-
摘要
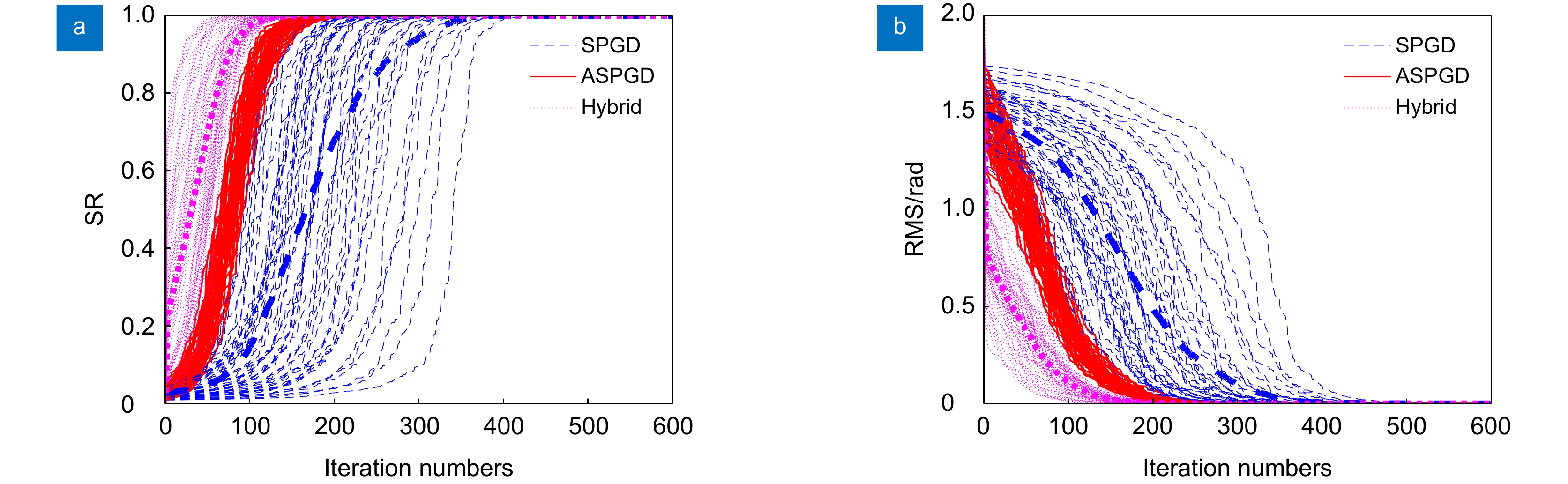
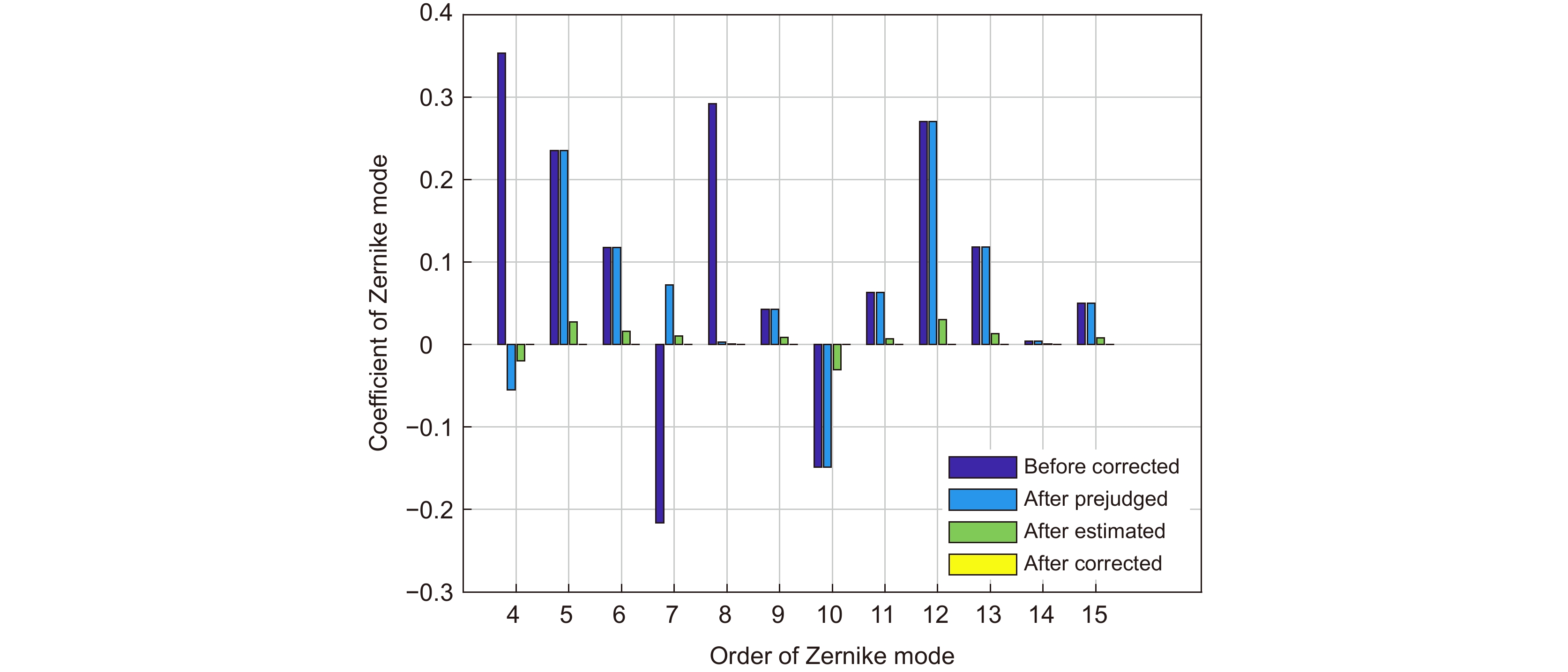
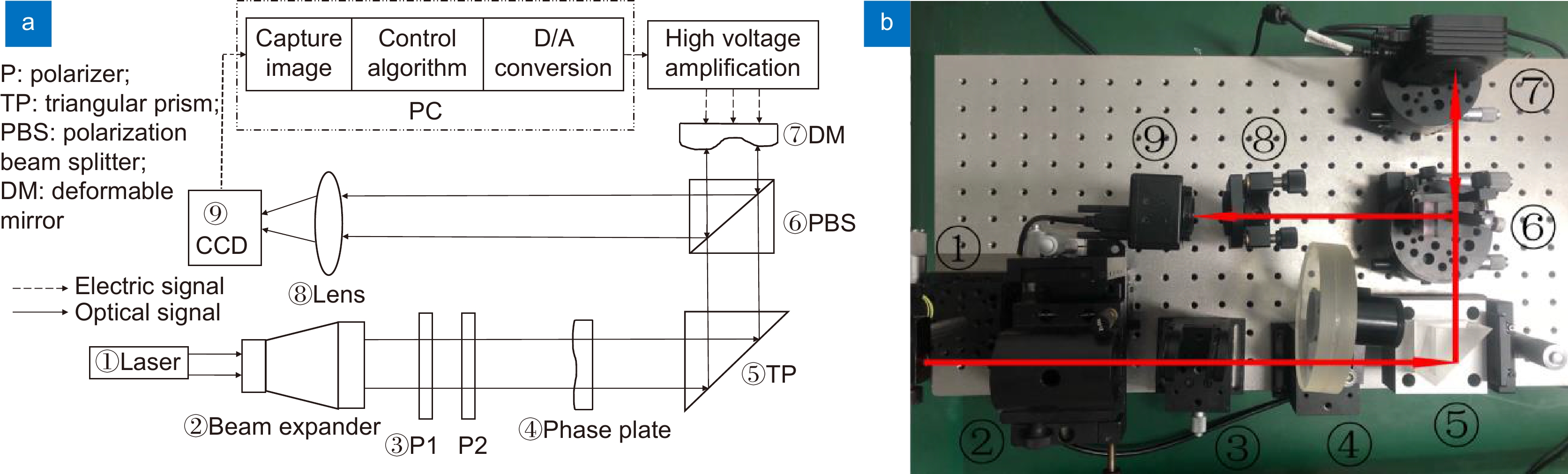
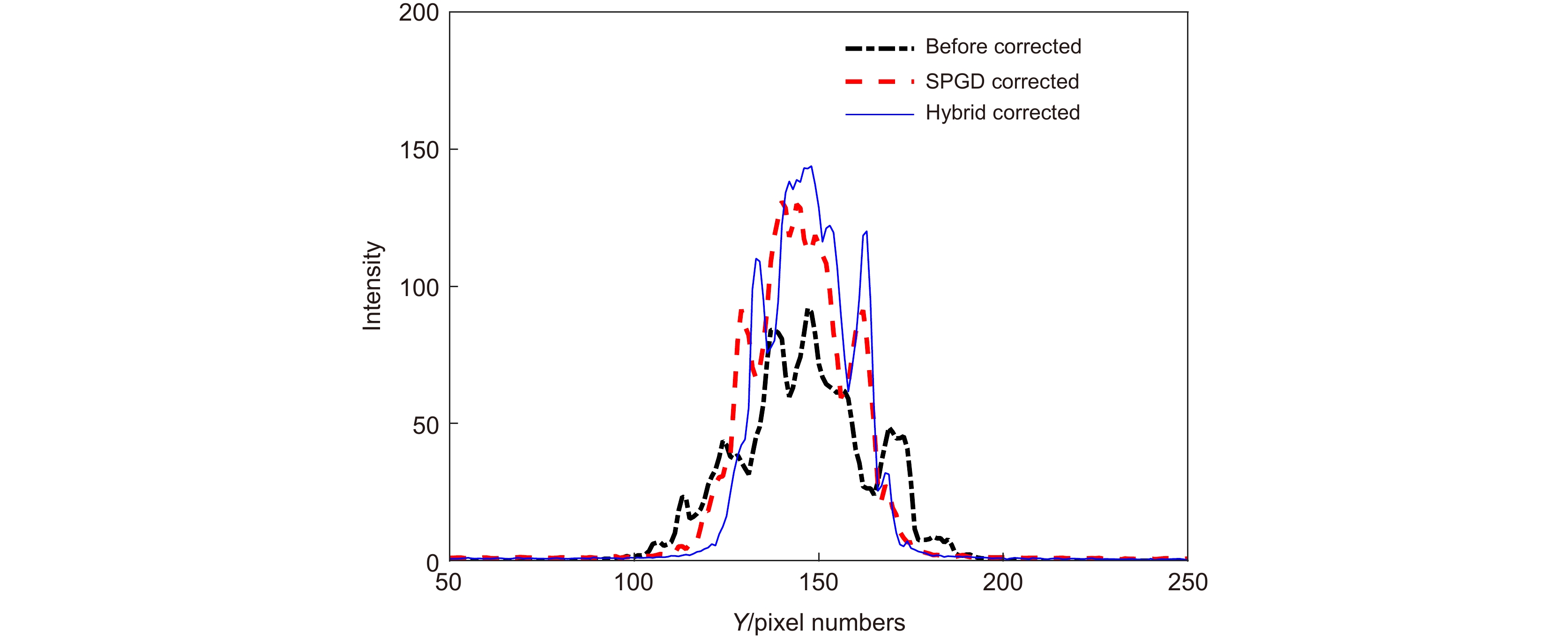
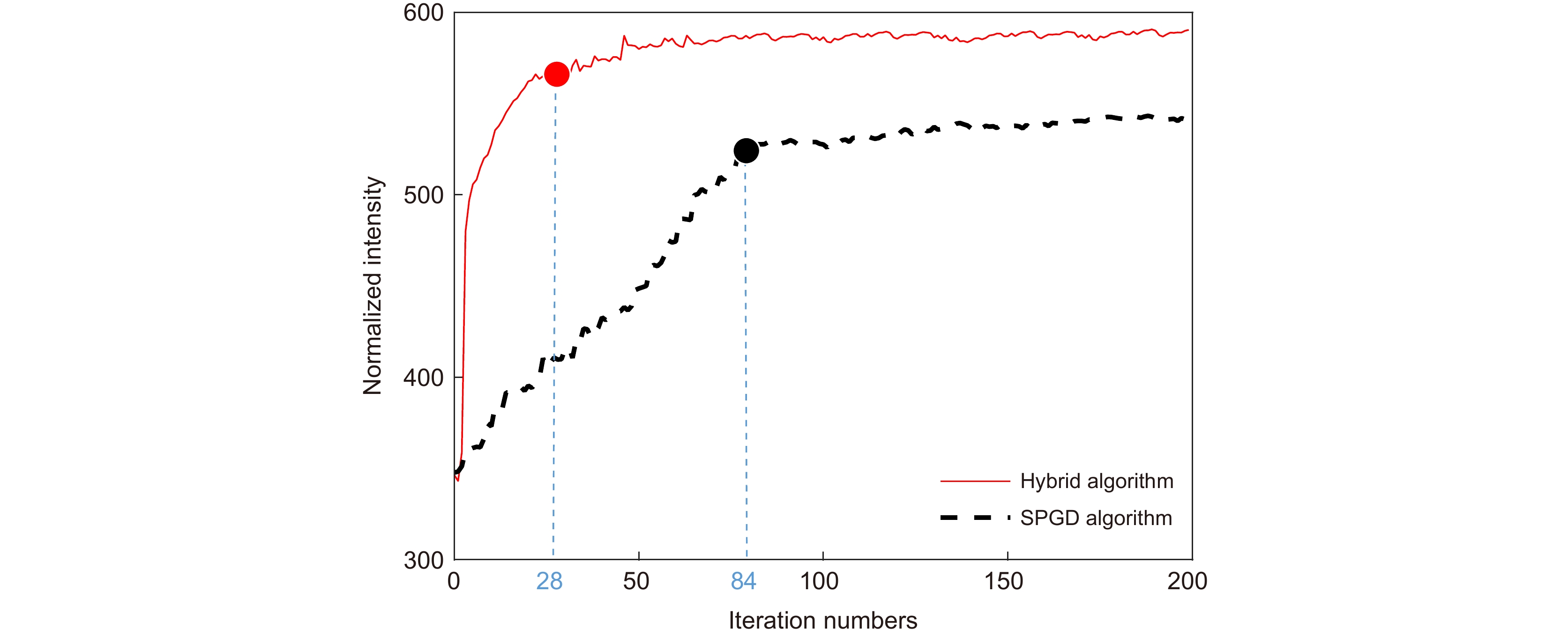
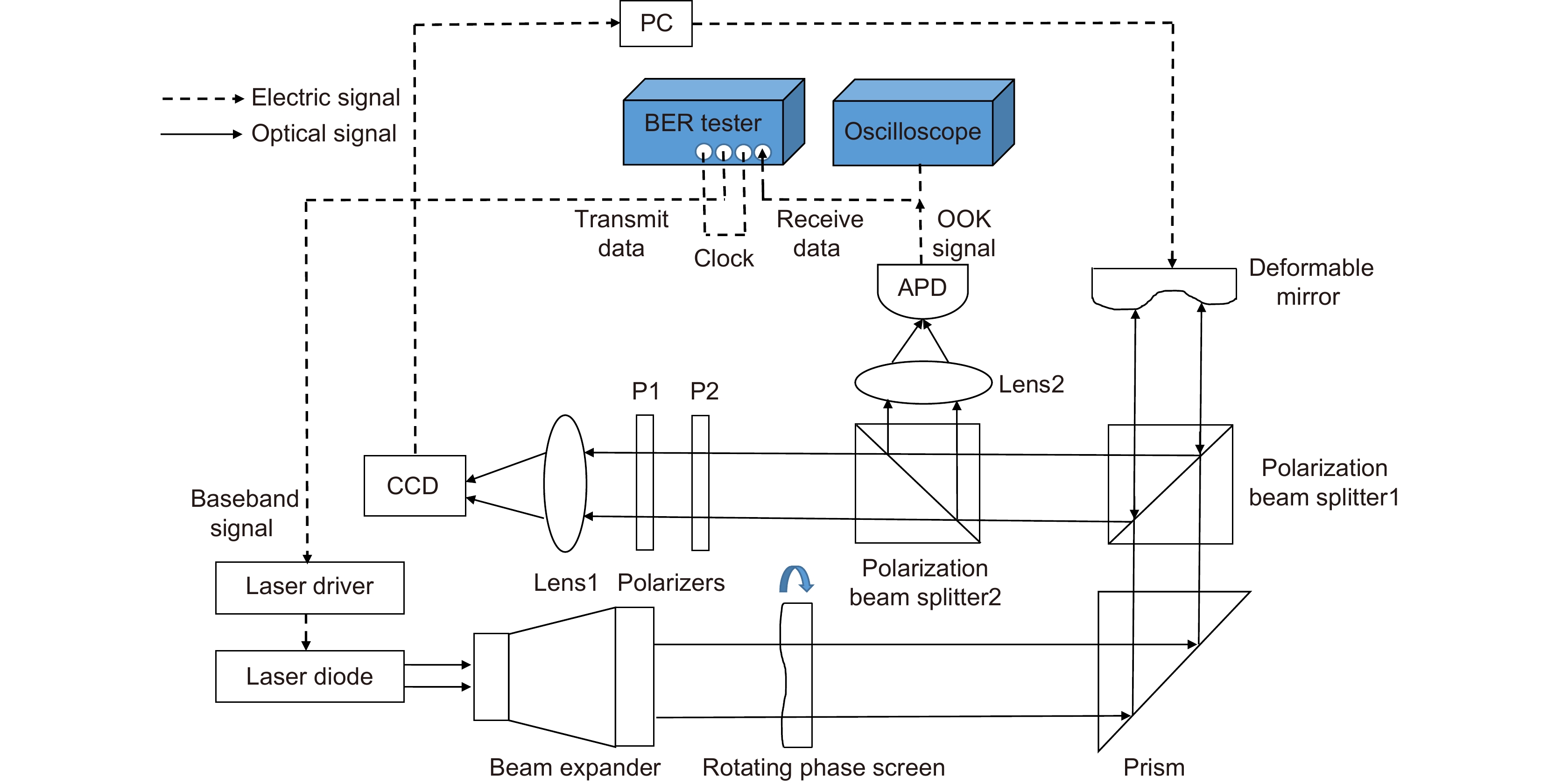
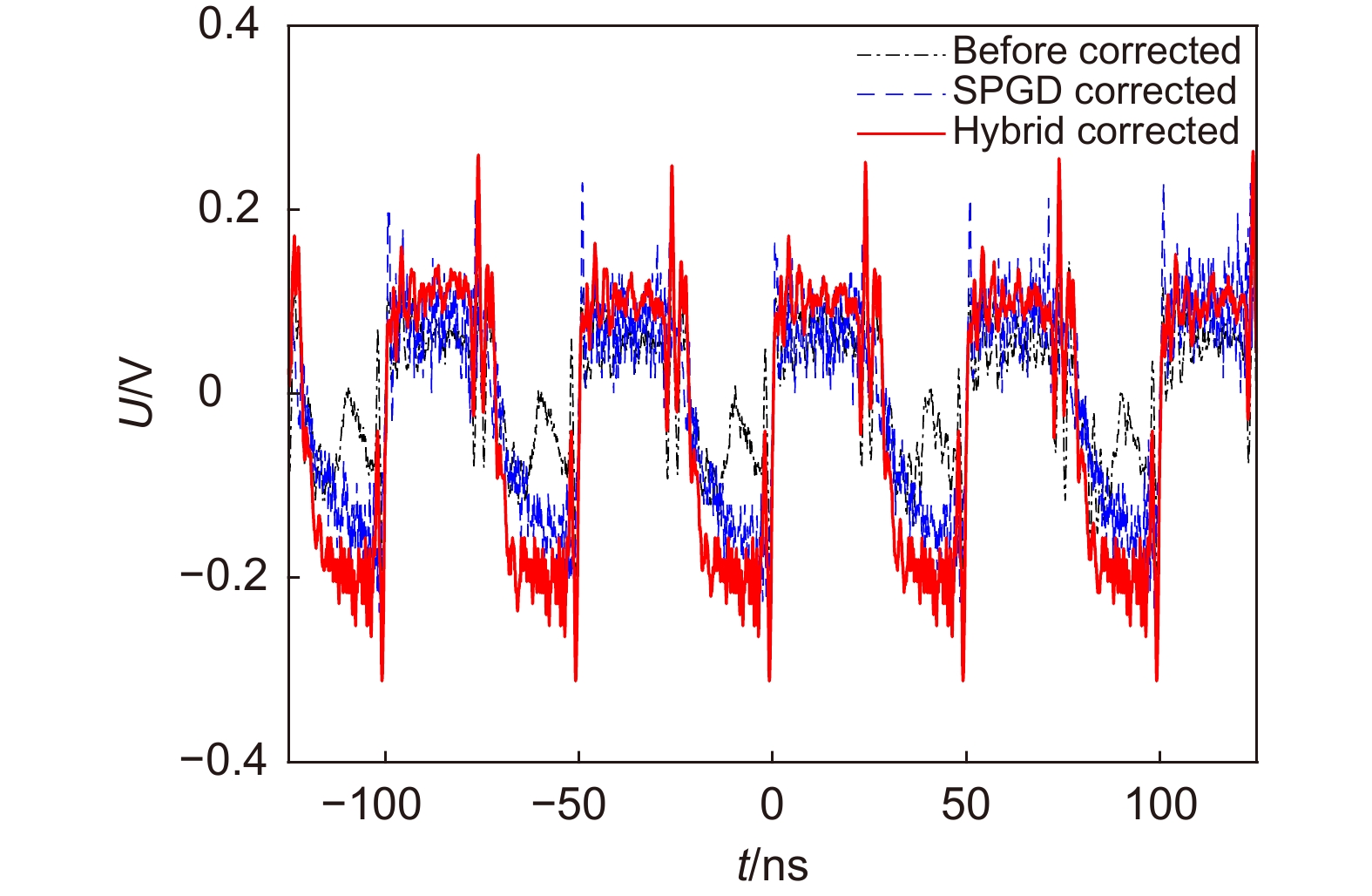
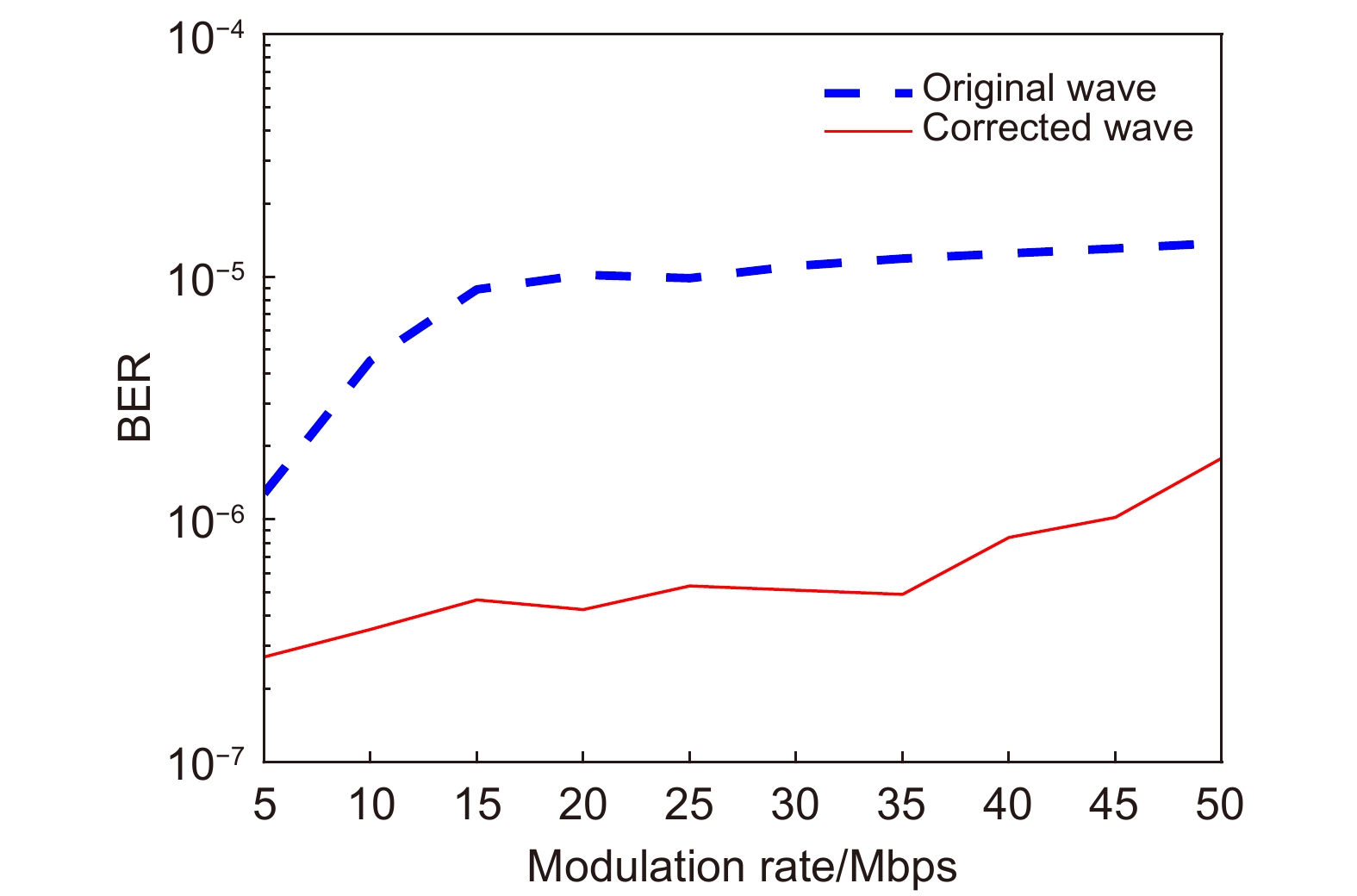
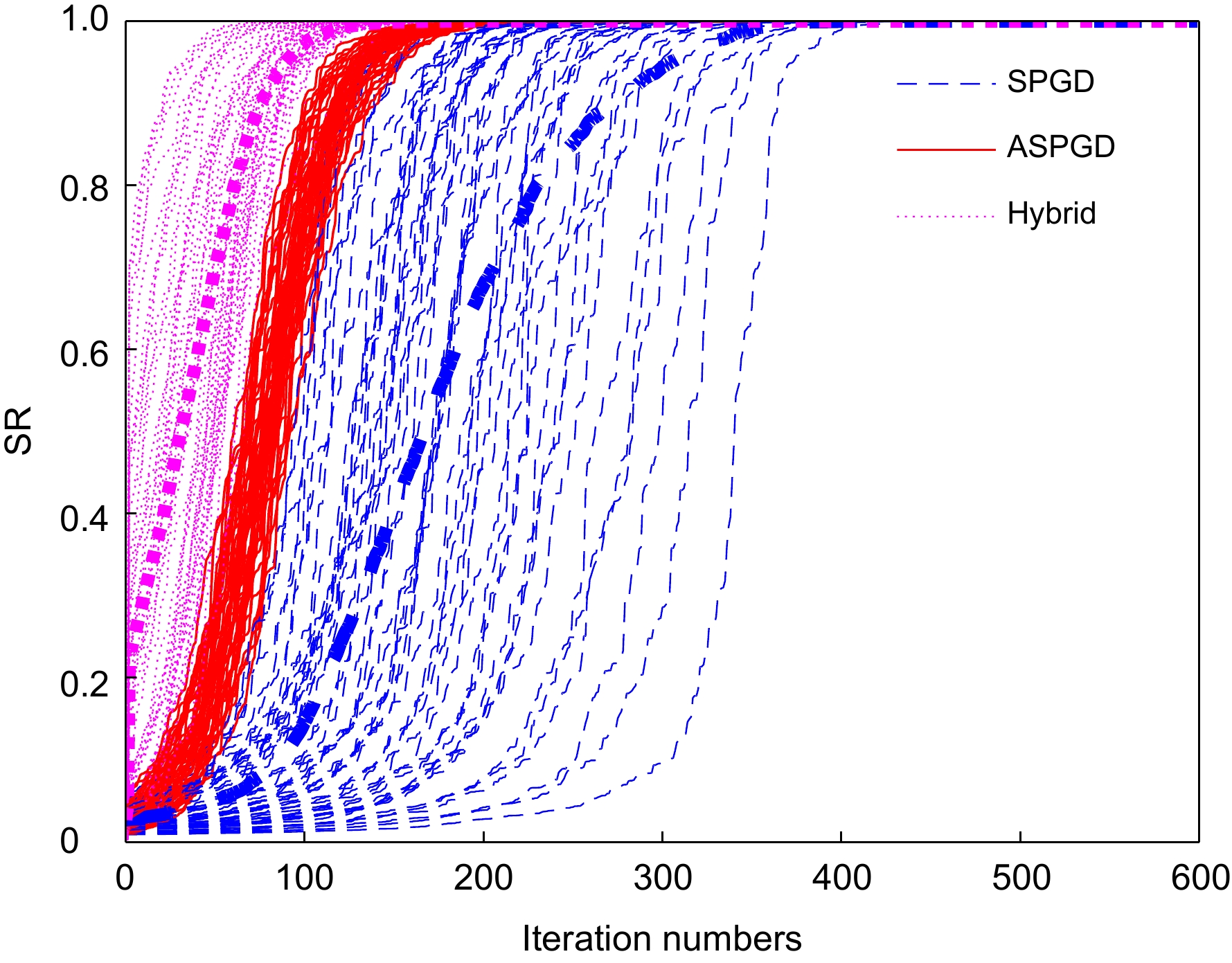
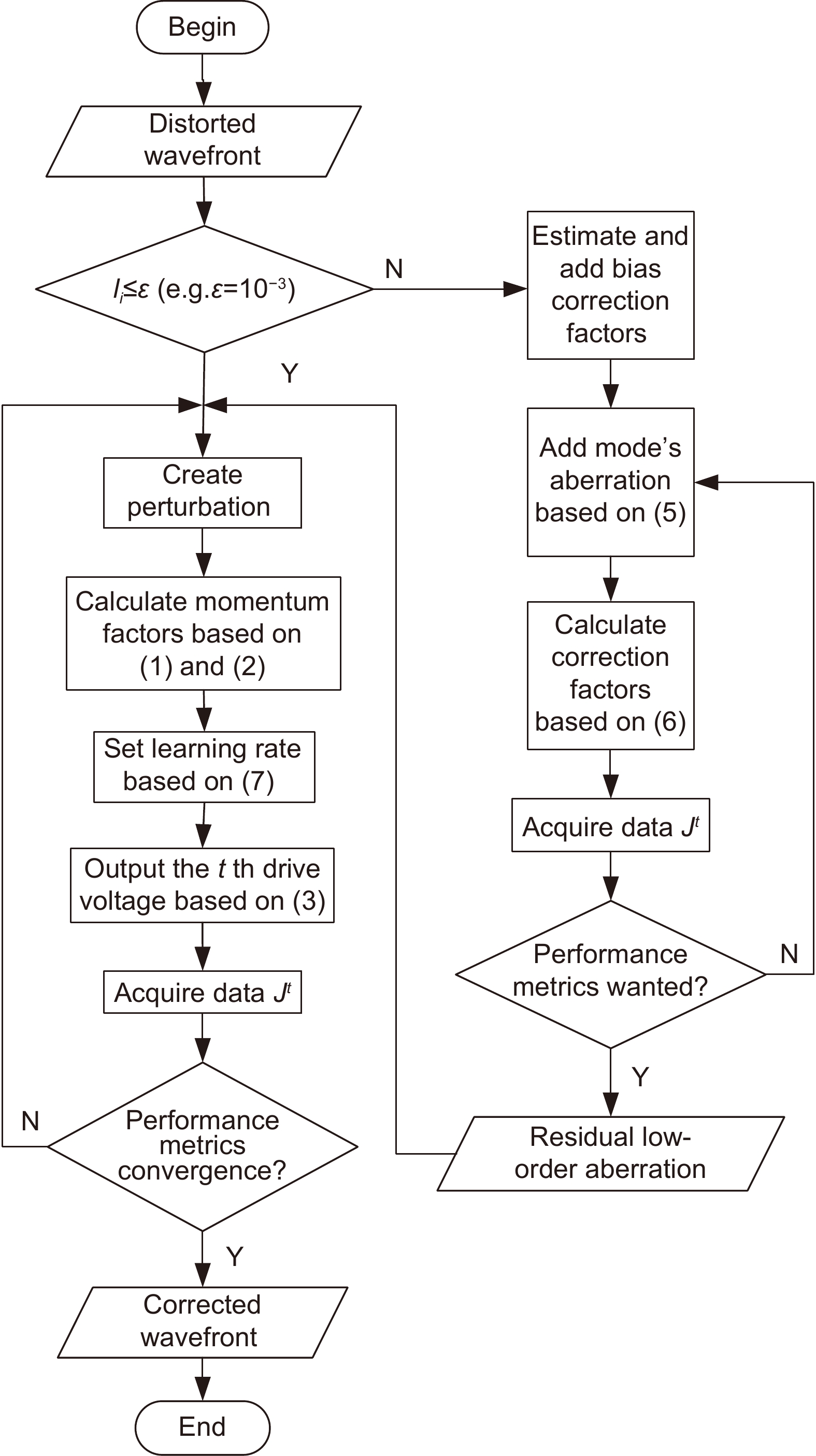
应用Lukosz预校正模型算法可以校正波前畸变的低阶像差,缩小迭代算法的搜寻范围;应用自适应余弦衰减的随机并行梯度下降(AcSPGD)算法可以补偿波前畸变的高阶像差,提升迭代算法的校正精度。本文提出了一种基于预校正模型和AcSPGD算法的混合模型算法,并将其应用于无波前传感自适应光学系统中校正湍流大气产生的畸变波前,最后搭建实验光路验证了算法的有效性。结果表明,混合模型算法的校正速率是常用的随机并行梯度下降(SPGD)算法的3倍,且校正精度比传统的Lukosz模型算法更高,应用于无波前传感自适应光学系统中有效减小了光场波前的相位起伏,提高了远场光斑斯特列尔比(SR),使自由空间光通信(FSO)系统的通信性能得到有效提升。
-
关键词:
- 自由空间光通信 /
- 无波前传感自适应光学 /
- 随机并行梯度下降算法 /
- Lukosz模型
Abstract
The Lukosz pre-correction modal algorithm can correct low-order aberrations of wavefront distortion and narrow the search range of iterative algorithms. The adaptive cosine-decay stochastic parallel gradient descent (AcSPGD) algorithm can compensate for high-order aberrations of wavefront distortion and improve the correction accuracy of iterative algorithms. In this paper, a new hybrid modal algorithm based on the pre-correction model and AcSPGD algorithm is applied to correct wavefront distortion in wavefront sensorless adaptive optics, and the feasibility of the optimization algorithm is also verified by the experiments. Experimental results show that the correction speed of the hybrid modal algorithm is two times faster than the commonly used stochastic parallel gradient descent (SPGD) algorithm, and the correction accuracy of the hybrid modal algorithm is better than the traditional Lukosz modal algorithm. Applied to wavefront sensorless adaptive optics, the optimization algorithm effectively reduces the phase fluctuation of the wavefront and improves the far-field Strehl ratio (SR), thus improving the communication performance of the free-space optical communication (FSO) system.
-
Overview
Overview: With the advent of the 5G era, the general demand for big data processing makes the stable transmission of high-speed and high-capacity links more and more important. However, when the laser is transmitted in the atmosphere, natural phenomena such as air flow, temperature change, rain, fog, and snow will seriously undermine the stability and reliability of atmospheric link transmission. Among all proposed methods of compensating for atmospheric turbulence effects, the wavefront sensorless adaptive optics becomes the most effective technology to correct wavefront distortion caused by atmospheric turbulence, which can improve communication performances when applied in atmospheric laser communications. The final correction results of wavefront sensorless adaptive optics are often determined by different optimization algorithms which can be divided into model-free optimization algorithms and model-based optimization algorithms. However, both types of algorithms have certain limitations. The iterations of the model-free algorithms are so numerous that the convergence rate is very slow. The model-based algorithms have great correction speed, but can only correct low-order aberrations of wavefront distortion, so they are too easy to fall into local convergence and their correction accuracy is very low. Therefore, a critical technical problem of free-space optical communications is how to improve the convergence rate and correction accuracy of the iterative algorithms at the same time.
The Lukosz pre-correction modal algorithm can correct low-order aberrations of wavefront distortion and narrow the search range of iterative algorithms. The adaptive cosine-decay stochastic parallel gradient descent (AcSPGD) algorithm can compensate for high-order aberrations of wavefront distortion and improve the correction accuracy of iterative algorithms. In this paper, a new hybrid modal algorithm based on the pre-correction model and AcSPGD algorithm is applied to correct wavefront distortion in wavefront sensorless adaptive optics, and the feasibility of the optimization algorithm is also verified by the experiments. Experimental results show that the correction speed of the hybrid modal algorithm is two times faster than the commonly used stochastic parallel gradient descent (SPGD) algorithm, and the correction accuracy of the hybrid modal algorithm is better than the traditional Lukosz modal algorithm. Applied to wavefront sensorless adaptive optics, the optimization algorithm effectively reduces the phase fluctuation of the wavefront and improves the far-field Strehl ratio, which thus improves the signal-to-noise ratio of the atmospheric laser communication system by 2.9 dB, reduces the bit error rate to 10−6, and improves the communication performance of the free-space optical communication system. The hybrid modal algorithm has great reference and application value.
-

-
表 1 湍流大气传输数值仿真参数列表
Table 1. System parameter settings in the simulation
Parameters Values Distance/km
Wavelength/m2
1550×10−9Beam waist/m 2×10−2 Sampling number 256 -
参考文献
[1] Zhou Z Y, Zhou X X, Yuan X H, et al. Research on characteristics of Bessel-Gaussian Schell-model beam in weak turbulence[J]. Opt Commun, 2020, 474: 126074. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2020.126074
[2] Li Q, Yuan X H. Experimental study on compensation of beam distortion caused by turbulence using a phase conjugate beam[J]. J Mod Opt, 2021, 68(11): 573−578. doi: 10.1080/09500340.2021.1936242
[3] Zhou X X, Zhou Z Y, Yuan X H. Research on performance of convex partially coherent flat-topped beams in vertical atmospheric turbulent paths[J]. Opt Commun, 2021, 482: 126577. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2020.126577
[4] 王铭淏, 元秀华, 李军, 等. 径向部分相干光束在各向异性非Kolmogorov湍流中的传输[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(3): 279−289. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0306003
Wang M H, Yuan X H, Li J, et al. Propagation of radial partially coherent beams in anisotropic non-Kolmogorov turbulence[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2018, 38(3): 279−289. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0306003
[5] 李军, 罗江华, 元秀华. 水表面波扰动对无线光通信影响[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41(7): 47−54. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.0706005
Li J, Luo J H, Yuan X H. Influence of water surface wave disturbance on wireless optical communication[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2021, 41(7): 47−54. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.0706005
[6] Guo Y M, Zhong L B, Min L, et al. Adaptive optics based on machine learning: a review[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2022, 5(7): 200082. doi: 10.29026/oea.2022.200082
[7] 周鑫, 李新阳. 基于运动估计的波前畸变预测方法研究[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(10): 210288. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.210288
Zhou X, Li X Y. Wavefront distortion prediction method based on motion estimation[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2021, 48(10): 210288. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.210288
[8] 郭庭, 张彬, 顾乃庭, 等. 偏振哈特曼波前探测技术研究[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(7): 210076. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.210076
Guo T, Zhang B, Gu N T, et al. Research on polarization Hartmann wavefront detection technology[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2021, 48(7): 210076. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.210076
[9] 张利宏, 沈锋, 兰斌. 涡旋光束轨道角动量在大气湍流传输下的特性分析[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(4): 190272. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190272
Zhang L H, Shen F, Lan B. Characteristic analysis of orbital angular momentum of vortex beam propagating in atmospheric turbulent[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(4): 190272. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190272
[10] 郭倩, 宋鹏, 张周强, 等. 基于OFDM的大气激光通信湍流抑制关键技术研究[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(3): 190619. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190619
Guo Q, Song P, Zhang Z Q, et al. Research on the key technology of turbulence suppression for atmospheric optical laser communication based on OFDM[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(3): 190619. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190619
[11] 牛超君, 于诗杰, 韩香娥. 无波前探测自适应光学对光通信性能影响分析[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2015, 52(8): 080102. doi: 10.3788/LOP52.080102
Niu C J, Yu S J, Han X E. Analysis about effect of wavefront sensorless adaptive optics on optical communication[J]. Laser Optoelectron Prog, 2015, 52(8): 080102. doi: 10.3788/LOP52.080102
[12] Gu H J, Gu J J, Liu W, et al. Model-free correction algorithm for wireless power transmission with adaptive optics system[J]. Optik, 2018, 172: 368−382. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.06.098
[13] Yang K X, Abulizi M, Li Y H, et al. Single-mode fiber coupling with a M-SPGD algorithm for long-range quantum communications[J]. Opt Express, 2020, 28(24): 36600−36610. doi: 10.1364/OE.411939
[14] Hu Q T, Zhen L L, Mao Y, et al. Adaptive stochastic parallel gradient descent approach for efficient fiber coupling[J]. Opt Express, 2020, 28(9): 13141−13154. doi: 10.1364/OE.390762
[15] Yue D, Nie H T, Li Y, et al. Fast correction approach for wavefront sensorless adaptive optics based on a linear phase diversity technique[J]. Appl Opt, 2018, 57(7): 1650−1656. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.001650
[16] He X, Zhao X H, Cui S Y, et al. A rapid hybrid wave front correction algorithm for sensor-less adaptive optics in free space optical communication[J]. Opt Commun, 2018, 429: 127−137. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.08.008
[17] Cui S Y, Zhao X H, He X, et al. A quick hybrid atmospheric-interference compensation method in a WFS-less free-space optical communication system[J]. Curr Opt Photon, 2018, 2(6): 612−622.
[18] Ren H X, Dong B. Improved model-based wavefront sensorless adaptive optics for extended objects using N + 2 images[J]. Opt Express, 2020, 28(10): 14414−14427. doi: 10.1364/OE.387913
[19] Gu H J, Liu M Q, Liu H Y, et al. An algorithm combining convolutional neural networks with SPGD for SLAO in FSOC[J]. Opt Commun, 2020, 475: 126243. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2020.126243
[20] Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, 2015.
[21] Braat J. Polynomial expansion of severely aberrated wave fronts[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 1987, 4(4): 643−650. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.4.000643
[22] Débarre D, Booth M J, Wilson T. Image based adaptive optics through optimisation of low spatial frequencies[J]. Opt Express, 2007, 15(13): 8176−8190. doi: 10.1364/oe.15.008176
[23] Dong B, Yu J. Hybrid approach used for extended image-based wavefront sensor-less adaptive optics[J]. Chin Opt Lett, 2015, 13(4): 041101. doi: 10.3788/COL201513.041101
[24] Booth M J. Wave front sensor-less adaptive optics: a model-based approach using sphere packings[J]. Opt Express, 2006, 14(4): 1339−1352. doi: 10.1364/oe.14.001339
[25] Loshchilov I, Hutter F. SGDR: stochastic gradient descent with warm restarts[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2017.
[26] Facomprez A, Beaurepaire E, Débarre D. Accuracy of correction in modal sensorless adaptive optics[J]. Opt Express, 2012, 20(3): 2598−2612. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.002598
[27] Liu J, Zhao W S, Liu C G, et al. Accurate aberration correction in confocal microscopy based on modal sensorless method[J]. Rev Sci Instrum, 2019, 90(5): 053703. doi: 10.1063/1.5088102
[28] Fleck J A Jr, Morris J R, Feit M D. Time-dependent propagation of high energy laser beams through the atmosphere[J]. Appl Phys, 1976, 10(2): 129−160. doi: 10.1007/BF00896333
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: