Research progress of imaging technology based on terahertz quantum well photodetector
-
摘要
太赫兹(THz)波对非极性材料有较好的穿透性,对生物医学组织无电离效应,因而非常适合无损检测、生物医学成像等应用。THz量子阱光电探测器(THz QWPs)具有响应速度快、响应率高、噪声等效功率低、体积小的特点。相较于其他探测器,THz QWPs作为成像系统接收器时,系统具有成像分辨率高、成像速度快、成像信噪比高、结构紧凑等优势。本文综述了基于THz QWPs的成像研究进展,并对成像系统核心指标的影响因素进行了分析和总结。采用更稳定的装置固定THz QWPs,提升器件响应速度、探测灵敏度、阵列规模,可以有效提升系统各项核心性能。
Abstract
Terahertz (THz) waves have a good transmissivity through non-polar materials, and have no ionization effects on biomedical tissues. Therefore, it is ideal for the applications such as non-destructive testing and biomedical imaging. The imaging system based on THz quantum well photodetectors (THz QWPs) has higher imaging resolution, faster imaging speed, higher signal-to-noise ratio, and more compact structure than the imaging systems based on other detectors, as the THz QWPs have fast response, high responsivity, low noise equivalent power, and tiny size. This paper reviews the research progress of the imaging technology based on THz QWPs. And the factors affecting the core indicators of the imaging system are analyzed and summarized. Using more stable fixtures to mount the THz QWPs, improving the device response speed, detection sensitivity, array size, can improve the key performance of imaging systems effectively.
-
Key words:
- terahertz /
- quantum well /
- photodetectors /
- imaging
-
Overview

Overview: Terahertz (THz) waves have a good transmissivity on non-polar materials and no ionization effects on biomedical tissues. Therefore it is ideal for the applications such as non-destructive testing and biomedical imaging. The imaging system based on THz quantum well photodetectors (THz QWPs) has higher imaging resolution, faster imaging speed, higher signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and more compact structure as the THz QWPs have fast response, high responsivity, low noise equivalent power, and tiny size. This paper reviews the research progress of the imaging system based on THz QWPs. The direct transmission and direct reflection imaging systems have simple light paths, and the 3D imaging system can obtain 3D information of objects. However, the imaging speed, the resolution and SNR are low. The archimedean spiral scanning imaging system progressed in imaging speed, but the resolution is still not high. The confocal scanning imaging system has a short imaging time and a relatively high imaging resolution, nevertheless, the SNR is low. The pixel-less imaging system has a diffraction-limited resolution, extremely short imaging time, and high SNR, is the most promising one above. There are some tips for system performance improvement. First, the imaging resolution can be optimized by the optical confocal methods. Second, the large imaging area can be achieved by optimized optical path design. Third, high imaging speed can be achieved with no mechanical stop scanning, multi-pixels detectors, or reducing signal acquisition time with an ultrafast detector. Forth, the SNR is mainly relying on the steady optical path, optical source power, and detector sensitivity. However, these factors are always competitive, a trade-off must be made to achieve an optimized imaging solution for a specific application. It improves the light output stability and beam quality with a more stable fixture for the source and the detector mounting. The improvement of the detector response speed, detection sensitivity, and array size are also working. It is believed that the THz imaging will become faster (real-time/ultra-fast), more accurate (higher resolution), and simpler (lower systems complexity) with these efforts. And it will play an important role in biomedical and industrial imaging in the future.
-

-
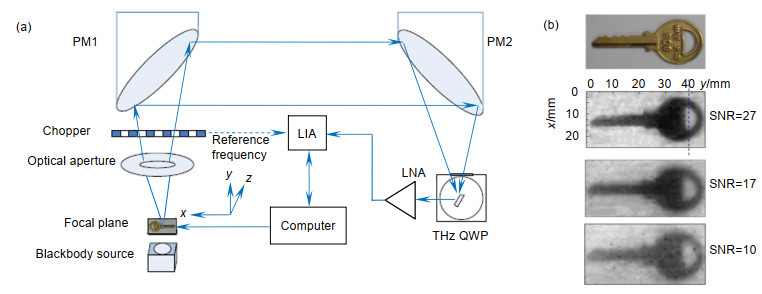
图 2 (a) THz栅格扫描透射成像装置(使用黑体作为辐射源);(b)对比隐藏的钥匙可见光图像(最上面)与信噪比分别为27、17、10(从上至下)时的THz成像图[40]
Figure 2. (a) Setup of the THz raster scanning transmission imaging system (with a blackbody as the source); (b) Comparison of visible image (top) and THz images for the hidden metal key with different SNR: 27, 17, and 10 (from top to bottom)[40]
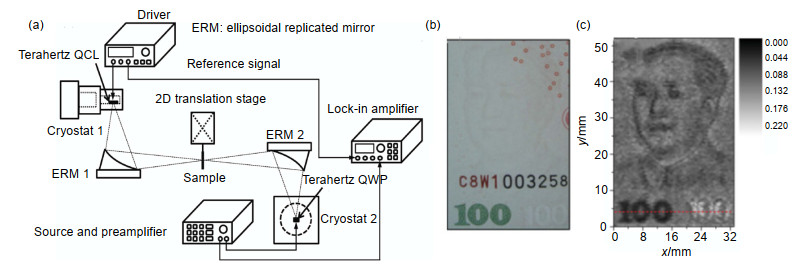
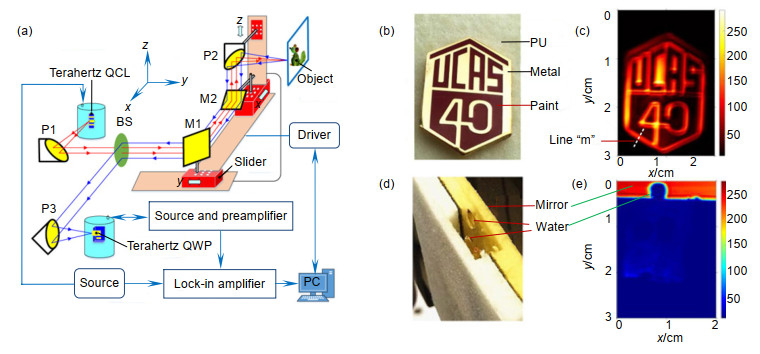
图 5 (a) THz栅格扫描反射成像装置(反射镜移动);(b),(c)中国科学院成立40周年纪念徽章的可见光成像图(b)与THz成像图(c);(d),(e)聚氨酯(PU)绝缘材料内壁三滴水的可见光成像图(d)与THz成像图(e) [43]
Figure 5. (a) Setup of the THz raster scanning reflection imaging system (with mirrors moving); (b), (c) Visible (b) and THz images (c) of a commemorative badge of the 40th anniversary of the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences; (d), (e) Visible (d) and THz images (e) of three drops of water covered with the polyurethane (PU) insulation materials[43]
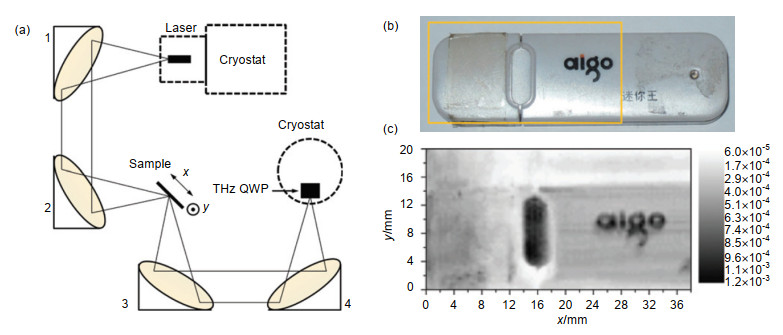
图 7 (a) THz阿基米德螺旋线扫描成像装置;(b),(c)塑料袋遮盖住一半叶子的可见光图(b)与THz成像图(c);(d),(e)聚乙烯盖板完全遮盖叶子的可见光图(d)与THz成像图(e)[45]
Figure 7. (a) Setup of the THz archimedes spiral scanning imaging system; (b), (c) Visible (b) and THz images (c) of a leaf half covered with a plastic bag; (d), (e) Visible (d) and THz images (e) of a leaf covered with a polyethylene lid[45]
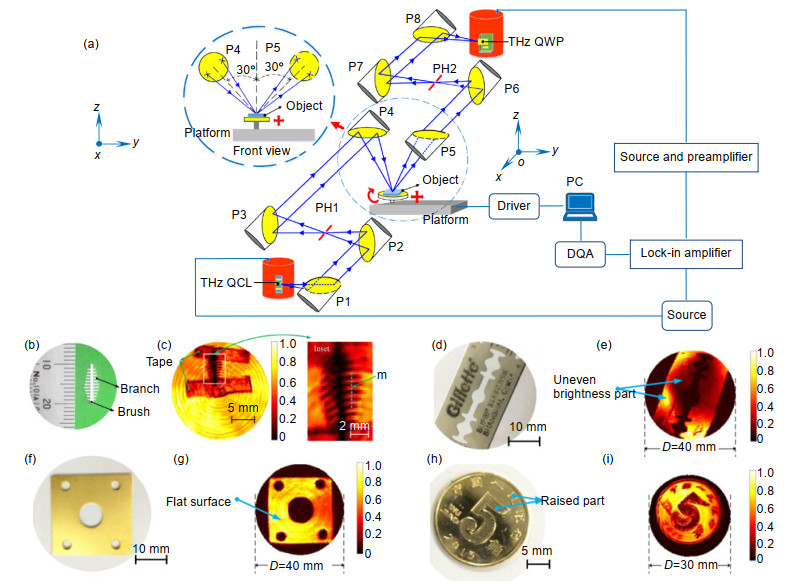
图 8 (a) THz共聚焦扫描成像装置;(b),(c)塑料刷子的可见光图(b)与用胶带固定的THz成像图(c);(d),(e)刮胡刀刀片的可见光图(d)与THz成像图(e);(f),(g)金属板的可见光图(f)与THz成像图(g);(h),(i)硬币的可见光图(h)与THz成像图(i)[46]
Figure 8. (a) Setup of the THz confocal scanning imaging system; (b), (c) Visible image (b) of a plastic brush and THz image (c) of it fixed by the tape; (d), (e) Visible (d) and THz images (e) of a razor blade; (f), (g) Visible (f) and THz images (g) of a metal plate; (h), (i) Visible (h) and THz images (i) of a coin[46]
表 1 常见THz探测器的主要特性比较。参考文献[10]更新数据
Table 1. Comparison of main features of common terahertz detectors. Updated with ref.[10]
Detectors NEP/(pW/Hz0.5) Response time/s Frequency/THz Golay cell, typical ~140 > 0.03 0.04~20 VOx bolometers ~40 > 0.01 1.0~10 LiTiO3 pyroelectric detectors ~400 > 0.01 0.2~30 Schottky barrier diodes ~100 10-10 0.1~10 Superconducting hot electron bolometers 0.1 times the quantum limited ~2×10-10 0.1~10 Si bolometers ~0.1 > 0.025 0.15~20 Pair-breaking detectors Close to quantum limit ~2×10-10 < 2.0 Glow discharge detector 12600 ~10-3 0.1~0.25 Terahertz quantum well photodetector ~0.1 ~10-10 1.5~7.6 & 8.8~20.5 表 2 基于THz QWP的成像系统参数
Table 2. Parameters of a imaging system based on THz QWP
Imaging type Frequency /THz Responsivity /(A/W) Detection array size/pixel Resolution/mm Imaging time Signal to noise ratio Transmission imaging 3.2 0.5 1 1~1.2 0.5 h 27/17/10 3.2 0.5 1 0.5 3 h ~100 Reflection imaging 3.2 0.5 1 ~0.4 1.5 h / 4.2 0.5 1 0.52 1 h / 3D imaging 3.2 0.5 1 1(x)/1.2(z) 24 h ~600 Archimedes spiral scanning imaging 4.2 0.5 1 0.45(x)/0.3(y) 5 s / Confocal scanning imaging 4.2 0.5 1 0.11(lateral)/0.32(axial) 5 s ~125 Pixel-less imaging 5.2 0.22 1 0.05 1 s ~10000 -
参考文献
[1] Abbott D, Zhang X C. Special issue on T-ray imaging, sensing, and retection[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2007, 95(8): 1509–1513. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2007.900894
[2] Hu B B, Nuss M C. Imaging with terahertz waves[J]. Optics Letters, 1995, 20(16): 1716–1718. doi: 10.1364/OL.20.001716
[3] Shi S C, Paine S, Yao Q J, et al. Terahertz and far-infrared windows opened at Dome A in Antarctica[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2016, 1: 0001. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Arxiv000001404155
[4] Luukanen A, Appleby R, Kemp M, et al. Millimeter-wave and terahertz imaging in security applications[M]//Peiponen K E, Zeitler A, Kuwata-Gonokami M. Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2012: 491–520.
[5] Yang X, Zhao X, Yang K, et al. Biomedical applications of terahertz spectroscopy and imaging[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2016, 34(10): 810–824. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.04.008
[6] Zhou Z T, Zhou T, Zhang S Q, et al. Multicolor T-ray imaging using multispectral metamaterials[J]. Advanced Science, 2018, 5(7): 1700982. doi: 10.1002/advs.201700982
[7] Abraham E, Younus A, Delagnes J C, et al. Non-invasive investigation of art paintings by terahertz imaging[J]. Applied Physics A, 2010, 100(3): 585–590. doi: 10.1007/s00339-010-5642-z
[8] Liu H C, Song C Y, SpringThorpe A J, et al. Terahertz quantum-well photodetector[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2004, 84(20): 4068–4070. doi: 10.1063/1.1751620
[9] Guo X G, Tan Z Y, Cao J C, et al. Many-body effects on terahertz quantum well detectors[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 94(20): 201101. doi: 10.1063/1.3134485
[10] Guo X G, Cao J C, Zhang R, et al. Recent progress in terahertz quantum-well photodetectors[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2013, 19(1): 8500508. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2012.2201136
[11] 郭旭光, 顾亮亮, 符张龙, 等.太赫兹量子阱探测器研究[J].激光与光电子学进展, 2015, 52(9): 092302. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb201506018
Guo X G, Gu L L, Fu Z L, et al. Research on terahertz quantum-well photodetectors[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2015, 52(9): 092302. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb201506018
[12] Zhang S, Wang T M, Hao M R, et al. Terahertz quantum-well photodetectors: design, performance, and improvements[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 114(19): 194507. doi: 10.1063/1.4826625
[13] 邵棣祥, 郭旭光, 张戎, 等.多体效应对太赫兹量子阱探测器的影响[J].光学学报, 2017, 37(10): 1004001. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201710007
Shao D X, Guo X G, Zhang R, et al. Influence of many-body effect on terahertz quantum well photodetectors[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(10): 1004001. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201710007
[14] Zhang Y M, Chen H B, Li Z F, et al. The optical coupling improvement of THz quantum well infrared photodetectors based on the plasmonic induced near-field effect[J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2010, 405(2): 552–554. doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2009.09.063
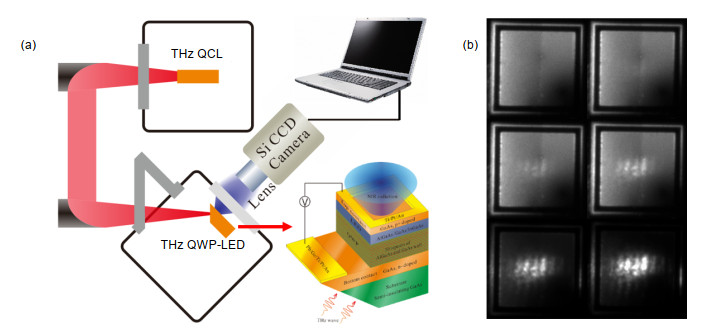
[15] Zhang R, Guo X G, Song C Y, et al. Metal-grating-coupled terahertz quantum-well photodetectors[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2011, 32(5): 659–661. doi: 10.1109/LED.2011.2112632
[16] Zhang R, Guo X G, Cao J C. Coupling efficiency of lamellar gratings for terahertz quantum-well photodetectors[J]. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2012, 60(8): 1233–1237. doi: 10.3938/jkps.60.1233
[17] Zhang R, Guo X G, Cao J C, et al. Asymmetric Fabry-Perot oscillations in metal grating-coupled terahertz quantum well photodetectors[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2012, 48(9): 1214–1219. doi: 10.1109/JQE.2012.2206798
[18] Zhang R, Fu Z L, Gu L L, et al. Terahertz quantum well photodetectors with reflection-grating couplers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 105(23): 231123. doi: 10.1063/1.4904221
[19] Zhang R, Shao D X, Fu Z L, et al. Terahertz quantum well photodetectors with metal-grating couplers[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2017, 23(4): 3800407.
[20] Li L J, Bai P, Zhang Y H, et al. Optical field simulation of edge coupled terahertz quantum well photodetectors[J]. AIP Advances, 2018, 8(3): 035214. doi: 10.1063/1.5011956
[21] Zhang Z Z, Fu Z L, Guo X G, et al. 4.3 THz quantum-well photodetectors with high detection sensitivity[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2018, 27(3): 030701. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/27/3/030701
[22] Shao D X, Zhang R, Fu Z L, et al. High responsivity random metal grating couplers for terahertz quantum well photodetectors[J]. Semiconductor Science and Technology, 2019, 34(7): 075029. doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/ab0a4a
[23] Palaferri D, Todorov Y, Chen Y N, et al. Patch antenna terahertz photodetectors[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2015, 106: 161102. doi: 10.1063/1.4918983
[24] Li H, Wan W J, Tan Z Y, et al. 6.2-GHz modulated terahertz light detection using fast terahertz quantum well photodetectors[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 3452. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03787-6
[25] Tan Z Y, Li H, Wan W J, et al. Direct detection of a fast modulated terahertz light with a spectrally matched quantum-well photodetector[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(2): 91–93. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.3099
[26] 张真真, 黎华, 曹俊诚.高速太赫兹探测器[J].物理学报, 2018, 67(9): 090702. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlxb201809001
Zhang Z Z, Li H, Cao J C. Ultrafast terahertz detectors[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2018, 67(9): 090702. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlxb201809001
[27] Luo H, Liu H C, Song C Y, et al. Background-limited terahertz quantum-well photodetector[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 86(23): 231103. doi: 10.1063/1.1947377
[28] Jia J Y, Gao J H, Hao M R, et al. Dark current mechanism of terahertz quantum-well photodetectors[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2014, 116(15): 154501. doi: 10.1063/1.4898036
[29] Jia J Y, Wang T M, Zhang Y H, et al. High-temperature photon-noise-limited performance terahertz quantum-well photodetectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2015, 5(5): 715–724. doi: 10.1109/TTHZ.2015.2453632
[30] Wang H X, Fu Z L, Shao D X, et al. Broadband bias-tunable terahertz photodetector using asymmetric GaAs/AlGaAs step multi-quantum well[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2018, 113(17): 171107. doi: 10.1063/1.5046881
[31] Cao J C, Chen Y L, Liu H C. Effect of optical phonons on the spectral shape of terahertz quantum-well photodetectors[J]. Superlattices and Microstructures, 2006, 40(2): 119–124. doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2006.06.001
[32] Xiong F, Guo X G, Cao J C. Simulation of photocurrents of terahertz quantum-well photodetectors[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2008, 25(5): 1895–1897. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/25/5/102
[33] Guo X G, Zhang R, Liu H C, et al. Photocurrent spectra of heavily doped terahertz quantum well photodetectors[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97(2): 021114. doi: 10.1063/1.3458829
[34] Gu L L, Zhang R, Tan Z Y, et al. Terahertz quantum well photo-detectors: grating versus 45° facet coupling[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2014, 47(16): 165101. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/47/16/165101
[35] Gu L L, Guo X G, Fu Z L, et al. Optical-phonon-mediated photocurrent in terahertz quantum-well photodetectors[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2015, 106(11): 111107. doi: 10.1063/1.4916084
[36] Yu C H, Zhang B, Lu W, et al. Strong enhancement of terahertz response in GaAs/AlGaAs quantum well photodetector by magnetic field[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97(2): 022102. doi: 10.1063/1.3462300
[37] Yu C H, Zhang B, Luo X D, et al. Wide tunability and electron transfer in GaAs/AlGaAs quantum well photodetector by magnetic field[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 110(19): 192102. doi: 10.1063/1.4983218
[38] Yu C H, Li L, Xu T F, et al. Strong terahertz response in quantum well photodetector based on intradonor transition by magnetic field[J]. AIP Advances, 2018, 8(12): 125014. doi: 10.1063/1.5051203
[39] Zhang G X, Guo X G, Wang H X, et al. Bias-polarity-dependent photocurrent spectra of terahertz stepped-quantum-well photodetectors[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2019, 12(2): 024035. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.12.024035
[40] Zhou T, Zhang R, Guo X G, et al. Terahertz imaging with quantum-well photodetectors[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2012, 24(13): 1109–1111. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2012.2196033
[41] Tan Z Y, Zhou T, Cao J C, et al. Terahertz imaging with quantum-cascade laser and quantum-well photodetector[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2013, 25(14): 1344–1346. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2013.2265303
[42] Tan Z Y, Zhou T, Fu Z L, et al. Reflection imaging with terahertz quantum-cascade laser and quantum-well photodetector[J]. Electronics Letters, 2014, 50(5): 389–391. doi: 10.1049/el.2013.4079
[43] Qiu F C, Tan Z Y, Wang C, et al. Terahertz optical scanning imaging of motionless polyurethane insulation materials[J]. Electronics Letters, 2019, 55(19): 1053–1055. doi: 10.1049/el.2019.2282
[44] Zhou T, Tan Z Y, Gu L, et al. Three-dimensional imaging with terahertz quantum cascade laser and quantum well photodetector[J]. Electronics Letters, 2015, 51(1): 85–86. doi: 10.1049/el.2014.3873
[45] Qiu F C, Tan Z Y, Fu Z L, et al. Reflective scanning imaging based on a fast terahertz photodetector[J]. Optics Communications, 2018, 427: 170–174. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.06.030
[46] Qiu F C, Fu Y Z, Wang C, et al. Fast terahertz reflective confocal scanning imaging with a quantum cascade laser and a photodetector[J]. Applied Physics B, 2019, 125(5): 86. doi: 10.1007/s00340-019-7198-8
[47] Fu Z L, Gu L L, Guo X G, et al. Frequency up-conversion photon-type terahertz imager[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 25383. doi: 10.1038/srep25383
[48] 符张龙, 邵棣祥, 张真真, 等.太赫兹频率上转换成像器件研究[J].深圳大学学报理工版, 2019, 36(2): 147–151. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/szdxxb201902005
Fu Z L, Shao D X, Zhang Z Z, et al. Terahertz frequency up-conversion imaging devices[J]. Journal of Shenzhen University Science and Engineering, 2019, 36(2): 147–151. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/szdxxb201902005
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: