-
摘要
对实时彩色三维动态显示的追求激发了学术界和产业界巨大的研究热情。随着“元宇宙”概念的提出,对高性能三维显示设备与技术的需求越发迫切。全息术是一种理想的三维显示方案,但传统光场调控器件却存在视场角狭窄、信息容量小等问题,阻碍了全息技术的进一步发展。而超表面作为一种新型光场调控器件,有望利用其像素尺寸小和光场调控能力强的特点在全息技术领域实现新的突破。本文主要从超表面全息器件的设计流程、调制方式、动态实现、制造技术四个方面给出了超表面全息十余年的概貌,并提出该领域未来发展的方向。
Abstract
The pursuit of real-time, full-color, three-dimension (3D), and dynamic display has inspired a rich body of industrial and academic research. With the introduction of "Metaverse", there is an increasing demand for high-performance 3D display devices and technologies. Holographic technology is an ideal approach for future naked-eye 3D display. However, traditional dynamic holographic devices have brought many shortcomings such as small field of view (FOV) and limited information capacity, which hinder the practical applications. As a new class of light field modulator, metasurface is expected to achieve remarkable breakthroughs in the field of holographic display with the advantages of their small pixel size and the emerging ability to manipulate light. This paper gives an overview of the development of meta-holography from four aspects: the design strategy, the modulation principle, the methods for realizing dynamic display and the micro-nano fabrication technologies for optical metasurface. We finally include a brief discussion of the future direction in this field.
-
Overview
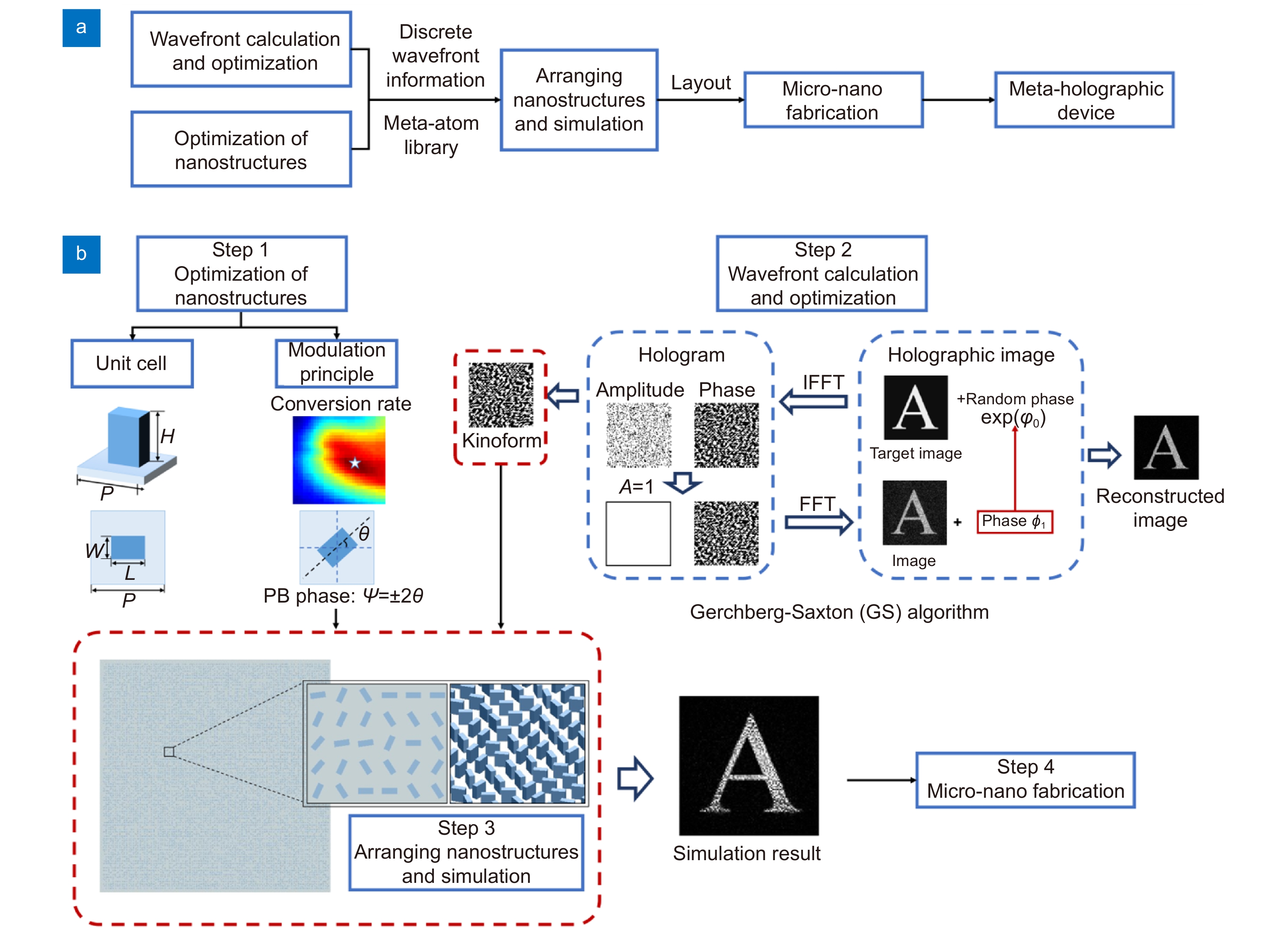
Overview: As an ideal 3D display technology, holography can reconstruct the wavefront of the whole light wave, and can provide all the 3D depth cues required by the human eyes, including binocular parallax, motion parallax, accommodation, occlusion, etc. Due to the limitation of the modulation principle, DMD and most SLM cannot optically reconstruct the complex amplitude of a wavefield, resulting in partial information loss and complex wavefront calculation. At the same time, the two devices have a pixel size larger than 6 μm, which is much larger than the wavelength of visible light. The limitation of large pixel size and modulation principle brings many disadvantages, such as narrow field of view, twin-image, narrow band, and multi-order diffraction, which greatly restrict the development of CGH. As a new class of light field modulators, metasurface can control the amplitude, phase, polarization and dispersion of the light simultaneously by optimizing the design and arrangement of the elements. Thanks to the previous exploration of micro-nano manufacturing technology and materials for metasurface, the size of the unit cell can be reduced to the order of sub-wavelength. According to the grating equation, the smaller the pixel size is, the larger the diffraction angle is. Therefore, metasurface can provide a diffraction angle close to 90°. As the loading medium of holograms, metasurface meets the requirements of holograms for high-precision and complex light field modulation and has the advantages of high design freedom, high spatial resolution, low noise, broadband and so on, providing a solution to some problems currently faced by CGH. In this paper, the basic process of designing meta-holography devices is discussed. Furthermore, the basic concepts and development of static meta-holography are introduced based on the principles of metasurfaces, including phase modulation, amplitude modulation, complex-amplitude modulation, and nonlinear modulation. However, such static meta-holography devices cannot change the display patterns after design and manufacture, which is inconsistent with the rapidly changing real world and requirements of diverse functions, limiting its applications. Therefore, the two methods of realizing dynamic meta-holography are introduced in detail. Finally, the micro-nano fabrication technologies for metasurface are discussed. In conclusion, this paper presents the design, principle, development, and manufacturing implementation of meta-holographic devices in an all-around way, and puts forward problems and possible solutions for the development of meta-holography at present.
-

-
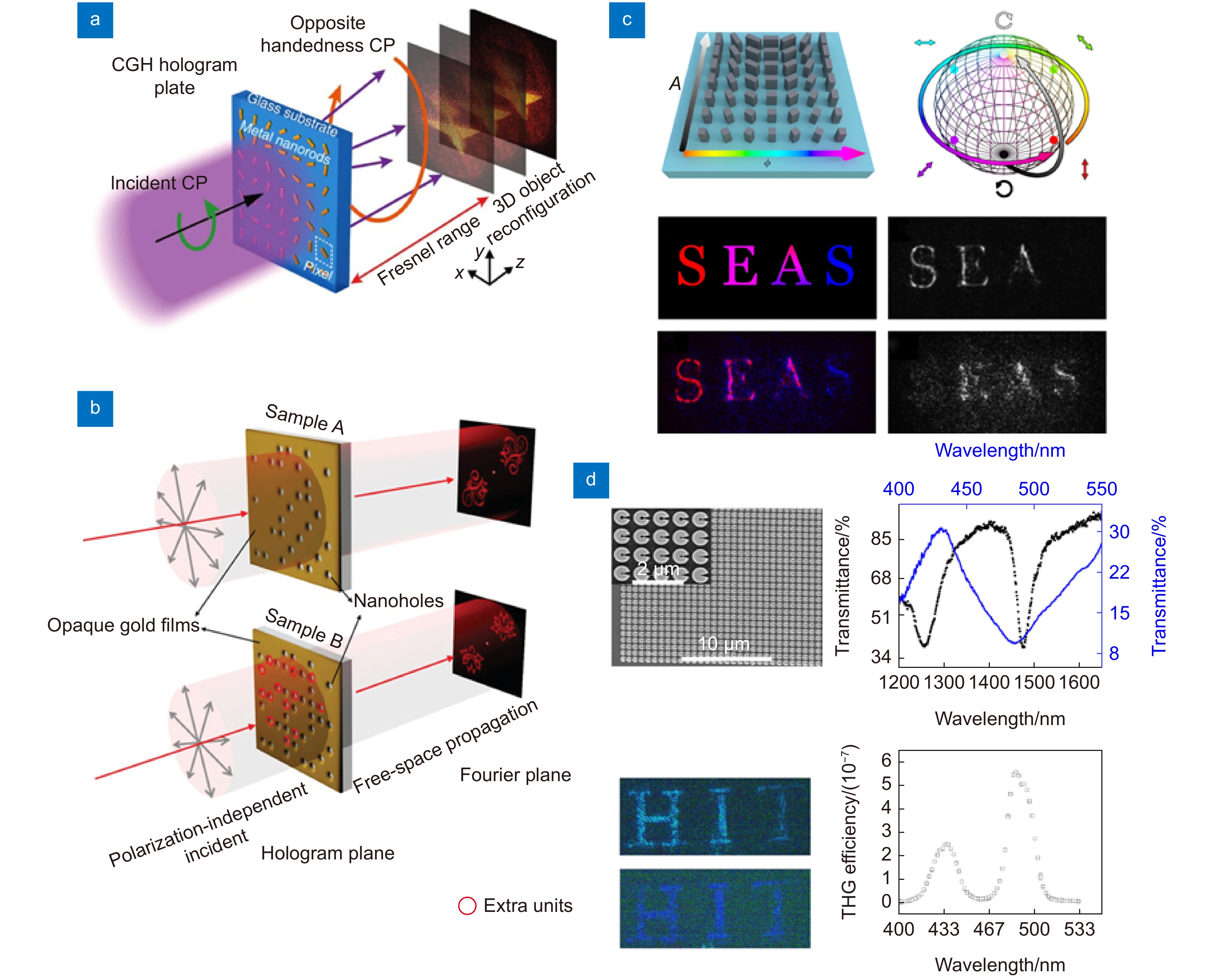
图 2 静态超表面全息。(a) 基于金纳米天线的几何相位调制3D轴上透射式全息图[32];(b) 两个具有集合关系的纳米筛振幅调制全息图[40];(c) 通过调整单元结构的取向角和几何参数来实现复振幅调制,分别重建了波长1.65 μm和0.94 μm入射下的全息图像[42];(d) 基于C形Si纳米天线的THG非线性调制青色和蓝色全息图[43]
Figure 2. Static meta-holography. (a) PB phase-modulated 3D on-axis transmission holograms based on gold nanoantennas[32]; (b) Two amplitude-modulated holograms of photon sieves with set relation[40]; (c) Complex amplitude modulation is achieved by adjusting the orientation angle and geometric parameters of the cell structure, and the holographic images at the wavelengths of 1.65 μm and 0.94 μm are reconstructed respectively[42]; (d) THG nonlinear modulated cyan and blue holograms based on C-shaped Si nanoantennas[43]
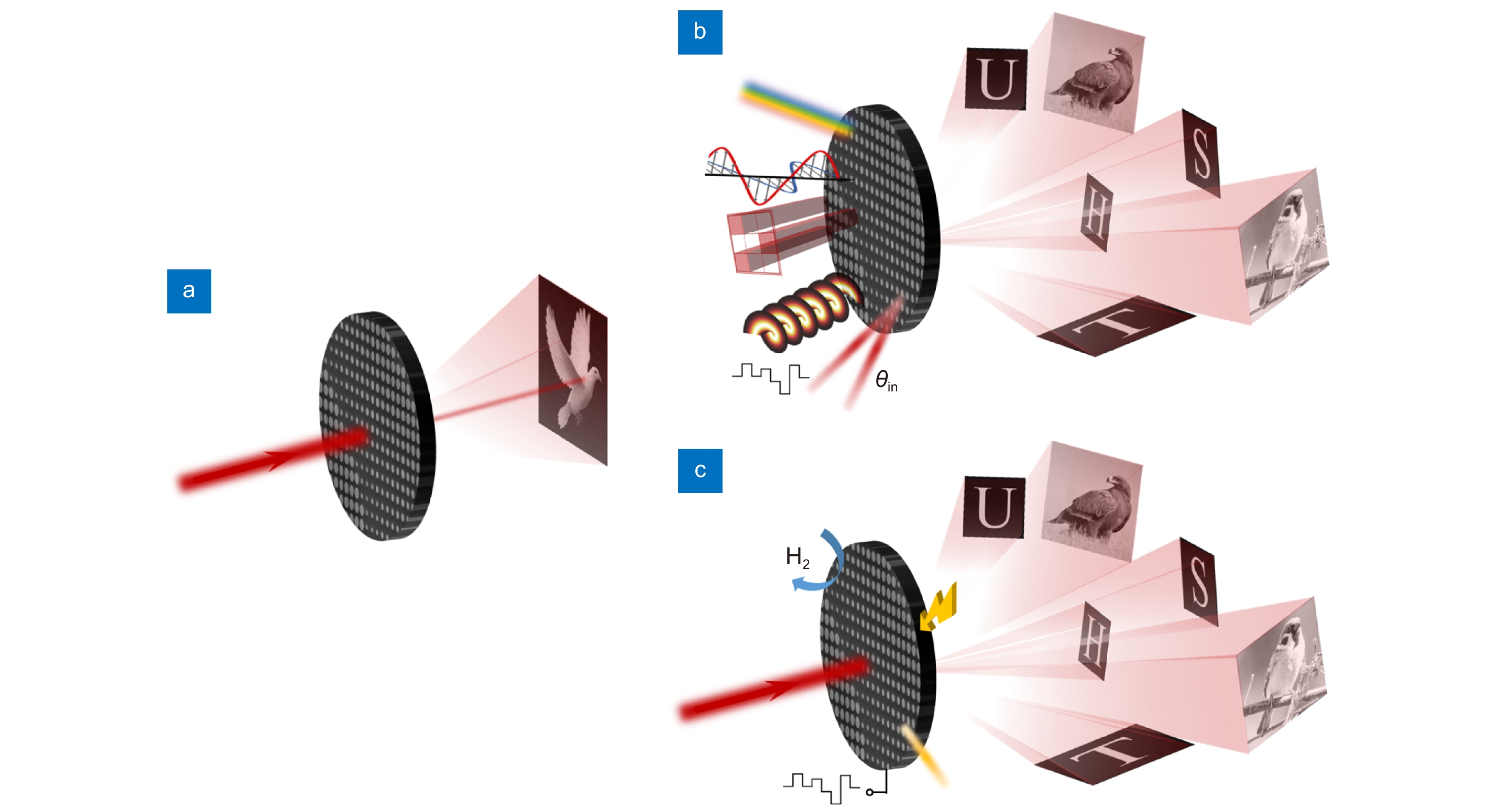
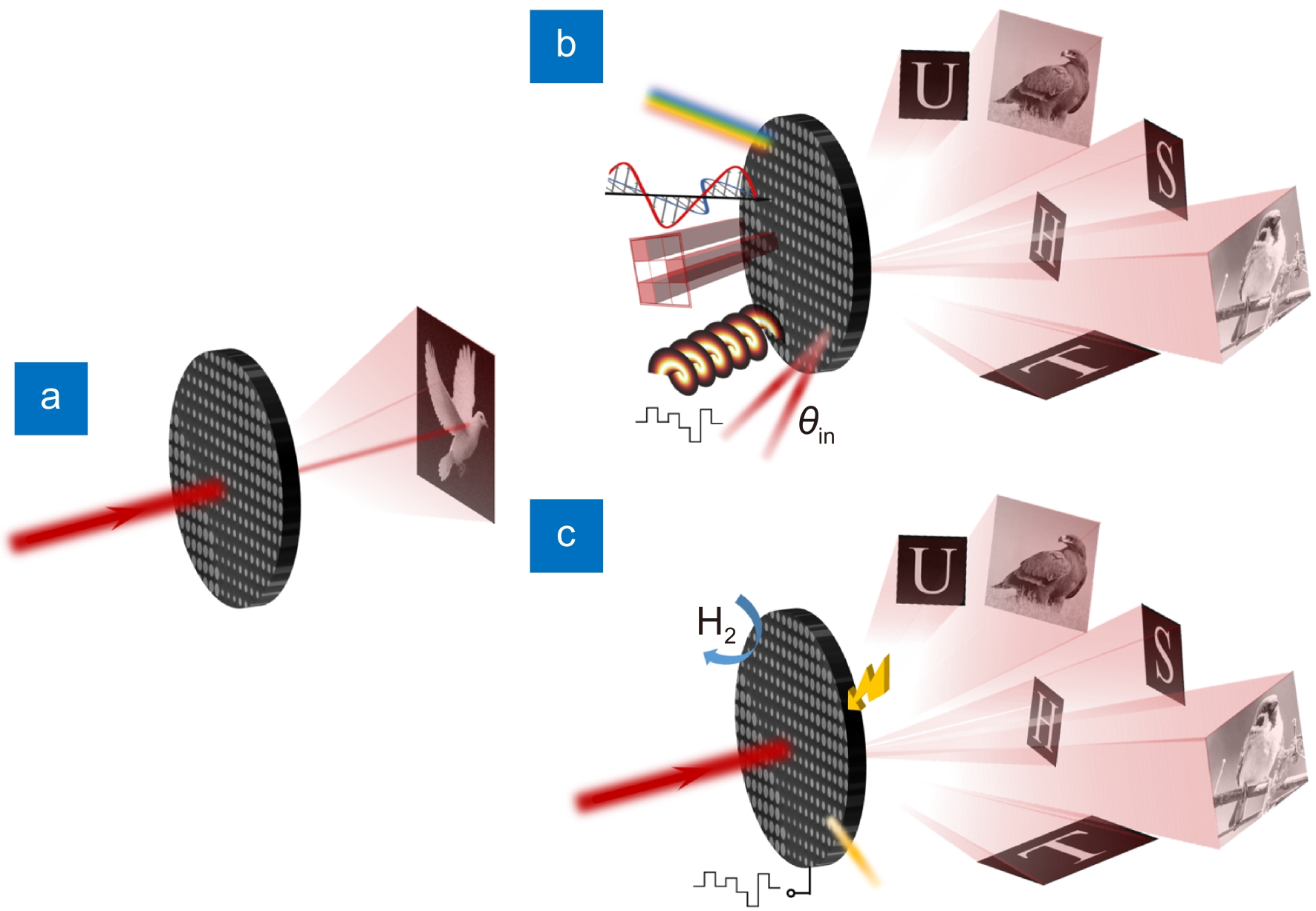
图 3 超表面全息技术示意图。(a) 静态超表面全息器件;(b) 多路复用超表面全息器件,通过改变前端入射光的光参量可以实现动态显示;(c) 主动式超表面全息器件,超表面器件本身可以响应光电热化学等刺激而产生变化
Figure 3. Schematic of meta-holography. (a) Static meta-holography; (b) Multiplexed meta-holography, which means dynamic display can be realized by controlling the fundamental properties of incident light; (c) Active meta-holography, which means metasurface itself can be changed in response to optical, electrical, thermal, or chemical stimuli
图 4 波长复用的超表面全息器件用于彩色全息的不同实现方法。(a) 空间交错排列型[64];(b) 多层设计及改进的GS算法[68];(c) 色散调控[70];(d) 结合角度复用技术[73]
Figure 4. Different methods for wavelength-multiplexed meta-holography to realize color holography. (a) Spatially staggered arrangement[64]; (b) Multilayer design and adjusted GS algorithm[68]; (c) Dispersion phase-based metasurface[70]; (d) Combined with angle multiplexing technology[73]
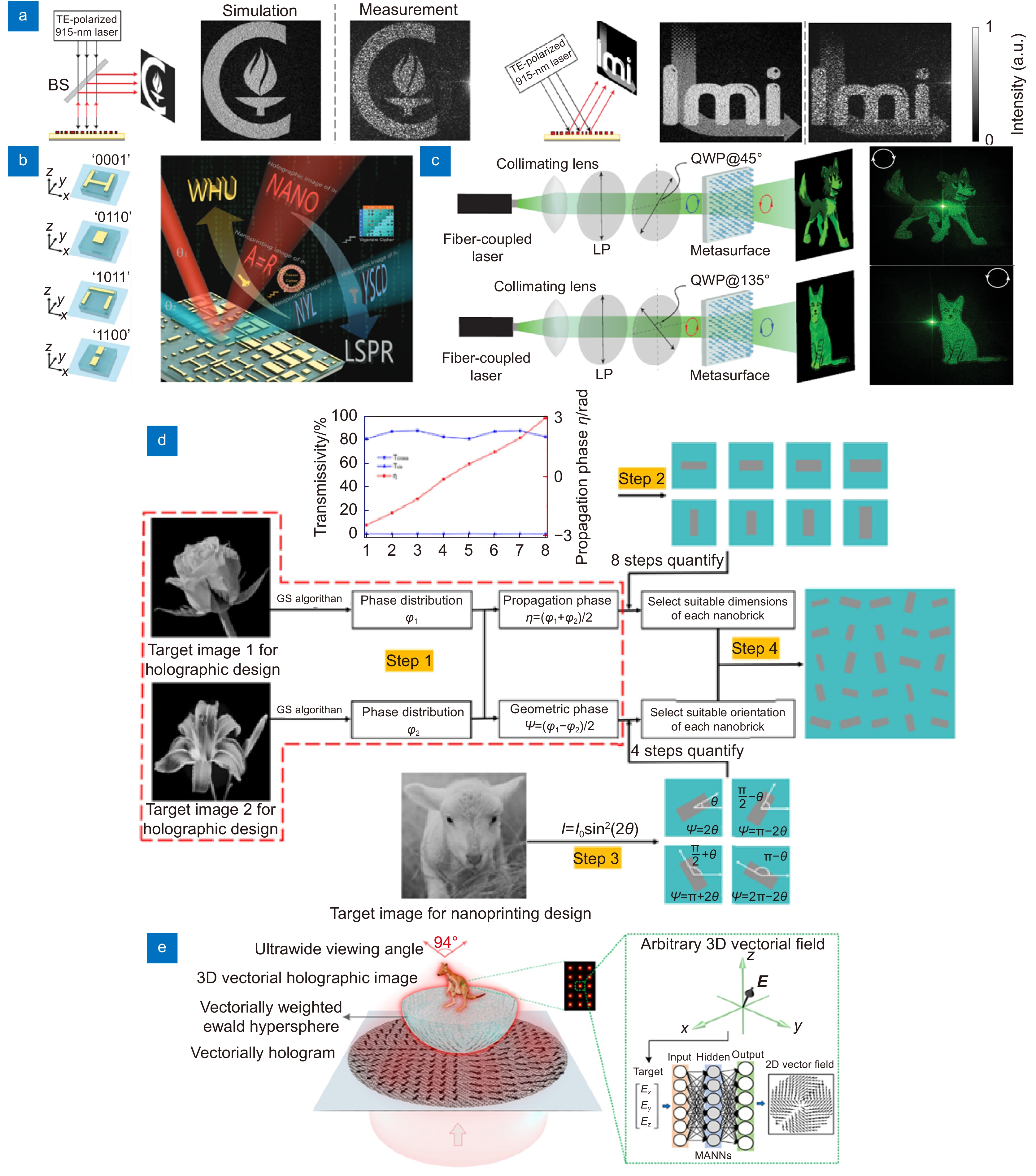
图 5 角度复用和偏振复用型超表面全息术。(a) 角度复用型超表面全息器件,可以分别在0°和30°入射角情况下显示不同的全息图案[77];(b) 结合纳米打印设计,可以实现四种不同图像的显示[80];(c) 利用传输相位结合几何相位实现左右旋圆偏振复用的设计方案[86];(d) 同时在近场记录一幅连续的灰度纳米打印图像并在远场投影两幅独立的全息像[87];(e) 利用机器学习逆向设计实现以超大视场角(94°)和高衍射效率(78%)重建三维的矢量全息图像[92]
Figure 5. Angle multiplexed and polarization multiplexed meta-holography. (a) Angle-multiplexed meta-holography, which can display different images at 0° and 30° incident angles, respectively[77]; (b) Combined with nanoprinting and four different images can be projected[80]; (c) Combine the propagation phase with the geometric phase to realize the multiplexing of LCP and RCP[86]; (d) Simultaneously record a continuous grayscale nanoprinting image in the near field and project two independent holographic images in the far field[87]; (e) Three-dimensional vectorial holography with a large field of view (94°) and high diffraction efficiency (78%) based on machine learning inverse design[92]
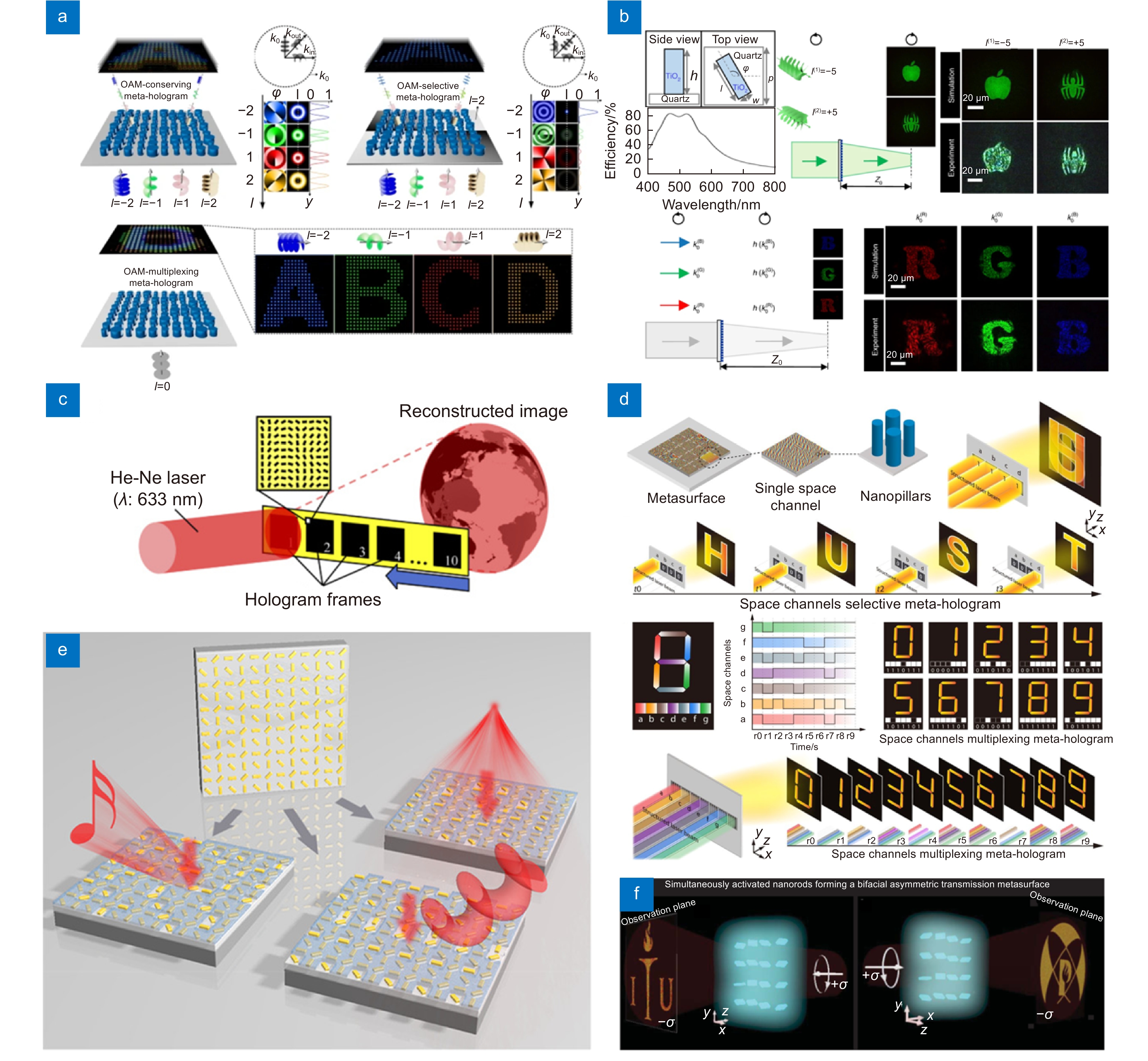
图 6 OAM复用、空间复用和非互易超表面全息术。(a) 离散空间频率分布的OAM复用超表面全息器件设计[98];(b) 可见光波段多动量介质超表面转换器[100],比例尺:20 μm;(c) 空间复用型超表面器件,以类似电影放映的方式实现动态全息视频显示[101];(d) 空间复用型超表面器件,可实现电影放映式动态全息显示或者结合结构光实现228个不同的帧显示[102];(e) 利用模板实现的空间信道选择超表面器件[104];(f) 非互易型超表面全息器件[108]
Figure 6. OAM multiplexed, space channel multiplexed and nonreciprocal meta-holography. (a) OAM-multiplexed meta-holography with discrete spatial frequency distribution[98]; (b) Dielectric multi-momentum meta-transformer in the visible[100], scale bar: 20 μm; (c) Space channel multiplexed metasurface, which can realize dynamic holographic video display in a way similar to cinematography[101]; (d) Space channel multiplexed metasurface, which can realize cinematography-inspired dynamic holographic display and display 228 different frames with structured laser beam[102]; (e) Space channel selecting metasurface realized by a template[104]; (f) Nonreciprocal meta-holographic device[108]
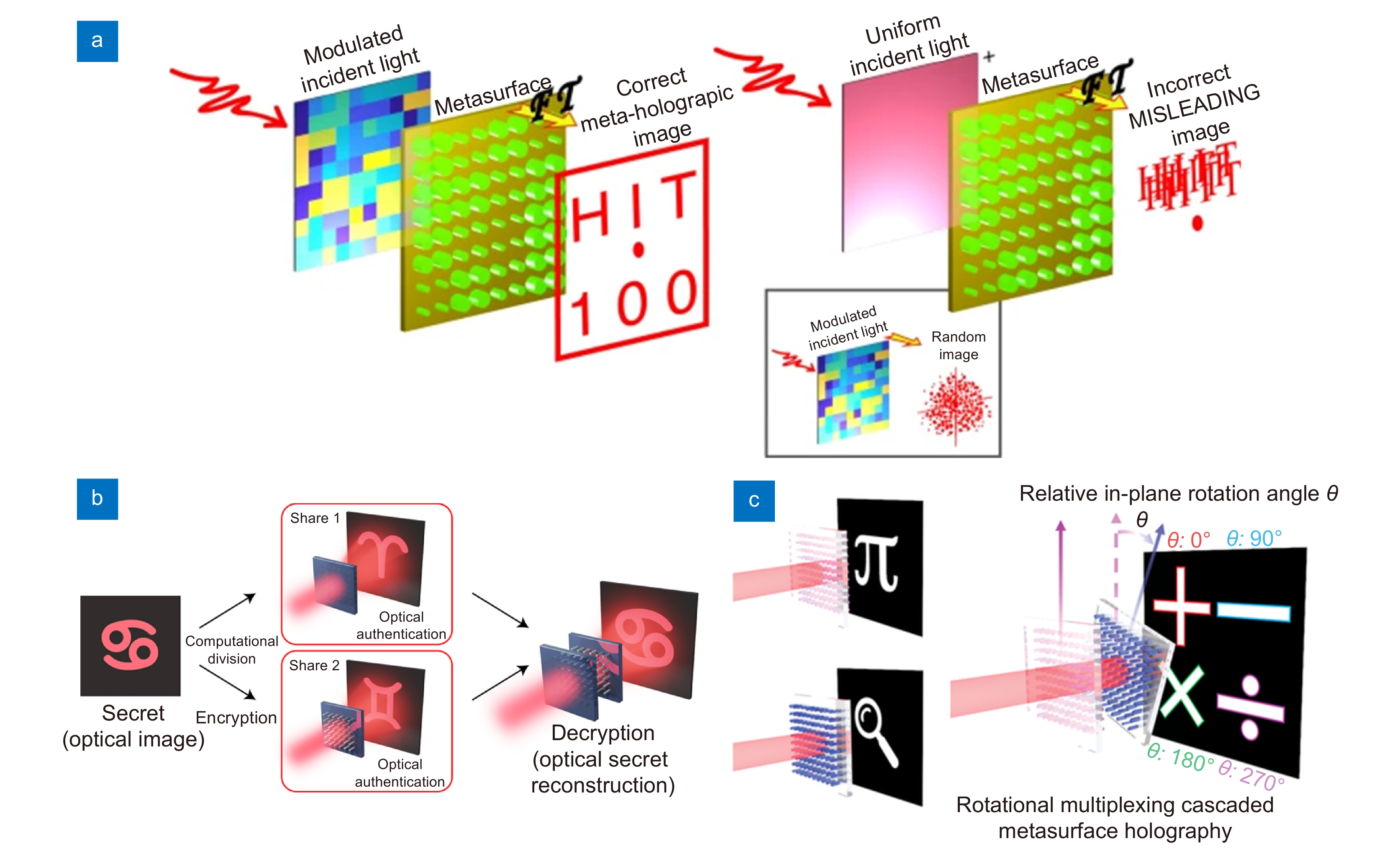
图 7 衍射光场复用型超表面全息器件。(a) 衍射光场复用型全息器件,可以通过利用空间光调制器改变入射光场实现动态显示[110];(b) 级联超表面,可以在单层或多层叠加的情况下显示不同的全息图像[111];(c) 利用两个级联超表面的面内旋转,引入旋转复用的概念,从而展示不同的图像[112]
Figure 7. Diffracted light field multiplexed meta-holography. (a) Diffracted light field multiplexed meta-holography, which can realize dynamic display by changing the incident light field with spatial light modulators[110]; (b) Cascaded metasurface, which can display different holographic images in the mood of single-layer or multi-layer[111]; (c) Use the in-plane rotation between two cascaded metasurface to introduce the concept of the rotational multiplexing method and display different images[112]
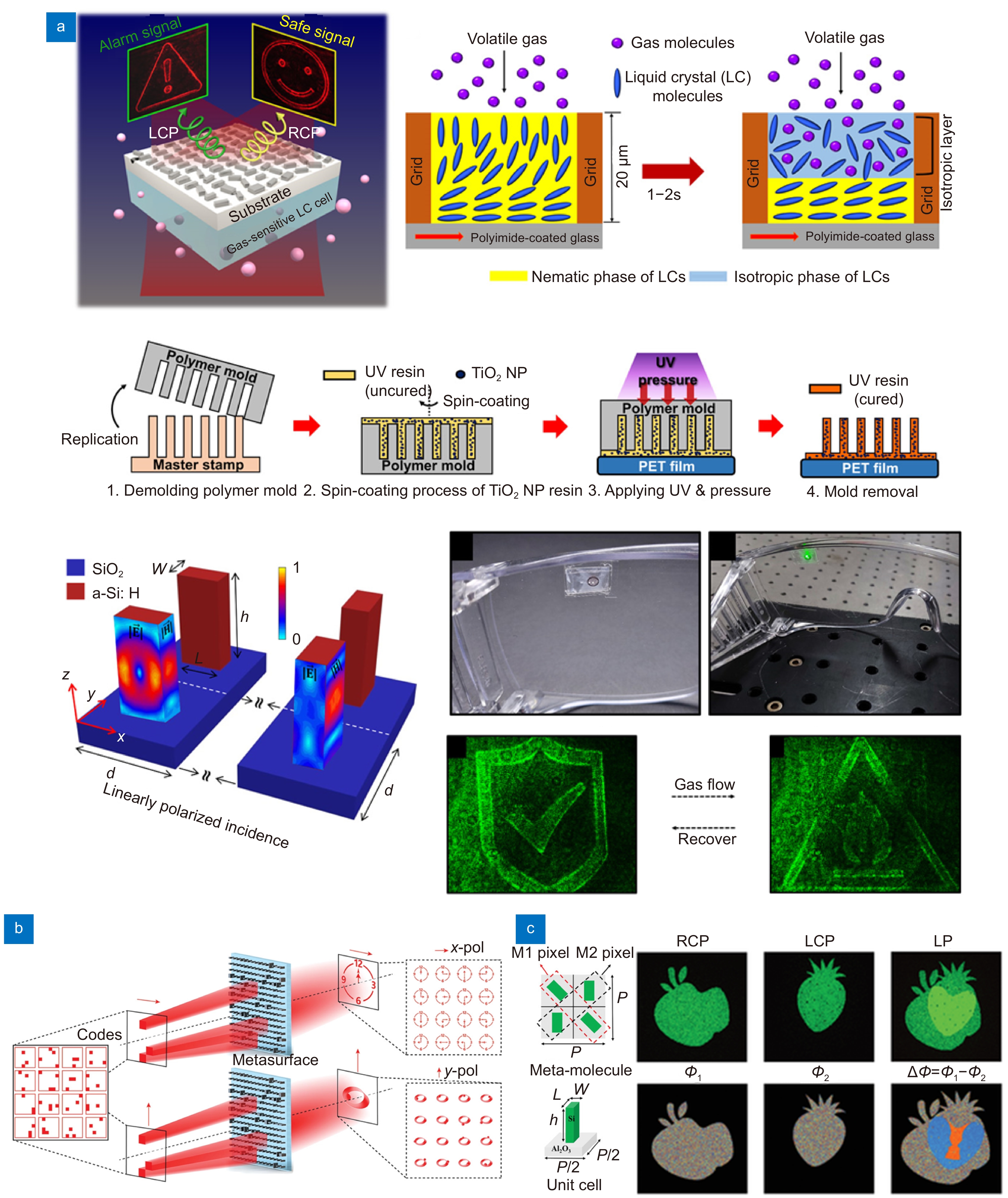
图 8 基于超表面复用全息术的应用。(a) 一种左右旋偏振复用全息器件用于气体传感,通过结合液晶材料,可以在不同的气体浓度下改变入射光的圆偏振特性在两个图像之间切换[117];(b) 码分复用型超表面器件[118];(c) 一种矢量全息器件,可以控制全息像面的相位信息,使在特定的输入输出条件下隐藏或显示图像信息[119]
Figure 8. Applications based on multiplexed meta-holography. (a) A polarization-multiplexed holographic device for gas sensing by combining liquid crystal materials and the circular polarization of incident light can be switched under different gas concentrations which leads to holographic image switching between two images[117]; (b) Code division multiplexed metasurface[118]; (c) A vectorial holographic device can control the phase information of the holographic image plane to hide or display image information under specific input and output conditions[119]
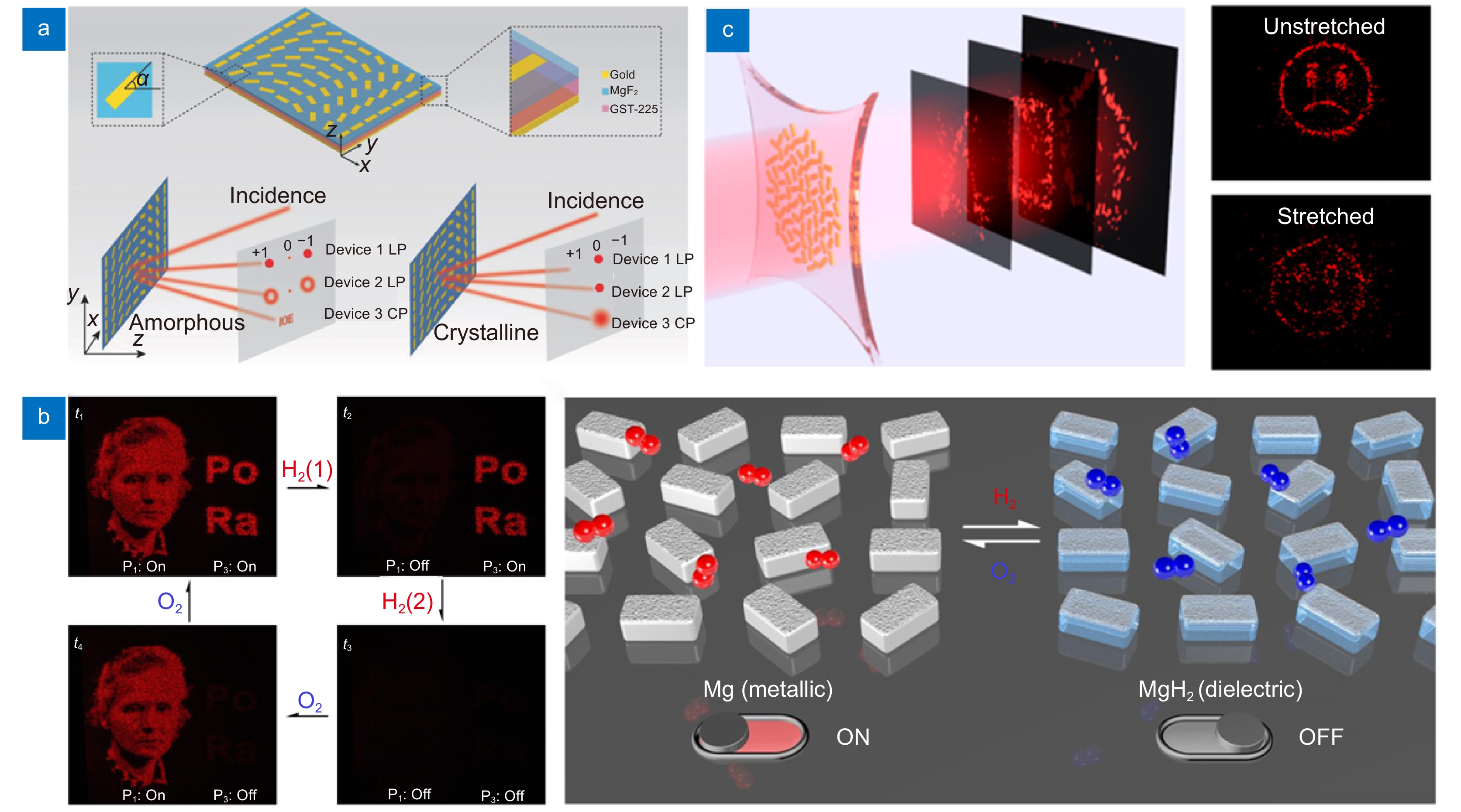
图 9 主动式超表面全息。(a) 基于GST相变特性的可切换自旋霍尔效应、涡旋光束产生和全息术[126];(b) 基于Mg氢化/脱氢特性的动态超表面全息[132];(c) 基于可拉伸PDMS基底的全息图像动态切换显示[135]
Figure 9. Active meta-holography. (a) Switchable spin Hall effect, vortex beam generation and holography based on GST phase transition properties[126]; (b) Dynamic metasurface holography based on Mg hydrogenation/dehydrogenation properties[132]; (c) Dynamic switching display of holographic image based on stretchable PDMS substrate[135]
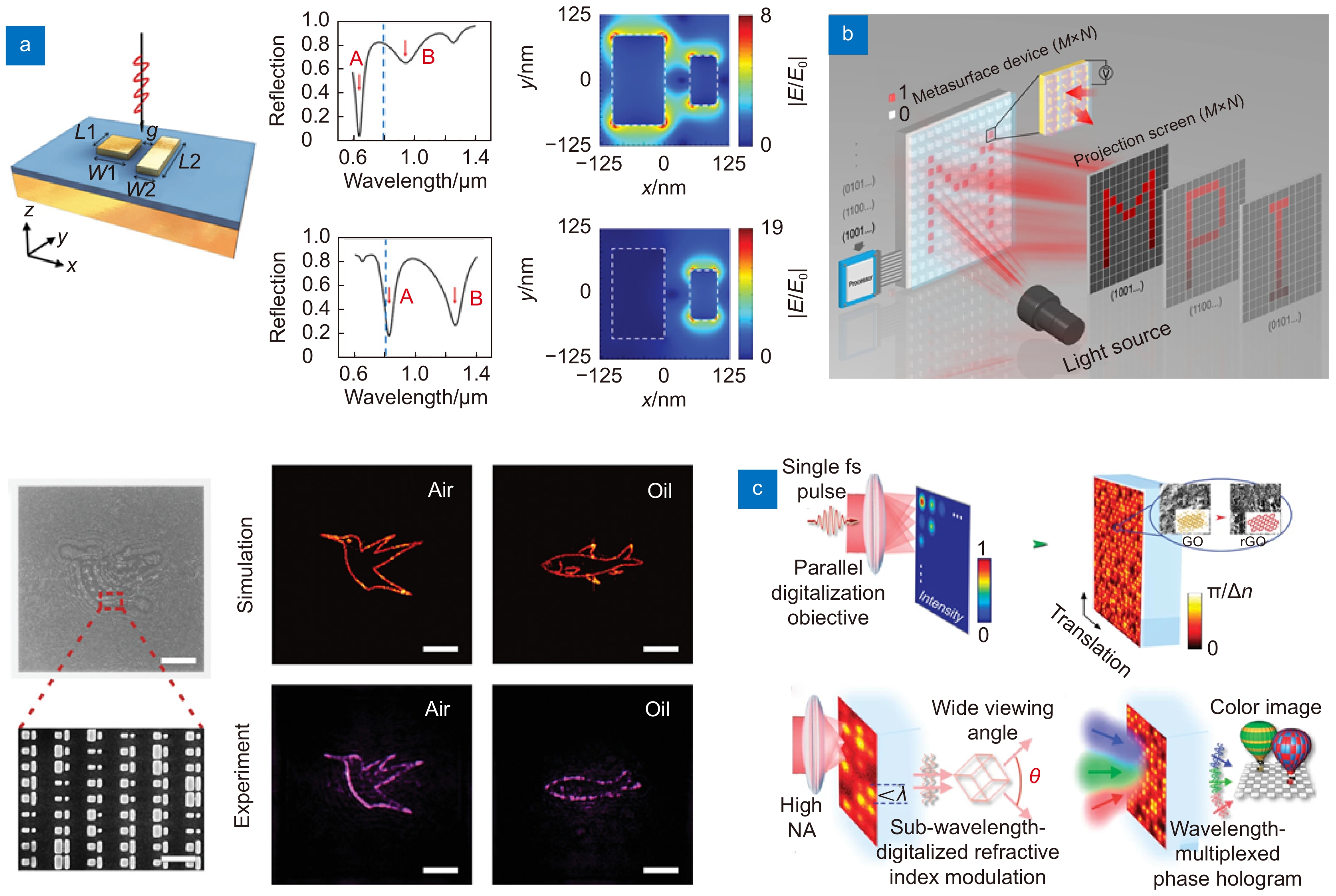
图 10 主动式超表面全息。(a) 基于对环境敏感的MIM结构的可切换超表面全息术[138],比例尺:40 μm;(b) 用于光投影显示的电控数字超表面设备[143];(c) 通过飞秒激光脉冲还原氧化石墨烯进行折射率调制以实现宽视场角3D全息图[148]
Figure 10. Active meta-holography. (a) Switchable meta-holographic device based on environmentally sensitive MIM structures[138], scale bar: 40 μm; (b) Electronically controlled digital metasurface for optical projection display[143]; (c) Refractive index modulation by femtosecond laser pulse reduction of to achieve wide-FOV 3D holograms[148]
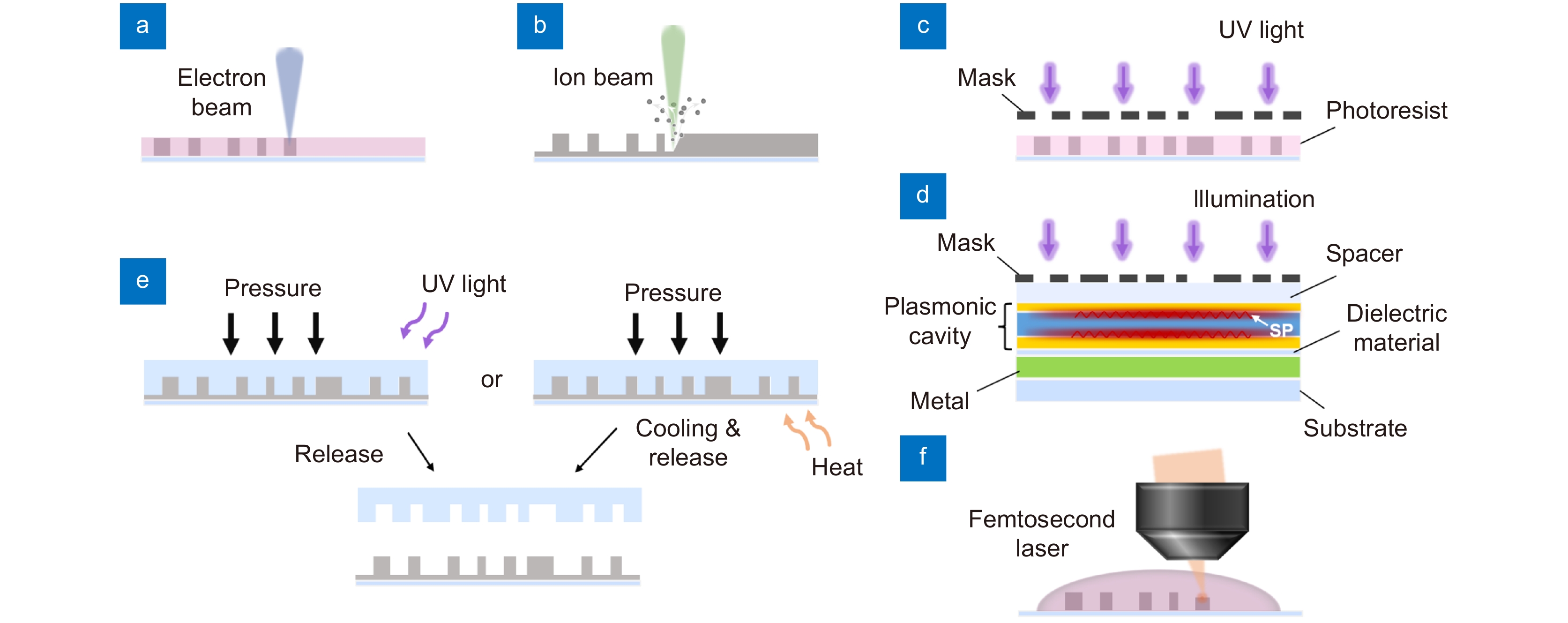
图 11 光学超表面微纳制造方法。(a) 电子束曝光;(b) 聚焦离子束;(c) 光刻;(d) 等离子体腔光刻;(e) 纳米压印;(f) 双光子聚合激光直写技术
Figure 11. Micro-nano fabrication technologies for optical metasurfaces (a) Electron beam lithography; (b) Focused ion beam; (c) Photolithography; (d) Plasmonic cavity lithography; (e) Nanoimprint lithography; (f) Two-photon polymerization laser direct writing
表 1 单色静态全息显示代表性工作
Table 1. Representative works of single-wavelength static holographic display
表 2 彩色全息显示代表性工作
Table 2. Representative works of color holographic display
表 3 动态流畅全息显示代表性工作
Table 3. Representative works of dynamic smooth holographic display
表 4 其他功能化应用的代表性工作
Table 4. Representative works of other functionalized applications
工作机理 工作模式 波长/nm 材料 功能 参考文献 波长复用 透射式 473、532、633 Si 多功能集成 [75] 角度复用 反射式 915 a-Si 全息加密、多功能集成 [77] 透射式 405 Au 全息加密、多功能集成 [81] 偏振复用 透射式 480 TiO2 全息加密、多功能集成 [87] 透射式 633;532 a-Si:H;功能性UV光刻胶,包含TiO2纳米粒子 传感 [117] OAM复用 透射式 632 GaN 高信息容量存储、全息加密、多功能集成 [98] 空间复用 透射式 633 a-Si 多功能集成 [103] 传输方向复用 透射式 632.8 a-Si:H 全息加密、多功能集成 [108] 衍射光场复用 透射式 740 Si 全息加密 [111] 相变材料调制 透射式 800(控制光)、
1550(探测光)GST-Al 全息加密 [128] 化学反应调制 反射式 633 Mg/Ti/Pd、Au、Mg/Ti/Pd/Cr 传感、全息加密 [132] 反射式 633 Mg/Ti/Pd-HSQ-SiO2-Ag 传感、多功能集成 [134] 机械调制 透射式 632.8 Au-PDMS 传感 [135] 介质环境调制 反射式 800;710、890 Au-SiO2-Au 传感 [138] 热调制 透射式 633 聚烯烃 传感、全息加密 [149] 备注:“/”代表参考文献中没有相关数据。 -
参考文献
[1] 金国藩, 张浩, 苏萍, 等. 计算机制全息图[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020.
Jin G F, Zhang H, Su P, et al. Computer-Generated Holography[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020.
[2] Brown B R, Lohmann A W. Complex spatial filtering with binary masks[J]. Appl Opt, 1966, 5(6): 967−969. doi: 10.1364/AO.5.000967
[3] Lohmann A W, Paris D P. Binary fraunhofer holograms, generated by computer[J]. Appl Opt, 1967, 6(10): 1739−1748. doi: 10.1364/AO.6.001739
[4] Samoylenko S R, Lisitsin A V, Schepanovich D, et al. Single atom movement with dynamic holographic optical tweezers[J]. Laser Phys Lett, 2020, 17(2): 025203. doi: 10.1088/1612-202X/ab6729
[5] Casasent D, Rozzi W A. Computer-generated and phase-only synthetic discriminant function filters[J]. Appl Opt, 1986, 25(20): 3767−3772. doi: 10.1364/AO.25.003767
[6] Slinger C, Cameron C, Stanley M. Computer-generated holography as a generic display technology[J]. Computer, 2005, 38(8): 46−53. doi: 10.1109/MC.2005.260
[7] Reichelt S, Tiziani H. Asphärenprüfung mit computergenerierten Hologrammen (Testing Aspheric Optics by Use of Computer-generated Holograms)[J]. tm - Tech Mess, 2006, 73(10): 554−565. doi: 10.1524/teme.2006.73.10.554
[8] Deng L G, Deng J, Guan Z Q, et al. Malus-metasurface-assisted polarization multiplexing[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2020, 9: 101. doi: 10.1038/s41377-020-0327-7
[9] Yu N F, Genevet P, Kats M A, et al. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6054): 333−337. doi: 10.1126/science.1210713
[10] Zhang S F, Huang L L, Li X, et al. Dynamic display of full-stokes vectorial holography based on metasurfaces[J]. ACS Photonics, 2021, 8(6): 1746−1753. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.1c00307
[11] Shrestha S, Overvig A C, Lu M, et al. Broadband achromatic dielectric metalenses[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2018, 7: 85. doi: 10.1038/s41377-018-0078-x
[12] 胡跃强, 李鑫, 王旭东, 等. 光学超构表面的微纳加工技术研究进展[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2020, 49(9): 20201035. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20201035
Hu Y Q, Li X, Wang X D, et al. Progress of micro-nano fabrication technologies for optical metasurfaces[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2020, 49(9): 20201035. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20201035
[13] Tseng M L, Hsiao H H, Chu C H, et al. Metalenses: advances and applications[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2018, 6(18): 1800554. doi: 10.1002/adom.201800554
[14] Chen X Y, Zou H J, Su M Y, et al. All-dielectric metasurface-based beam splitter with arbitrary splitting ratio[J]. Nanomaterials (Basel), 2021, 11(5): 1137. doi: 10.3390/nano11051137
[15] Haghtalab M, Tamagnone M, Zhu A Y, et al. Ultrahigh angular selectivity of disorder-engineered metasurfaces[J]. ACS Photonics, 2020, 7(4): 991−1000. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.9b01655
[16] Larouche S, Tsai Y J, Tyler T, et al. Infrared metamaterial phase holograms[J]. Nat Mater, 2012, 11(5): 450−454. doi: 10.1038/nmat3278
[17] Walther B, Helgert C, Rockstuhl C, et al. Diffractive optical elements based on plasmonic metamaterials[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 98(19): 191101. doi: 10.1063/1.3587622
[18] Gao H, Fan X H, Xiong W, et al. Recent advances in optical dynamic meta-holography[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2021, 4(11): 210030. doi: 10.29026/oea.2021.210030
[19] Pang H, Wang J Z, Cao A X, et al. Accurate hologram generation using layer-based method and iterative Fourier transform algorithm[J]. IEEE Photonics J, 2017, 9(1): 1−8. doi: 10.1109/jphot.2016.2634783
[20] Gerchberg R W, Saxton W O. A practical algorithm for the determination of phase from image and diffraction plane pictures[J]. Optik, 1972, 35(2): 237−246.
[21] Feldman M R, Guest C C. Iterative encoding of high-efficiency holograms for generation of spot arrays[J]. Opt Lett, 1989, 14(10): 479−481. doi: 10.1364/OL.14.000479
[22] Yoshikawa N, Itoh M, Yatagai T. Quantized phase optimization of two-dimensional Fourier kinoforms by a genetic algorithm[J]. Opt Lett, 1995, 20(7): 752−754. doi: 10.1364/OL.20.000752
[23] Pang H, Wang J Z, Cao A X, et al. High-accuracy method for holographic image projection with suppressed speckle noise[J]. Opt Express, 2016, 24(20): 22766−22776. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.022766
[24] Liu S C, Chu D P. Deep learning for hologram generation[J]. Opt Express, 2021, 29(17): 27373−27395. doi: 10.1364/OE.418803
[25] Lee J, Jeong J, Cho J, et al. Deep neural network for multi-depth hologram generation and its training strategy[J]. Opt Express, 2020, 28(18): 27137−27154. doi: 10.1364/OE.402317
[26] Lee G Y, Yoon G, Lee S Y, et al. Complete amplitude and phase control of light using broadband holographic metasurfaces[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(9): 4237−4245. doi: 10.1039/C7NR07154J
[27] 李雄, 马晓亮, 罗先刚. 超表面相位调控原理及应用[J]. 光电工程, 2017, 44(3): 255−275. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.03.001
Li X, Ma X L, Luo X G. Principles and applications of metasurfaces with phase modulation[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2017, 44(3): 255−275. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.03.001
[28] Wang E W, Sell D, Phan T, et al. Robust design of topology-optimized metasurfaces[J]. Opt Mater Express, 2019, 9(2): 469−482. doi: 10.1364/OME.9.000469
[29] Xu M F, Pu M B, Sang D, et al. Topology-optimized catenary-like metasurface for wide-angle and high-efficiency deflection: from a discrete to continuous geometric phase[J]. Opt Express, 2021, 29(7): 10181−10191. doi: 10.1364/OE.422112
[30] Wan W W, Gao J, Yang X D. Metasurface holograms for holographic imaging[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2017, 5(21): 1700541. doi: 10.1002/adom.201700541
[31] Xie X, Pu M B, Jin J J, et al. Generalized pancharatnam-berry phase in rotationally symmetric meta-atoms[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2021, 126(18): 183902. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.183902
[32] Huang L L, Chen X Z, Mühlenbernd H, et al. Three-dimensional optical holography using a plasmonic metasurface[J]. Nat Commun, 2013, 4(1): 2808. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3808
[33] Zheng G X, Mühlenbernd H, Kenney M, et al. Metasurface holograms reaching 80% efficiency[J]. Nat Nanotechnol, 2015, 10(4): 308−312. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.2
[34] Zhang X H, Jin J J, Wang Y Q, et al. Metasurface-based broadband hologram with high tolerance to fabrication errors[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 19856. doi: 10.1038/srep19856
[35] Wang L, Kruk S, Tang H Z, et al. Grayscale transparent metasurface holograms[J]. Optica, 2016, 3(12): 1504−1505. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.3.001504
[36] Devlin R C, Khorasaninejad M, Chen W T, et al. Broadband high-efficiency dielectric metasurfaces for the visible spectrum[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2016, 113(38): 10473−10478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611740113
[37] 付娆, 李子乐, 郑国兴. 超构表面的振幅调控及其功能器件研究进展[J]. 中国光学, 2021, 14(4): 886−899. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0017
Fu R, Li Z L, Zheng G X, et al. Research development of amplitude-modulated metasurfaces and their functional devices[J]. Chin Opt, 2021, 14(4): 886−899. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0017
[38] Butt H, Montelongo Y, Butler T, et al. Carbon nanotube based high resolution holograms[J]. Adv Mater, 2012, 24(44): OP331−OP336. doi: 10.1002/adma.201202593
[39] Huang K, Liu H, Garcia-Vidal F J, et al. Ultrahigh-capacity non-periodic photon sieves operating in visible light[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 7059. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8059
[40] Xu Z T, Huang L L, Li X W, et al. Quantitatively correlated amplitude holography based on photon sieves[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2020, 8(2): 1901169. doi: 10.1002/adom.201901169
[41] Fu R, Deng L G, Guan Z Q, et al. Zero-order-free meta-holograms in a broadband visible range[J]. Photonics Res, 2020, 8(5): 723−728. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.387397
[42] Overvig A C, Shrestha S, Malek S C, et al. Dielectric metasurfaces for complete and independent control of the optical amplitude and phase[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2019, 8: 92. doi: 10.1038/s41377-019-0201-7
[43] Gao Y S, Fan Y B, Wang Y J, et al. Nonlinear holographic all-dielectric metasurfaces[J]. Nano Lett, 2018, 18(12): 8054−8061. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04311
[44] 隋晓萌, 何泽浩, 曹良才, 等. 基于液晶空间光调制器的复振幅全息显示进展[J]. 液晶与显示, 2021, 36(6): 797−809. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2021-0049
Sui X M, He Z H, Cao L C, et al. Recent progress in complex-modulated holographic display based on liquid crystal spatial light modulators[J]. Chin J Liq Cryst Dis, 2021, 36(6): 797−809. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2021-0049
[45] Ni X J, Kildishev A V, Shalaev V M. Metasurface holograms for visible light[J]. Nat Commun, 2013, 4(1): 2807. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3807
[46] Wang Q, Zhang X Q, Xu Y H, et al. Broadband metasurface holograms: toward complete phase and amplitude engineering[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 32867. doi: 10.1038/srep32867
[47] Jiang Q, Cao L C, Huang L L, et al. A complex-amplitude hologram using an ultra-thin dielectric metasurface[J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(47): 24162−24168. doi: 10.1039/D0NR06461K
[48] Huang T Y, Zhao X, Zeng S W, et al. Planar nonlinear metasurface optics and their applications[J]. Rep Prog Phys, 2020, 83(12): 126101. doi: 10.1088/1361-6633/abb56e
[49] 石鸣谦, 刘俊, 陈卓, 等. 基于超构表面的非线性光学与量子光学[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2020, 49(9): 20201028. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20201028
Shi M Q, Liu J, Chen Z, et al. Nonlinear optics and quantum optics based on metasurface[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2020, 49(9): 20201028. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20201028
[50] Frese D, Wei Q S, Wang Y T, et al. Nonlinear bicolor holography using plasmonic metasurfaces[J]. ACS Photonics, 2021, 8(4): 1013−1019. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.1c00028
[51] Mao N B, Tang Y T, Jin M K, et al. Nonlinear wavefront engineering with metasurface decorated quartz crystal[J]. Nanophotonics, 2022, 11(4): 797−803. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2021-0464
[52] Mao N B, Zhang G Q, Tang Y T, et al. Nonlinear vectorial holography with quad-atom metasurfaces[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2022, 119(22): e2204418119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2204418119
[53] Deng Z L, Wang Z Q, Li F J, et al. Multi-freedom metasurface empowered vectorial holography[J]. Nanophotonics, 2022, 11(9): 1725−1739. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2021-0662
[54] Tan H Y, Deng J H, Zhao R Z, et al. A free-space orbital angular momentum multiplexing communication system based on a metasurface[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2019, 13(6): 1800278. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201800278
[55] Li Z F, He C, Zhu W R. Secret sharing holographic encryption with off-axis dual-channel metasurface[C]//2020 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and North American Radio Science Meeting, 2020: 815–816. doi: 10.1109/IEEECONF35879.2020.9330314.
[56] Li Z F, Premaratne M, Zhu W R. Advanced encryption method realized by secret shared phase encoding scheme using a multi-wavelength metasurface[J]. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(11): 3687−3696. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2020-0298
[57] Xiong Y J, Vandenhoute M, Cankaya H C. Control architecture in optical burst-switched WDM networks[J]. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun, 2000, 18(10): 1838−1851. doi: 10.1109/49.887906
[58] Nakayama H, Takada N, Ichihashi Y, et al. Real-time color electroholography using multiple graphics processing units and multiple high-definition liquid-crystal display panels[J]. Appl Opt, 2010, 49(31): 5993−5996. doi: 10.1364/AO.49.005993
[59] Zeng Z X, Zheng H F, Yu Y J, et al. Full-color holographic display with increased-viewing-angle [Invited][J]. Appl Opt, 2017, 56(13): F112−F120. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.00F112
[60] Makowski M, Ducin I, Sypek M, et al. Color image projection based on Fourier holograms[J]. Opt Lett, 2010, 35(8): 1227−1229. doi: 10.1364/OL.35.001227
[61] Makowski M, Sypek M, Kolodziejczyk A. Colorful reconstructions from a thin multi-plane phase hologram[J]. Opt Express, 2008, 16(15): 11618−11623. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.011618
[62] Kozacki T, Chlipala M. Color holographic display with white light LED source and single phase only SLM[J]. Opt Express, 2016, 24(3): 2189−2199. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.002189
[63] Zhao W Y, Liu B Y, Jiang H, et al. Full-color hologram using spatial multiplexing of dielectric metasurface[J]. Opt Lett, 2016, 41(1): 147−150. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.000147
[64] Wang B, Dong F L, Li Q T, et al. Visible-frequency dielectric metasurfaces for multiwavelength achromatic and highly dispersive holograms[J]. Nano Lett, 2016, 16(8): 5235−5240. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b02326
[65] Zhang F, Pu M B, Gao P, et al. Simultaneous full-color printing and holography enabled by centimeter-scale plasmonic metasurfaces[J]. Adv Sci, 2020, 7(10): 1903156. doi: 10.1002/advs.201903156
[66] Guo X Y, Zhong J Z, Li B J, et al. Full-color holographic display and encryption with full-polarization degree of freedom[J]. Adv Mater, 2022, 34(3): 2103192. doi: 10.1002/adma.202103192
[67] Ma D N, Li Z C, Liu W W, et al. Deep-learning enabled multicolor meta-holography[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2022, 10(15): 2102628. doi: 10.1002/ADOM.202102628
[68] Hu Y Q, Luo X H, Chen Y Q, et al. 3D-Integrated metasurfaces for full-colour holography[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2019, 8: 86. doi: 10.1038/s41377-019-0198-y
[69] Lim K T P, Liu H L, Liu Y J, et al. Holographic colour prints for enhanced optical security by combined phase and amplitude control[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 25. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07808-4
[70] Shi Z J, Khorasaninejad M, Huang Y W, et al. Single-layer metasurface with controllable multiwavelength functions[J]. Nano Lett, 2018, 18(4): 2420−2427. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b05458
[71] Hu Y Q, Li L, Wang Y J, et al. Trichromatic and tripolarization-channel holography with noninterleaved dielectric metasurface[J]. Nano Lett, 2020, 20(2): 994−1002. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b04107
[72] Li X, Chen L W, Li Y, et al. Multicolor 3D meta-holography by broadband plasmonic modulation[J]. Sci Adv, 2016, 2(11): e1601102. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1601102
[73] Deng Z L, Jin M K, Ye X, et al. Full-color complex-amplitude vectorial holograms based on multi-freedom metasurfaces[J]. Adv Funct Mater, 2020, 30(21): 1910610. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201910610
[74] Huo P C, Song M W, Zhu W Q, et al. Photorealistic full-color nanopainting enabled by a low-loss metasurface[J]. Optica, 2020, 7(9): 1171−1172. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.403092
[75] Bao Y J, Yu Y, Xu H F, et al. Full-colour nanoprint-hologram synchronous metasurface with arbitrary hue-saturation-brightness control[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2019, 8: 95. doi: 10.1038/s41377-019-0206-2
[76] Wei Q S, Sain B, Wang Y T, et al. Simultaneous spectral and spatial modulation for color printing and holography using all-dielectric metasurfaces[J]. Nano Lett, 2019, 19(12): 8964−8971. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b03957
[77] Kamali S M, Arbabi E, Arbabi A, et al. Angle-multiplexed metasurfaces: encoding independent wavefronts in a single metasurface under different illumination angles[J]. Phys Rev X, 2017, 7(4): 041056. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.7.041056
[78] Jang J, Lee G Y, Sung J, et al. Independent multichannel wavefront modulation for angle multiplexed meta-holograms[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2021, 9(17): 2100678. doi: 10.1002/adom.202100678
[79] Wang E L, Niu J B, Liang Y H, et al. Complete control of multichannel, angle-multiplexed, and arbitrary spatially varying polarization fields[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2020, 8(6): 1901674. doi: 10.1002/adom.201901674
[80] Wan S, Tang J, Wan C W, et al. Angular-encrypted quad-fold display of nanoprinting and meta-holography for optical information storage[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2022, 10(11): 2102820. doi: 10.1002/adom.202102820
[81] Zhang X H, Jin J J, Pu M B, et al. Ultrahigh-capacity dynamic holographic displays via anisotropic nanoholes[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(4): 1409−1415. doi: 10.1039/C6NR07854K
[82] Wang J Y, Tan X D, Qi P L, et al. Linear polarization holography[J]. Opto-Electron Sci, 2022, 1(2): 210009. doi: 10.29026/oes.2022.210009
[83] Chen W T, Yang K Y, Wang C M, et al. High-efficiency broadband meta-hologram with polarization-controlled dual images[J]. Nano Lett, 2014, 14(1): 225−230. doi: 10.1021/nl403811d
[84] Montelongo Y, Tenorio-Pearl J O, Milne W I, et al. Polarization switchable diffraction based on subwavelength plasmonic nanoantennas[J]. Nano Lett, 2014, 14(1): 294−298. doi: 10.1021/nl4039967
[85] Wen D D, Yue F Y, Li G X, et al. Helicity multiplexed broadband metasurface holograms[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 8241. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9241
[86] Mueller J P B, Rubin N A, Devlin R C, et al. Metasurface polarization optics: independent phase control of arbitrary orthogonal states of polarization[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2017, 118(11): 113901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.113901
[87] Li Z L, Chen C, Guan Z Q, et al. Three-channel metasurfaces for simultaneous meta-holography and meta-nanoprinting: a single-cell design approach[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2020, 14(6): 2000032. doi: 10.1002/lpor.202000032
[88] Kuroda K. Theory of polarization holography[C]//2011 10th Euro-American Workshop on Information Optics, 2011: 1–3,doi: 10.1109/WIO.2011.5981446.
[89] Zhao R Z, Sain B, Wei Q S, et al. Multichannel vectorial holographic display and encryption[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2018, 7: 95. doi: 10.1038/s41377-018-0091-0
[90] Deng Z L, Deng J H, Zhuang X, et al. Diatomic metasurface for vectorial holography[J]. Nano Lett, 2018, 18(5): 2885−2892. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b00047
[91] Arbabi E, Kamali S M, Arbabi A, et al. Vectorial holograms with a dielectric metasurface: ultimate polarization pattern generation[J]. ACS Photonics, 2019, 6(11): 2712−2718. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.9b00678
[92] Ren H R, Shao W, Li Y, et al. Three-dimensional vectorial holography based on machine learning inverse design[J]. Sci Adv, 2020, 6(16): eaaz4261. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz4261
[93] Wang J, Yang J Y, Fazal I M, et al. Terabit free-space data transmission employing orbital angular momentum multiplexing[J]. Nat Photonics, 2012, 6(7): 488−496. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.138
[94] Bozinovic N, Yue Y, Ren Y X, et al. Terabit-scale orbital angular momentum mode division multiplexing in fibers[J]. Science, 2013, 340(6140): 1545−1548. doi: 10.1126/science.1237861
[95] Mair A, Vaziri A, Weihs G, et al. Entanglement of the orbital angular momentum states of photons[J]. Nature, 2001, 412(6844): 313−316. doi: 10.1038/35085529
[96] Fickler R, Lapkiewicz R, Plick W N, et al. Quantum entanglement of high angular momenta[J]. Science, 2012, 338(6107): 640−643. doi: 10.1126/science.1227193
[97] O’Neil A T, MacVicar I, Allen L, et al. Intrinsic and extrinsic nature of the orbital angular momentum of a light beam[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 88(5): 053601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.053601
[98] Ren H R, Briere G, Fang X Y, et al. Metasurface orbital angular momentum holography[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 2986. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11030-1
[99] Ren H R, Fang X Y, Jang J, et al. Complex-amplitude metasurface-based orbital angular momentum holography in momentum space[J]. Nat Nanotechnol, 2020, 15(11): 948−955. doi: 10.1038/s41565-020-0768-4
[100] Jin L, Huang Y W, Jin Z W, et al. Dielectric multi-momentum meta-transformer in the visible[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 4789. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12637-0
[101] Izumi R, Ikezawa S, Iwami K. Metasurface holographic movie: a cinematographic approach[J]. Opt Express, 2020, 28(16): 23761−23770. doi: 10.1364/OE.399369
[102] Gao H, Wang Y X, Fan X H, et al. Dynamic 3D meta-holography in visible range with large frame number and high frame rate[J]. Sci Adv, 2020, 6(28): eaba8595. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aba8595
[103] Tang J, Wan S, Shi Y Y, et al. Dynamic augmented reality display by layer-folded metasurface via electrical-driven liquid crystal[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2022, 10(12): 2200418. doi: 10.1002/adom.202200418
[104] Li J X, Yu P, Zhang S, et al. A reusable metasurface template[J]. Nano Lett, 2020, 20(9): 6845−6851. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c02876
[105] Sounas D L, Alù A. Non-reciprocal photonics based on time modulation[J]. Nat Photonics, 2017, 11(12): 774−783. doi: 10.1038/s41566-017-0051-x
[106] Frese D, Wei Q S, Wang Y T, et al. Nonreciprocal asymmetric polarization encryption by layered plasmonic metasurfaces[J]. Nano Lett, 2019, 19(6): 3976−3980. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b01298
[107] Ansari M A, Kim I, Rukhlenko I D, et al. Engineering spin and antiferromagnetic resonances to realize an efficient direction-multiplexed visible meta-hologram[J]. Nanoscale Horiz, 2020, 5(1): 57−64. doi: 10.1039/C9NH00460B
[108] Naveed M A, Ansari M A, Kim I, et al. Optical spin-symmetry breaking for high-efficiency directional helicity-multiplexed metaholograms[J]. Microsyst Nanoeng, 2021, 7: 5. doi: 10.1038/S41378-020-00226-X
[109] Kruk S S, Wang L, Sain B, et al. Asymmetric parametric generation of images with nonlinear dielectric metasurfaces[J]. Nat Photonics, 2022, 16(8): 561−565. doi: 10.1038/S41566-022-01018-7
[110] Qu G Y, Yang W H, Song Q H, et al. Reprogrammable meta-hologram for optical encryption[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 5484. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19312-9
[111] Georgi P, Wei Q S, Sain B, et al. Optical secret sharing with cascaded metasurface holography[J]. Sci Adv, 2021, 7(16): eabf9718. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abf9718
[112] Wei Q S, Huang L L, Zhao R Z, et al. Rotational multiplexing method based on cascaded metasurface holography[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2022, 10(8): 2102166. doi: 10.1002/adom.202102166
[113] Zhang X H, Pu M B, Guo Y H, et al. Colorful metahologram with independently controlled images in transmission and reflection spaces[J]. Adv Funct Mater, 2019, 29(22): 1809145. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201809145
[114] Zheng G X, Zhou N, Deng L G, et al. Full-space metasurface holograms in the visible range[J]. Opt Express, 2021, 29(2): 2920−2930. doi: 10.1364/OE.417202
[115] Zhao R Z, Geng G Z, Wei Q S, et al. Controllable polarization and diffraction modulated multi-functionality based on metasurface[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2022, 10(8): 2102596. doi: 10.1002/adom.202102596
[116] Li X, Zhang X, Zhao R Z, et al. Independent light field manipulation in diffraction orders of metasurface holography[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2022, 16(8): 2100592. doi: 10.1002/LPOR.202100592
[117] Kim I, Kim W S, Kim K, et al. Holographic metasurface gas sensors for instantaneous visual alarms[J]. Sci Adv, 2021, 7(15): eabe9943. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abe9943
[118] Li X, Zhao R Z, Wei Q S, et al. Code division multiplexing inspired dynamic metasurface holography[J]. Adv Funct Mater, 2021, 31(35): 2103326. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202103326
[119] Wan W P, Yang W H, Feng H, et al. Multiplexing vectorial holographic images with arbitrary metaholograms[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2021, 9(20): 2100626. doi: 10.1002/adom.202100626
[120] Ding F, Deshpande R, Bozhevolnyi S I. Bifunctional gap-plasmon metasurfaces for visible light: polarization-controlled unidirectional surface plasmon excitation and beam steering at normal incidence[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2018, 7(4): 17178. doi: 10.1038/lsa.2017.178
[121] Sun S L, He Q, Xiao S Y, et al. Gradient-index meta-surfaces as a bridge linking propagating waves and surface waves[J]. Nat Mater, 2012, 11(5): 426−431. doi: 10.1038/nmat3292
[122] Huang Z Q, Marks D L, Smith D R. Polarization-selective waveguide holography in the visible spectrum[J]. Opt Express, 2019, 27(24): 35631−35645. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.035631
[123] Huang Z Q, Marks D L, Smith D R. Out-of-plane computer-generated multicolor waveguide holography[J]. Optica, 2019, 6(2): 119−124. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.6.000119
[124] Ha Y L, Guo Y H, Pu M B, et al. Monolithic-integrated multiplexed devices based on metasurface-driven guided waves[J]. Adv Theory Simul, 2021, 4(2): 2000239. doi: 10.1002/adts.202000239
[125] Shi Y Y, Wan C W, Dai C J, et al. Augmented reality enabled by on-chip meta-holography multiplexing[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2022, 16(6): 2100638. doi: 10.1002/lpor.202100638
[126] Zhang M, Pu M B, Zhang F, et al. Plasmonic metasurfaces for switchable photonic spin-orbit interactions based on phase change materials[J]. Adv Sci, 2018, 5(10): 1800835. doi: 10.1002/advs.201800835
[127] Zhou H Q, Wang Y T, Li X W, et al. Switchable active phase modulation and holography encryption based on hybrid metasurfaces[J]. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(4): 905−912. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2019-0519
[128] Choi C, Mun S E, Sung J, et al. Hybrid state engineering of phase-change metasurface for all-optical cryptography[J]. Adv Funct Mater, 2021, 31(4): 2007210. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202007210
[129] Tripathi A, John J, Kruk S, et al. Tunable Mie-resonant dielectric metasurfaces based on VO2 phase-transition materials[J]. ACS Photonics, 2021, 8(4): 1206−1213. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.1c00124
[130] Liu X B, Wang Q, Zhang X Q, et al. Thermally dependent dynamic meta-holography using a vanadium dioxide integrated metasurface[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2019, 7(12): 1900175. doi: 10.1002/adom.201900175
[131] Yang J K, Jeong H S. Switchable metasurface with VO2 thin film at visible light by changing temperature[J]. Photonics, 2021, 8(2): 57. doi: 10.3390/photonics8020057
[132] Li J X, Kamin S, Zheng G X, et al. Addressable metasurfaces for dynamic holography and optical information encryption[J]. Sci Adv, 2018, 4(6): eaar6768. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aar6768
[133] Li T Y, Wei Q S, Reineke B, et al. Reconfigurable metasurface hologram by utilizing addressable dynamic pixels[J]. Opt Express, 2019, 27(15): 21153−21162. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.021153
[134] Li J X, Chen Y Q, Hu Y Q, et al. Magnesium-based metasurfaces for dual-function switching between dynamic holography and dynamic color display[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(7): 7892−7898. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c01469
[135] Malek S C, Ee H S, Agarwal R. Strain multiplexed metasurface holograms on a stretchable substrate[J]. Nano Lett, 2017, 17(6): 3641−3645. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b00807
[136] Kim I, Ansari M A, Mehmood M Q, et al. Stimuli-responsive dynamic metaholographic displays with designer liquid crystal modulators[J]. Adv Mater, 2020, 32(50): 2004664. doi: 10.1002/adma.202004664
[137] Xu Q, Su X Q, Zhang X Q, et al. Mechanically reprogrammable Pancharatnam–Berry metasurface for microwaves[J]. Adv Photonics, 2022, 4(1): 016002. doi: 10.1117/1.AP.4.1.016002
[138] Xiong B, Xu Y H, Wang J N, et al. Realizing colorful holographic mimicry by metasurfaces[J]. Adv Mater, 2021, 33(21): 2005864. doi: 10.1002/adma.202005864
[139] Cai H G, Dolan J A, Gordon G S D, et al. Polarization-insensitive medium-switchable holographic metasurfaces[J]. ACS Photonics, 2021, 8(9): 2581−2589. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.1c00836
[140] Yang R, Wan S, Shi Y Y, et al. Immersive tuning the guided waves for multifunctional on-chip metaoptics[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2022, 16(8): 2200127. doi: 10.1002/LPOR.202200127
[141] Badloe T, Lee J, Seong J, et al. Tunable metasurfaces: the path to fully active nanophotonics[J]. Adv Photonics Res, 2021, 2(9): 2000205. doi: 10.1002/adpr.202000205
[142] Hu Y Q, Ou X N, Zeng T B, et al. Electrically tunable multifunctional polarization-dependent metasurfaces integrated with liquid crystals in the visible region[J]. Nano Lett, 2021, 21(11): 4554−4562. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c00104
[143] Li J X, Yu P, Zhang S, et al. Electrically-controlled digital metasurface device for light projection displays[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 3574. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17390-3
[144] Yu P, Li J X, Liu N. Electrically tunable optical metasurfaces for dynamic polarization conversion[J]. Nano Lett, 2021, 21(15): 6690−6695. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c02318
[145] Kaissner R, Li J X, Lu W Z, et al. Electrochemically controlled metasurfaces with high-contrast switching at visible frequencies[J]. Sci Adv, 2021, 7(19): eabd9450. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abd9450
[146] Li L L, Jun Cui T, Ji W, et al. Electromagnetic reprogrammable coding-metasurface holograms[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1): 197. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00164-9
[147] Venkatesh S, Lu X Y, Saeidi H, et al. A high-speed programmable and scalable terahertz holographic metasurface based on tiled CMOS chips[J]. Nat Electron, 2020, 3(12): 785−793. doi: 10.1038/s41928-020-00497-2
[148] Li X P, Ren H R, Chen X, et al. Athermally photoreduced graphene oxides for three-dimensional holographic images[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 6984. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7984
[149] Wang Z P, Jiang L, Li X W, et al. Thermally reconfigurable hologram fabricated by spatially modulated femtosecond pulses on a heat-shrinkable shape memory polymer for holographic multiplexing[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2021, 13(43): 51736−51745. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c15012
[150] Hsu W L, Chen Y C, Yeh S P, et al. Review of metasurfaces and metadevices: advantages of different materials and fabrications[J]. Nanomaterials (Basel), 2022, 12(12): 1973. doi: 10.3390/nano12121973
[151] Arbabi A, Arbabi E, Kamali S M, et al. Miniature optical planar camera based on a wide-angle metasurface doublet corrected for monochromatic aberrations[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 13682. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13682
[152] Zhou Y, Kravchenko I I, Wang H, et al. Multilayer noninteracting dielectric metasurfaces for multiwavelength metaoptics[J]. Nano Lett, 2018, 18(12): 7529−7537. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b03017
[153] Groever B, Chen W T, Capasso F. Meta-lens doublet in the visible region[J]. Nano Lett, 2017, 17(8): 4902−4907. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b01888
[154] Hong Y, Zhao D, Wang J Y, et al. Solvent-free nanofabrication based on ice-assisted electron-beam lithography[J]. Nano Lett, 2020, 20(12): 8841−8846. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c03809
[155] Chen Y Q, Xiang Q, Li Z Q, et al. “Sketch and peel” lithography for high-resolution multiscale patterning[J]. Nano Lett, 2016, 16(5): 3253−3259. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b00788
[156] Chen Y Q, Bi K X, Wang Q J, et al. Rapid focused ion beam milling based fabrication of plasmonic nanoparticles and assemblies via “sketch and peel” strategy[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(12): 11228−11236. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b06290
[157] She A L, Zhang S Y, Shian S, et al. Large area metalenses: design, characterization, and mass manufacturing[J]. Opt Express, 2018, 26(2): 1573−1585. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.001573
[158] Luo J, Zeng B, Wang C T, et al. Fabrication of anisotropically arrayed Nano-slots metasurfaces using reflective plasmonic lithography[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(44): 18805−18812. doi: 10.1039/C5NR05153C
[159] Liu L Q, Zhang X H, Zhao Z Y, et al. Batch fabrication of metasurface holograms enabled by plasmonic cavity lithography[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2017, 5(21): 1700429. doi: 10.1002/adom.201700429
[160] Pu M B, Guo Y H, Li X, et al. Revisitation of extraordinary young’s interference: from catenary optical fields to spin–orbit interaction in metasurfaces[J]. ACS Photonics, 2018, 5(8): 3198−3204. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.8b00437
[161] Oh D K, Lee T, Ko B, et al. Nanoimprint lithography for high-throughput fabrication of metasurfaces[J]. Front Optoelectron, 2021, 14(2): 229−251. doi: 10.1007/s12200-021-1121-8
[162] Atighilorestani M, Jiang H, Kaminska B. Electrochromic-polymer-based switchable plasmonic color devices using surface-relief nanostructure pixels[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2018, 6(23): 1801179. doi: 10.1002/adom.201801179
[163] Lee G Y, Hong J Y, Hwang S, et al. Metasurface eyepiece for augmented reality[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 4562. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07011-5
[164] Makarov S V, Milichko V, Ushakova E V, et al. Multifold emission enhancement in nanoimprinted hybrid perovskite metasurfaces[J]. ACS Photonics, 2017, 4(4): 728−735. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.6b00940
[165] Faniayeu I, Mizeikis V. Realization of a helix-based perfect absorber for IR spectral range using the direct laser write technique[J]. Opt Mater Express, 2017, 7(5): 1453−1462. doi: 10.1364/OME.7.001453
[166] Balli F, Sultan M, Lami S K, et al. A hybrid achromatic metalens[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 3892. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17646-y
[167] 曹良才, 何泽浩, 刘珂瑄, 等. 元宇宙中的动态全息三维显示: 发展与挑战(特邀)[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2022, 51(1): 20210935. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210935
Cao L C, He Z H, Liu K X, et al. Progress and challenges in dynamic holographic 3D display for the metaverse (Invited)[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2022, 51(1): 20210935. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210935
[168] Zhang C L, Zhang D F, Bian Z P. Dynamic full-color digital holographic 3D display on single DMD[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2021, 4(3): 200049. doi: 10.29026/oea.2021.200049
[169] Zheng P X, Li J X, Li Z L, et al. Compressive imaging encryption with secret sharing metasurfaces[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2022, 10(15): 2200257. doi: 10.1002/adom.202200257
[170] 玛地娜, 李智, 程化, 等. 超表面多维光场调控及基于机器学习的优化[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(18): 1824−1844. doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0023
Ma D N, Li Z, Cheng H, et al. Multi-dimensional manipulation of optical field withmetasurfaces and its optimization based on machine learning[J]. Chin Sci Bull, 2020, 65(18): 1824−1844. doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0023
[171] Shi L, Li B C, Kim C, et al. Towards real-time photorealistic 3D holography with deep neural networks[J]. Nature, 2021, 591(7849): 234−239. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-03152-0
[172] Shi Z J, Zhu A Y, Li Z Y, et al. Continuous angle-tunable birefringence with freeform metasurfaces for arbitrary polarization conversion[J]. Sci Adv, 2020, 6(23): eaba3367. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aba3367
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: