-
摘要:
手背静脉图像的采集过程中,由于图像采集设备、光照、皮下脂肪厚度等因素的影响,手背静脉图像的对比度比较低,同时图像噪声严重影响静脉提取。针对此问题,本文提出了一种基于静脉灰度值特征的图像分割与对比度增强算法。首先提取ROI(有效的感兴趣区域)和对ROI进行维纳滤波;然后采用新的图像分割算法对静脉图像进行静脉提取,利用8-邻接内边界跟踪方法和形态学处理方法对静脉二值图像进行去噪;最后将ROI与去噪后的图像进行加权叠加得到对比度增强的静脉图像。实验结果表明,通过采用基于静脉灰度值特征的图像分割算法可以很好地获取到静脉脉络,最终可以获得高对比度的静脉图像。
 Abstract:
Abstract:In the process of collecting hand vein images, due to the influence of image acquisition equipment, illumination and subcutaneous fat thickness, the contrast of hand vein images is relatively low. Meanwhile, vein extraction is seriously affected by image noise. To solve this problem, an algorithm of image segmentation and contrast enhancement based on features of venous gray value is proposed in this paper. Firstly, effective region of interest (ROI) is extracted and filtered through Wiener filtering. Secondly, a new image segmentation algorithm is obtained to extract vein image. The venous binary image is denoised by an 8-adjacent inner boundary tracking method and morphological processing. Finally, contrast-enhanced venous images are obtained by weight stack of the ROI and denoised images. The experiments results show that intravenous veins can be obtained perfectly by using the image segmentation algorithm based on features of venous gray value. Moreover, the high contrast venous images can be obtained.
-

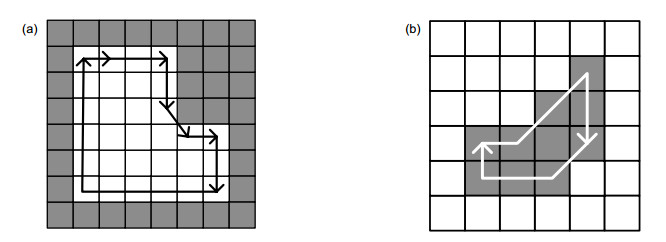
Overview: In the process of collecting hand vein images, due to the influence of image acquisition equipment, illumination and subcutaneous fat thickness, the contrast of hand vein images is relatively low. Meanwhile, vein extraction was seriously affected by image noise. To solve this problem, an algorithm of image segmentation and contrast enhancement based on features of venous gray value is proposed in this paper. The algorithm is divided into the following six steps. 1) The OTSU is used to determine the threshold value of gray level between hand and background. The threshold is 75. According to the threshold of hand vein images, the gray value of the hand is set as 255, and the gray value of the background is set as zero. 2) The gray value distribution of hand is used to determine the centroid coordinates of hand, and the area of region of interest (ROI) is set as one-third of the hand area. ROI is extracted from the hand vein images based on center of mass coordinates and area. 3) Before the image segmentation, Wiener filtering is performed on the ROI by using a 3×3 template. 4) According to the gray value distribution of the ROI images, the ROI image is segmented using a threshold of one and a step size of eight. 5) After segmentation of the ROI images, in addition to containing veins, these noises of spots, holes and burrs are included. The boundary coordinates of the spots and holes and the numbers of pixels on the boundary are obtained by using the 8-adjacent inner boundary tracking method. When the number of pixels is less than 300, the area can be judged as a spot or hole. According to the boundary coordinates, the gray value of all the pixels in the spot are changed as 0, and the gray value of all the pixels in the hole are changed as 250. After removal of spots and holes, morphological treatments are used to remove burrs. 6) After the noise is removed, contrast enhanced venous images are obtained by weight stack of the venous binary and ROI images. The coefficient of the venous binary image is set as -0.04, and the coefficient of the ROI image is set as 1.2. The experiments results show that intravenous veins can be obtained perfectly by using the image segmentation algorithm based on features of the venous gray value. In the end, the high contrast venous images can be obtained by weighted stack of the images.
-

-
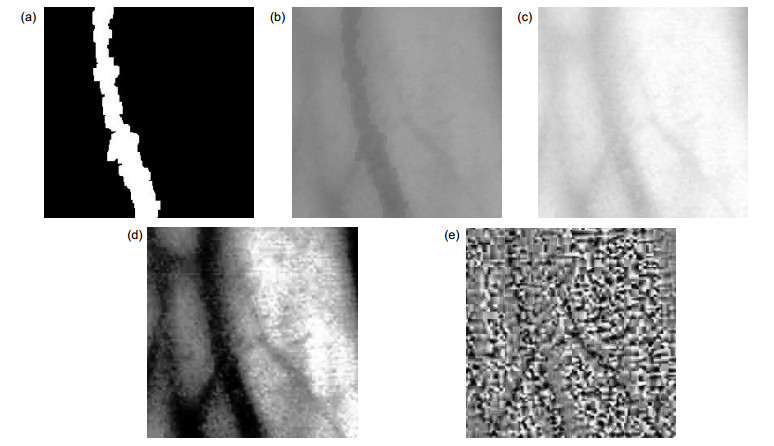
图 7 各种算法对比度增强图。(a)本文去噪后二值图;(b)本文对比度增强图;(c) Retinex增强图;(d)直方图均衡化增强图;(e)子块部分重叠直方图均衡化增强图
Figure 7. Contrast enhancement images by various algorithms. (a) Two value image after being denoised in this paper; (b) Contrast enhancement image in this paper; (c) Retinex enhancement image; (d) Histogram equalization enhancement image; (e) Partially overlapping sub-block histogram equalization enhancement image
-
[1] 李威, 苑玮琦.不同波长近红外光下手掌静脉图像质量分析[J].计算机工程与应用, 2011, 47(30): 15-18. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2011.30.005
Li W, Yuan W Q. Imaging quality analysis on palm vein under different wavelengths near-IR[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2011, 47(30): 15-18. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2011.30.005
[2] 蔡超峰, 任景英.基于直方图均衡化的手背静脉图像对比度增强[J].计算机应用, 2013, 33(4): 1125-1127. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjyy201304059
Cai C F, Ren J Y. Contrast enhancement of hand vein images based on histogram equalization[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2013, 33(4): 1125-1127. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjyy201304059
[3] 杨晓鹏, 蔡超峰, 潘珩, 等.手背静脉图像预处理算法研究[J].中国医疗设备, 2013, 28(10): 20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1633.2013.10.005
Yang X P, Cai C F, Pan H, et al. Research on Pretreatment Algorithm of Hand Vein Image[J]. China Medical Devices, 2013, 28(10): 20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1633.2013.10.005
[4] Wang H B, Tao L. Novel algorithm for enhancement of hand vein images based on adaptive filtering and retinex method[C]//Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Conference on Information Science and Technology, 2012: 857-860.
[5] 胡学友.手背静脉图像增强和分割方法[J].电脑知识与技术, 2014, 10(21): 5080-5082. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dnzsyjs-itrzyksb201421052
Hu X Y. Novel algorithm for hand vein image enhancement and segmentation[J]. Computer Knowledge and Technology, 2014, 10(21): 5080-5082. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dnzsyjs-itrzyksb201421052
[6] 王镇东, 孙红星, 邓永娣, 等.手背静脉识别的图像处理算法[J].辽宁科技大学学报, 2010, 33(5): 499-502, 508. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1048.2010.05.013
Wang Z D, Sun H X, Deng Y D, et al. Image processing algorithm for hand vein recognition[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Liaoning, 2010, 33(5): 499-502, 508. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1048.2010.05.013
[7] Funt B V, Ciurea F, Mccann J J. Retinex in Matlab[C]//Color and Imaging Conference, 2000(10): 112-121.
[8] Otsu N. A. Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms[J]. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. & Cybern, 2007, 9(1): 62-66. http://jamia.oxfordjournals.org/lookup/external-ref?access_num=10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076&link_type=DOI
[9] 韩笑.人体手背静脉识别算法研究[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2007.
Han X. Research on algorithm for human dorsal hand vein recognition[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2007.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-2007095392.htm [10] Suresh K, Papendra K, Manoj G, et al. Performance Comparison of Median and Wiener Filter in Image De-noising[J]. International Journal of Computer Applications, 2010, 12(4): 24-28. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_a632c08512f40a5909e07cc89b175d29
[11] 图像处理、分析与机器视觉[M].北京: 清华大学出版社, 2011: 230-231.
Milan Sonka, Vaclav Hlavac, Roger Boyle. Image processing, Analysis and Machine Vision[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2011: 230-231. Milan Sonka, Vaclav Hlavac, Roger Boyle.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: