-
摘要
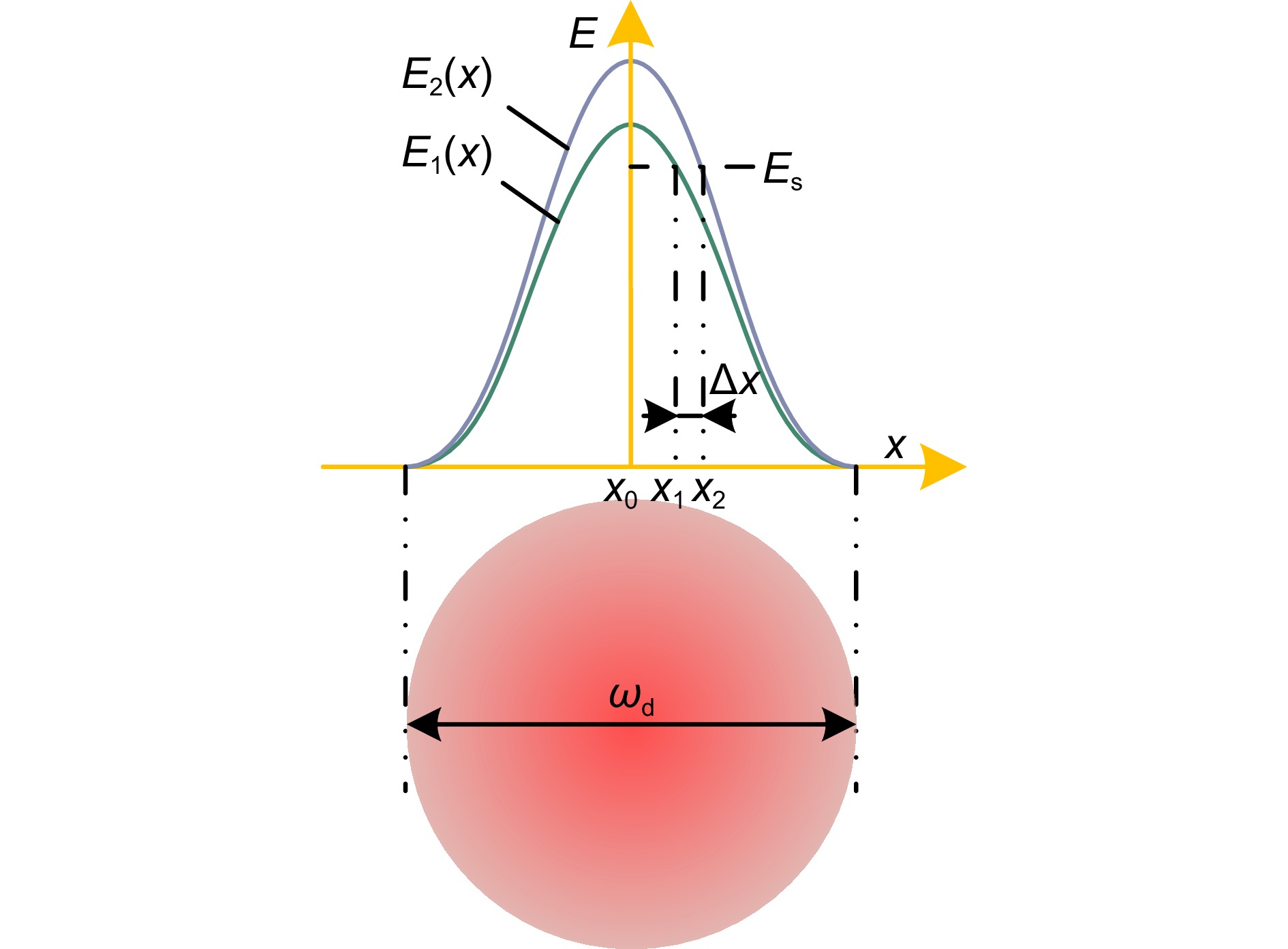
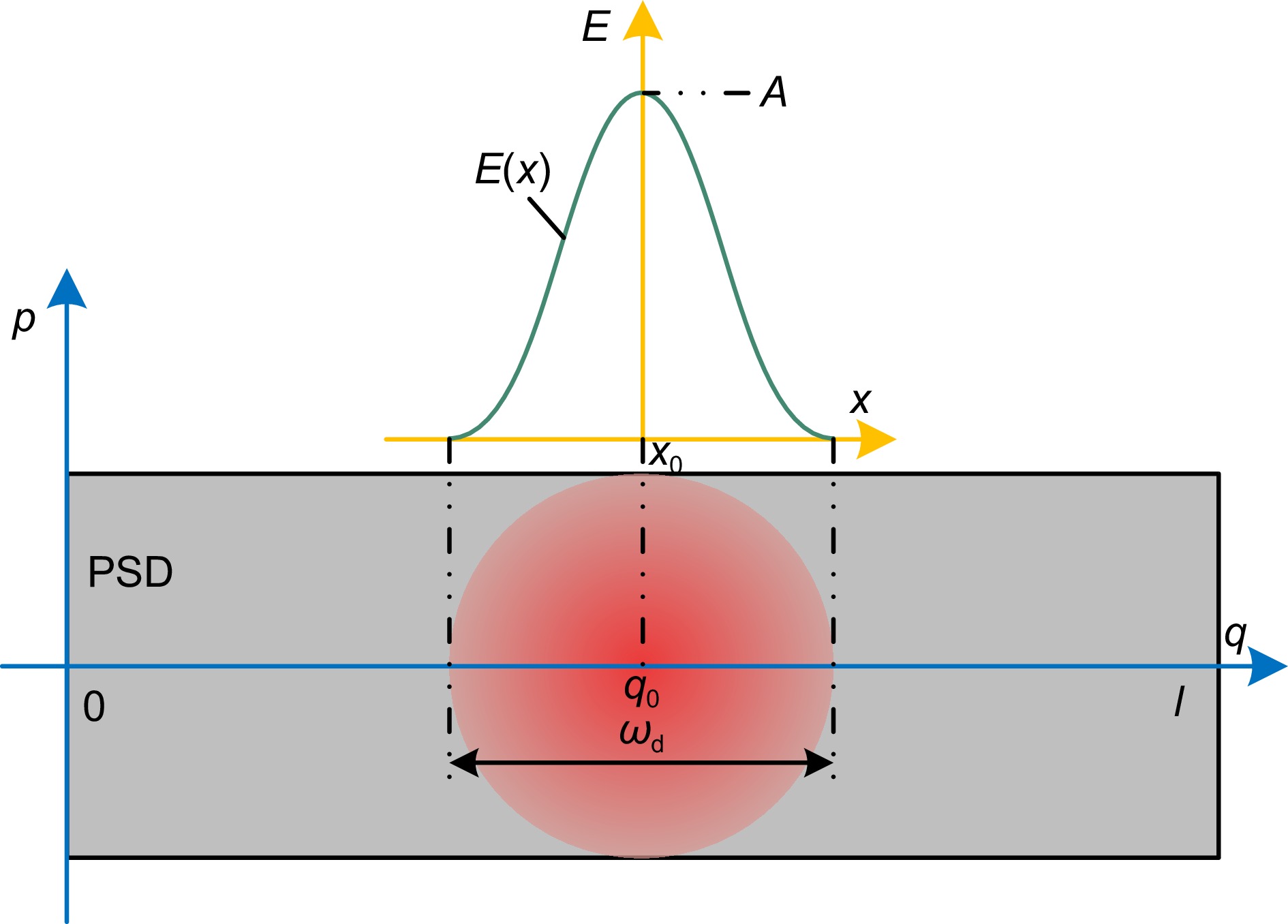
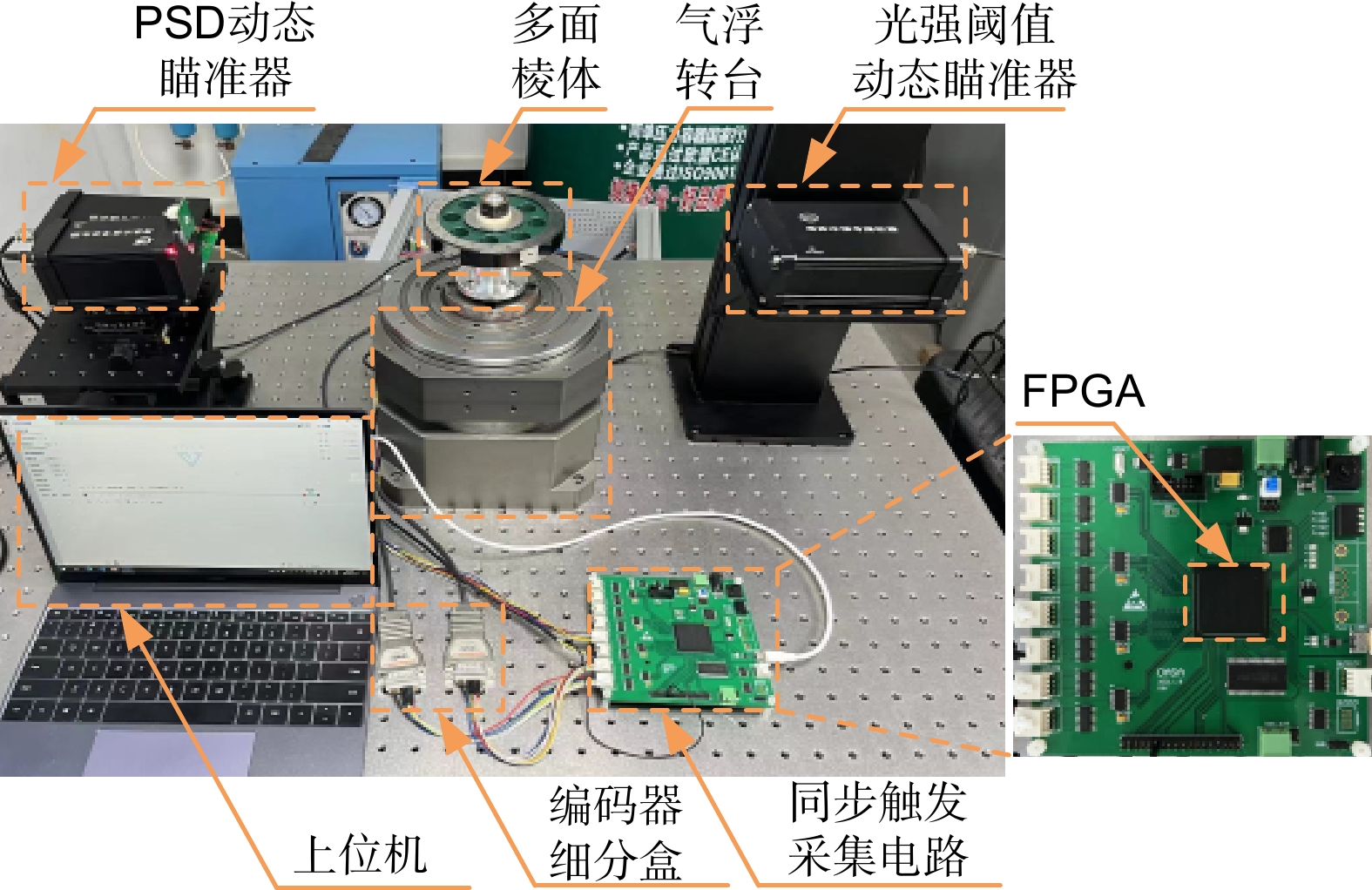
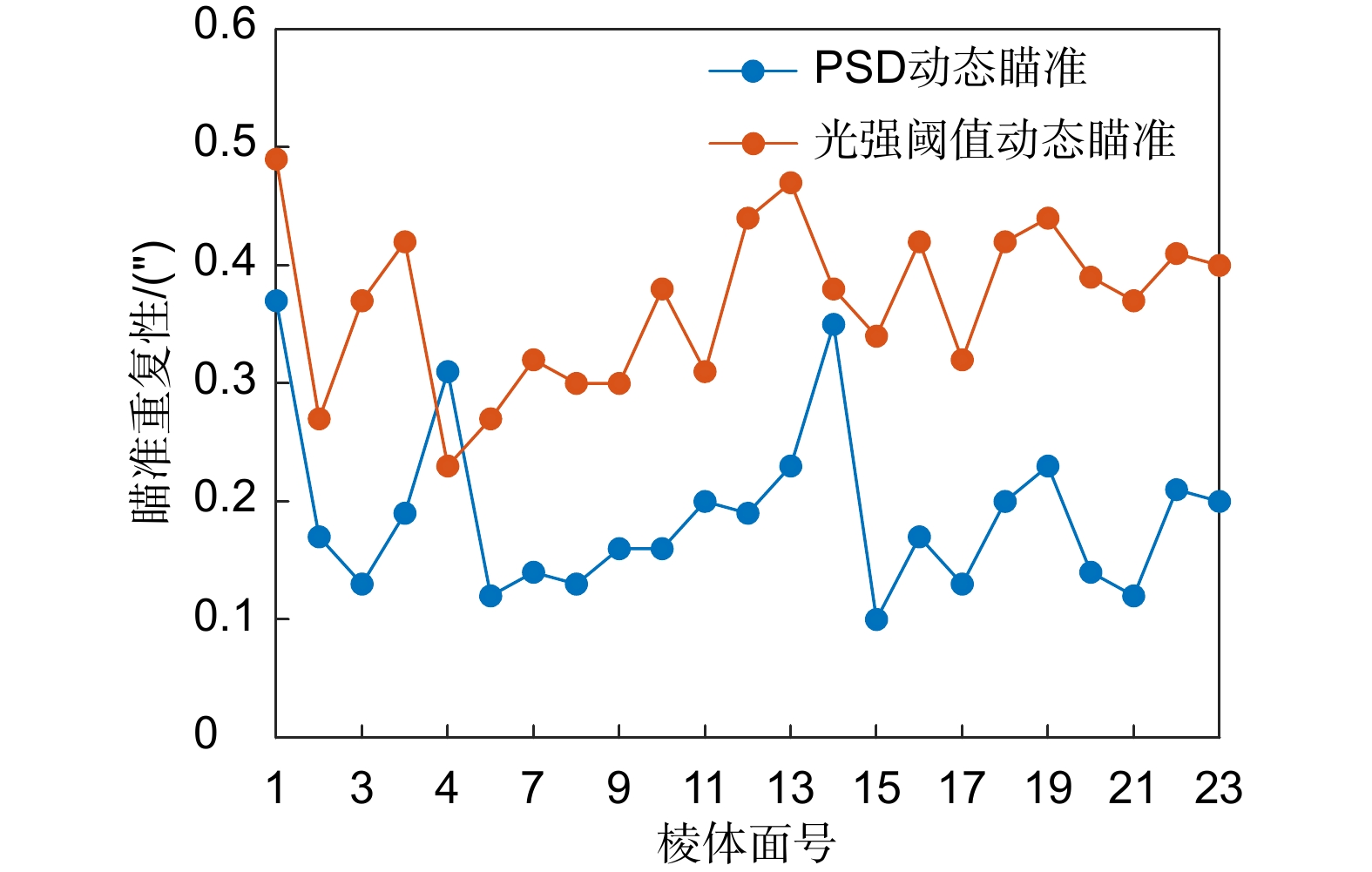
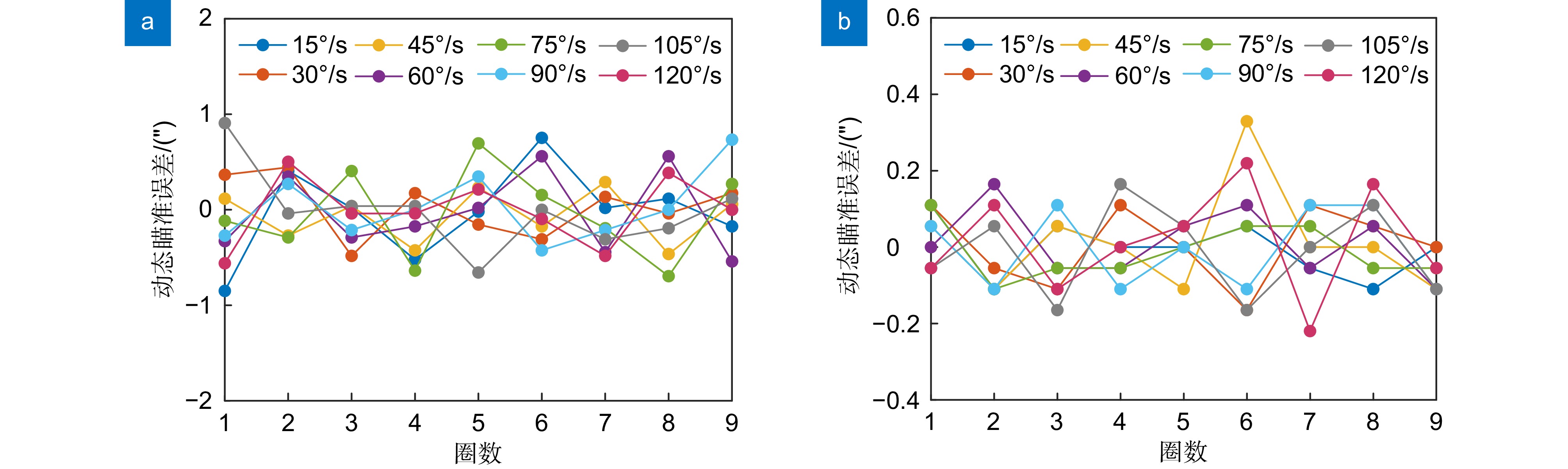
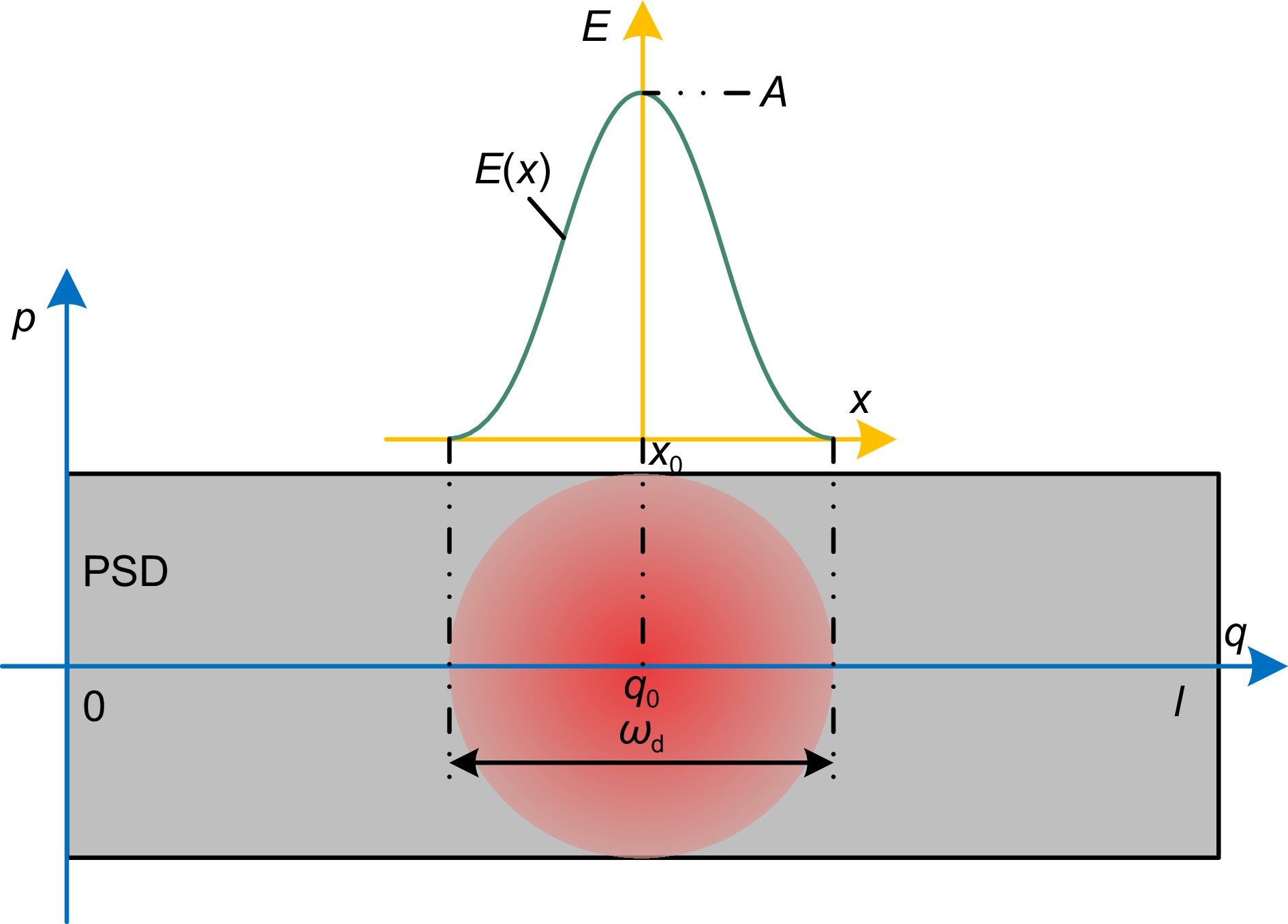
本文针对动态测角仪精度容易受瞄准过程中光强稳定性影响的问题,开展动态瞄准误差抑制方法研究。在建立高斯光斑光强分布模型的基础上,分析动态瞄准误差的产生机理,证明了基于横向光电效应的动态瞄准误差抑制方法原理;搭建动态瞄准系统,分别对本文提出方法的瞄准重复性、瞄准精度进行实验验证,实验结果表明瞄准重复性为0.19″,瞄准精度为0.15″,相比较于光强阈值瞄准方法,瞄准误差降低了66%;开展角度块动态测量实验,将本文提出的动态瞄准方法应用于动态测角系统,实验结果证明系统精度能够满足1级角度块的校准需求。
Abstract
This study investigates methods for suppressing dynamic aiming errors, addressing the issue of dynamic goniometer accuracy being easily affected by light intensity stability during aiming. A Gaussian spotlight intensity distribution model is established, and the mechanism of dynamic aiming error generation is analyzed. The principle of the suppression method based on the lateral photovoltaic effect is demonstrated. A dynamic aiming system is constructed, and experiments are conducted to validate the aiming repeatability and accuracy of the proposed method. The results show that the aiming repeatability is 0.19″, and the aiming accuracy is 0.15″. Compared to the light intensity threshold aiming method, the aiming error is reduced by 66%. Dynamic measurement experiments with angle blocks are conducted, applying the proposed method to the dynamic goniometer system. The results demonstrate that the system accuracy meets the calibration requirements for the grade 1 angle block gauge.
-
Key words:
- dynamic goniometer /
- aiming error /
- Gaussian spot /
- transverse photoelectric effect
-
Overview
Overview: Dynamic goniometers are widely used in precision engineering and calibration tasks, but their accuracy is often compromised by aiming errors caused by light intensity fluctuations. These errors, prevalent during dynamic operations, limit the reliability of angle measurements and hinder their broader application. To address this issue, this study focuses on developing a robust aiming error suppression method to enhance the precision and repeatability of dynamic goniometers. The research is motivated by the need for stable and accurate aiming mechanisms under varying light conditions. A Gaussian spotlight intensity distribution model is proposed to analyze the mechanism of aiming error generation, providing a theoretical basis for error suppression strategies. Based on this model, a dynamic aiming system leveraging the lateral photovoltaic effect is designed. Unlike traditional methods reliant on intensity thresholds, this approach employs a position-sensitive detector (PSD) to detect spot center positions by utilizing the proportional relationship between electrode currents, effectively reducing dependency on absolute light intensity. Built a dynamic angle measurement system to evaluate the accuracy and repeatability of different aiming methods. Results showed that the system achieved the aiming repeatability of 0.19" and the aiming accuracy of 0.15", representing a 66% reduction in aiming errors compared to conventional methods. Furthermore, dynamic angle measurements were performed using the system on Grade 1 angle blocks, demonstrating that the system meets stringent calibration requirements. The method also exhibited consistent performance under varying rotational speeds, highlighting its robustness and adaptability to different operational conditions. This study contributes to the field by presenting an innovative suppression method for dynamic aiming errors. The findings underscore the potential of PSD-based lateral photovoltaic detection to improve measurement accuracy in dynamic environments. The proposed system not only advances the precision and repeatability of dynamic goniometers but also lays a foundation for further development of dynamic angle measurement technologies.
-

-
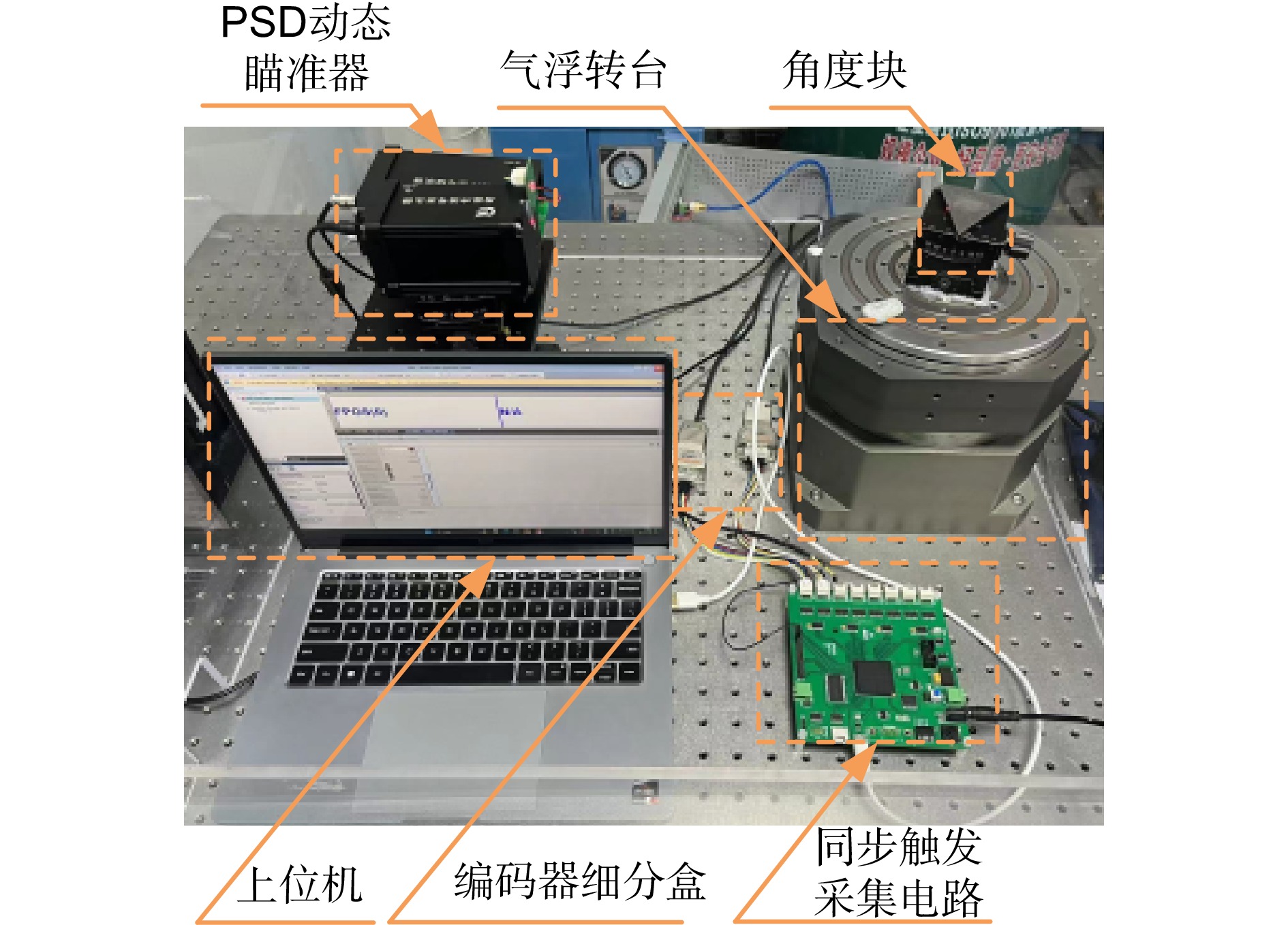
表 1 主要仪器规格
Table 1. Specifications of main instruments
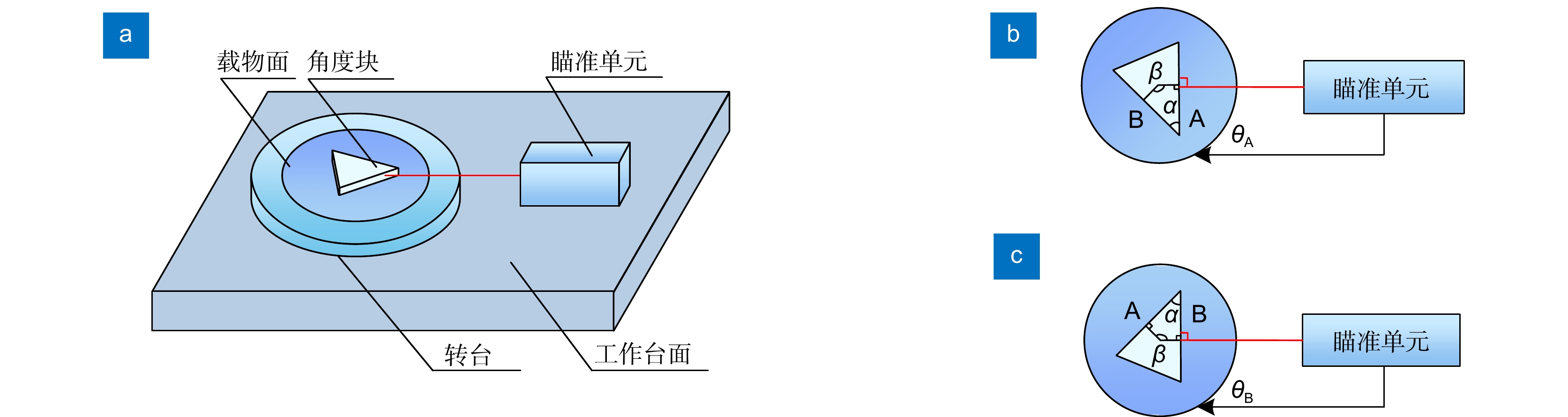
仪器名称 型号(制造商) 技术参数 气浮转台 / 重复性:±0.2″; 最高转速:200°/s 圆光栅盘 RESM20 USA150(Renishaw) 23600刻线 栅矩:20 μm 编码器读数头\细分盒 T1011-30A\Ti1000(Renishaw) 细分倍率:1000; 角分辨力:0.055″ 23面多面棱体 上海荣量 等级:三等扩展; 不确定度:0.1″ FPGA电路 自制 工作频率:50 MHz 光强阈值动态瞄准器 自制 RS422差分触发 PSD动态瞄准器 自制 RS422差分触发 表 2 角度块测量结果
Table 2. Angle block measurement results
测量次数 A面测角值 B面测角值 工作角测量值 1 290°36′25.34″ 65°6′22.80″ 45°30′2.54″ 2 290°36′25.18″ 65°6′22.91″ 45°30′2.27″ 3 290°36′25.29″ 65°6′22.91″ 45°30′2.38″ 4 290°36′25.23″ 65°6′22.80″ 45°30′2.43″ 5 290°36′25.18″ 65°6′22.91″ 45°30′2.27″ 6 290°36′25.40″ 65°6′23.02″ 45°30′2.38″ 7 290°36′25.07″ 65°6′22.80″ 45°30′2.27″ 8 290°36′25.23″ 65°6′22.86″ 45°30′2.37″ 9 290°36′25.34″ 65°6′22.86″ 45°30′2.48″ 10 290°36′25.29″ 65°6′22.80″ 45°30′2.49″ -
参考文献
[1] Wang S T, Ma R, Cao F F, et al. A review: high-precision angle measurement technologies[J]. Sensors (Basel), 2024, 24(6): 1755. doi: 10.3390/s24061755
[2] Kumar A S A, George B, Mukhopadhyay S C. Technologies and applications of angle sensors: a review[J]. IEEE Sens J, 2021, 21(6): 7195−7206. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3045461
[3] 马新宇, 朱维斌, 黄垚, 等. 基于Kalman的动态角度测量方法研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2023, 44(3): 119−127. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2210697
Ma X Y, Zhu W B, Huang Y, et al. Research on the dynamic angle measurement method based on Kalman[J]. Chin J Sci Instrum, 2023, 44(3): 119−127. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2210697
[4] Filatov Y V, Bohkman E D, Ivanov P A, et al. Calibration of angle-measurement system for direction measurements[J]. Proc SPIE, 2016, 10023: 100230W. doi: 10.1117/12.2245626
[5] 程霖. 基于自准直仪的绝对式测角仪装置设计与研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2021. https://doi.org/10.27356/d.cnki.gtjdu.2021.000667.
Cheng L. Design and research of absolute goniometer device based on autocollimator[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2021. https://doi.org/10.27356/d.cnki.gtjdu.2021.000667.
[6] Filatov Y V, Pavlov P A, Velikoseltsev A A, et al. Precision angle measurement systems on the basis of ring laser gyro[J]. Sensors (Basel), 2020, 20(23): 6930. doi: 10.3390/s20236930
[7] Hsieh T H, Lin M X, Yeh K T, et al. Calibration of a rotary encoder and a polygon using a two-autocollimator method[J]. Appl Sci, 2023, 13(3): 1865. doi: 10.3390/app13031865
[8] Larichev R A, Filatov Y V. A model of angle measurement using an autocollimator and optical polygon[J]. Photonics, 2023, 10(12): 1359. doi: 10.3390/photonics10121359
[9] 徐兴晨, 朱维斌, 黄垚, 等. 一种转台测角系统动态比对的信号同步方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2022, 43(12): 112−119. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2210598
Xu X C, Zhu W B, Huang Y, et al. Signal synchronization method for dynamic comparison of turntable angle measurement system[J]. Chin J Sci Instrum, 2022, 43(12): 112−119. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2210598
[10] Zhang J Y, Fan T Q, Cao X D. Dynamic photoelectric autocollimator based on two-dimension position sensitive detector[J]. Proc SPIE, 2007, 6723: 672315. doi: 10.1117/12.783135
[11] 黄云, 黄海乐, 刘贱平, 等. 高精度双光束干涉指零仪的研制[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2012, 41(9): 2498−2502. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2012.09.046
Huang Y, Huang H L, Liu J P, et al. Development on a high precision null-indicator by using two-beam interference[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2012, 41(9): 2498−2502. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2012.09.046
[12] Guo Y, Cheng H B, Wen Y F, et al. High-frequency small angle measurement using a dynamic autocollimator based on an improved k-means algorithm[J]. Opt Eng, 2018, 57(6): 064109. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.57.6.064109
[13] Mou J P, Su J J, Miao L J, et al. Research on field application technology of dynamic angle measurement based on fiber optic gyroscope and autocollimator[J]. IEEE Sens J, 2021, 21(13): 15308−15317. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3072641
[14] Larichev R A, Filatov Y V, Venediktov V. Dynamic angle measurements involving different optical null-indicator types[J]. Proc SPIE, 2023, 12769: 127690Q. doi: 10.1117/12.2687596
[15] 陈建清. 半导体激光器光束准直微透镜的研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2005.
Chen J Q, Study on microlens applied in semiconductor laser beam collimation[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2005.
[16] 张辉, 陈云善, 耿天文, 等. 四象限探测器位置检测精度的主要影响因素研究[J]. 中国激光, 2015, 42(12): 1217002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201542.1217002
Zhang H, Chen Y S, Geng T W, et al. Study on main factors affecting position detection accuracy of four-quadrant detector[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2015, 42(12): 1217002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201542.1217002
[17] 仇浩, 刘晓杰, 刘书钢. 基于四象限探测器的激光稳定集成化系统设计[J]. 光通信技术, 2022, 46(6): 44−49. doi: 10.13921/j.cnki.issn1002-5561.2022.06.009
Qiu H, Liu X J, Liu S G. Design of laser stabilization integrated system based on four-quadrant detector[J]. Opt Commun Technol, 2022, 46(6): 44−49. doi: 10.13921/j.cnki.issn1002-5561.2022.06.009
[18] Lucovsky G. Photoeffects in nonuniformly irradiated p-n junctions[J]. J Appl Phys, 1960, 31(6): 1088−1095. doi: 10.1063/1.1735750
[19] 尚鸿雁, 张广军. 不同光源模式下位置敏感探测器响应特性分析[J]. 光电工程, 2005, 32(1): 93−96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2005.01.025
Shang H Y, Zhang G J. Analysis of the response characteristics of position sensitive detector under different modes of light source[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2005, 32(1): 93−96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2005.01.025
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: