-
摘要:
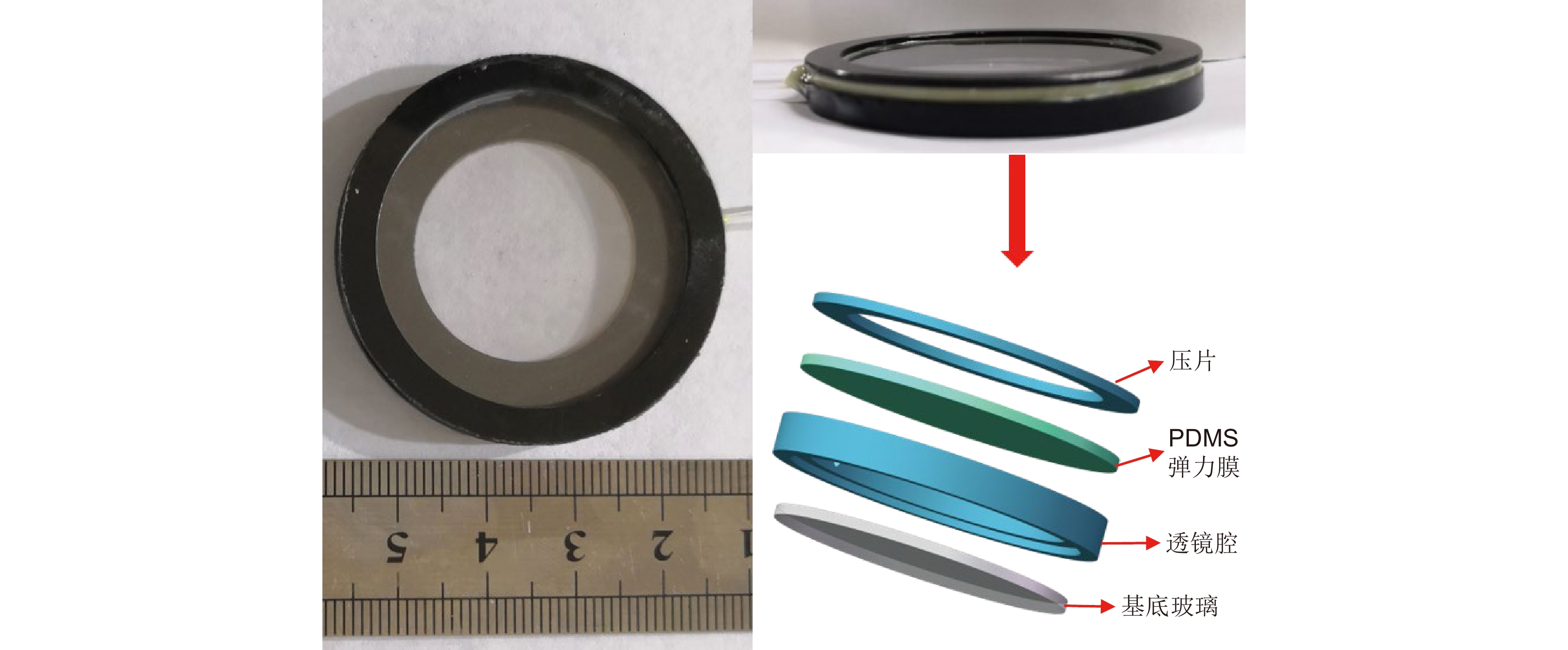
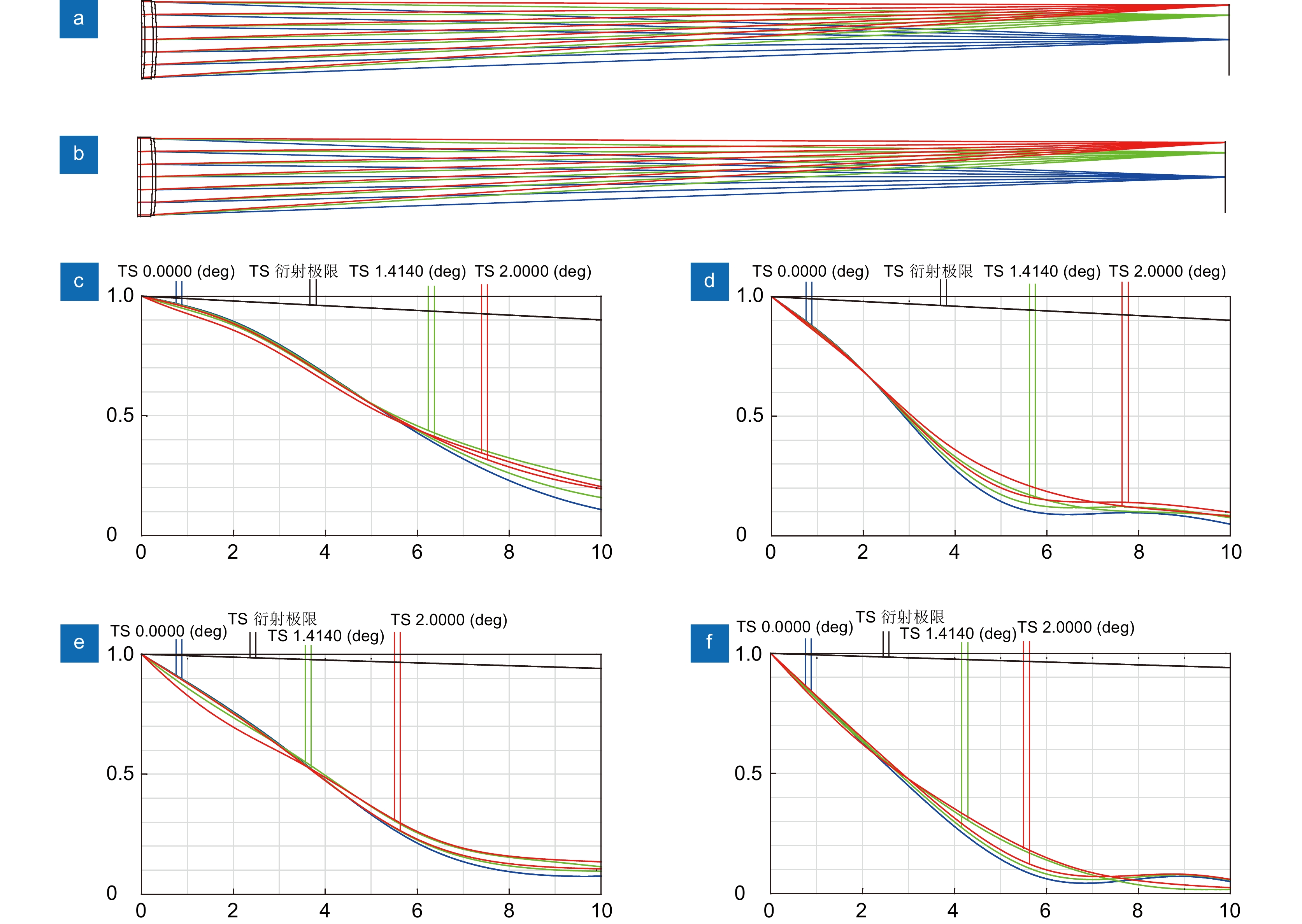
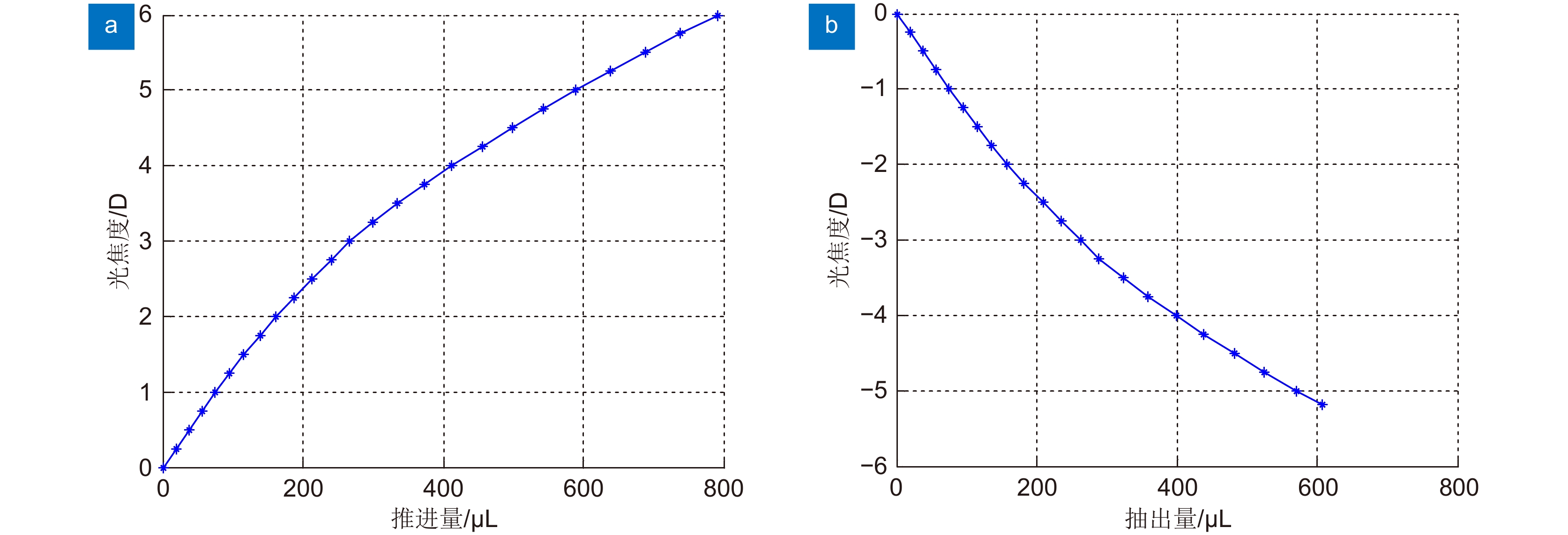
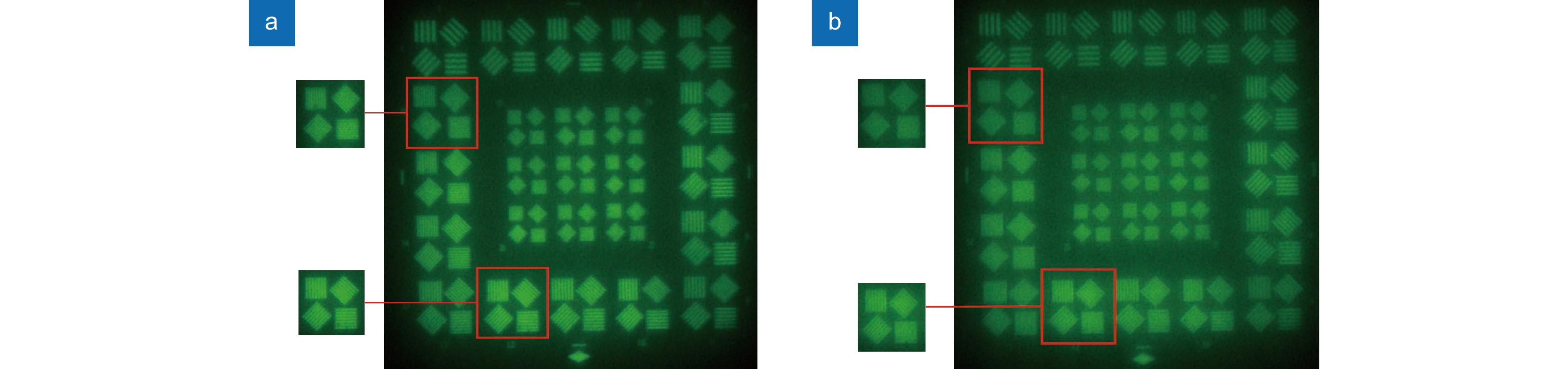
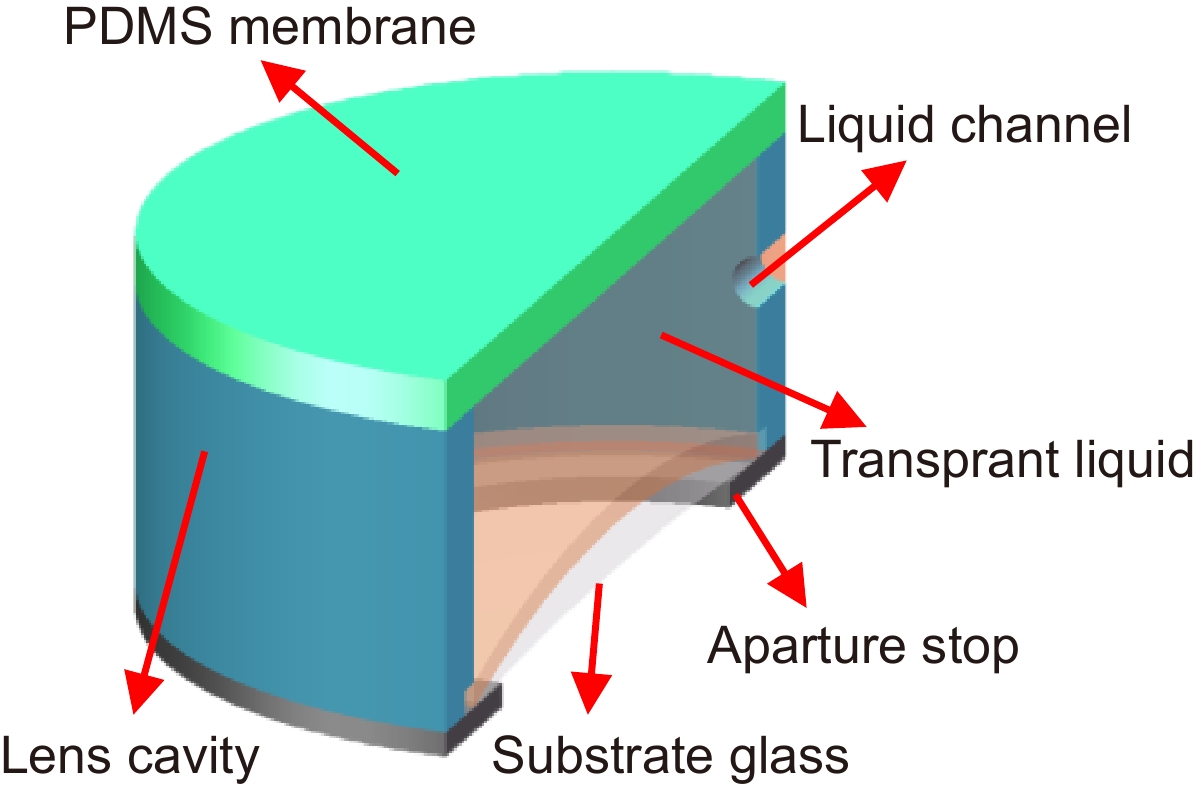
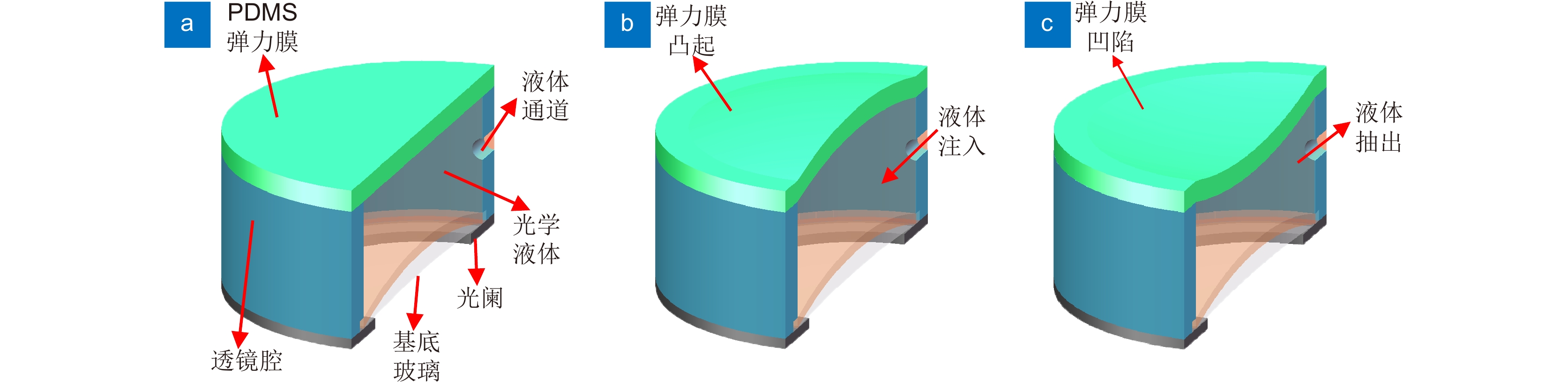
聚二甲基硅氧烷(Polydimethylsiloxane,PDMS)液体透镜具有大口径、高光焦度的优点,然而存在比较严重的像差。本文提出了一种可补偿像差的PDMS液体透镜,由PDMS膜、液体材料和补偿基底组成。根据建立的抛物面面形的PDMS液体透镜的光学模型,采用具有高折射率的液体材料(1-乙基-3-甲基咪唑三氟甲磺酸)和特殊设计的基底进行整体像差校正和提高光焦度的设计。我们对提出的透镜进行了加工制作和实验验证,其有效光学口径为25 mm,光焦度范围为−5 D ~ +6 D,在可见光波段透过率超过90%。对比传统的PDMS液体透镜,本文提出的液体透镜可以改善成像质量,在+5 D光焦度时分辨率可达到15 lp/mm,在大口径的光学成像系统,比如望远镜、AR、VR等,具有潜在的应用前景。
Abstract:Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) liquid lens has the advantages of large aperture and high power, but its aberration is serious. In this paper, a PDMS membrane liquid lens for correcting aberrations is proposed. The proposed lens is composed of a PDMS membrane, liquid material, and compensation substrate. Based on the paraboloid membrane model, an optical model of the liquid lens is established. The high refractive index liquid (1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate) and a compensatory substrate are used for correcting the aberration and improving the optical power. The proposed liquid lens is fabricated and the experimental results show that the effective optical aperture is 25 mm, the power range is -5 D ~ +6 D, and the transmittance in the visible band is more than 90%. Compared with the traditional lenses, the proposed liquid lens can improve the image quality, and the resolution is 15 lp/mm at +5D power. The proposed liquid lens has potential applications in large aperture optical imaging systems, such as telescopes, AR, VR, etc.
-
Key words:
- liquid lens /
- polydimethylsiloxane /
- large aperture /
- lens
-
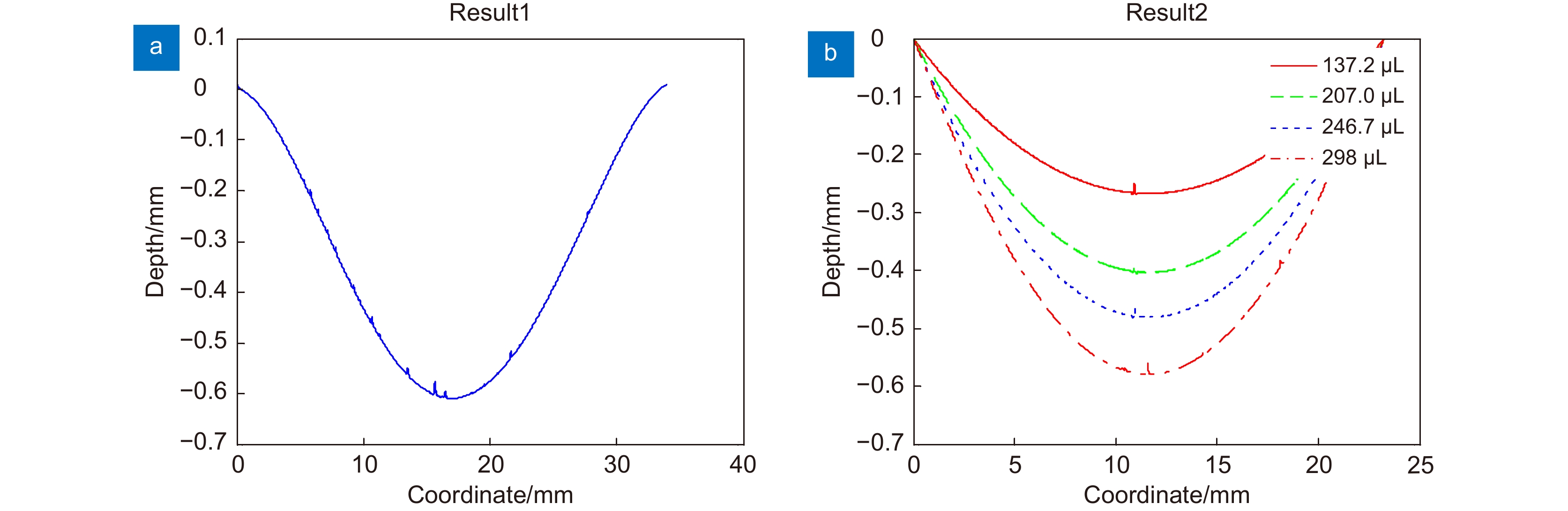
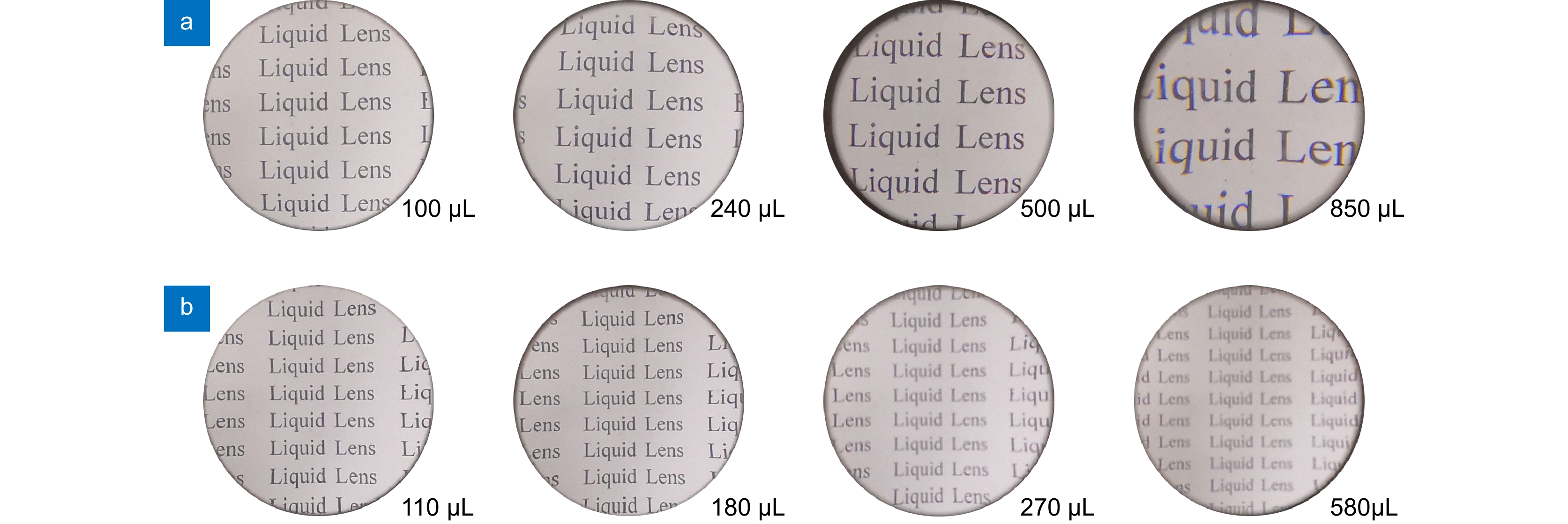
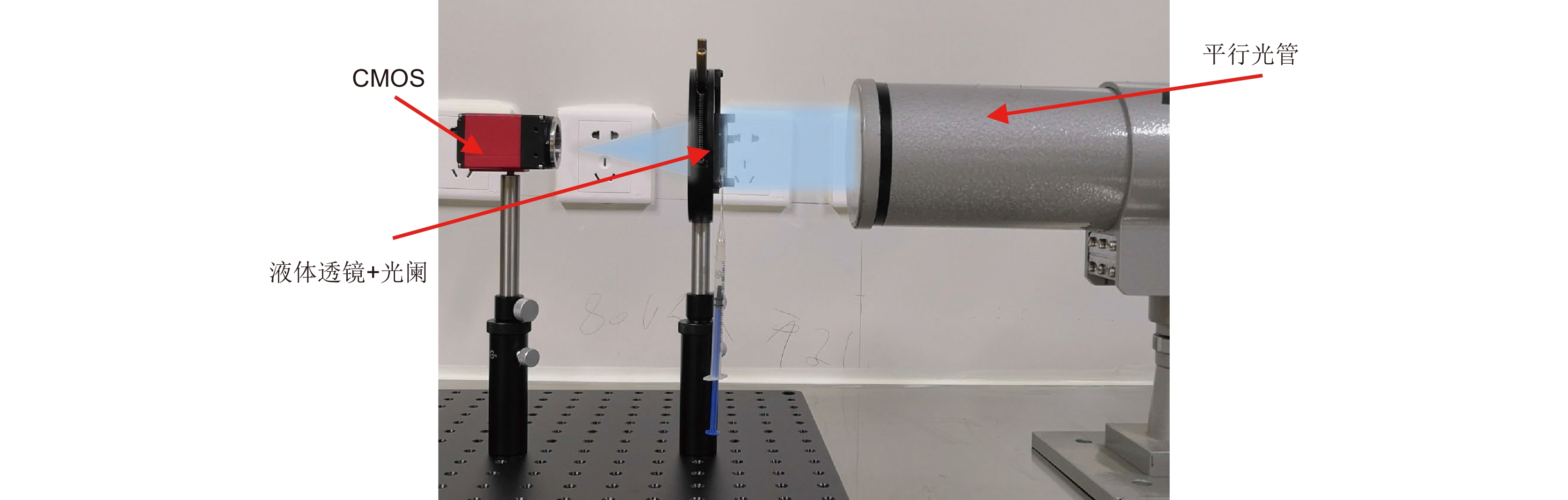
Overview: As an important device of adaptive optics, Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) liquid lens has the advantages of large aperture and high power. By changing the amount of liquid in the cavity, the lens focusing can be realized with the deformation of the membrane. This kind of lens has been studied for more than half a century. However, the development and application of PDMS liquid lens were restricted because of its aberration. PDMS is an excellent optical material, but as a hyper-elastomer, its deformation characteristics are complex. Moreover, the deformable membrane can be susceptible to gravity effects. As a result, the aberration of the PDMS liquid lens is serious. In this paper, a PDMS membrane liquid lens for correcting aberrations is proposed. The proposed liquid lens is composed of a PDMS membrane, liquid material, and compensation substrate. The aberrations caused by the compensatory substrate were opposite to the liquid part and the overall aberrations reduce. The work is divided into three steps. The first step is to measure and fit the surface profile of the PDMS membrane. Firstly, using a three-dimensional profilometer, the surface profile of the liquid lens at different power was scanned by the scanning probe stylus. Then curve fitting for depth data was performed to find the surface characteristics, and the results show that the PDMS membrane has a paraboloid profile during deformation. In the second step, an optical model of the liquid lens was established based on the paraboloid membrane model. Through optimization by Zemax software, the compensatory substrate parameters were determined. The high refractive index liquid (1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate) and a compensatory substrate are used for correcting the aberration and improving the optical power. In the third step, the proposed liquid lens is fabricated. Measurement with a focimeter for the relationship between optical power and liquid variation of the proposed liquid lens was conducted. The experimental results show that the effective optical aperture of the liquid lens is 25 mm and the power range is -5 D ~ +6 D. Finally, the optical performance was measured. Photos imaged through the proposed liquid lens were taken by a phone camera. An experimental system was designed for the resolution test, where the resolution target in a collimator was imaged through the liquid lens. What’s more, the transmittance of the liquid in the visible band is more than 90%. Compared with the traditional lens, the proposed liquid lens can improve the image quality, and the resolution is 15 lp/mm at +5D power. The proposed liquid lens has potential applications in large aperture optical imaging systems, such as telescopes, glasses, AR, VR, etc.
-

-
表 1 液体透镜材料关键参数
Table 1. Key parameters of liquid lens materials
面 材料 折射率 阿贝数 厚度/mm 液体 1-乙基-3甲基咪唑三氟甲磺酸 1.434 40.6 边缘2.5 弹力膜 PDMS 1.411 40.0 1 基底玻璃 D-FK61 1.500 81.6 中心1 -
[1] Berge B, Peseux J. Variable focal lens controlled by an external voltage: an application of electrowetting[J]. Eur Phys J E, 2000, 3(2): 159−163. doi: 10.1007/s101890070029
[2] Li L, Xiao L, Wang J H, et al. Movable electrowetting optofluidic lens for optical axial scanning in microscopy[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2019, 2(2): 180025.
[3] 赵瑞, 彭超, 张凯, 等. 介电润湿液体透镜仿生复眼的设计与仿真[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(2): 49−56.
Zhao R, Peng C, Zhang K, et al. Design and simulation of bionic compound eye with electrowetting liquid lens[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2021, 48(2): 49−56.
[4] Knollman G C, Bellin J L S, Weaver J L. Variable‐focus liquid‐filled hydroacoustic lens[J]. J Acoust Soc Am, 1971, 49(1B): 253−261. doi: 10.1121/1.1912324
[5] Sugiura N, Morita S. Variable-focus liquid-filled optical lens[J]. Appl Opt, 1993, 32(22): 4181−186. doi: 10.1364/AO.32.004181
[6] Zhang D Y, Lien V, Berdichevsky Y, et al. Fluidic adaptive lens with high focal length tunability[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 82(19): 3171−3172. doi: 10.1063/1.1573337
[7] Zhang D Y, Justis N, Lo Y H. Fluidic adaptive lens of transformable lens type[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 84(21): 4194−4196. doi: 10.1063/1.1756679
[8] Ren H W, Wu S T. Variable-focus liquid lens by changing aperture[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86(21): 211107. doi: 10.1063/1.1935749
[9] Ren H W, Fox D, Anderson P A, et al. Tunable-focus liquid lens controlled using a servo motor[J]. Opt Express, 2006, 14(18): 8031−8036. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.008031
[10] Ren H W, Wu S T. Variable-focus liquid lens[J]. Opt Express, 2007, 15(10): 5931−5936. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.005931
[11] Xu S, Ren H W, Lin Y J, et al. Adaptive liquid lens actuated by photo-polymer[J]. Opt Express, 2009, 17(20): 17590−17595. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.017590
[12] Yu H B, Zhou G Y, Siong C F, et al. Lens with transformable-type and tunable-focal-length characteristics[J]. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron, 2009, 15(5): 1317−1322. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2009.2021566
[13] 陈帅. PDMS薄膜型可变焦液体透镜研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018.
Chen S. Study on the variable focus liquid lens using PDMS membrane[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018.
[14] Zhou H, Zhang X F, Xu Z J, et al. Universal membrane-based tunable liquid lens design for dynamically correcting spherical aberration over user-defined focal length range[J]. Opt Express, 2019, 27(26): 37667−37679. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.037667
[15] Huang X, Jin H, Lin S Y, et al. Adaptive electrofluid-actuated liquid lens[J]. Opt Lett, 2020, 45(2): 331−334. doi: 10.1364/OL.45.000331
[16] Duffy D C, McDonald J C, Schueller O J A, et al. Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane)[J]. Anal Chem, 1998, 70(23): 4974−4984. doi: 10.1021/ac980656z
[17] Schneider F, Draheim J, Kamberger R, et al. Process and material properties of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) for Optical MEMS[J]. Sens Actuators A Phys, 2009, 151(2): 95−99. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2009.01.026
[18] Ozkan E, Mondal A, Douglass M, et al. Bioinspired ultra-low fouling coatings on medical devices to prevent device-associated infections and thrombosis[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2022, 608: 1015−1024. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.09.183
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: