-
摘要
激光对准是激光无线电能传输系统中接收端获得稳定能源的前提,激光传能对对准精度、稳定性和实时性提出了较高的要求,因此,提出了一种激光对准系统设计方法,并对感兴趣区域提取以及图像预处理方法进行了优化改进:一方面,通过引入MobileNet、增加空间注意力机制以及融合语义的方式改进SSD (single shot multi-Box detector)模型,使用改进模型训练并预测感兴趣区域,相较于原始模型,训练速度提升了71.67%,模型大小减小了52.48%,实时检测速度提升了295.30%,检测偏差显著减小;另一方面,对灰度化的权值进行了优化,并利用直方图实现阈值的自适应选取,采用椭圆拟合法及形心法检测光斑与信标中心点,优化图像处理方法能够有效提取光斑,减小光斑定位的误差。实验结果表明,改进的激光对准系统精度稳定在95%以上,能够满足实际应用中精度、速度与稳定性的要求。
Abstract
Laser alignment is a prerequisite for stable energy acquisition at the receiver end in laser wireless power transmission systems. Laser power transfer imposes high requirements on alignment accuracy, stability, and real-time performance. Therefore, a laser alignment system design method is proposed, and optimizations are made to the region of interest extraction and image preprocessing methods. On one hand, the SSD (single shot multi-Box detector) model is improved by introducing MobileNet, incorporating spatial attention mechanism, and fusing semantics. The improved model is used for training and predicting the regions of interest. Compared to the original model, the training speed is improved by 71.67%, the model size is reduced by 52.48%, the real-time detection speed is increased by 295.30%, and the detection error is significantly reduced. On the other hand, the weights of grayscale conversion are optimized, and an adaptive threshold selection using a histogram is implemented. The elliptical fitting method and centroid method are employed to detect the spot and beacon center, reducing the error in spot localization. Experimental results show that the improved laser alignment system achieves a stable accuracy of over 95% and meets the requirements of accuracy, speed, and stability in application.
-
Key words:
- laser alignment /
- SSD network /
- image process /
- object detection
-
Overview
Overview: Laser alignment is a prerequisite for stable energy acquisition at the receiver end in laser-based wireless power transmission systems. A laser alignment system requires high accuracy, stability, and real-time performance. Therefore, an overall design method for laser alignment systems is proposed: Firstly, the image of the plane where the photovoltaic array is located is captured by the camera. Secondly, the improved SSD (single shot multi-Box detector) network which has been trained is used to predict the region of interest containing laser spots and two beacon spots. Then, preprocessing the image which contains grayscale processing, threshold segmentation, filtering and denoising, and using ellipse fitting and centroid method to locate the center points of the laser spot and beacon spots. Finally, position control signals are output to the pan-tilt after coordinate conversion calculation, and the pan-tilt is driven to align the light spot with the photovoltaic array.
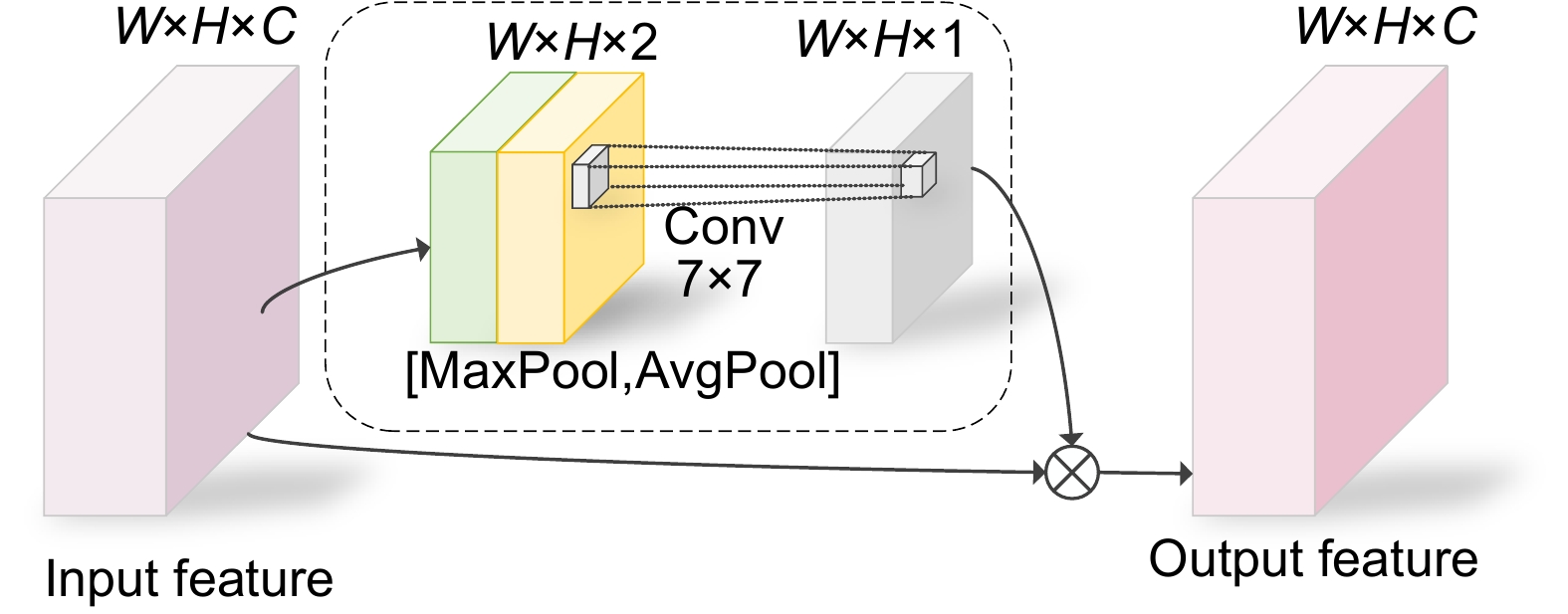
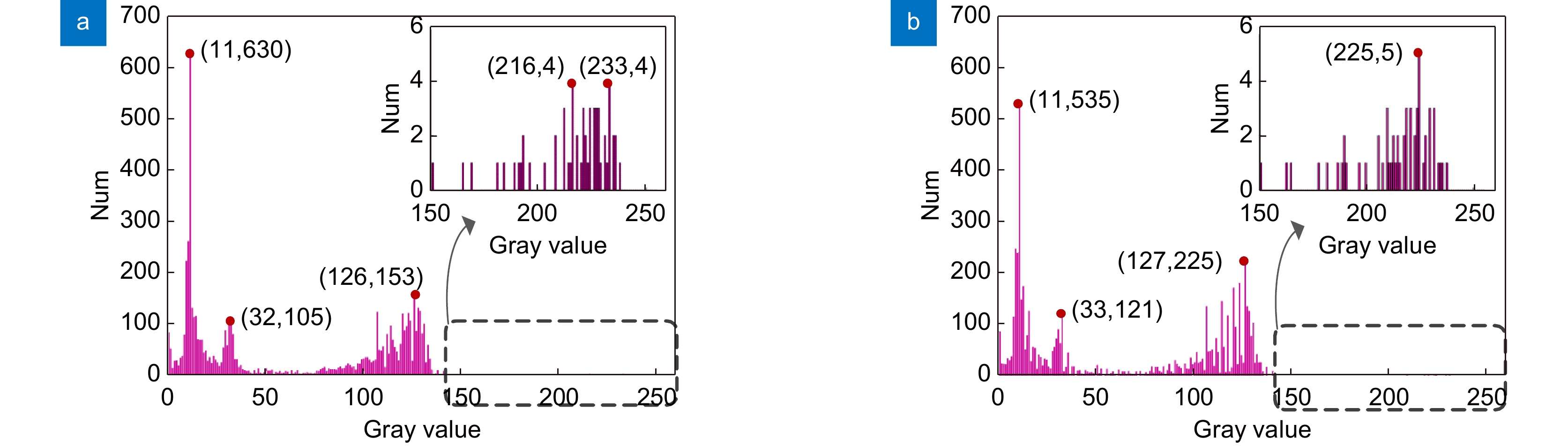
Image processing is the key to system design. Thus, the optimization and improvement are made for the adaptive extraction of the region of interest and image processing in system design. On the one hand, the SSD model is improved by introducing MobileNet, spatial attention mechanism, and semantic fusion. The improved neural network model is used to train and achieve adaptive prediction of regions of interest. The improved model proposed in this paper has a training speed increase of 71.67%, a model size reduction of 52.48%, and a real-time detection speed increase of 295.30% compared to the original model. On the other hand, based on the characteristics of the laser spot, the weight values in the process of converting color images to grayscale images are optimized. With the optimized grayscale processing method, the peaks and valleys of the grayscale histogram are more pronounced, based on which, adaptive selection of the threshold in the threshold segmentation stage is achieved. When processing images, optimizing the grayscale processing of three channel weights and adaptive threshold segmentation can effectively extract light spots and reduce the error of light spot positioning. The experimental results show that the improved laser alignment system has a stable accuracy of over 95% with the best accuracy has reached 99.55%, which can meet the requirements of accuracy, speed, and stability in engineering practice.
-

-
表 1 不同网络模型性能比较
Table 1. Performance comparison of different network models
Net FPS Size/MB Time/h Errx/% Erry/% VGG16-SSD 4.68 90.7 30.0 17.5 28.1 MobileNet-SSD 18.92 24.0 7.5 13.6 3.1 Improved-MobileNet-SSD 18.50 43.1 8.5 0.3 0 -
参考文献
[1] 程时杰, 陈小良, 王军华, 等. 无线输电关键技术及其应用[J]. 电工技术学报, 2015, 30(19): 68−84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2015.19.011
Cheng S J, Chen X L, Wang J H, et al. Key technologies and applications of wireless power transmission[J]. Trans China Electrotech Soc, 2015, 30(19): 68−84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2015.19.011
[2] 范兴明, 莫小勇, 张鑫. 无线电能传输技术的研究现状与应用[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35(10): 2584−2600. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2015.10.026
Fan X M, Mo X Y, Zhang X. Research status and application of wireless power transmission technology[J]. Proc CSEE, 2015, 35(10): 2584−2600. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2015.10.026
[3] 时振磊, 孟文文, 申景诗, 等. 无人机激光无线能量传输APT系统跟踪设计[J]. 激光技术, 2019, 43(6): 809−814. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2019.06.015
Shi Z L, Meng W W, Shen J S, et al. Tracking design of APT system of laser wireless energy transmission for unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Laser Technol, 2019, 43(6): 809−814. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2019.06.015
[4] 梁静远, 陈瑞东, 姚海峰, 等. 无线光通信系统捕获、瞄准和跟踪研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(8): 210439. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210439
Liang J Y, Chen R D, Yao H F, et al. Research progress of acquisition, pointing and tracking in optical wireless communication system[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2022, 49(8): 210439. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210439
[5] 赵馨, 宋延嵩, 佟首峰, 等. 空间激光通信捕获、对准、跟踪系统动态演示实验[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(10): 0305005.
Zhao X, Song Y S, Tong S F, et al. Dynamic demonstration experiment of acquisition, pointing and tracking system in space laser communications[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2014, 41(10): 0305005.
[6] 程坤, 董昊, 蔡卓燃, 等. 高效率远距离激光无线能量传输方案设计[J]. 航天器工程, 2015, 24(1): 8−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2015.01.002
Cheng K, Dong H, Cai Z R, et al. Scheme design of high efficiency long distance laser power transmission[J]. Spacecr Eng, 2015, 24(1): 8−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2015.01.002
[7] 李志鹏, 张燕革, 艾勇, 等. 无人机激光跟踪与无线供能系统[J]. 激光技术, 2018, 42(3): 306−310. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2018.03.004
Li Z P, Zhang Y G, Ai Y, et al. Laser tracking and wireless power supply system for unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Laser Technol, 2018, 42(3): 306−310. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2018.03.004
[8] 张港, 董大兴, 杨雁南. 激光对微型无人机跟瞄充电系统的设计与实现[J]. 激光技术, 2022, 46(2): 169−174. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2022.02.004
Zhang G, Dong D X, Yang Y N. Design and implementation of a laser tracking, aiming and charging system for micro-unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Laser Technol, 2022, 46(2): 169−174. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2022.02.004
[9] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.81.
[10] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.169.
[11] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2017, 39(6): 1137−1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
[12] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.91.
[13] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot MultiBox detector[C]//Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2.
[14] Howard A G, Zhu M L, Chen B, et al. MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[Z]. arXiv: 1704.04861, 2017. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1704.04861.
[15] Hu J, Shen L, Albanie S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2020, 42(8): 2011−2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372
[16] Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2018: 3–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1.
[17] Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.106.
[18] 刘兆蓉, 王志乾, 刘绍锦, 等. 激光光斑中心精确定位算法研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2011, 28(5): 399−401,409. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2011.05.097
Liu Z R, Wang Z Q, Liu S J, et al. Research of PreciseLaser spot center location algorithm[J]. Comput Simul, 2011, 28(5): 399−401,409. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2011.05.097
[19] 何佳凯, 黄来玉, 杨德振, 等. 远近场自适应激光光斑能量中心检测[J]. 激光与红外, 2022, 52(4): 620−624. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2022.04.023
He J K, Huang L Y, Yang D Z, et al. Adaptive detection for near-far field laser spot energy center[J]. Laser Infrared, 2022, 52(4): 620−624. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2022.04.023
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: