-
摘要
本文提出了一种可以实现光纤高阶模式(HOM)在激光腔内振荡的锁模掺镱光纤激光器。通过使用一对级联的模式选择耦合器(MSC)作为有效的模式转换器,获得光纤锁模激光腔内HOM产生。其中,制备的MSC中心波长为1064 nm,可实现80 nm的模式转换带宽和94%的高阶模式纯度。通过搭建掺镱锁模光纤激光器,实验获得了3 dB谱宽7.4 nm、脉冲重复频率10.9 MHz、射频信噪比55 dB的锁模脉冲激光,输出功率的斜率效率为2.3%。实验证明,这种方法可在激光器内部通过模式级联转换,且能参与腔内锁模过程获得脉冲HOM激光。

Abstract
We demonstrate a mode-locked Yb-doped fiber laser (YDFL) that enables fiber high-order mode (HOM) oscillation inside the ring cavity, by using a pair of mode selective couplers (MSCs) as an effective mode converter, the optical fiber HOM is obtained. The central wavelength of MSC is located at 1064 nm, which can achieve 80 nm mode conversion bandwidth and 94% high-order mode purity. A mode-locked pulsed fiber laser with a 3 dB spectral width of 7.4 nm, a pulse repetition frequency of 10.9 MHz, and a radio frequency signal-to-noise ratio of 55 dB is obtained, and the slope efficiency of the output power is 2.3%. These results show that the HOM can be directly oscillated by the cascaded MSCs in the fiber laser and participated in the mode-locking process to obtain a pulsed HOM laser.
-
Key words:
- mode-selective couplers /
- high-order mode /
- Yb-doped fibers /
- mode-locking fiber lasers
-
Overview

Overview: High-order modes (HOMs), surpassing the capacity barrier in the traditional single-mode fiber (SMF) communication system, have attracted extensive attention and been widely applied in the fiber laser, optical communication, particle trapping, remote sensing technology, and so on. The HOMs include linear polarization LP11, LP21, LP02, LP31, and even higher-order modes, which can be generated by using free-space and fiber-based mode conversion devices. LP11 mode is one of the most important HOMs, which has four vector eigenmodes. These eigenmodes are called as cylindrical vector beams (CVBs) with the axially symmetric polarization and circular intensity distribution. A polarization controller (PC) added on the fiber can effectively eliminate the degeneracy of LP11 mode to excite individual vector modes in different polarization states. Additionally, the orbital angular momentum (OAM) characterized by helical wavefront can be generated by superimposing two orthogonal vector modes. Recently, ultrafast fiber lasers combined by HOMs have been reported owing to their outstanding characteristics, such as compactness, high peak power, narrow pulse width, and low cost. However, the HOMs were converted outside the laser, and the fundamental mode (LP01) was still transmitted in the laser cavity.
In this paper, a HOM directly oscillating in a mode-locked Yb-doped fiber laser (YDFL) is demonstrated. Two PCs and a polarization-dependent isolator are used to achieve the mode-locked mechanism of nonlinear polarization rotation. A pair of home-made mode selective couplers (MSCs) connecting through their few-mode fiber (FMF) ports, acts as an efficient mode convertor to generate and oscillate HOMs in the FMF section of the YDFL. A MSC is composed of a SMF and a FMF, which are fused by using hydrogen oxygen flame technology to keep two fiber cores close to each other. The claddings of two fibers are partly fused to form a coupling region. If the phase matching condition is satisfied, the LP01 mode is transferred to the LP11 mode in the coupling region. The MSC has a central wavelength of 1064 nm, a mode conversion bandwidth of 80 nm, and a HOM purity of 94%. Meanwhile, according to the reversibility of MSCs, the LP11 mode can be lunched in the FMF port and output the LP01 mode in the SMF port. The pulsed laser with a 3 dB spectral width of 7.4 nm, a pulse repetition frequency of 10.9 MHz, and a signal-to-noise ratio of radio frequency of 55 dB is obtained, and the slope efficiency of the pump and output power is 2.3%. The pulse LP11 mode, CVB, and first-order OAM are obtained from the YDFL. These results demonstrate that the HOM can be generated by the MSC and be directly oscillated in the YDFL, and this approach is promising for directly generating pure and efficient HOMs in all-FMF ultrafast Yb-doped fiber lasers.
-

-
图 3 Output1端口监测锁模激光器的输出特性。(a)光谱;(b)脉冲序列;(c)中心频率为10.9 MHz的频谱图,插图:频谱范围为300 MHz的频谱图;(d)输出功率和泵浦功率的关系
Figure 3. Output1 characteristics of YDFL. (a) Optical spectrum; (b) Pulse trains; (c) The radio frequency (RF) spectrum with the central frequency of 10.9 MHz, inset: the RF spectrum with a 300 MHz span; (d) The YDFL output power and repetition rate variation along with elevating pump power
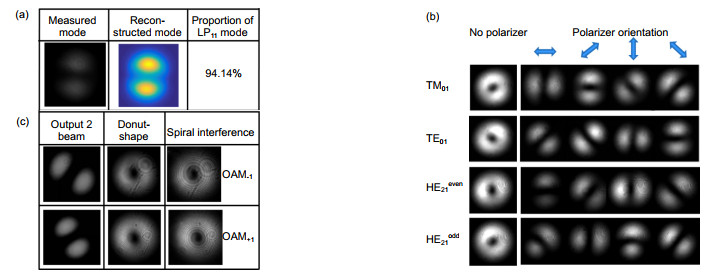
图 4 Output2端口监测模式的模场分布图。(a)测量和重构光场的线偏振LP11模式的模场分布,以及LP11模式的纯度;(b)柱矢量光束TM01、TE01、HE21even和HE21odd的模场分布;(c)线偏振LP11模、环状涡旋光及其干涉条纹的模场分布
Figure 4. Mode field distributions of output2. (a) Measured and reconstructed mode fields, and the LP11 mode purity; (b) Near-filed intensity distribution of TM01, TE01, HE21even and HE21odd modes; the first column: vector modes with donut-shape intensity profiles; the later four columns: distributions of each vector mode with a polarizer placed in front of CCD; (c) Intensity distributions of lobe-shaped LP11 mode, donut-shaped OAMs and their spiral interferences
-
参考文献
[1] Ren F, Li J H, Wu Z Y, et al. All-fiber optical mode switching based on cascaded mode selective couplers for short-reach MDM networks[J]. Optical Engineering, 2017, 56(4): 046104. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.56.4.046104
[2] Leon-Saval S G, Fontaine N K, Salazar-Gil J R, et al. Mode-selective photonic lanterns for space-division multiplexing[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(1): 1036-1044. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.001036
[3] Gasulla I, Kahn J M. Performance of direct-detection mode-group-division multiplexing using fused fiber couplers[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2015, 33(9): 1748-1760. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2015.2392255
[4] Dong J L, Chiang K S. Mode-locked fiber laser with transverse-mode selection based on a two-mode FBG[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2014, 26(17): 1766-1769. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2014.2335892
[5] Huang Y P, Shi F, Wang T, et al. High-order mode Yb-doped fiber lasers based on mode-selective couplers[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(15): 19171-19181. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.019171
[6] Wang T X, Zhao Y H, Wang C L, et al. Passively Q-switched erbium fiber laser using few-mode fiber long-period grating and carbon nanotube for cylindrical vector beam generation[C]//2017 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, San Jose, 2017: 1-2.
[7] Shi F, Cheng P K, Huang Y P, et al. Mode-locked all-fiber laser emitting two-color high-order transverse mode[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2019, 31(7): 497-500. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2019.2892843
[8] Kawauchi H, Yonezawa K, Kozawa Y, et al. Calculation of optical trapping forces on a dielectric sphere in the ray optics regime produced by a radially polarized laser beam[J]. Optics Letters, 2007, 32(13): 1839-1841. doi: 10.1364/OL.32.001839
[9] Milione G, Wang T, Han J, et al. Remotely sensing an object's rotational orientation using the orbital angular momentum of light (Invited Paper)[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2017, 15(3): 030012. doi: 10.3788/COL201715.030012
[10] Igarashi K, Park K J, Tsuritani T, et al. All-fiber-based selective mode multiplexer and demultiplexer for weakly-coupled mode-division multiplexed systems[J]. Optics Communications, 2018, 408: 58-62. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2017.08.049
[11] Bozinovic N, Yue Y, Ren Y X, et al. Terabit-scale orbital angular momentum mode division multiplexing in fibers[J]. Science, 2013, 340(6140): 1545-1548. doi: 10.1126/science.1237861
[12] Novotny L, Beversluis M R, Youngworth K S, et al. Longitudinal field modes probed by single molecules[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2001, 86(23): 5251-5254. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.86.5251
[13] Hamazaki J, Morita R, Chujo K, et al. Optical-vortex laser ablation[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(3): 2144-2151. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.002144
[14] Piccirillo B, D'Ambrosio V, Slussarenko S, et al. Photon spin-to-orbital angular momentum conversion via an electrically tunable q-plate[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97(24): 241104. doi: 10.1063/1.3527083
[15] Lee W M, Yuan X C, Cheong W C. Optical vortex beam shaping by use of highly efficient irregular spiral phase plates for optical micromanipulation[J]. Optics Letters, 2004, 29(15): 1796-1798. doi: 10.1364/OL.29.001796
[16] Bouchal Z, Haderka O, Čelechovský R. Selective excitation of vortex fibre modes using a spatial light modulator[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2005, 7(1): 125. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/7/1/125
[17] Huang K, Zeng J, Gan J W, et al. Controlled generation of ultrafast vector vortex beams from a mode-locked fiber laser[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(16): 3933-3936. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.003933
[18] Shen Y, Ren G B, Yang Y G, et al. Generation of the tunable second-order optical vortex beams in narrow linewidth fiber laser[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2017, 29(19): 1659-1662. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2742519
[19] Zhou Y, Wang A T, Gu C, et al. Actively mode-locked all fiber laser with cylindrical vector beam output[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(3): 548-550. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.000548
[20] Ismaeel R, Lee T, Oduro B, et al. All-fiber fused directional coupler for highly efficient spatial mode conversion[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(10): 11610-11619. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.011610
[21] 肖亚玲, 刘艳格, 王志, 等.基于少模光纤的全光纤熔融模式选择耦合器的设计及实验研究[J].物理学报, 2015, 64(20): 204207. doi: 10.7498/aps.64.204207
Xiao Y L, Liu Y G, Wang Z, et al. Design and experimental study of mode selective all-fiber fused mode coupler based on few mode fiber[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(20): 204207. doi: 10.7498/aps.64.204207
[22] Yao S Z, Ren G B, Shen Y, et al. Tunable orbital angular momentum generation using all-fiber fused coupler[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2018, 30(1): 99-102. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2776981
[23] Wang T, Wang F, Shi F, et al. Generation of femtosecond optical vortex beams in all-fiber mode-locked fiber laser using mode selective coupler[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2017, 35(11): 2161-2166. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2017.2676241
[24] Bale B G, Kutz J N, Chong A, et al. Spectral filtering for high-energy mode-locking in normal dispersion fiber lasers[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2008, 25(10): 1763-1770. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.25.001763
[25] Popa D, Sun Z, Hasan T, et al. 74-fs nanotube-mode-locked fiber laser[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 101(15): 153107. doi: 10.1063/1.4757293
[26] Huang L J, Guo S F, Leng J Y, et al. Real-time mode decomposition for few-mode fiber based on numerical method[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(4): 4620-4629. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.004620
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: