-
摘要:
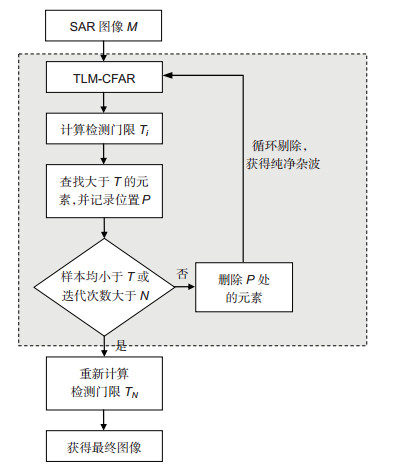
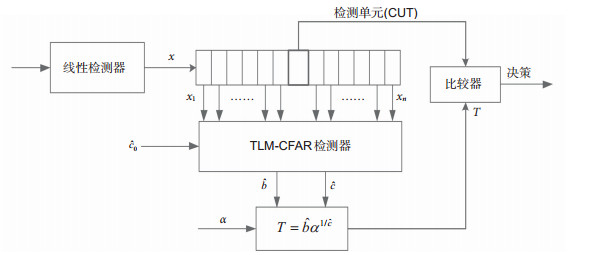
针对韦布尔分布杂波背景中的目标检测问题,本文提出了一种CFAR检测器—循环剔除TLM-CFAR检测器。该检测器基于TL矩估计方法,首先获得韦布尔分布的两参数估计值,进而确定CFAR检测门限,然后利用循环剔除法剔除干扰目标和强散射点的影响。文中证明了TLM-CFAR检测器具有恒虚警性,利用Monte Carlo仿真方法研究了这种检测器的性能,并与MLH-CFAR检测器进行了比较。仿真结果和实验结果表明,这种检测器不仅可以达到MLH-CFAR检测器的性能,同时避免了最大似然估计需要迭代计算的繁琐性,提高了检测算法的效率和适用性。
 Abstract:
Abstract:For the problem of constant false alarm rate (CFAR) detection in Weibull clutter background, a CFAR detector—cycle elimination TLME-CFAR detector is proposed. The detector calculates its detection threshold through the estimation of two parameters of Weibull distribution, which is based on TL-moment estimation. The effect of the interference target and the strong scattering point are then eliminated by the cyclic elimination method. This paper proved that the proposed detector is a CFAR detector, and then the performance of the detector is studied by Monte Carlo simulation and compared with the MLH-CFAR detector. The result shows that the cyclic elimination TLM-CFAR detector has very nearly the same performance with MLH-CFAR detector. The detector avoids iterated operation of maximum likelihood estimation, and improves the efficiency and applicability of detection algorithm.
-
Key words:
- Weibull distribution /
- TL-moment estimation /
- CFAR /
- detection performance
-

Overview: Target detection in a changing clutter and keeping the probability of false alarm constant is one of the important issues which cannot be avoided by each system and designer. CFAR technology is the most important tool in the control of false alarm rate in automatic radar target detection system, which plays an important role in the process of automatic radar detection. CFAR processing refers to adjusting the detection threshold by estimating the average clutter power of reference cells near cell under test under the condition of a constant false alarm rate. The classic CFAR detectors include ML-CFAR detectors and OS-CFAR detectors, and others are combination of the two detectors. However ML-CFAR detectors and OS-CFAR detectors are single-parameter CFAR detectors, while the Weibull PDF is a two-parameter distribution. If both the shape parameter and the scale parameter are taken into account, the two-parameter estimation CFAR detection method should be used.
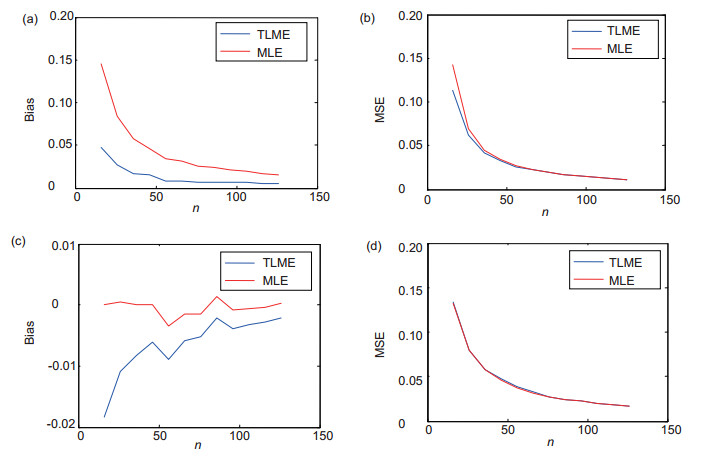
The shape parameter and scale parameter of Weibull distribution are estimated by using the reference samples in the reference sliding window. Werber and Haykin propose a method to set the detection threshold using two ordered statistical samples which is known as Werber-Haykin algorithm internationally, referred to as WH algorithm. Levanon and Ravid proposed the maximum likelihood CFAR algorithm (MLH-CFAR). Levanon has pointed out that CFAR loss is related to the accuracy of shape parameter estimation. MLH is an option when estimating the two parameters, but MLH estimator does not have a closed-form expression for estimation of shape and scale parameters and needs to be computed by the iterative process, thus reducing usability. In order to reduce the estimated variance of shape parameters and improve the efficiency of the algorithm, we estimate the two parameters of Weibull distribution by TL-moment estimation (TLME), and propose a cyclic elimination TLM-CFAR detection device.
For the problem of constant false alarm rate (CFAR) detection in Weibull clutter background, a CFAR detector—cycle elimination TLME-CFAR detector is proposed. The detector calculates its detection threshold through the estimation of two parameters of Weibull distribution, which is based on TL-moment estimation. The two parameters (shape and scale) of the background statistics are estimated using a TL-moment estimation algorithm. A CFAR threshold based on parameters estimated in this way exhibits a smaller variance, and hence a smaller CFAR loss, than thresholds based on other estimation algorithms such as moments. The effect of the interference target and the strong scattering point are then eliminated by the cyclic elimination method which analyzes detector performance in comparison with MLH-CFAR detector, and the cyclic elimination TLM-CFAR detector has very nearly the same performance with MLH-CFAR detector. The detector avoids iterated operation of maximum likelihood estimation, and improves the efficiency and applicability of detection algorithm.
-

-
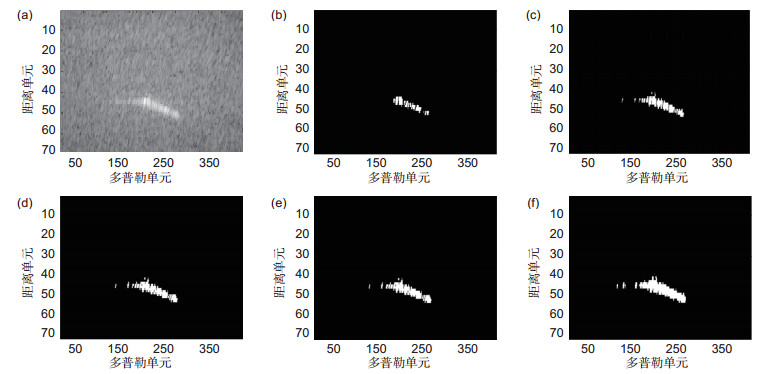
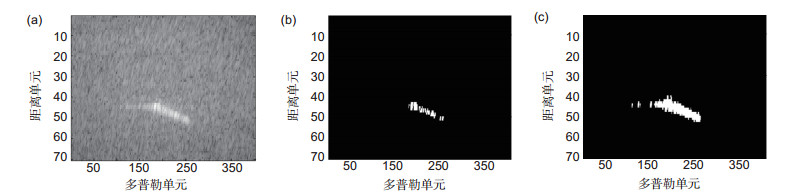
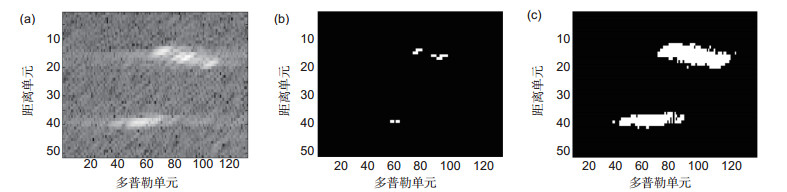
图 5 循环剔除过程中的检测结果。(a)原图像;(b)一次剔除结果;(c)二次剔除结果;(d)三次剔除结果;(e)四次剔除结果;(f)最终结果
Figure 5. The detection results of cycle elimination process. (a) Original SAR image; (b) First elimination result; (c) Second elimination result; (d) Third elimination result; (e) Fourth elimination result; (f) Fifth elimination result
表 1 循环剔除过程中的计算结果
Table 1. The calculation results of cycle elimination process
剔除次数 尺度参数 形状参数 剩余目标像素个数/个 检测门限 1 0.2231 1.0184 156 2.9395 2 0.2028 1.3443 137 1.4300 3 0.1955 1.4701 47 1.1666 4 0.1939 1.4976 10 1.1197 5 0.1936 1.5027 2 1.1113 表 2 两种估计方法用时对比
Table 2. Comparison of two estimation methods
最大似然估计 TL矩估计 倍数 100次估计平均用时/s 1.8e-3 5.1e-5 36.1 200次估计平均用时/s 1.4e-3 3.6e-5 37.6 500次估计平均用时/s 1.2e-3 2.8e-5 42.8 1000次估计平均用时/s 1.1e-3 2.3e-5 48.5 表 3 两种检测器的恒虚警损失对比
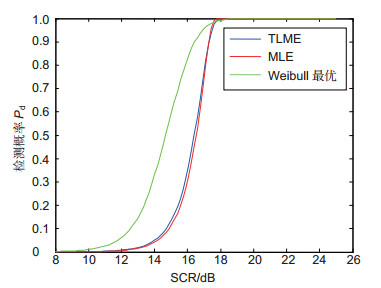
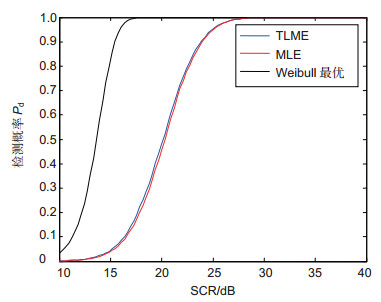
Table 3. The comparison of CFAR loss of two detectors
MLH-CFAR TLM-CFAR CFAR loss (Pd=0.9)/dB 8.79 8.49 CFAR loss (Pd=0.5)/dB 6.66 6.36 CFAR loss (Pd=0.2)/dB 5.68 5.38 表 4 两种检测算法的效率对比
Table 4. Comparison of the efficiency of the two detection algorithms
MLH-CFAR 本文算法 100次平均时间/s 0.2505 0.0894 200次平均时间/s 0.2498 0.0880 500次平均时间/s 0.2507 0.0883 1000次平均时间/s 0.2584 0.0891 -
[1] 何友, 关键, 孟祥伟, 等.雷达目标检测与恒虚警处理[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 2011.
He Y, Guan J, Meng X W, et al. Radar target detection and CFAR processing[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2011.
[2] Weber P, Haykin S. Ordered statistic CFAR processing for two-parameter distributions with variable skewness[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1985, AES–21(6): 819–821. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1985.310668
[3] Ravid R, Levanon N. Maximum-likelihood CFAR for Weibull background[J]. IEE Proceedings F-Radar and Signal Processing, 1992, 139(3): 256–264. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1992.0033
[4] Levanon N, Shor M. Order statistics CFAR for Weibull background[J]. IEE Proceedings F-Radar and Signal Processing, 1990, 137(3): 157–162. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1990.0023
[5] Teimouri M, Hoseini S M, Nadarajah S. Comparison of estimation methods for the Weibull distribution[J]. Statistics, 2013, 47(1): 93–109. doi: 10.1080/02331888.2011.559657
[6] Akram M, Hayat A. Comparison of estimators of the Weibull distribution[J]. Journal of Statistical Theory and Practice, 2014, 8(2): 238–259. doi: 10.1080/15598608.2014.847771
[7] Hosking J R M. L-moments: Analysis and estimation of distributions using linear combinations of order statistics[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B, 1990, 52(1): 105–124. https://www.jstor.org/stable/2345653
[8] Elamir E A H, Seheult A H. Trimmed L-moments[J]. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2003, 43(3): 299–314. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167947302002505
[9] 李军, 王雪松, 王涛.基于分数阶矩估计的非参量CFAR检测[J].电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(3): 642–645. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkxxk201103023
Li J, Wang X S, Wang T. Nonparametric CFAR detection based on fractional moment estimations[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2011, 33(3): 642–645. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkxxk201103023
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: