-
摘要:
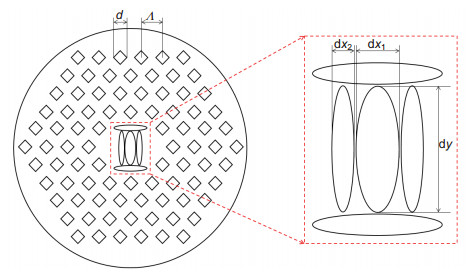
为了同时获得高双折射和色散平坦特性的光子晶体光纤,本文提出了一种包层以椭圆空气孔为纤芯,四周环绕正方形空气孔的光子晶体光纤结构。基于不同纤芯椭圆率、不同纤芯填充材料,对所提光子晶体光纤结构的双折射、色散、非线性等性能进行了讨论。结果表明,在波长1.55 μm处,当纤芯椭圆率不同,填充材料相同时,最大双折射值为0.37,最大非线性系数值277.76 W-1·km-1;当纤芯填充材料不同,椭圆率相同时,最大双折射值为0.34,最大非线性系数值为307 W-1·km-1。在波段1.26 μm~1.8 μm范围,色散呈现出近零色散平坦特性,变化范围不超过±12.5 ps/(nm·km),带宽0.6 μm。
 Abstract:
Abstract:In order to obtain photonic crystal fiber with high birefringence and flattened dispersion, we propose a new photonic crystal fiber structure with an elliptical air hole as the core surrounded by square air holes. In this paper, the effects of different fiber core ellipticity and different filled material on birefringence, dispersion and nonlinearity of photonic crystal fiber are discussed. The results show that at the wavelength of 1.55 μm, when the core ellipticity of the filled material is the same, the maximum birefringence value is 0.37 and the maximum value of nonlinear system is 277.76 W-1·km-1. When the fiber is filled with different materials, the maximum birefringence value is 0.34 and maximum nonlinear value is 307 W-1·km-1. In addition, in the wavelength range of 1.26 μm~1.8 μm, the nearly zerodispersion flattened characteristics are achieved. The range of variations is no more than ±12.5 ps/(nm·km), and the bandwidth is 0.6 μm.
-
Key words:
- photonic crystal fiber /
- square air hole /
- high birefringence /
- high nonlinearity
-

Overview: Photonic crystal fibers (PCFs) have attracted a considerable amount of attention recently because of their unique properties that can not be realized in conventional optical fibers. Owning to their flexible design for the cross section, PCFs can realize particular properties such as high birefringence, high nonlinearity, ultra-flatten dispersion, large effective mode area, endlessly single mode, and etc. In this paper, in order to achieve high birefringence and flattened chromatic dispersion at the same time, a smaller sized elliptical air hole in the core is introduced as a defected core in square air holes. The present design has the asymmetry in both fiber core and the cladding region by one kind of air holes (elliptical). The role of an elliptical defected core in the proposed fiber is not only to control the chromatic dispersion to be flattened, but also to increase the value of birefringence up to the order of 10-1. Among them, the structure of the square air hole is not easy to be deformed and thus has a more stable characteristic. Hexagonal structure of square air holes is the best way to obtain high birefringence and flattened chromatic dispersion. In the designed structure, one elliptical air hole is arranged in the core region and four elliptical air holes are ordered in the upper and lower sides. In our simulation, the plane wave expansion method and full-vector finite element method (FEM) with the perfectly matched layer (PML) boundary condition are applied, which have been the most common and accurate methods to investigate the eigen-mode problems of guided modes in PCFs. The effects of different core ellipticity and core filling materials on the birefringence, dispersion and nonlinearity of the photonic crystal fiber are discussed. The results show that the birefringence and maximum nonlinear coefficient are up to the value of 0.37 and 277.76 W-1·km-1 at 1.55 μm when the ellipticity of the core is different and the filling material is the same. The birefringence and maximum nonlinear coefficient are up to the value of 0.34 and 307 W-1·km-1 at 1.55 μm in the condition where the ellipticity of the core is the same and the filling material is different. Besides, the dispersion has a dispersionless flat characteristic. The range of change is not more than ±12.5 ps/(nm·km), and the bandwidth is 0.6 μm in the range of wavelengths from 1.26 μm to 1.8 μm.
-

-
表 1 材料名称以及各系数值
Table 1. Materials and corresponding coefficients
材料名称 A B C D E SiO2 3.9×10-5 2.92×10-3 1.45 -3.26×10-3 -3.13×10-5 As2S3 2.76×10-4 7.07×10-3 1.66 -2.15×10-3 -1.99×10-6 TT(20Tl2O.80TeO2) 3.11×10-3 2.39×10-2 2.10 -2.28×10-3 7.48×10-6 TS(20Tl2O.80Sb2O3) 2.40×10-3 3.04×10-2 2.07 -1.82×10-3 9.88×10-7 PG(80PbO.20Ga2O3) 4.85×10-3 3.18×10-2 2.16 -2.02×10-3 1.05×10-5 表 2 不同纤芯椭圆率对双折射值、色散值和非线性系数影响对比(λ=1.55 μm)
Table 2. Comparison of the effects of different core ellipticity on birefringence, dispersion and non-linear coefficients(λ=1.55 μm)
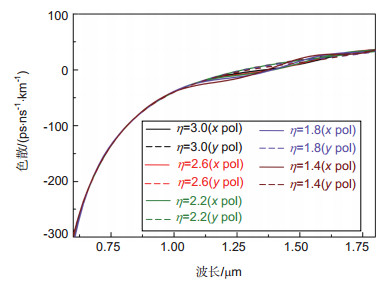
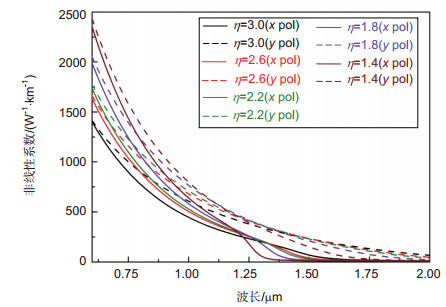
PCF椭圆η 双折射nBi 色散D/(ps·nm-1·km-1) 非线性系数γ /(W-1·km-1) y轴 x轴 1.4 0.140 0 111.00 11.70 1.8 0.180 0 177.30 14.47 2.2 0.210 0 201.04 21.07 2.6 0.225 0 206.18 26.27 3 0.240 0 209.12 46.09 表 3 纤芯填充玻璃材料在λ=1.55 μm处折射率
Table 3. Refractive index of core-filled glass material at λ=1.55 μm
材料名称 As2S3 TT(20Tl2O.80TeO2) TS(20Tl2O.80Sb2O3) PG(80PbO.20Ga2O3) 有效折射率 2.437271706 2.114833102 2.082505791 2.165137141 表 4 不同填充物的双折射值、色散值和非线性系数对比(λ=1.55 μm)
Table 4. Comparison of birefringence, dispersion and non-linearity of different fillers (λ=1.55 μm)
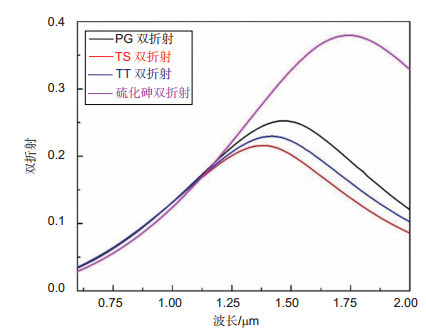
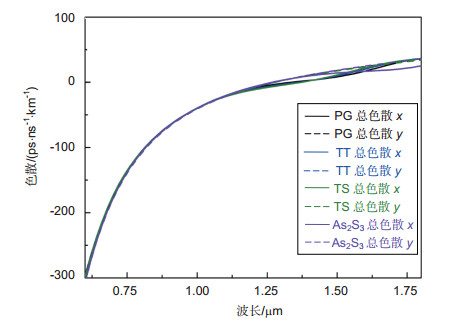
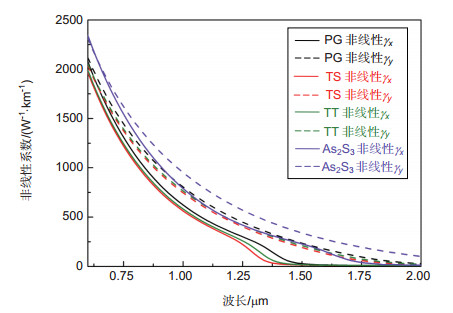
填充物 双折射nBi 色散D/(ps·nm-1·km-1) 非线性系数γ/(W-1·km-1) y轴 x轴 TT 0.22 20.80 110.82 11.73 TS 0.18 20.58 88.5 11.4 PG 0.25 21 147.88 12.7 As2S3 0.37 21.7 277.76 132.07 -
[1] Saitoh K, Sato Y, Koshiba M. Coupling characteristics of dual-core photonic crystal fiber couplers[J]. Optics Express, 2003, 11(24): 3188–3195. doi: 10.1364/OE.11.003188
[2] 隋宁菠, 杭利军, 刘杰, 等.光纤光栅用柚子型光子晶体光纤的设计与制备[J].光电工程, 2011, 38(12): 110–114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2011.12.021 http://www.gdgc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1073.shtml
Sui N B, Hang L J, Liu J, et al. The design and fabrication of the grapefruit PCF for the fiber gratings[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2011, 38(12): 110–114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2011.12.021 http://www.gdgc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1073.shtml
[3] Ferrando A, Silvestre E, Andrés P, et al. Designing the properties of dispersion-flattened photonic crystal fibers[J]. Optics Express, 2001, 9(13): 687–697. doi: 10.1364/OE.9.000687
[4] Yang T Y, Wang E L, Jiang H M, et al. High birefringence photonic crystal fiber with high nonlinearity and low confinement loss[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(7): 8329–8337. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.008329
[5] Tsuchida Y, Saitoh K, Koshiba M. Design of single-moded holey fibers with large-mode-area and low bending losses: The significance of the ring-core region[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(4): 1794–1803. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.001794
[6] Birks T A, Knight J C, Russell P S J. Endlessly single-mode photonic crystal fiber[J]. Optics Letters, 1997, 22(13): 961–963. doi: 10.1364/OL.22.000961
[7] Kim S E, Kim B H, Lee C G, et al. Elliptical defected core photonic crystal fiber with high birefringence and negative flattened dispersion[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(2): 1385–1391. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.001385
[8] Steel M J, Osgood Jr R M. Elliptical-hole photonic crystal fibers[J]. Optics Letters, 2001, 26(4): 229–231. doi: 10.1364/OL.26.000229
[9] Ortigosa-Blanch A, Knight J C, Wadsworth W J, et al. Highly birefringent photonic crystal fibers[J]. Optics Letters, 2000, 25(18): 1325–1327. doi: 10.1364/OL.25.001325
[10] Limpert J, Schmidt O, Rothhardt J, et al. Extended single-mode photonic crystal fiber lasers[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(7): 2715–2720. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.002715
[11] Tan X J, Zhu X S. Optical fiber sensor based on Bloch surface wave in photonic crystals[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(14): 16016–16026. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.016016
[12] 芦鑫, 毕卫红, 麻硕, 等.保偏光子晶体光纤模间干涉的研究[J].光电工程, 2011, 38(9): 60–64. http://www.gdgc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract407.shtml
Lu X, Bi W H, Ma S, et al. Modular interference of polarization maintaining photonic crystal fiber[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2011, 38(9): 60–64. http://www.gdgc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract407.shtml
[13] Zhang Y J, Kainerstorfer J, Knight J C, et al. Experimental measurement of supercontinuum coherence in highly nonlinear soft-glass photonic crystal fibers[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(16): 18842–18852. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.018842
[14] 曹晔, 李荣敏, 童峥嵘.一种新型高双折射光子晶体光纤特性研究[J].物理学报, 2013, 62(8): 084215. http://wulixb.iphy.ac.cn/EN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=53250
Cao Y, Li R M, Tong Z R. Investigation of a new kind of high birefringence photonic crystal fiber[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(8): 084215. http://wulixb.iphy.ac.cn/EN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=53250
[15] Ferrando A, Silvestre E, Miret J J, et al. Nearly zero ultraflattened dispersion in photonic crystal fibers[J]. Optics Letters, 2000, 25(11): 790–792. doi: 10.1364/OL.25.000790
[16] Steel M J, Osgood Jr R M. Polarization and dispersive properties of elliptical-hole photonic crystal fibers[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2001, 19(4): 495–503. doi: 10.1109/50.920847
[17] 吴宵宵, 范万德, 廖文英, 等.石墨烯包层结构光子晶体光纤的高双折射特性[J].光子学报, 2016, 45(1): 0106002. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/hk/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_gzxb201601007
Wu X X, Fan W D, Liao W Y, et al. High birefringence in graphene structure photonic crystal fiber[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2016, 45(1): 0106002. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/hk/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_gzxb201601007
[18] Reeves W H, Knight J C, Russell P S J, et al. Demonstration of ultra-flattened dispersion in photonic crystal fibers[J]. Optics Express, 2002, 10(14): 609–613. doi: 10.1364/OE.10.000609
[19] Saitoh K, Florous N, Koshiba M. Ultra-flattened chromatic dispersion controllability using a defected-core photonic crystal fiber with low confinement losses[J]. Optics Express, 2005, 13(21): 8365–8371. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.13.008365
[20] Dabas B, Sinha R K. Dispersion characteristic of hexagonal and square lattice chalcogenide As2Se3 glass photonic crystal fiber[J]. Optics Communications, 2010, 283(7): 1331–1337. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2009.11.091
[21] 陈瑰, 蒋作文, 彭景刚, 等.空气包层大模场面积掺镱光子晶体光纤研究[J].物理学报, 2012, 61(14): 144206. doi: 10.7498/aps.61.144206
Chen G, Jiang Z W, Peng J G, et al. Study of air-clad large-mode-area ytterbium doped photonic crystal fiber[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61(14): 144206. doi: 10.7498/aps.61.144206
[22] Kumar V V R K, George A K, Knight J C, et al. Tellurite photonic crystal fiber[J]. Optics Express, 2003, 11(20): 2641–2645. doi: 10.1364/OE.11.002641
[23] 刘永兴, 张培晴, 许银生, 等. Ge20Sb15Se65硫系玻璃光子晶体光纤的中红外色散特性[J].光子学报, 2012, 41(5): 516–521. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93651A/201205/1001857149.html
Liu Y X, Zhang P Q, Xu Y S, et al. Dispersion properties of Ge20Sb15Se65 chalcogenide glass photonic crystal fiber for mid-ir region[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2012, 41(5): 516–521. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93651A/201205/1001857149.html
[24] 陈月娥, 侯蓝田. Yb3+掺杂双包层光子晶体光纤制备研究[J].光电工程, 2009, 36(2): 62–66. http://www.gdgc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract907.shtml
Chen Y E, Hou L T. Preparation of Yb3+doped double-clad photonic crystal fiber[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2009, 36(2): 62–66. http://www.gdgc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract907.shtml
[25] Inci H D, Ozsoy S. Birefringence, dispersion and loss properties for PCFs with rectangular air-holes[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2014, 67: 354–358. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1350449514001662
[26] Yajima T, Yamamoto J, Ishii F, et al. Low-loss photonic crystal fiber fabricated by a slurry casting method[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(25): 30500–30506. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.030500
[27] Yang S G, Zhang Y J, Peng X Z, et al. Theoretical study and experimental fabrication of high negative dispersion photonic crystal fiber with large area mode field[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(7): 3015–3023. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.003015
[28] Ohkubo T, Tsuchida E, Kenzo D, et al. Insights from ab initio molecular dynamics simulations for a multicomponent oxide glass[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(3): 1122–1134. doi: 10.1111/jace.2018.101.issue-3
[29] Lines M E. Oxide glasses for fast photonic switching: A comparative study[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1991, 69(10): 6876–6884. doi: 10.1063/1.347677
[30] Mito T, Fujino S, Takebe H, et al. Refractive index and material dispersions of multi-component oxide glasses[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1997, 210(2–3): 155–162. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3093(96)00609-6
[31] Karasawa N. Dispersion properties of liquid crystal core photonic crystal fibers calculated by a multipole method modified for anisotropic inclusions[J]. Optics Communications, 2015, 338: 123–127. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2014.10.046
[32] Coen S, Chau A H L, Leonhardt R, et al. White-light supercontinuum generation with 60-ps pump pulses in a photonic crystal fiber[J]. Optics Letters, 2001, 26(17): 1356–1358. doi: 10.1364/OL.26.001356
[33] Shi F F, Wu Y, Li M C, et al. Highly birefringent two-mode photonic crystal fibers with near-zero flattened dispersion[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2011, 3(6): 1181–1188. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2011.2176480
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: