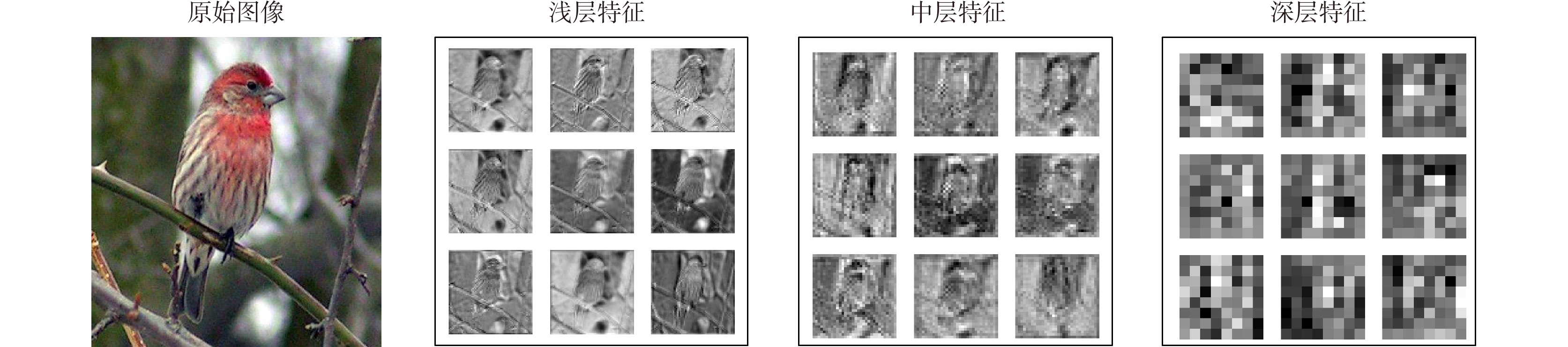
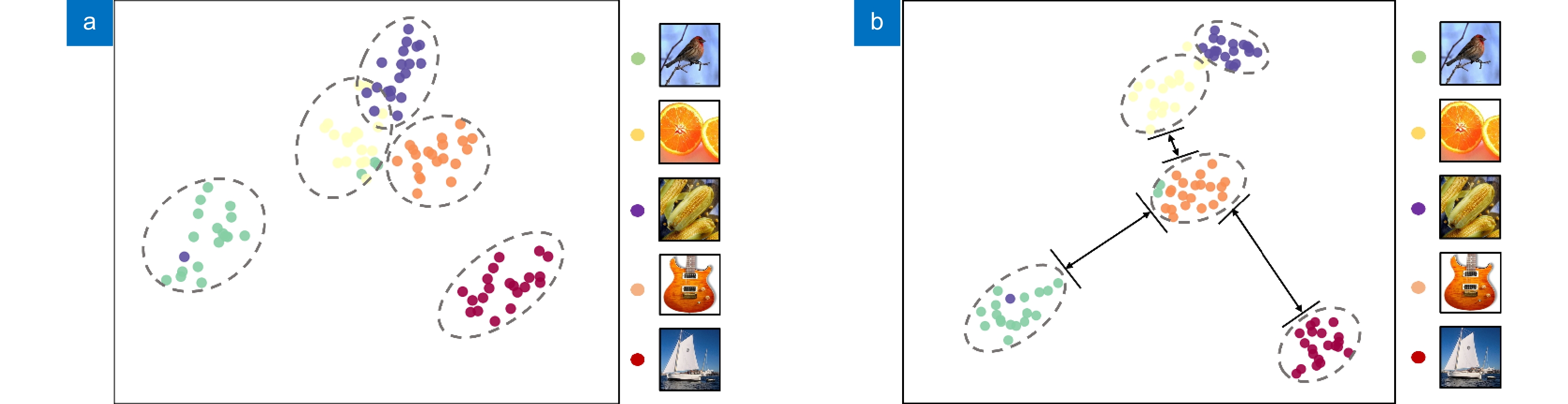
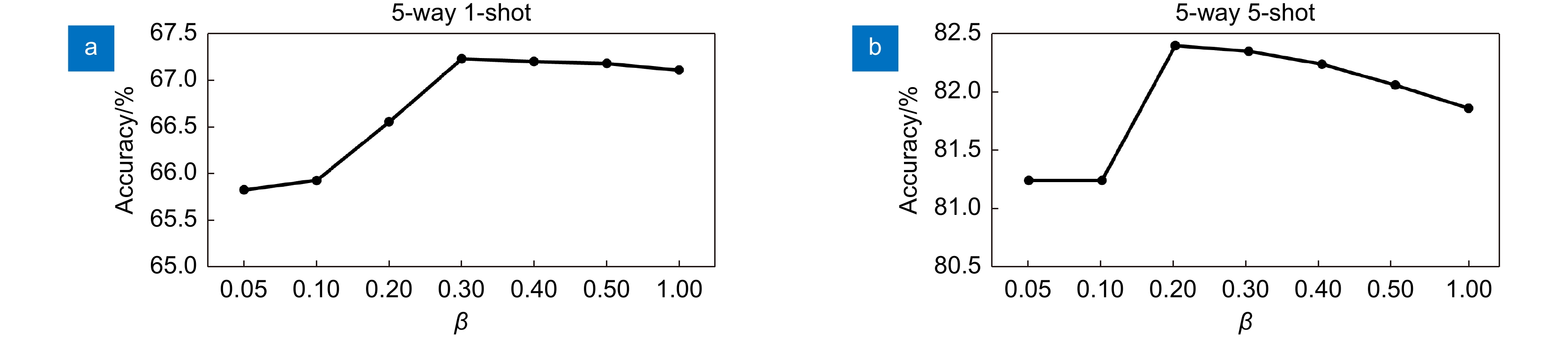
-
摘要:
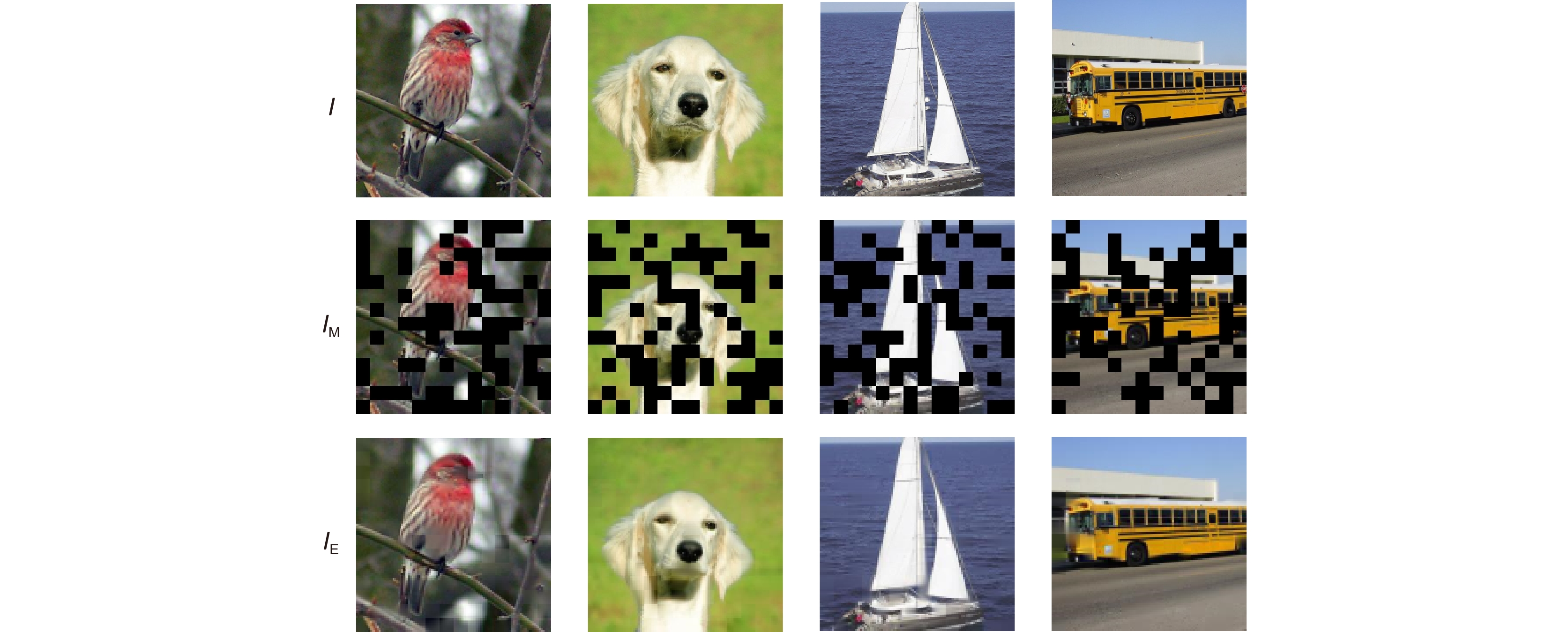
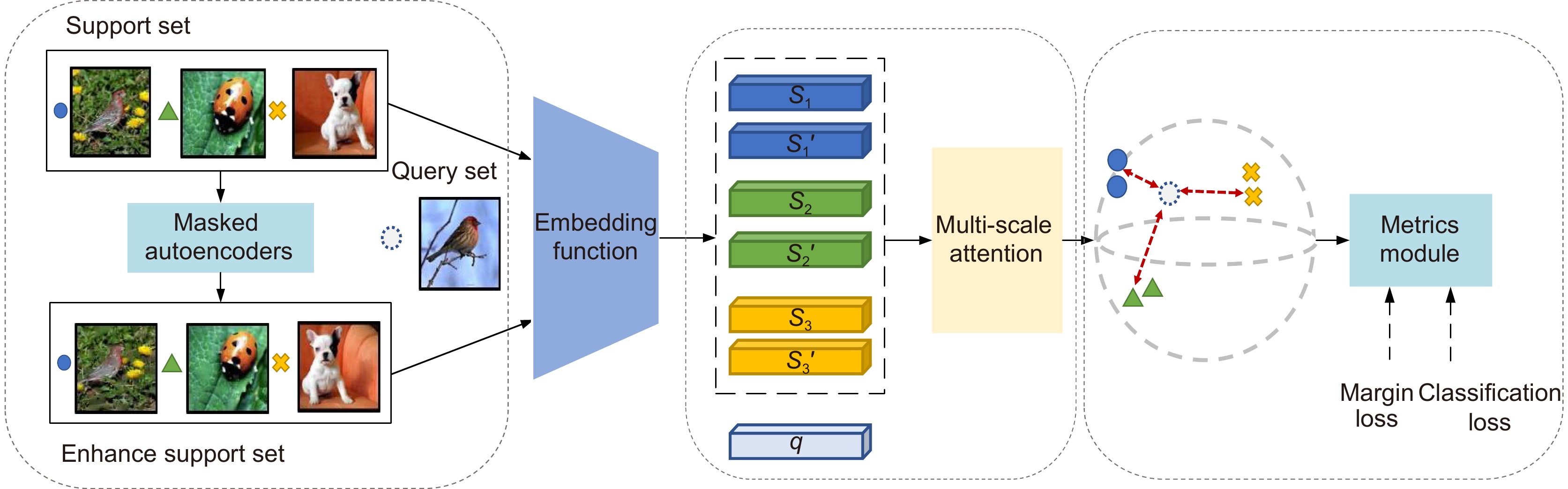
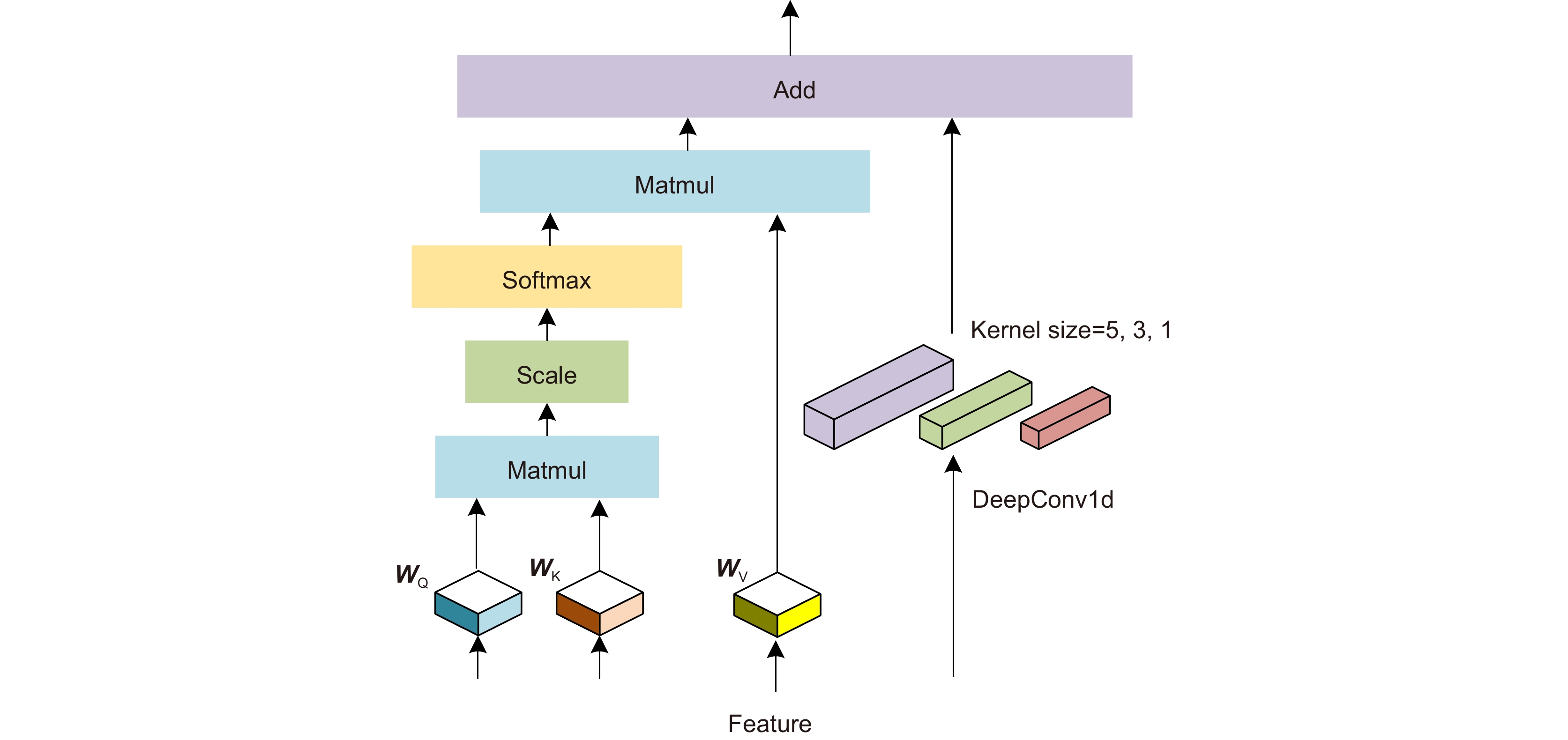
小样本图像识别是计算机视觉中的关键问题。针对小样本情况下度量学习方法的类别原型不准确、泛化能力差问题,本文采用以下措施来提高小样本图像识别准确率:第一、为减缓样本稀缺问题,利用掩膜自编码器进行图像扩充,提高样本复杂度。第二、设计多尺度注意力模块,突出类别相关特征,解决类别原型偏差大的问题。第三、提出领域自适应模块,引入间隔损失函数,优化嵌入函数的表征能力,实现新类样本的精确表征,增强模型的泛化能力。通过在多个公开数据集上进行实验表明,本文方法可以有效提升小样本图像识别准确率。
Abstract:Learning with limited data is a challenging field for computer visual recognition. Prototypes calculated by the metric learning method are inaccurate when samples are limited. In addition, the generalization ability of the model is poor. To improve the performance of few-shot image classification, the following measures are adopted. Firstly, to tackle the problem of limited samples, the masked autoencoder is used to enhance data. Secondly, prototypes are calculated by task-specific features, which are obtained by the multi-scale attention mechanism. The attention mechanism makes prototypes more accurate. Thirdly, the domain adaptation module is added with a margin loss function. The margin loss pushes different prototypes away from each other in the feature space. Sufficient margin space improves the generalization performance of the method. The experimental results show the proposed method achieves better performance on few-shot classification.
-

-
表 1 骨架网络的模型结构
Table 1. Structure of the backbone
模型结构 输出尺寸 ResNet-12 Conv4 卷积层1 42$ \times $42 [3×3,64] × 3 [3×3,64] 卷积层2 21$ \times $21 [3×3,160] × 3 [3×3,64] 卷积层3 10$ \times $10 [3×3,320] × 3 [3×3,64] 卷积层4 5$ \times $5 [3×3,640] × 3 [3×3,64] 池化层 1$ \times $1 5×5 Pool 5×5 Pool 参数量 50 MB 0.46 MB 表 2 MiniImageNet数据集置信度95%小样本分类准确率 (episodes为10000)
Table 2. Few-shot classification accuracies with 95 confidence interval on the miniImageNet dataset (the number of episodes is 10000)
模型 骨架网络 5-way 1-shot 5-way 5-shot Matching Net [12] Conv4 43.56±0.84 55.31±0.37 Proto Net [13] Conv4 49.42±0.78 68.20±0.66 Relation Net [21] Conv4 50.44±0.82 65.32±0.70 MAML [9] Conv4 48.70±1.84 63.11±0.92 DN4 [14] Conv4 51.24±0.74 71.02±0.64 DSN [23] Conv4 51.78±0.96 68.99±0.69 BOIL [25] Conv4 49.61±0.16 66.45±0.37 MADA(ours) Conv4 55.27±0.20 72.12±0.16 Matching Net [12] ResNet-12 65.64±0.20 78.73±0.15 Proto Net [13] ResNet-12 60.37±0.83 78.02±0.75 DN4 [14] ResNet-12 54.37±0.36 74.44±0.29 DSN [23] ResNet-12 62.64±0.66 78.73±0.45 SNAIL [22] ResNet-12 55.71±0.99 68.88±0.92 CTM [24] ResNet-12 64.12±0.82 80.51±0.14 MADA(ours) ResNet-12 67.45±0.20 82.77±0.13 表 3 TieredImageNet数据集置信度95%小样本分类准确率 (episodes为10000)
Table 3. Few-shot classification accuracies with 95 confidence interval on the tieredImageNet dataset (the number of episodes is 10000)
模型 骨架网络 5-way 1-shot 5-way 5-shot Matching Net [12] ResNet-12 68.50±0.92 80.60±0.71 Proto Net [13] ResNet-12 65.65±0.92 83.40±0.65 MetaOpt Net [26] ResNet-12 65.99±0.72 81.56±0.53 TPN [27] ResNet-12 59.91±0.94 73.30±0.75 CTM [24] ResNet-12 68.41±0.39 84.28±1.74 LEO [10] ResNet-12 66.63±0.05 81.44±0.09 MADA(ours) ResNet-12 70.67±0.22 85.10±0.15 表 4 CUB数据集置信度95%小样本分类准确率 (episodes为10000)
Table 4. Few-shot classification accuracies with 95 confidence interval on the CUB dataset (the number of episodes is 10000)
表 5 在miniImageNet数据集上置信度95%小样本分类的消融实验 (episodes为10000)
Table 5. Ablation study of few-shot classification accuracies with 95 confidence interval on the miniImageNet (the number of episodes is 10000)
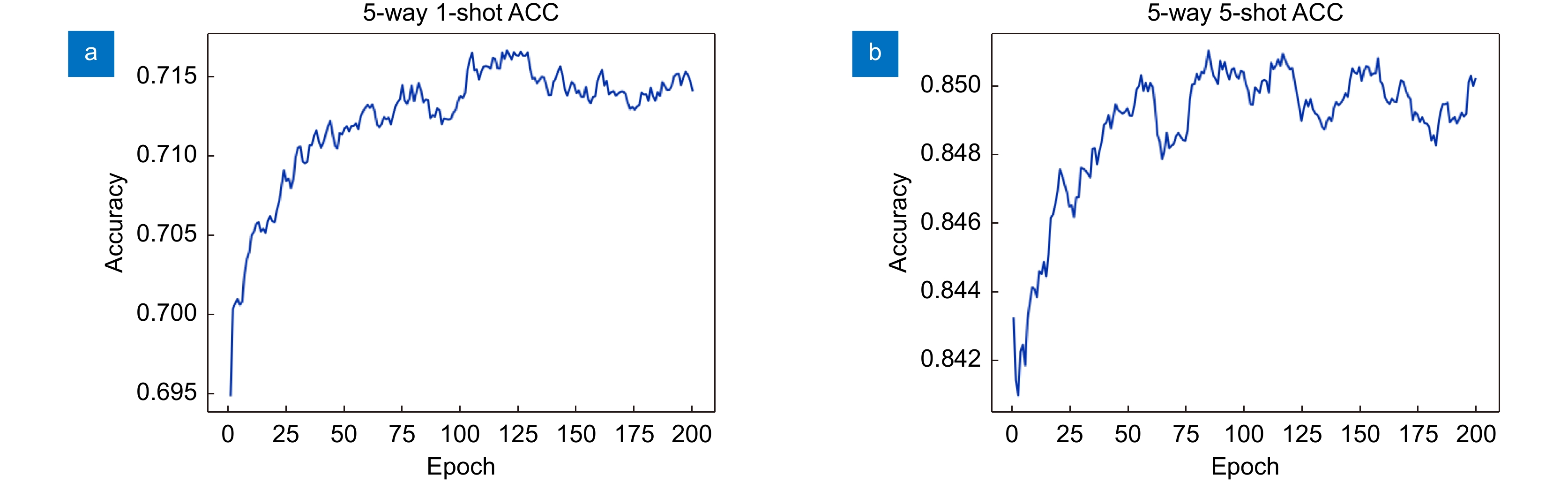
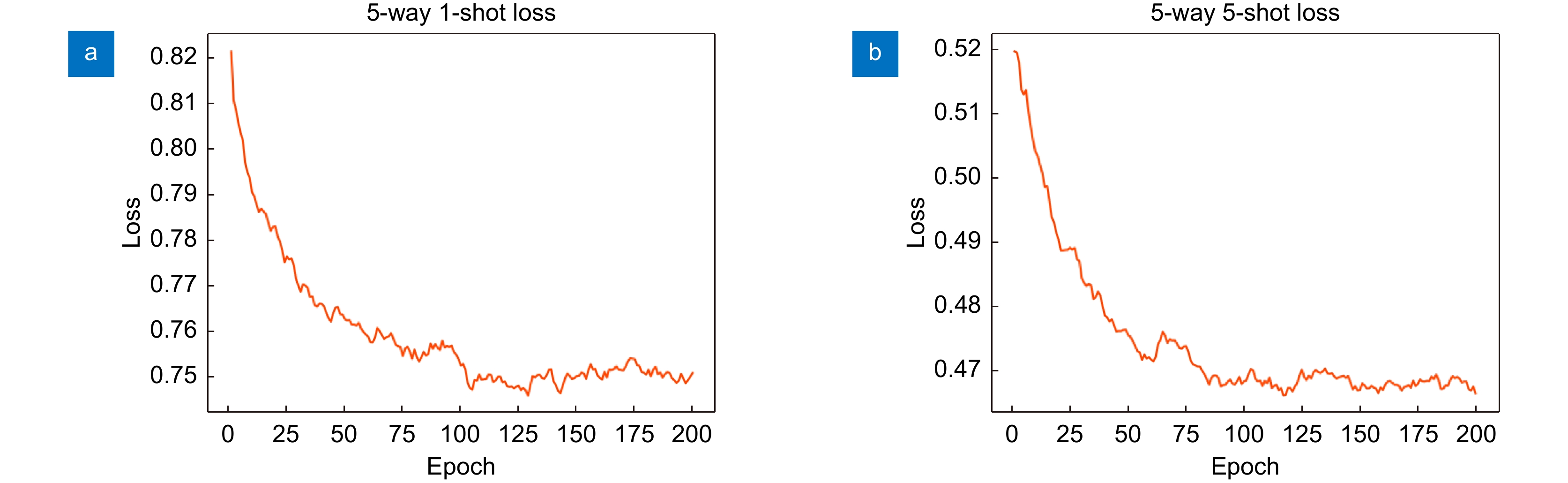
网络 MA DA DE 5-way 1-shot 5-way 5-shot Baseline × × × 60.37±0.83 78.02±0.75 MA √ × × 65.84±0.23 81.94±0.34 MADA √ √ × 67.21±0.18 82.41±0.48 MADA+ √ √ √ 67.45±0.20 82.77±0.13 -
[1] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 770–778. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90.
[2] Devlin J, Chang M W, Lee K, et al. BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C]//Proceedings of 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, 2019: 4171–4186. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/N19-1423.
[3] 赵春梅, 陈忠碧, 张建林. 基于深度学习的飞机目标跟踪应用研究[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(9): 180261. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180261
Zhao C M, Chen Z B, Zhang J L. Application of aircraft target tracking based on deep learning[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(9): 180261. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180261
[4] 石超, 陈恩庆, 齐林. 红外视频中的舰船检测[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(6): 170748. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170748
Shi C, Chen E Q, Qi L. Ship detection from infrared video[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2018, 45(6): 170748. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170748
[5] Tan J R, Wang C B, Li B Y, et al. Equalization loss for long-tailed object recognition[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 11659–11668. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01168.
[6] Li F F, Fergus R, Perona P. A Bayesian approach to unsupervised one-shot learning of object categories[C]//Proceedings of the Ninth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2003: 1134−1141. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2003.1238476.
[7] Mehrotra A, Dukkipati A. Generative adversarial residual pairwise networks for one shot learning[Z]. arXiv: 1703.08033, 2017. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1703.08033.
[8] Chen Z T, Fu Y W, Zhang Y D, et al. Multi-level semantic feature augmentation for one-shot learning[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2019, 28(9): 4594−4605. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2910052
[9] Finn C, Abbeel P, Levine S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks[C]//Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2017: 1126–1135. https://doi.org/10.5555/3305381.3305498.
[10] Rusu A A, Rao D, Sygnowski J, et al. Meta-learning with latent embedding optimization[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2019.
[11] Frikha A, Krompaß D, Köpken H G, et al. Few-shot one-class classification via meta-learning[J]. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell, 2021, 35(8): 7448−7456. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i8.16913
[12] Vinyals O, Blundell C, Lillicrap T, et al. Matching networks for one shot learning[C]//Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2016: 3637–3645. https://doi.org/10.5555/3157382.3157504.
[13] Snell J, Swersky K, Zemel R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017: 4077–4087.
[14] Li W B, Wang L, Huo J L, et al. Revisiting local descriptor based image-to-class measure for few-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 7253−7260. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00743.
[15] Luo X, Wei L H, Wen L J, et al. Rectifying the shortcut learning of background for few-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of the 35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021.
[16] Chen Y H, Li W, Sakaridis C, et al. Domain adaptive faster R-CNN for object detection in the wild[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 3339−3348. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00352.
[17] Gong R, Li W, Chen Y H, et al. DLOW: domain flow for adaptation and generalization[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 2472–2481. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00258.
[18] He K M, Chen X L, Xie S N, et al. Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners[C]//Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022: 15979–15988. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01553.
[19] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017: 6000–6010. https://doi.org/10.5555/3295222.3295349.
[20] Ren M Y, Triantafillou E, Ravi S, et al. Meta-learning for semi-supervised few-shot classification[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2018.
[21] Sung F, Yang Y X, Zhang L, et al. Learning to compare: relation network for few-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 1199–1208. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00131.
[22] Mishra N, Rohaninejad M, Chen X, et al. A simple neural attentive meta-learner[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2018.
[23] Simon C, Koniusz P, Nock R, et al. Adaptive subspaces for few-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 4135–4144. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00419.
[24] Li H Y, Eigen D, Dodge S, et al. Finding task-relevant features for few-shot learning by category traversal[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00009.
[25] Oh J, Yoo H, Kim C H, et al. BOIL: towards representation change for few-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021.
[26] Lee K, Maji S, Ravichandran A, et al. Meta-learning with differentiable convex optimization[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 10649–10657. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.01091.
[27] Liu Y B, Lee J, Park M, et al. Learning to propagate labels: Transductive propagation network for few-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2019.
[28] Chen W Y, Liu Y C, Kira Z, et al. A closer look at few-shot classification[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2019.
[29] 陈旭, 彭冬亮, 谷雨. 基于改进YOLOv5s的无人机图像实时目标检测[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(3): 210372. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210372
Chen X, Peng D L, Gu Y. Real-time object detection for UAV images based on improved YOLOv5s[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2022, 49(3): 210372. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210372
[30] 李珣, 李林鹏, Lazovik A, 等. 基于改进双流卷积递归神经网络的RGB-D物体识别方法[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(2): 200069. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.200069
Li X, Li L P, Lazovik A, et al. RGB-D object recognition algorithm based on improved double stream convolution recursive neural network[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2021, 48(2): 200069. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.200069
[31] 曹志, 尚丽丹, 尹东. 一种车辆识别代号检测和识别的弱监督学习方法[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(2): 200270. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.200270
Cao Z, Shang L D, Yin D. A weakly supervised learning method for vehicle identification code detection and recognition[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2021, 48(2): 200270. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.200270
[32] van der Maaten L, Hinton G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J]. J Mach Learn Res, 2008, 9(86): 2579−2605.
[33] 唐彪, 金炜, 李纲, 等. 结合稀疏表示和子空间投影的云图检索[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(10): 180627. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180627
Tang B, Jin W, Li G, et al. The cloud retrieval of combining sparse representation with subspace projection[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(10): 180627. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180627
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
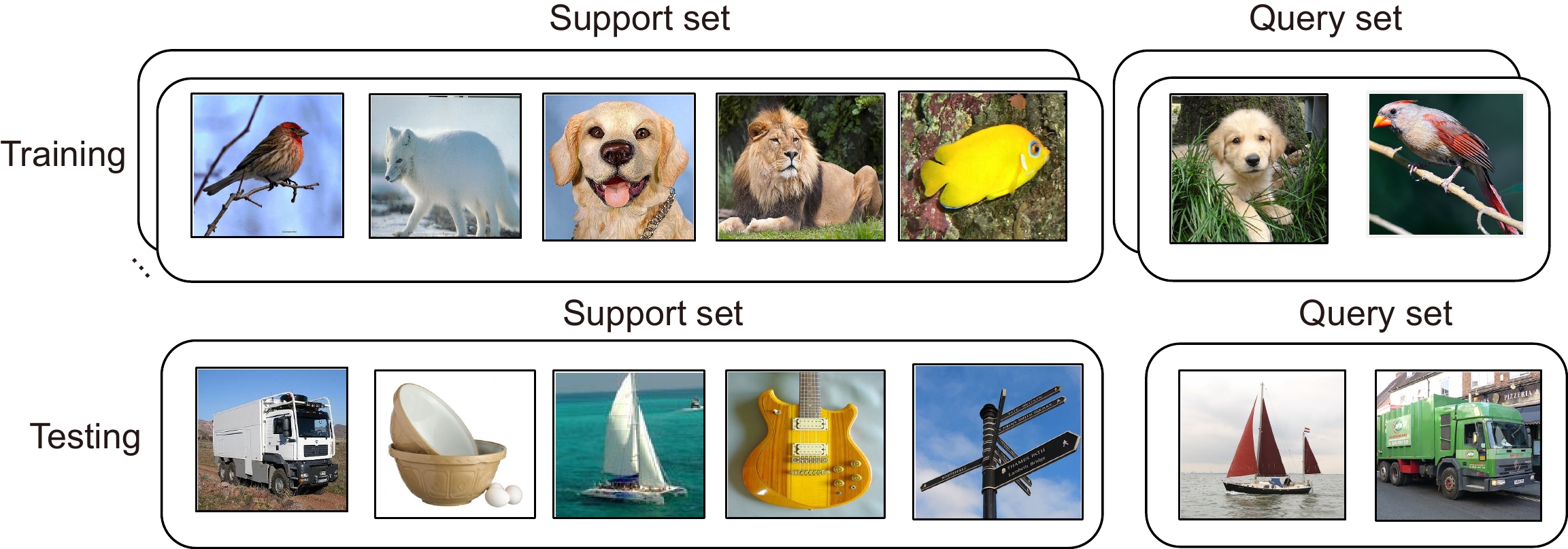
 下载:
下载: