-
摘要
红外视频中的舰船目标检测在渔政管理、港口监控等领域具有广泛的应用价值。传统的背景减除方法,如高斯混合模型(GMM)、码本算法(Codebook)和ViBe算法等,在海面红外视频舰船检测过程中容易受到海浪的影响导致错误检测。本文提出一种新的算法框架实现红外海面视频中的舰船检测任务。该算法框架采用了Top-Hat操作对红外图像进行预处理,从而有效过滤杂波,随后应用改进ViBe算法完成对舰船目标的检测。实验结果表明,本文算法可以有效抑制背景噪声,取得了较好的检测效果。

Abstract
The ship detection in infrared video has wide application value in fishery administration, port monitoring and other fields. Traditional background modeling methods, such as GMM(Gaussian mixture model), Codebook, and ViBe, will make more false detection in the ship detection from the infrared ocean video because of the impact of the waves. The paper proposes a new algorithm to detect ships in the infrared ocean video. The algorithm framework adopts the Top-Hat operation to preprocess the infrared image to filter the clutter effectively, then improves Vibe algorithm to detect the moving ship target. Experimental results show that the method can effectively suppress the background noise and get better detection results.
-
Key words:
- ship detection /
- moving targets detection /
- ViBe /
- infrared video
-
Overview

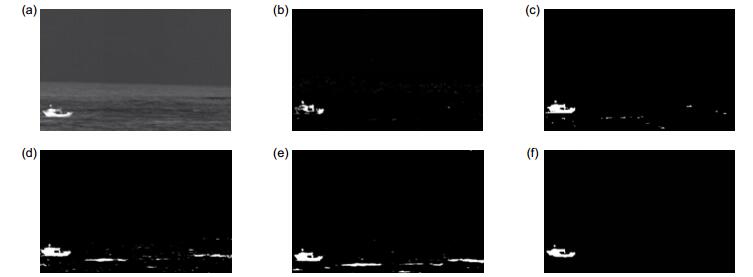
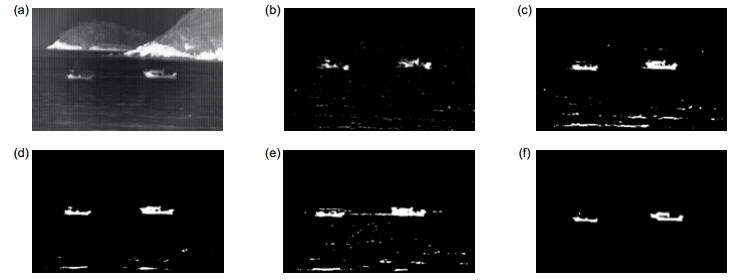
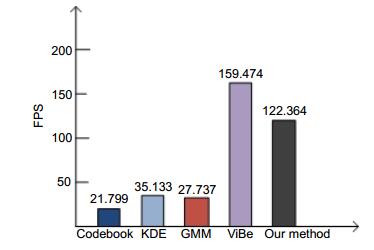
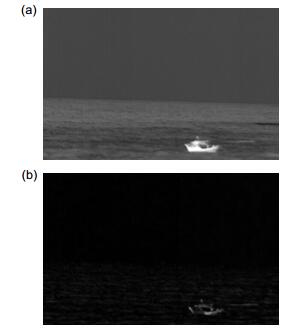
Overview: Moving target detection on the sea surface is a very complicated work. Due to the complex environment of the surface, there are a lot of clutter, so it is difficult to detect the ship on the sea surface. Most of the moving object detection algorithms are applicable to the field of visible light, but visible light imaging is only suitable for daytime work and cannot continuously detect the target at night. Infrared camera can continue to work at night, so it has certain advantages compared with the visible light camera. At present, the moving target detection based on infrared video is a popular research direction. The ship detection from infrared video has wide application value in fishery administration, port monitoring and other fields. In the infrared sea video, the background is more complicated and the waves are irregular, which undoubtedly will increase the difficulty of detecting the ship. Traditional background modeling methods contain Gaussian Mixture Model, Codebook and ViBe, etc. In the process of ship detection from the infrared video, the Gaussian Mixture Model is easy to produce hollow, and it will lead to the detected ship to be incomplete; The Codebook only can adapt to the background of the small periodic motion, unable to cope with the irregular change of the sea clutter; ViBe which uses the single frame for background modeling, can quickly detect foreground targets, but it is prone to ghost and cannot deal with the complex sea environment. Above these algorithms are easily affected by the waves leading to false detection. So this paper proposes a new algorithm framework to detect ship from the infrared video. First of all, the algorithm adopts a Top-Hat operation for preprocessing of the infrared images to suppress the background clutter effectively and highlight the ship target, and then improves ViBe to detect the moving ship target. The paper using adaptive threshold replaces the original fixed threshold of Vibe to deal with the complex environment of the sea surface. In addition, the paper introduces the color distortion as the judgment standard to complete the ship target detection. In the experiment of FPS contrast chart, the algorithm can achieve real-time requirements. In addition, the experimental results show that the algorithm can effectively suppress background noise, and the selection of adaptive threshold can better cope with the complex and varied waves on the sea. Compared with other algorithms, it is shown that the proposed algorithm can achieve better detection results and robustness.
-

-
-
参考文献
[1] 高飞, 蒋建国, 安红新, 等.一种快速运动目标检测算法[J].合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 35(2): 180-183. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/ZXLJ200720208.htm
Gao F, Jiang J G, An H X, et al. A fast detection algorithm for moving object[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2012, 35(2): 180-183. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/ZXLJ200720208.htm
[2] Bathia H V P K. An efficient algorithm for real time moving object detection using GMM and optical flow[J]. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering, 2015, 3(6): 5096-5101. doi: 10.15680/ijircce
[3] Zhang S S, Jiang T, Peng Y X, et al. A new pixel-level background subtraction algorithm in machine vision[C]//Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications, 2017: 520-531.
[4] St-Charles P L, Bilodeau G A. Improving background subtraction using Local Binary Similarity Patterns[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2014: 509-515.
[5] Ge W F, Dong Y H, Guo Z H, et al. Background subtraction with dynamic noise sampling and complementary learning[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2014: 2341-2346.
[6] Lee H, Kim H S, Kim J I. Background subtraction using background sets with image- and color-space reduction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2016, 18(10): 2093-2103. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2016.2595262
[7] Xu Y, Dong J X, Zhang B, et al. Background modeling methods in video analysis: a review and comparative evaluation[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology, 2016, 1(1): 43-60. doi: 10.1016/j.trit.2016.03.005
[8] Wang H, Gao J, Yu L J, et al. Combined improved Frequency-Tuned with GMM algorithm for moving target detection[C]//Proceedings of 2017 International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, 2017: 1848-1852.
[9] Kim K, Chalidabhongse T H, Harwood D, et al. Real-time foreground-background segmentation using codebook model[J]. Real-Time Imaging, 2005, 11(3): 172-185. doi: 10.1016/j.rti.2004.12.004
[10] 许晓航, 肖刚, 云霄, 等.复杂背景及遮挡条件下的运动目标跟踪[J].光电工程, 2013, 40(1): 23-30. http://www.oee.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1250.shtml
Xu X H, Xiao G, Yun X, et al. Moving object tracking in complex background and occlusion conditions[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2013, 40(1): 23-30. http://www.oee.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1250.shtml
[11] Barnich O, Van Droogenbroeck M. ViBe: a powerful random technique to estimate the background in video sequences[C]//Proceedings of 2009 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 2009: 945-948.
[12] Barnich O, Van Droogenbroeck M. ViBe: a universal background subtraction algorithm for video sequences[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(6): 1709-1724. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2101613
[13] Van Droogenbroeck M, Paquot O. Background subtraction: experiments and improvements for ViBe[C]//Proceedings of 2012 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2012: 32-37.
[14] Elgammal A, Harwood D, Davis L. Non-parametric model for background subtraction[C]//Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2000: 751-767.
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: