Multi-frame blind deconvolution of solar images via second-order total generalized variation
-
摘要
盲解卷积是常用的自适应光学图像事后重建方法之一。为提高盲解卷积对太阳(自适应光学)图像的重建效果,本文提出了基于二阶广义总变分的空变多帧盲解卷积算法。该算法首先利用交替最小化和半二次分裂方法求解本文提出的二阶广义总变分约束的空不变多帧盲解卷积模型;然后针对非等晕大视场太阳图像特性,利用重叠分块与加权拼接实现空变盲解卷积扩展。在一米新真空太阳望远镜(NVST)观测的真实太阳图像上进行的重建实验与分析表明,本文算法在主观视觉效果和客观指标上均具有较好的图像重建效果。
Abstract
Blind deconvolution is one of the commonly used post-reconstruction methods for adaptive optics images. In order to improve the reconstruction performance of blind deconvolution on solar (adaptive optics) images, a space-variant multi-frame blind deconvolution model based on second-order total generalized variation is proposed. It first solves the proposed space-invariant blind deconvolution model via second-order total generalized variation by the alternating minimization and half-quadratic splitting method. Then, according to the characteristics of wide field-of-view solar images which are anisoplanatic, the space-variant in the proposed algorithm is implemented by overlapping image segmentation and weighted stitching. Finally, the reconstruction experiment and analysis are carried out on the real solar images observed by the one-meter New Vacuum Solar Telescope (NVST). The results show that the proposed algorithm has good image reconstruction performance in both subjective visual effects and objective indexes.
-
Overview
Overview: Ground-based optical telescopes are important tools for astronomical observation. However, atmospheric turbulence distorts the wavefront of the light waves from the target, resulting in a serious decline in the imaging resolution of optical telescopes. Although adaptive optics (AO) technology can reduce the influence of atmospheric turbulence, due to the limitation of hardware performance, the AO system can only achieve partial correction, and there is still residual aberration in the observed images, which require post-reconstruction.
At present, almost all large-aperture solar telescopes at home and abroad are equipped with AO systems, and the collected solar (adaptive optics) images can be reconstructed by blind deconvolution, phase diversity, speckle reconstruction, or deep learning, to further improve the image quality. Among the four post-reconstruction methods, blind deconvolution is the most flexible. Based on the maximum a posteriori (MAP), image and PSF regularization can be used to design blind deconvolution models to reduce the ill-posedness of the image reconstruction problem. However, blind deconvolution is difficult to achieve the ideal reconstruction effect due to the complex structure and texture features, strong noise, and anisoplanatism of solar images.
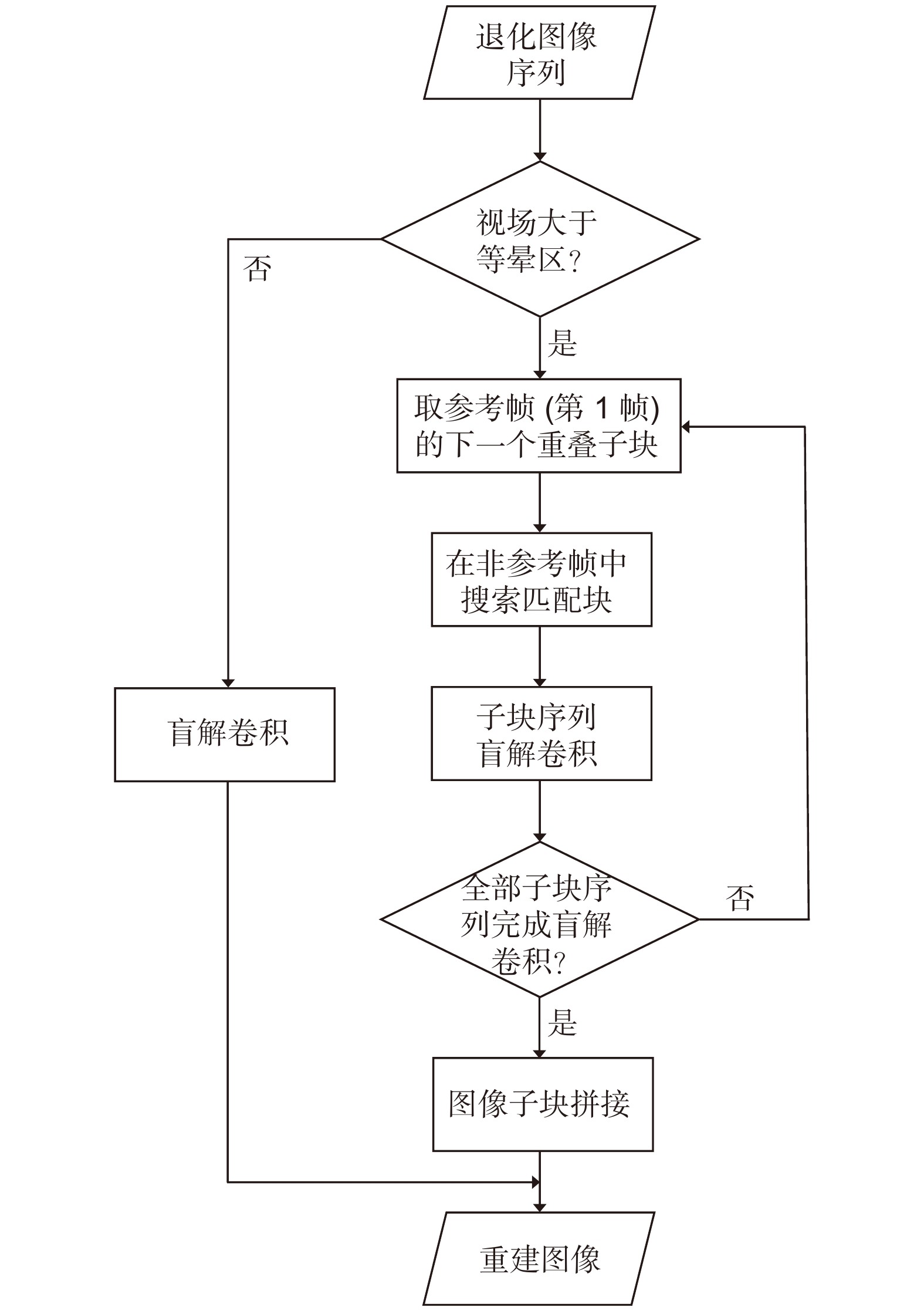
Total generalized variation is effective and widely used in natural image denoising and deblurring due to its ability to suppress the staircase effect while preserving image edges and details. In order to improve the reconstruction performance of blind deconvolution on solar images, total generalized variation and PSF regularization are introduced into the reconstruction of solar images. A space-invariant multi-frame blind deconvolution model via second-order total generalized variation is proposed in this paper to improve the robustness of noise and recover more texture details. The model is solved by alternating minimization of the image sub-model and the PSF sub-model, where the image sub-model can be solved by the half-quadratic splitting method. Combined with the non-blind deconvolution based on hyper-Laplacian prior, a space-invariant multi-frame blind deconvolution algorithm can be established under the multi-scale framework. Then, by overlapping image segmentation and weighted stitching, the space-invariant blind deconvolution algorithm is extended to a reconstruction algorithm suitable for wide field-of-view solar images, which can reduce reconstruction errors caused by anisoplanatism. Finally, the reconstruction experiment and analysis are carried out on the real solar images observed by the one-meter New Vacuum Solar Telescope (NVST) in southwest China. The results show that the algorithm has good image reconstruction performance in both subjective visual effects and objective indexes. Second-order total generalized variation regularization and multi-frame can improve the stability and reliability of solar image reconstruction.
-

-
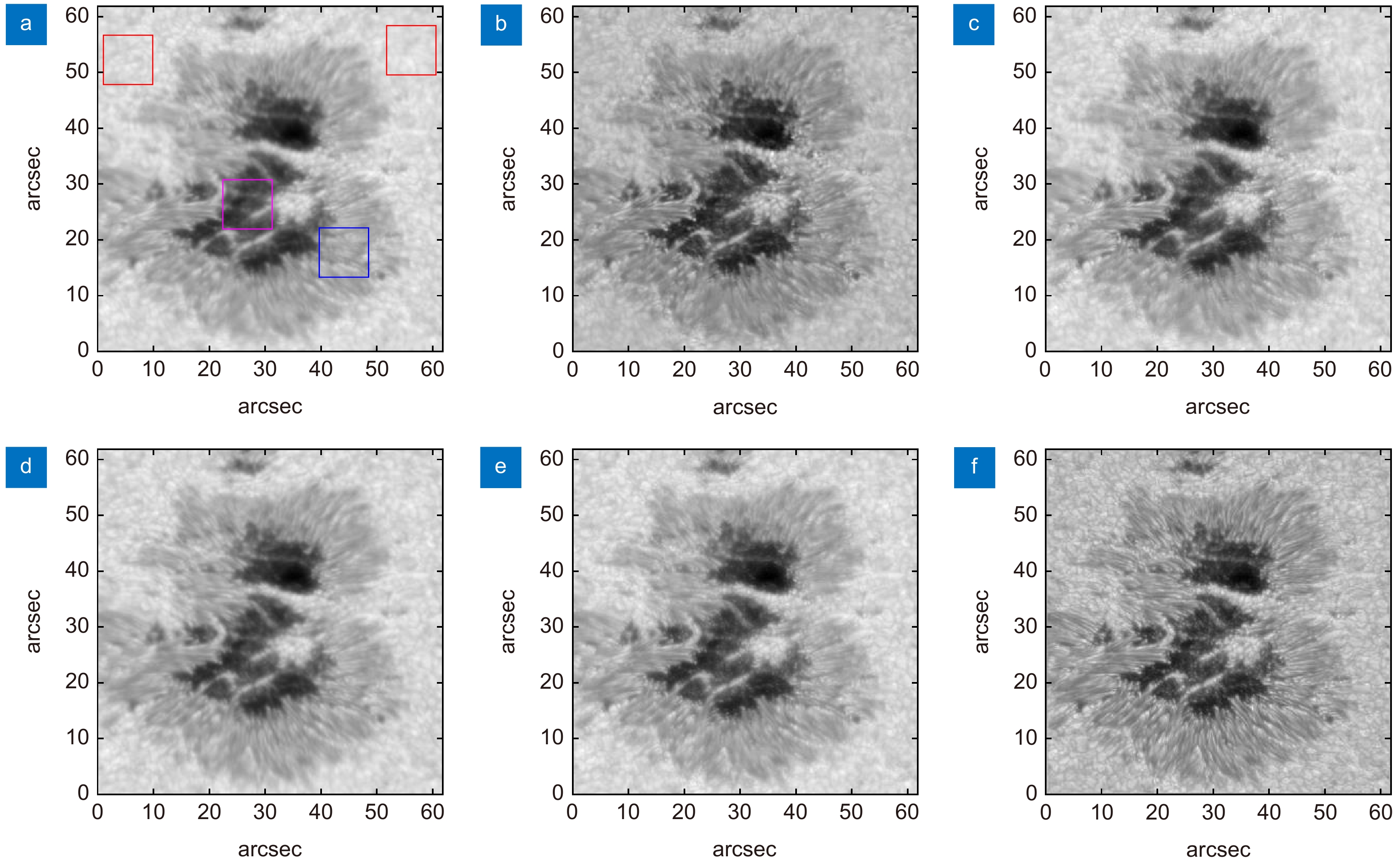
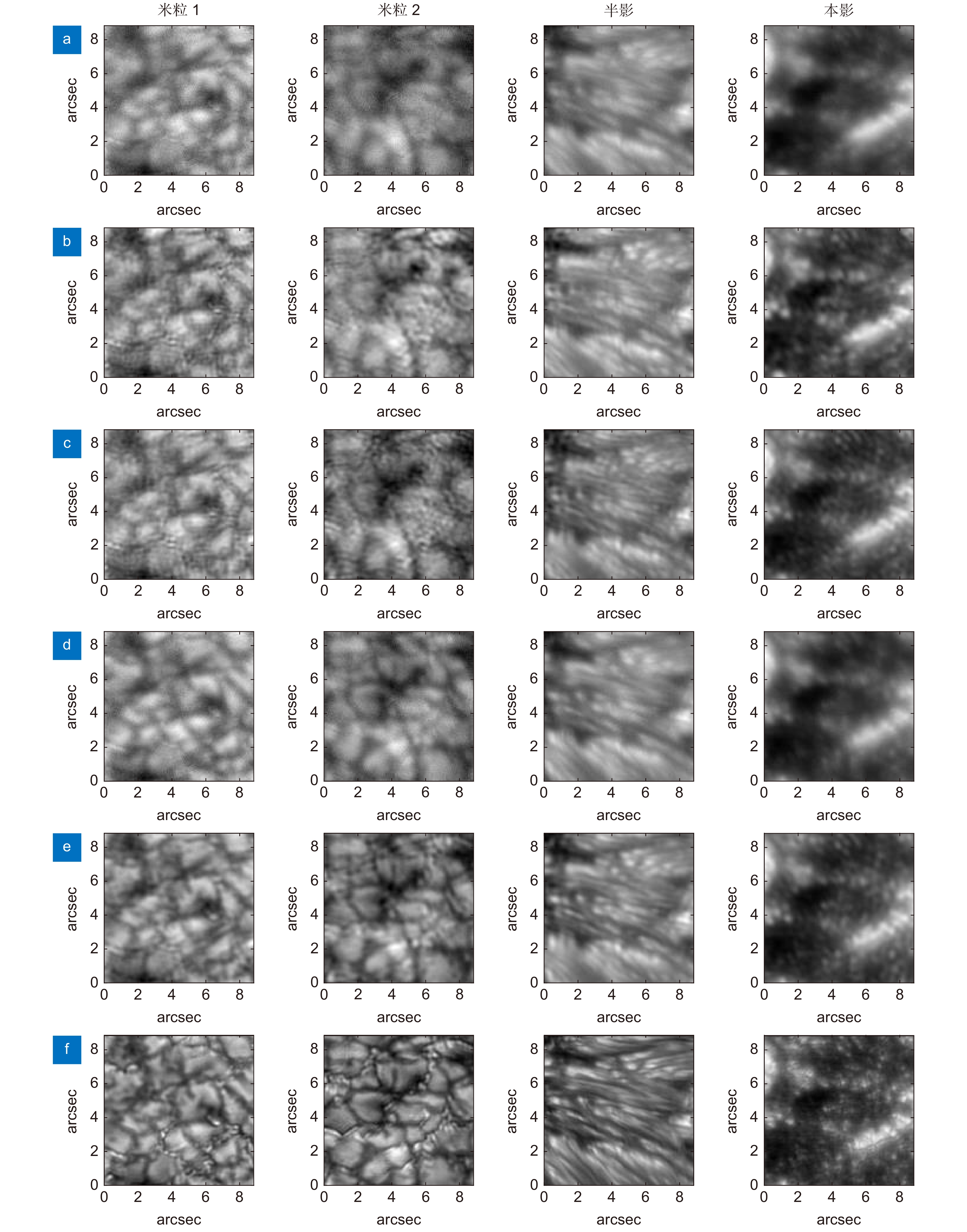
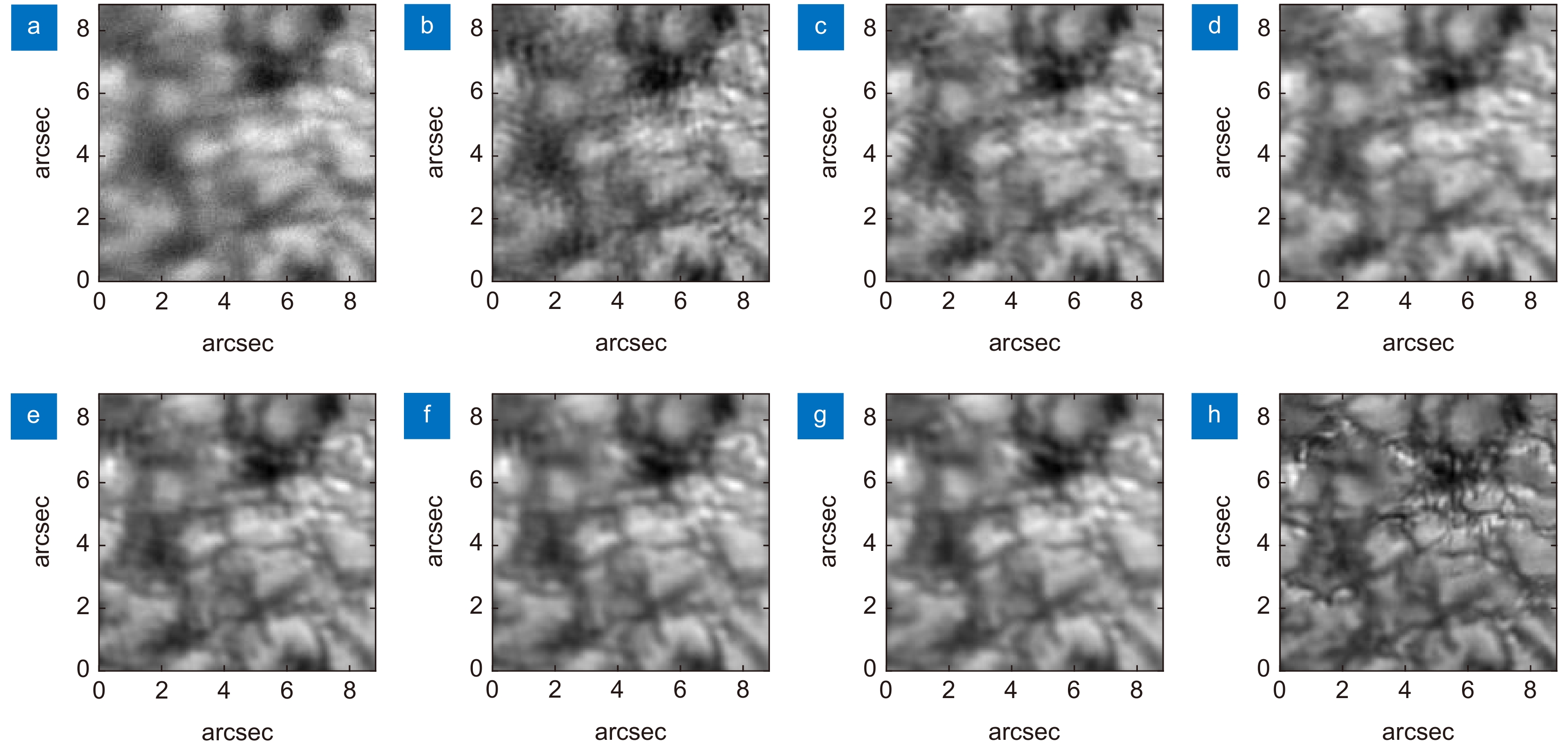
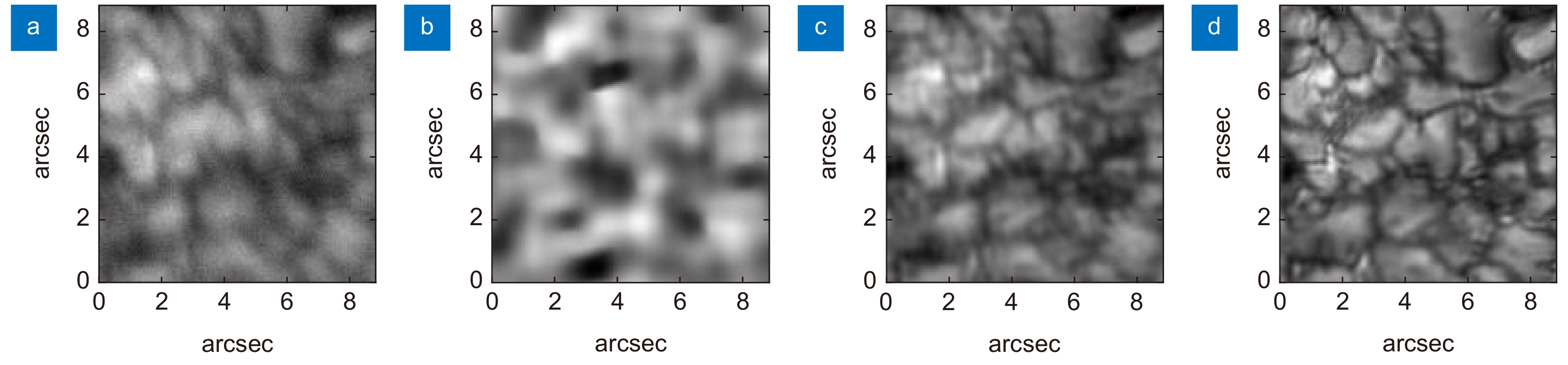
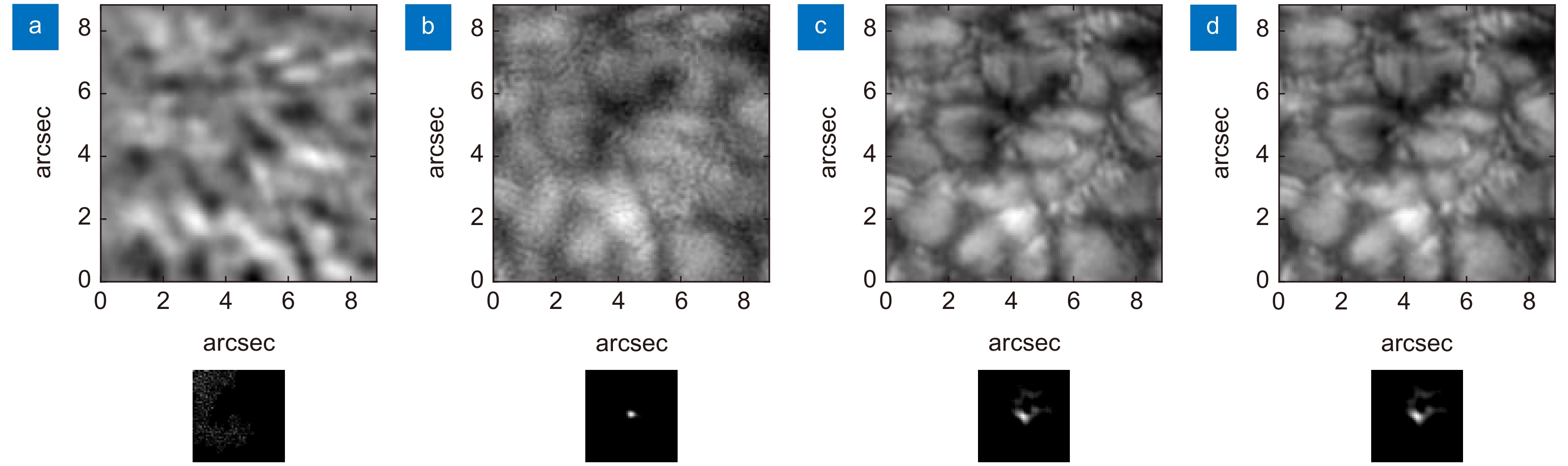
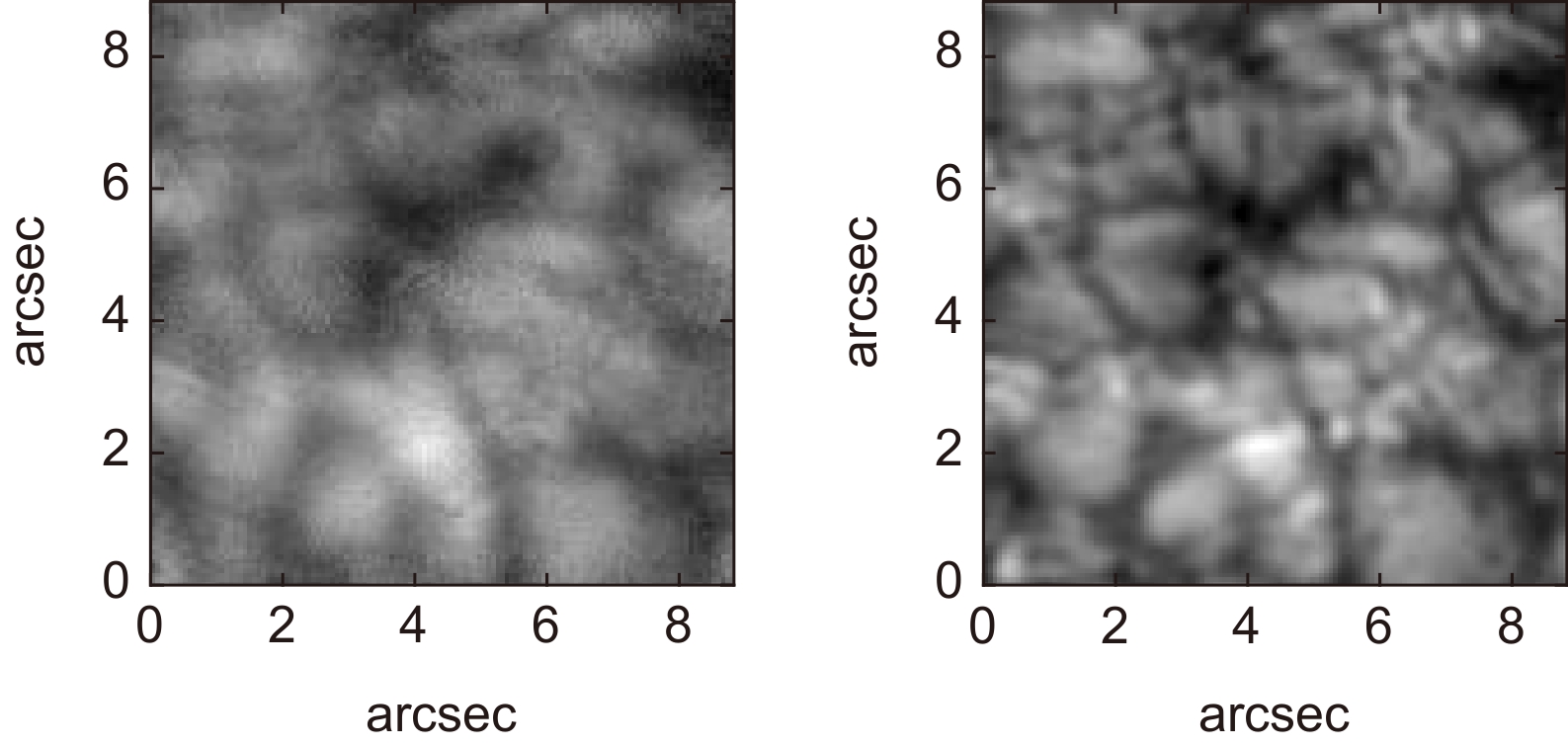
图 4 不同输入帧数的重建结果。(a) 输入序列的其中1帧;(b) ~ (g) 分别对应输入1、2、3、5、10、20帧的重建结果;(h) 斑点重建
Figure 4. Reconstruction results of different input frames. (a) One frame in the input sequence; (b) ~ (g) The reconstruction results corresponding to input 1, 2, 3, 5, 10 and 20 frames respectively (h) Speckle reconstruction
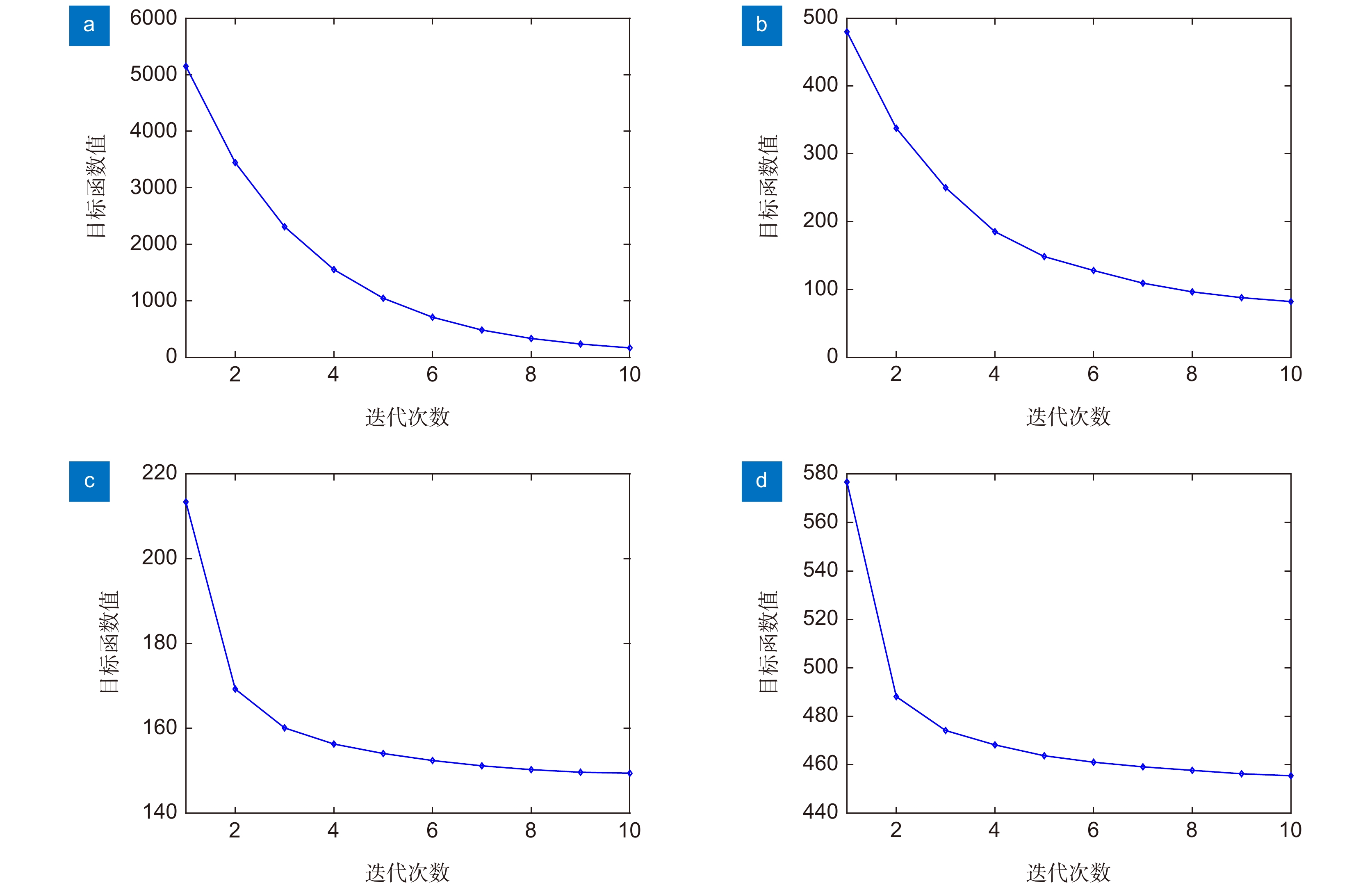
表 1 重建结果定量评价(PSNR(dB)/SSIM)
Table 1. Quantitative evaluation of reconstruction results (PSNR(dB)/SSIM)
输入序列中总
体质量最好帧TVBD S-TGV OBD M-TGV 米粒1 32.68/0.9060 32.05/0.9058 32.27/0.9127 32.70/0.9082 32.79/0.9173 米粒2 33.63/0.9198 33.60/0.9269 33.45/0.9302 34.00/0.9219 34.48/0.9396 半影 29.41/0.8434 29.00/0.8424 29.57/0.8576 29.70/0.8542 30.38/0.8785 本影 29.65/0.8771 29.68/0.8721 30.08/0.8927 30.09/0.8843 30.30/0.8975 整帧图像 31.06/0.8806 30.77/0.8793 30.96/0.8892 31.25/0.8855 31.31/0.8969 表 2 算法运行时间
Table 2. Running time of different algorithms
算法 TVBD S-TGV OBD M-TGV 时间/s 715.37 12.35 156.61 27.68 -
参考文献
[1] 鲍华, 饶长辉, 田雨, 等. 自适应光学图像事后重建技术研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(3): 170730. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170730
Bao H, Rao C H, Tian Y, et al. Research progress on adaptive optical image post reconstruction[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2018, 45(3): 170730. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170730
[2] Miura N, Baba N. Segmentation-based multiframe blind deconvolution of solar images[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 1995, 12(9): 1858−1866. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.12.001858
[3] Löfdahl M G, Scharmer G B. Wavefront sensing and image restoration from focused and defocused solar images[J]. Astron Astrophys, 1994, 107: 243−264.
[4] Seldin J H, Paxman R G. Phase-diverse speckle reconstruction of solar data[J]. Proc SPIE, 1994, 2302: 268−280. doi: 10.1117/12.188044
[5] 龙潇, 鲍华, 饶长辉, 等. 一种并行加速改进的快速相位解包裹算法[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(12): 200111. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.200111
Long X, Bao H, Rao C H, et al. Improved fast phase unwrapping algorithm based on parallel acceleration[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(12): 200111. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.200111
[6] Von Der Lüehe O. Speckle imaging of solar small scale structure. I-methods[J]. Astron Astrophys, 1993, 268(1): 374−390.
[7] Ramos A A, De La Cruz Rodríguez J, Yabar A P. Real-time, multiframe, blind deconvolution of solar images[J]. Astron Astrophys, 2018, 620: A73. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201833648
[8] Wang S, Chen Q Q, He C Y, et al. Blind restoration of solar images via the Channel Sharing Spatio-temporal Network[J]. Astron Astrophys, 2021, 652: A50. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/202140376
[9] Guo Y M, Zhong L B, Min L, et al. Adaptive optics based on machine learning: a review[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2022, 5(7): 200082. doi: 10.29026/oea.2022.200082
[10] Ayers G R, Dainty J C. Iterative blind deconvolution method and its applications[J]. Opt Lett, 1988, 13(7): 547−549. doi: 10.1364/OL.13.000547
[11] Davey B L K, Lane R G, Bates R H T. Blind deconvolution of noisy complex-valued image[J]. Opt Commun, 1989, 69(5–6): 353−356. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(89)90018-7
[12] Fish D A, Brinicombe A M, Pike E R, et al. Blind deconvolution by means of the Richardson–Lucy algorithm[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 1995, 12(1): 58−65. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.12.000058
[13] Kundur D, Hatzinakos D. A novel blind deconvolution scheme for image restoration using recursive filtering[J]. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 1998, 46(2): 375−390. doi: 10.1109/78.655423
[14] Chan T F, Wong C K. Total variation blind deconvolution[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 1998, 7(3): 370−375. doi: 10.1109/83.661187
[15] Schulz T J. Multiframe blind deconvolution of astronomical images[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 1993, 10(5): 1064−1073. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.10.001064
[16] Harmeling S, Hirsch M, Sra S, et al. Online blind deconvolution for astronomical imaging[C]//2009 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), San Francisco, 2009: 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCPHOT.2009.5559014.
[17] Hirsch M, Harmeling S, Sra S, et al. Online multi-frame blind deconvolution with super-resolution and saturation correction[J]. Astron Astrophys, 2011, 531: A9. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/200913955
[18] Fergus R, Singh B, Hertzmann A, et al. Removing camera shake from a single photograph[C]//ACM SIGGRAPH 2006 Papers, Massachusetts, 2006: 787–794. https://doi.org/10.1145/1179352.1141956.
[19] Babacan S D, Molina R, Do M N, et al. Bayesian blind deconvolution with general sparse image priors[C]//Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, 2012: 341–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33783-3_25.
[20] Levin A, Weiss Y, Durand F, et al. Efficient marginal likelihood optimization in blind deconvolution[C]//CVPR 2011, Colorado Springs, 2011: 2657–2664. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995308.
[21] Levin A, Weiss Y, Durand F, et al. Understanding blind deconvolution algorithms[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2011, 33(12): 2354−2367. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.148
[22] Krishnan D, Tay T, Fergus R. Blind deconvolution using a normalized sparsity measure[C]//CVPR 2011, Colorado Springs, 2011: 233–240. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995521.
[23] Xu L, Zheng S C, Jia J Y. Unnatural l0 sparse representation for natural image deblurring[C]//Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, 2013: 1107–1114. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.147.
[24] Sun L B, Cho S, Wang J, et al. Edge-based blur kernel estimation using patch priors[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), Cambridge, 2013: 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCPhot.2013.6528301.
[25] Michaeli T, Irani M. Blind deblurring using internal patch recurrence[C]//Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, 2014: 783–798. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10578-9_51.
[26] Pan J S, Hu Z, Su Z X, et al. Deblurring text images via L0-regularized intensity and gradient prior[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, 2014: 2901–2908. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.371.
[27] Pan J S, Liu R S, Su Z X, et al. Motion blur kernel estimation via salient edges and low rank prior[C]//2014 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Chengdu, 2014: 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME.2014.6890182.
[28] Ren W Q, Cao X C, Pan J S, et al. Image deblurring via enhanced low-rank prior[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2016, 25(7): 3426−3437. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2571062
[29] Pan J S, Sun D Q, Pfister H, et al. Blind image deblurring using dark channel prior[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, 2016: 1628–1636. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.180.
[30] Cho S, Lee S. Fast motion deblurring[C]//ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2009 Papers, Yokohama, 2009: 145. https://doi.org/10.1145/1661412.1618491.
[31] Xu L, Jia J Y. Two-phase kernel estimation for robust motion deblurring[C]//Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, 2010: 157–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15549-9_12.
[32] Rudin L I, Osher S, Fatemi E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms[J]. Phys D: Nonlinear Phenom, 1992, 60(1–4): 259−268. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(92)90242-F
[33] Perrone D, Favaro P. Total variation blind deconvolution: the devil is in the details[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, 2014: 2909–2916. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.372.
[34] Bredies K, Kunisch K, Pock T. Total generalized variation[J]. SIAM J Imag Sci, 2010, 3(3): 492−526. doi: 10.1137/090769521
[35] 许建楼, 冯象初, 郝岩. 自适应二阶总广义变分图像恢复方法[J]. 光电子·激光, 2013, 24(2): 378−383. doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2013.02.028
Xu J L, Feng X C, Hao Y. Image restoration method with adaptive second order total generalized variation[J]. J Optoelectron·Laser, 2013, 24(2): 378−383. doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2013.02.028
[36] Shao W Z, Wang F, Huang L L. Adapting total generalized variation for blind image restoration[J]. Multidimens Syst Signal Process, 2019, 30(2): 857−883. doi: 10.1007/s11045-018-0586-0
[37] Zhang X X, Wang R G, Tian Y H, et al. Image deblurring using robust sparsity priors[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec City, 2015: 138–142. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2015.7350775.
[38] Xu L, Lu C W, Xu Y, et al. Image smoothing via L0 gradient minimization[C]//Proceedings of the 2011 SIGGRAPH Asia Conference, Hong Kong, China, 2011: 174. https://doi.org/10.1145/2024156.2024208.
[39] Krishnan D, Fergus R. Fast image deconvolution using hyper-Laplacian priors[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, 2009: 1033–1041.
[40] Liu R T, Jia J Y. Reducing boundary artifacts in image deconvolution[C]//2008 15th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, San Diego, 2008: 505–508. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2008.4711802.
[41] Zhong L B, Tian Y, Rao C H. The speckle image reconstruction of the solar small scale features[J]. Proc SPIE, 2014, 9301: 93012X. doi: 10.1117/12.2073104
[42] 张姣, 李俊山, 杨亚威. 结合仿射变换和多层B样条配准的湍流畸变图像校正[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2015, 23(3): 846−854. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152303.0846
Zhang J, Li J S, Yang Y W. Turbulence distorted image correction using affine transformation and multilevel B-spline registration[J]. Opt Precis Eng, 2015, 23(3): 846−854. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152303.0846
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: