Image dehazing algorithm by combining light field multi-cues and atmospheric scattering model
-
摘要:
雾天拍摄的图像通常会存在对比度低、图像质量差的问题,而这些退化图像会对计算机视觉的应用产生显著的负面影响。针对这些问题,本文首次提出一种将光场与大气散射模型相结合的图像去雾方法。首先利用光场相机捕获多视角信息的优势提取散焦线索和匹配线索估计雾天图像的深度信息,并利用获取的深度信息计算场景初始透射率。然后利用场景深度信息构建新的权重函数,并将其与1-范数上下文规则化相结合对初始透射率图迭代优化。最后利用大气散射模型对光场中心视角图像进行去雾以获得最终的无雾图像。在合成雾天图像和真实雾天图像上的实验结果表明,与现有的单幅图像去雾算法相比,峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高约2 dB,结构相似性(SSIM)提高约0.04,本文方法更好地保留了图像的结构信息,同时去雾后的图像较好地保持了图像的色彩信息,能获得更优的图像去雾效果。
 Abstract:
Abstract:Image captured in foggy weather often exhibits low contrast and poor image quality, which may have a negative impact on computer vision applications. Aiming at these problems, we propose an image dehazing algorithm by combining light field technology with atmospheric scattering model. Firstly, taking the advantages of capturing multi-view information from light field camera is used to extracting defocus cues and correspondence cues, which are used to estimating the depth information of hazy images, and use the obtained depth information to calculating the scene's initial transmission. Then use scene depth information to build a new weight function, and combined it with 1-norm context regularization to optimizing the initial transmission map iteratively. Finally, the central perspective image of hazy light field images is dehazed using atmospheric scattering model to obtain the final dehazed images. Experimental results on synthetic hazy images and real hazy images demonstrate that, compared to existing single image dehazing algorithms, the peak signal to noise ratio get 2 dB improvement and the structural similarity raise about 0.04. Moreover, our approach preserves more fine structural information of images and has faithful color fidelity, thus yielding a superior image dehazing result.
-
Key words:
- image dehazing /
- light field /
- defocus cues /
- correspondence cues /
- depth estimation /
- atmospheric scattering model
-

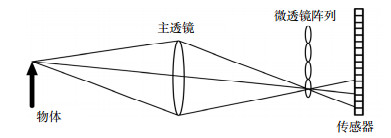
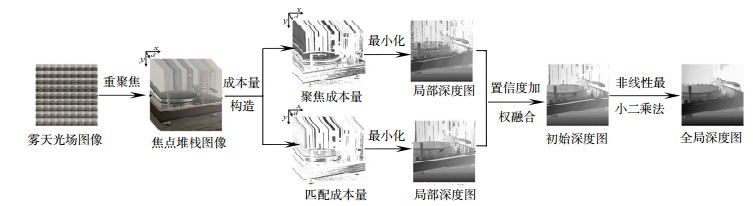
Overview: Under severe weather conditions such as fog, rain, and haze, the scattering of atmospheric particles degrades the images captured by camera. Image contrast and color fidelity will be reduced to some extent, which may have a negative impact on computer vision applications. At the same time, due to the limited information provided by single image, it is difficult to extract the depth information of the scene for image dehazing. Thus, studies on image dehazing methods have great significance. In this paper, we first present an image dehazing algorithm by combining light field technology with atmospheric scattering model. Firstly, taking the advantages of light field refocusing and capturing multi-view information, we extract defocus and correspondence cues. After that, we extract the depth information of the scene by defocusing and correspondence cues, respectively, and the attainable maximum likelihood (AML) is taken as confidence measure method, which can be used to calculate confidence to synthesize the depth maps. Secondly, the scene transmission is calculated according to the exponential relationship between the scene depth and scene transmission. After that, we construct a weight function to constrain the singular value of the scene transmission by using the obtained depth information, and introducing the weight function into weighted 1-norm context constraint to optimize the transmission map iteratively. Finally, the obtained scene transmission and the central view image of the hazy light field images are introduced into the atmospheric scattering model to achieve image dehazing. The experiments were tested on synthetic hazy images and real hazy images respectively. Experiments results on the synthetic hazy images evaluate the performance of eight dehazing methods. In quantitative analysis, compared to seven kinds of single image dehazing algorithms, the peak signal to noise ratio get 2 dB improvement and the structural similarity raise about 0.04. In qualitative analysis, our method has achieved the best results in five scenarios, and images after dehazing has higher contrast and color fidelity for better visual effects. Experiments results on real hazy images demonstrate that our method can achieve superior dehazing results. Images after dehazing with our method have higher contrast and color fidelity. At the same time, our method has a certain inhibitory effect on noise in the images. The comparison results of noise contained in images after dehazing by different algorithms show that there is less noise in the images by our method, and the images have the highest contrast and visibility. In general, compared with seven single image dehazing algorithms, our method achieves the best dehazing effect, images contrast and structural similarity after dehazing have been greatly improved.
-

-
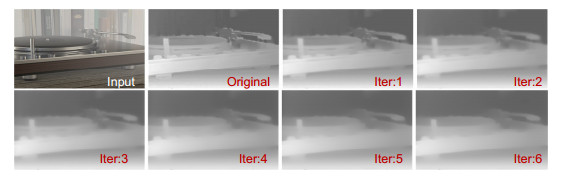
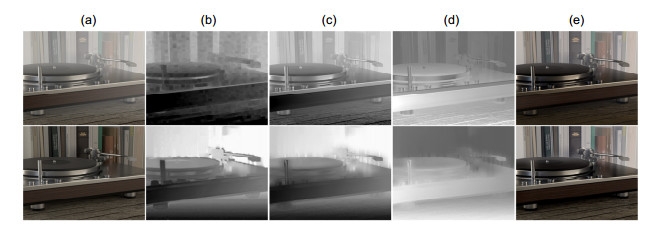
图 8 利用文献[13]方法与本文方法提取的场景深度进行图像去雾的结果对比。(a)分别为雾天图像和真实无雾图像;(b)初始深度图;(c)引导滤波优化后的深度图;(d)透射率图;(e)复原图像
Figure 8. Comparison of image dehazing results using the depth extracted by the method of Ref. [13] and the depth extracted by our method. (a) Hazy image and haze-free image; (b) Initial depth map; (c) Optimized depth map using guided filtering; (d) Transmission map; (e) Restored image
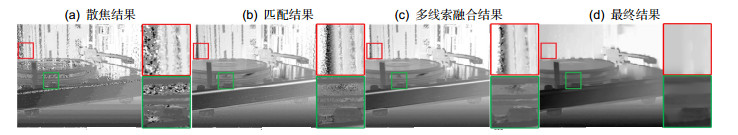
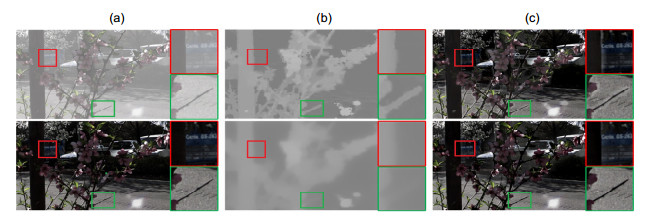
图 9 光场单线索与多线索融合的去雾结果对比。(a)原始雾天图像及无雾图像真值;(b)单独使用散焦线索获取的透射率及其对应的去雾结果;(c)单独使用匹配线索获取的透射率及其对应的去雾结果;(d)本文方法获取的透射率图及其对应的去雾结果
Figure 9. Comparison of dehazing results between light field single cue and multi-cues fusion. (a) Input hazy image and ground truth (from top to bottom); (b) Transmission map obtained from defocusing cue alone and corresponding dehazing result; (c) Transmission map obtained from correspondence cue alone and corresponding dehazing result; (d) Transmission map obtained by our method and corresponding dehazing result
图 10 透射率优化对图像去雾结果的影响。(a)分别为雾天图像与原始无雾图像;(b)分别为场景初始透射率与优化后的场景透射率;(c)分别为使用初始透射率和优化后的透射率进行去雾的结果
Figure 10. Effect of transmission map optimization on image dehazing results. (a) Input hazy image and ground truth (from top to bottom); (b) Initial scene transmission map and optimized transmission map; (c) Dehazing results by using (b)
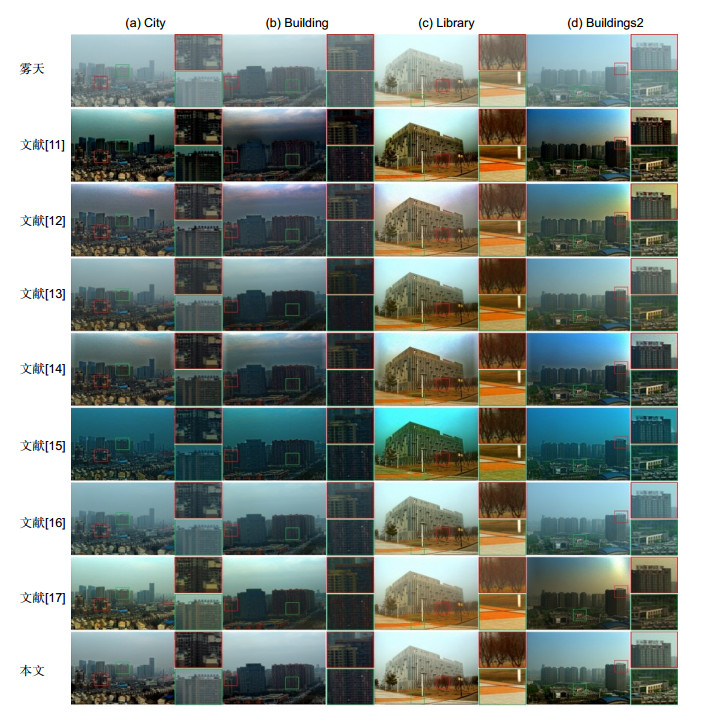
图 12 合成雾天图像的去雾结果。第一行为雾天图像;第二行至第八行为文献[11~17]方法去雾结果;第九行为本文方法去雾结果;第十行为无雾图像真值
Figure 12. Comparisons of dehazing results on synthetic hazy images. The first line is hazy images; the second line to the eighth line are the dehazing results of Ref. [11~17] methods; the ninth line is the dehazing results of our method; and the tenth line is ground truth
表 1 合成雾天场景上去雾结果的定量评价(PSNR)
Table 1. Quantitative comparison of dehazing results on synthetic hazy scenes (PSNR)
场景名 Vinyl Buildings Buildings2 Flower Court Average 文献[11]方法 63.53 68.03 71.46 62.37 62.81 65.64 文献[12]方法 66.50 66.90 70.60 66.61 66.26 67.37 文献[13]方法 64.19 62.54 67.16 67.79 58.80 64.10 文献[14]方法 65.62 70.51 77.03 70.38 66.47 70.00 文献[15]方法 67.34 67.62 75.03 67.25 67.91 69.03 文献[16]方法 67.91 61.32 65.24 65.65 60.36 64.10 文献[17]方法 59.60 64.85 76.19 65.82 59.93 65.28 本文方法 68.13 72.97 77.47 74.90 68.80 72.45 表 2 合成雾天场景上去雾结果的定量评价(SSIM)
Table 2. Quantitative comparison of dehazing results on synthetic hazy scenes (SSIM)
场景名 Vinyl Buildings Buildings2 Flower Court Average 文献[11]方法 0.647 0.905 0.841 0.605 0.687 0.737 文献[12]方法 0.792 0.668 0.756 0.712 0.732 0.732 文献[13]方法 0.760 0.556 0.653 0.727 0.588 0.657 文献[14]方法 0.714 0.766 0.874 0.825 0.773 0.790 文献[15]方法 0.748 0.816 0.846 0.717 0.847 0.795 文献[16]方法 0.742 0.531 0.620 0.703 0.636 0.646 文献[17]方法 0.738 0.668 0.870 0.715 0.627 0.724 本文方法 0.813 0.886 0.897 0.862 0.916 0.875 -
[1] Shao L, Liu L, Li X L. Feature learning for image classification via multiobjective genetic programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(7): 1359–1371. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2293418
[2] Crebolder J M, Sloan R B. Determining the effects of eyewear fogging on visual task performance[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2004, 35(4): 371–381. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2004.02.005
[3] 肖创柏, 赵宏宇, 禹晶, 等.基于WLS的雾天交通图像恢复方法[J].红外与激光工程, 2015, 44(3): 1080–1084. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hwyjggc201503052
Xiao C B, Zhao H Y, Yu J, et al. Traffic image defogging method based on WLS[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 44(3): 1080–1084. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hwyjggc201503052
[4] Zhu F, Shao L. Weakly-supervised cross-domain dictionary learning for visual recognition[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2014, 109(1–2): 42–59. doi: 10.1007/s11263-014-0703-y
[5] Zhang Z, Tao D C. Slow feature analysis for human action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(3): 436–450. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.157
[6] Wang L J, Zhu R. Image defogging algorithm of single color image based on wavelet transform and histogram equalization[J]. Applied Mathematical Sciences, 2013, 7(79): 3913–3921. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Doaj000003429590
[7] Shen H F, Li H F, Qian Y, et al. An effective thin cloud removal procedure for visible remote sensing images[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2014, 96: 224–235. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.06.011
[8] Pei S C, Lee T Y. Nighttime haze removal using color transfer pre-processing and Dark Channel Prior[C]//Proceedings of the 2012 19th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Orlando, FL, USA, 2012.
[9] Zhu Q S, Yang S, Heng P A, et al. An adaptive and effective single image dehazing algorithm based on dark channel prior[C]//Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Shenzhen, China, 2013.
[10] Oakley J P, Satherley B L. Improving image quality in poor visibility conditions using a physical model for contrast degradation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1988, 7(2): 167–169. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=aa78c3638a940b8532bb0e9f26bad129
[11] Berman D, Treibitz T, Avidan S. Non-local image dehazing[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 1674–1682.
[12] Meng G F, Wang Y, Duan J Y, et al. Efficient image dehazing with boundary constraint and contextual regularization[C]//Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2013.
[13] Zhu Q S, Mai J M, Shao L. A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 3522–3533. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2446191
[14] He K M, Sun J, Tang X O. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341–2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168
[15] Tarel J P, Hautière N. Fast visibility restoration from a single color or gray level image[C]//Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 2009.
[16] Cai B L, Xu X M, Jia K, et al. DehazeNet: an end-to-end system for single image haze removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(11): 5187–5198. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2598681
[17] Zhu Y Y, Tang G Y, Zhang X Y, et al. Haze removal method for natural restoration of images with sky[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 275: 499–510. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.08.055
[18] Schechner Y Y, Narasimhan S G, Nayar S K. Polarization-based vision through haze[J]. Applied Optics, 2003, 42(3): 511–525. doi: 10.1364/AO.42.000511
[19] Raikwar S C, Tapaswi S. An improved linear depth model for single image fog removal[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2018, 77(15): 19719–19744. doi: 10.1007/s11042-017-5398-y
[20] Ng R, Levoy M, Brédif M, et al. Light field photography with a hand-held plenoptic camera[J]. Computer Science Technical Report CSTR, 2005, 2(11): 1–11. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10025989130
[21] Tao M W, Srinivasan P P, Malik J, et al. Depth from shading, defocus, and correspondence using light-field angular coherence[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 2015.
[22] Raj A S, Lowney M, Shah R. Light-field database creation and depth estimation[R]. Palo Alto, USA: Stanford University, 2016.
[23] Wang T C, Efros A A, Ramamoorthi R. Occlusion-aware depth estimation using light-field cameras[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015.
[24] Williem W, Park I K. Robust light field depth estimation for noisy scene with occlusion[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 4396–4404.
[25] Wang M, Zhou S D, Huang F, et al. The study of color image defogging based on wavelet transform and single scale retinex[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2011, 8194: 81940F. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CC0212514212
[26] Ramya C, Rani D S. Contrast enhancement for fog degraded video sequences using BPDFHE[J]. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies, 2012, 3(2): 3463–3468. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/267844146_Contrast_Enhancement_for_Fog_Degraded_Video_Sequences_Using
[27] Xu Z Y, Liu X M, Chen X N. Fog removal from video sequences using contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization[C]//Proceedings of 2009 International Computational Intelligence and Software Engineering, Wuhan, China, 2009.
[28] Howard J N. Book Reviews: Scattering Phenomena[J]. Science, 1977, 196(4294): 1084–1085. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1977Sci...196.1084M
[29] Narasimhan S G, Nayar S K. Contrast restoration of weather degraded images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2003, 25(6): 713–724. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2003.1201821
[30] Narasimhan S G, Nayar S K. Vision and the atmosphere[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2002, 48(3): 233–254. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b619651bb1a84a4d7a31d397fb0f9386
[31] 熊伟, 张骏, 高欣健, 等.自适应成本量的抗遮挡光场深度估计算法[J].中国图象图形学报, 2018, 22(12): 1709–1722. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgtxtxxb-a201712007
Xiong W, Zhang J, Gao X J, et al. Anti-occlusion light-field depth estimation from adaptive cost volume[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2018, 22(12): 1709–1722. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgtxtxxb-a201712007
[32] Sun J, Shum H Y, Zheng N N. Stereo matching using belief propagation[C]//Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Computer Vision, Denmark, 2002: 510–524.
[33] Hu X Y, Mordohai P. A quantitative evaluation of confidence measures for stereo vision[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(11): 2121–2133. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.46
[34] Tan R T. Visibility in bad weather from a single image[C]//Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 2008.
[35] Tang K, Yang J C, Wang J. Investigating haze-relevant features in a learning framework for image dehazing[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 2014.
[36] Ying Z Q, Li G, Gao W. A bio-inspired multi-exposure fusion framework for low-light image enhancement[Z]. arXiv: 1711.00591[cs], 2017.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: