-
摘要:
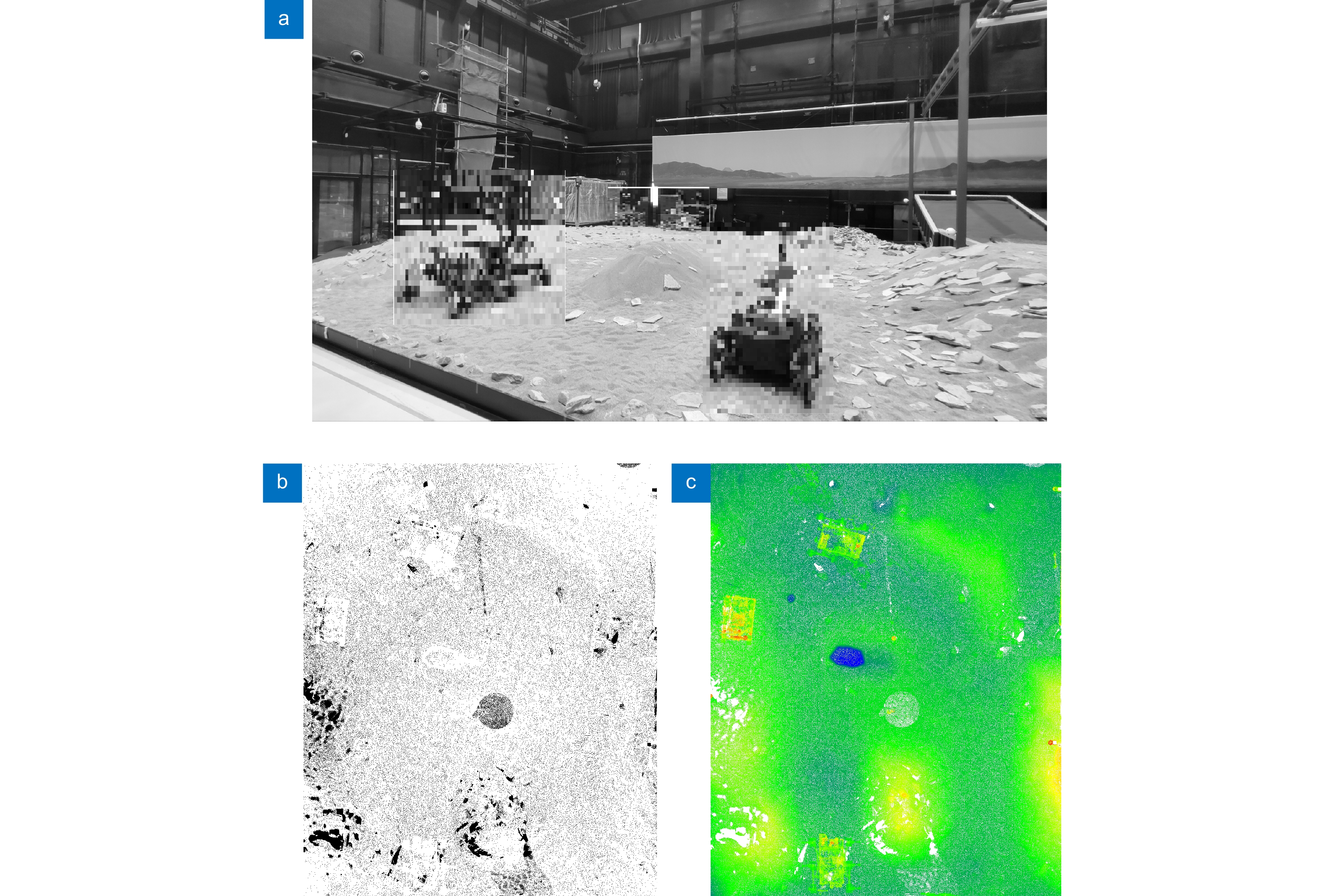
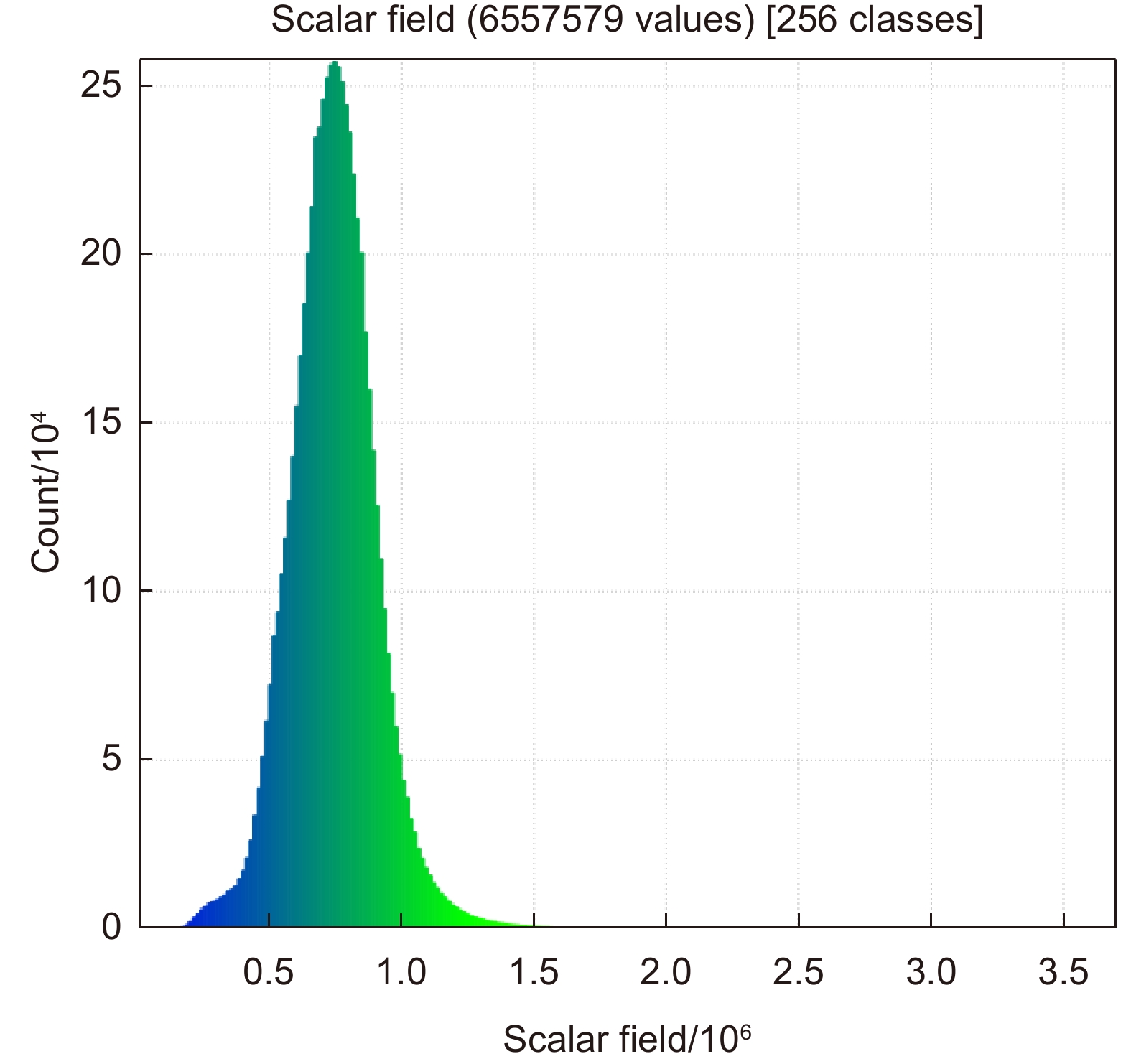
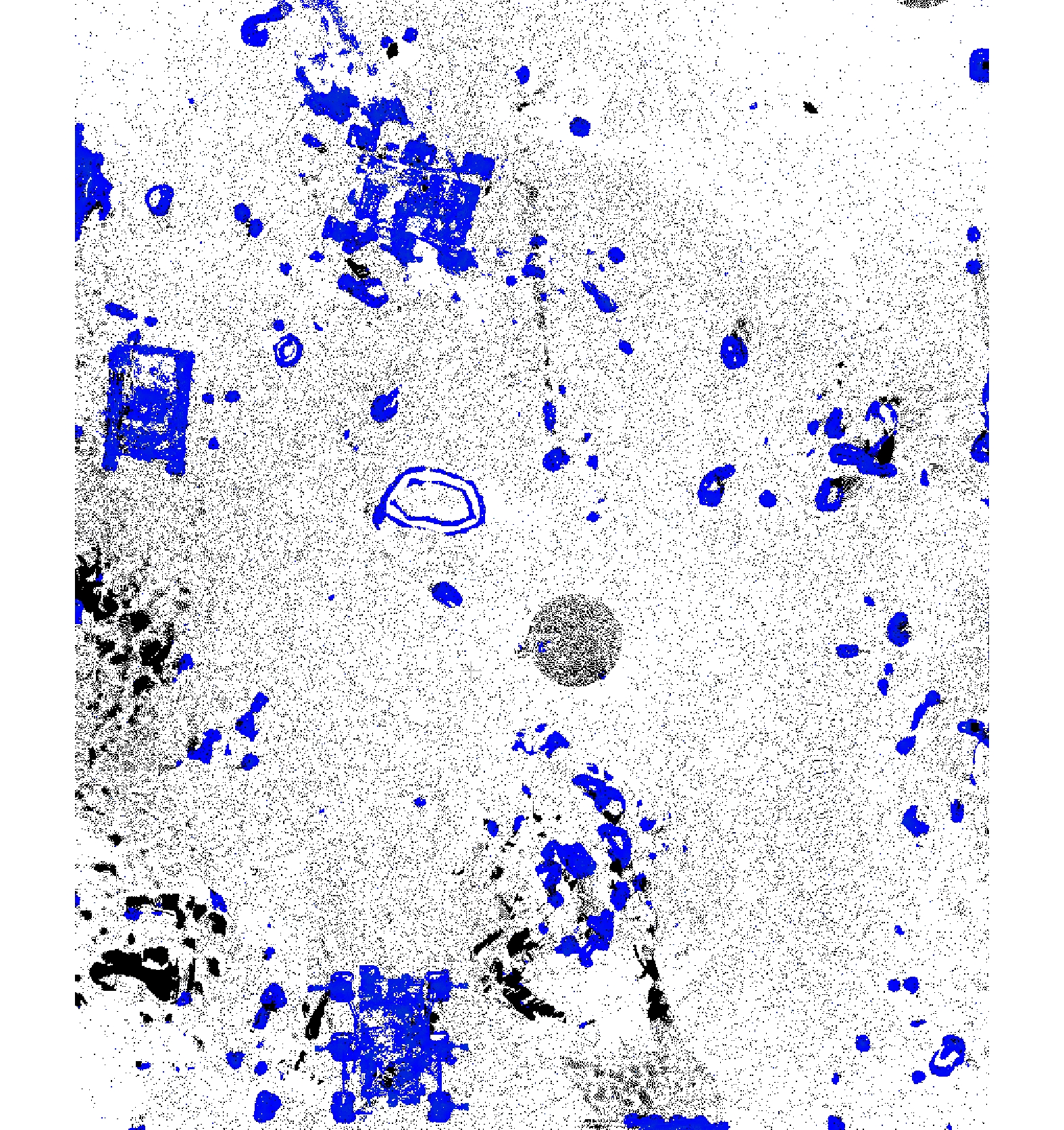
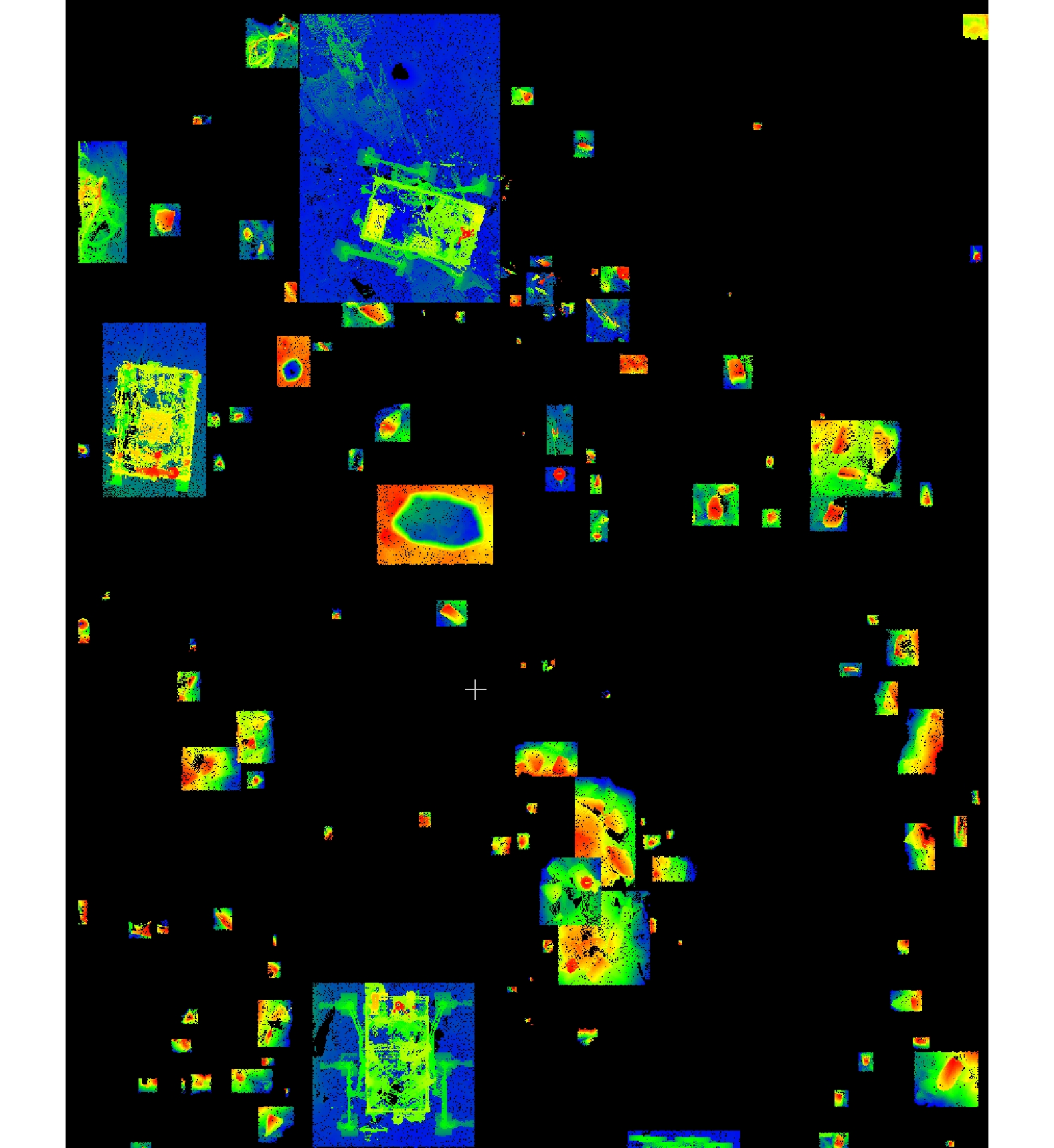
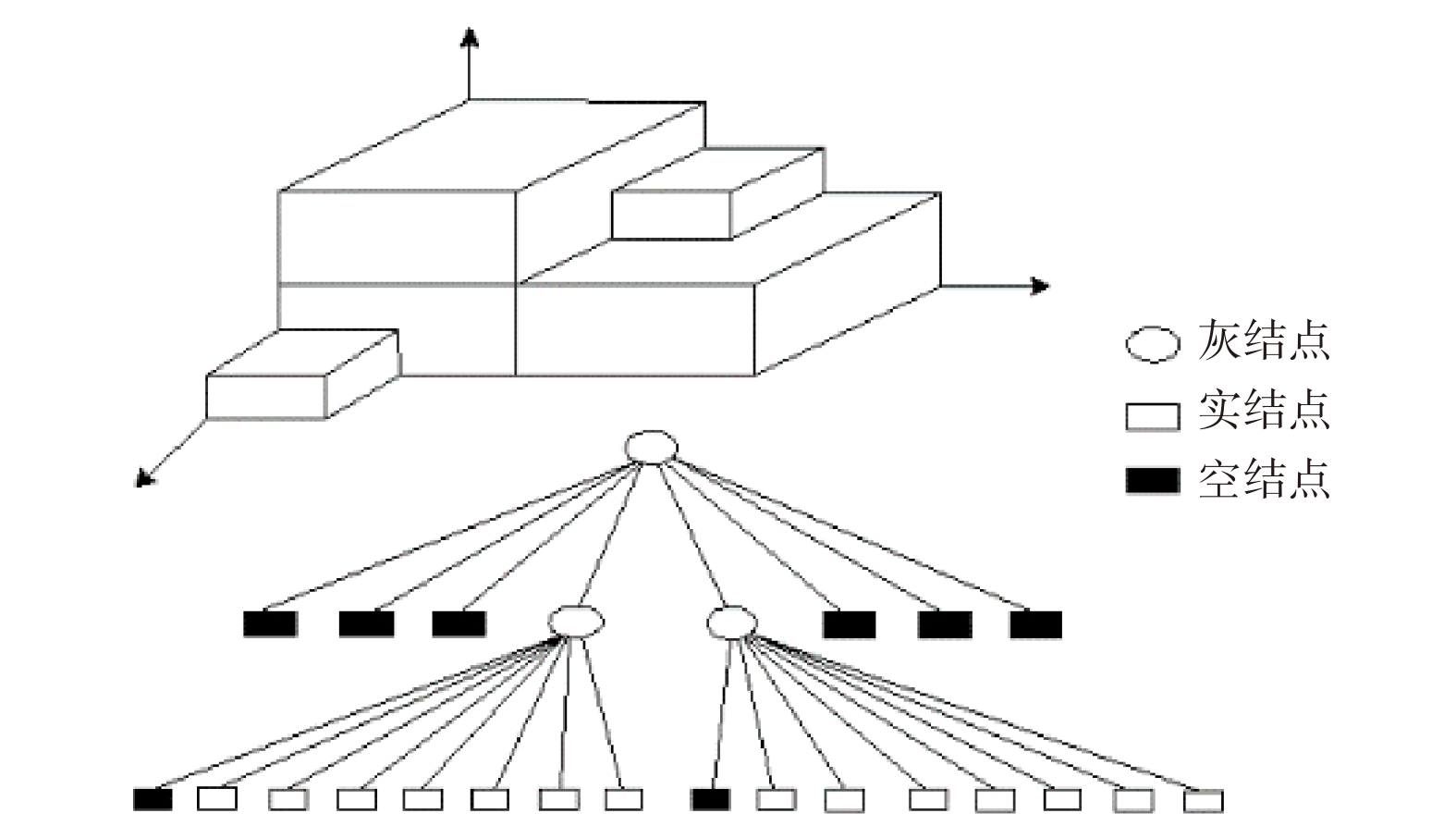
火星车的环境感知能力是其进行智能移动和探测的基础,而障碍物检测识别是环境感知中的一个重要方面,识别效果直接决定了火星车工作能力和安全性。本文提出一种基于激光雷达数据的火星表面障碍物自动识别方法。通过获取的激光雷达点云数据,首先在分析激光反射强度理论的基础上,通过强度补偿理论将点云强度根据距离、角度因素进行修正,进而构建激光雷达强度值与目标特征的反射关系。通过大津法自动求取全局阈值,自适应的将火星表面点云分类为障碍物点云和非障碍物点云;然后通过曲率约束剔除不符合条件的障碍物点云;最后利用基于八叉树叶节点的连通性聚类,实现火星表面障碍物点云的识别。模拟实验结果表明,该方法可实现激光雷达点云中的火星表面障碍物有效提取,典型障碍物识别精度接近90%,为基于火星车障碍物检测和环境感知相关研究提供借鉴。
Abstract:The environment perception ability of the Mars rover is the basis of its intelligent movement and detection. Obstacle detection is an important aspect of environment perception, which directly determines the working ability and safety of the Mars rover. In this paper, a method of identifying obstacles on the surface of Mars based on LiDAR data is proposed. Based on the obtained LiDAR point cloud data, the intensity of the point cloud is modified according to the distance and angle factors through the intensity compensation theory based on the analysis of the laser reflection intensity theory, and then the reflection relationship between the lidar intensity value and the target characteristics is constructed. The global threshold is automatically obtained through the Otsu method, and the Mars surface point cloud is adaptively classified into an obstacle point cloud and a non-obstacle point cloud. Then, the obstacle point cloud which does not meet the conditions is removed by curvature constraint. Finally, using the connectivity clustering based on Octree-based leaf nodes, the recognition of the obstacle point cloud on the surface of Mars is realized. Through the simulation experiment, the results show that this method can effectively extract the obstacles on the surface of Mars from the LiDAR point cloud, and provide a reference for the related research based on the obstacle monitoring of the Mars rover and environmental perception.
-
Key words:
- Mars surface /
- LiDAR /
- point cloud data /
- obstacle recognition
-

-
表 1 障碍物目标识别精度统计
Table 1. Accuracy statistics of obstacle recognition
I class error/% Ⅱ class error/% Total error/% 11.5 3.48 4.91 -
[1] 吴伟仁, 刘晓川. 国外深空探测的发展研究[J]. 中国航天, 2004(1): 26−29.
Wu W R, Liu X C. A survey of deep space exploration activities abroad[J]. Aerosp China, 2004(1): 26−29.
[2] Golombek M P, Arvidson R E, Bell III J F, et al. Assessment of Mars Exploration Rover landing site predictions[J]. Nature, 2005, 436(7047): 44−48. doi: 10.1038/nature03600
[3] 沈鹏. 多源火星形貌数据处理与信息服务系统构建关键技术研究[D]. 郑州: 解放军信息工程大学, 2017.
Shen P. Research on the key technology of multi source mars data processing and spatial information service system[D]. Zhengzhou: PLA Information Engineering University, 2017.
[4] Kirk R L, Howington-Kraus E, Rosiek M R. Recent planetary topographic mapping at the USGS, Flagstaff: moon, Mars, Venus, and beyond[C]//Proceedings of XIXth ISPRS Congress Technical Commission IV: Mapping and Geographic Systems, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2000: 476–490.
[5] 冯伟, 易旺民, 杨旺, 等. “天问一号”探测器舱体抛离试验系统设计与验证[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2021, 42(3): 23−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2021.03.003
Feng W, Yi W M, Yang W, et al. Design and verification of tianwen-1 probe cabin separation test system[J]. Spacecr Recovery Remote Sens, 2021, 42(3): 23−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2021.03.003
[6] 马友青, 彭松, 张建利, 等. 祝融号火星车在轨高精度视觉定位与地形重建[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(23): 2790−2801. doi: 10.1360/TB-2021-1273
Ma Y Q, Peng S, Zhang J L, et al. Precise visual localization and terrain reconstruction for China’s Zhurong Mars rover on orbit[J]. Chin Sci Bull, 2022, 67(23): 2790−2801. doi: 10.1360/TB-2021-1273
[7] 王东署, 王佳. 未知环境中移动机器人环境感知技术研究综述[J]. 机床与液压, 2013, 41(15): 187−191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2013.15.050
Wang D S, Wang J. Research review of environmental cognition techniques of mobile robots in unknown environment[J]. Mach Tool Hydraul, 2013, 41(15): 187−191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2013.15.050
[8] 李国庆. 行星表面障碍检测与地形相关导航方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.
Li G Q. Research on methods of autonomous hazard detection on planetary surface and terrain relative navigation[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018.
[9] 肖学明. 火星表面障碍检测方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.
Xiao X M. Research on Martian hazard detection method[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017.
[10] 赵一兵, 王荣本, 李琳辉, 等. 基于多传感器信息的前方障碍物检测[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2007, 43(26): 174−177,226. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2007.26.051
Zhao Y B, Wang R B, Li L H, et al. Approach of obstacle detection based on laser sensor and single camera[J]. Comput Eng Appl, 2007, 43(26): 174−177,226. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2007.26.051
[11] 侯建. 月球车立体视觉与视觉导航方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2007.
Hou J. Research on stereo vision and visual navigation for a lunar rover[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2007.
[12] 石德乐, 叶培建, 贾阳. 我国月面巡视探测器定位方法研究[J]. 航天器工程, 2006, 15(4): 14−20.
Shi D L, Ye P J, Jia Y. Study on Chinese lunar rover location methods[J]. Spacecr Eng, 2006, 15(4): 14−20.
[13] 郭丽, 李金岭, 童锋贤, 等. 同波束VLBI技术对嫦娥三号巡视器的高精度相对定位[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2016, 41(8): 1125−1130. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20140439
Guo L, Li J L, Tong F X, et al. Precisely relative positioning of Chang’e 3 rover with SBI delta VLBI delay measurements[J]. Geomat Inf Sci Wuhan Univ, 2016, 41(8): 1125−1130. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20140439
[14] Li R X, Ma F, Xu F L, et al. Large scale mars mapping and rover localization using descent and rover imagery[J]. Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens, 2000, 33: 579−586.
[15] Di K C, Xu F L, Wang J, et al. Photogrammetric processing of rover imagery of the 2003 Mars Exploration Rover mission[J]. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens, 2008, 63(2): 181−201. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2007.07.007
[16] Alexander D A, Deen R G, Andres P M, et al. Processing of Mars Exploration Rover imagery for science and operations planning[J]. J Geophys Res:Planets, 2006, 111(E2): E02S02. doi: 10.1029/2005JE002462
[17] 刘继周. 面向无人驾驶的智能车系统平台研究与应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017.
Liu J Z. Research and application towards autonomous driving-system and platform[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017.
[18] 张振华. 基于激光点云数据的障碍物检测算法研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2020.
Zhang Z H. Research on obstacle detection algorithm based on laser point cloud data[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2020.
[19] 肖志鹏. 无人车动态场景分析关键技术研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2018.
Xiao Z P. Research on key technologies of dynamic scene analysis for autonomous vehicles[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2018.
[20] 刘建伟. 多路径激光雷达三维数据处理技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2018.
Liu J W. Research on technology of processing 3D data about multi-path of Lidar[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018.
[21] 张桢瑶. 基于路侧三维激光雷达的交通信息提取方法研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2020.
Zhang Z Y. Traffic data extraction based on roadside 3D LiDAR[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2020.
[22] 姚辰. 四足机器人非结构环境3D状态感知与自主定位方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020.
Yao C. Research on 3D state sensing and autonomous localization of quadruped robot in unstructured environment[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020.
[23] Pfeifer N, Höfle B, Briese C, et al. Analysis of the backscattered energy in terrestrial laser scanning data[C]//Proceedings of the XXI Congress: Silk Road for Information from Imagery: the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Beijing, 2008: 1045–1051.
[24] 戴永江. 激光雷达原理[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2002.
Dai Y J. The Principle of Lidar[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2002.
[25] 童祎, 夏珉, 杨克成, 等. 基于激光雷达强度值的目标反射特征提取[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(10): 102802. doi: 10.3788/LOP55.102802
Tong Y, Xia M, Yang K C, et al. Target reflection feature extraction based on Lidar intensity value[J]. Laser Optoelectron Prog, 2018, 55(10): 102802. doi: 10.3788/LOP55.102802
[26] 王仕儒. 基于分数阶布谷鸟优化的Otsu图像分割算法研究[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2022. https://doi.org/10.27257/d.cnki.gnxhc.2022.000623.
Wang S R. Research on otsu image segmentation algorithm based on fractional-order cuckoo optimization[D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2022. https://doi.org/10.27257/d.cnki.gnxhc.2022.000623.
[27] 苏天科. 单期点云的高斯曲率定位桥梁潜在损伤技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学, 2022. https://doi.org/10.26943/d.cnki.gbjzc.2022.000287.
Su T K. Research on potential damage locating technique of bridge by Gaussian curvature with single phase point cloud[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2022. https://doi.org/10.26943/d.cnki.gbjzc.2022.000287.
[28] 王丽英, 王鑫宁. 多值体素连通区域构建下的机载LIDAR数据三维平面提取[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2021, 23(9): 1598−1607. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2021.200579
Wang L Y, Wang X N. Multi-value voxel connected region construction based on 3D plane extraction for airborne LIDAR data[J]. J Geo-Inf Sci, 2021, 23(9): 1598−1607. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2021.200579
[29] 张蕊. 基于激光点云的复杂三维场景多态目标语义分割技术研究[D]. 郑州: 战略支援部队信息工程大学, 2018.
Zhang R. Research on polymorphic object semantic segmentation of complex 3D scenes based on laser point clouds[D]. Zhengzhou: PLA Strategic Support Force Information Engineering University, 2018.
[30] Sithole G, Vosselman G. Experimental comparison of filter algorithms for bare-Earth extraction from airborne laser scanning point clouds[J]. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens, 2004, 59(1–2): 85−101. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2004.05.004
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: