-
摘要
表面等离激元结构色是一种由可见光与金属微纳结构相互作用而产生的颜色。为了分析不同金属微纳结构对可见光特性的调控特性,本文选取了几种典型结构包括纳米光栅、亚波长孔阵列及多层堆叠结构,探究了其选频机理以及滤色效果。本文主要介绍了近几年来相关领域的最新发展成果,并对不同器件的应用范围,现存问题以及发展趋势做出了评述。表面等离激元结构色微纳器件优秀的滤波特性以及良好的电学响应,使其在超高分辨率显示和远程实时光调控等领域具备重大潜力。
Abstract
Plasmonic structural colors originate from the interaction between light and metallic nanostructures. Rapid development in nanofabrication and characterization of plasmonic structures provides an efficient way to control light properties at subwavelength scale, which can generate plasmonic structural colors. Here we introduce several representative plasmonic nanostructures which can generate visible structural colors, including nanogratings, perforated metallic films, metal-insulator-metal resonators, dynamically tunable color generators and perfect absorbers. We highlight the properties of plasmonic colors and discuss the intrinsic plasmonic resonance mechanisms. Plasmonic structural colors have the advantages such as ultra-small patterns and rapid response of external change, which are believed to offer a promising future in high-resolution color displays and real-time colors controlling.
-
Key words:
- plasmonics /
- color filtering /
- nanofabrication /
- metallic nanostructures
-
Overview

Abstract:Perception of color with our eyes is one of the major sources of information that we gain from our surroundings. The color of an object depends on which portion of light (range of wavelengths) reaches our eyes. In nature, structural colors are often caused by the interaction of light with dielectric structures whose dimensions are on the order of visible-light wavelengths. For example, in beetles, the color is originated from the microstructure of the skin which is acting as scattering center; while in some butterflies, the colorful patterns are routed from the reflection from the top of the wings. Different optical interactions, including multilayer interference, light scattering and photonic crystal effect, give rise to selective transmission or reflection of particular light wavelengths, which leads to the generation of structural colors. With the consumption of dyes and pigments, recycling of colored discarded materials has been a very difficult issue because of the hardships in relation to the dissociation of diverse chemical compounds present in the colorant agents. Plasmonic colors therefore draw attention as they enable generation of vivid colors only by geometrical arrangement of metals which not only eases the recycling but also enhances the chemical stability of the colors. Plasmonic colors are structural colors that originate from the interaction between light and metallic nanostructures. Rapid development in nanofabrication and characterization of plasmonic structures provides an efficient way to control light properties at subwavelength scale, which can generate plasmonic structural colors. The engineering of plasmonic colors is a promising, rapidly emerging research field that could have a large technological impact. Artificial surfaces, in particular, on which the colors are generated via a resonant interaction between light and subwavelength metallic nanostructures, have emerged as nanomaterials or metamaterials for the realization of structural colors. Here we introduce several representative plasmonic nanostructures which can generate visible structural colors, including nanogratings, perforated metallic films, metal-insulator-metal resonators, dynamically tunable color generators and perfect absorbers. We highlight the properties of plasmonic colors and discuss the intrinsic plasmonic resonance mechanisms. Plasmonic structural colors have features of sub-diffraction localization, high-fidelity color rendering and rapid responses of external changes, which are believed to offer a promising future in the applications including ultra-high resolution color display, spectral filtering and sensing, holography, three-dimensional stereoscopic imaging and real-time colors controlling with extremely compact device architectures.
-

-
图 2 (a) 光入射到半径为5 nm的金属颗粒上,电场E0造成了金属颗粒表面电子的位移与极化,造成了金属表面电子的震荡——表面等离激元. (b)当光子能量为3.5 eV时,金属颗粒背面的外界电场(黑色箭头)被大大增强。颗粒内部的电场方向一致(红色箭头)且强度与外界电场在同一量级[21].
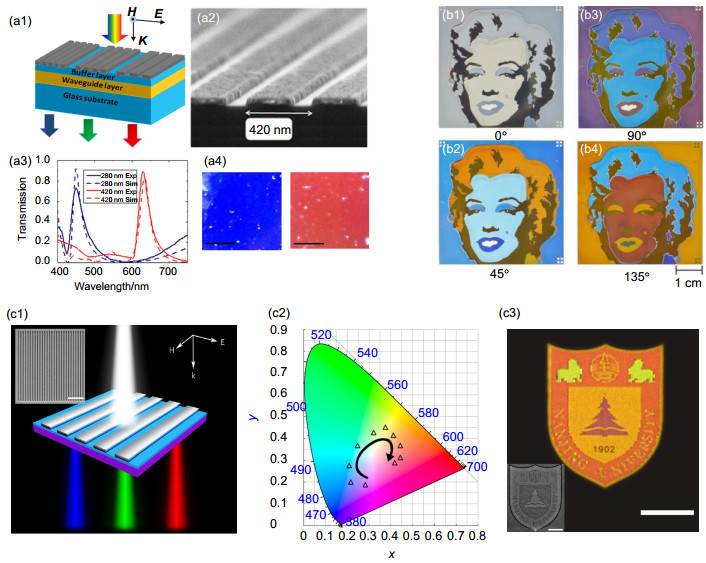
图 3 周期性光栅产生结构色. (a1)银光栅耦合波导颜色滤波器示意图. (a2)器件的SEM图像,周期为420 nm. (a3)周期为280 nm与420 nm的理论与实验测得的透射率. (a4)为与(a3)中两条谱线相对应的蓝色与红色[28]. (b1)~(b4)为基于银光栅结构的滤波成像(经过0°,45°,90°,135°产生不同颜色的图像)[36]. (c1)超薄无基底薄膜波导的结构示意图,其中最上方为铝光栅,蓝色层为MgF2覆盖层,紫色层为Si3N4波导层,内图为结构的SEM图,比例尺为400 nm. (c2)实验测得颜色在CIE1931色空间的反演图. (c3) 100倍物镜下制造的南京大学校徽显微图(42 μm ×34 μm),其中内图为其SEM图,比例尺均为10 μm[38].
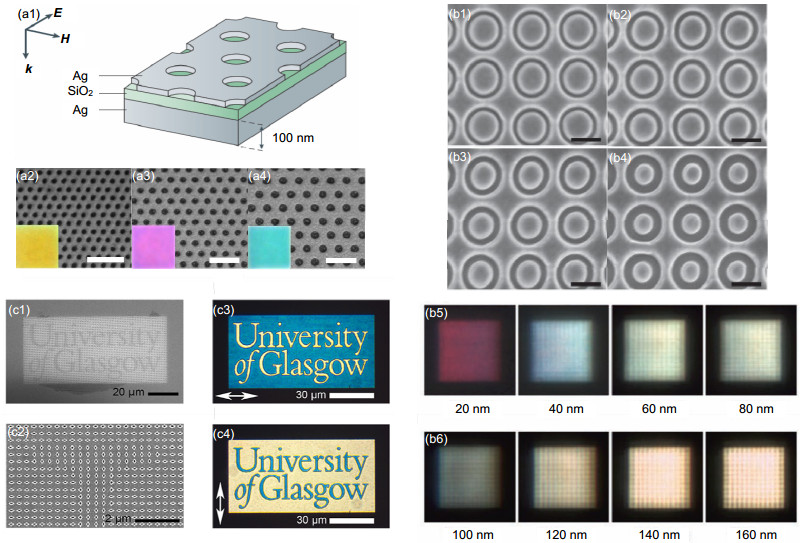
图 5 金属-绝缘体-金属(MIM)结构产生结构色. (a1)设置有输入狭缝与输出狭缝的MIM结构示意图,dsep为两狭缝的间距. (a2) MIM波导结构的光学显微图,器件1~3分别对应dsep为2.5 μm, 3.5 μm和4 μm [59]. (b1) MIM谐振结构的示意图,插图是其SEM图. (b2)白光激发下的光学颜色显微图[60]. (c1)有源MIM结构示意图. (c2)器件的光电效应函数图,圆点,方点和三角点分别对应蓝绿,品红和黄色滤波器的光电效应行为.太阳能电池的性能参数比如短路电流密度(Jsc),开路电压(Voc),填充因数(FF)和光电转换效率(PCE)总结如下:蓝绿色(Jsc=5.28 mA·cm-2, Voc=0.51 V, FF=57.5%, PCE= 1.55%),品红色(Jsc=5.04 mA·cm-2, Voc=0.49 V, FF=33.1%, PCE=0.82%),黄色(Jsc=3.98 mA·cm-2, Voc=0.48 V, FF= 31.2%, PCE=0.60%)[61].
图 6 (a1)铝光栅电致变色器件结构示意图,光栅周期从240 nm到390 nm(步长30 nm),铝和氮化硅的厚度分别为250 nm和170 nm. (a2) PolyProDOT-Me2还原态和氧化态的化学式. (a3)和(a4)分别为光开关为ON和OFF状态,测得的透射光谱及其颜色显微图[66]. (b1)液晶结合金属纳米阵列的结构示意图,放大部分为液晶分子在各项同性与各向异性之间的转换过程. (b2)当液晶分子分别为棒状和弯曲状时,对应的归一化吸收谱线,其中红色谱线对应液晶分子呈现棒状,蓝色谱线对应液晶分子呈现弯曲状. (b3)分别当紫外光激发10 s,20 s,30 s,40 s,50 s,60 s时,结构所对应的透射谱[68].
图 7 (a1)金属-介质多层堆叠结构示意图. (a2) Cr(200 nm)/Ge(33 nm) /Si(32 nm) /TiO2(56 nm)/MgF2(118 nm)堆叠结构的吸收谱,红线为模拟结果,蓝线为实验结果;(a3)入射光为0°~70°的吸收谱,红线为模拟结果,蓝线为实验结果;(a4)该器件的照片[73]. (b1) NPT的结构示意图. (b2) NPT与Au/NPT的对比照片. (b3),(b4) Au/NPT与Au/D-NPT的SEM图,插图为对应的傅里叶变换图. (b5) Au/NPT与Au/D-NPT在0.2 μm~10 μm吸收谱对比图
-
参考文献
[1] Armstrong E, O'Dwyer C. Artificial opal photonic crystals and inverse opal structures – fundamentals and applications from optics to energy storage[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2015, 3(24): 6109-6143. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c00f9b0f4c9c1b5357fe6353c37f1fd6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[2] Xu Ting, Shi Haofei, Wu Y K, et al. Structural colors: from plasmonic to carbon nanostructures[J]. Small, 2011, 7(22): 3128-3136. doi: 10.1002/smll.v7.22 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=71b5c7d9d34aca06cfa0d22a952bfc07&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[3] Padovani S, Puzzovio D, Sada C, et al. XAFS study of copper and silver nanoparticles in glazes of medieval middle-east lustreware (10th-13th century)[J]. Applied Physics A, 2006, 83(4): 521-528. doi: 10.1007/s00339-006-3558-4 https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007%2Fs00339-006-3558-4.pdf
[4] Colomban P. The use of metal nanoparticles to produce yellow, red and iridescent colour, from bronze age to present times in lustre pottery and glass: solid state chemistry, spectroscopy and nanostructure[J]. Journal of Nano Research, 2010, 8(27): 109-132. https://www.scientific.net/JNanoR.8.109
[5] Faraday M. The bakerian lecture: experimental relations of gold (and other metals) to light[J].Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1857, 147: 145-181. doi: 10.1098/rstl.1857.0011 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5937c3bc4e9efc591dd15d9ad3eedfcd&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[6] Mie G. Beiträge zur optik trüber medien, speziell kolloidaler metallüsungen[J]. Annalen Der Physik, 1908, 330(3): 377-445. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3889 https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/andp.19083300302
[7] Hedayati M K, Faupel F, Elbahri M. Review of plasmonic nanocomposite metamaterial absorber[J]. Materials, 2014, 7(2): 1221-1248. doi: 10.3390/ma7021221 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a17e35820d9f55a52608efa5c31053bd&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[8] Murray W A, Barnes W L. Plasmonic materials[J]. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(22): 3771-3782. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4095
[9] Kildishev A V, Boltasseva A, Shalaev V M. Planar Photonics with Metasurfaces[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6125):1232009 doi: 10.1126/science.1232009 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=64987b34caa0ebabd3c760e032ad1b64&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[10] Gu Yinghong, Zhang Lei, Yang J K W, et al. Color generation via subwavelength plasmonic nanostructures[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(15): 6409-6419. doi: 10.1039/C5NR00578G http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlepdf/2015/NR/C5NR00578G
[11] Al-Salem S M, Lettieri P, Baeyens J. Recycling and recovery routes of plastic solid waste (PSW): a review[J]. Waste Management, 2009, 29(10): 2625-2643. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2009.06.004 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0956053X09002190
[12] Kumar K, Duan Huigao, Hegde R S, et al. Printing colour at the optical diffraction limit[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2012, 7(9): 557-561. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2012.128 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=327d5b4be75bc4bf1ec0d3abea339dcc&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[13] Roberts A S, Pors A, Albrektsen O, et al. Subwavelength plasmonic color printing protected for ambient use[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(2): 783-787. doi: 10.1021/nl404129n http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=630d602d15a39774d0e27a10eb012743&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[14] Tan S J, Zhang Lei, Zhu Di, et al. Plasmonic color palettes for photorealistic printing with aluminum nanostructures[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(7): 4023-4029. doi: 10.1021/nl501460x http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=767b1bca5938db80f27c1d6c4db6fcad&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[15] Lueder E. Liquid crystal displays: addressing schemes and electro-optical effects[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley Publishing, 2010.
[16] Singh R R, Ho D, Nilchi A, et al. A CMOS/thin-film fluorescence contact imaging microsystem for DNA analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2010, 57(5): 1029-1038. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2010.2043990 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a2802f8a488c1014fa46e6244c79a1f0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[17] Yokogawa S, Burgos S P, Atwater H A. Plasmonic color filters for CMOS image sensor applications[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(8): 4349-4354. doi: 10.1021/nl302110z http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=9e40d634efcf633cfafd97e4b6ca196b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[18] Cho Y, Choi Y K, Sohn S H. Optical properties of neodymium-containing polymethylmethacrylate films for the organic light emitting diode color filter[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 89(5): 051102. doi: 10.1063/1.2244042 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=77a4a23e56d1540a24ffb0326ec2e763&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[19] Xin J Z, Hui K C, Wang K, et al. Thermal tuning of surface plasmon resonance: Ag gratings on barium strontium titanate thin films[J]. Applied Physics A, 2012, 107(1): 101-107. doi: 10.1007/s00339-011-6742-0 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00339-011-6742-0
[20] Ozbay E. Plasmonics: merging photonics and electronics at nanoscale dimensions[J]. Science, 2006, 311(5758): 189-193. doi: 10.1126/science.1114849 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3c61fe9ccbb1d9fb1e4c9244fe01914d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[21] Stockman M I. Nanoplasmonics: the physics behind the applications[J]. Physics Today, 2011, 64(2): 39-44. doi: 10.1063/1.3554315 http://www.physics.gsu.edu/stockman/data/Stockman_Phys_Today_2011_Physics_behind_Applications.pdf
[22] Arsenault A C, Míguez H, Kitaev V, et al. A polychromic, fast response metallopolymer gel photonic crystal with solvent and redox tunability: a step towards photonic ink (P-Ink)[J]. Advanced Materials, 2003, 15(6): 503-507. doi: 10.1002/adma.200390116 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=31f76a8ab1eeeaaaad04687d1c118a9e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[23] Kim H, Ge Jianping, Kim J, et al. Structural colour printing using a magnetically tunable and lithographically fixable photonic crystal[J]. Nature Photonics, 2009, 3(9): 534-540. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2009.141 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=323a617593f1fdb6c1a56824027f4142&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[24] Cao Linyou, Fan Pengyu, Barnard E S, et al. Tuning the color of silicon nanostructures[J]. Nano Letters, 2010, 10(7): 2649-2654. doi: 10.1021/nl1013794 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ba82af04f95322159b13a246720999e6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[25] Seo K, Wober M, Steinvurzel P, et al. Multicolored vertical silicon nanowires[J].Nano Letters, 2011, 11(4): 1851-1856. doi: 10.1021/nl200201b http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=85906db1b77b6ee1eba3696a67c5f67c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[26] Ritchie R H, Arakawa E T, Cowan J J, et al. Surface-plasmon resonance effect in grating diffraction[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1968, 21(22): 1530-1533. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.21.1530 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b7ad57f45546a2214237fa6beb026e22&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[27] Homola J, Koudela I, Yee S S. Surface plasmon resonance sensors based on diffraction gratings and prism couplers: sensitivity comparison[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 1999, 54(1-2): 16-24. doi: 10.1016/S0925-4005(98)00322-0 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925400598003220
[28] Kaplan A F, Xu Ting, Guo L J. High efficiency resonance-based spectrum filters with tunable transmission bandwidth fabricated using nanoimprint lithography[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99(14): 143111. doi: 10.1063/1.3647633 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=59db1a583b7683e44af485dd5c8a7809&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[29] Zeng Beibei, Gao Yongkang, Bartoli F J. Ultrathin nanostructured metals for highly transmissive plasmonic subtractive color filters[J]. Scientific Reports, 2013, 3: 2840. doi: 10.1038/srep02840 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=592f94b75af68b31a4e202626744ef9b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[30] Yoon Y T, Park C H, Lee S S. Highly efficient color filter incorporating a thin metal-dielectric resonant structure[J]. Applied Physics Express, 2012, 5(2): 022501. doi: 10.1143/APEX.5.022501 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=31538708df0e84401474b93adf4868b2&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[31] Park C H, Yoon Y T, Shrestha V R, et al. Electrically tunable color filter based on a polarization-tailored nano-photonic dichroic resonator featuring an asymmetric subwavelength grating[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(23): 28783-28793. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.028783 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=954ad6b59771d871e4fb5048222a3bb4&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[32] Honma H, Takahashi K, Fukuhara M, et al. Free-standing aluminium nanowire arrays for high-transmission plasmonic colour filters[J]. IET Micro & Nano Letters, 2014, 9(12): 891-895. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3fea4703296ec68fd67c23fc6363cb8f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[33] Shrestha V R, Lee S S, Kim E S, et al. Polarization-tuned dynamic color filters incorporating a dielectric-loaded aluminum nanowire array[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 12450. doi: 10.1038/srep12450 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=28622b42138f780882fd71ad997de01c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[34] Ye M, Hu X L, Sun L B, et al. Duty cycle dependency of the optical transmission spectrum in an ultrathin nanostructured Ag film[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 621: 244-249. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.09.202 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925838814023858
[35] Kedawat G, Kumar P, Vijay Y K, et al. Fabrication of highly efficient resonant structure assisted ultrathin artificially stacked Ag/ZnS/Ag multilayer films for color filter applications[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2015, 3(26): 6745-6754. doi: 10.1039/C5TC00678C http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4813ee127e49f8a7fff5700065fa1463&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[36] Duempelmann L, Luu-Dinh A, Gallinet B, et al. Four-fold color filter based on plasmonic phase retarder[J]. ACS Photonics, 2016, 3(2): 190-196. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.5b00604 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=7424f953702c6d28ea8ef1e3d022d255&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[37] Kaplan A F, Xu Ting, Wu Y K, et al. Multilayer pattern transfer for plasmonic color filter applications[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, Nanotechnology and Microelectronics: Materials, Processing, Measurement, and Phenomena, 2010, 28(6): C6060-C6063. https://avs.scitation.org/doi/abs/10.1116/1.3511430?journalCode=jvb
[38] Wang Jiaxing, Fan Qingbin, Zhang Si, et al. Ultra-thin plasmonic color filters incorporating free-standing resonant membrane waveguides with high transmission efficiency[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, in press.
[39] Ebbesen T W, Lezec H J, Ghaemi H F, et al. Extraordinary optical transmission through sub-wavelength hole arrays[J]. Nature, 1998, 391(6668): 667-669. doi: 10.1038/35570 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f313e22fa572ab02934d0e85da28b1b9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[40] Ghaemi H F, Thio T, Grupp D E, et al. Surface plasmons enhance optical transmission through subwavelength holes[J]. Physical Review B, 1998, 58(11): 6779. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.58.6779 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a7cdb6403bb79618c593c650daf4fa60&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[41] Genet C, Ebbesen T W. Light in tiny holes[J]. Nature, 2007, 445(7123): 39-46. doi: 10.1038/nature05350 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=187d40bbc4d3fc1f544ee0b253aa578b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[42] Cheng F, Gao J, Luk T S, et al. Structural color printing based on plasmonic metasurfaces of perfect light absorption[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5:11045. doi: 10.1038/srep11045 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=853983670db05bfefcd61cae1db485c7&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[43] Liu Y J, Si G Y, Leong E S, et al. Light-driven plasmonic color filters by overlaying photoresponsive liquid crystals on gold annular aperture arrays.[J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(23):OP131-5. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=19d3c83449e8c2ab7def9f103847c2a8&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[44] Li Zhibo, Clark A W, Cooper J M. Dual color plasmonic pixels create a polarization controlled nano color palette[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(1): 492-498. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b05411 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=381b04abfe3fb5a3a82260a7b0ff30f2&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[45] Lee H S, Yoon Y T, Lee S S, et al. Color filter based on a subwavelength patterned metal grating[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(23): 15457-15463. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.015457 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5398919caa010f3ffe0bf577658bd848&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[46] Chen Qin, Cumming D R S. High transmission and low color cross-talk plasmonic color filters using triangular-lattice hole arrays in aluminum films[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(13): 14056-14062. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.014056 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=65c54b51595da973c8b43032f57ed566&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[47] Chen Qin, Chitnis D, Walls K, et al. CMOS photodetectors integrated with plasmonic color filters[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2012, 24(3): 197-199. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2011.2176333 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4a2d88ef436b9648b83388b8a58eb81e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[48] Rajasekharan R, Balaur E, Minovich A, et al. Filling schemes at submicron scale: development of submicron sized plasmonic colour filters[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6435. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=afd8bb6c327a76c318afd5eb27ae9fad&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[49] Park C H, Yoon Y T, Lee S S. Polarization-independent visible wavelength filter incorporating a symmetric metal-dielectric resonant structure[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(21): 23769-23777. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.023769 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c9b5655dd90663bd25fea86a13235333&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[50] Yu Yan, Chen Qin, Wen Long, et al. Spatial optical crosstalk in CMOS image sensors integrated with plasmonic color filters[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(17): 21994-22003. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.021994 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a98bb362a868c02ac555e03984870e59&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[51] Degiron A, Ebbesen T W. The role of localized surface plasmon modes in the enhanced transmission of periodic subwavelength apertures[J]. Journal of Optics A: Pure and Applied Optics, 2005, 7(2): S90-S96. doi: 10.1088/1464-4258/7/2/012 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f6727ab1d143f529f332b79580f6dc8b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[52] Sun L B, Hu X L, Zeng Beibei, et al. Effect of relative nanohole position on colour purity of ultrathin plasmonic subtractive colour filters[J]. Nanotechnology, 2015, 26(30): 305204. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/26/30/305204 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d51670b281f3776bf8b9ce822c60d070&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[53] Dionne J A, Sweatlock L A, Atwater H A, et al. Plasmon slot waveguides: towards chip-scale propagation with subwavelength-scale localization[J]. Physical Review B, 2006, 73(3): 035407. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.73.035407 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6d9884ad289f5dee73c0ab058bf5ef6a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[54] Bozhevolnyi S I, Volkov V S, Devaux E, et al. Channel plasmon subwavelength waveguide components including interferometers and ring resonators[J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7083): 508-511. doi: 10.1038/nature04594 http://www.docin.com/p-99364613.html
[55] Lindquist N C, Luhman W A, Oh S H, et al. Plasmonic nanocavity arrays for enhanced efficiency in organic photovoltaic cells[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93(12): 123308. doi: 10.1063/1.2988287 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8884b37a71290914249f5927c9bf3f83&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[56] Kang M G, Xu Ting, Park H J, et al. Efficiency enhancement of organic solar cells using transparent plasmonic Ag nanowire electrodes[J]. Advanced Materials, 2010, 22(39): 4378-4383. doi: 10.1002/adma.v22:39 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6be660cd1240ae746ecfe5c5047eed6c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[57] Lezec H J, Dionne J A, Atwater H A. Negative refraction at visible frequencies[J]. Science, 2007, 316(5823): 430-432. doi: 10.1126/science.1139266 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=155e235e6aee052235277de019ab9cc3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[58] Chen Huajin, Liu Shiyang. Manipulating electromagnetic wave with the magnetic surface plasmon based metamaterials[J]. Applied Physics A, 2012, 107(2): 363-370. doi: 10.1007/s00339-012-6802-0 https://rd.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007%2Fs00339-012-6802-0.pdf
[59] Diest K, Dionne J A, Spain M, et al. Tunable color filters based on metal-insulator-metal resonators[J]. Nano Letters, 2009, 9(7): 2579-2583. doi: 10.1021/nl900755b http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=caf1176bca7b209f15e00d2ae384fe13&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[60] Xu Ting, Wu Y K, Luo Xiangang, et al. Plasmonic nanoresonators for high-resolution colour filtering and spectral imaging[J]. Nature Communications, 2010, 1: 59. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=58b721149f760b10cc4ef8316eacff88&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[61] Park H J, Xu Ting, Lee J Y, et al. Photonic color filters integrated with organic solar cells for energy harvesting[J]. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(9): 7055-7060. doi: 10.1021/nn201767e http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2a9fa0c714e00bb8befb457ba75c65c0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[62] Chen Houtong, Padilla W J, Zide J M O, et al. Active terahertz metamaterial devices[J]. Nature, 2006, 444(7119): 597-600. doi: 10.1038/nature05343 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0bbad4cf2023c62194bb2663176099c0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[63] Shaltout A, Liu Jingjing, Shalaev V M, Kildishev A V. Optically active metasurface with non-chiral plasmonic nanoantennas[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(8): 4426-4431. doi: 10.1021/nl501396d http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d175c79566180711fb0f78c9d8335abd&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[64] Yoo M, Lim S. Active metasurface for controlling reflection and absorption properties[J]. Applied Physics Express, 2014, 7(11): 112204. doi: 10.7567/APEX.7.112204 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=799b9ff2abbdd66e5ed1c49dc3da9613&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[65] Si Guangyuan, Zhao Yanhui, Leong E S P, et al. Liquid-crystal-enabled active plasmonics: a review[J]. Materials, 2014, 7(2): 1296-1317. doi: 10.3390/ma7021296 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5a2fa24e91c5b234926dc0dc2f3fd762&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[66] Xu Ting, Walter E C, Agrawal A, et al. High-contrast and fast electrochromic switching enabled by plasmonics[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 10479. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10479 http://ws680.nist.gov/publication/get_pdf.cfm?pub_id=915780
[67] Wang Guoping, Chen Xuechen, Liu Sheng, et al. Mechanical chameleon through dynamic real-time plasmonic tuning[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(2): 1788–1794. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b07472 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=9ace5e2ebf80bdbfb64fa1d641655dfb&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[68] Liu Y J, Si G Y, Leong E S P, et al. Optically tunable plasmonic color filters[J]. Applied Physics A, 2012, 107(1): 49-54. doi: 10.1007/s00339-011-6736-y http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8080283513de391f85e8fbdef52d9a11&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[69] Boltasseva A, Atwater H A. Low-loss plasmonic metamaterials[J]. Science, 2011, 331(6015): 290-291. doi: 10.1126/science.1198258 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4f2ea11b1cb0252a876357ace4730fa5&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[70] Hedayati M K, Faupel F, Elbahri M. Review of plasmonic nanocomposite metamaterial absorber[J]. Materials, 2014, 7(2): http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a17e35820d9f55a52608efa5c31053bd&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[71] Asadchy V S, Faniayeu I A, Ra'di Y, et al. Broadband reflectionless metasheets: frequency-selective transmission and perfect absorption[J]. Physical Review X, 2015, 5(3): 031005. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.5.031005 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6477fe23c080a980d1b352e83435e141&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[72] Ra'di Y, Simovski C R, Tretyakov S A. Thin perfect absorbers for electromagnetic waves: theory, design, and realizations[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2015, 3(3): 037001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.3.037001 http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2015PhRvP...3c7001R
[73] Yang Chenying, Ji Chengang, Shen Weidong, et al. Compact multilayer film structures for ultrabroadband, omnidirectional, and efficient absorption[J]. ACS Photonics, 2016, 3(4): 590–596. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.5b00689 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4283af7c6f2cc733c91869b358f5c71e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[74] Liang Qiuqun, Wang Taisheng, Lu Zhenwu, et al. Metamaterial-based two dimensional plasmonic subwavelength structures offer the broadest waveband light harvesting[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2013, 1(1): 43-49. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f31e400514cd4606f391d33672db1aa6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[75] He S, Ding F, Mo L, et al. Light absorber with an ultra-broad flat band based on multi-sized slow-wave hyperbolic metamaterial thin-films[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2014, 147: 69-79. doi: 10.2528/PIER14040306 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=665cd9eb491efe8d8561e762e07f8f20&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[76] Zhou Lin, Tan Yingling, Ji Dengxin, et al. Self-assembly of highly efficient, broadband plasmonic absorbers for solar steam generation[J]. Science Advances, 2016, 2(4): e1501227. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1501227 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=154bef5359ba00d94fee63ceed77c2bd&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[77] Hedayati M K, Elbahri M. Review of Metasurface Plasmonic Structural Color[J]. Plasmonics, 2016:1-17. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s11468-016-0407-y.pdf
[78] Kristensen A, Yang J K W, Bozhevolnyi S I, et al. Plasmonic colour generation[J]. Nature Review Materials, 2016, 2:16088. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/310744617_Plasmonic_colour_generation
[79] Jardret V, Lucas B N, Oliver W, et al. Scratch durability of automotive clear coatings: a quantitative, reliable and robust methodology[J]. Journal of Coatings Technology, 2000, 72(8): 79-88. doi: 10.1007/BF02698026 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02698026
[80] Schulz U, Wachtendorf V, Klimmasch T, et al. The influence of weathering on scratches and on scratch and mar resistance of automotive coatings[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2001, 42(1-2): 38-48. doi: 10.1016/S0300-9440(01)00148-5 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0300944001001485
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: