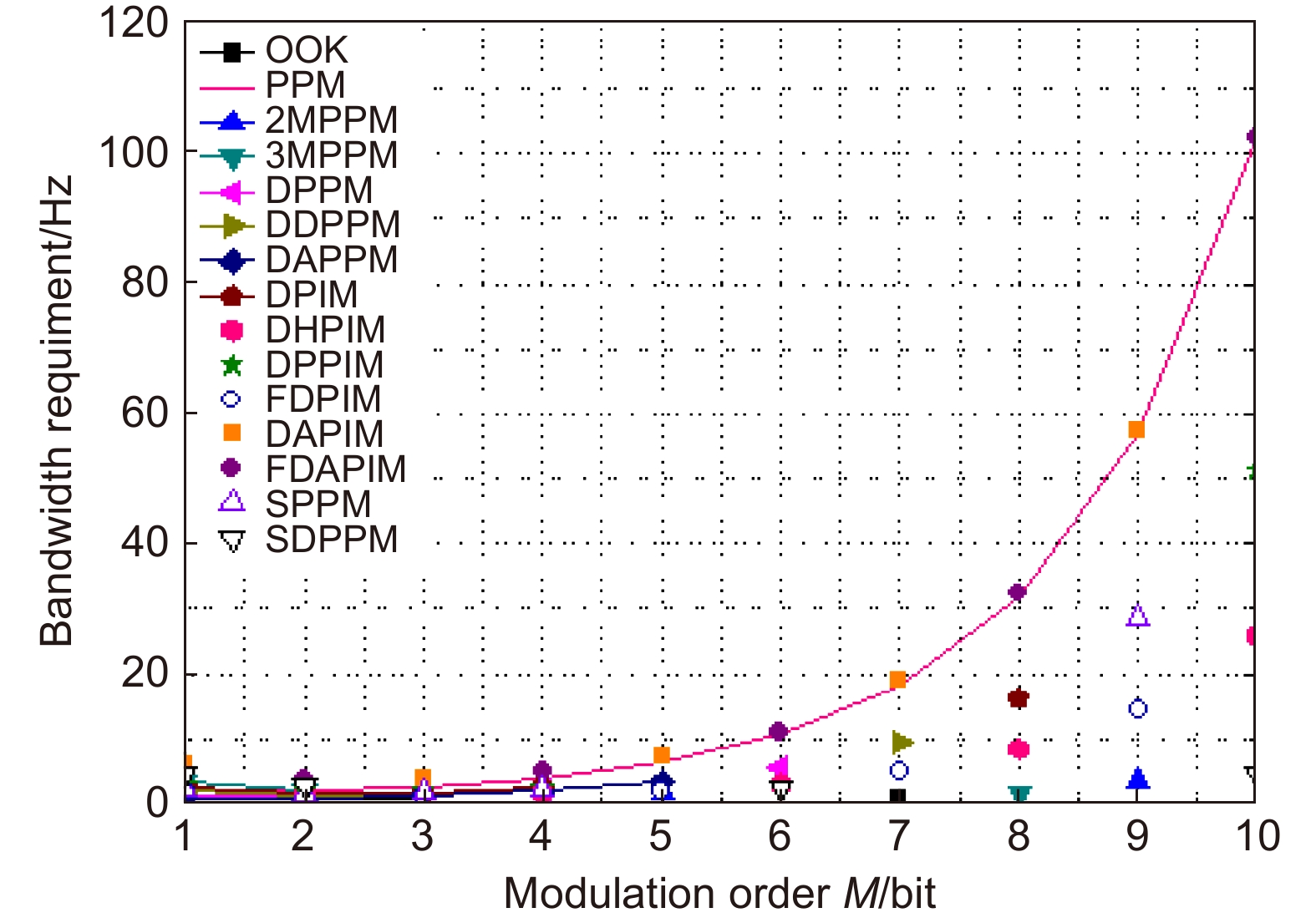
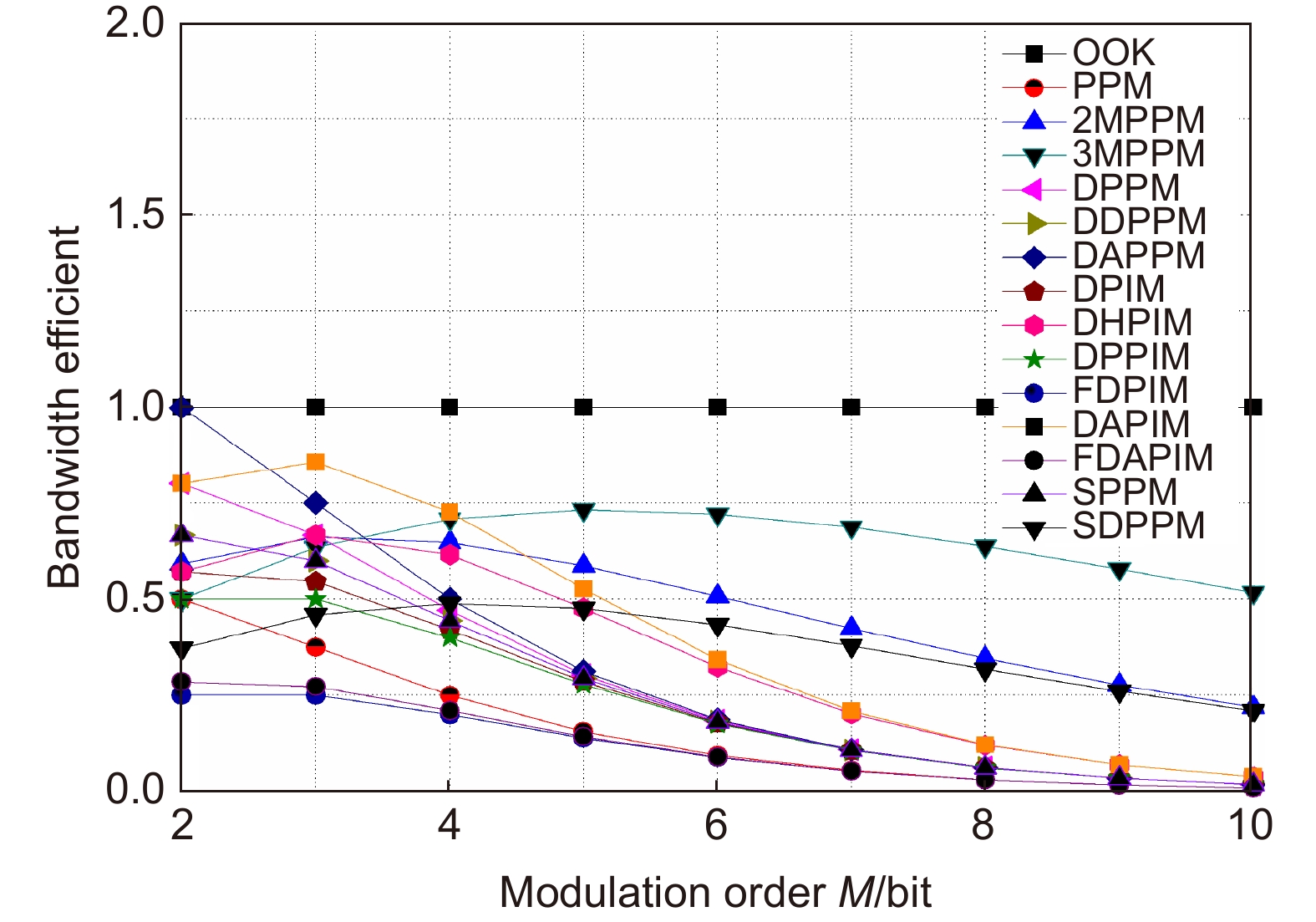
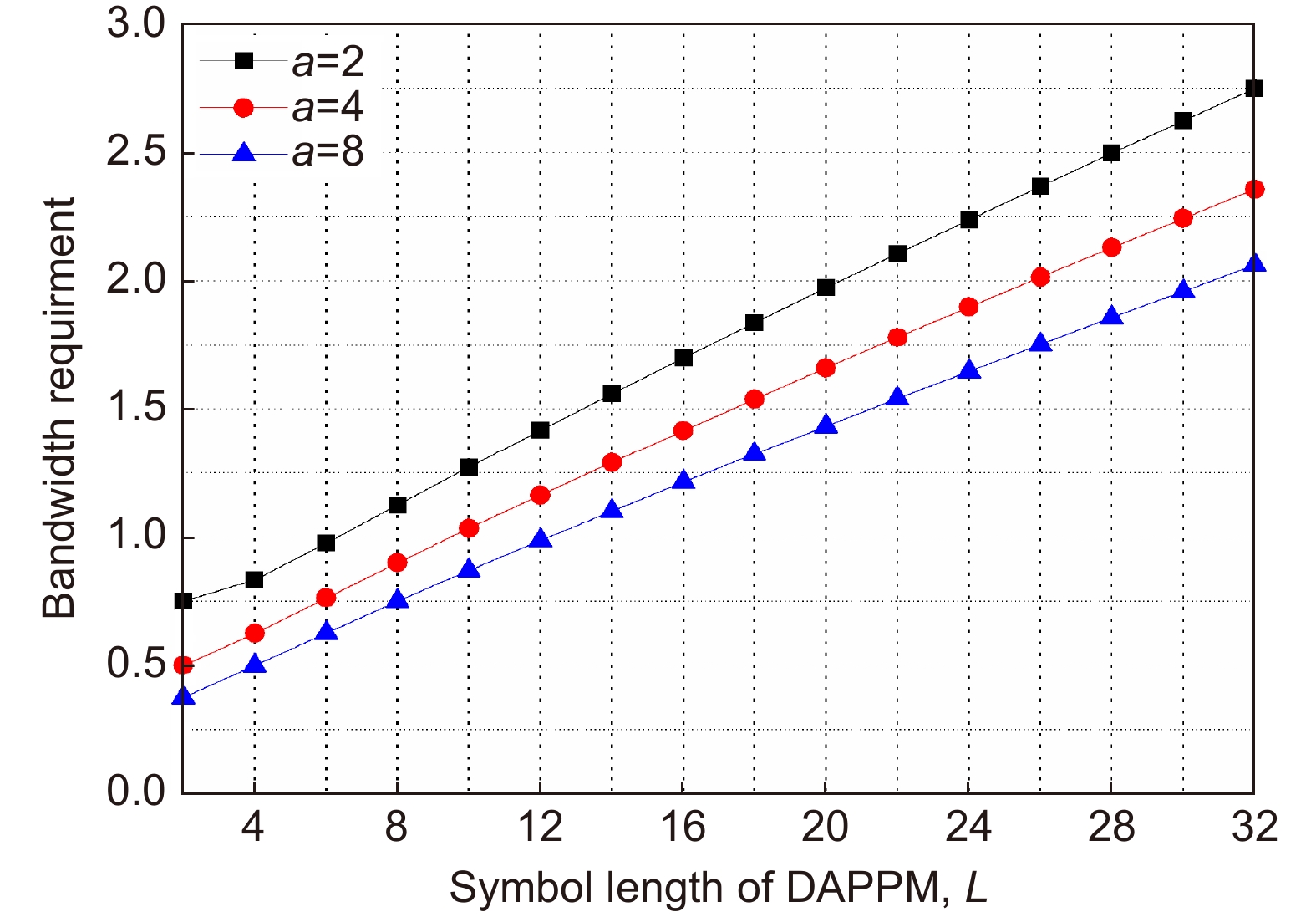
表 1 各调制方式的平均符号长度、带宽需求、平均发射功率
Table 1. The average symbol length, bandwidth requirement and average transmit power
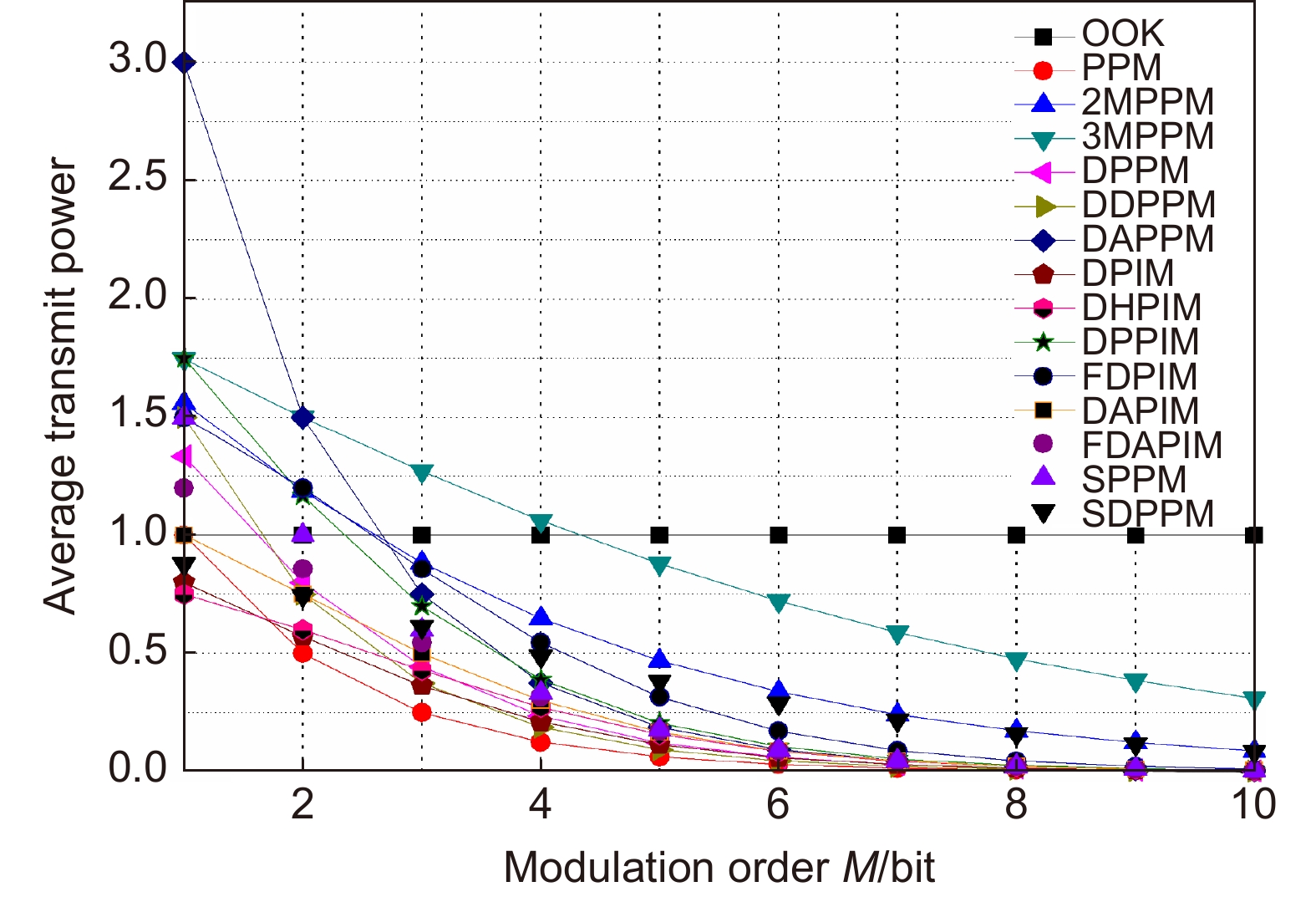
调制方式 平均符号长度 带宽需求 平均发射功率 OOK $ M $ $ {R_{\rm{b}}} $ $ \dfrac{{{P_{\rm{c}}}}}{2} $ PPM ${2^M}$ $\dfrac{{{2^M}{R_{\rm{b}}}}}{M}$ $\dfrac{{{P_{\rm{c}}}}}{{{2^M}}}$ MPPM n(含p个脉冲) $\dfrac{{n{R_{\rm{b}}}}}{M}$ $\dfrac{{p{P_{\rm{c}}}}}{n}$ DPPM $\dfrac{{{2^M} + 1}}{2}$ $\dfrac{{{2^M} + 1}}{{2M}}{R_{\rm{b}}}$ $\dfrac{2}{{{2^M} + 1}}{P_{\rm{c}}}$ DDPPM ${2^{M - 1}} + \alpha - 1$ $\dfrac{{{2^M} + 2\alpha - 2}}{{\alpha M}}{R_{\rm{b}}}$ $\dfrac{ {3\alpha } }{ { { {2^{M + 1} } + 4\alpha - 4} } }{P_{\rm{c} } }$ DAPPM ${2^{M - 1}}$ $\dfrac{{{2^{M - 1}}}}{M}{R_{\rm{b}}}$ $\dfrac{{1 + \beta }}{{{2^M}}}{P_{\rm{c}}}$ PIM $\dfrac{{{2^M} + 1}}{2}$ $\dfrac{{{2^M} + 1}}{{2M}}{R_{\rm{b}}}$ $\dfrac{2}{{{2^M} + 1}}{P_{\rm{c}}}$ DPIM $\dfrac{{{2^M} + 3}}{2}$ $\dfrac{{{2^M} + 3}}{{2M}}{R_{\rm{b}}}$ $\dfrac{2}{{{2^M} + 3}}{P_{\rm{c}}}$ DHPIM $\dfrac{{{2^{M - 1}} + 2\alpha + 1}}{2}$ $\dfrac{{{2^{M - 1}} + 2\alpha + 1}}{{\alpha M}}{R_{\rm{b}}}$ $\dfrac{{3\alpha }}{{ {{2^M} + 4\alpha + 2} }}{P_{\rm{c}}}$ DPPIM $ {2^{M - 1}} + \alpha $ $\dfrac{{{2^M} + 2\alpha }}{{\alpha M}}{R_{\rm{b}}}$ $\dfrac{{4 + 3\alpha }}{{{2^{M + 1}} + 4\alpha }}{P_{\rm{c}}}$ DAPIM $\dfrac{{{2^{M - 1}} + 3}}{2}$ $\dfrac{{{2^{M - 1}} + 3}}{{2M}}{R_{\rm{b}}}$ $\dfrac{{1 + \beta }}{{{2^{M - 1}} + 3}}{P_{\rm{c}}}$ FDPIM $ {2^M} + 4 $ $\dfrac{{{2^M} + 4}}{M}{R_{\rm{b}}}$ $\dfrac{3}{ { {2^M} + 4} }{P_{\rm{t}} }$ FDAPIM $ {2^M} + 3 $ $\dfrac{{{2^M} + 3}}{M}{R_{\rm{b}}}$ $\dfrac{{1 + \beta }}{{{2^M} + 3}}{P_{\rm{c}}}$ SPPM $1 + {2^{M - 1}}$ $\dfrac{{{2^{M - 1}} + 1}}{M}{R_{\rm{b}}}$ $\dfrac{3}{{{2^M} + 2}}{P_{\rm{c}}}$ SDPPM ${n_{\rm{s}}}$ ${{{n_{\rm{s}}}{R_{\rm{b}}}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{n_s}{R_{\rm{b}}}} M}} \right. } M}$ $ {{2{P_{\rm{c}}}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{2{P_{\rm{c}}}} {{n_{\rm{s}}}}}} \right. } {{n_{\rm{s}}}}} $ -
[1] 柯熙政, 殷致云. 无线激光通信系统中的编码理论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 8–10.
Ke X Z, Yin Z Y. Coding Theory in Wireless Laser Communication System[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 8–10.
[2] 柯熙政, 邓莉君. 无线光通信[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 10–13.
Ke X Z, Deng L J. Wireless Optical Communication[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 10–13.
[3] Pierce J R. Optical channels: practical limits with photon counting[J]. IEEE Trans Commun, 1978, 26(12): 1819−1821. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1978.1094043
[4] Prati G, Gagliardi R. Block encoding and decoding for the optical PPM channel (Corresp.)[J]. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 1982, 28(1): 100−105. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1982.1056439
[5] Prati G, Gagliardi R. Decoding with stretched pulses in laser PPM communications[J]. IEEE Trans Commun, 1983, 31(9): 1037−1045. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1983.1095933
[6] Garrett I. Pulse-position modulation for transmission over optical fibers with direct or heterodyne detection[J]. IEEE Trans Commun, 1983, 31(4): 518−527. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1983.1095842
[7] Chen C C, Gardner C. Performance of PLL synchronized optical PPM communication systems[J]. IEEE Trans Commun, 1986, 34(10): 988−994. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1986.1096445
[8] Georghiades C. Optimum joint slot and symbol synchronization for the optical PPM channel[J]. IEEE Trans Commun, 1987, 35(6): 632−636. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1987.1096824
[9] Davidson F M, Sun X L. Gaussian approximation versus nearly exact performance analysis of optical communication systems with PPM signaling and APD receivers[J]. IEEE Trans Commun, 1988, 36(11): 1185−1192. doi: 10.1109/26.8924
[10] Davidson F M, Sun X. Slot clock recovery in optical PPM communication systems with avalanche photodiode photodetectors[J]. IEEE Trans Commun, 1989, 37(11): 1164−1172. doi: 10.1109/26.46510
[11] Zwillinger D. Differential PPM has a higher throughput than PPM for the band-limited and average-power-limited optical channel[J]. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 1988, 34(5): 1269−1273. doi: 10.1109/18.21255
[12] Sugiyama H, Nosu K. MPPM: a method for improving the band-utilization efficiency in optical PPM[J]. J Lightw Technol, 1989, 7(3): 465−472. doi: 10.1109/50.16882
[13] Barry J R. Sequence detection and equalization for pulse-position modulation[C]//Proceedings of 1994 International Conference on Communications, 1994: 1561–1565.
[14] Audeh M D, Kahn J M, Barry J R. Performance of pulse-position modulation on measured non-directed indoor infrared channels[J]. IEEE Trans Commun, 1996, 44(6): 654−659. doi: 10.1109/26.506380
[15] Lee D C M, Kahn J M, Audeh M D. Trellis-coded pulse-position modulation for indoor wireless infrared communications[J]. IEEE Trans Commun, 1997, 45(9): 1080−1087. doi: 10.1109/26.623072
[16] Park H, Barry J R. Trellis-coded multiple-pulse position modulation for wireless infrared communications[C]//Proceedings of IEEE GLOBECOM 1998, 1998.
[17] Shiu D S, Kahn J M. Differential pulse-position modulation for power-efficient optical communication[J]. IEEE Trans Commun, 1999, 47(8): 1201−1210. doi: 10.1109/26.780456
[18] Rulkov N F, Sushchik M M, Tsimring L S, et al. Digital communication using chaotic-pulse-position modulation[J]. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Fundam Theory Appl, 2001, 48(12): 1436−1444. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2001.972850
[19] Aldibbiat N M, Ghassemlooy Z, McLaughlin R. Dual header pulse interval modulation for dispersive indoor optical wireless communication systems[J]. IEE Proc Circuits Dev Syst, 2002, 149(3): 187−192. doi: 10.1049/ip-cds:20020422
[20] Moision B, Hamkins J. Coded Modulation for the Deep-Space Optical Channel: Serially Concatenated Pulse-Position Modulation[J]. Dev Biol, 2005, 4(5): 1−25.
[21] Kiasaleh K. Performance of APD-based, PPM free-space optical communication systems in atmospheric turbulence[J]. IEEE Trans Commun, 2005, 53(9): 1455−1461. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2005.855009
[22] Wilson S G, Brandt-Pearce M, Cao Q L, et al. Free-space optical MIMO transmission with Q-ary PPM[J]. IEEE Trans Commun, 2005, 53(8): 1402−1412. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2005.852836
[23] Djordjevic I B, Vasic B, Neifeld M A. Multilevel coding in free-space optical MIMO transmission with Q-ary PPM over the atmospheric turbulence channel[J]. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2006, 18(14): 1491−1493. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2006.877576
[24] Barsoum M F, Moision B, Fitz M, et al. Iterative coded pulse-position-modulation for deep-space optical communications[C]//Proceedings of 2007 IEEE Information Theory Workshop, 2007.
[25] Sethakaset U, Gulliver T A. Performance of differential pulse-position modulation (DPPM) with concatenated coding over optical wireless communications[J]. IET Commun, 2008, 2(1): 45−52. doi: 10.1049/iet-com:20050530
[26] Xu F, Khalighi M A, Bourennane S. Coded PPM and multipulse PPM and iterative detection for free-space optical links[J]. J Opt Commun Network, 2009, 1(5): 404−415. doi: 10.1364/JOCN.1.000404
[27] Popoola W O, Poves E, Haas H. Spatial pulse position modulation for optical communications[J]. J Lightw Technol, 2012, 30(18): 2948−2954. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2012.2208940
[28] Correia D G, Sales J C, Pinto P V F, et al. Analysis of the performance of a PAM/PPM/OOK system operating with OCDMA, under nonlinear optical effects in optical fiber propagation[J]. J Opt Commun, 2016, 37(2): 233−246.
[29] Farhat Z A, Ahfayd M H, Mather P J, et al. Practical implementation of duobinary pulse position modulation using FPGA and visible light communication[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 15th Student Conference on Research and Development, 2017.
[30] Sharma K, Grewal S K. Performance assessment of hybrid PPM-BPSK-SIM based FSO communication system using time and wavelength diversity under variant atmospheric turbulence[J]. Opt Quant Electron, 2020, 52(10): 430. doi: 10.1007/s11082-020-02547-7
[31] Zaiton A M, Eng C H, Jasman F. Pulse position modulation characterization for indoor visible light communication system[J]. J Phys Conf Ser, 2020, 1502: 012005. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1502/1/012005
[32] 尹冰琳, 王福昌. PPM光通信相关式数字锁相环时隙同步器[J]. 光通信技术, 1998, 22(3): 211−215.
Yin B L, Wang F C. Relational digital phase lock loop slot synchronizer for PPM laser communication system[J]. Opt Commun Technol, 1998, 22(3): 211−215.
[33] 苏勇, 姚武川, 黄本雄, 等. 用EPLD设计与实现PPM调制器[J]. 光通信技术, 1999, 23(4): 272−277.
Su Y, Yao W C, Huang B X, et al. Design and implementation of PPM modulator using EPLD[J]. Opt Commun Technol, 1999, 23(4): 272−277.
[34] 张淼, 邱昆, 邱琪, 等. 脉冲位置调制的字同步技术[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2000, 29(4): 381−383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2000.04.012
Zhang M, Qiu K, Qiu Q, et al. Word synchronization of pulse position modulation[J]. J Univ Electron Sci Technol China, 2000, 29(4): 381−383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2000.04.012
[35] 杜瑜, 邹传云. 红外无线PPM的调制解调电路设计[J]. 桂林电子工业学院学报, 2000, 20(3): 5−10.
Du Y, Zou C Y. The circuit design for PPM encoder and decoder[J]. J Guilin Instit Electron Technol, 2000, 20(3): 5−10.
[36] 汪井源, 张正线. 无线光通信中的PPM调制[J]. 电讯技术, 2000, 40(5): 81−84.
Wang J Y, Zhang Z X. PPM in wireless infrared communication[J]. Telecommun Eng, 2000, 40(5): 81−84.
[37] 庞志勇, 朴大志, 邹传云. 光通信中几种调制方式的性能比较[J]. 桂林电子工业学院学报, 2002, 22(5): 1−4.
Pang Z Y, Piao D Z, Zou C Y. Performance comparisons of several modulation schemes for optical wireless communication[J]. J Guilin Instit Electron Technol, 2002, 22(5): 1−4.
[38] 胡宗敏, 汤俊雄. 大气无线光通信系统中数字脉冲间隔调制研究[J]. 通信学报, 2005, 26(3): 75−79. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-436X.2005.03.013
Hu Z M, Tang J X. Digital pulse interval modulation for atmospheric optical wireless communications[J]. J Commun, 2005, 26(3): 75−79. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-436X.2005.03.013
[39] 朱乐君, 张江鑫. 基于FPGA的无线光通信PPM调制系统的设计[J]. 光通信技术, 2006, 30(12): 57−59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5561.2006.12.019
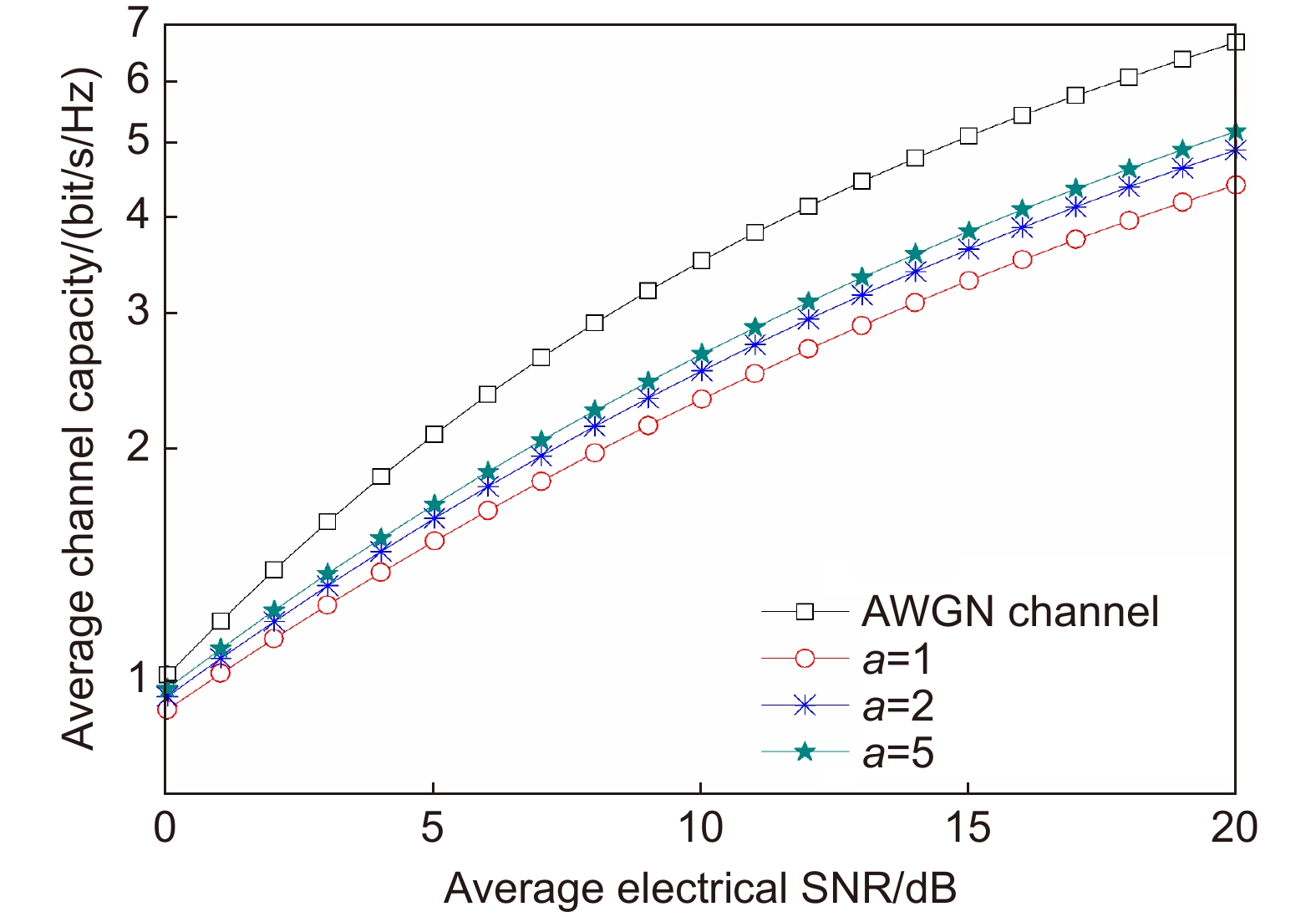
Zhu L J, Zhang J X. Design of PPM system in optical wireless communication based on FPGA[J]. Opt Commun Technol, 2006, 30(12): 57−59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5561.2006.12.019
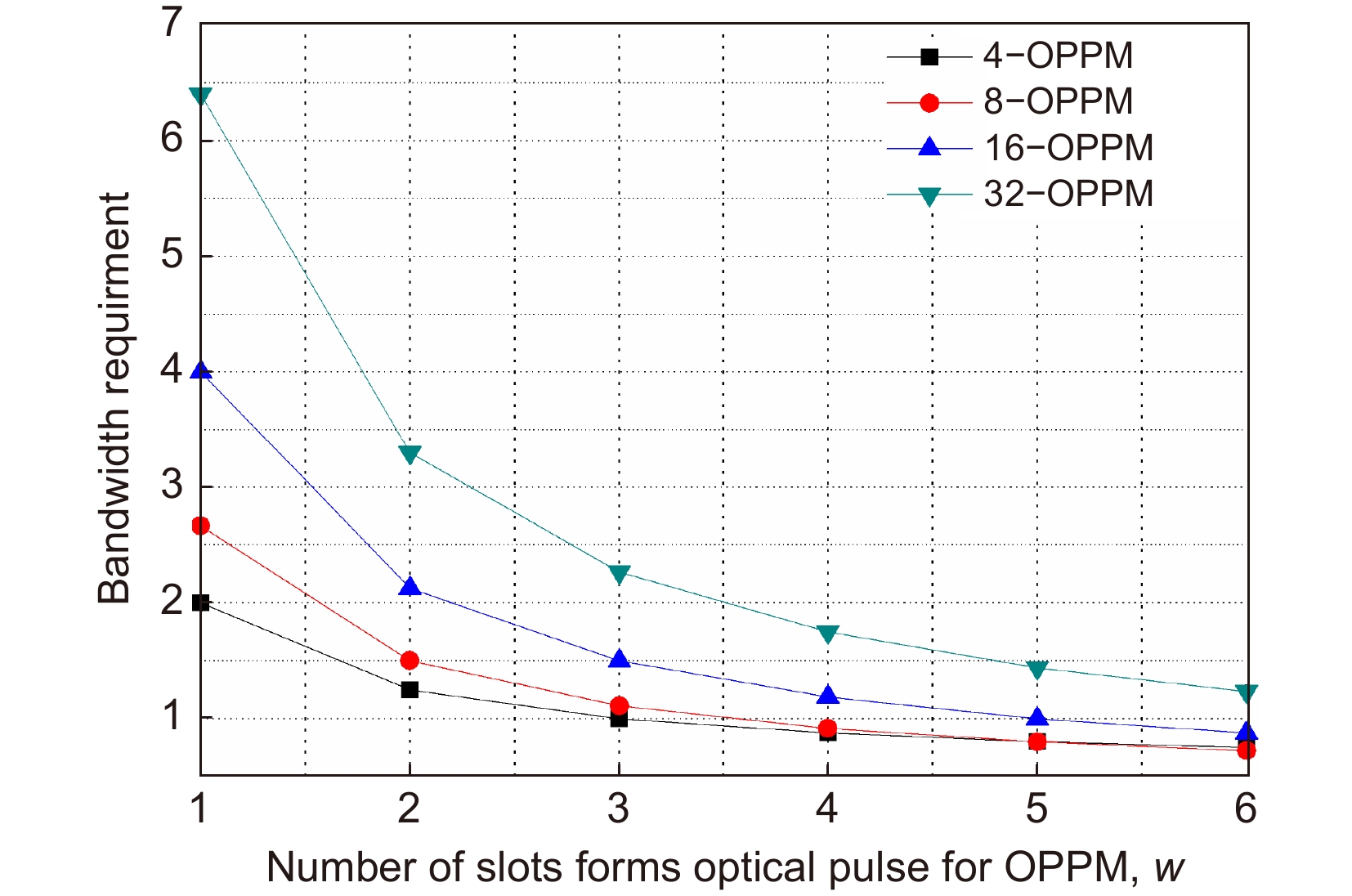
[40] 程刚, 王红星, 吴龙刚, 等. 大气无线光通信调制方式性能分析[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2007, 2(5): 485−489. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2007.05.009
Cheng G, Wang H X, Wu L G, et al. Performance analysis of modulation scheme for atmospheric optical wireless communications[J]. J China Acad Electron Inf Technol, 2007, 2(5): 485−489. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2007.05.009
[41] Dou Z, Sha X J, Wang Y, et al. LDPC-coded optical PPM communication system over the atmosphere turbulence channels[C]//Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, 2010.
[42] 程刚, 王红星, 孙晓明, 等. 一种新型的无线光通信调制方法[J]. 中国激光, 2008, 35(12): 1914−1918. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2008.12.011
Cheng G, Wang H X, Sun X M, et al. A new modulation scheme of optical wireless communications[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2008, 35(12): 1914−1918. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2008.12.011
[43] 程刚, 王红星, 孙晓明, 等. 无线光通信双脉冲间隔调制方法[J]. 中国激光, 2010, 37(7): 1750−1755. doi: 10.3788/CJL20103707.1750
Cheng G, Wang H X, Sun X M, et al. Dual pulse-pulse interval modulation for optical wireless communications[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2010, 37(7): 1750−1755. doi: 10.3788/CJL20103707.1750
[44] 向劲松, 吴涛, 黄胜, 等. 串行级联脉冲位置调制码辅助的时隙同步技术[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(8): 0806006. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0806006
Xiang J S, Wu T, Huang S, et al. Slot synchronization aided by serial concatenated pulse position modulation code system[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2016, 36(8): 0806006. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0806006
[45] 向劲松, 陈雪莉, 张培, 等. 基于保护时隙的一倍时隙频率采样光PPM时钟同步技术[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(10): 226−234.
Xiang J S, Chen X L, Zhang P, et al. Clock synchronization technology for pulse position modulation with guard time at sampling frequency of 1 slot[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2018, 45(10): 226−234.
[46] Jiang T, Zhao L, Liu H Z, et al. Performance improvement for mixed RF–FSO communication system by adopting hybrid subcarrier intensity modulation[J]. Appl Sci, 2019, 9(18): 3724. doi: 10.3390/app9183724
[47] 张凯. 无线光通信双幅度脉冲间隔调制研究及其在光波ETC中的应用[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2004.
Zhang K. Dual-amplitude pulse interval modulation for optical wireless communications and optical ETC prototype[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2004.
[48] 徐艳红, 郭瑛, 秦岭. 基于DPIM调制可见光通信系统性能分析[J]. 中国新通信, 2020, 22(17): 27−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4866.2020.17.013
Xu Y H, Guo Y, Qin L. Performance analysis of visible light communication system based on DPIM modulation[J]. China New Telecommun, 2020, 22(17): 27−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4866.2020.17.013
[49] 丁德强. 大气激光通信PPM调制解调系统设计[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2005.
Ding D Q. Design of PPM for laser communication in atmosphere[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2005.
[50] 秦岭. 大气激光通信中多脉冲调制系统的设计[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2007.
Qin L. Design of MPPM in atmospheric laser communication[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2007.
[51] 杜安源, 柯熙政. 大气信道对激光PPM信号的影响的研究[J]. 激光杂志, 2006, 27(1): 73−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2743.2006.01.037
Du A Y, Ke X Z. Study on atmosphere channel that influencing on laser PPM signal[J]. Laser J, 2006, 27(1): 73−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2743.2006.01.037
[52] 王丽黎, 柯熙政, 席晓莉. 激光在雨中传输的分析与计算[J]. 光散射学报, 2005, 17(2): 148−153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5929.2005.02.007
Wang L L, Ke X Z, Xi X L. Analyze and calculate for laser transmit through rain[J]. Chin J Light Scatt, 2005, 17(2): 148−153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5929.2005.02.007
[53] 柯熙政, 赵黎, 殷致云, 等. 无线激光通信中差错控制实验研究[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2009, 23(6): 18−23.
Ke X Z, Zhao L, Yin Z Y, et al. Experimental research on the error control of wireless laser communication[J]. J Electron Meas Instrum, 2009, 23(6): 18−23.
[54] 王丽黎, 柯熙政, 陈丽新. 基于大气激光通信系统的实验测量研究[J]. 光散射学报, 2005, 17(4): 378−383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5929.2005.04.013
Wang L L, Ke X Z, Chen L X. The testing system for optical power through atmosphere[J]. Chin J Light Scatt, 2005, 17(4): 378−383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5929.2005.04.013
[55] 刘长城, 柯熙政. 空间光通信中PSD光斑的位置特性仿真研究[J]. 光通信技术, 2004, 28(6): 16−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5561.2004.06.005
Liu C C, Ke X Z. Simulation about PSD facular position in space optical communication[J]. Opt Commun Technol, 2004, 28(6): 16−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5561.2004.06.005
[56] 丁德强, 柯熙政. 大气激光通信PPM调制解调系统设计与仿真研究[J]. 光通信技术, 2005, 29(1): 50−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5561.2005.01.015
Ding D Q, Ke X Z. Design of PPM for laser communication in atmosphere[J]. Opt Commun Technol, 2005, 29(1): 50−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5561.2005.01.015
[57] 柯熙政, 赵黎, 丁德强. 一种大气激光通信中时隙同步和帧同步的实现[J]. 半导体光电, 2007, 28(5): 721−724. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5868.2007.05.030
Ke X Z, Zhao L, Ding D Q. The achievement of time-slot and frame synchronization in atmosphere laser communication[J]. Semicond Optoelectron, 2007, 28(5): 721−724. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5868.2007.05.030
[58] 殷致云, 柯熙政, 张波. 无线激光通信中GF(3)域上的纠错编码研究[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2009, 23(7): 23−28.
Yin Z Y, Ke X Z, Zhang B. Research on error-correcting code in wireless laser communications over GF(3)[J]. J Electron Meas Inst, 2009, 23(7): 23−28.
[59] 秦岭, 柯熙政. 一种二脉冲的MPPM编码映射方法研究[J]. 西安理工大学学报, 2007, 23(3): 269−272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4710.2007.03.010
Qin L, Ke X Z. A study of mapping scheme for dual-pulse MPPM[J]. J Xi’an Univ Technol, 2007, 23(3): 269−272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4710.2007.03.010
[60] 秦岭, 柯熙政. 无背景噪声下的光MPPM信道容量分析[J]. 光电工程, 2007, 34(7): 107−110.
Qin L, Ke X Z. Analysis of optical MPPM channel capacity without background noise[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2007, 34(7): 107−110.
[61] 黄蕾, 柯熙政, 吴鹏飞. 面向OPPM的TCM系统设计与仿真[J]. 光通信研究, 2008(5): 13−15,70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8788.2008.05.005
Huang L, Ke X Z, Wu P F. Design and simulation of OPPM-oriented TCM system[J]. Study Opt Commun, 2008(5): 13−15,70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8788.2008.05.005
[62] 赵黎, 柯熙政, 刘健. OWC中DPPM调制解调技术研究[J]. 激光杂志, 2007, 28(2): 63−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2743.2007.02.031
Zhao L, Ke X Z, Liu J. Research on differential pulse-position modulation in optical wireless communication[J]. Laser J, 2007, 28(2): 63−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2743.2007.02.031
[63] 柯熙政, 殷致云, 杨利红. 大气激光通信中光PPM偏振调制方案及其关键技术[J]. 半导体光电, 2007, 28(4): 553−555,560. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5868.2007.04.027
Ke X Z, Yin Z Y, Yang L H. Light polarization modulation with PPM and its key technique in atmospheric laser communication[J]. Semicond Optoelectron, 2007, 28(4): 553−555,560. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5868.2007.04.027
[64] 杨利红, 柯熙政, 马冬冬. 偏振激光在大气传输中的退偏研究[J]. 光电工程, 2008, 35(11): 62−67.
Yang L H, Ke X Z, Ma D D. Depolarization characteristics of the polarized laser in atmosphere[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2008, 35(11): 62−67.
[65] 杨利红, 柯熙政. 基于大气光通信偏振PPM的误码率研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2010, 31(7): 1664−1668.
Yang L H, Ke X Z. BER of polarization PPM based on atmospheric optical communication[J]. Chin J Sci Inst, 2010, 31(7): 1664−1668.
[66] 柯熙政, 解孟其, 高海涛, 等. 自由空间光通信中的空时网格码[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2012, 41(4): 1022−1027. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2012.04.035
Ke X Z, Xie M Q, Gao H T, et al. Free space optical communication based on space-time trellis coding[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2012, 41(4): 1022−1027. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2012.04.035
[67] 柯熙政, 陈锦妮. 无线激光通信类脉冲位置调制性能比较[J]. 激光技术, 2012, 36(1): 67−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3806.2012.01.018
Ke X Z, Chen J N. Performance comparison of various pulse position modulation in wireless laser communication[J]. Laser Technol, 2012, 36(1): 67−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3806.2012.01.018
[68] 马丽娜. 大气激光通信中PPM偏振调制及其实验研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2009.
Ma L N. PPM polarization modulation in atmosphere laser communication and experiment research[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2009.
[69] 赵黎. 大气激光通信DPPM调制解调技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2006: 13–28.
Zhao L. Research of DPPM for laser communication in atmosphere[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2006: 13–28.
[70] 黄蕾. TCM技术在大气激光通信系统中的应用研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2007.
Huang L. The application of TCM in atmosphere laser communication system[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2007.
[71] 孙长梅. 大气激光通信DAPPM调制解调系统仿真研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2011: 9–20.
Sun C M. Simulation and research of DAPPM system for laser communication in atmosphere[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2011: 9–20.
[72] 贾超. 大气激光通信DHPIM调制解调技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2011: 14–30.
Jia C. Research on DHPIM modulation and demodulation for atmospheric laser communication[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2011: 14–30.
[73] 柳美平. 无线光通信中类脉冲位置调制性能分析[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2013: 13–33.
Liu M P. Performances analysis of PPMS' in wireless optical communication[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2013: 13–33.
[74] 石碧瑶. 无线光通信系统中64-QAM调制实验研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2016.
Shi B Y. Expermental of 64-QAM modulation in wireless optical communication system[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2016.
[75] 田晓超. 强湍流下大气激光通信接收信号的自适应处理[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2015.
Tian X C. Adaptive signal processing to receive the strong turbulence atmosphere laser communication[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2015.
[76] 裴国强. 湍流大气中多光束发射/多孔径接收技术的性能研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2012.
Pei G Q. Performance research on multi-beam transmission and multi-aperture reception in turbulent atmosphere[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2012.
[77] 刘昭辉. 半导体激光器和光电探测器响应特性的研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2019.
Liu Z H. Research on response characteristics of semiconductor lasers and photodetectors[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2019.
[78] 张颖, 高悦, 柯熙政. 预编码室内MIMO可见光通信系统空间相关性分析[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(3): 190666.
Zhang Y, Gao Y, Ke X Z. Analysis of spatial correlation of precoding indoor MIMO visible light communication system[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(3): 190666.
[79] 林鹏, 王天枢, 马万卓, 等. 2.07μm光纤激光在弱湍流条件下的传输特性研究[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(3): 190588.
Lin P, Wang T S, Ma W Z, et al. Propagation characteristics of 2.07 μm fiber laser in weak turbulence condition[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(3): 190588.
[80] 王珂, 徐智勇, 李雪松, 等. 逆向调制无线光通信空间分集分析[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(3): 190701.
Wang K, Xu Z Y, Li X S, et al. Analysis of space diversity method in modulating retro-reflector optical communication[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(3): 190701.
[81] 吴一, 刘宏展, 郝源, 等. 无线光通信中喷泉码的发展现状与展望[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(3): 190623.
Wu Y, Liu H Z, He Y, et al. Development and prospect of fountain codes in optical wireless communication[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(3): 190623.
[82] 毛一聪, 王惠琴, 张悦, 等. 光空间调制技术的研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(3): 190712.
Mao Y C, Wang H Q, Zhang Y, et al. Research status and development of optical spatial modulation technology[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(3): 190712.
[83] 柯熙政, 吴加丽. 无线光相干通信原理及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019.
Ke X Z, Wu J L. Principle and Application of Wireless Optical Coherent Communication[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019.
[84] 柯熙政, 杨尚君, 吴加丽, 等. 西安理工大学无线光通信系统自适应光学技术研究进展[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33(8): 081003.
Ke X Z, Yang S J, Wu J L, et al. Research progress of adaptive optics in wireless optical communication system for Xi'an Universityof Technology[J]. High Power Laser Part Beams, 2021, 33(8): 081003.
[85] 柯熙政, 吴加丽, 杨尚君. 面向无线光通信的大气湍流研究进展与展望[J]. 电波科学学报, 2021, 36(3): 323−339. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2020116
Ke X Z, Wu J L, Yang S J. Research progress and prospect of atmospheric turbulence for wireless optical communication[J]. Chin J Radio Sci, 2021, 36(3): 323−339. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2020116
[86] 柯熙政, 殷致云. 无线激光通信系统中的编码理论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.
Ke X Z, Yin Z Y. Coding Theory in Wireless Laser Communication System[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009.
[87] 柯熙政, 丁德强. 一种大气激光通信PPM同步器: CN201066849Y[P]. 2008-05-28.
Ke X Z, Ding D Q. A PPM synchronizer for atmospheric laser communication: CN201066849Y[P]. 2008-05-28.
[88] 柯熙政, 刘健. 无线激光通信PPM偏振调制解调方法: CN101110649A[P]. 2008-01-23.
Ke X Z, Liu J. Wireless laser communication PPM polarization modulation and demodulation method: CN101110649A[P]. 2008-01-23.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: