-
摘要:
太赫兹(THz)波是频率位于0.1 THz~10 THz的电磁波。因其具有非电离性,以及可与多数生物分子产生共振响应等特性,在生物医学领域有着巨大应用潜力,尤其在肿瘤检测方面。太赫兹成像技术作为生物医学领域一种新的成像技术,吸引国内外多个研究小组对其开展深入研究。本文列举分析了多种太赫兹成像技术在肿瘤检测的应用,其中可分为太赫兹扫描成像、太赫兹层析成像、太赫兹全息成像以及太赫兹近场成像,介绍了这些成像方式的基本原理以及国内外研究现状,最后对太赫兹成像技术在生物领域的未来做出展望。
Abstract:Terahertz radiation is an electromagnetic wave whose frequency is in the range of 0.1 THz~10 THz. With its many features such as non-ionizing and resonance to many biomolecules, THz wave has great potential applications in biomedical field, especially in tumor detection. Terahertz imaging technology, as a new imaging technology in biomedical field, is studied by many research groups around the world. In this paper, we listed and analyzed many terahertz imaging methods in tumor detection, including terahertz scanning imaging, terahertz tomography, terahertz holography, and terahertz near-field imaging. We introduced the basic principle of these imaging methods and the works done by different groups worldwide. At last, we presented the prospect of terahertz imaging technology applied in biomedical field.
-

Overview: Terahertz (THz) wave exhibits many features including non-ionizing, non-invasive, phase-sensitive to polar substances, spectral fingerprinting, relatively good resolution, coherent detection properties, and penetration capabilities. For tumor detection, traditional imaging methods such as magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography will cause radiation damage to biotissue, while THz imaging can provide quick, non-destructive, and accurate imaging of biotissue. Two kinds of terahertz sources are mainly used: pulse THz wave source and continuous THz wave source. Pulse THz wave source provides multi-dimensional information for the analysis of sample, while continuous THz wave source can only provide amplitude or phase images for delineation different areas. But imaging system using continuous THz source are more concise compared to that using pulse THz source. Currently, based on these two THz sources, there are four kinds of imaging technologies:
1) THz far-field scanning imaging is the most commonly used, where THz signal is collected by scanning the sample point by point and then images are constructed by these data. The resolution depends on the spot diameter and step size of the scanning, therefore, long measuring time are required for high-resolution imaging.
2) THz tomography combined THz far-field imaging system with tomography algorithm. By collecting the THz signal from different angle of sample, and then using the algorithm for analysis, 3D images of sample can be obtained. Internal structure of the sample can be observed by THz tomography. However, it will take much more time to measure the signal from different angle.
3) For THz holography, different array detectors, such as charge coupled device, pyroelectric detector, and microbolometer, are used in THz far-field imaging system. Instead of point-by-point measurement of common far-field THz imaging system, THz digital holography collects the THz signal of the whole sample at once, which greatly reduce the measurement time.
4) THz near-field imaging method collects the signal of evanescent field near the sample surface and uses these data to calculate images. So, THz near-field imaging can break the diffraction limit (λ/2) and provides the resolution three magnitudes higher than THz far-field imaging.
In the paper, we introduced the studies of these four THz imaging technologies done by different groups worldwide. At last, we presented the prospect of terahertz imaging technology applied in biomedical field.
-

-
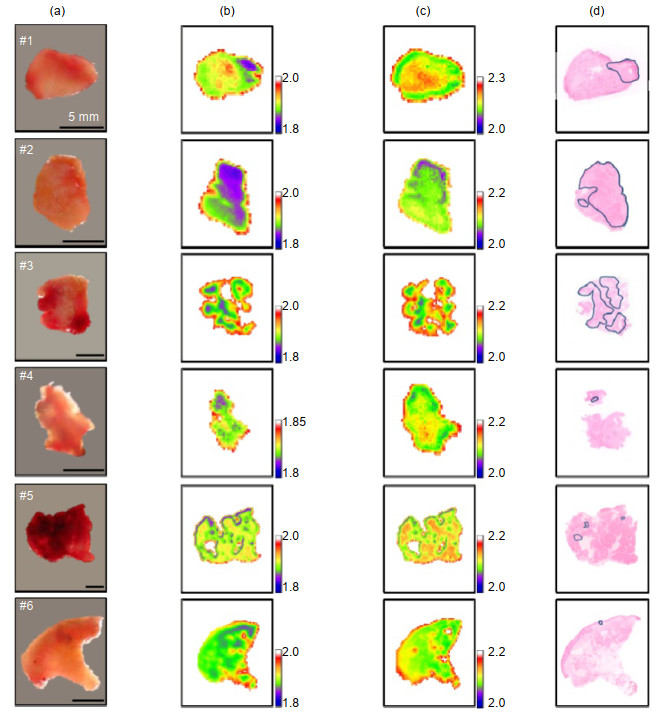
图 3 六个口腔样品的(a)光学图像;(b) -20 ℃的THz图像;(c)室温THz图像;(d)组织病理学图像。THz图像反映样本在0.5 THz的折射率,在组织学图像中癌变区域用蓝色环标记[34]
Figure 3. (a) Optical images, (b) frozen and (c) room temperature THz images, and (d) histopathological images of six oral samples. THz images are displayed by the index of refraction at 0.5 THz, and the cancerous areas are marked with blue loops in the histological images[34]
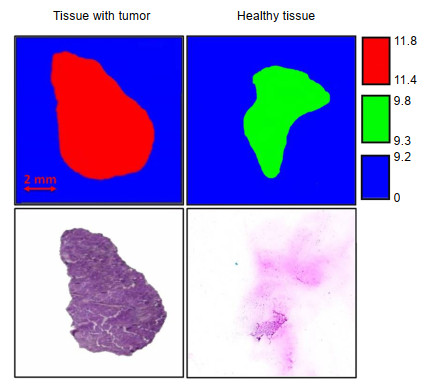
图 5 人类肝细胞癌组织的(a)全息数据采集后的样品照片;(b)在选定探测器位置获得的归一化全息图;(c)重构吸收分布a(x, y);(d)重构相移分布φ(x, y)[49]
Figure 5. (a) Photo of the sample after holographic data acquisition; (b) Normalised hologram obtained at a selected detector position; (c) Reconstructed absorption distribution a(x, y); (d) Reconstructed phase-shift distribution φ(x, y)[49]
-
[1] 张兴宁, 陈稷, 周泽魁.太赫兹时域光谱技术[J].激光与光电子学进展, 2005, 42(7): 35-38. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb200806008
Zhang X N, Chen J, Zhou Z K. THz time-domain spectroscopy technology[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2005, 42(7): 35-38. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb200806008
[2] Zhou L, Chen L G, Ren G H, et al. Monitoring cis-to-trans isomerization of azobenzene using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2018, 20(42): 27205-27213. doi: 10.1039/C8CP04570D
[3] Li T, Ma H Y, Peng Y, et al. Gaussian numerical analysis and terahertz spectroscopic measurement of homocysteine[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2018, 9(11): 5467-5476. doi: 10.1364/BOE.9.005467
[4] Shen Y C, Upadhya P C, Linfield E H, et al. Temperature-dependent low-frequency vibrational spectra of purine and adenine[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2003, 82(14): 2350-2352. doi: 10.1063/1.1565680
[5] Peng Y, Shi C J, Xu M Q, et al. Qualitative and quantitative identification of components in mixture by terahertz spectroscopy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2018, 8(6): 696-701. doi: 10.1109/TTHZ.2018.2867816
[6] Pickwell E, Wallace V P. Biomedical applications of terahertz technology[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2006, 39(17): R301-R310. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/39/17/R01
[7] Kawase K, Ogawa Y, Watanabe Y, et al. Non-destructive terahertz imaging of illicit drugs using spectral fingerprints[J]. Optics Express, 2003, 11(20): 2549-2554. doi: 10.1364/OE.11.002549
[8] Danciu M, Alexa-Stratulat T, Stefanescu C, et al. Terahertz spectroscopy and imaging: a cutting-edge method for diagnosing digestive cancers[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(9): 1519. doi: 10.3390/ma12091519
[9] Kasban H, El-Bendary M A M, Salama D H. A comparative study of medical imaging techniques[J]. International Journal of Information Science and Intelligent System, 2015, 4(2): 37-58. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_a1ecabb775d4abf0e863a84a7cb6a1e9
[10] 张蕾, 徐新龙, 李福利.太赫兹(THz)成像的进展概况[J].量子电子学报, 2005, 22(2): 129-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5461.2005.02.001
Zhang L, Xu X L, Li F L. Review of the progress of T-ray imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2005, 22(2): 129-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5461.2005.02.001
[11] 杨昆, 赵国忠, 梁承森, 等.脉冲太赫兹波成像与连续波太赫兹成像特性的比较[J].中国激光, 2009, 36(11): 2853-2858. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgjg200911014
Yang K, Zhao G Z, Liang C S, et al. Comparison between pulsed terahertz imaging and continuous-wave terahertz imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2009, 36(11): 2853-2858. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgjg200911014
[12] 潘中良, 陈翎, 谌贻会.太赫兹波的层析成像[J].数字技术与应用, 2013(12): 29-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/szjsyyy201312025
Pan Z L, Chen L, Shen Y H. Terahertz tomography[J]. Digital Technology & Application, 2013(12): 29-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/szjsyyy201312025
[13] 石敬, 王新柯, 郑显华, 等.太赫兹数字全息术的研究进展[J].中国光学, 2017, 10(1): 131-147. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxyyygxwz201701012
Shi J, Wang X K, Zheng X H, et al. Recent advances in terahertz digital holography[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(1): 131-147. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxyyygxwz201701012
[14] 刘宏翔, 姚建铨, 王与烨, 等.太赫兹波近场成像综述[J].红外与毫米波学报, 2016, 35(3): 300-309, 376. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb201603009
Liu H X, Yao J Q, Wang Y Y, et al. Review of THz near-field imaging[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2016, 35(3): 300-309, 376. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb201603009
[15] 孙卫东, 耿国帅, 杨忠波, 等.猪肉组织的近场太赫兹成像检测研究[J].红外与毫米波学报, 2018, 37(6): 769-774. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb201806022
Sun W D, Geng G S, Yang Z B, et al. Imaging porcine tissue using a near-field terahertz microscopy technique[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2018, 37(6): 769-774. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb201806022
[16] Cole B E, Woodward R M, Crawley D A, et al. Terahertz imaging and spectroscopy of human skin in vivo[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2001, 4276: 1-10. doi: 10.1117/12.428010
[17] Woodward R M, Cole B E, Wallace V P, et al. Terahertz pulse imaging in reflection geometry of human skin cancer and skin tissue[J]. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2002, 47(21): 3853-3863. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/47/21/325
[18] Woodward R M, Wallace V P, Pye R J, et al. Terahertz pulse imaging of ex vivo basal cell carcinoma[J]. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 2003, 120(1): 72-78. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12013.x
[19] Woodward R M, Wallace V P, Arnone D D, et al. Terahertz pulsed imaging of skin cancer in the time and frequency domain[J]. Journal of Biological Physics, 2003, 29(2-3): 257-259. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1023-A-1024409329416/
[20] Wallace V P, Fitzgerald A J, Shankar S, et al. Terahertz pulsed imaging of basal cell carcinoma ex vivo and in vivo[J]. British Journal of Dermatology, 2004, 151(2): 424-432. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.06129.x
[21] Fitzgerald A J, Wallace V P, Jimenez-Linan M, et al. Terahertz pulsed imaging of human breast tumors[J]. Radiology, 2006, 239(2): 533-540. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2392041315
[22] Huang S Y, Wang Y X J, Yeung D K W, et al. Tissue characterization using terahertz pulsed imaging in reflection geometry[J]. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2008, 54(1): 149-160. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0f969a48f2cdaf7ca5b9afd19d954ae3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[23] Kan W C, Lee W S, Cheung W H, et al. Terahertz pulsed imaging of knee cartilage[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2010, 1(3): 967-974. doi: 10.1364/BOE.1.000967
[24] Fitzgerald A J, Wallace V P, Pinder S E, et al. Classification of terahertz-pulsed imaging data from excised breast tissue[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2012, 17(1): 016005. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.17.1.016005
[25] Oh S J, Kim S H, Jeong K, et al. Measurement depth enhancement in terahertz imaging of biological tissues[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(18): 21299-21305. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.021299
[26] Oh S J, Kim S H, Ji Y B, et al. Study of freshly excised brain tissues using terahertz imaging[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2014, 5(8): 2837-2842. doi: 10.1364/BOE.5.002837
[27] Ho L, Müller R, Römer M, et al. Analysis of sustained-release tablet film coats using terahertz pulsed imaging[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2007, 119(3): 253-261. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.03.011
[28] Enatsu T, Kitahara H, Takano K, et al. Terahertz spectroscopic imaging of paraffin-embedded liver cancer samples[C]//Proceedings of the Joint 32nd International Conference on Infrared and Millimeter Waves and the 15th International Conference on Terahertz Electronics, Cardiff, UK, 2007: 557-558.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4516627?denied= [29] Shen Y C, Taday P F. Development and application of terahertz pulsed imaging for nondestructive inspection of pharmaceutical tablet[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2008, 14(2): 407-415. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2007.911309
[30] Taylor Z D, Singh R S, Culjat M O, et al. Reflective terahertz imaging of porcine skin burns[J]. Optics Letters, 2008, 33(11): 1258-1260. doi: 10.1364/OL.33.001258
[31] Hoshina H, Hayashi A, Miyoshi N, et al. Terahertz pulsed imaging of frozen biological tissues[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 94(12): 123901. doi: 10.1063/1.3106616
[32] Brun M A, Formanek F, Yasuda A, et al. Terahertz imaging applied to cancer diagnosis[J]. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2010, 55(16): 4615-4623. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/16/001
[33] May R K, Su K, Han L H, et al. Hardness and density distributions of pharmaceutical tablets measured by terahertz pulsed imaging[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2013, 102(7): 2179-2186. doi: 10.1002/jps.23560
[34] Sim Y C, Park J Y, Ahn K M, et al. Terahertz imaging of excised oral cancer at frozen temperature[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2013, 4(8): 1413-1421. doi: 10.1364/BOE.4.001413
[35] Bowman T C, El-Shenawee M, Campbell L K. Terahertz imaging of excised breast tumor tissue on paraffin sections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2015, 63(5): 2088-2097. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2015.2406893
[36] Yamaguchi S, Fukushi Y, Kubota O, et al. Brain tumor imaging of rat fresh tissue using terahertz spectroscopy[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 30124. doi: 10.1038/srep30124
[37] 蒋玉英, 葛宏义, 张元.基于太赫兹成像技术的小麦麦芽糖定量检测研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(10): 3017-3022. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201810005
Jiang Y Y, Ge H Y, Zhang Y. Quantitative determination of maltose concentration in wheat by using terahertz imaging[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(10): 3017-3022. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201810005
[38] Wahaia F, Valusis G, Bernardo L M, et al. Detection of colon cancer by terahertz techniques[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2011, 1006(1-3): 77-82. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2011.05.049
[39] Joseph C S, Yaroslavsky A N, Neel V A, et al. Continuous wave terahertz transmission imaging of nonmelanoma skin cancers[J]. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, 2011, 43(6): 457-462. doi: 10.1002/lsm.21078
[40] Lee Y K, Choi S W, Han S T, et al. Detection of foreign bodies in foods using continuous wave terahertz imaging[J]. Journal of Food Protection, 2012, 75(1): 179-183. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-11-181
[41] Joseph C S, Patel R, Neel V A, et al. Imaging of ex vivo nonmelanoma skin cancers in the optical and terahertz spectral regions optical and terahertz skin cancers imaging[J]. Journal of Biophotonics, 2014, 7(5): 295-303. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201200111
[42] Doradla P, Alavi K, Joseph C S, et al. Detection of colon cancer by continuous-wave terahertz polarization imaging technique[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2013, 18(9): 090504. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.9.090504
[43] Martin J P, Joseph C S, Giles R H. Continuous-wave circular polarization terahertz imaging[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2016, 21(7): 070502. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.21.7.070502
[44] Yang X, Shi J, Wang Y Y, et al. Label‐free bacterial colony detection and viability assessment by continuous‐wave terahertz transmission imaging[J]. Journal of Biophotonics, 2018, 11(8): e201700386. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201700386
[45] Wu L M, Xu D G, Wang Y Y, et al. Study of in vivo brain glioma in a mouse model using continuous-wave terahertz reflection imaging[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2019, 10(8): 3953-3962. doi: 10.1364/BOE.10.003953
[46] Bessou M, Chassagne B, Caumes J P, et al. Three-dimensional terahertz computed tomography of human bones[J]. Applied Optics, 2012, 51(28): 6738-6744. doi: 10.1364/AO.51.006738
[47] Li B, Wang D Y, Rong L, et al. Application of continuous-wave terahertz computed tomography for the analysis of chicken bone structure[J]. Optical Engineering, 2018, 57(2): 023105. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8b07e05d04c1ad3e00db32dc7908e040
[48] Rong L, Latychevskaia T, Zhou X, et al. Dynamic dehydration observation based on terahertz in-line digital holography[C]//Digital Holography & 3-D Imaging, Shanghai, China, 2015: DTh1A.2.
https://www.osapublishing.org/abstract.cfm?uri=DH-2015-DTh1A.2 [49] Rong L, Latychevskaia T, Chen C H, et al. Terahertz in-line digital holography of human hepatocellular carcinoma tissue[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 8445. doi: 10.1038/srep08445
[50] Guo L H, Wang X K, Zhang Y. Terahertz digital holographic imaging of biological tissues[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Ultrafast Phenomena and Terahertz Waves, Chongqing, China, 2016: IW4B.3.
http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GXJM201703009.htm [51] Guo L H, Wang X K, Han P, et al. Observation of dehydration dynamics in biological tissues with terahertz digital holography[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(13): F173-F178. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.00F173
[52] Schade U, Holldack K, Martin M C, et al. THz near-field imaging of biological tissues employing synchrotron radiation[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5725: 46-52. doi: 10.1117/12.590731
[53] Chen H, Ma S H, Yang W X, et al. The diagnosis of human liver cancer by using THz fiber-scanning near-field imaging[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2013, 30(3): 030702. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/30/3/030702
[54] Chen H, Ma S H, Wu X, et al. Diagnose human colonic tissues by terahertz near-field imaging[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2015, 20(3): 036017. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.20.3.036017
[55] Tseng T F, Yang S C, Shih Y T, et al. Near-field sub-THz transmission-type image system for vessel imaging in-vivo[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(19): 25058-25071. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.025058
[56] Fawole O C, Tabib-Azar M. Terahertz near-field imaging of biological samples with horn antenna-excited probes[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(24): 8752-8760. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2582387
[57] Peng Y, Yuan X R, Zou X, et al. Terahertz identification and quantification of neurotransmitter and neurotrophy mixture[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2016, 7(11): 4472-4479. doi: 10.1364/BOE.7.004472
[58] Chen W Q, Peng Y, Jiang X K, et al. Isomers identification of 2-hydroxyglutarate acid disodium salt (2HG) by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 12166. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11527-z
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: