Research on the application of RANSAC algorithm in electro-optical tracking of space targets
-
摘要
基于光电跟踪设备对空间目标进行跟踪测量时,由于电磁干扰、云层遮挡或者地影等因素的影响,造成空间目标成像在设备视场中无法提取,严重时甚至导致系统闭环跟踪不能平稳进行。此时可以采用理论引导的方式,利用预测轨迹继续进行跟踪搜索。本文将广泛用于计算机视觉领域特征提取的随机抽样一致性(RANSAC)算法引入轨迹预测,并根据观测数据分布的特点进行改进提出WRANSAC算法,用于实时处理有限的历史观测数据,进行轨迹预测。引入该算法后,在对空间目标轨迹预测时,对历史观测数据的容错能力提高,对模型的敏感性降低,预测结果的准确性和鲁棒性远远优于最小二乘法。通过对比预测轨迹和实际轨迹,证明了该算法的有效性。

Abstract
When the electro-optic tracking system is used for space target tracking, it is difficult to extract the target from the field of view occasionally due to the impact of electromagnetic interference, cloud cover or earth shadow etc., and the closed-loop tracking system can barely work in severe cases. At this point the predicted orbit can be used to guide the system to ensure smooth scanning and tracking. In this paper, random sample consensus (RANSAC) algorithm is introduced, which has been widely used in feature extraction in computer vision, to achieve higher prediction accuracy. The loss function of RANSAC algorithm is improved and the WRANSAC algorithm is proposed according to the distribution of observed data, which is used to deal with the limited observation data in real time to track the space target. After the algorithm is adopted, the fault tolerance of observation data is improved and the sensitivity of the model is reduced. The accuracy and robustness of the prediction results are much better than that of the least squares method. The validity of the WRANSAC algorithm is proved by the comparison between the predicted trajectory and the actual trajectory.
-
Key words:
- parameter estimation /
- RANSAC /
- loss function /
- space target /
- orbit prediction
-
Overview

Overview: Monitoring and tracking the space debris (referred to as space target) is an important work of electro-optic tracking system. When measuring and tracking space targets in medium and high orbits, due to the long distance between the targets and observation station, the equivalent magnitude is relatively high. In order to enhance the detection capacity of tracking system, the aperture of electro-optic detectors is generally designed to be large. Meanwhile, the field of view of electro-optic detectors is usually small, namely angular component level, for the sake of suppressing the stray light in atmospheric channel. When the space target is shielded by clouds or enters the shadows or penumbra of the earth, the target image cannot be extracted from the field of view of CCD (charge coupled device) camera, the closed-loop tracking of the system cannot be barely work in severe cases. In this case, theoretical orbital data can be used to guide the mount of the system, which keeps track of the target in a short time. However, a large number of high-precision observation data in previous tracking process is discarded. In the absence of multi-station intersection measurement and orbit determination for space targets, guiding and tracking by predicting trajectory is an important way to solve this problem. In this paper, a real-time prediction and tracking algorithm based on short-arc observation data is studied in the background of single station which cannot be intersected.
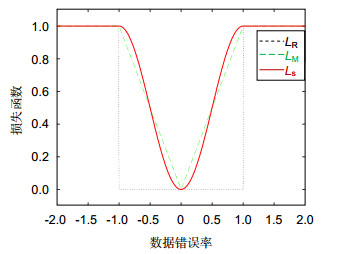
Random sample consensus (RANSAC) algorithm, which has been widely used in feature extraction in computer vision, is introduced in this paper to achieve higher prediction accuracy. The loss function of RANSAC algorithm is improved according to the distribution of observed data. Considering the fact that smaller errors are usually caused by noise from the interior point and larger errors may be affected by external points, and the boundary between the inner points and the outer points is usually imprecise in practice, the error within the threshold range is taken into account to increase the penalty for larger errors and decrease the penalty for smaller errors. What's more, the improved loss function has a continuous first derivative and varies more gently near the threshold, the sensitivity of the algorithm to threshold is further reduced. The improved algorithm is called WRANSAC algorithm.
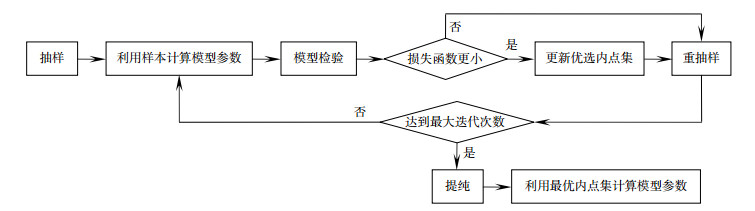
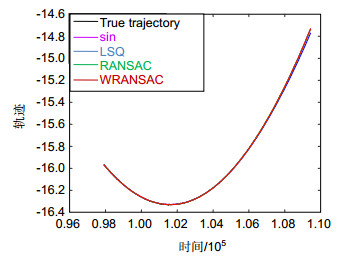
The WRANSAC algorithm is proposed according to the distribution of observed data, which is used to deal with the limited observation data in real time to track the space target. After the algorithm is adopted, the fault tolerance of observation data is improved and the sensitivity of the model is reduced. The accuracy and robustness of the prediction results are much better than that of the least squares method. The validity of the WRANSAC algorithm is proved by the comparison between the predicted trajectory and the actual trajectory.
-

-
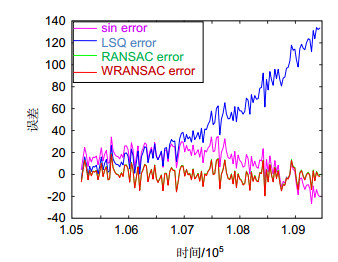
表 1 15 min、30 min和72 min预测误差特性
Table 1. Prediction error statistics for 15/30/72 minutes
预测时长/min 算法 sin LSQ RANSAC WRANSAC 15 最大值/(″) 34.9151 29.1957 19.5649 17.0257 最小值/(″) -6.9270 -10.8216 -17.7444 -16.8968 均值/(″) 15.1429 0.1934 2.4577 0.9701 方差 124.3353 90.9505 59.9375 57.9286 30 最大值/(″) 36.3312 32.0761 11.1779 10.8932 最小值/(″) -13.1593 -18.8263 -23.3834 -21.5939 均值/(″) 13.0059 -0.6765 -2.0592 -4.6598 方差 218.0527 163.9206 84.8496 82.1343 72 最大值/(″) 6.6790 286.3128 26.8620 17.7788 最小值/(″) -120.0175 -207.9139 -19.1023 -18.0916 均值/(″) -32.2389 6.0681 0.7308 -0.7330 方差 602.6599 15953.6643 118.8533 89.7496 -
参考文献
[1] 马佳光.捕获跟踪与瞄准系统的基本技术问题[J].光学工程, 1989(3): 1-42. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000558704
Ma J G. The basic technologies of the acquisition, tracking and pointing systems[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 1989(3): 1-42. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000558704
[2] 蔡怀宇, 丁蕾, 黄战华, 等.球幕点目标投影跟踪系统的精确标定方法[J].光电工程, 2018, 45(8): 170656. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170656
Cai H Y, Ding L, Huang Z H, et al. An accurate calibration method of the ball screen projection point targets tracking system[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2018, 45(8): 170656. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170656
[3] 张沛露, 王建军.车载跟瞄设备低轨卫星预测方法研究[J].数学的实践与认识, 2015, 45(6): 128-132. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sxdsjyrs201506014
Zhang P L, Wang J J. Research of LEO satellite orbit prediction for vehicle-borne optical measuring equipment[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2015, 45(6): 128-132. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sxdsjyrs201506014
[4] 李涛, 张金成.单机动目标跟踪精度分析[J].弹箭与制导学报, 2004, 24(2): 94-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2004.02.031
Li T, Zhang J C. The tracking accurancy analysis of single maneuvering targets[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2004, 24(2): 94-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2004.02.031
[5] 魏刚, 江传富, 杨坤涛.方位角准确预测法在光电跟踪中的应用研究[J].光电工程, 2006, 33(5): 6-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2006.05.002
Wei G, Jiang C F, Yang K T. Precision azimuth prediction method for electro-optical tracking[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2006, 33(5): 6-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2006.05.002
[6] 潘晓刚, 周海银, 王炯琦, 等.基于单站短弧段光学观测的低轨卫星轨道预报算法[J].天文学报, 2009, 50(4): 445-458. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5245.2009.04.011
Pan X G, Zhou H Y, Wang J Q, et al. Orbit prediction algorithm of LEO satellite based on optical measurement in short arc with single station[J]. Acta Astronomica Sinica, 2009, 50(4): 445-458. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5245.2009.04.011
[7] Choi S, Kim T, Yu W. Robust video stabilization to outlier motion using adaptive RANSAC[C]//2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 2009: 1897-1902.
[8] Chum O, Matas J. Optimal randomized RANSAC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2008, 30(8): 1472-1482. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.70787
[9] 黄宗福, 汪金真, 陈曾平.光电探测中空间目标和恒星目标运动特性分析[J].光电工程, 2012, 39(4): 67-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2012.04.012
Huang Z F, Wang J Z, Chen Z P. Motion characteristics analysis of space target and stellar target in opto-electronic observation[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2012, 39(4): 67-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2012.04.012
[10] 罗浩, 毛银盾, 于涌, 等.利用超大视场光电望远镜观测GEO中的目标识别方法[J].光电工程, 2017, 44(4): 418-426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.04.006
Luo H, Mao Y D, Yu Y, et al. A method of GEO targets recognition in wide-field opto-electronic telescope observation[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(4): 418-426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.04.006
[11] 岑明, 傅承毓, 刘兴法, 等.误差空间估计的卫星跟踪位置预测[J].光电工程, 2007, 34(6): 15-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2007.06.004
Cen M, Fu C Y, Liu X F, et al. Position prediction method for satellite tracking based on error-space estimate[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2007, 34(6): 15-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2007.06.004
[12] 程卫亮, 王向军, 万子敬, 等.压缩域目标跟踪算法在小型化DSP平台上的研究与实现[J].光电工程, 2017, 44(10): 972-982. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.10.005
Cheng W L, Wang X J, Wan Z J, et al. Research and implementation of target tracking algorithm in compression domain on miniaturized DSP platform[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(10): 972-982. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.10.005
[13] 李振伟, 张涛, 孙明国.星空背景下空间目标的快速识别与精密定位[J].光学精密工程, 2015, 23(2): 589-599. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201502035
Li Z W, Zhang T, Sun M G. Fast recognition and precise orientation of space objects in star background[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(2): 589-599. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201502035
[14] Xu M, Lu J. Distributed RANSAC for the robust estimation of three-dimensional reconstruction[J]. IET Computer Vision, 2012, 6(4): 324-333. doi: 10.1049/iet-cvi.2010.0223
[15] 陈付幸, 王润生.基于预检验的快速随机抽样一致性算法[J].软件学报, 2005, 16(8): 1431-1437. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb200508009
Chen F X, Wang R S. Fast RANSAC with preview model parameters evaluation[J]. Journal of Software, 2005, 16(8): 1431-1437. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb200508009
[16] Hast A, Nysjö J, Marchetti A. Optimal RANSAC-towards a repeatable algorithm for finding the optimal set[J]. Journal of WSCG, 2013, 21(1): 21-30.
[17] Chum O, Matas J, Kittler J. Locally optimized RANSAC[C]//Proceedings of 25th DAGM Symposiumon Pattern Recognition, Magdeburg, Germany, 2003, 2781: 236-243.
[18] Subbarao R, Meer P. Beyond RANSAC: user independent robust regression[C]//2006 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop (CVPRW'06), New York, NY, USA, 2006.
[19] 肖春宝, 冯大政, 冯祥卫.重抽样优化的快速随机抽样一致性算法[J].计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2016, 28(4): 606-613. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9775.2016.04.010
Xiao C B, Feng D Z, Feng X W. Fast RANSAC algorithm with resample optimization[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2016, 28(4): 606-613. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9775.2016.04.010
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: