Optical color image asymmetric compressed encryption in fractional Fourier transform domain
-
摘要:
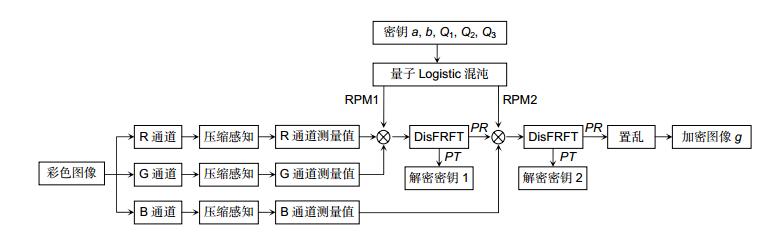
为了提高传统双随机相位编码图像光学加密系统的安全性,并减少其所需要处理的数据量,提出了一种基于压缩感知及量子Logistic混沌映射的彩色图像非对称光学加密方法。针对彩色图像加密过程中所需要处理数据量过大问题,首先利用压缩感知理论减少加密系统所需要处理的数据量,其次,将彩色图像三通道转换为单通道加密来减少数据量。针对传统光学加密系统为线性系统问题,采用基于相位截断的非对称光学加密方法进行加密。针对光学加密系统加密密钥为随机相位板不方便传输问题,利用量子混沌产生系统所需要的随机相位板。结果表明,此算法可以获得较为理想的图像加密和解密效果。
 Abstract:
Abstract:In order to improve the security of traditional optical image encryption and reduce the amount of data what needs to process, we propose a color image asymmetric optical encryption method based on compressed sensing and quantum logistic map, and use the compressive sensing theory and single-channel encrypted method to deal with the problem of large amount of data in the process of color image encryption. Aiming at the linear problem of the traditional optical cryptosystem, we use asymmetric optical encryption based on phase truncation fractional Fourier transform. We also use quantum logistic map to generate the random phase masks for the convenience of transmitting random phase masks. The results show that the proposed algorithm can obtain better image encryption and decryption results.
-
Key words:
- compressive sensing /
- optical encryption /
- quantum logistic map /
- single-channel
-

Overview: In recent years, with the development of multimedia technology, various kinds of information such as pictures, videos can be transmitted conveniently and quickly through the internet. People's work and study also increasingly depend on the network and information system. Therefore, the security of information has drawn more and more attention. Image security is especially important because image information can convey people's thoughts more clearly.
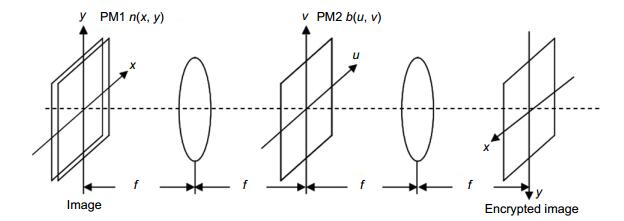
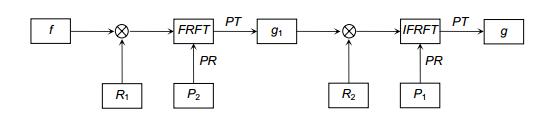
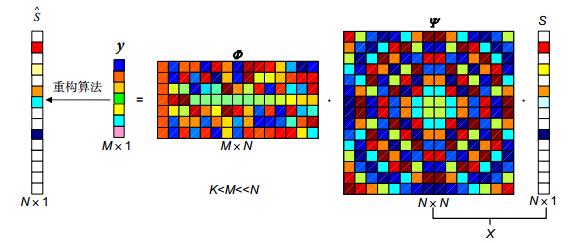
In this paper, we present a novel color image encrypted system based on compressed sensing and quantum logistic map. On the one hand, the system significantly decreases the number of transferred data in the cryptosystem; on the other hand, it increases the security of an encryption system. First, two steps are used to reduce the number of data. Step one, color image traditional encrypted process needs to deal with the data of three channels. In order to convert three-channel of color image to single-channel encrypted, we use some mathematical transformations to convert the green channel and the blue channel into two phase masks and add them into the optical cryptosystem. Single-channel can not only reduce the amount of data what it needs to process, it also simplifies the optical encryption system. Step two, this system significantly decreases the number of data processed in the cryptosystem by utilizing compressed sensing (CS). The most attractive characteristic of CS is that with far fewer samples or measurements than traditional Nyquist sampling methods, one can perfectly reconstruct certain signals. The CS also provides a mechanism for data security because the signal can only be reconstructed if the sensing matrix is known. Second, to enhance security, the proposed algorithm increases the robustness of the system used asymmetric optical encryption system based on the phase truncation fractional Fourier transform. This method can make the system resistant to plaintext attacks, and also make the encryption result a real value, which can save storage space and provide convenience in transmission. At the same time, the parameters of fractional Fourier transform are the keys of the cryptosystem, it adds the number of the keys to enhance security. Finally, to simplify the key exchange, we use quantum logistic chaotic to generate the random phase masks. Instead of transmitting the random phase masks which is hard and inconvenient to transmit and save, only five parameters of quantum logistic map are required. The encryption keys of the cryptosystem are the truncated phase, the fractional orders in the fractional Fourier transform and the parameters of quantum logistic map. The results show that this algorithm can obtain better image encryption and decryption results.
-

-
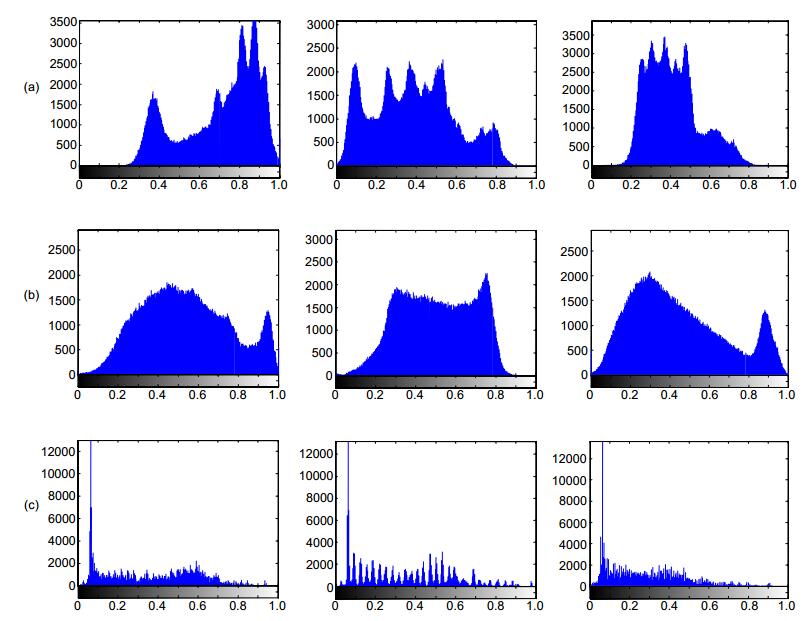
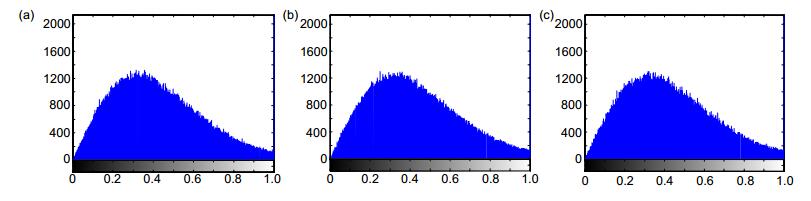
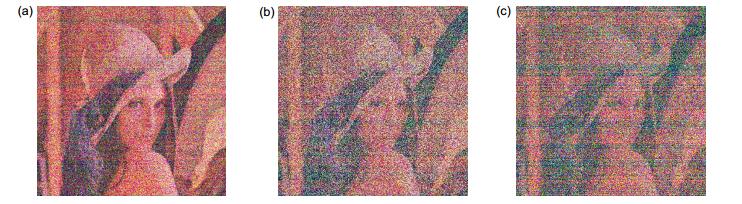
图 8 加密图像受到噪声攻击时的解密图像。(a)噪声攻击强度为0.001时的解密图像;(b)噪声攻击强度为0.01时的解密图像;(c)噪声攻击强度为0.1时的解密图像
Figure 8. The decryption image when the encrypted image attacked by noise. (a) The decrypted image with the noise attacked intensity of 0.001; (b) The decrypted image with the noise attacked intensity of 0.01; (c) The decrypted image with the noise attacked intensity of 0.1
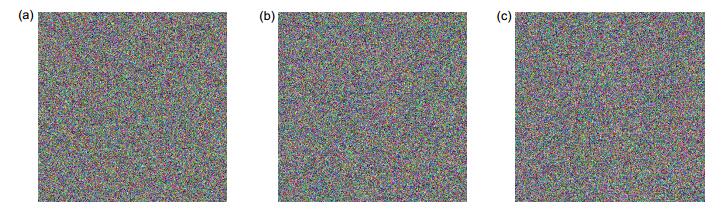
图 11 错误密钥时的解密图像。(a)分数傅里叶变换参数分别减少0.1时的解密图像;(b)采用随机矩阵代替截断相位时的解密图像;(c)压缩感知测量为随机矩阵时的解密图像
Figure 11. The decryption images using wrong keys. (a) The decrypted image with the parameters of FRFT reduced by 0.1; (b) The decrypted image replaced the truncated mask with the random matrix; (c) The decrypted image replaced measurement matrix with the random matrix
表 1 Lena图像与planet图像恢复图像平均峰值信噪比对比
Table 1. Average PSNR comparison on the reconstructed image in Lena and planet
dB 压缩率 0.9 bpp 0.8 bpp 0.7 bpp 0.6 bpp 0.5 bpp 0.3 bpp Lena-CS 37.1021 34.1527 32.2742 31.3325 25.1043 20.1543 Planet-CS 40.3420 36.8588 34.4556 32.9497 30.1059 24.5717 表 2 实验对比表
Table 2. The table of the experiments comparison
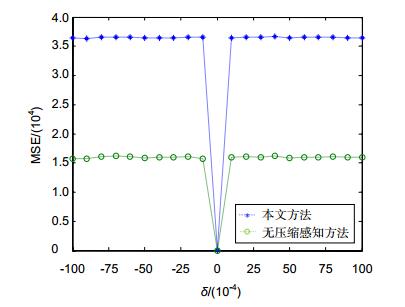
方法 PSNR 是否减少数据量 安全性 密钥数据量 方法一 Inf 否 低 小 方法二 56.92 否 中 小 方法三 342.42 否 中 大 本文算法 34.78 11.3% 高 中 -
[1] Piao Y R, Shin D, Kim E S. Robust image encryption by combined use of integral imaging and pixel scrambling techniques[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2009, 47(11): 1273-1281. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2009.05.007
[2] Panduranga H T, Naveen Kumar S K. Hybrid approach for image encryption using SCAN patterns and carrier images[J]. International Journal on Computer Science and Engineering, 2010, 2(2): 297-300.
[3] Zhang Q, Guo L, Wei X P. Image encryption using DNA addition combining with chaotic maps[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 2010, 52(11-12): 2028-2035. doi: 10.1016/j.mcm.2010.06.005
[4] Refregier P, Javidi B. Optical image encryption based on input plane and Fourier plane random encoding[J]. Optics Letters, 1995, 20(7): 767-769. doi: 10.1364/OL.20.000767
[5] Liu S T, Yu L, Zhu B H. Optical image encryption by cascaded fractional Fourier transforms with random phase filtering[J]. Optics Communication, 2001, 187(1-3): 57-63. doi: 10.1016/S0030-4018(00)01093-2
[6] Hennelly B, Sheridan J T. Optical image encryption by random shifting in fractional Fourier domains[J]. Optics Letters, 2003, 28(4): 269-271. doi: 10.1364/OL.28.000269
[7] Singh N, Sinha A. Optical image encryption using fractional Fourier transform and chaos[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2008, 46(2): 117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2007.09.001
[8] Lang J. Image encryption based on the reality-preserving multiple-parameter fractional Fourier transform[J]. Optics Communications, 2012, 285(10-11): 2584-2590. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2012.01.085
[9] Zhong Z, Zhang Y J, Shan M G, et al. Optical movie encryption based on a discrete multiple-parameter fractional Fourier transform[J]. Journal of Optics, 2014, 16(12): 125404. doi: 10.1088/2040-8978/16/12/125404
[10] Qin W, Peng X. Asymmetric cryptosystem based on phase-truncated Fourier transforms[J]. Optics Letters, 2010, 35(2): 118-120. doi: 10.1364/OL.35.000118
[11] 巩琼, 王志鹏, 杨兴强, 等.基于衍射成像原理结合相位板抽取的加密方法[J].光电工程, 2016, 43(1): 88-94. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90982A/201601/667898216.html
Gong Q, Wang Z P, Yang X Q, et al. An encryption method based on diffraction imaging principle and phase mask removal method[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2016, 43(1): 88-94. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90982A/201601/667898216.html
[12] Zhou N R, Wang Y X, Gong L H, et al. Novel single-channel color image encryption algorithm based on chaos and fractional Fourier transform[J]. Optics Communications, 2011, 284(12): 2789-2796. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2011.02.066
[13] Joshi M, Chandrashakher, Singh K. Color image encryption and decryption using fractional Fourier transform[J]. Optics Communications, 2007, 279(1): 35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2007.07.012
[14] Yuan W T, Yang X L, Guo W, et al. A double-domain image encryption using hyper chaos[C]// Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks, 2017: 1-4.
[15] Chen J X, Bao N, Li J C, et al. Cryptanalysis of optical ciphers integrating double random phase encoding with permutation[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 16124-16129. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2735420
[16] Candès E J, Romberg J, Tao T. Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(2): 489-509. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.862083
[17] Donoho D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 32(4): 1289-1306.
[18] 焦李成, 杨淑媛, 刘芳, 等.压缩感知回顾与展望[J].电子学报, 2011, 39(7): 1651-1662. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DZXU201107030.htm
Jiao L C, Yang S Y, Liu F, et al. Development and prospect of compressive sensing[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2011, 39(7): 1651-1662. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DZXU201107030.htm
[19] Huang R, Sakurai K. A robust and compression-combined digital image encryption method based on compressive sensing[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, 2011, 53: 105-108.
[20] 周南润, 张艾华, 吴建华, 等. 测量矩阵受控的图像压缩感知与图像加密方法: 102833514A[P]. 2012-12-19.
Zhou N R, Zhang A H, Wu J H, et al. Measurement-matrix-controlled image compressive sensing and image encryption method: 102833514A[P]. 2012-12-19.
[21] Lu P, Xu Z Y, Lu X, et al. Digital image information encryption based on Compressive Sensing and double random-phase encoding technique[J]. Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2013, 124(16): 2514-1518. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2012.08.017
[22] Liu X Y, Cao Y P, Lu P, et al. Optical image encryption technique based on compressed sensing and Arnold transformation[J]. Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2013, 124(24): 6590-6593. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2013.05.092
[23] EI-Latif A A A, Li L, Wang N, et al. A new approach to chaotic image encryption based on quantum chaotic system, exploiting color spaces[J]. Signal Processing, 2013, 93(11): 2986-3000. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.03.031
[24] Tropp J A, Gilbert A C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2008, 53(12): 4655-4666.
[25] Chen S S, Donoho D L, Saunders M A. Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit[J]. SIAM Review, 2001, 43(1): 129-159. doi: 10.1137/S003614450037906X
[26] Berry M V, Balazs N L, Tabor M, et al. Quantum maps[J]. Annals of Physics, 1979, 122(1): 26-63. doi: 10.1016/0003-4916(79)90296-3
[27] Goggin M E, Sundaram B, Milonni P W. Quantum Logistic map[J]. Physical Review A, 1990, 41(10): 5705-5708. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.41.5705
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: