Color correction of electrowetting electronic paper based on color space transformation
-
摘要
电润湿电子纸采用减色混色系统进行色彩显示,色域较小,容易发生色彩失真,且依赖环境光的漫反射,亮度不足。为解决这些问题,提出一种基于彩色电润湿的色彩空间转换和图像自适应增强算法。该算法将图像从RGB色彩空间转换到HSV空间,并使用CLAHE对饱和度进行均匀分布处理,改善色彩表现。亮度通道通过引导滤波和改进的Retinex算法进行增强,保留细节与边缘信息,使电润湿电子纸在相同光照下依旧保持真实视觉效果。实验结果表明,该算法在PSNR、SSIM、FSIM和FSIMc上分别提高了19%、10.8%、19.19%和19.54%,显著优化电润湿电子纸的显示效果,为其市场化应用提供有力支撑。
Abstract
Electrowetting electronic paper employs a subtractive color mixing system for color display, which results in a smaller color gamut and potential color distortion. Additionally, it relies on ambient light's diffuse reflection, leading to insufficient brightness. To address these issues, this paper proposes a color space transformation and image adaptive enhancement algorithm for color electrowetting. The algorithm converts the image from the RGB color space to the HSV space, using CLAHE to evenly distribute saturation and improve color performance. The luminance channel is enhanced through guided filtering combined with an improved Retinex algorithm, preserving detail and edge information, and ensuring the electrowetting display maintains realistic visual effects under the same lighting conditions. Experimental results show that the algorithm improves PSNR, SSIM, FSIM, and FSIMc by 19%, 10.8%, 19.19%, and 19.54%, respectively. This algorithm significantly enhances the display performance of electrowetting electronic paper, laying a solid foundation for its commercialization.
-
Overview
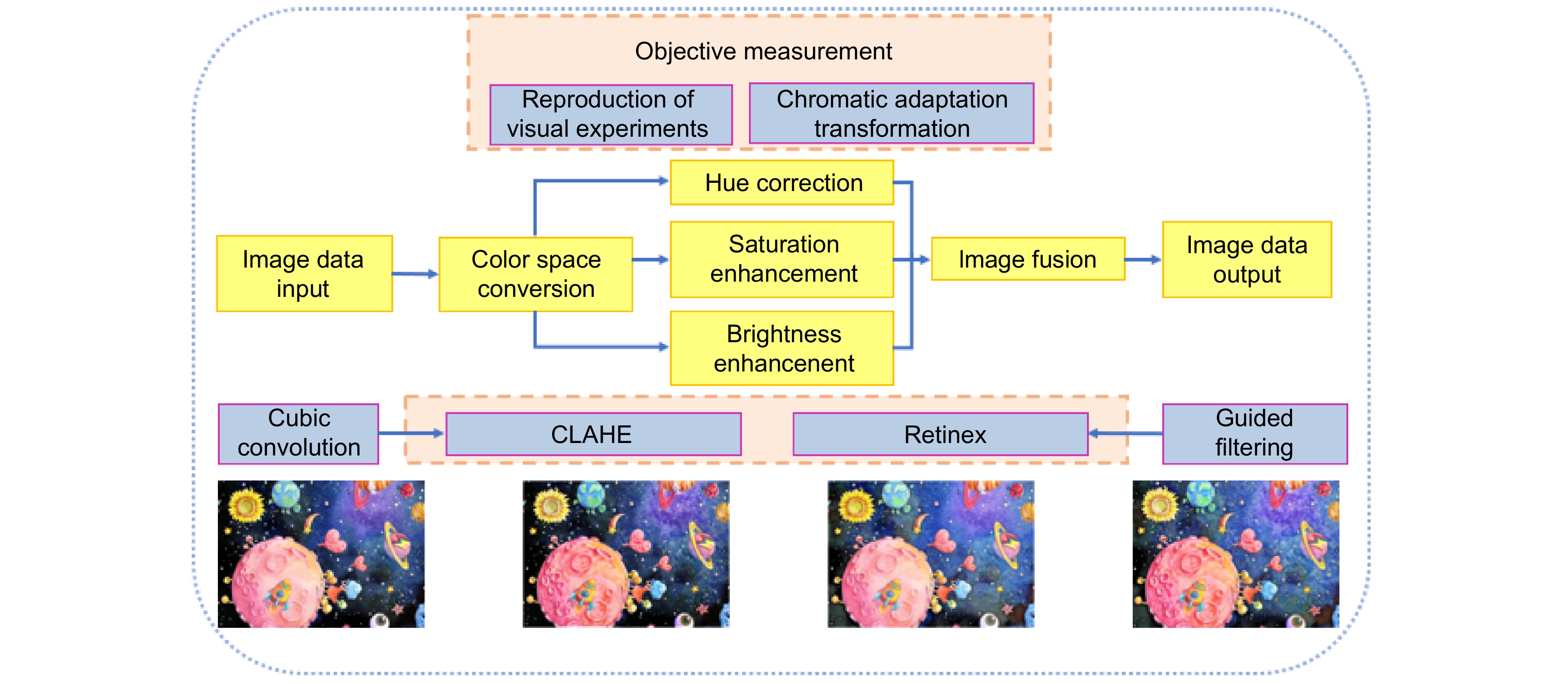
Overview: Electrowetting electronic paper uses a subtractive color-mixing system with three primary inks (cyan, magenta, and yellow), which results in a reduced color gamut and colorimetric distortion. These issues arise from the difference between subtractive color mixing and traditional additive RGB systems. Electrowetting displays also depend on ambient light, but diffuse reflection from the display surface often leads to insufficient brightness. This negatively impacts the display quality and visual clarity, especially in low-light conditions.
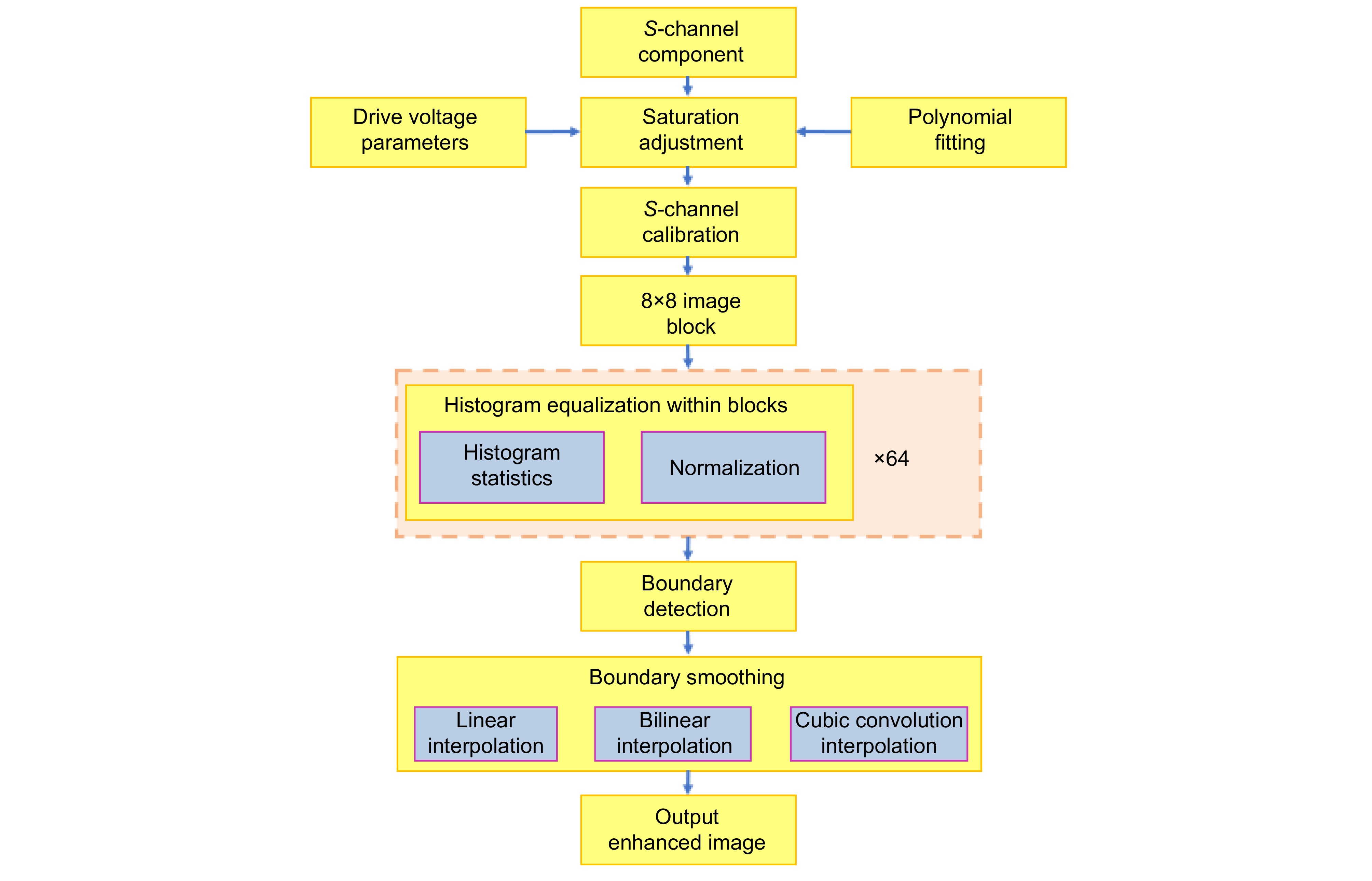
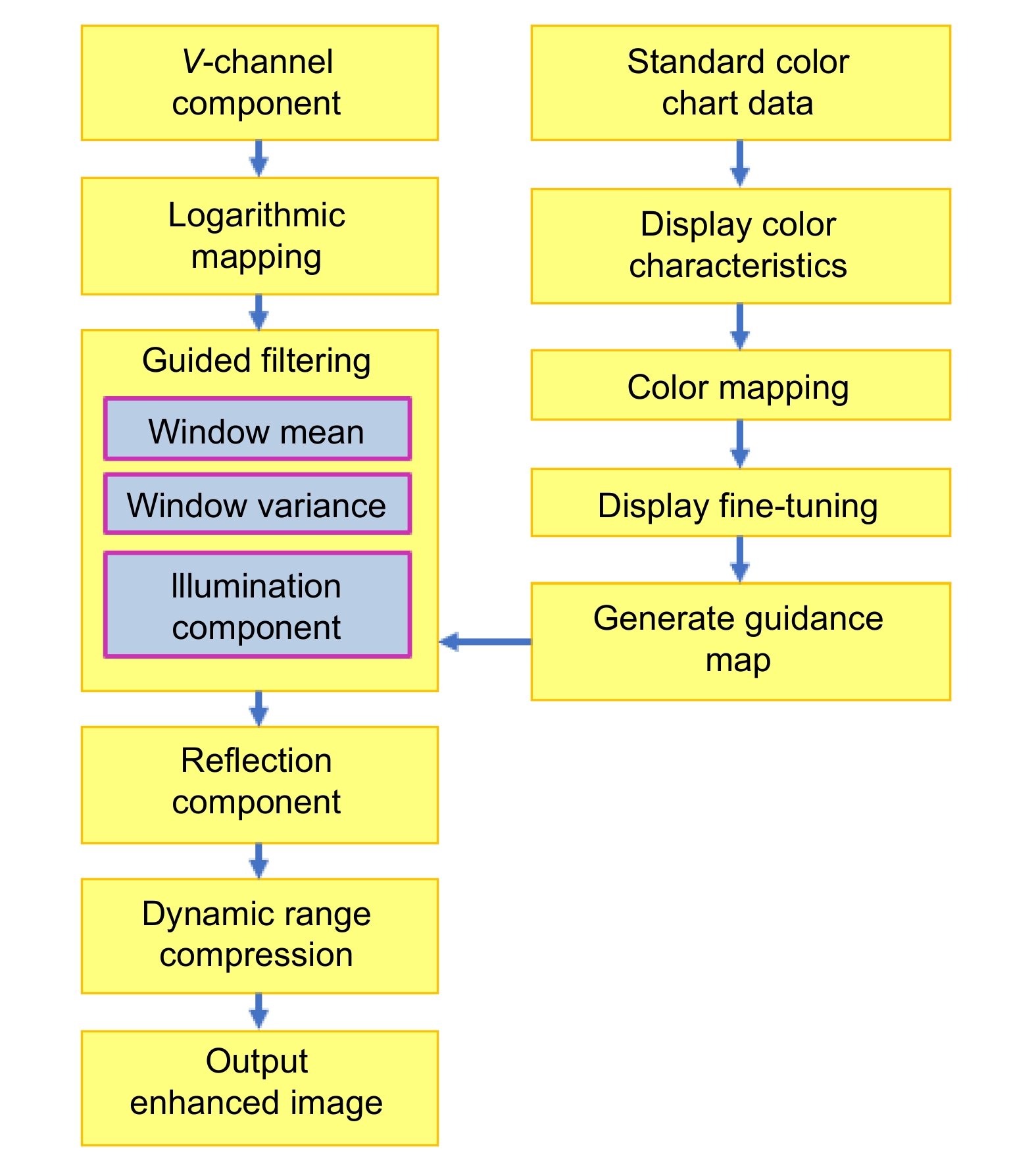
To address these issues, a color space conversion and image self-adaptive enhancement algorithm is proposed for electrowetting color displays. The objective is to improve color accuracy, increase brightness, and maintain image clarity while overcoming the challenges posed by the reflective nature of the display. The algorithm converts RGB images into the HSV color space, enabling more effective manipulation of color and brightness components. CLAHE (contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization) is applied to the saturation channel (S channel), redistributing saturation more evenly and avoiding over-saturation in specific hues, resulting in a more balanced and vivid color presentation. The brightness channel (V channel) is enhanced by using an improved Retinex algorithm combined with a guidance filter. This method improves brightness and contrast while preserving details and edges, addressing the issue of insufficient brightness caused by the reflective display surface. The algorithm ensures that the electrowetting display maintains realistic and stable visual performance under different lighting conditions.
Experimental results show significant improvements in image quality, with PSNR of 70.5047 dB and SSIM of 0.8378. FSIM and FSIMc, which are used to measure human visual perception, reach 0.8409 and 0.84, respectively. Compared to the FHRPHS algorithm, the proposed method improves PSNR by 19%, SSIM by 10.8%, and FSIM and FSIMc by 19.19% and 19.54%, respectively. These improvements highlight the effectiveness of the approach in enhancing color performance and image clarity, especially in scenarios with limited color gamut, making it suitable for improving electrowetting electronic paper display quality.
-

-
图 7 不同消融实验前后图像效果的比较。(a) RGB原始图像;(b)直接映射的CMY图像;(c)仅进行V通道处理的图像;(d)仅进行S通道处理的图像;(e)本文处理算法
Figure 7. Comparison of image effects before and after different ablation experiments. (a) RGB original image; (b) Directly mapped CMY image; (c) V-channel processed image only; (d) S-channel processed image only; (e) Ours
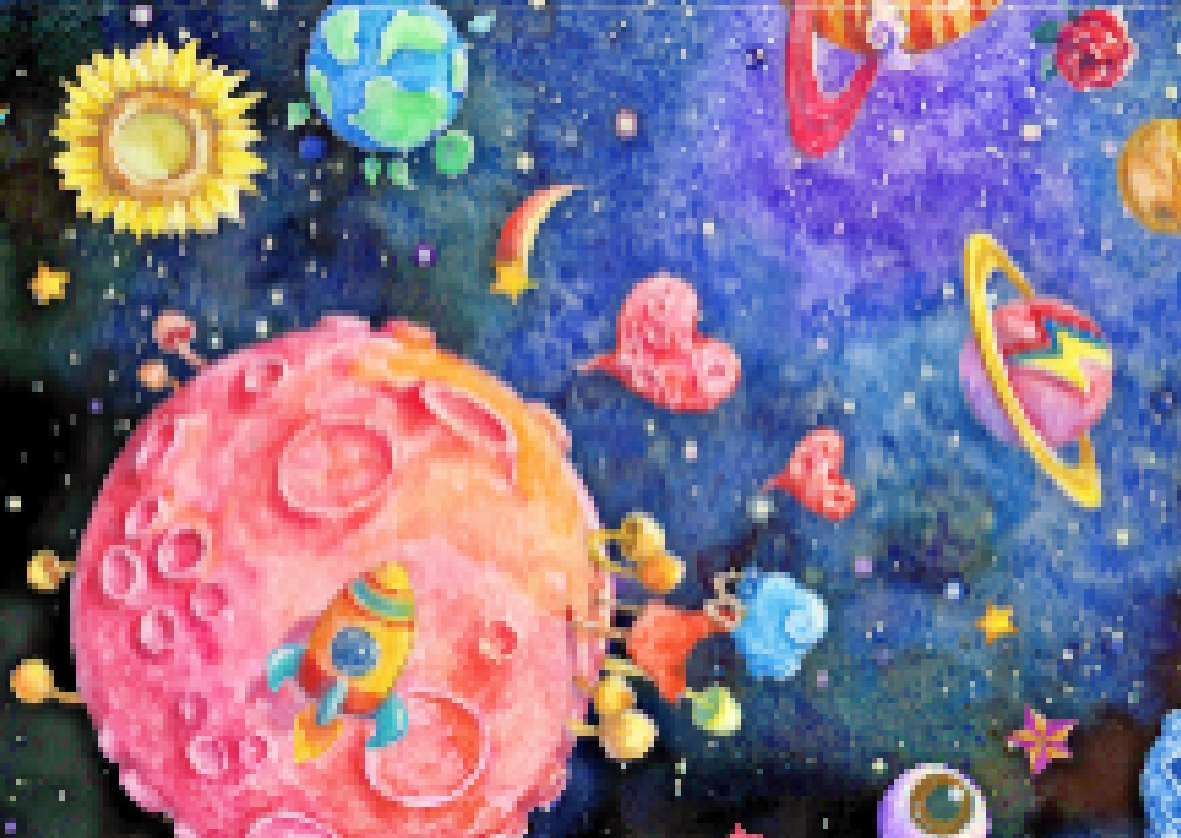
图 9 彩色电润湿显示器显示效果对比图。(a)原始图;(b)所提算法处理后的图;(c)局部放大原始图; (d)局部放大处理后的图
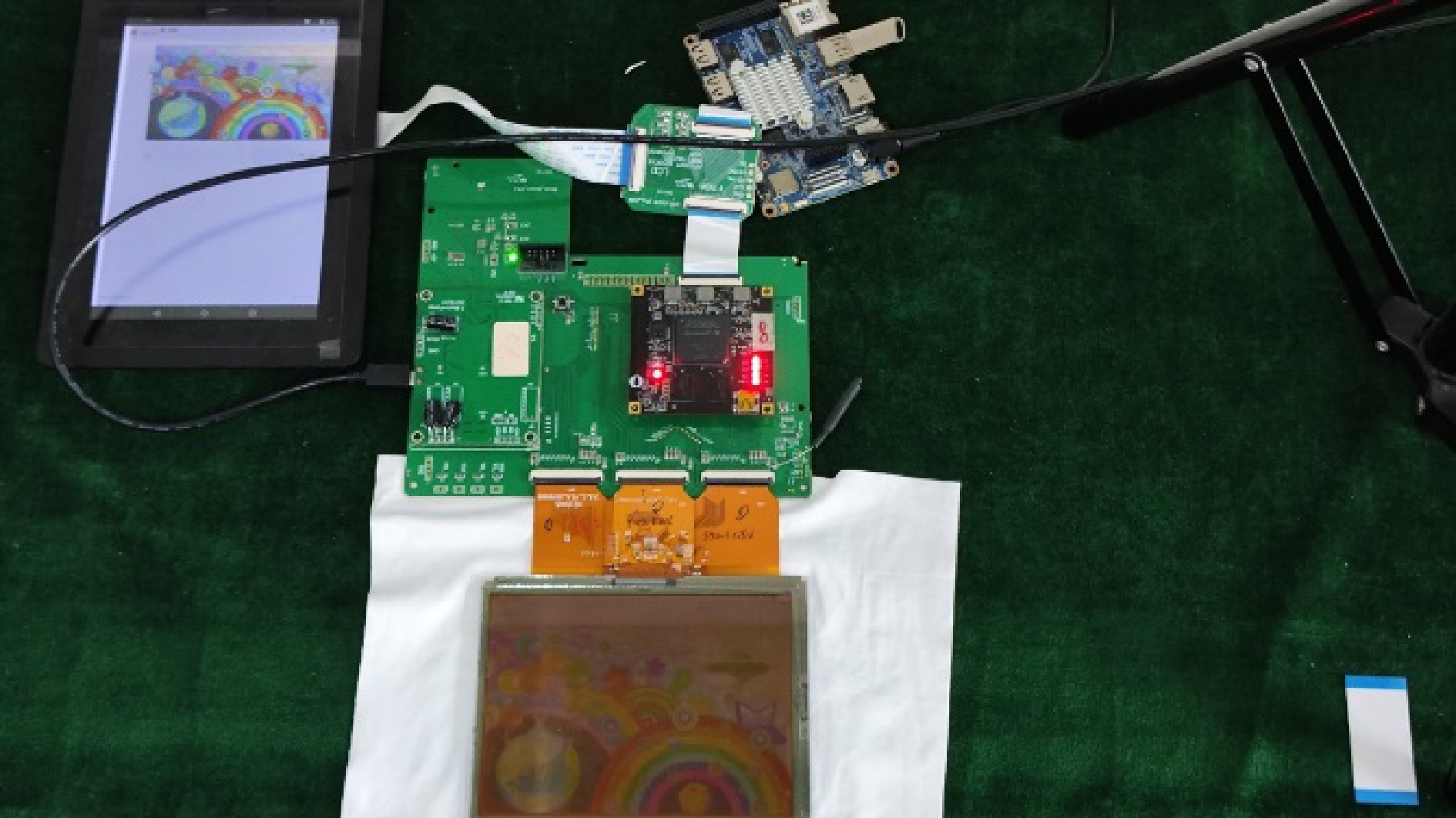
Figure 9. Comparison of the display effect on the color electrowetting display. (a) Original image; (b) Image processed by the proposed algorithm; (c) Local magnification of the original image; (d) Local magnification of the processed image
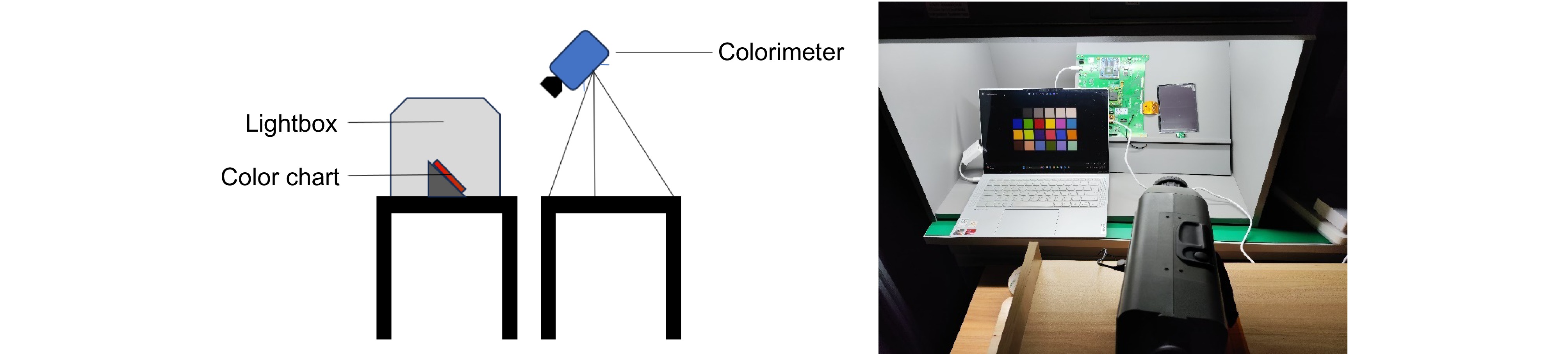
表 1 不同显示效果图的Z-score
Table 1. Z-scores for different display renderings
Images Z-scores Before After Image 1 −0.53 0.53 Image 2 −0.72 0.72 Image 3 −1.74 1.74 Image 4 −0.84 0.84 Image 5 −0.36 0.36 Image 6 −0.51 0.51 表 2 不同图像视觉信息的
$ {\chi }^{2} $ Table 2.
$ {\chi }^{2} $ $ {\chi }^{2} $ test results Image 1 Image 2 Image 3 Image 4 Image 5 Image 6 HB 1.1579 0.7869 0.0382 0.9542 0.1428 0.6567 MB 0.1891 0.0429 0.3323 0.2242 0.5980 0.1663 LB 1.1647 1.0190 0.0554 0.5877 1.1517 0.1792 HS 1.1486 1.1208 0.1166 0.5347 0.4085 0.3090 MS 0.5825 0.8145 0.9881 0.7756 0.7023 1.0089 LS 0.9603 0.9093 0.8338 0.8512 0.2686 0.3051 HC 0.1703 0.8918 0.3805 0.9056 0.9015 0.9771 MC 0.5061 0.4707 1.1403 0.3312 0.3061 0.2922 LC 1.0989 0.7866 0.0413 0.8156 0.6071 1.1151 OR 0.9506 0.2054 0.5265 0.7861 0.8389 0.4200 PR 1.1514 0.8473 0.4579 0.1951 1.0691 0.2359 表 3 不同算法处理后图像的H、CE、PSNR、SSIM、FSIM和FSIMc值
Table 3. H, CE, PSNR, SSIM, FSIM, and FSIMc values of images processed by different algorithms
Algorithm H CE PSNR SSIM FSIM FSIMc Original 1.7981 —— —— —— —— —— MEMBHE 1.9607 12.2554 60.1529 0.4997 0.7908 0.7896 MMBEBHE 1.9004 16.9650 59.9130 0.4867 0.7903 0.7890 FHRPHS 2.3987 0.7000 59.2433 0.7559 0.7055 0.7027 Ours 2.4978 0.1161 70.5047 0.8378 0.8409 0.8400 表 4 系统资源消耗对比
Table 4. Comparison of system resource consumption
LUT LUTRAM FF BRAM DSP BUFG Software to HLS 208650 12787 129549 43 77 1 Hardware 57252 11442 43729 32 19 2 -
参考文献
[1] 郭媛媛, 蒋洪伟, 袁冬, 等. 电润湿显示材料与器件技术研究进展[J]. 液晶与显示, 2022, 37(8): 925−941. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2022-0165
Guo Y Y, Jiang H W, Yuan D, et al. Progress in electrowetting display materials and device technology[J]. Chin J Liq Cryst Disp, 2022, 37(8): 925−941. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2022-0165
[2] 卜倩倩, 王丹, 邱云, 等. 反射显示技术的研究进展[J]. 液晶与显示, 2019, 34(2): 169−176. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193402.0169
Bu Q Q, Wang D, Qiu Y, et al. Progress of reflective display technology[J]. Chin J Liq Cryst Disp, 2019, 34(2): 169−176. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193402.0169
[3] 钱明勇, 林珊玲, 曾素云, 等. 电润湿电子纸的实时动态显示驱动系统实现[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(6): 180623. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180623
Qian M Y, Lin S L, Zeng S Y, et al. Real-time dynamic driving system implementation of electrowetting display[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(6): 180623. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180623
[4] Chen M Z, Lin S L, Mei T, et al. Research on hydrodynamic characteristics of electronic paper pixels based on electrowetting[J]. Micromachines, 2023, 14(10): 1918. doi: 10.3390/mi14101918
[5] 马鑫, 喻春雨, 陈刚, 等. 分区自适应伽马校正的非均匀光照图像增强[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2024, 61(14): 1437006. doi: 10.3788/LOP232516
Ma X, Yu C Y, Chen G, et al. Adaptive gamma correction of subregion for non-uniform illumination image enhancement[J]. Laser Optoelectron Prog, 2024, 61(14): 1437006. doi: 10.3788/LOP232516
[6] 游达章, 陶加涛, 张业鹏, 等. 基于灰度变换及改进Retinex的低照度图像增强[J]. 红外技术, 2023, 45(2): 161−170.
You D Z, Tao J T, Zhang Y P, et al. Low-light image enhancement based on gray scale transformation and improved retinex[J]. Infrared Technol, 2023, 45(2): 161−170.
[7] 刘予敏, 林珊玲, 林志贤, 等. 不同色温环境光下彩色电润湿电子纸的色彩校正[J]. 液晶与显示, 2024, 39(1): 32−39. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2023-0379
Liu Y M, Lin S L, Lin Z X, et al. Color correction of color electrowetting display under ambient light with different color temperatures[J]. Chin J Liq Cryst Disp, 2024, 39(1): 32−39. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2023-0379
[8] Chen M Z, Lin S L, Lin J P, et al. Adaptive enhancement display of chromatic electrowetting based on color conversion[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 2389−2397. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3347892
[9] 王浩, 张叶, 沈宏海, 等. 图像增强算法综述[J]. 中国光学, 2017, 10(4): 438−448. doi: 10.3788/CO.20171004.0438
Wang H, Zhang Y, Shen H H, et al. Review of image enhancement algorithms[J]. Chin Opt, 2017, 10(4): 438−448. doi: 10.3788/CO.20171004.0438
[10] Kim Y T. Contrast enhancement using brightness preserving bi-histogram equalization[J]. IEEE Trans Consumer Electron, 1997, 43(1): 1−8. doi: 10.1109/30.580378
[11] Wang Y, Chen Q, Zhang B. Image enhancement based on equal area dualistic sub-image histogram equalization method[J]. IEEE Trans Consumer Electron, 1999, 45(1): 68−75. doi: 10.1109/30.754419
[12] Chen S D, Ramli A R. Minimum mean brightness error bi-histogram equalization in contrast enhancement[J]. IEEE Trans Consumer Electron, 2003, 49(4): 1310−1319. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2003.1261234
[13] Nikolova M, Steidl G. Fast hue and range preserving histogram specification: theory and new algorithms for color image enhancement[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2014, 23(9): 4087−4100. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2337755
[14] Hellwig L, Fairchild M D. Brightness, lightness, colorfulness, and Chroma in CIECAM02 and CAM16[J]. Color Res Appl, 2022, 47(5): 1083−1095. doi: 10.1002/col.22792
[15] Kuo S W, Chang Y P, Cheng W Y, et al. Novel development of multi-color electrowetting display[J]. SID Symp Dig Tech Pap, 2009, 40(1): 483−486. doi: 10.1889/1.3256821
[16] Kuo S W, Lo K L, Cheng W Y, et al. Single layer multi-color electrowetting display by using ink jet printing technology and fluid motion prediction with simulation[J]. SID Symp Dig Tech Pap, 2010, 41(1): 939−942. doi: 10.1889/1.3500636
[17] You H, Steckl A J. Three-color electrowetting display device for electronic paper[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 97(2): 023514. doi: 10.1063/1.3464963
[18] 林珊玲, 李甜甜, 曾素云, 等. 基于人眼视觉的电润湿电子纸显示器亮度非线性校正方法[J]. 光子学报, 2019, 48(8): 0812004. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194808.0812004
Lin S L, Li T T, Zeng S Y, et al. Nonlinear correction method of electrowetting display brightness based on human visual system[J]. Acta Photonica Sin, 2019, 48(8): 0812004. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194808.0812004
[19] 熊铃铃, 林珊玲, 林志贤, 等. 改进电润湿电子纸图像自适应增强算法[J]. 电子技术应用, 2021, 47(11): 76−80. doi: 10.16157/j.issn.0258-7998.201106
Xiong L L, Lin S L, Lin Z X, et al. Improved image adaptive enhancement algorithm for electrowetting electronic paper[J]. Appl Electron Tech, 2021, 47(11): 76−80. doi: 10.16157/j.issn.0258-7998.201106
[20] 万俊霞, 林珊玲, 梅婷, 等. 基于图像分割和动态直方图均衡的电润湿显示器图像增强算法[J]. 光子学报, 2022, 51(2): 0210005. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20225102.0210005
Wan J X, Lin S L, Mei T, et al. Image enhancement algorithm of electrowetting display based on image segmentation and dynamic histogram equalization[J]. Acta Photonica Sin, 2022, 51(2): 0210005. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20225102.0210005
[21] 林珊玲, 谢欣欣, 林坚普, 等. 增强彩色电子纸饱和度的误差扩散优化[J]. 光电工程, 2024, 51(1): 230309. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.230309
Lin S L, Xie X X, Lin J P, et al. Error diffusion optimization to enhance the saturation of colored e-paper[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2024, 51(1): 230309. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.230309
[22] 林珊玲, 陈燕, 张雪, 等. 结合色彩校正和结构信息的双路低光照图像增强[J]. 光电工程, 2024, 51(9): 240142. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240142
Lin S L, Chen Y, Zhang X, et al. Dual low-light images combining color correction and structural information enhance[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2024, 51(9): 240142. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240142
[23] Fahnestock J D, Schowengerdt R A. Spatially variant contrast enhancement using local range modification[J]. Opt Eng, 1983, 22(3): 223378. doi: 10.1117/12.7973124
[24] Keys R. Cubic convolution interpolation for digital image processing[J]. IEEE Trans Acoust, Speech, Signal Process, 1981, 29(6): 1153−1160. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1981.1163711
[25] 罗浩, 仲佳嘉, 李祥. 基于改进多尺度Retinex的单幅彩色图像增强算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(理学版), 2019, 57(2): 369−374. doi: 10.13413/j.cnki.jdxblxb.2018152
Luo H, Zhong J J, Li X. Single color image enhancement algorithm based on improved multi-scale retinex[J]. J Jilin Univ (Sci Ed), 2019, 57(2): 369−374. doi: 10.13413/j.cnki.jdxblxb.2018152
[26] He K M, Sun J, Tang X O. Guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2013, 35(6): 1397−1409. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.213
[27] Yang G S, Wang B Y, Chang Z Q, et al. Design, fabrication and measurement of full-color reflective electrowetting displays[J]. Micromachines, 2022, 13(11): 2034. doi: 10.3390/mi13112034
[28] 果佳. 基于颜色管理系统的跨媒体颜色复现比较研究[D]. 鞍山: 辽宁科技大学, 2019: 34–44. https://doi.org/10.26923/d.cnki.gasgc.2019.000180.
Guo J. A comparative study of color reproduction cross-media based on color management system[D]. Anshan: Liaoning University of Science and Technology, 2019: 34–44. https://doi.org/10.26923/d.cnki.gasgc.2019.000180.
[29] 许向阳. 与视觉认知过程相关的图像色貌建模的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2016: 79–97.
Xu X Y. A research of image color appearance modeling based on cognition processing of human vision[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2016: 79–97.
[30] 卢沧龙. 基于CIECAM02的跨媒体颜色复现评价研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013: 37–39.
Lu C L. Study of cross-media color reproduction assessment based on CIECAM02[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013: 37–39.
[31] IEC. Multimedia systems and equipment-colour measurement and management-part 4: equipment using liquid crystal display panels: IEC 61966–4[S]. Geneva: IEC, 2000: 7–8.
[32] 陈哲亮, 林珊玲, 林志贤, 等. 低功耗电润湿显示器视频显示驱动系统设计[J]. 光子学报, 2020, 49(2): 0222002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20204902.0222002
Chen Z L, Lin S L, Lin Z X, et al. Design of video display driving system for low-power electrowetting display[J]. Acta Photonica Sin, 2020, 49(2): 0222002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20204902.0222002
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: