-
摘要
超分辨重建算法是一种将低分辨率图像恢复为高分辨率图像的算法,被广泛用于医学、遥感、军事安防以及人脸识别等领域。在黑夜、远场场景下构建数据集比较困难,基于深度学习的超分辨重建算法应用受到阻碍。而微扫描成像技术扫描模式固定,对器件到位精度要求高。针对这两个问题,我们提出一种基于主动位移成像的图像超分辨率重建算法。具体地,在控制相机随机移动的同时记录采样时刻位移,通过解算、映射选图、精确匹配图像序列并获取多帧图像间的亚像素信息,然后对估计图像进行迭代和更新,最后重建获得高分辨率图像。实验结果表明,本算法在PSNR、SSIM和平均梯度三个指标上都优于最近提出的基于POCS的图像超分辨率重建算法MFPOCS,与基于CNN的方法ACNet相比具有竞争力。值得提出的是,本算法无需固定的扫描模式,降低了微扫描技术对器件实时到位精度的要求,同时,本算法可以保证重建初始帧的优良选取,有效规避了POCS算法的固有缺点。
Abstract
The super-resolution reconstruction algorithm is an algorithm that restores low-resolution images to high-resolution images, which is widely applied in the fields of medicine, remote sensing, military security, and face recognition. It is hard to construct datasets in some specific scenarios, such that the application of super-resolution reconstruction algorithms based on deep learning is limited. The scanning pattern of micro-scanning imaging technology is fixed, which requires high precision of the device. To address these two problems, we propose an image super-resolution reconstruction algorithm based on active displacement imaging. Specifically, we control the camera to move randomly while recording the displacement at the sampling moment and then reconstruct the high-resolution images by solving, mapping, and selecting zones, obtaining the sub-pixel information between multiple frames, and finally iteratively updating the reconstruction. The experimental results show that this algorithm outperforms the latest multi-featured super-resolution reconstruction algorithms for POCS images in terms of PSNR, SSIM, and mean gradient. What's more, the present algorithm does not require a fixed scanning pattern, which reduces the requirement of the micro-scanning technique on the device in place accuracy.
-
Key words:
- super-resolution reconstruction /
- subpixel /
- image processing /
- micro-scanning
-
Overview
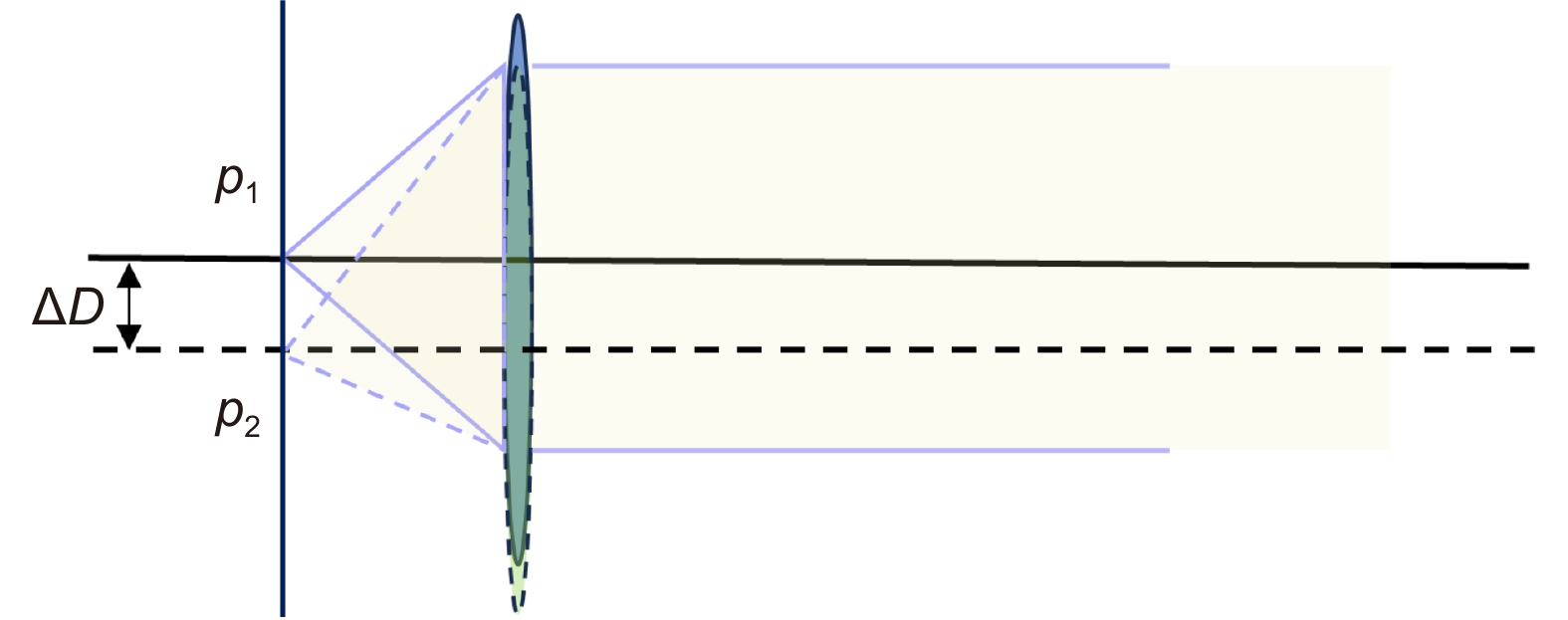
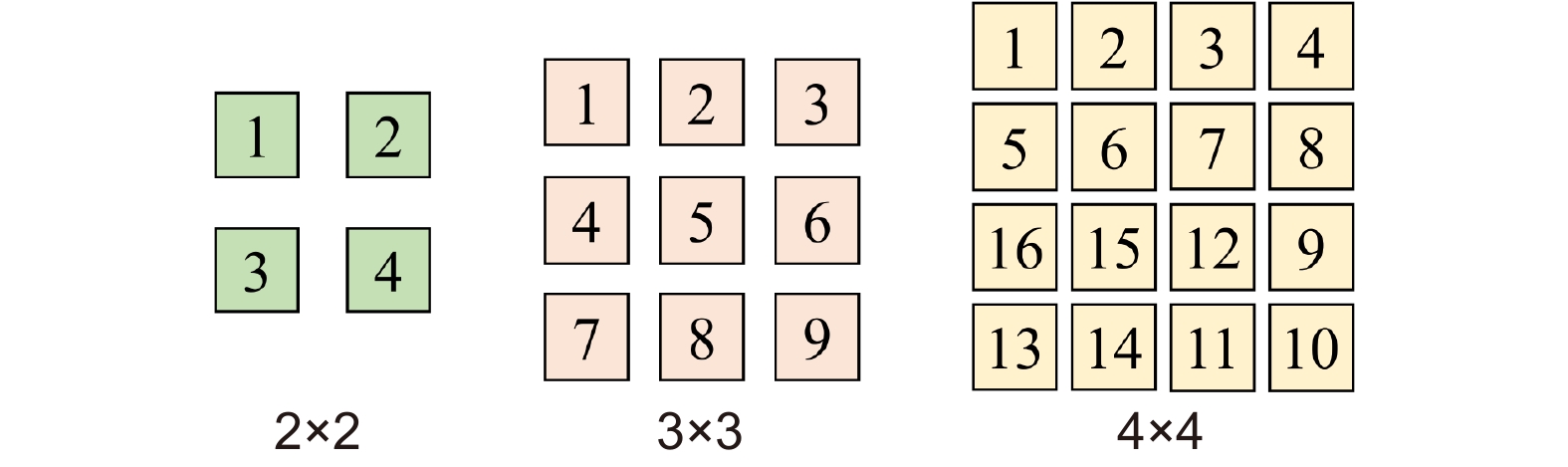
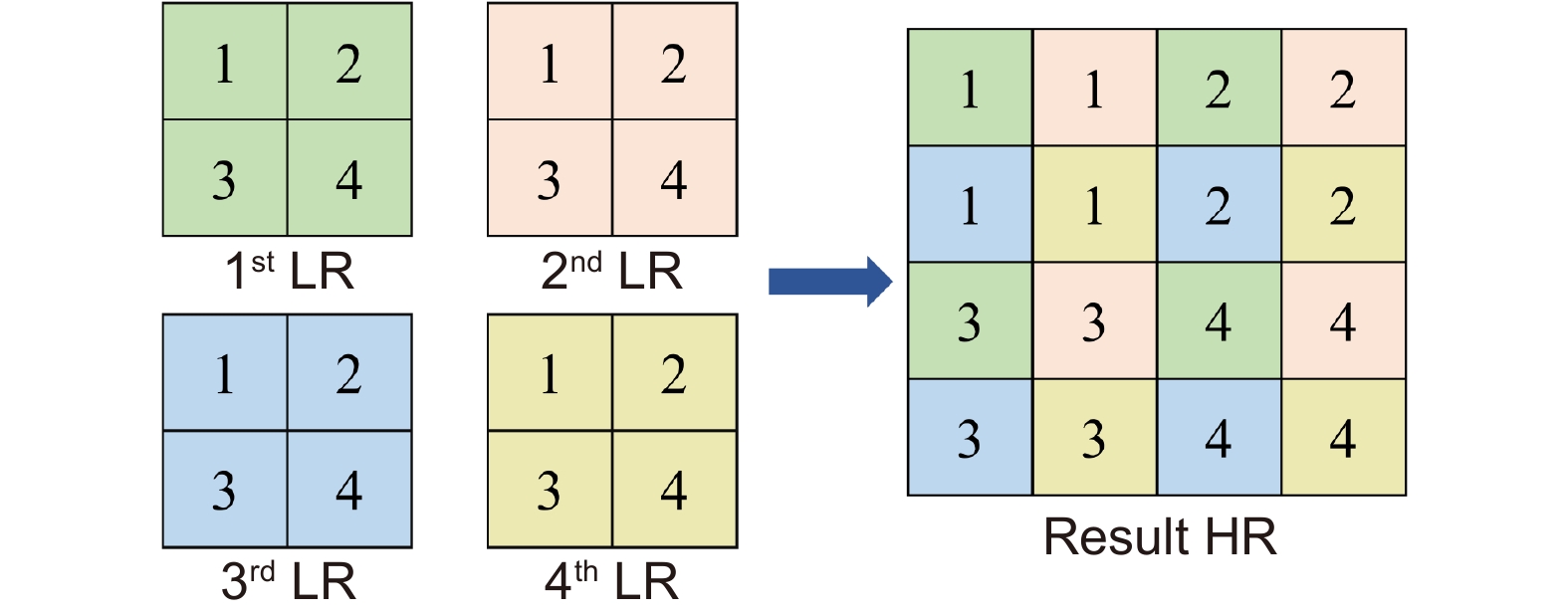
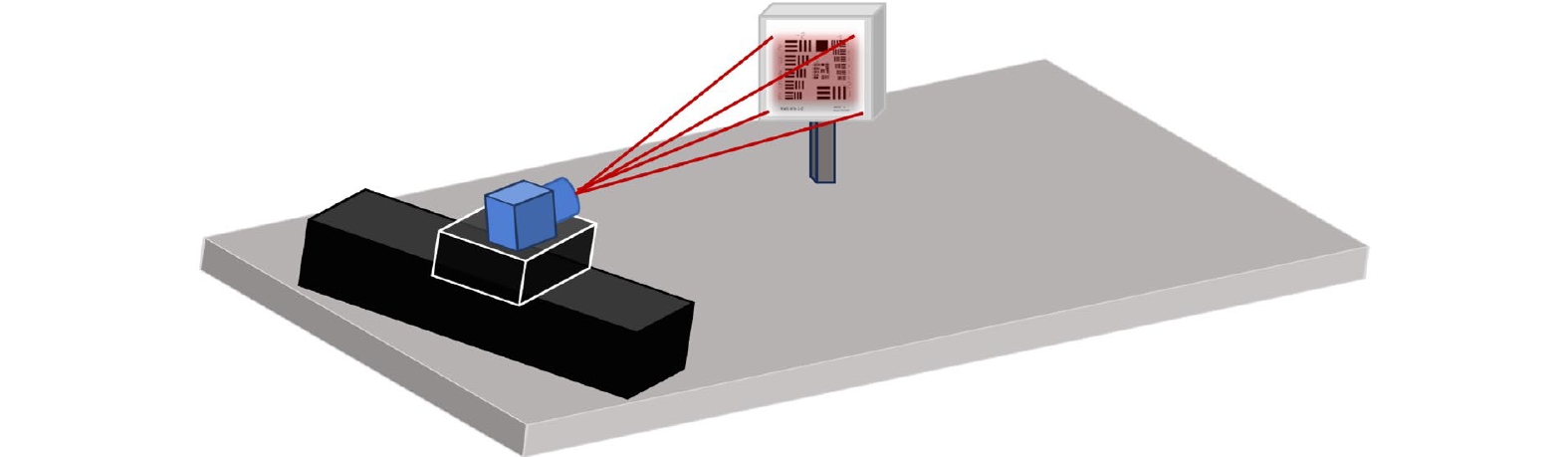
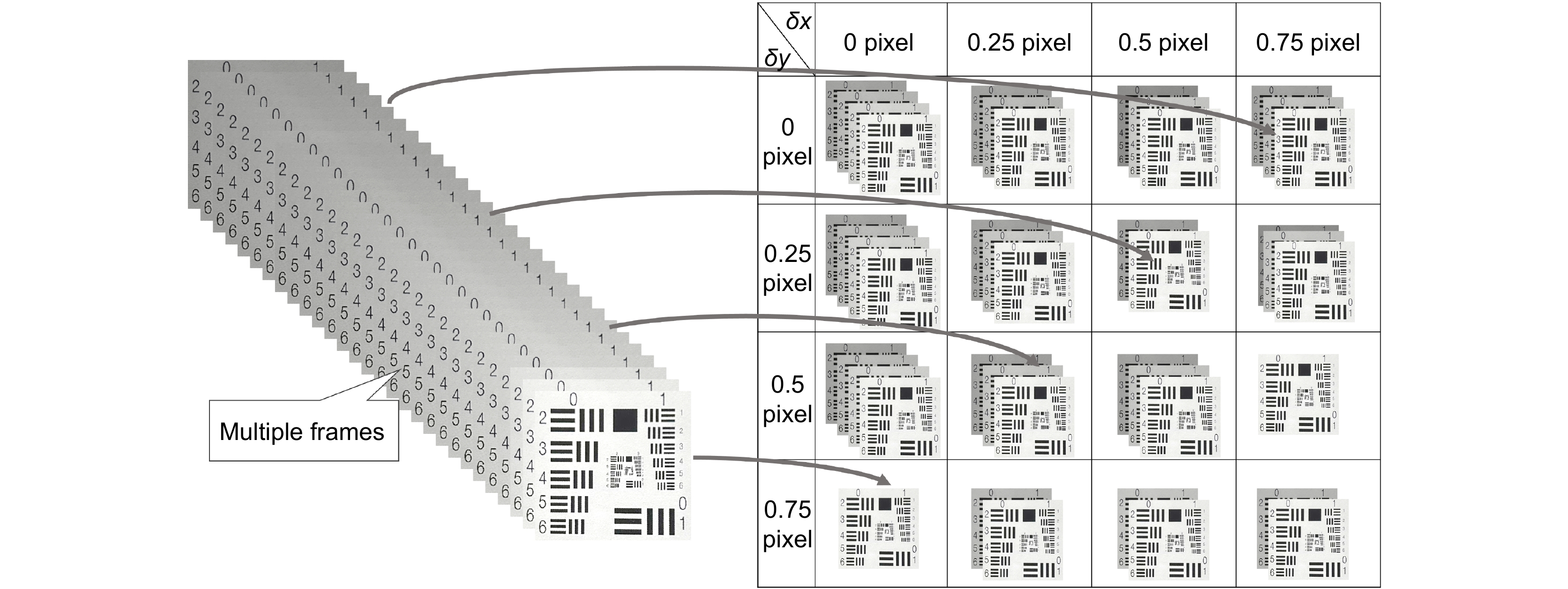
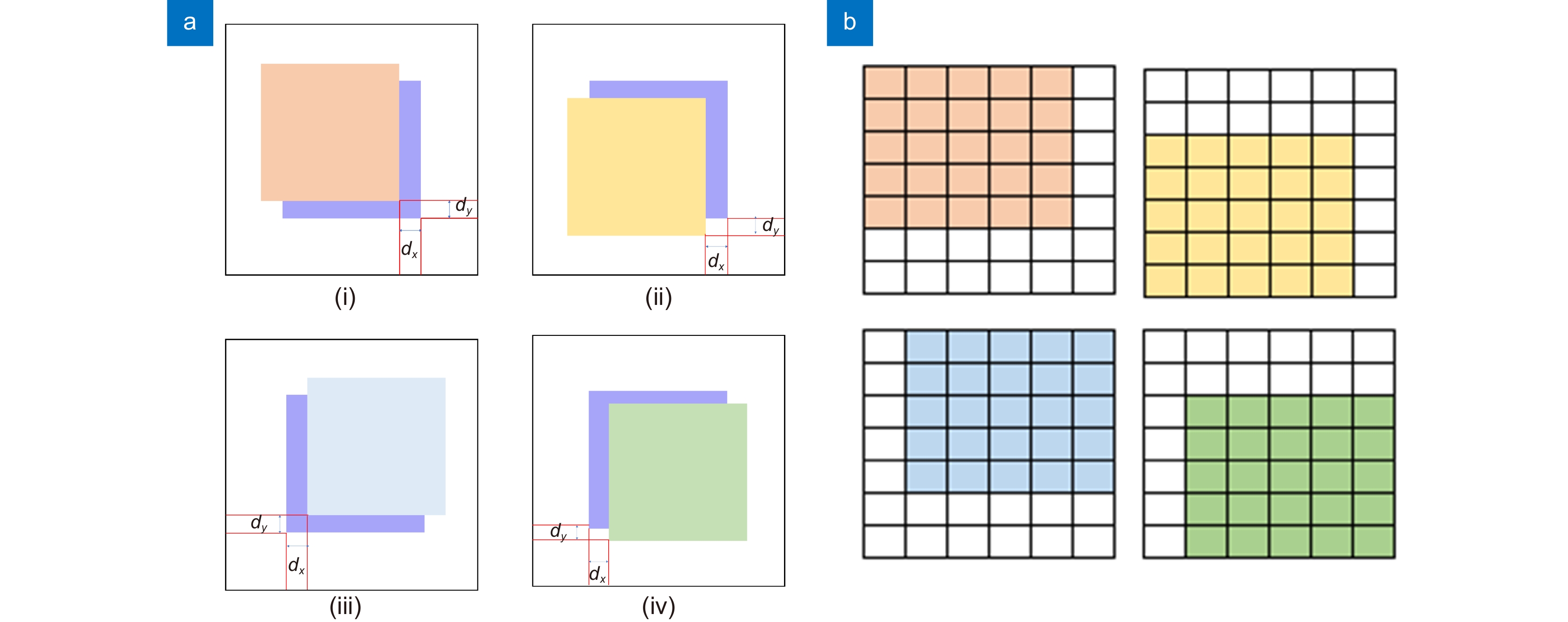
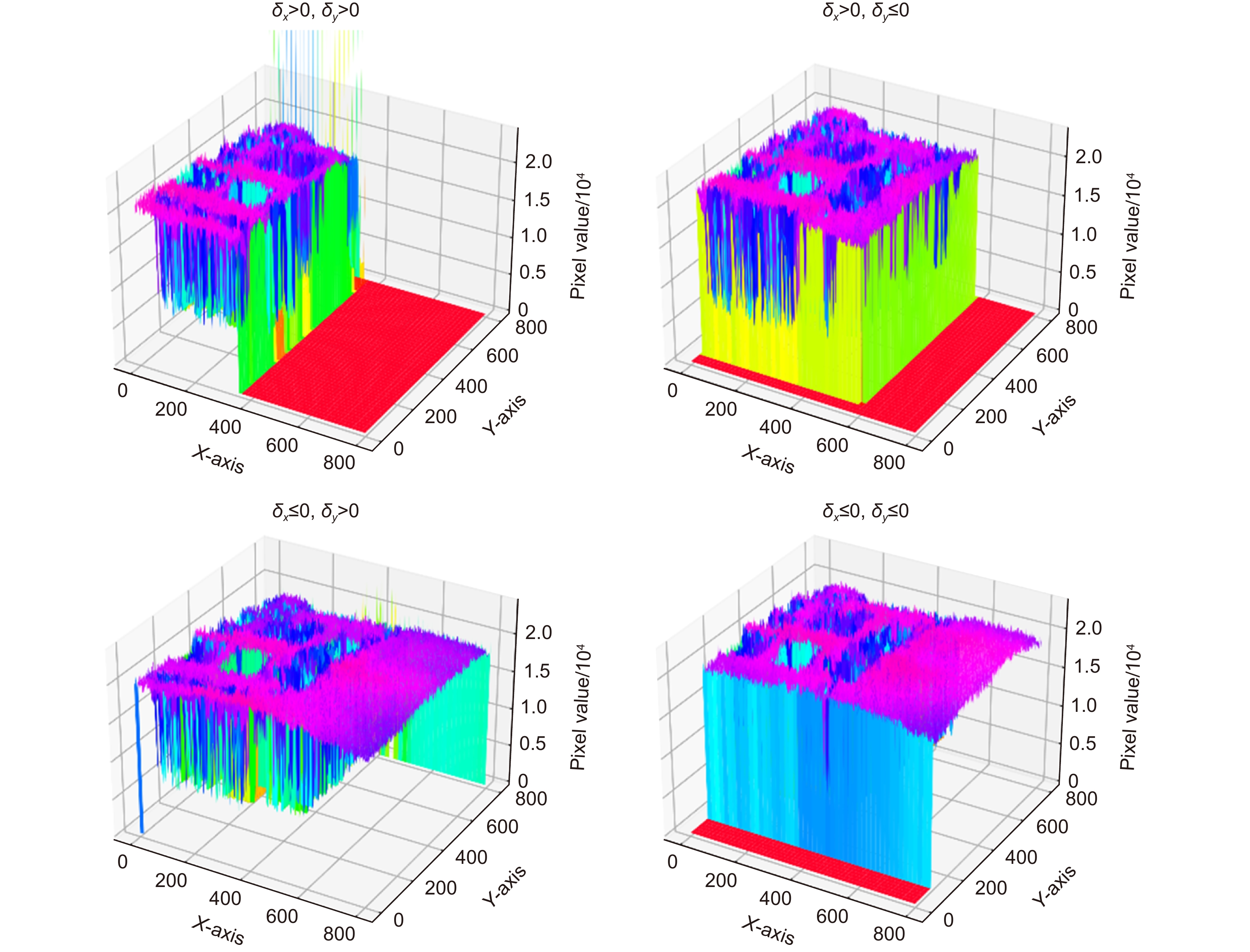
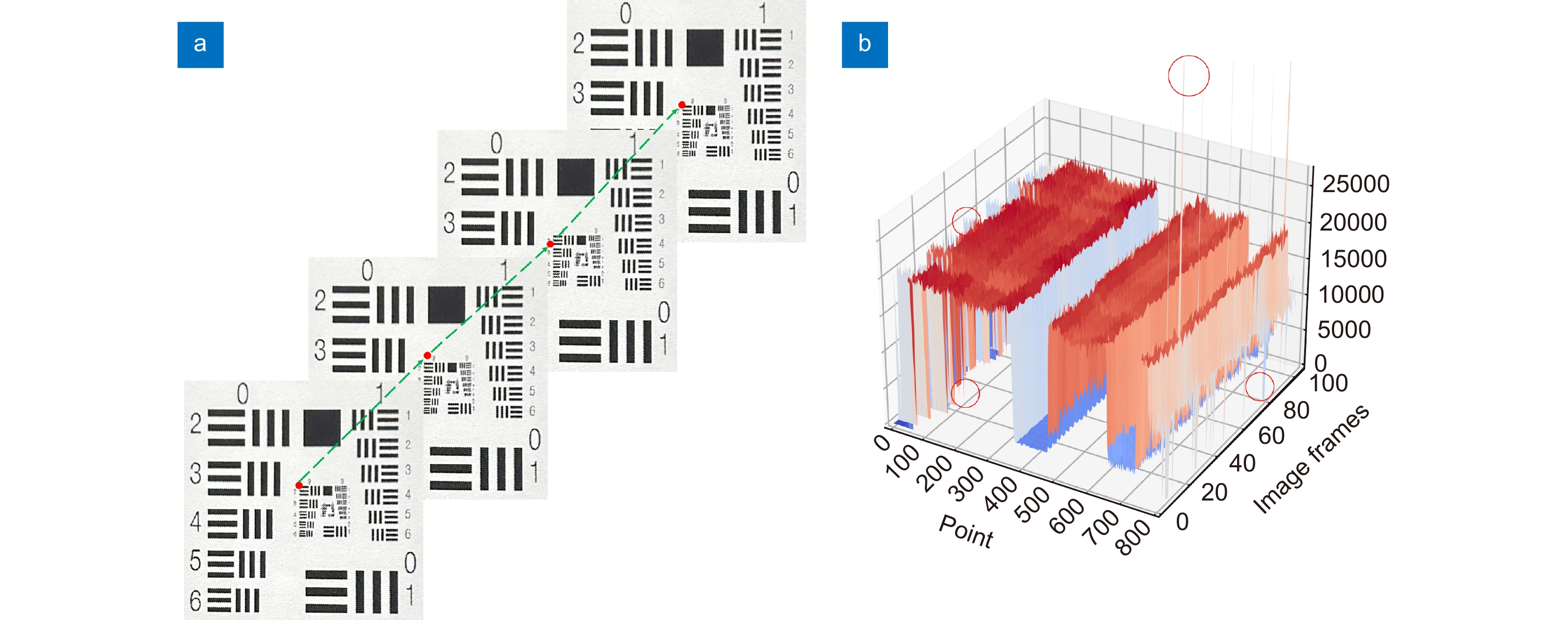
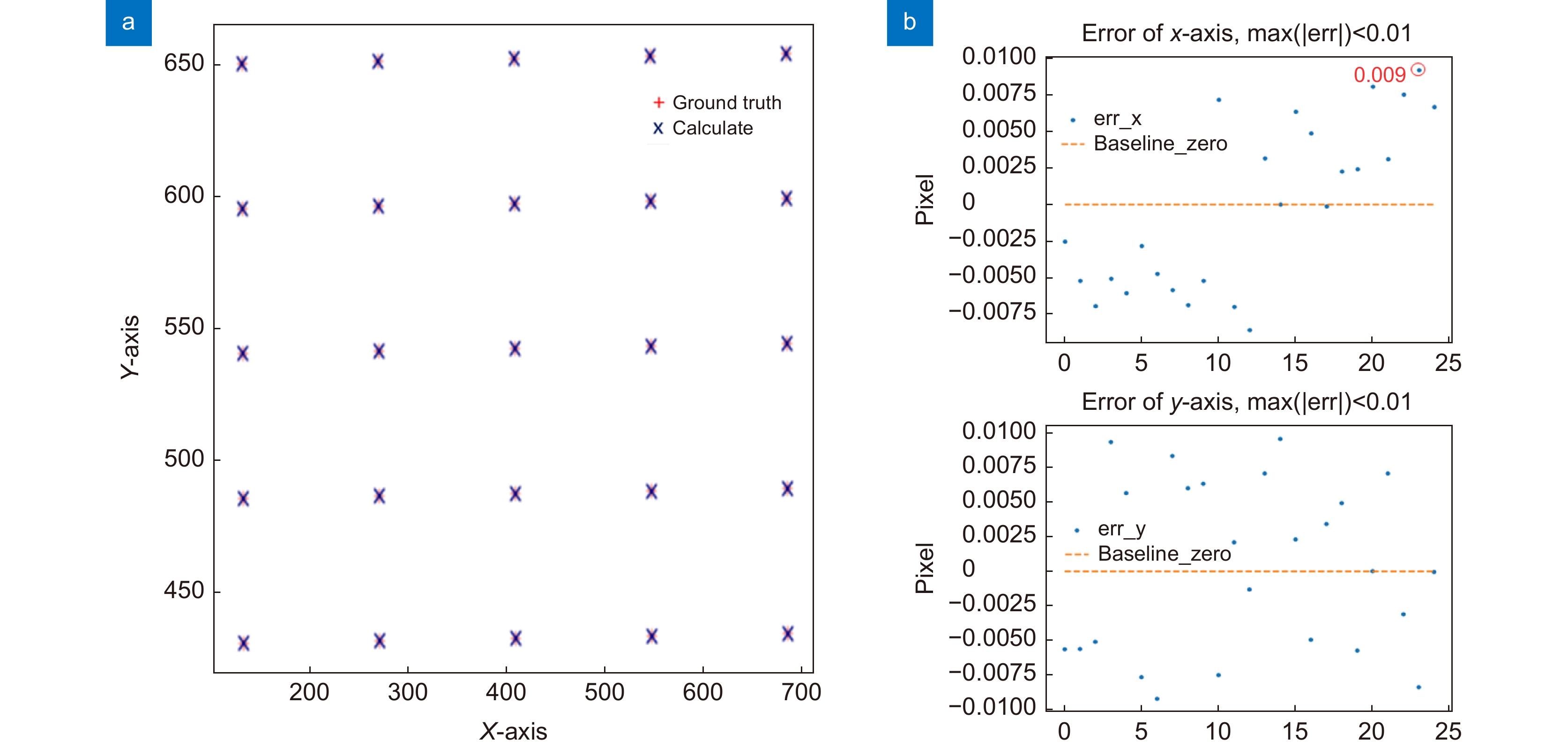
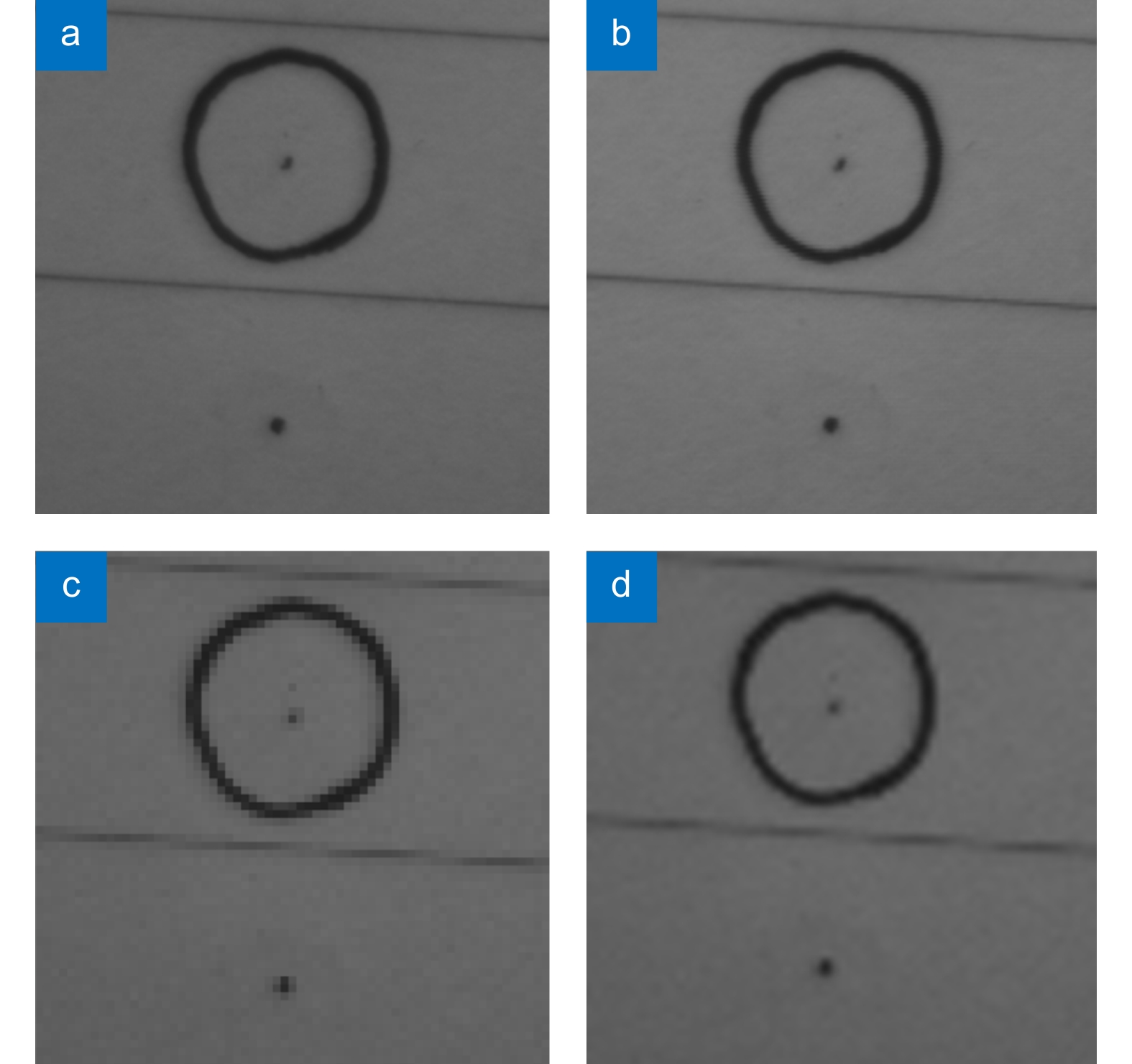
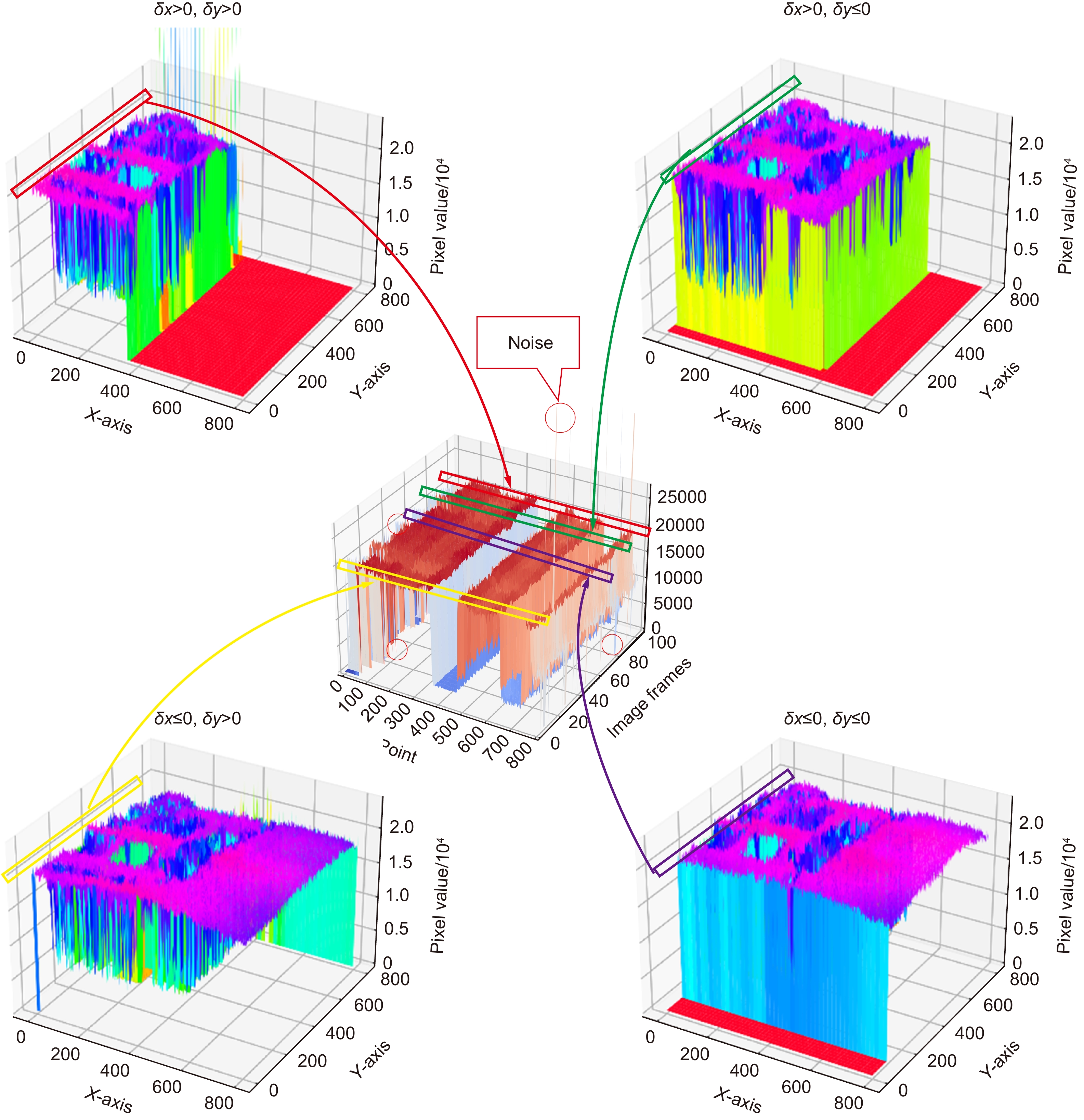
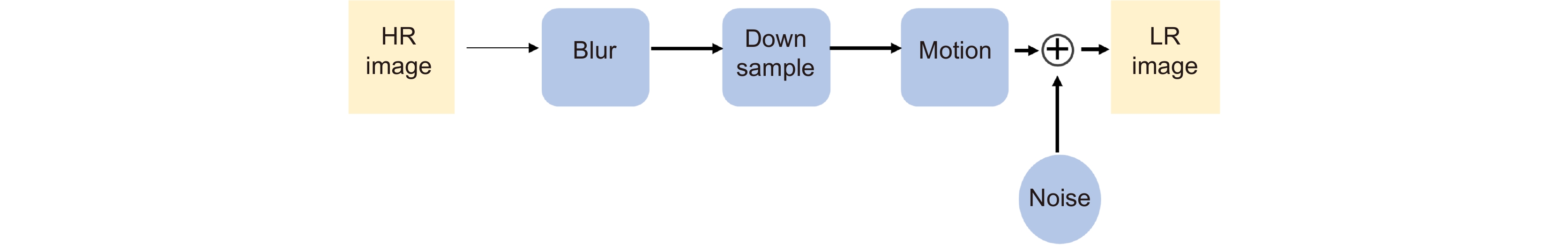
Overview: The super-resolution reconstruction algorithm is an algorithm that restores low-resolution images to high-resolution images. It finds wide applications in the fields of medicine, remote sensing, military security, and face recognition. Multiple frames provide more information than a single image. Moreover, multiple frames super-resolution reconstruction yields better result images than single-image super-resolution reconstruction. Micro-scanning is one of the most effective imaging ways of obtaining multiple frames for super-resolution reconstruction. However, the scanning pattern of micro-scanning imaging technology is fixed. Additionally, it requires high precision of the device, including position accuracy and control in time accuracy. Regarding the reconstruction algorithm, traditional interpolate algorithms can only resize images without improving image quality. Reconstruction algorithms based on deep learning perform well in resizing and improving quality. They perform well in many scenarios. However, when they are applied in some specific scenarios that are hard to construct datasets, their performances are reduced. To degrade the precision requirement of the device and achieve good performance without datasets, we propose an image super-resolution reconstruction algorithm based on active displacement imaging. This algorithm is inspired by micro-scanning imaging and POCS (Projection Onto Convex Set). Specifically, we control the camera to move randomly while recording the displacement at the sampling moment. Then, we reconstruct the high-resolution images by solving, mapping, selecting zones, matching multiple frames in sub-pixel precisions (below 0.01 pixel), obtaining the sub-pixel information between multiple frames, and iteratively updating the reconstruction. Finally, we generate super-resolution reconstruction results.
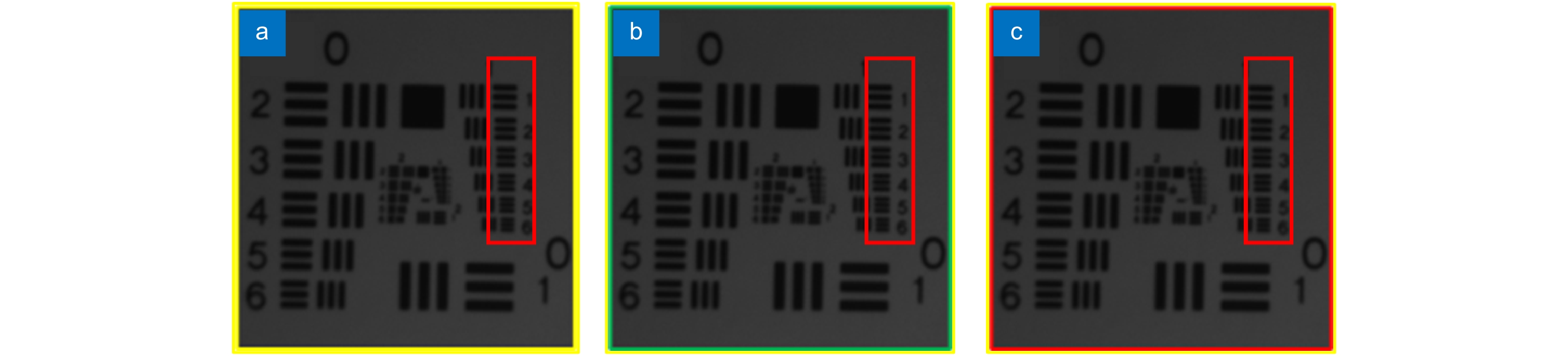
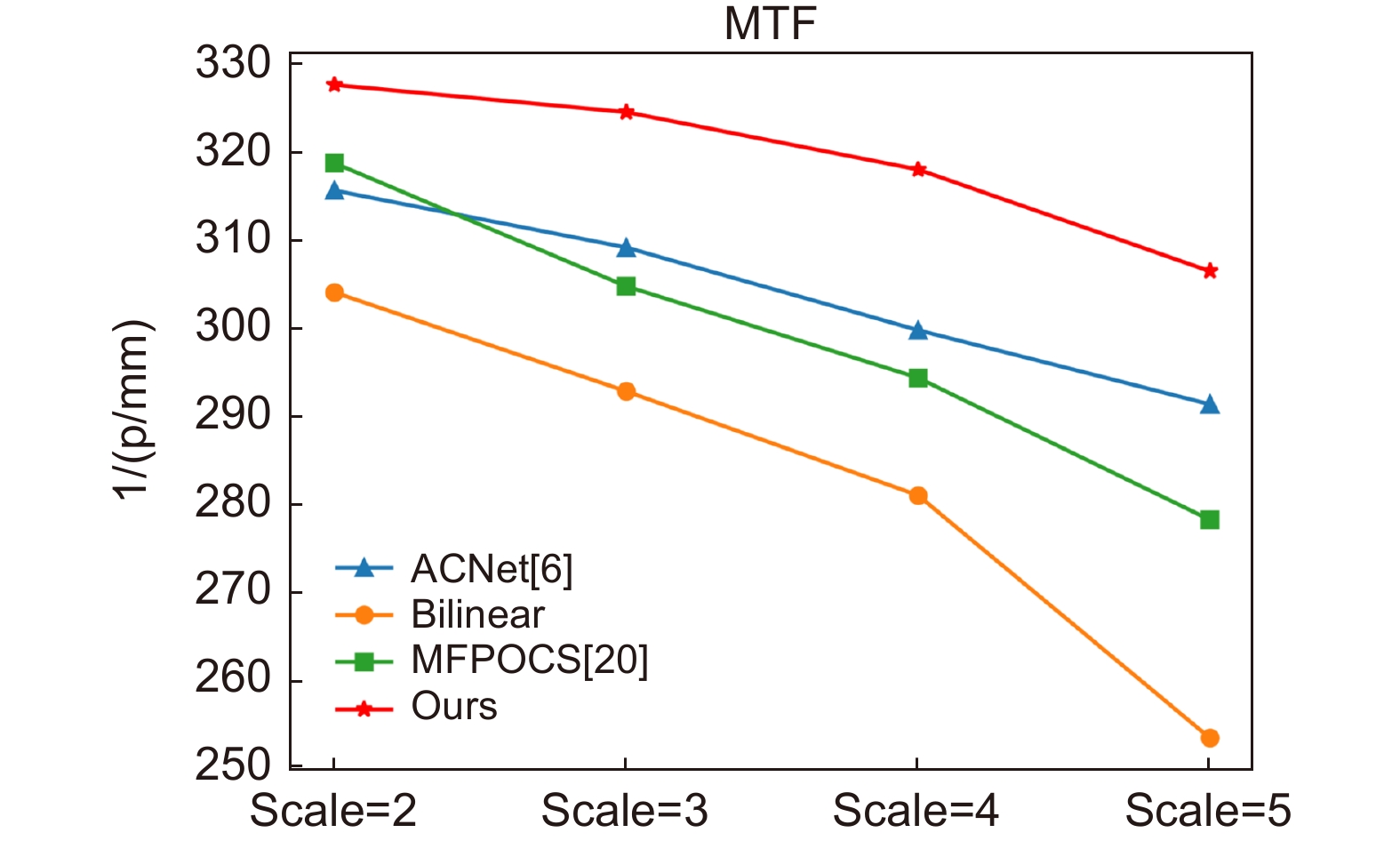
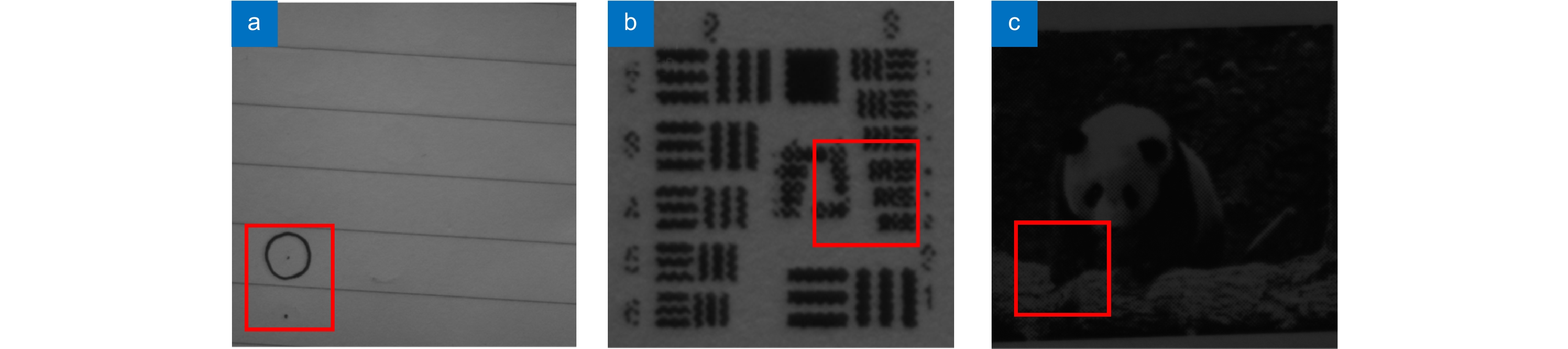
Our present algorithm removes fixed scanning patterns and doesn’t require constructing new datasets. We compare the reconstruction results of our method, recent POCS (tradition), and SRCNN (deep learning). The experimental results show that our algorithm outperforms the latest multi-featured super-resolution reconstruction algorithms of POCS and SRCNN methods in terms of PSNR, SSIM, and mean gradient. Results indicate that this algorithm reduces the requirement of the micro-scanning technique on the device in place accuracy and can be applied in those scenarios without datasets.
-

-
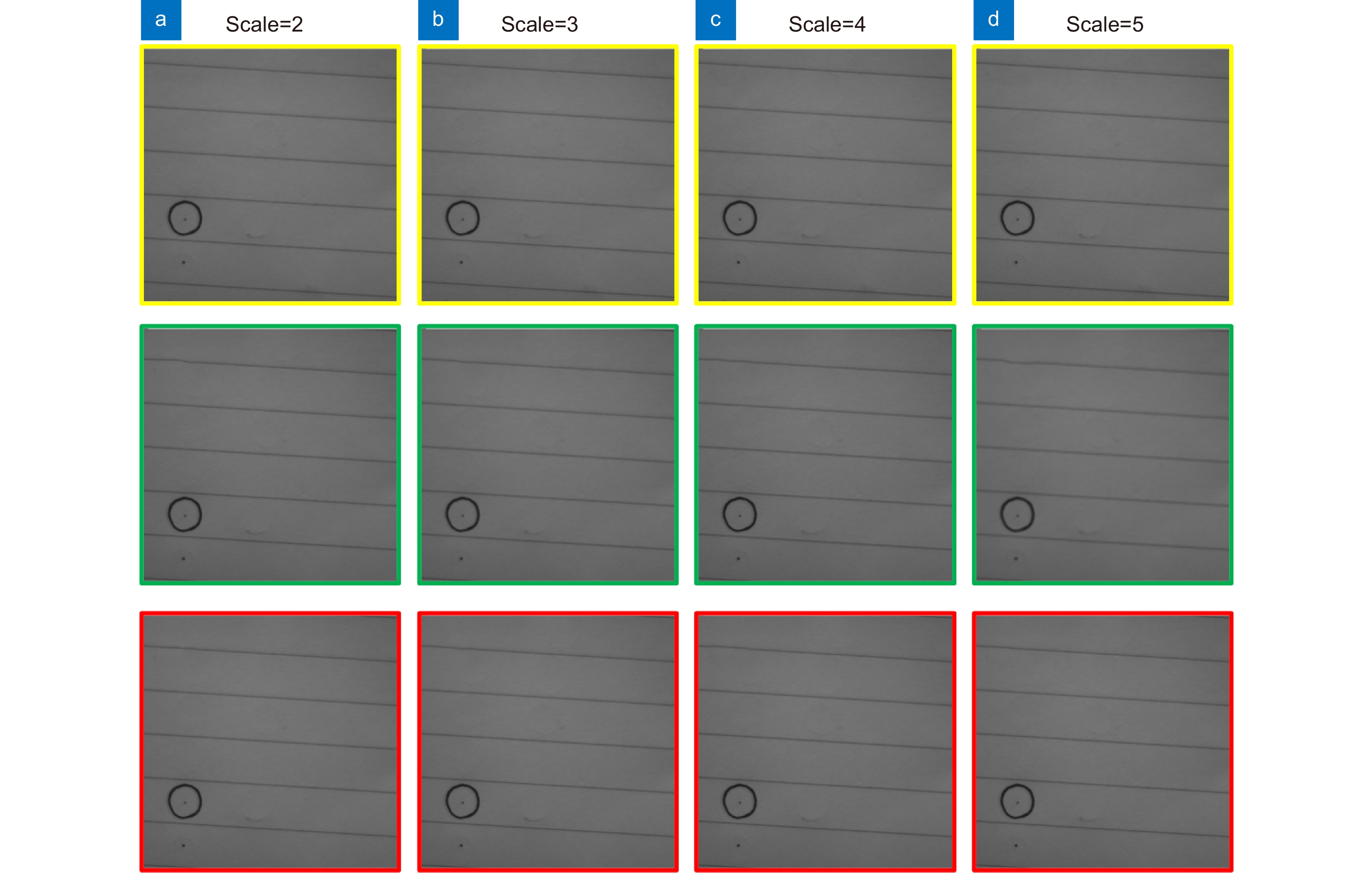
表 1 三种算法重建结果的SSIM对比
Table 1. SSIM of three algorithms
Images Scale 2 3 4 5 Simple
imagePOCS[20] 0.8493 0.8093 0.8568 0.8330 ACNet[6] 0.9876 0.9764 0.9623 0.9418 Ours 0.9921 0.9694 0.9949 0.9778 Complex
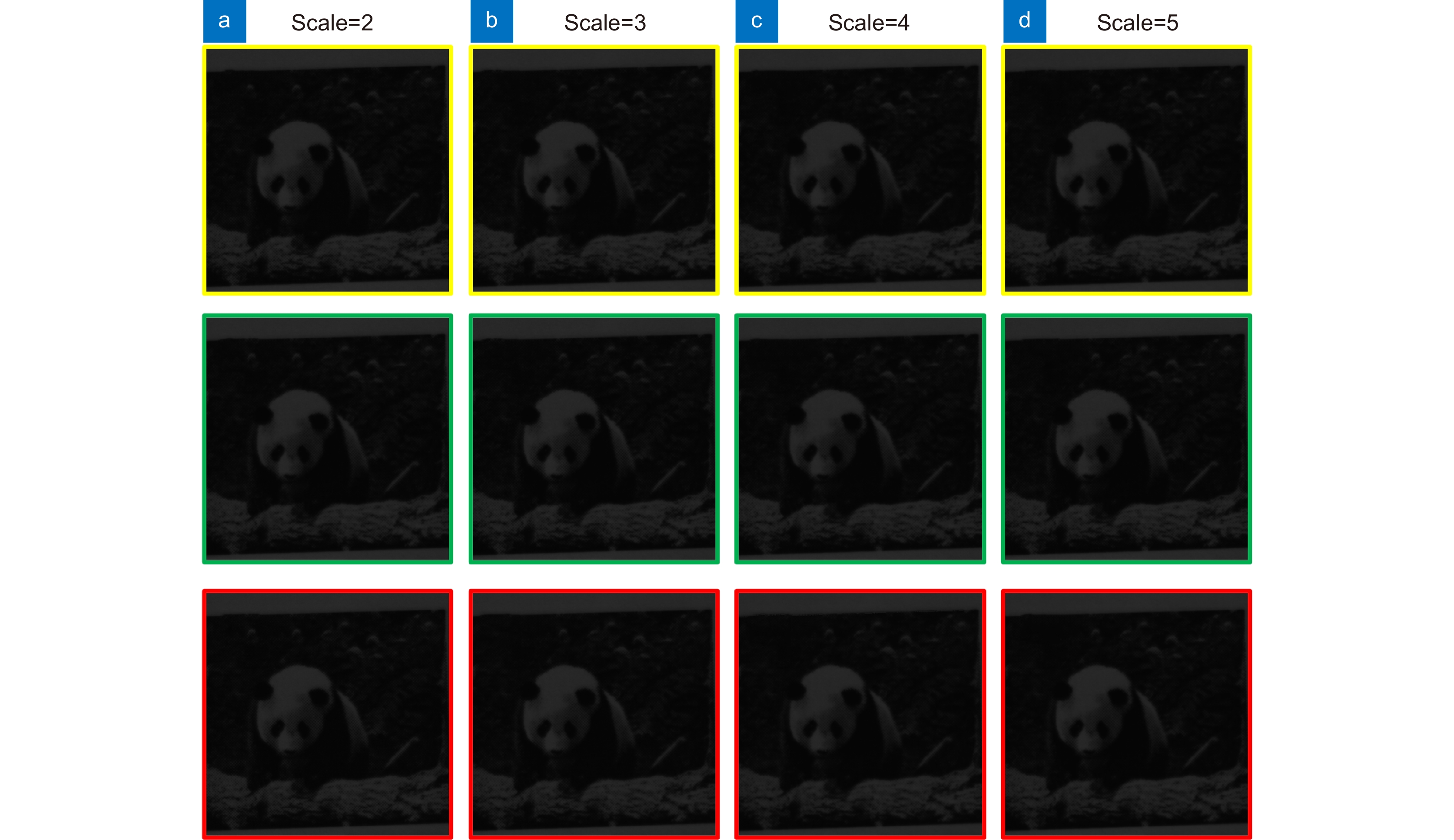
imageMFPOCS[20] 0.6838 0.6539 0.6880 0.6714 ACNet[6] 0.9462 0.8926 0.8051 0.7358 Ours 0.9517 0.9183 0.9592 0.9250 Panda MFPOCS[20] 0.6263 0.6187 0.5748 0.5653 ACNet[6] 0.7046 0.6789 0.6014 0.5736 Ours 0.6696 0.6215 0.6255 0.6002 表 2 三种算法重建结果的PSNR对比
Table 2. PSNR of three algorithms
Images Scale 2 3 4 5 Simple
imageMFPOCS[20] 29.4390 26.4232 29.4868 26.4090 ACNet[6] 47.7125 43.6358 39.2593 36.5734 Ours 46.7883 45.5723 43.9699 39.1457 Complex
ImageMFPOCS[20] 20.2672 20.1293 20.1270 20.1398 ACNet[6] 29.1521 27.7453 24.1961 21.9834 Ours 27.4424 29.5396 28.9332 26.6562 Panda MFPOCS[20] 24.0725 22.3215 20.4376 19.8857 ACNet[6] 25.7617 23.5169 19.5048 18.3985 Ours 24.0031 23.1915 21.9751 21.7718 表 3 三种算法重建结果的平均梯度对比
Table 3. Mean gradient of three algorithms
Images Scale 2 3 4 5 Simple
imageMFPOCS[20] 314.7994 211.4553 131.7388 105.3359 ACNet [6] 338.4507 294.9276 201.8644 145.9228 Ours 320.5050 265.3140 215.9100 184.1190 Complex
ImageMFPOCS[20] 350.7845 242.5359 162.4356 129.1925 ACNet [6] 471.1172 395.2651 275.1865 216.5397 Ours 446.9067 383.5727 350.1874 314.0308 Panda MFPOCS[20] 214.7590 147.4026 91.8175 77.1331 ACNet [5] 271.9497 263.0891 191.2695 163.3797 Ours 253.5610 389.1927 497.7272 205.6040 -
参考文献
[1] Dong C, Loy C C, He K M, et al. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, 2014: 184–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10593-2_13.
[2] Dong C, Loy C C, Tang X O. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network[C]//Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, 2016: 391–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_25.
[3] Lai W S, Huang J B, Ahuja N, et al. Fast and accurate image super-resolution with deep laplacian pyramid networks[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2019, 41(11): 2599−2613. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2865304
[4] Basak H, Kundu R, Agarwal A, et al. Single image super-resolution using residual channel attention network[C]//2020 IEEE 15th International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS), Rupnagar, 2020: 219–224. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIIS51140.2020.9342688.
[5] Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, 2016: 1646–1654. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.182.
[6] Tian C W, Xu Y, Zuo W M, et al. Asymmetric CNN for image superresolution[J]. IEEE Trans Syst, Man, Cybern:Syst, 2022, 52(6): 3718−3730. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3069265
[7] Tai Y, Yang J, Liu X M. Image super-resolution via deep recursive residual network[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, 2017: 2790–2798. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.298.
[8] Ledig C, Theis L, Huszár F, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, 2017: 105–114. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.19.
[9] Talab M A, Awang S, Najim S A D M. Super-low resolution face recognition using integrated efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network (ESPCN) and convolutional neural network (CNN)[C]//2019 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Control and Intelligent Systems (I2CACIS), Selangor, 2019: 331–335. https://doi.org/10.1109/I2CACIS.2019.8825083.
[10] Tsai R Y, Huang T S. Multiframe image restoration and registration[J]. Adv Comput Vis Image Process, 1984, 1: 317−339.
[11] Irani M, Peleg S. Motion analysis for image enhancement: resolution, occlusion, and transparency[J]. J Vis Commun Image Represent, 1993, 4(4): 324−335. doi: 10.1006/jvci.1993.1030
[12] Schultz R R, Stevenson R L. Extraction of high-resolution frames from video sequences[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 1996, 5(6): 996−1011. doi: 10.1109/83.503915
[13] Patti A J, Altunbasak Y. Artifact reduction for set theoretic super resolution image reconstruction with edge adaptive constraints and higher-order interpolants[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2001, 10(1): 179−186. doi: 10.1109/83.892456
[14] 杜玉萍, 刘严严. 基于POCS的微扫描超分辨率图像重建算法研究[J]. 光电技术应用, 2019, 34(6): 25−28,44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2019.06.006
Du Y P, Liu Y Y. Research on micro-scanning super-resolution image reconstruction algorithm based on POCS[J]. Electro-Opt Technol Appl, 2019, 34(6): 25−28,44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2019.06.006
[15] Yao D, Liang H G, Campos J, et al. Calculation and restoration of lost spatial information in division-of-focal-plane polarization remote sensing using polarization super-resolution technology[J]. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf, 2023, 116: 103155. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2022.103155
[16] 赵浩光, 曲涵石, 王鑫, 等. 高速微扫描图像超分辨重建[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2021, 29(10): 2456−2464. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212910.2456
Zhao H G, Qu H S, Wang X, et al. Super-resolution reconstruction of micro-scanning images[J]. Opt Precis Eng, 2021, 29(10): 2456−2464. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212910.2456
[17] 于快快, 郝克, 刘严严, 等. 红外微扫描超分辨率仿真分析与实验研究[J]. 光电技术应用, 2023, 38(1): 46−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2023.01.008
Yu K K, Hao K, Liu Y Y, et al. Simulation analysis and experimental study of infrared micro-scanning super-resolution[J]. Electro-Opt Technol Appl, 2023, 38(1): 46−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2023.01.008
[18] Zhang Y, Sun J Y, Qiu R D, et al. Spatial scale effect of a typical polarized remote sensor on detecting ground objects[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(13): 4418. doi: 10.3390/s21134418
[19] Zhang X F, Huang W, Xu M F, et al. Super-resolution imaging for infrared micro-scanning optical system[J]. Opt Express, 2019, 27(5): 7719−7737. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.007719
[20] 白旭, 卜丽静, 赵国忱, 等. 多特征的POCS图像超分辨率重建方法[J]. 测绘科学, 2022, 47(12): 174−183. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2022.12.022
Bai X, Bu L J, Zhao G C, et al. POCS image super-resolution reconstruction method based on multi-feature[J]. Sci Surv Mapp, 2022, 47(12): 174−183. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2022.12.022
[21] 金伟其, 陈翼男, 王霞, 等. 考虑探测器填充率及微扫描对位偏差的扫描型亚像元热成像算法[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2008, 27(4): 308−312. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9014.2008.04.015
Jin W Q, Chen Y N, Wang X, et al. Scanning type sub-pixel thermal imaging algorithm taking account of detector filling rate and micro-scanning contraposition bias[J]. J Infrared Millim Waves, 2008, 27(4): 308−312. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9014.2008.04.015
[22] Sanders J G, Wan W H, Harris V, et al. Compact airborne staring FPA sensor with microscanning[J]. Proc SPIE, 1996, 2743: 158−168. doi: 10.1117/12.241958
[23] 邹晶, 耿星杰, 廖可梁, 等. 基于亚像素扫描的超分辨技术在高分辨X射线显微镜中的应用[J]. 光子学报, 2017, 46(12): 1211001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20174612.1211001
Zou J, Geng X J, Liao K L, et al. Application of super-resolution technique based on sub-pixel scanning in high-resolution X-ray microscopy[J]. Acta Photonica Sin, 2017, 46(12): 1211001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20174612.1211001
[24] Sun M J, Edgar M P, Phillips D B, et al. Improving the signal-to-noise ratio of single-pixel imaging using digital microscanning[J]. Opt Express, 2016, 24(10): 10476−10485. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.010476
[25] Gui C, Wang D T, Huang X W, et al. Super-resolution and wide-field-of-view imaging based on large-angle deflection with risley prisms[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(4): 1793. doi: 10.3390/s23041793
[26] Cui H, Cao J, Hao Q, et al. Improving the quality of panoramic ghost imaging via rotation and scaling invariances[J]. Opt Laser Technol, 2023, 160: 109102. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2022.109102
[27] Chen J, Li Y, Cao L H. Research on region selection super resolution restoration algorithm based on infrared micro-scanning optical imaging model[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 2852. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82119-1
[28] Liang K Y, Wang B W, Zuo C. Super-resolution-imaging based on circular coded aperture[J]. Proc SPIE, 2023, 12523: 95−99. doi: 10.1117/12.2664916
[29] Ameer S, Basir O. Objective image quality measure based on Weber-weighted mean absolute error[C]//2008 9th International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, 2008: 728–732. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICOSP.2008.4697233.
[30] Cheng D Q, Chen L L, Lv C, et al. Light-guided and cross-fusion U-Net for anti-illumination image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol, 2022, 32(12): 8436−8449. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3194169
[31] Chen L L, Guo L, Cheng D Q, et al. Structure-preserving and color-restoring up-sampling for single low-light image[J]. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol, 2022, 32(4): 1889−1902. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3086598
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: