-
摘要
对太阳大气进行大视场高分辨力光学成像观测是开展太阳物理、空间天气等基础与应用研究的重要前提。对于地基太阳望远镜而言,为了消除地球大气湍流对光学系统的影响,自适应光学是高分辨力成像观测必备的技术手段,与此同时,为了突破大气非等晕性对传统自适应光学校正视场的限制,近年来多层共轭自适应光学技术等大视场自适应光学得到极大发展。本文首先梳理国外太阳自适应光学系统研制情况,重点介绍国内太阳自适应光学技术发展及应用情况,并进一步介绍了后续大视场太阳自适应光学技术发展情况以及目前所取得的成果。
Abstract
Solar images with high spatial resolution, high temporal resolution across a large field of view (FoV) are aspired for solar physics and space weather. Ground-based high spatial resolution imaging of the Sun is severely limited by wavefront disturbances induced by the Earth's atmosphere turbulence. Therefore, solar adaptive optics aims at these requirements and it has revitalized ground-based solar astronomy at existing telescopes. Meanwhile, multi-conjugate adaptive optics has been proved to overcome the anisoplanatism and obtain the high resolution images with a large field of view in solar observation by compensating for the turbulence with several deformable mirrors conjugated to different heights. In this review, we give some summarization of the development of solar adaptive abroad, and emphatically introduce several adaptive optics systems in China and the progress of large FoV adaptive optics.
-
Key words:
- solar observation /
- adaptive optics /
- multi-conjugate adaptive optics
-
Overview

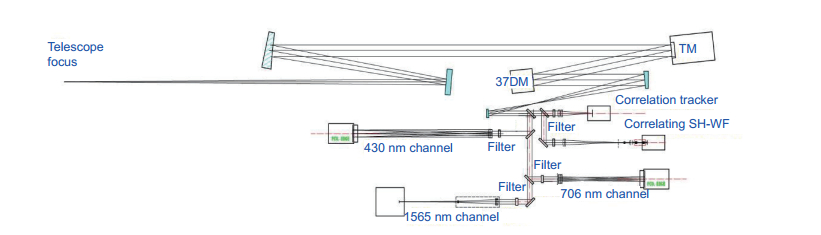
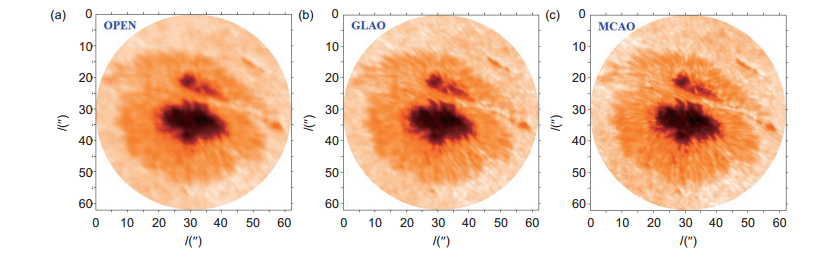
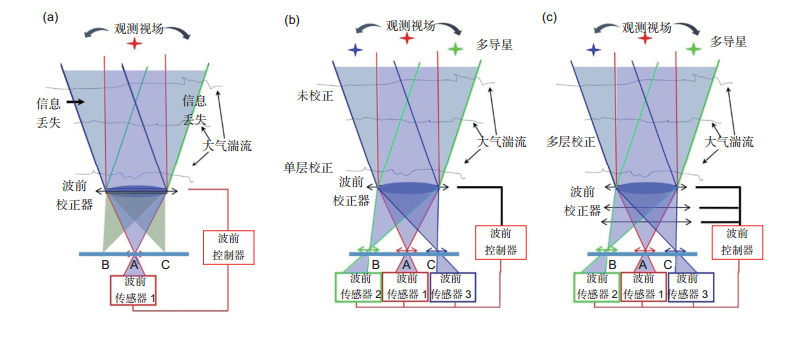
Overview: High spatial resolution imaging of the Sun is severely limited by the Earth’s atmosphere turbulence for ground-based solar telescope. Solar adaptive optics (AO) aims at the problems and has revitalized ground-based solar astronomy at existing telescopes. Meanwhile, multi-conjugate adaptive optics (MCAO) and ground layer adaptive optics (GLAO) have been proved to overcome the anisoplanatism and obtain the high resolution images with a large field of view in solar observation by compensating for the turbulence with several deformable mirrors conjugated to different heights. Over the three decades AO systems have been deployed at major ground-based solar telescopes and become an indispensable tool for obtaining high-resolution solar images today. Now the AO308 at the 1.6 m Goode Solar Telescope (GST) represents the highest level of solar AO, which consists of a 308-subaperture correlating Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor, a 357-element deformable mirror and a high-order wavefront correction controller. The first solar MCAO system Clear which is built at the GST saw the first light in 2017. In China, the development of solar AO dates back to 2002, in which the tip/tilt correction system was developed by Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and built at the 43-cm Solar Telescope of Nanjing University. After that, a 37-element AO experiment system was designed for the 26-cm solar fine structure telescope at Yunnan Astronomical Observatory. During 2012 to 2015, based on 1-m New Vacuum Solar Telescope (NVST) at Fuxian Solar Observatory, two generation solar AO systems were successfully developed. Meanwhile, MCAO and GLAO were under research to widen the correction field of view, a GLAO and MCAO prototype system were developed and built for the NVST. In this review, we give some summarization of the development of solar adaptive abroad, and emphatically introduce several adaptive optics systems in China and the progress of large FoV adaptive optics.
-

-
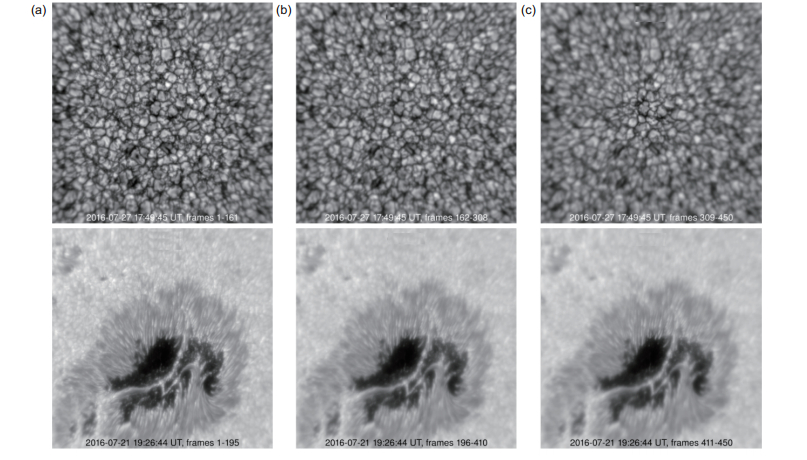
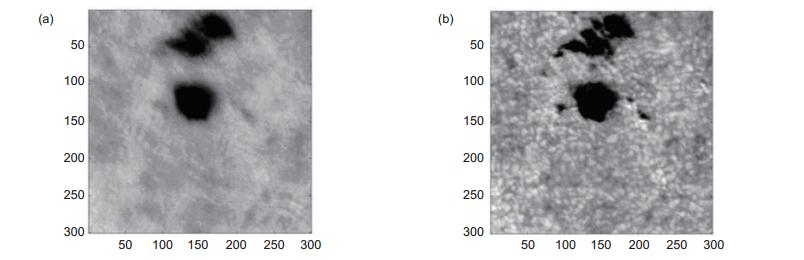
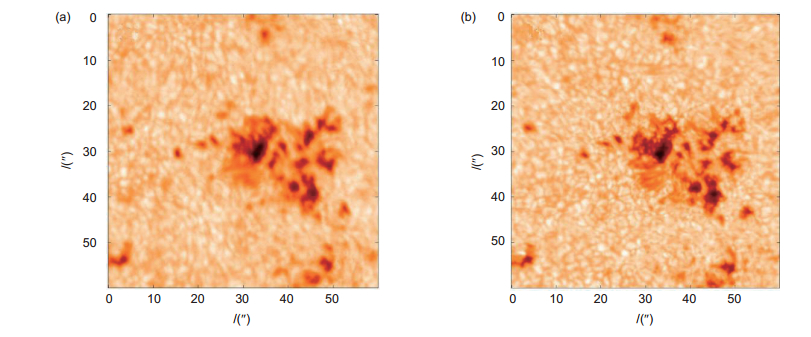
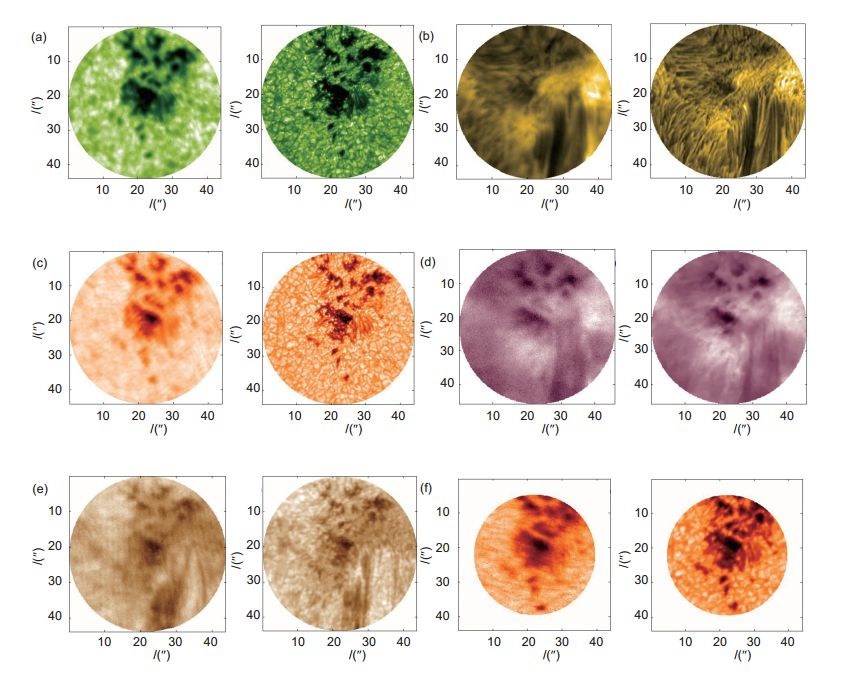
图 8 太阳多波段层析成像系统采集的151单元太阳AO校正前后太阳观测结果。图中展示了6个通道的成像结果,(a) G band;(b) Hα line;(c) TiO band;(d) Ca Ⅱ IR line;(e) He Ⅰ line;(f) Fe Ⅰ line [21]
Figure 8. Comparison of the observed results between without SAO and with speckle reconstruction of SAO image. These images were taken from the six imaging channels. (a) G band; (b) Hα line; (c) TiO band; (d) Ca Ⅱ IR line; (e) He Ⅰ line; (f) Fe Ⅰ line[21]
表 1 国外曾经使用过以及正在使用的太阳AO系统
Table 1. Developed/developing solar AO systems
望远镜/自适应光学 子孔径数 驱动器数 采样频率/kHz 硬件架构 首次观测/年 76 cm DST/Lockheed 19 57 2 Analog circuits 1986 76 cm DST/LOAO 24 97 <1.6 24 DSPs 1998 48 cm SVST 19 19 0.955 566 MHz alpha 1999 76 cm DST/HOAO 76 97 2.5 40 DSPs 2002 70 cm VTT/KAOS 36 35 0.955 8×900 MHz Sun 2002 1.5 m McMath-Pierce 120~200 37 0.955 1 GHz Pentium Ⅲ 2002 97 cm SST 37 37 0.955 1.4 GHz Athlon 2003 65 cm BBSO/HOAO 76 97 2.5 40 DSPs 2004 1.6 m NST/HOAO 76 97 2.5 40 DSPs 2010 1.6 m NST/HOAO 308 349 2 DSP clusters 2013 1.5 m GREGOR/HOAO 156 256 2 Multiple-CPU SMP 2012 4 m ATST/HOAO 1232 1313 - DSP clusters - 表 2 NVST上两套自适应光学系统主要技术参数
Table 2. The main parameters of the two generation solar adaptive optic systems
系统参数 一代37单元低阶AO系统 二代151单元高阶AO系统 校正阶数 20 65 波前探测子孔径数 30 102 探测器视场 12"×10" 24"×20" 探测像素分辨率/" 0.5 1 探测相机 MC1362 Phantom V311 探测帧频/Hz 2100 3500 校正器单元数 37 151 波前探测算法 Absolute difference Absolute difference square 处理机架构 Xilinx FPGA V6 + TI DSP C6747 Xilinx FPGA K7 + TI DSP C6678 -
参考文献
[1] Rimmele T R. Solar adaptive optics[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2000, 4007: 218-232. doi: 10.1117/12.390301
[2] 姜文汉.自适应光学技术[J].自然杂志, 2006, 28(1): 7-13. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zrzz200601002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Jiang W H. Adaptive optical technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2006, 28(1): 7-13. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zrzz200601002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[3] Esposito S. Introduction to multi-conjugate adaptive optics systems[J]. Comptes Rendus Physique, 2005, 6(10): 1039-1048. doi: 10.1016/j.crhy.2005.11.016
[4] Hubin N, Arsenault R, Conzelmann R, et al. Ground layer adaptive optics[J]. Comptes Rendus Physique, 2005, 6(10): 1099-1109. doi: 10.1016/j.crhy.2005.10.005
[5] Hardy J W. Solar imaging experiment: final report[R]. Lexington, MA: Air Force Geophysics Laboratory, 1980.
[6] Acton D S, Smithson R C. Solar imaging with a segmented adaptive mirror[J]. Applied Optics, 1992, 31(16): 3161-3169. doi: 10.1364/AO.31.003161
[7] Berkefeld T, Schmidt D, Soltau D, et al. The GREGOR adaptive optics system[J]. Astronomische Nachrichten, 2012, 333(9): 863-871. doi: 10.1002/asna.v333.9
[8] Dirk S, Thomas B, Frank H, et al. GREGOR MCAO looking at the Sun[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2000, 4007: 218. doi: 10.1117/12.390301
[9] Shumko S, Gorceix N, Choi S, et al. AO-308: the high-order adaptive optics system at Big Bear Solar Observatory[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9148: 914835. doi: 10.1117/12.2056731
[10] Schmidt D, Berkefeld T, Heidecke F, et al. GREGOR MCAO looking at the Sun[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014: 9148: 91481T. http://www.spie.org/Publications/Proceedings/Paper/10.1117/12.2055154
[11] Schmidt D, Gorceix N, Goode P R, et al. Clear widens the field for observations of the Sun with multi-conjugate adaptive optics[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2017, 597: L8. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312192517_Clear_widens_the_field_for_observations_of_the_Sun_with_multi-conjugate_adaptive_optics
[12] Kong L, Zhang L Q, Zhu L, et al. Prototype of solar ground layer adaptive optics at the 1 m New Vacuum Solar Telescope[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2016, 14(10): 100102. doi: 10.3788/COL
[13] 饶长辉, 姜文汉, 凌宁, 等.太阳表面米粒结构观测对比度分析[J].天文学报, 2001, 42(2): 134-139. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=twxb200102004
Rao C H, Jiang W H, Ling N, et al. Analysis of the observed R. M. S. contrast in solar granulation[J]. Acta Astronomica Sinica, 2001, 42(2): 134-139. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=twxb200102004
[14] 饶长辉, 张学军, 姜文汉.太阳米粒结构相关哈特曼-夏克波前传感模拟研究[J].光学学报, 2002, 22(3): 285-289. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/e5d1dcec561252d380eb6ebb.html
Rao C H, Zhang X J, Jiang W H. Simulation study on correlating Hartmann-Shack Wavefront sensor for solar granulation[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2002, 22(3): 285-289. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/e5d1dcec561252d380eb6ebb.html
[15] Rao C H, Jiang W H, Ling N. Adaptive-optics compensation by distributed beacons for non-Kolmogorov turbulence[J]. Applied Optics, 2001, 40(21): 3441-3449. doi: 10.1364/AO.40.003441
[16] Rao C H, Jiang W H, Fang C, et al. A tilt-correction adaptive optical system for the solar telescope of Nanjing University[J]. Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2003, 3(6): 576-586. doi: 10.1088/1009-9271/3/6/576
[17] Rao C H, Zhu L, Rao X J, et al. Performance of the 37-element solar adaptive optics for the 26 cm solar fine structure telescope at Yunnan Astronomical Observatory[J]. Applied Optics, 2010, 49(31): G129-G135. doi: 10.1364/AO.49.00G129
[18] Rao C H, Zhu L, Rao X J, et al. First generation solar adaptive optics system for 1-m New Vacuum Solar Telescope at Fuxian Solar Observatory[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2016, 16(2): 023. http://www.opticsinfobase.org/abstract.cfm?uri=col-13-12-120101
[19] Rao C H, Zhu L, Rao X J, et al. Instrument description and performance evaluation of a high-order adaptive optics system for the 1 m new vacuum solar telescope at Fuxian solar observatory[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2016, 833(2): 210. doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/833/2/210
[20] Rao C H, Zhu L, Gu N T, et al. A high-resolution multi-wavelength simultaneous imaging system with solar adaptive optics[J]. The Astronomical Journal, 2017, 154(4): 143. doi: 10.3847/1538-3881/aa84b4
[21] Kong L, Zhu L, Zhang L Q, et al. Real-time controller based on FPGA and DSP for solar ground layer adaptive optics prototype system at 1-m NVST[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2017, 9(2): 7801411. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275223545_Solar_Ground-Layer_Adaptive_Optics
[22] 张兰强, 顾乃庭, 饶长辉.大气湍流三维波前探测模式层析算法分析[J].物理学报, 2013, 62(16): 169501. doi: 10.7498/aps.62.169501
Zhang L Q, Gu N T, Rao C H. Analysis of modal tomography for three-dimensional wavefront sensing of atmosphere turbulence[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(16): 169501. doi: 10.7498/aps.62.169501
[23] Zhang L Q, Guo Y M, Rao C H. Solar multi-conjugate adaptive optics based on high order ground layer adaptive optics and low order high altitude correction[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(4): 4356-4367. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.004356
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: