Multi-resolution feature fusion for point cloud classification and segmentation network
-
摘要:
针对现有网络难以有效学习点云局部几何信息的问题,提出一种融合点云多分辨率特征的图卷积网络。首先,通过k-最近邻算法对点云构建局部图结构,以更好地表示点云的局部几何结构。其次,基于最远点采样算法提出一个并行通道分支,该分支通过对点云进行下采样来获得不同分辨率的点云,然后对其进行分组处理;为克服点云的稀疏特性,提出一种几何映射模块对分组点云执行正态化操作。最后,提出一种特征融合模块对图特征和多分辨率特征进行聚合,以更有效地获得全局特征。实验使用ModelNet40、ScanObjectNN和ShapeNet Part数据集进行评估,结果表明,提出的网络具有良好的分类与分割性能。
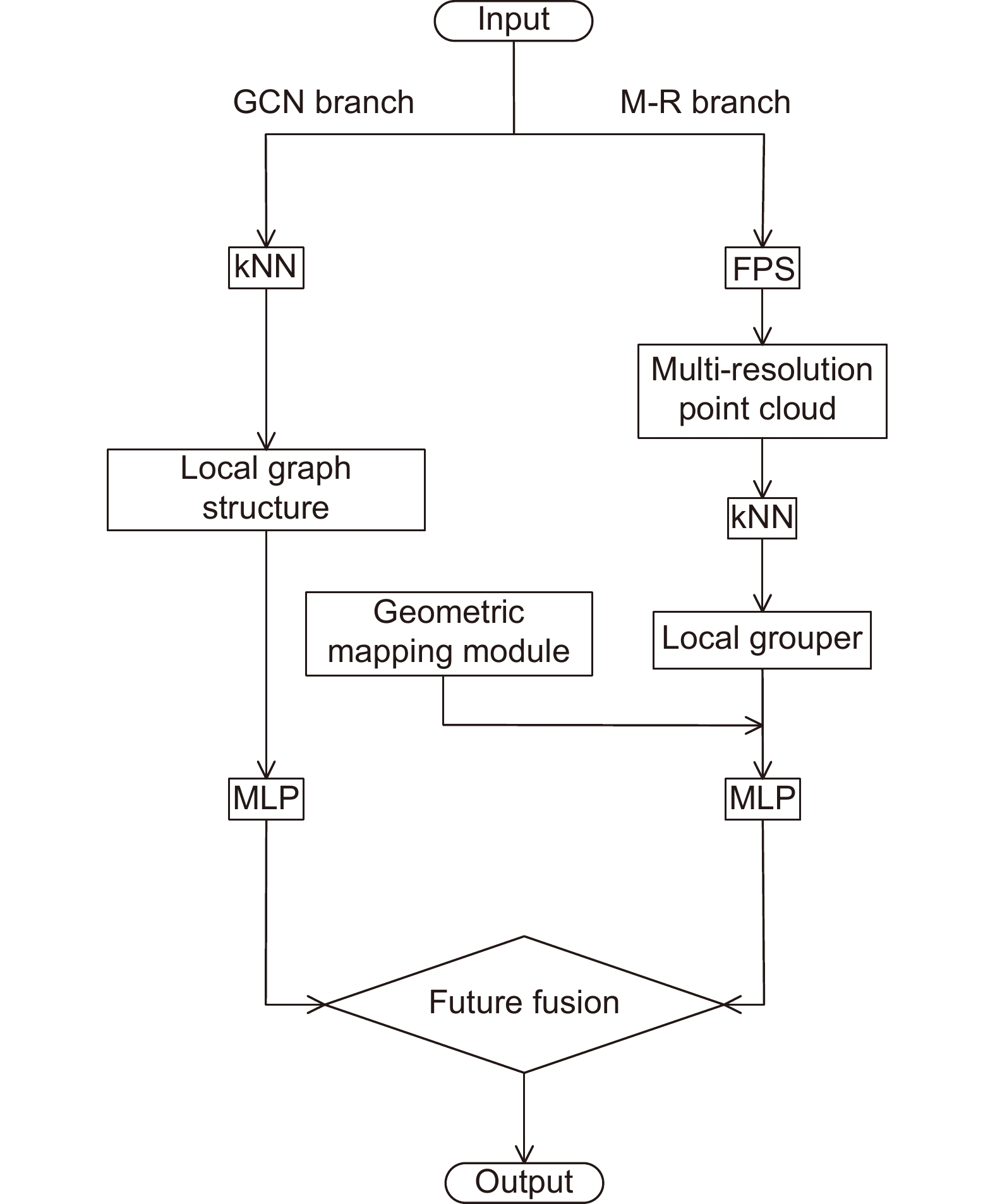
Abstract:To address the problem that existing networks find it difficult to learn local geometric information of point cloud effectively, a graph convolutional network that fuses multi-resolution features of point cloud is proposed. First, the local graph structure of the point cloud is constructed by the k-nearest neighbor algorithm to better represent the local geometric structure of the point cloud. Second, a parallel channel branch is proposed based on the farthest point sampling algorithm, which obtains point clouds with different resolutions by downsampling them and then groups them. To overcome the sparse characteristics of the point cloud, a geometric mapping module is proposed to perform normalization operations on the grouped point cloud. Finally, a feature fusion module is proposed to aggregate graph features and multi-resolution features to obtain global features more effectively. Experiments are evaluated using ModelNet40, ScanObjectNN, and ShapeNet Part datasets. The experimental results show that the proposed network has state-of-the-art classification and segmentation performance.
-
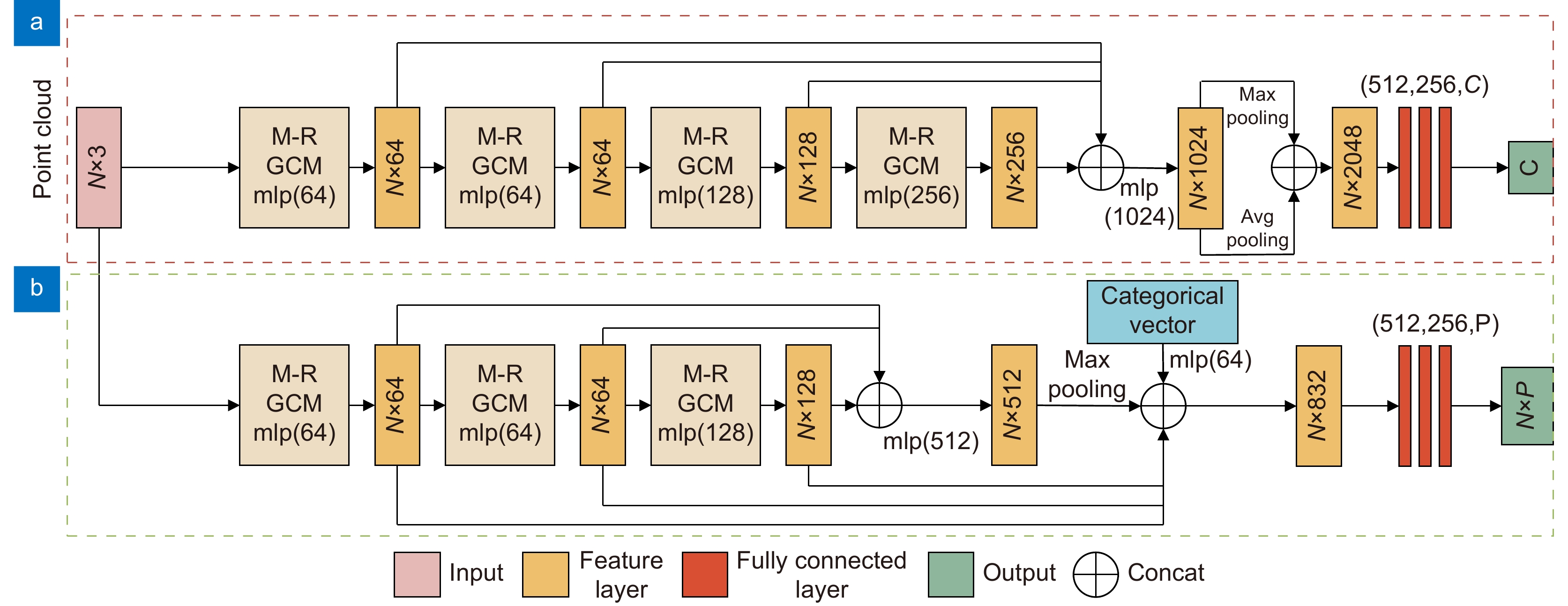
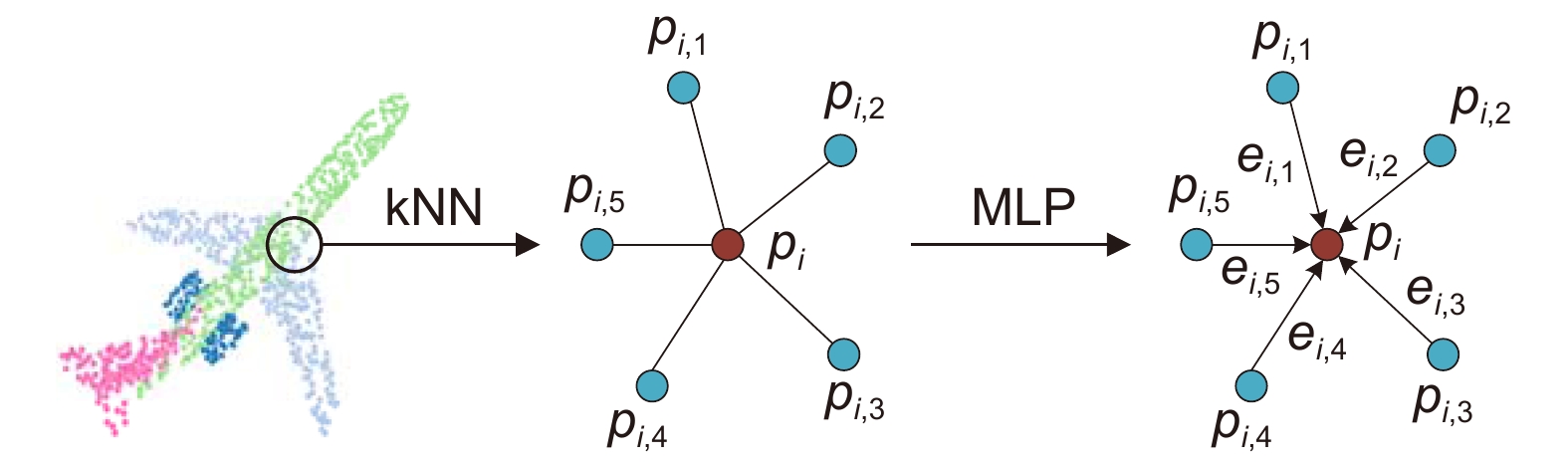
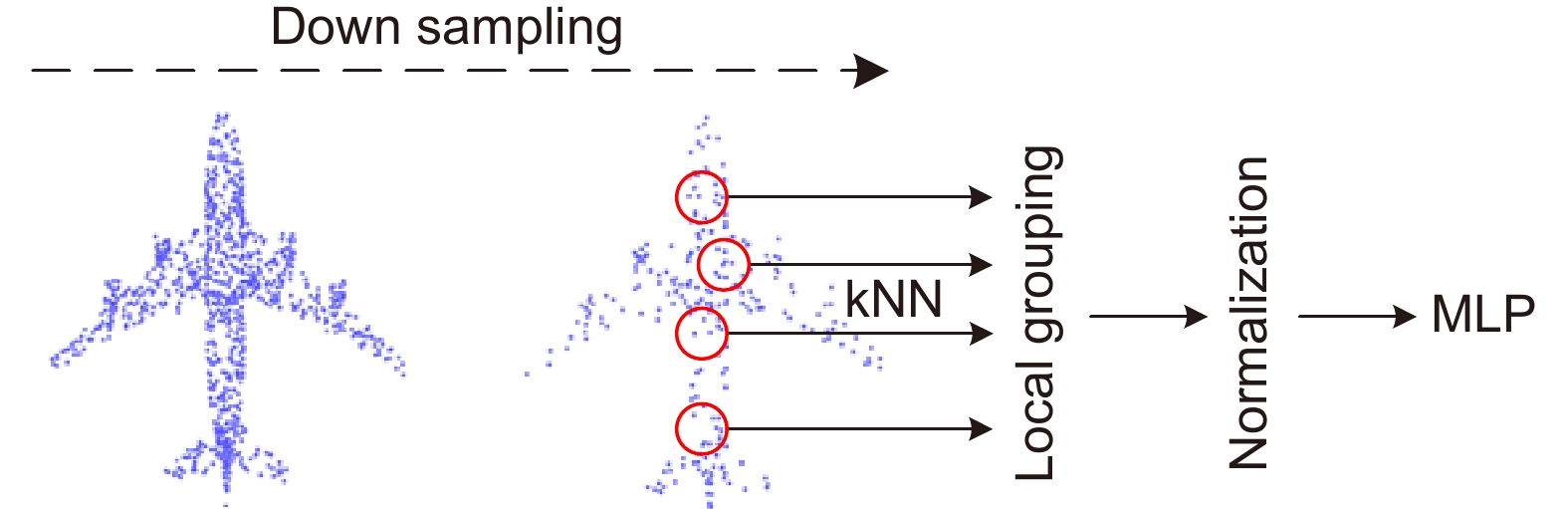
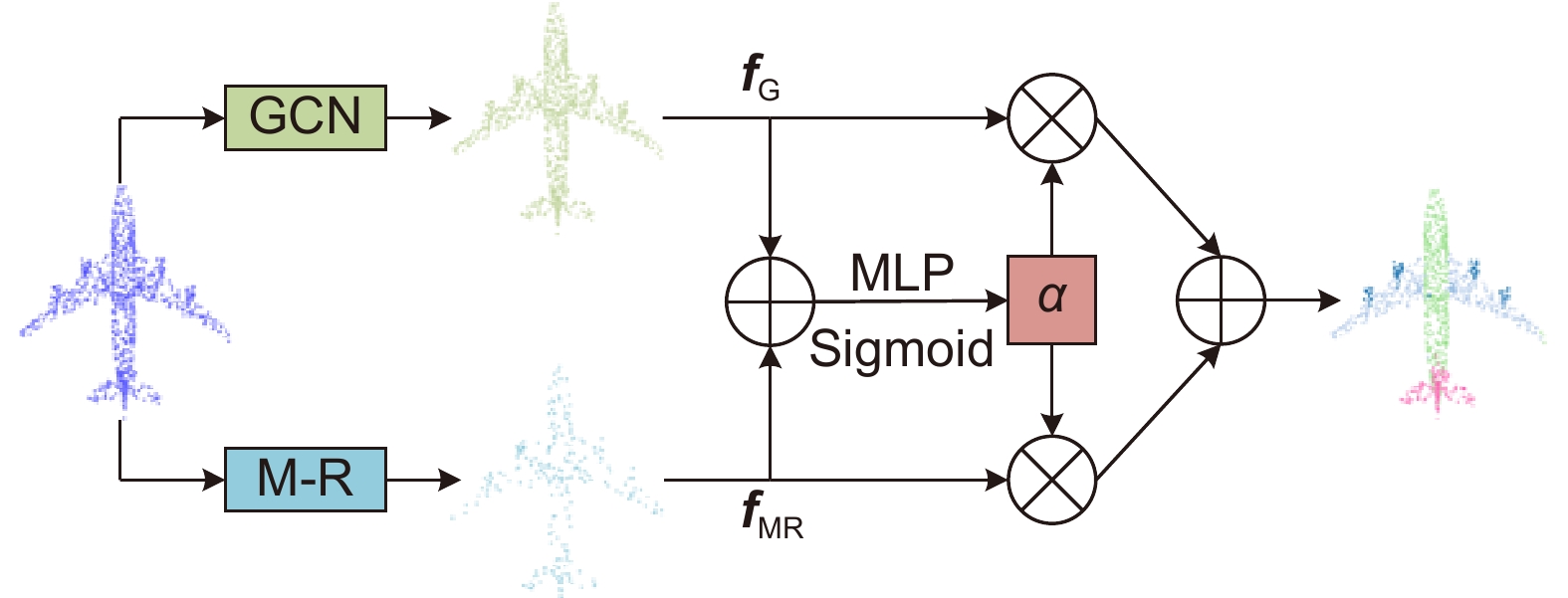
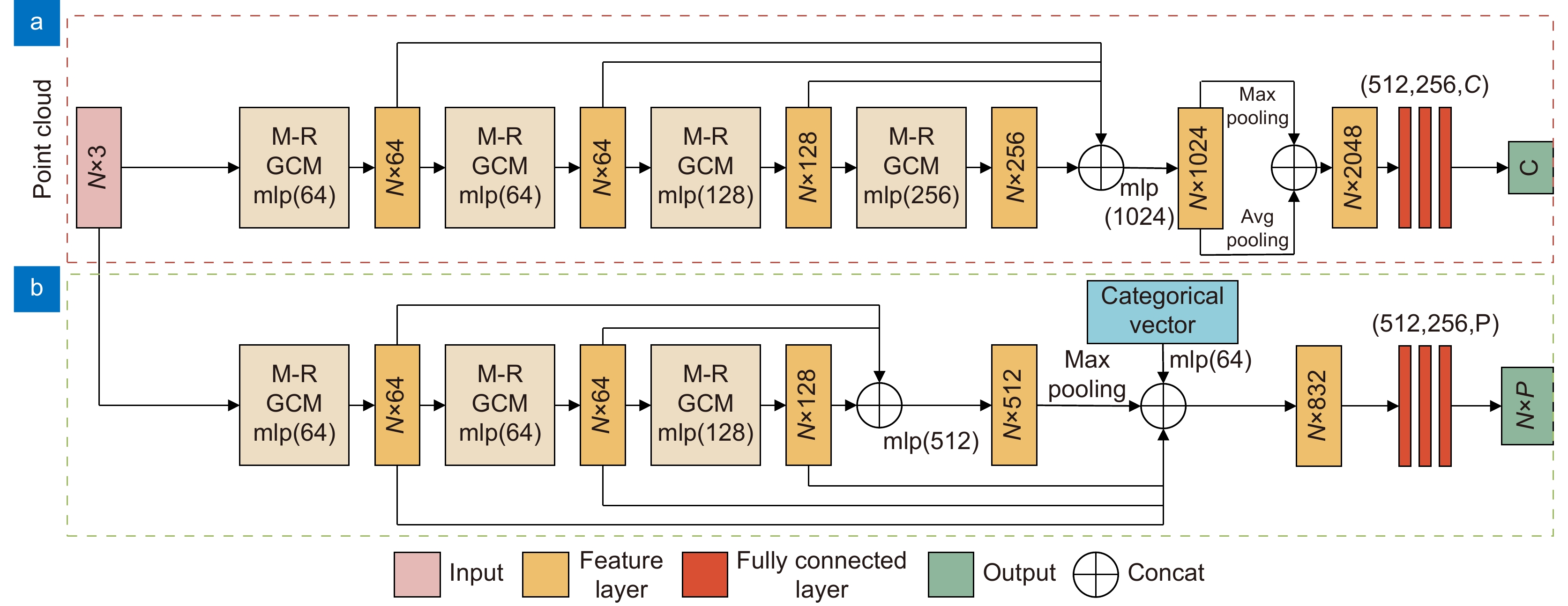
Overview: In recent years, 3D point cloud analysis has become a hot topic in computer vision and been widely used in mapping, medical imaging, and autonomous driving. As a 3D image representation, point cloud contains rich geometric information. With the development of 3D scanning technologies such as LiDAR, the acquisition of point clouds is becoming more accessible. Since convolutional neural networks (CNN) have greatly improved the results of computer vision tasks, neural networks are becoming a mainstream approach in image processing. Traditional 2D images comprise regular and dense pixels, and CNNs apply to 2D image processing. However, point cloud data are sparse and disordered; each point does not contain additional information (e.g., RGB). Using traditional CNNs for point cloud learning tasks is a challenging task. The graph-like structure can effectively represent non-Euclidean data like point clouds, and this method largely solves the problem of difficulty in learning the local features of point clouds. Since the graph structure construction process is generally based on the k-nearest neighbor algorithm (kNN), the size of the predefined neighborhood limits the effectiveness of the local graph structure. If the value of k is too small, it will lead to an incomplete representation of local information. At the same time, too large a value of k will introduce information redundancy, leading to performance degradation. To this end, we propose a multi-resolution graph convolutional network to perform the point cloud analysis task. The network learns the local features of point clouds by constructing graph structures and then downsamples the point clouds using the farthest point sampling method (FPS) to obtain multi-resolution point cloud data, followed by feature learning for point clouds at different resolutions. To overcome the effect of predefined neighborhoods, we compensate local features with multi-resolution features and efficiently aggregate point cloud features by the feature fusion module. To verify the classification and segmentation performance of the model, we perform classification experiments on ModelNet40 and ScanObjectNN datasets and part segmentation experiments on ShapeNet Part dataset. It is experimentally verified that the compensation of point cloud local graph structure information with multi-resolution features can enhance point clouds' local feature learning ability. The multi-resolution graph convolutional network proposed in this paper can effectively capture the local features of point clouds and achieve good results in classification and segmentation tasks. A large number of ablation experiments verify the effectiveness and robustness of the model.
-

-
表 1 实验参数设置
Table 1. Experimental parameter setting
参数项 分类网络 分割网络 输入点数 1024 2048 多分辨率点云点数 [896,768,640,512] [896,768,640] 图卷积分支k取值 20 20 训练周期 250 300 优化器 SGD SGD 训练批次 32 32 测试批次 16 16 初始学习速率 0.1 0.003 表 2 不同方法在ModelNet40数据集上的分类精度对比
Table 2. Comparison of classification accuracy with different methods on ModelNet40 dataset
方法 输入 点数/103 mAcc/% OA/% VoxNet[8] 体素 - 83.0 85.9 MVCNN[11] 多视图 - - 90.1 PointNet[12] 坐标 1 86.0 89.2 PointNet++[13] 坐标+法线 5 - 91.9 文献[24] 坐标+法线 1 89.8 91.6 文献[25] 坐标+法线 1 - 93.0 3D-GCN[26] 坐标 1 - 92.1 DGCNN[15] 坐标 1 90.2 92.9 LDGCNN[16] 坐标 1 90.3 92.9 DDGCN[27] 坐标 1 90.4 92.7 DRNet[28] 坐标 1 - 93.1 DGANet[29] 坐标 1 89.4 92.3 PCT[19] 坐标 1 - 93.2 AFM-Net[30] 坐标 1 89.4 92.85 文献[31] 坐标 1 89.02 92.5 Our 坐标 1 91.2 93.4 表 3 不同方法在ScanObjectNN数据集上的分类精度对比
Table 3. Comparison of classification accuracy with different methods on ScanObjectNN dataset
表 4 ShapeNet Part数据集上的部分分割结果
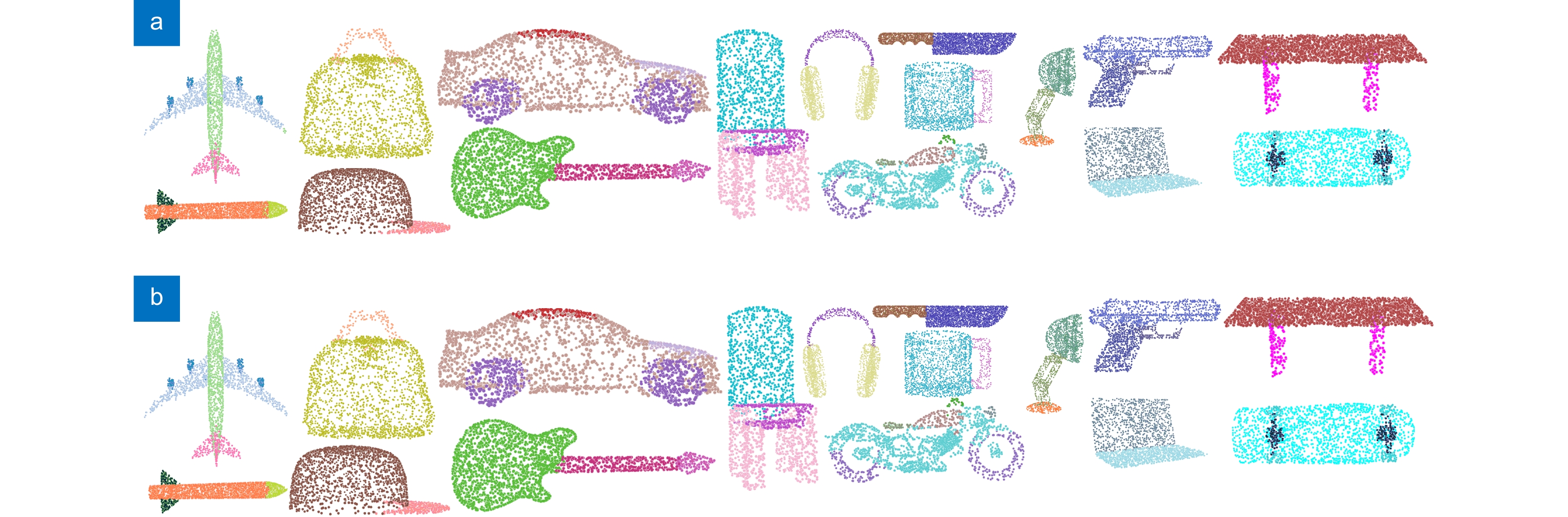
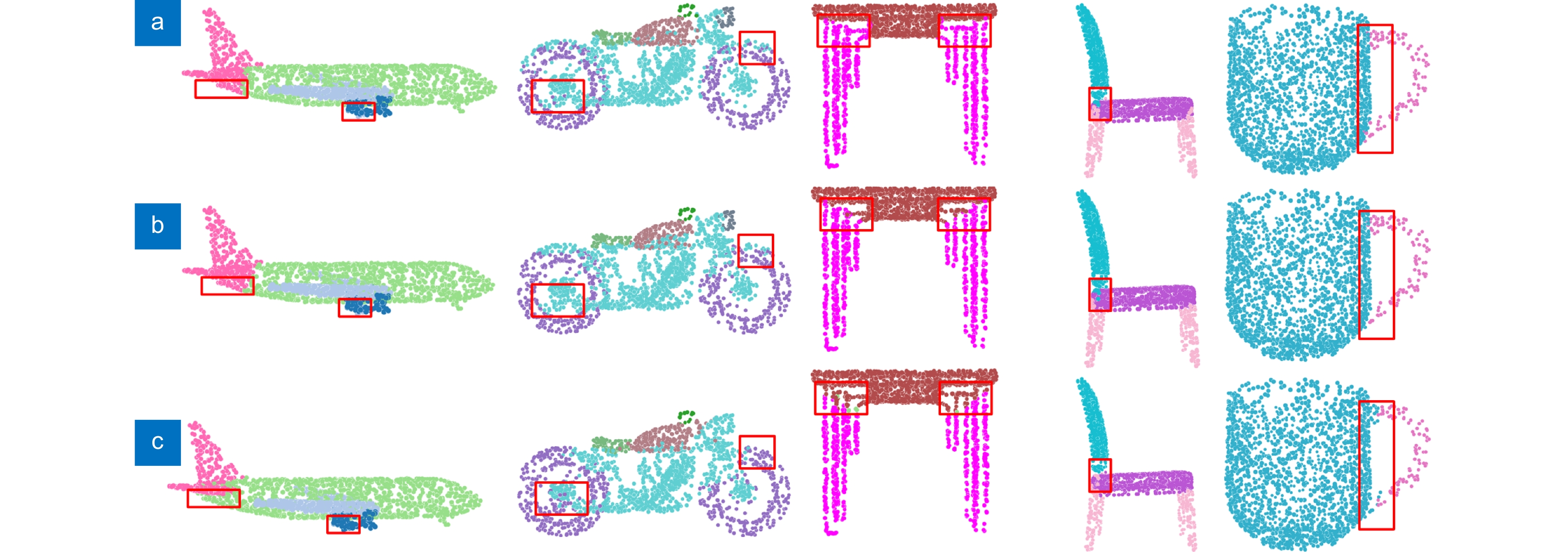
Table 4. Part segmentation results on the ShapeNet Part dataset
方法 PointNet[12] PointNet++[13] 文献[25] 3D-GCN[26] LDGCNN[16] DGANet[29] DGCSA[34] DGCNN[15] 本文 飞机 83.4 82.4 83.8 83.1 84.0 84.6 84.2 84.0 83.6 包 78.7 79.0 77.5 84.0 83.0 85.7 73.3 83.4 83.4 帐篷 82.5 87.7 87.9 86.6 84.9 87.8 82.3 86.7 88.4↑ 车 74.9 77.3 78.7 77.5 78.4 78.5 77.7 77.8 78.4↑ 椅子 89.6 90.8 90.8 90.3 90.6 91.0 91.0 90.6 89.7 耳机 73.0 71.8 77.3 74.1 74.4 77.3 75.3 74.7 80.5↑ 吉他 91.5 91.0 91.8 90.9 91.0 91.2 91.2 91.2 91.8↑ 刀 85.9 85.9 87.9 86.4 88.1 87.9 88.6 87.5 88.6↑ 台灯 80.8 83.7 84.2 83.8 83.4 82.4 85.3 82.8 81.6 手提电脑 95.3 95.3 95.9 95.6 95.8 95.8 95.9 95.7 95.8↑ 摩托 65.2 71.6 71.8 66.8 67.4 67.8 58.9 66.3 69.6↑ 马克杯 93.0 94.1 95.1 94.8 94.9 94.2 94.3 94.9 94.4 手枪 81.2 81.3 80.9 81.3 82.3 81.1 81.8 81.1 83.7↑ 火箭 57.9 58.7 59.6 59.6 59.2 59.7 56.9 63.5 62.5 滑板 72.8 76.4 76.6 75.7 76.0 75.7 75.4 74.5 82.0↑ 桌子 80.6 82.6 82.4 82.8 81.9 82.0 82.7 82.6 83.0↑ mIoU 83.7 85.1 85.4 85.1 85.1 85.2 85.3 85.2 85.4↑ 表 5 不同k值对模型性能的影响
Table 5. Effect of different k values on model performance
k OA(%) 用多分辨率分支补偿后OA/% 提升/% 5 20.7 35.1 +14.4 10 85.4 88.3 +2.9 15 91.9 92.1 +0.2 20 92.5 93.4 +0.9 25 92.1 92.3 +0.2 表 6 多分辨率图卷积模块消融实验
Table 6. Ablation experiments of multi-resolution GCN module
实验 GCN分支 M-R分支 融合 mAcc/% OA/% 1 √ × × 89.9 92.5 2 × √ × 84.0 89.1 3 √ √ × 89.9 92.6 4 √ √ √ 91.2 93.4 表 7 不同分辨率点云对网络性能的影响
Table 7. The effect of different resolution point cloud on network performance
不同分辨率的点云 mAcc/% OA/% [512,384,256,128] 90.4 92.7 [640,512,384,256] 90.6 92.8 [768,640,512,384] 90.9 93.0 [896,768,640,512] 91.2 93.4 表 8 多种模型的噪声鲁棒性比较
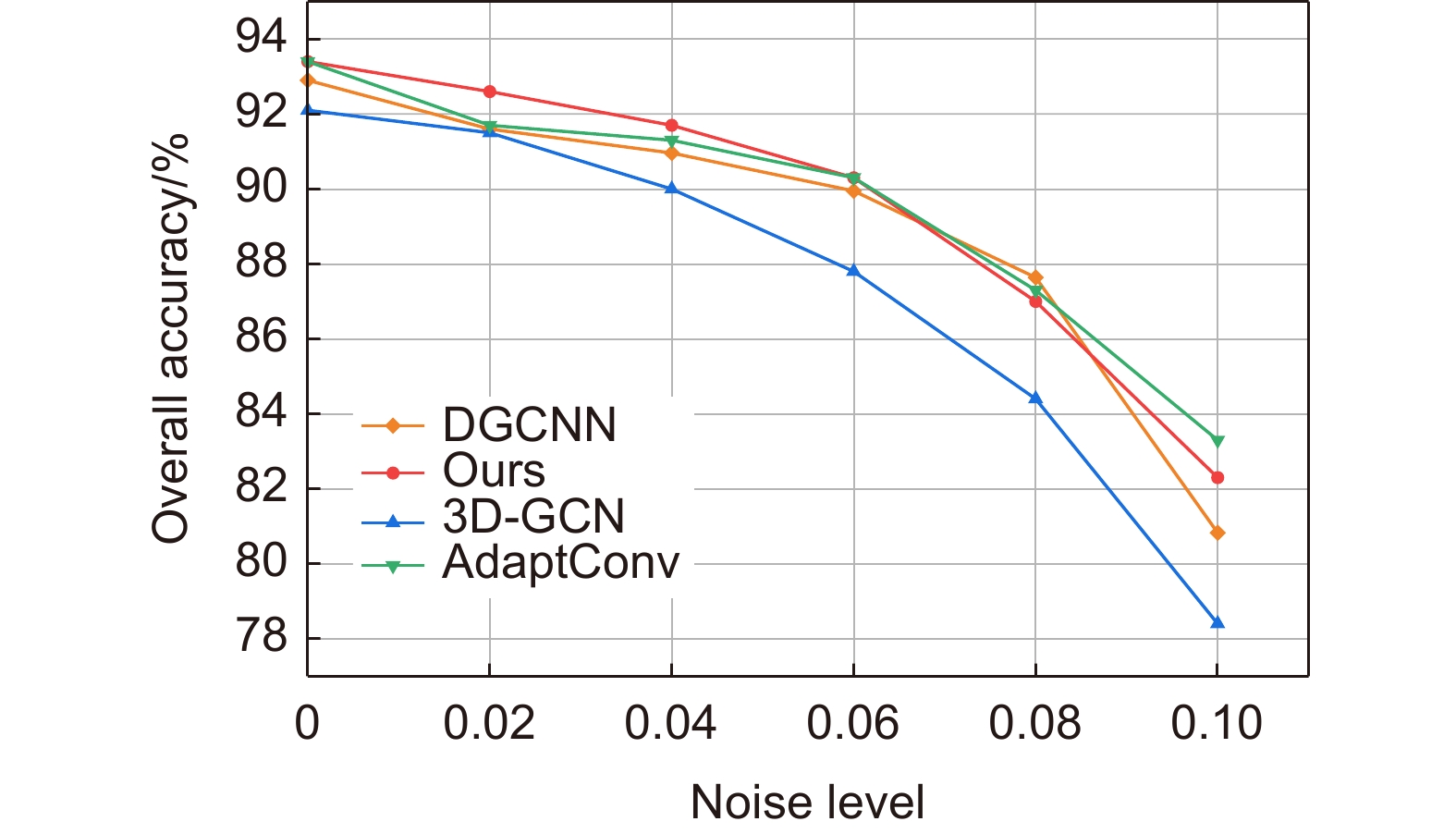
Table 8. Comparison of the noise robustness of the several methods
噪声水平 下降程度 3D-GCN AdaptConv DGCNN Ours 0.02 0.7↓ 1.8↓ 1.4↓ 0.9↓ 0.04 2.2↓ 2.2↓ 2.2↓ 1.8↓ 0.06 4.6↓ 3.3↓ 3.2↓ 3.1↓ 0.08 8.4↓ 6.5↓ 5.7↓ 6.4↓ 0.1 14.9↓ 10.8↓ 13.1↓ 11.7↓ 表 9 不同数量特征提取模块对网络性能的影响
Table 9. The impact of different number of feature extraction modules on network performance
模块数量 mAcc/% OA/% 每轮训练时间/s 模型参数量/M 3 89.7 92.4 63 2.8 4 91.2 93.4 139 3.6 5 90.6 93.1 323 4.8 -
[1] 张昕怡, 陈茂霖, 刘祥江, 等. 顾及点密度与未知角分辨率的地面点云分类[J]. 激光技术, 2023, 47(1): 59−66. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2023.01.009
Zhang X Y, Chen M L, Liu X J, et al. Classification of terrestrial point cloud considering point density and unknown angular resolution[J]. Laser Technol, 2023, 47(1): 59−66. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2023.01.009
[2] 李佳男, 王泽, 许廷发. 基于点云数据的三维目标检测技术研究进展[J]. 光学学报, 2023, 43(15): 1515001. doi: 10.3788/AOS230745
Li J N, Wang Z, Xu T F. Three-dimensional object detection technology based on point cloud data[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2023, 43(15): 1515001. doi: 10.3788/AOS230745
[3] 陆康亮, 薛俊, 陶重犇. 融合空间掩膜预测与点云投影的多目标跟踪[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(9): 220024. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.220024
Lu K L, Xue J, Tao C B. Multi target tracking based on spatial mask prediction and point cloud projection[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2022, 49(9): 220024. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.220024
[4] 陈仲生, 李潮林, 左旺, 等. 双重下采样增强的点云改进配准算法研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2023, 45(4): 572−578. doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2023.04.005
Chen Z S, Li C L, Zuo W, et al. Study on improved point cloud registration algorithm enhanced by double down-sampling[J]. Automot Eng, 2023, 45(4): 572−578. doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2023.04.005
[5] 李美佳, 于泽宽, 刘晓, 等. 点云算法在医学领域的研究进展[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(10): 2013−2023. doi: 10.11834/jig.200253
Li M J, Yu Z K, Liu X, et al. Progress of point cloud algorithm in medical field[J]. J Image Graphics, 2020, 25(10): 2013−2023. doi: 10.11834/jig.200253
[6] 夏金泽, 孙浩铭, 胡盛辉, 等. 基于图像信息约束的三维激光点云聚类方法[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(2): 220148. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220148
Xia J Z, Sun H M, Hu S H, et al. 3D laser point cloud clustering method based on image information constraints[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(2): 220148. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220148
[7] 柏宏强, 夏永华, 杨明龙, 等. 基于三维激光点云特征线提取的溶洞多分辨率三维重建方法研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(20): 202802. doi: 10.3788/LOP57.202802
Bai H Q, Xia Y H, Yang M L, et al. Multi-resolution 3D reconstruction of karst caves based on the feature line extraction of 3D laser point cloud[J]. Laser Optoelectron Prog, 2020, 57(20): 202802. doi: 10.3788/LOP57.202802
[8] Maturana D, Scherer S. Voxnet: a 3D convolutional neural network for real-time object recognition[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2015: 922–928. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2015.7353481.
[9] Riegler G, Osman Ulusoy A, Geiger A. OctNet: learning deep 3D representations at high resolutions[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 6620–6629. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.701.
[10] 肖正涛, 高健, 吴东庆, 等. 一种基于体素网格的三维点云均匀降采样方法[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2023(8): 180−184. doi: 10.19356/j.cnki.1001-3997.20230310.025
Xiao Z T, Gao J, Wu D Q, et al. A uniform downsampling method for three-dimensional point clouds based on voxel grids[J]. Mach Des Manuf, 2023(8): 180−184. doi: 10.19356/j.cnki.1001-3997.20230310.025
[11] Su H, Maji S, Kalogerakis E, et al. Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2015: 945–953. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.114.
[12] Charles R Q, Su H, Mo K C, et al. PointNet: deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 77–85. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.16
[13] Qi C R, Yi L, Su H, et al. PointNet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017: 5105–5114. https://doi.org/10.5555/3295222.3295263.
[14] Simonovsky M, Komodakis N. Dynamic edge-conditioned filters in convolutional neural networks on graphs[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 29–38. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.11.
[15] Wang Y, Sun Y B, Liu Z W, et al. Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds[J]. ACM Trans Graphics, 2019, 38(5): 146. doi: 10.1145/3326362
[16] Zhang K G, Hao M, Wang J, et al. Linked dynamic graph CNN: learning on point cloud via linking hierarchical features[Z]. arXiv: 1904.10014, 2019. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1904.10014.
[17] 刘斌, 樊云超. 基于改进动态图卷积的点云分类模型[J]. 中国科技论文, 2022, 17(11): 1230−1235, 1266. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2022.11.009
Liu B, Fan Y C. A point cloud classification model based on improved dynamic graph convolution[J]. China Sci, 2022, 17(11): 1230−1235, 1266. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2022.11.009
[18] Sun Q, Liu H Y, He J, et al. DAGC: employing dual attention and graph convolution for point cloud based place recognition[C]//Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, 2020: 224–232. https://doi.org/10.1145/3372278.3390693.
[19] Guo M H, Cai J X, Liu Z N, et al. PCT: point cloud transformer[J]. Comput Vis Med, 2021, 7(2): 187−199. doi: 10.1007/s41095-021-0229-5
[20] Liu H, Tian S H. Deep 3D point cloud classification and segmentation network based on GateNet[J]. Vis Comput, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02826-w.
[21] Wu Z R, Song S R, Khosla A, et al. 3D shapeNets: a deep representation for volumetric shapes[C]/Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2015: 1912–1920. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298801.
[22] Uy M A, Pham Q H, Hua B S, et al. Revisiting point cloud classification: a new benchmark dataset and classification model on real-world data[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019: 1588–1597. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00167.
[23] Yi L, Kim V G, Ceylan D, et al. A scalable active framework for region annotation in 3D shape collections[J]. ACM Trans Graphics, 2016, 35(6): 210. doi: 10.1145/2980179.2980238
[24] 王子璇, 任明武. DST-Pointnet++: 基于Pointnet++改进的点云分类网络[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2022, 50(11): 2497−2501. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2022.11.026
Wang Z X, Ren M W. DST-Pointnet++: A novel point cloud classification network based on pointnet++[J]. Comput Digit Eng, 2022, 50(11): 2497−2501. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2022.11.026
[25] 王本杰, 农丽萍, 张文辉, 等. 基于Spider卷积的三维点云分类与分割网络[J]. 计算机应用, 2020, 40(6): 1607−1612. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2019101879
Wang B J, Nong L P, Zhang W H, et al. 3D point cloud classification and segmentation network based on Spider convolution[J]. J Comput Appl, 2020, 40(6): 1607−1612. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2019101879
[26] Lin Z H, Huang S Y, Wang Y C F. Convolution in the cloud: learning deformable kernels in 3D graph convolution networks for point cloud analysis[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 1797–1806. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00187.
[27] Chen L F, Zhang Q. DDGCN: graph convolution network based on direction and distance for point cloud learning[J]. Vis Comput, 2023, 39(3): 863−873. doi: 10.1007/s00371-021-02351-8
[28] Qiu S, Anwar S, Barnes N. Dense-resolution network for point cloud classification and segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2021: 3812–3821. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV48630.2021.00386.
[29] Wan J, Xie Z, Xu Y Y, et al. DGANet: a dilated graph attention-based network for local feature extraction on 3D point clouds[J]. Remote Sens, 2021, 13(17): 3484. doi: 10.3390/rs13173484
[30] 张润梅, 程婷, 尹蕾, 等. 一种注意力融合的多尺度点云分类网络[J]. 淮北师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(1): 70−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-8248.2023.01.012
Zhang R M, Cheng T, Yin L, et al. Attention fusion and multi-scale point cloud classification network[J]. J Huaibei Normal Univ (Natl Sci), 2023, 44(1): 70−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-8248.2023.01.012
[31] 国玉恩, 任明武. 基于PointConv改进的点云分类网络[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2022, 50(12): 2737−2740, 2764. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2022.12.026
Guo Y E, Ren M W. Improved point cloud classification network based on PointConv[J]. Comput Digit Eng, 2022, 50(12): 2737−2740, 2764. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2022.12.026
[32] Qiu S, Anwar S, Barnes N. Geometric back-projection network for point cloud classification[J]. IEEE Trans Multimedia, 2021, 24: 1943−1955. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2021.3074240
[33] Cheng S L, Chen X W, He X W, et al. PRA-Net: point relation-aware network for 3D point cloud analysis[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2021, 30: 4436−4448. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3072214
[34] 宋巍, 蔡万源, 何盛琪, 等. 结合动态图卷积和空间注意力的点云分类与分割[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2021, 26(11): 2691−2702. doi: 10.11834/jig.200550
Song W, Cai W Y, He S Q, et al. Dynamic graph convolution with spatial attention for point cloud classification and segmentation[J]. J Image Graphics, 2021, 26(11): 2691−2702. doi: 10.11834/jig.200550
[35] Zhou H R, Feng Y D, Fang M S, et al. Adaptive graph convolution for point cloud analysis[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2021: 4945–4954. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00492.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: