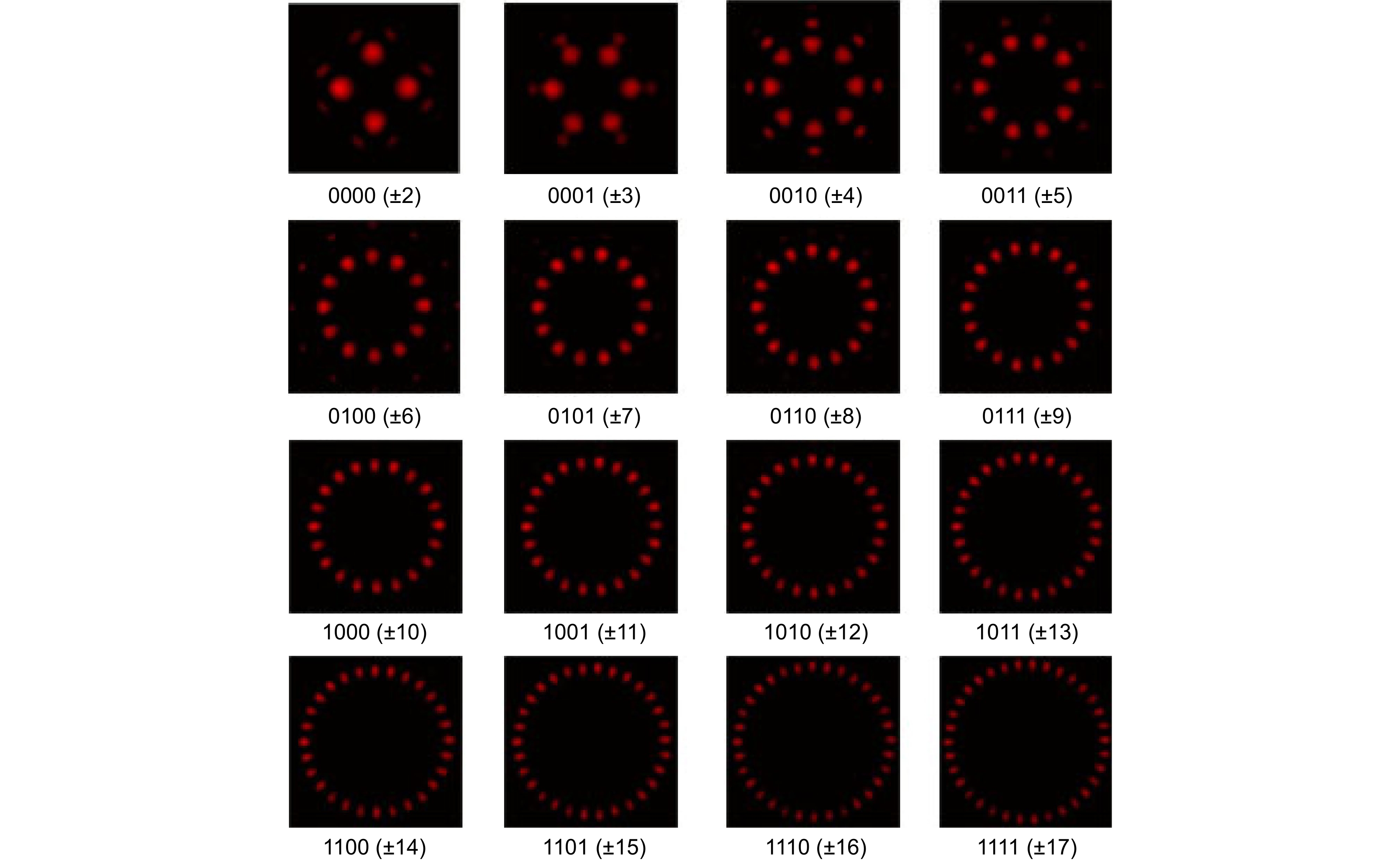
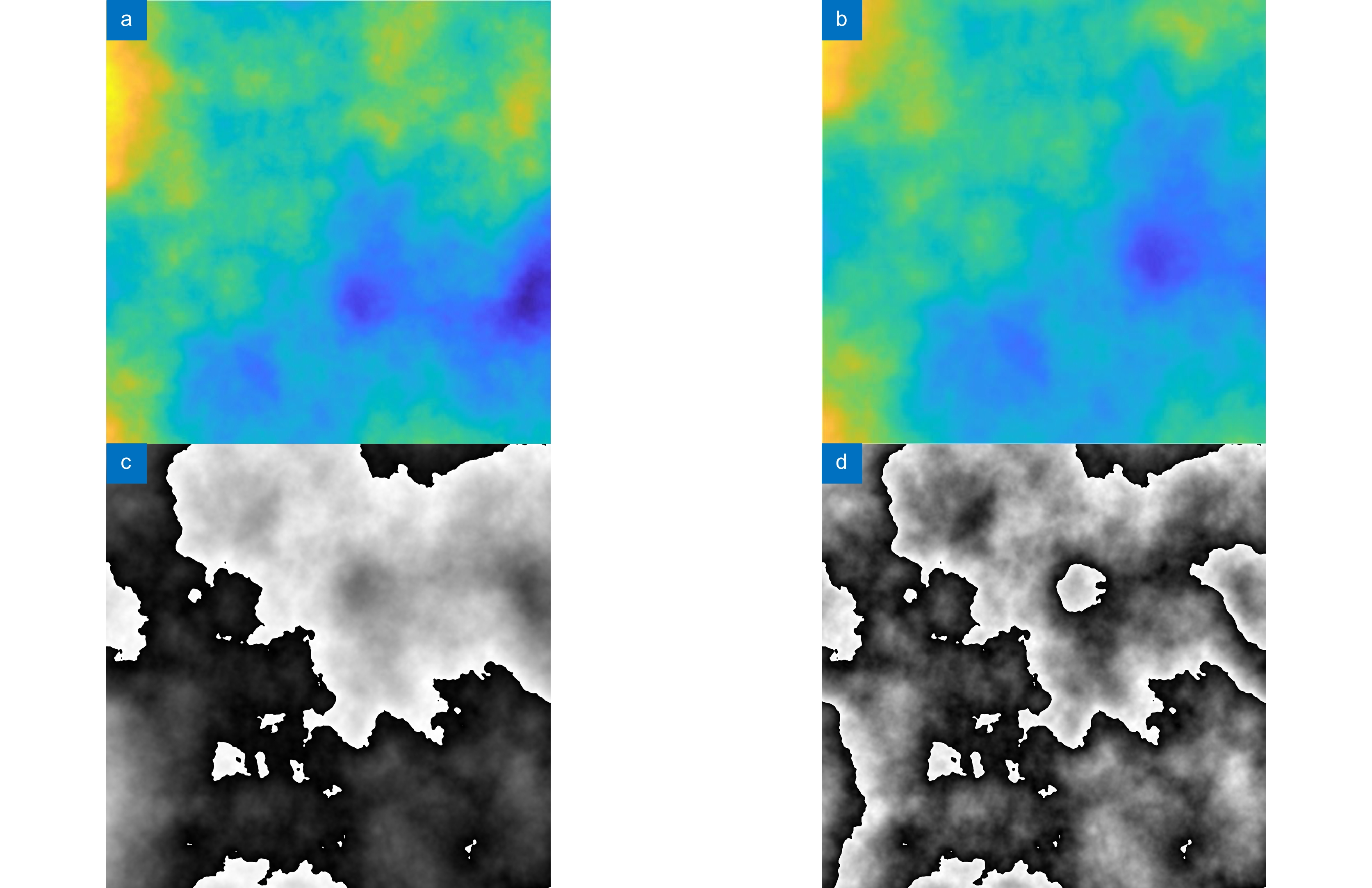
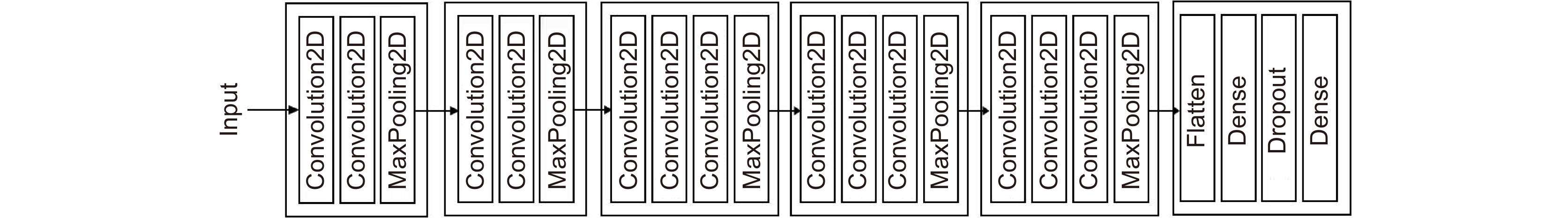
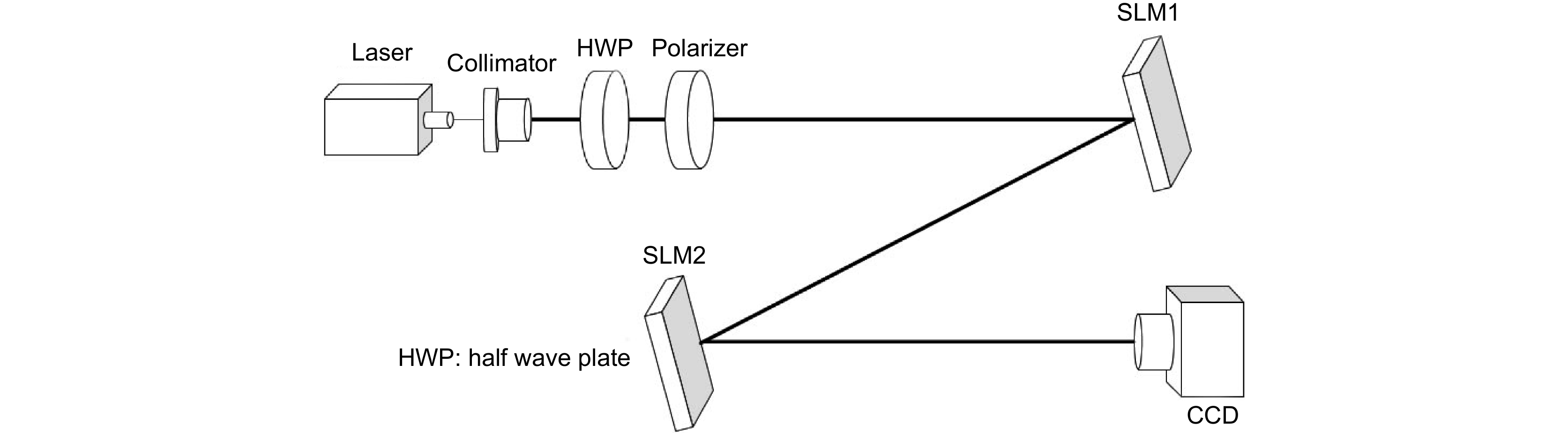
-
摘要:
为了加快基于深度学习的轨道角动量光束识别模型的训练速度,提出使用迁移学习的方式识别轨道角动量光束,并利用次谐波法生成大气湍流相位屏仿真大气湍流,以空间光调制器加载相位屏的方式搭建模拟湍流环境,基于迁移学习的轨道角动量光束识别系统在弱湍流和中湍流环境下均获得了90%以上的识别率。并与传统深度学习方式在模型训练速度、识别率等方面进行性能对比,证明了在弱、中湍流环境中,基于迁移学习的轨道角动量光束识别方法在保持较高识别率的前提下可以减少训练时间。
Abstract:This paper proposes a transfer learning method to recognize the orbital angular momentum beam to speed up the training speed of the orbital angular momentum beam recognition model based on deep learning. In order to simulate the atmospheric turbulence, we generate the atmospheric turbulence phase screen by the sub-harmonic method and build the simulated turbulence environment by loading the phase screen on the spatial light modulator. The orbital angular momentum beam recognition system based on transfer learning has achieved a recognition rate of more than 90% in both weak and medium turbulent environments. Compared with the traditional deep learning method in the aspects of model training speed and recognition rate, it is proved that the orbital angular momentum beam recognition method based on transfer learning can reduce the training time while maintaining a high recognition rate in the weak and medium turbulent environment.
-
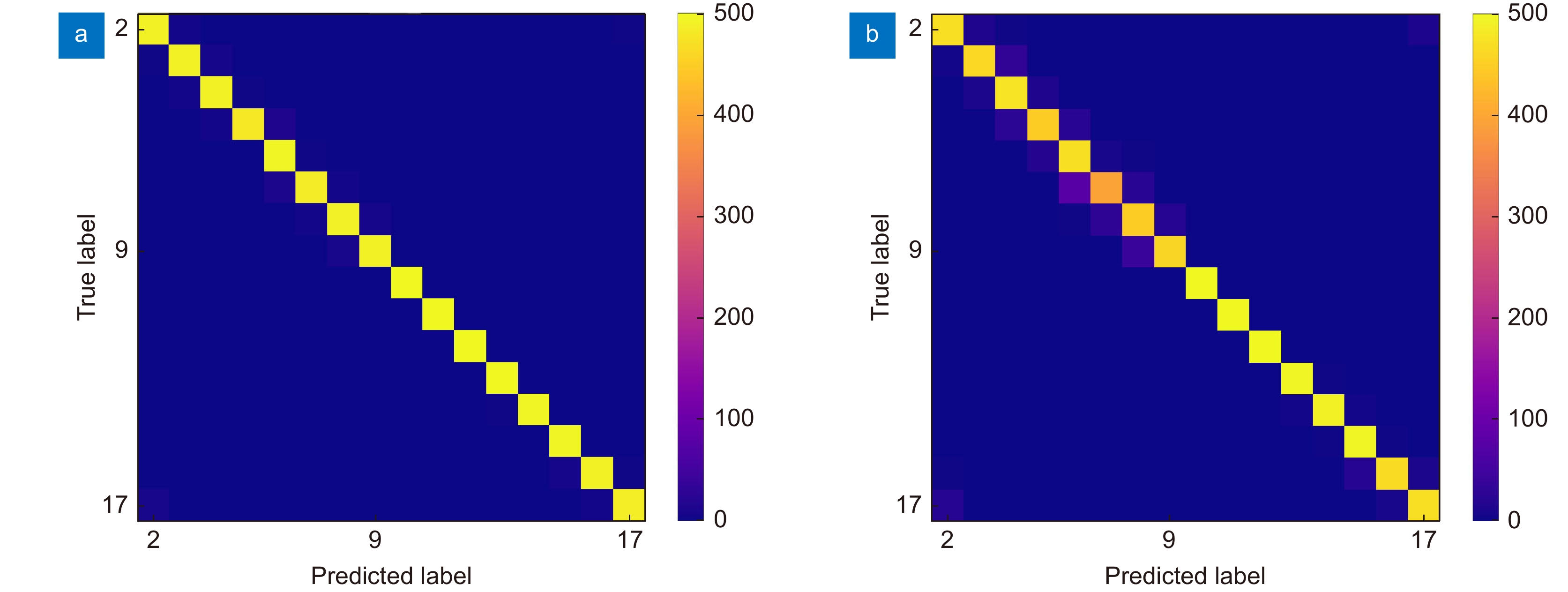
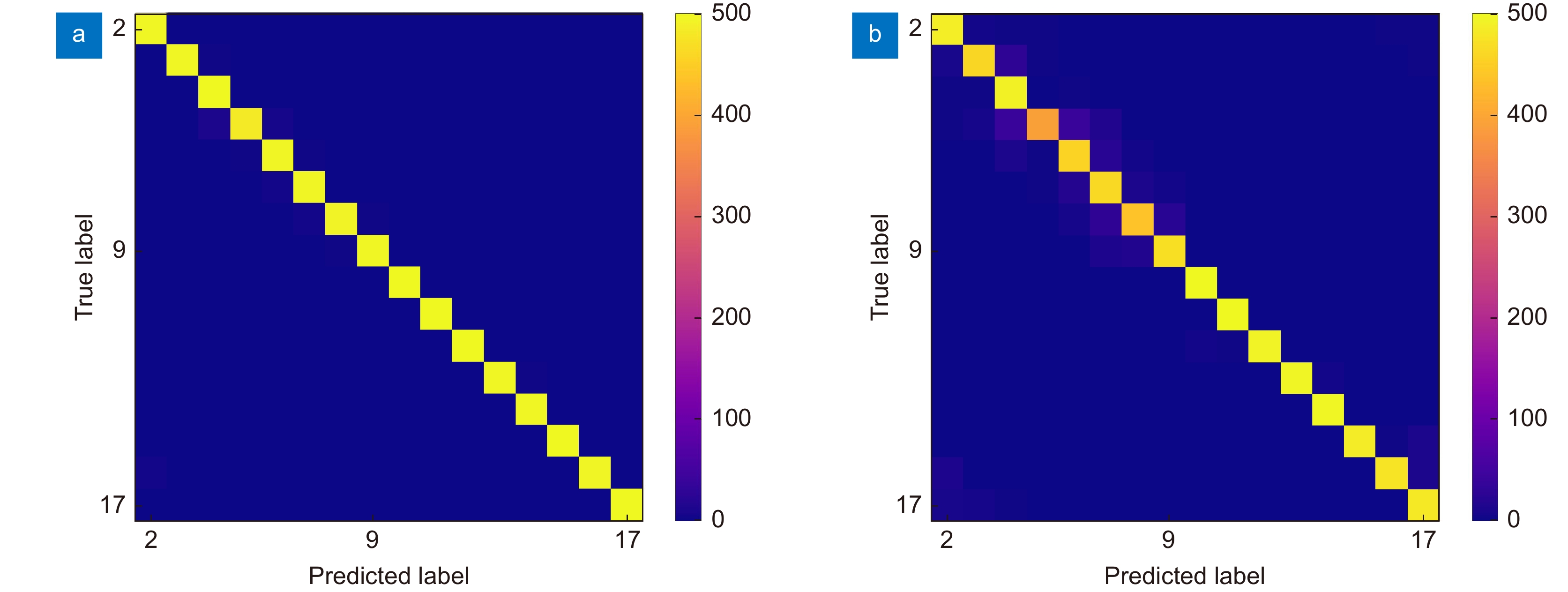
Overview: With the development of the computer and the artificial intelligence technology, the orbital angular momentum shift keying system decoding method based on the machine learning has emerged. The orbital angular momentum demodulation scheme using machine learning has advantages of the simple structure, wide recognition range and high recognition accuracy. The development of deep learning has further improved the recognition accuracy of orbital angular momentum. And the development of deep learning has further improved the recognition accuracy of orbital angular momentum. In order to speed up the training speed of the orbital angular momentum beam recognition model based on deep learning, this paper proposes to use the transfer learning method to identify the orbital angular momentum beam, and build the transfer learning recognition model based on the VGG16 architecture. To simulate the transmission of orbital angular momentum beams in a turbulent environment, this paper use the sub-harmonic method to generate an atmospheric turbulence phase screen and build a simulated turbulent environment by loading the phase screen with the spatial light modulator. The orbital angular momentum recognition task was carried out in a weakly turbulent environment with D/r0=1.5 and a medium turbulent environment with D/r0=4. And high recognition rates of 98.62% and 94.37% were obtained in weak turbulence environment with D/r0=1.5 and a medium turbulence environment with D/r0=4, respectively. The feasibility of an orbital angular momentum recognition system based on the transfer learning is proved. At the same time, in terms of the model training speed and recognition rate, this paper compares the performance of the transfer learning model and the original VGG16 model, and visualizes the recognition results of each beam by using the confusion matrix. The VGG16 model obtains the recognition rates of 99.39% and 94.81% in the weak turbulence environment with D/r0=1.5 and the medium turbulence environment with D/r0=4, respectively. The recognition rate is reduced by less than 1%, but the model training speed is improved by 2.3 times. This paper proves the feasibility of the orbital angular momentum recognition system based on transfer learning. At the same time, it is proved that the orbital angular momentum recognition system based on transfer learning model can greatly reduce the time required for model training under the condition of maintaining high recognition rate. This paper provides an idea for the rapid construction of orbital angular momentum shift keying system which based on convolutional neural network in the future.
-

-
表 1 模型评价指标
Table 1. Model evaluation indicators
Indicators Transfer learning model VGG16 model Highest validation accuracy/% 96.56 98.25 Total parameters 6426896 134301520 Total training time/s 13887 32022 Average epoch training time/s 694.35 1601.1 -
[1] Allen L, Beijersbergen M W, Spreeuw R J C, et al. Orbital angular momentum of light and the transformation of Laguerre-Gaussian laser modes[J]. Phys Rev A, 1992, 45(11): 8185−8189. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.45.8185
[2] Wang J, Yang J Y, Fazal I M, et al. Terabit free-space data transmission employing orbital angular momentum multiplexing[J]. Nat Photonics, 2012, 6(7): 488−496. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.138
[3] Fu S Y, Zhai Y W, Zhou H, et al. Experimental demonstration of free-space multi-state orbital angular momentum shift keying[J]. Opt Express, 2019, 27(23): 33111−33119. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.033111
[4] Fu S Y, Zhai Y W, Zhou H, et al. Demonstration of free-space one-to-many multicasting link from orbital angular momentum encoding[J]. Opt Lett, 2019, 44(19): 4753−4756. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.004753
[5] Fu S Y, Zhai Y W, Zhou H, et al. Demonstration of high-dimensional free-space data coding/decoding through multi-ring optical vortices[J]. Chin Opt Lett, 2019, 17(8): 080602. doi: 10.3788/COL201917.080602
[6] Krenn M, Fickler R, Fink M, et al. Communication with spatially modulated light through turbulent air across Vienna[J]. New J Phys, 2014, 16(11): 113028. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/16/11/113028
[7] Doster T, Watnik A T. Machine learning approach to OAM beam demultiplexing via convolutional neural networks[J]. Appl Opt, 2017, 56(12): 3386−3396. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.003386
[8] Li J, Zhang M, Wang D S. Adaptive demodulator using machine learning for orbital angular momentum shift keying[J]. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2017, 29(17): 1455−1458. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2726139
[9] Li J, Zhang M, Wang D S, et al. Joint atmospheric turbulence detection and adaptive demodulation technique using the CNN for the OAM-FSO communication[J]. Opt Express, 2018, 26(8): 10494−10508. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.010494
[10] Park S R, Cattell L, Nichols J M, et al. De-multiplexing vortex modes in optical communications using transport-based pattern recognition[J]. Opt Express, 2018, 26(4): 4004−4022. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.004004
[11] Cui X Z, Yin X L, Chang H, et al. Analysis of an adaptive orbital angular momentum shift keying decoder based on machine learning under oceanic turbulence channels[J]. Opt Commun, 2018, 429: 138−143. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.08.011
[12] Zhao Q S, Hao S Q, Wang Y, et al. Mode detection of misaligned orbital angular momentum beams based on convolutional neural network[J]. Appl Opt, 2018, 57(35): 10152−10158. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.010152
[13] Tian Q H, Li Z, Hu K, et al. Turbo-coded 16-ary OAM shift keying FSO communication system combining the CNN-based adaptive demodulator[J]. Opt Express, 2018, 26(21): 27849−27864. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.027849
[14] Wang Z K, Dedo M I, Guo K, et al. Efficient recognition of the propagated orbital angular momentum modes in turbulences with the convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Photonics J, 2019, 11(3): 7903614.
[15] Li S H, Chen S, Gao C Q, et al. Atmospheric turbulence compensation in orbital angular momentum communications: advances and perspectives[J]. Opt Commun, 2018, 408: 68−81. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2017.09.034
[16] Li J, Chen X, McDuffie S, et al. Mitigation of atmospheric turbulence with random light carrying OAM[J]. Opt Commun, 2019, 446: 178−185. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.04.026
[17] Jiang S Q, Chi H, Yu X B, et al. Coherently demodulated orbital angular momentum shift keying system using a CNN-based image identifier as demodulator[J]. Opt Commun, 2019, 435: 367−373. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.11.054
[18] Chi H, Jiang S Q, Ou J, et al. Comprehensive study of orbital angular momentum shift keying systems with a CNN-based image identifier[J]. Opt Commun, 2020, 454: 124518. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.124518
[19] 郭忠义, 龚超凡, 刘洪郡, 等. OAM光通信技术研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(3): 190593.
Guo Z Y, Gong C F, Liu H J, et al. Research advances of orbital angular momentum based optical communication technology[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(3): 190593.
[20] 张利宏, 沈锋, 兰斌. 涡旋光束轨道角动量在大气湍流传输下的特性分析[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(4): 190272.
Zhang L H, Shen F, Lan B. Characteristic analysis of orbital angular momentum of vortex beam propagating in atmospheric turbulent[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(4): 190272.
[21] 贺锋涛, 房伟, 张建磊, 等. 汉克-贝塞尔光束在各向异性海洋湍流中轨道角动量传输特性分析[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(6): 190591.
He F T, Fang W, Zhang J L, et al. Analysis of the transmission characteristics of Hank-Bessel beam in anisotropic ocean turbulence[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(6): 190591.
[22] 林鹏, 王天枢, 马万卓, 等. 2.07μm光纤激光在弱湍流条件下的传输特性研究[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(3): 190588.
Lin P, Wang T S, Ma W Z, et al. Propagation characteristics of 2.07 μm fiber laser in weak turbulence condition[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(3): 190588.
[23] Lane R G, Glindemann A, Dainty J C. Simulation of a Kolmogorov phase screen[J]. Waves Random Media, 1992, 2(3): 209−224. doi: 10.1088/0959-7174/2/3/003
[24] Pan S J, Yang Q. A survey on transfer learning[J]. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng, 2010, 22(10): 1345−1359. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2009.191
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: