-
摘要:
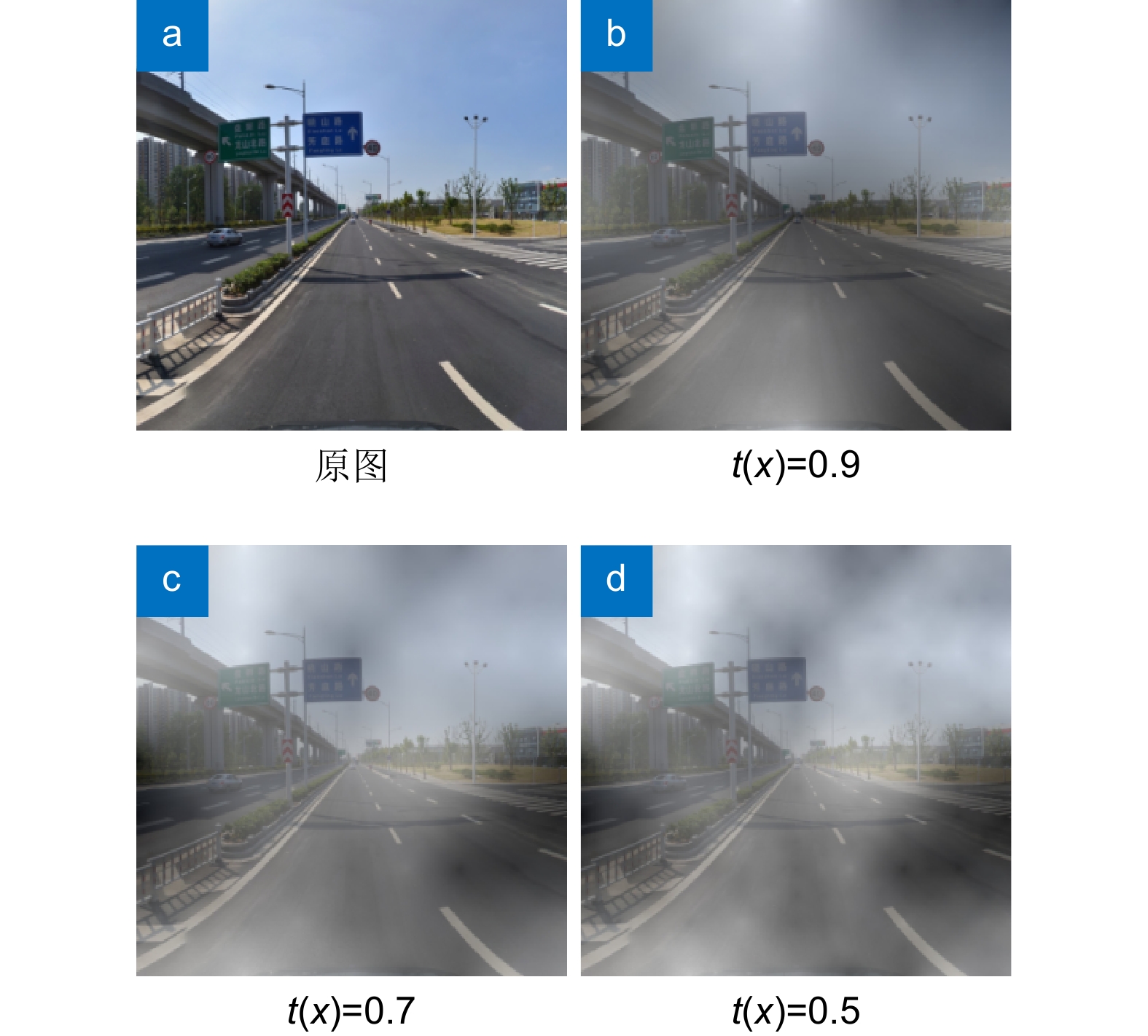
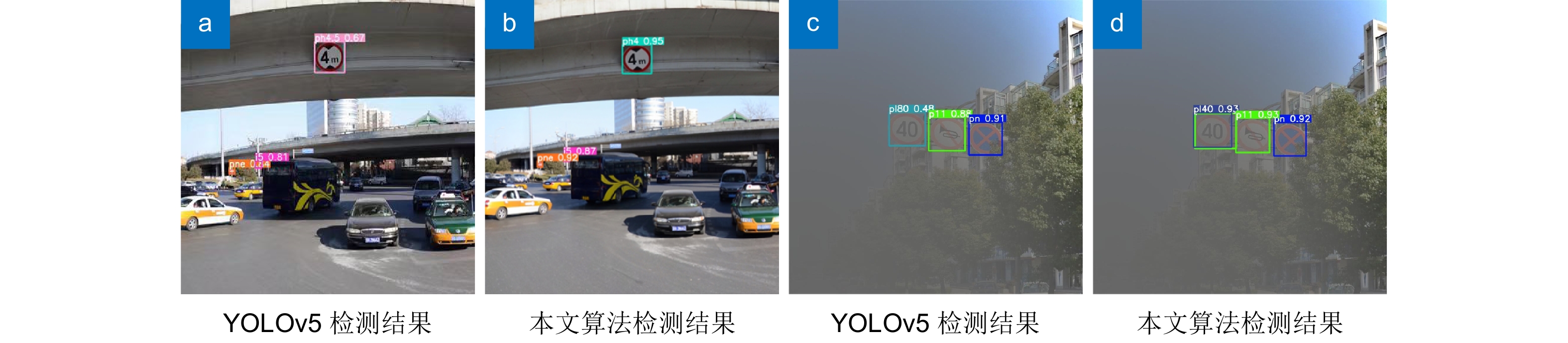
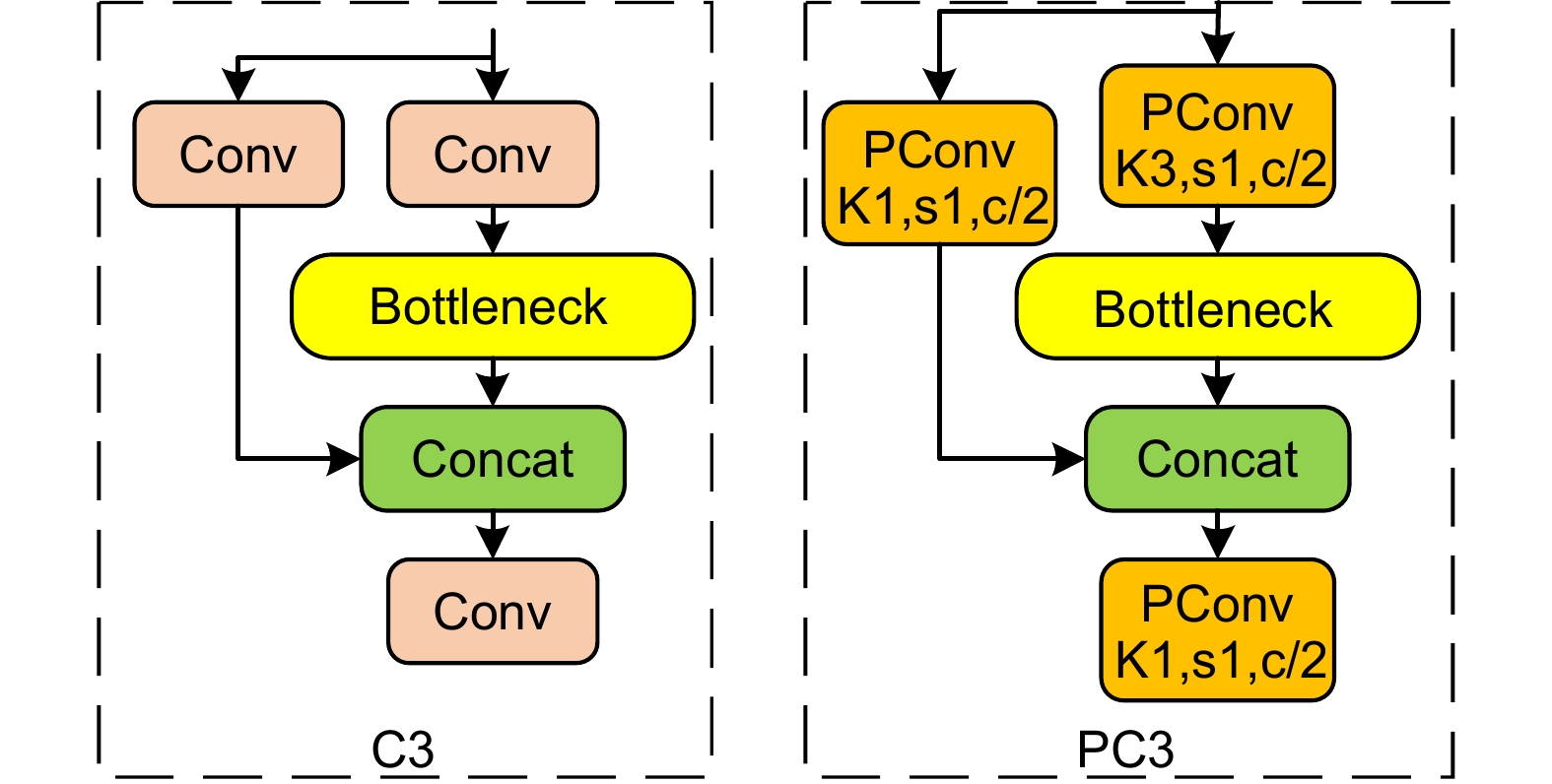
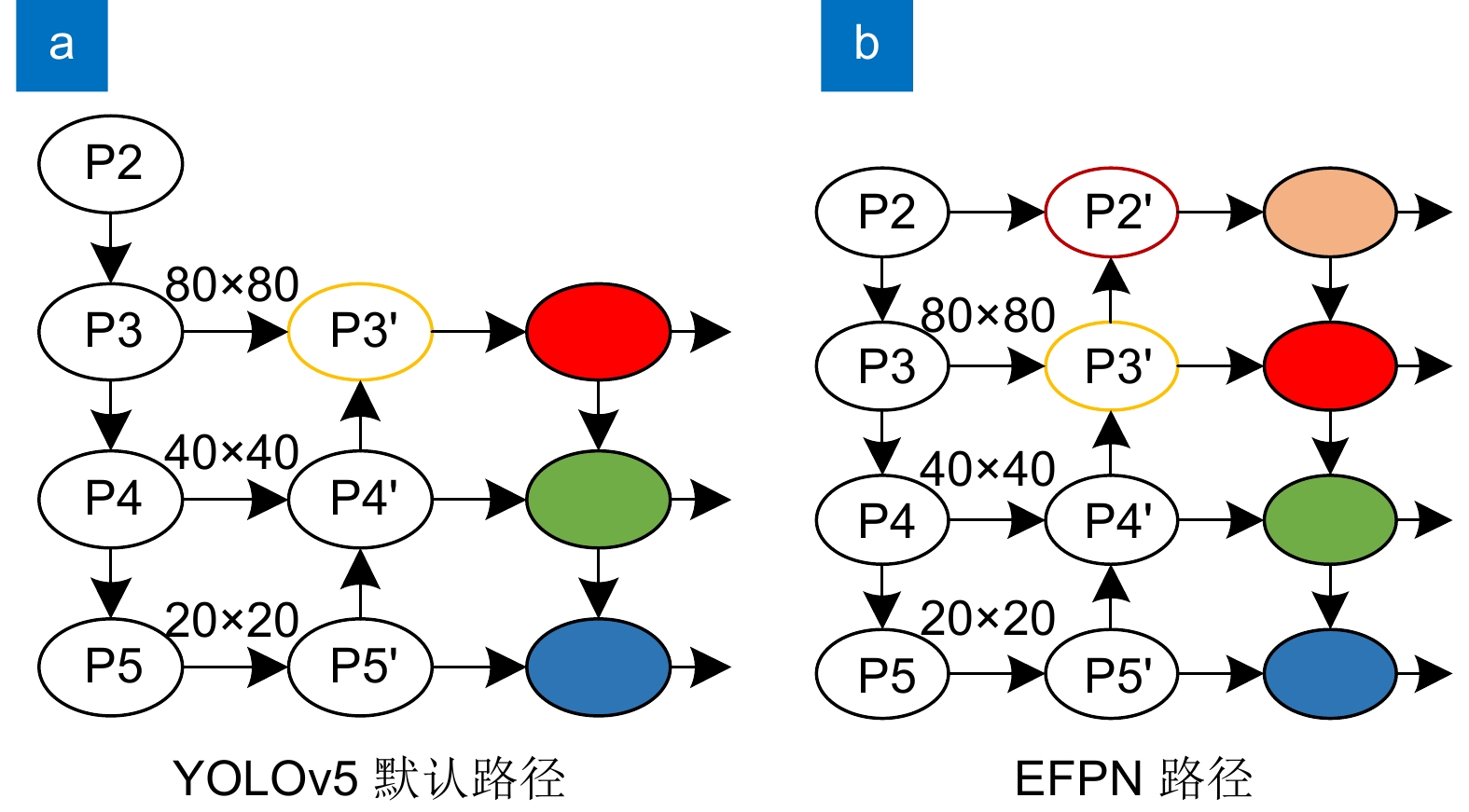
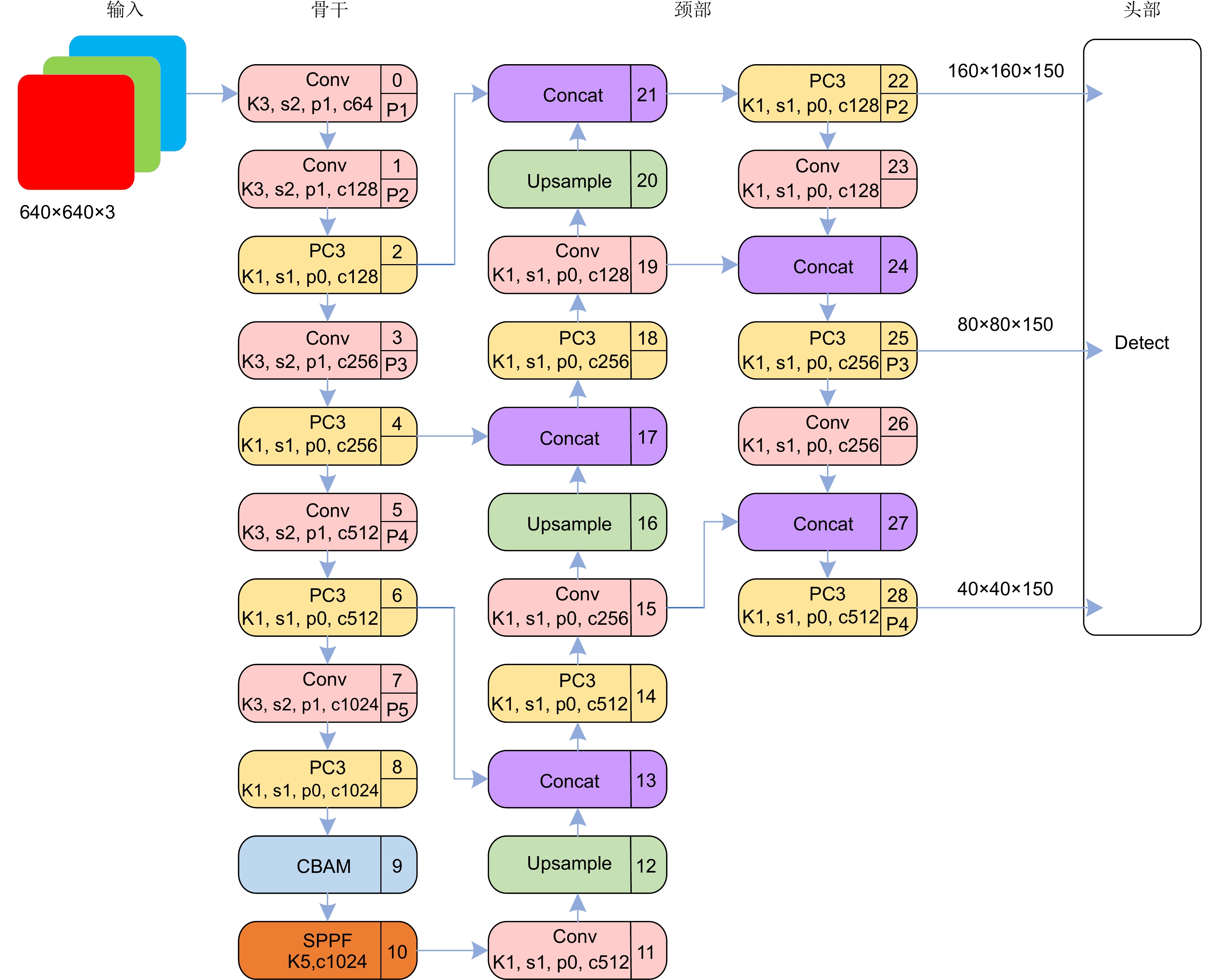
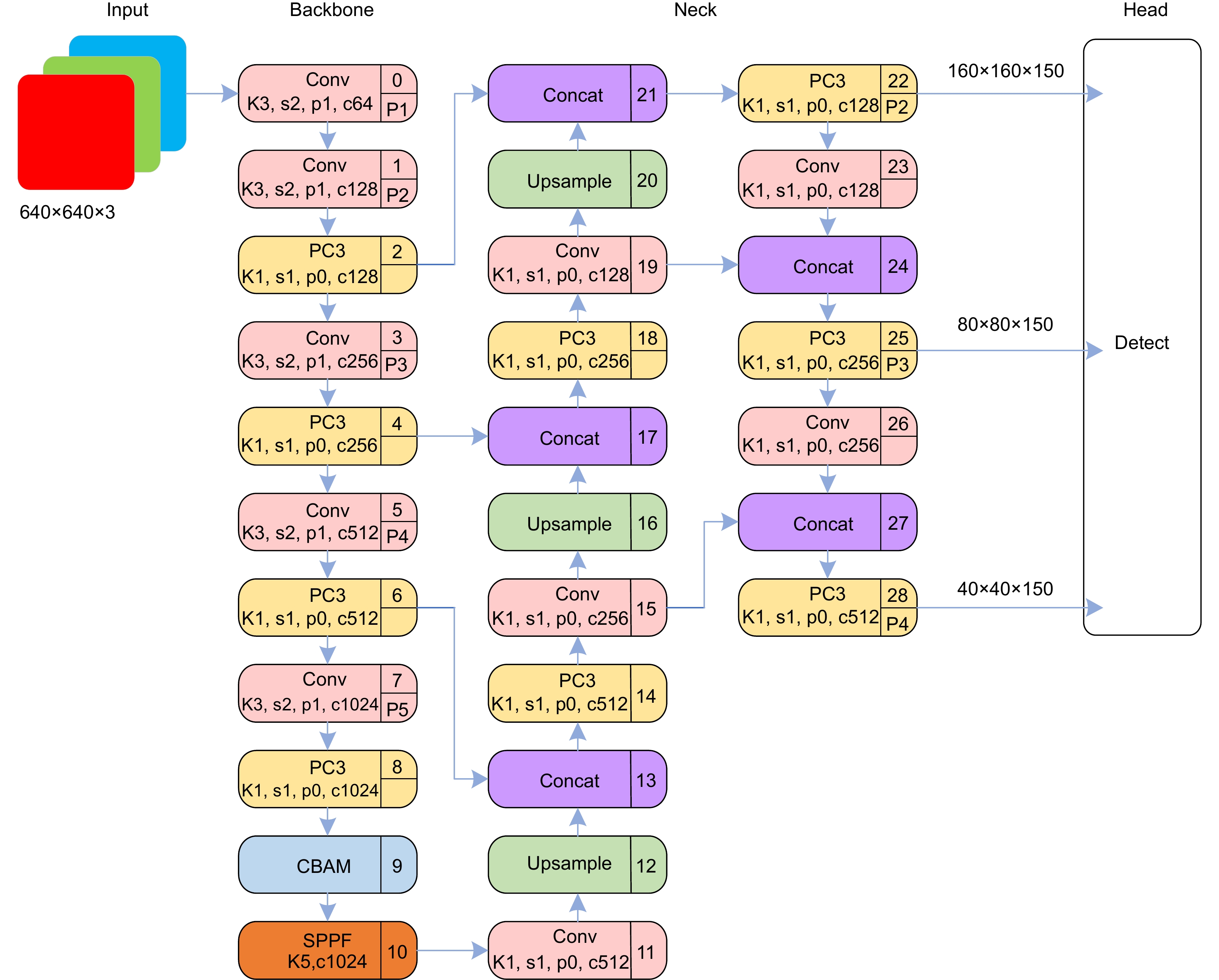
交通标志检测是自动驾驶领域重要的环节,针对当前交通标志的识别存在漏检、误检、模型参数多,以及常见且复杂的代表性真实环境情况,如雾天鲁棒性差的问题,提出一种改进YOLOv5的小目标交通标志识别算法。首先对数据集进行雾化操作以适应在雾天情况下的准确识别,使用更加轻量的部分卷积(partial convolution, PConv)构建PC3特征提取模块;随后在颈部网络中提出延伸的特征金字塔(extended feature pyramid network, EFPN),为小目标添加一个小目标检测头,同时删去原始颈部网络中针对大目标的检测头,提高小目标识别准确率的同时降低网络参数;最后引入Focal-EIOU替换CIOU作为损失函数,以此来解决小目标的误检和漏检问题,嵌入CBAM注意力机制,提升网络模型的特征提取能力。改进的模型性能在TT100K数据集上得到验证,与原YOLOv5算法相比,改进模型在精确率(
P )、mAP0.5上分别提高了8.9%、4.4%,参数量降低了44.4%,在NVIDIA 3080设备上FPS值为151.5,可满足真实场景中交通标志的实时检测。Abstract:Traffic sign detection is an important link in the field of autonomous driving, and given the problems of missed detections, false detections, many model parameters, and common and complex representative real environment conditions, such as poor robustness in foggy days, an improved YOLOv5 micro-target traffic sign recognition algorithm was proposed. Firstly, the dataset was atomized to adapt to the accurate identification in the foggy weather, and the PC3 feature extraction module was constructed by using a lighter partial convolution (PConv), and then the Extended Feature Pyramid Network (EFPN) was proposed in the neck network Finally, Focal-EIOU is introduced to replace CIOU as the loss function to solve the problem of false detection and missed detection of micro targets, and the CBAM attention mechanism is embedded to realize the lightweight model and significantly improves the feature extraction ability of the network model. Compared with the original YOLOv5 algorithm, the improved model is increased by 8.9% and 4.4% respectively on P and mAP0.5, the number of parameters is reduced by 44.4%, and the FPS value on NVIDIA 3080 device is 151.5, which can meet the real-time detection of traffic signs in the real scenes.
-
Key words:
- small object detection /
- deep learning /
- YOLOv5 /
- lightweight convolution /
- EFPN /
- loss function
-
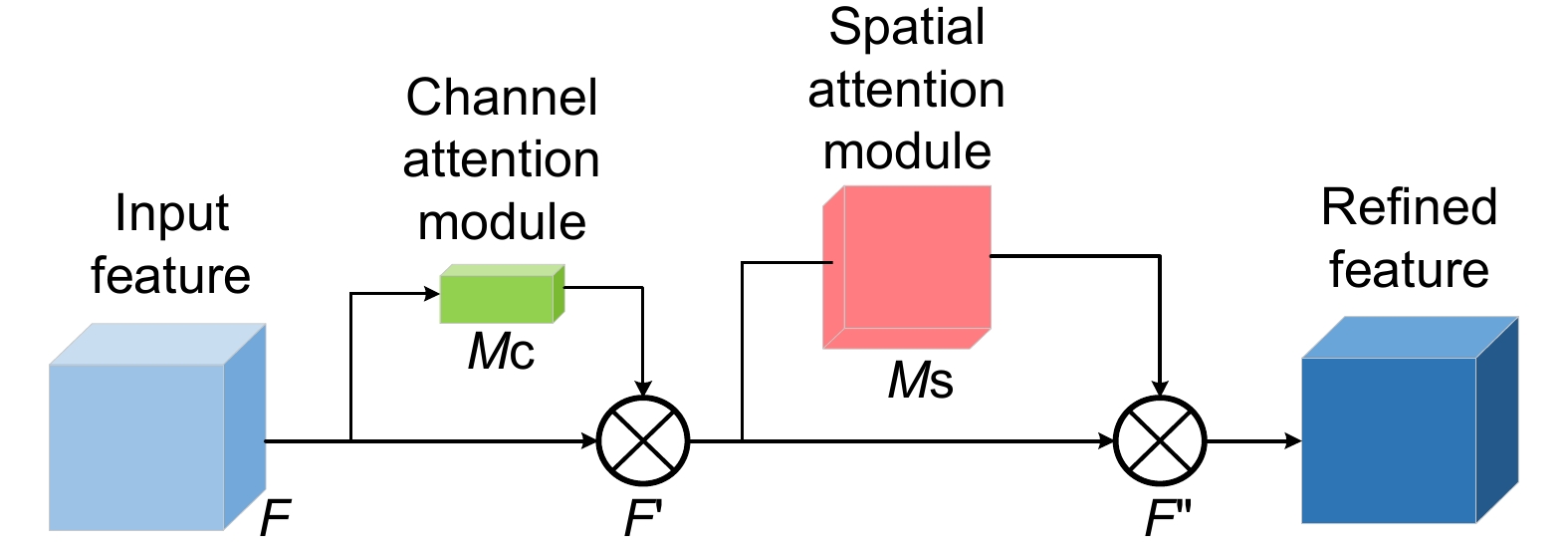
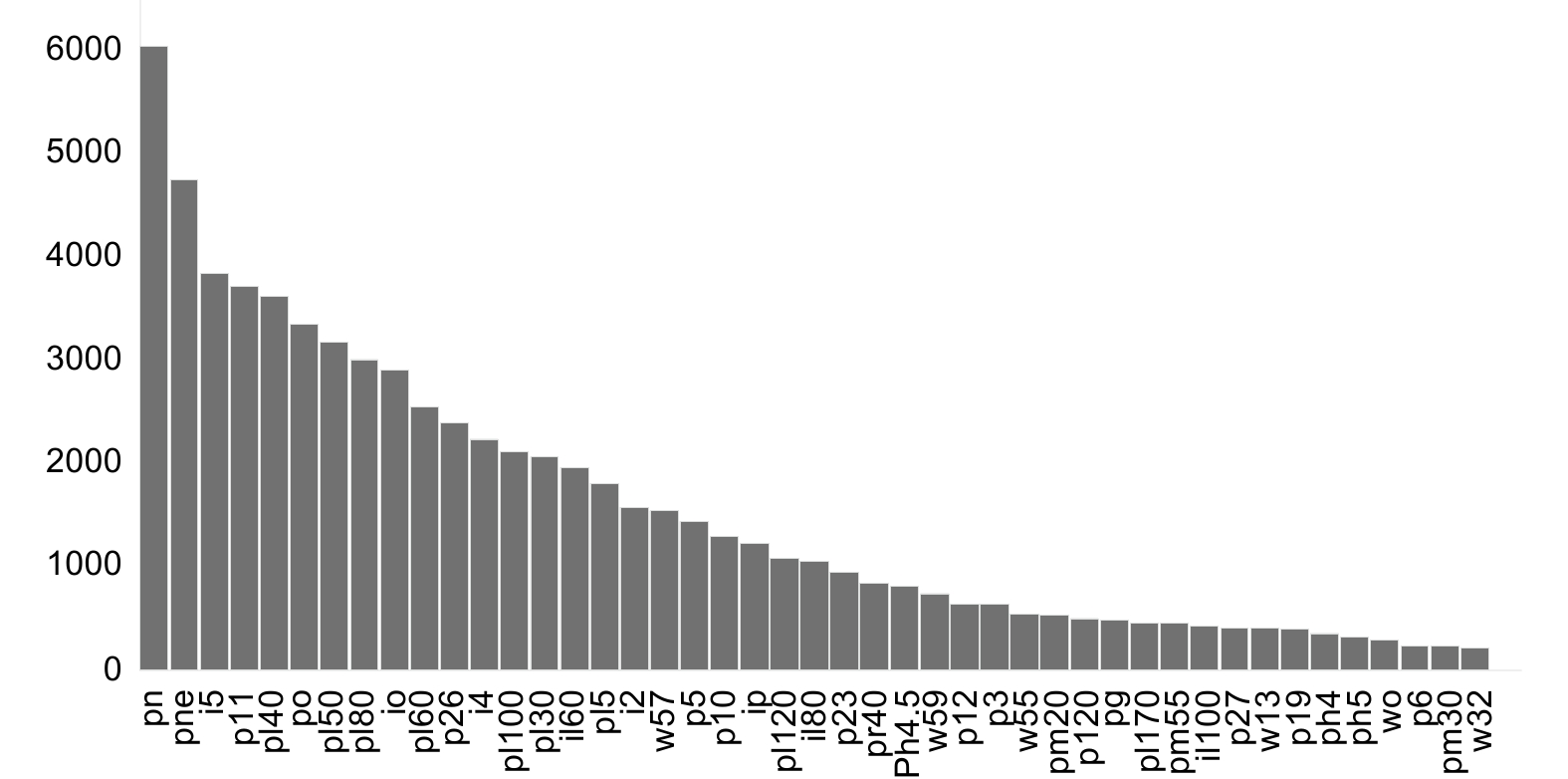
Overview: Traffic sign detection is a crucial component in the field of autonomous driving. Current traffic sign recognition methods face challenges such as missed detections, false positives, high model complexity, and poor robustness in these representative and complex real-world conditions, particularly under the foggy weather. To address these issues, this paper proposes an improved method for small traffic sign detection based on YOLOv5. Firstly, to tackle the problem of imbalanced sample data, the traffic sign dataset is augmented with foggy conditions to enhance the model's generalization capability. This augmentation helps the model to better handle diverse environmental conditions, improving its robustness. Secondly, a lightweight Partial Convolution (PConv) is introduced to construct the PC3 feature extraction module, replacing the C3 module in the original YOLOv5 model. This modification reduces the number of model parameters and enhances processing speed without compromising detection performance. Subsequently, an Extended Feature Pyramid Network (EFPN) is employed in the neck network, adding detection heads specifically for small objects while removing the heads for large object detection. This specialization optimizes the model's performance for small object detection. Additionally, the K-means clustering algorithm is used on the TT100K dataset to recalculate and adjust the size and ratio of anchor boxes, better accommodating small object detection. The Focal-EIOU loss function replaces the original CIOU loss function to address class imbalance and false positive issues in small object detection. Finally, a Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) is embedded in the backbone network. This module performs attention operations on both channel and spatial dimensions, further enhancing the model's feature extraction capability. Compared with the original YOLOv5 algorithm, ablation experiments on the TT100K dataset show that the improved model achieves an 8.9% increase in precision (P) and a 4.4% increase in mean Average Precision (mAP0.5), with a 44.4% reduction in parameter count, reaching a frame rate (FPS) of 151.5 on NVIDIA 3080 devices. Furthermore, comparative experiments with mainstream object detection algorithms such as Faster RCNN, YOLOv7, and YOLOv8 demonstrate that the improved model achieves optimal P and mAP0.5, reaching 91.7% and 89.9% respectively, leading other models in detection accuracy. The model parameter count is 3.95M, realizing a lightweight design while maintaining high detection performance for small traffic signs. This improved model is suitable for real-time traffic sign detection in real-world scenarios, ensuring the reliable operation in autonomous driving systems.
-

-
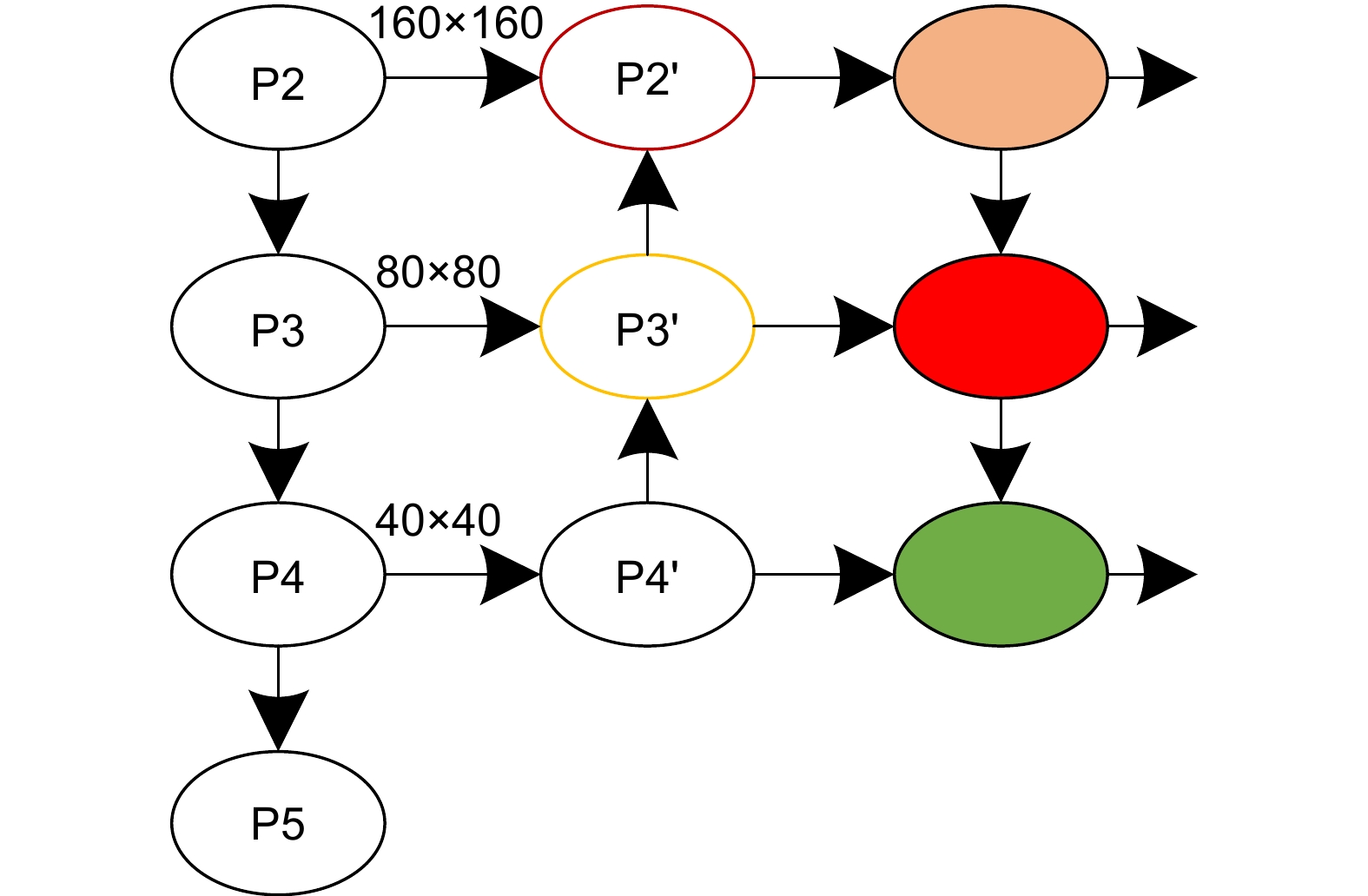
表 1 EFPN与EFPN'结构对比
Table 1. Comparison of EFPN and EFPN' structures
改进方法 精确率P/% Params/M pn w32 ph4 YOLOv5+PC3+EFPN 0.93 0.70 0.76 4.96 YOLOv5+PC3+ EFPN ' 0.96 0.96 0.98 3.80 模型说明:YOLOv5+PC3+EFPN表示YOLOv5中C3中的普通卷积用轻量化部分卷积PConv替换,构成PC3替换掉原C3结构,检测头用EFPN替换;YOLOv5+PC3+EFPN'表示YOLOv5中C3中的普通卷积用轻量化部分卷积PConv替换,构成PC3替换掉原C3结构,检测头用EFPN'替换。 表 2 YOLOv5默认锚框大小
Table 2. YOLOv5 default anchor box size
检测尺度 Anchor1 Anchor2 Anchor3 小尺寸 [10,13] [16,30] [33,23] 中尺寸 [30,61] [62,45] [59,119] 大尺寸 [116,90] [156,198] [373,326] 表 3 K均值聚类算法结果
Table 3. Results of K-means clustering algorithm
检测尺度 Anchor1 Anchor2 Anchor3 小尺寸 [5,5] [6,7] [8,9] 中尺寸 [9,14] [9,14] [14,15] 大尺寸 [19,20] [19,20] [25,26] 表 4 消融实验结果
Table 4. Results of ablation experiment
编号 模型 P R mAP0.5 FPS L/ms Params/M 0 YOLOv5 0.842 0.824 0.861 145.7 6.9 7.10 1 YOLOv5+FOG 0.893 0.838 0.870 145.7 6.9 7.10 2 YOLOv5+FOG+PC3 0.853 0.768 0.840 166.7 6.0 4.87 3 YOLOv5+FOG+PC3+EFPN 0.862 0.759 0.842 135.1 7.4 4.96 4 YOLOv5+FOG+PC3+EFPN' 0.876 0.782 0.854 161.3 6.2 3.80 5 YOLOv5+FOG+PC3+EFPN'+Focal-EIoU 0.906 0.790 0.860 161.3 6.2 3.80 6 YOLOv5+FOG+PC3+EFPN'+Focal-EIoU+CBAM 0.917 0.853 0.899 151.5 6.7 3.95 模型说明:FOG代表扩充雾化数据集TT100K-FOG;PC3代表使用更加轻量的PConv构建PC3特征提取模块来取代YOLOv5骨干和颈部网络中的C3模块;EFPN代表采用延伸的特征金字塔结构,替代YOLOv5中检测头;EFPN'代表在EFPN结构中删除大目标检测层后,替代YOLOv5中检测头;Focal-EIoU代表采用Focal-EloU取代YOLOv5默认函数CIoU;CBAM代表在YOLOv5主干网络中嵌入空间和通道注意力模块。 表 5 与其它算法的性能对比
Table 5. Performance comparison with other algorithms
模型 平台 主干网 类型 P/% mAP0.5 /% FPS Faster R-CNN MMDetection ResNet50 Anchor-based 71.9 79.9 57.7 YOLOv4 Darknet Darknet Anchor-based 58.7 82.2 80.9 YOLOv5 YOLOv5 Darknet Anchor-based 84.2 86.1 145.7 YOLOX MMDetection Darknet Anchor-free 72.6 79.7 93.6 YOLOv6 YOLOv6 EfficientRep Anchor-free 77.7 81.1 162.8 YOLOv7 YOLOv7 E-ELAN Anchor-based 72.0 77.4 130.2 YOLOv8 YOLOv8 Darknet Anchor-free 87.7 83.7 171.4 Ours YOLOv5 Darknet Anchor-based 91.7 89.9 151.5 -
[1] 王若萱, 吴建平, 徐辉. 自动驾驶汽车感知系统仿真的研究及应用综述[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2022, 34(12): 2507−2521. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.22-FZ0921
Wang R X, Wu J P, Xu H. Overview of research and application on autonomous vehicle oriented perception system simulation[J]. J Syst Simul, 2022, 34(12): 2507−2521. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.22-FZ0921
[2] Acharya S, Nanda P K. Adjacent LBP and LTP based background modeling with mixed-mode learning for foreground detection[J]. Pattern Anal Appl, 2021, 24(3): 1047−1074. doi: 10.1007/s10044-021-00967-z
[3] Shao F M, Wang X Q, Meng F J, et al. Real-time traffic sign detection and recognition method based on simplified Gabor wavelets and CNNs[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3192. doi: 10.3390/s18103192
[4] Maria Dominic Savio M, Deepa T, Bonasu A, et al. Image processing for face recognition using HAAR, HOG, and SVM algorithms[J]. J Phys Conf Ser, 2021, 1964(6): 062023. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1964/6/062023
[5] Burges C J C. A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition[J]. Data Min Knowl Discovery, 1998, 2(2): 121−167. doi: 10.1023/A:1009715923555
[6] Thamilselvan P. Lung cancer prediction and classification using adaboost data mining algorithm[J]. Int J Comput Theory Eng, 2022, 14(4): 149−154. doi: 10.7763/IJCTE.2022.V14.1322
[7] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.81.
[8] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.169.
[9] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2017, 39(6): 1137−1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
[10] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot MultiBox detector[C]//The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2.
[11] Bochkovskiy A, Wang C Y, Liao H Y M. YOLOv4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[Z]. arXiv: 2004.10934, 2020. https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934v1.
[12] Ultralytics. YOLOv5[EB/OL]. https://github.com/ultralytics/YOLOv5.
[13] Ge Z, Liu S T, Wang F, et al. YOLOX: exceeding YOLO series in 2021[Z]. arXiv: 2107.08430, 2021. https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.08430.
[14] Li C Y, Li L L, Jiang H L, et al. YOLOv6: a single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications[Z]. arXiv: 2209.02976, 2022. https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.02976.
[15] Wang C Y, Bochkovskiy A, Liao H Y M. YOLOv7: trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors[C]//2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 7464–7475. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00721.
[16] Reis D, Kupec J, Hong J, et al. Real-time flying object detection with YOLOv8[Z]. arXiv: 2305.09972, 2024. https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.09972.
[17] 陈旭, 彭冬亮, 谷雨. 基于改进YOLOv5s的无人机图像实时目标检测[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(3): 210372. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210372
Chen X, Peng D L, Gu Y. Real-time object detection for UAV images based on improved YOLOv5s[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2022, 49(3): 210372. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210372
[18] Yang J, Sun T, Zhu W C, et al. A lightweight traffic sign recognition model based on improved YOLOv5[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 115998−116010. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3326000
[19] 陈龙, 张建林, 彭昊, 等. 多尺度注意力与领域自适应的小样本图像识别[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(4): 220232. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220232
Chen L, Zhang J L, Peng H, et al. Few-shot image classification via multi-scale attention and domain adaptation[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(4): 220232. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220232
[20] Zhang J M, Xie Z P, Sun J, et al. A cascaded R-CNN with multiscale attention and imbalanced samples for traffic sign detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 29742−29754. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2972338
[21] Zhang H B, Qin L F, Li J et al. Real-time detection method for small traffic signs based on Yolov3[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 64145−64156. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2984554
[22] 郭迎, 梁睿琳, 王润民. 基于CNN图像增强的雾天跨域自适应目标检测[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2023, 59(16): 187−195. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2211-0132
Guo Y, Liang R L, Wang R M. Cross-domain adaptive object detection based on CNN image enhancement in foggy conditions[J]. Comput Eng Appl, 2023, 59(16): 187−195. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2211-0132
[23] Lin H B, Zhou J L, Chen M Z. Traffic sign detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv4[C]//2022 IEEE 10th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 2022: 2156–2160. https://doi.org/10.1109/ITAIC54216.2022.9836923.
[24] 汪昱东, 郭继昌, 王天保. 一种改进的雾天图像行人和车辆检测算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2020, 47(4): 70−77. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2020.04.010
Wang Y D, Guo J C, Wang T B. Algorithm for foggy-image pedestrian and vehicle detection[J]. J Xidian Univ, 2020, 47(4): 70−77. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2020.04.010
[25] 郎斌柯, 吕斌, 吴建清, 等. 基于CA-BIFPN的交通标志检测模型[J]. 深圳大学学报(理工版), 2023, 40(3): 335−343. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1249.2023.03335
Lang B K, Lü B, Wu J Q, et al. A traffic sign detection model based on coordinate attention-bidirectional feature pyramid network[J]. J Shenzhen Univ (Sci Eng), 2023, 40(3): 335−343. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1249.2023.03335
[26] 朱宏禹, 韩建宁, 徐勇. 基于改进型YOLOv5s的印刷线路板瑕疵检测[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2023, 42(3): 152−159. doi: 10.19652/j.cnki.femt.2204501
Zhu H Y, Han J N, Xu Y. Printed circuit board blemishes detection based on the improved YOLOv5s[J]. Foreign Electron Meas Technol, 2023, 42(3): 152−159. doi: 10.19652/j.cnki.femt.2204501
[27] 王屹伟, 路寅, 寇艳红, 等. 基于K-means聚类的GPS同步式欺骗识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(11): 4137−4149. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230837
Wang Y W, Lu Y, Dou Y H, et al. Synchronous GPS spoofing Identification based on K-means clustering[J]. J Electron Inf Technol, 2023, 45(11): 4137−4149. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230837
[28] Zhang Z D, Tan M L, Lan Z C, et al. CDNet: a real-time and robust crosswalk detection network on Jetson nano based on YOLOv5[J]. Neural Comput Appl, 2022, 34(13): 10719−10730. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07007-9
[29] Chen C Y, Liu M Y, Tuzel O, et al. R-CNN for small object detection[C]//Proceeding of the 13th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Taipei, China, 2016: 214–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54193-8_14.
[30] Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2020, 42(2): 318−327. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826
[31] Woo S, Park J, Lee J T, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]//15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: