-
摘要
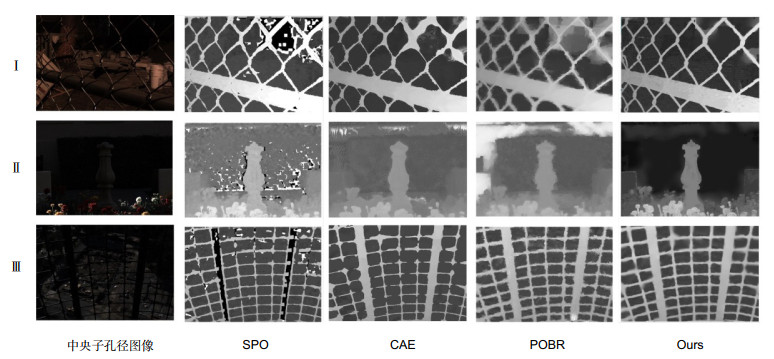
光场相机通过单次曝光同时从多个视角采样单个场景,在深度估计领域具有独特优势。噪声场景下的深度获取是光场图像深度估计的难点之一。传统针对噪声场景的深度获取方法大多仅适用于非遮挡情况,无法较好处理包含遮挡区域的噪声场景。针对含遮挡的噪声场景深度估计问题,提出了基于内联遮挡处理的深度估计方法。该方法采用内联遮挡处理框架,通过将遮挡处理集成进抗噪成本量中,在保证抗噪性能的同时提升算法的抗遮挡能力。在成本量建立完成后,为进一步滤除剩余噪声,采用提出的适应遮挡的多模板滤波策略对成本量进行遮挡感知优化,该策略通过为不同方向的遮挡分别设计滤波模板,在滤波的同时能较好保留图像的边缘结构,有效改善了传统滤波算法无法保留遮挡边界的问题。实验结果表明,相比其它先进深度估计算法,该方法在高噪场景下具有显著优势,并能更好处理噪声场景深度估计的遮挡问题。

Abstract
A light field camera can simultaneously sample a scene from multiple viewpoints with a single exposure, which has unique advantages in portability and depth accuracy over other depth sensors. Noise is a challenging issue for light field depth estimation. Most of the traditional depth estimation methods for noisy scenes are only suitable for non-occluded scenes, and cannot handle the noisy scenes with occluded regions. To solve this problem, we present a light field depth estimation method based on inline occlusion handling. The proposed method integrates the occlusion handling into the anti-noise cost volume, which can improve the anti-occlusion capability while maintaining the anti-noise performance. After the cost volume is constructed, we propose a multi-template filtering algorithm to smooth the data cost while preserving the edge structure. Experimental results show that the proposed method has better performance over other state-of-the-art depth estimation methods in high noise scenes, and can better handle the occlusion problem of depth estimation in noisy scenes.
-
Key words:
- light field /
- depth estimation /
- defocus cue /
- noise suppression /
- occlusion handling
-
Overview

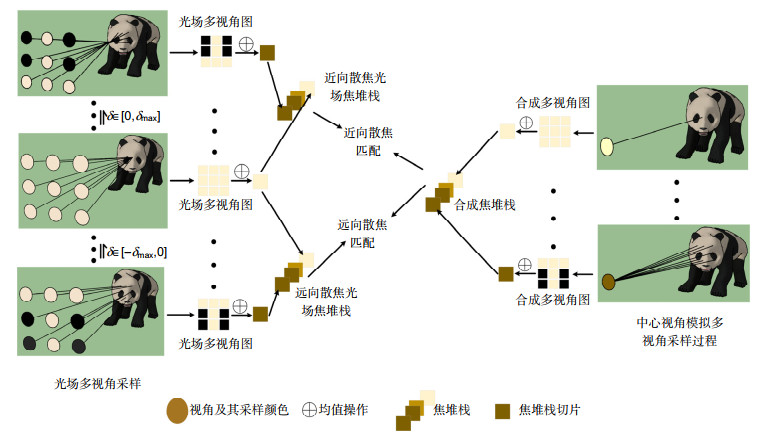
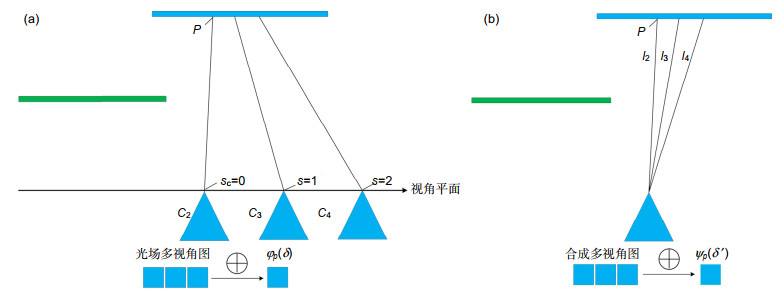
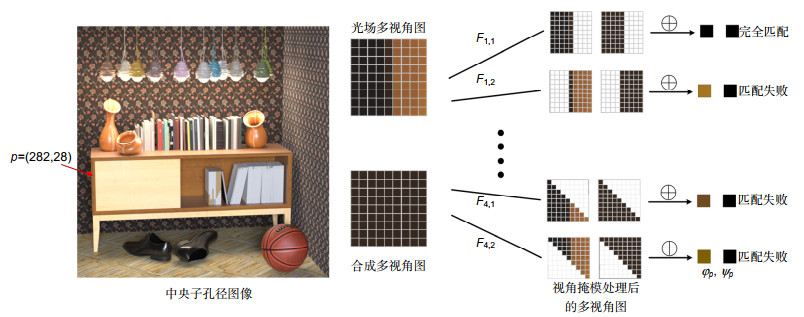
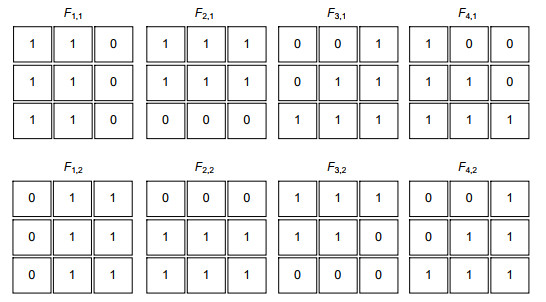
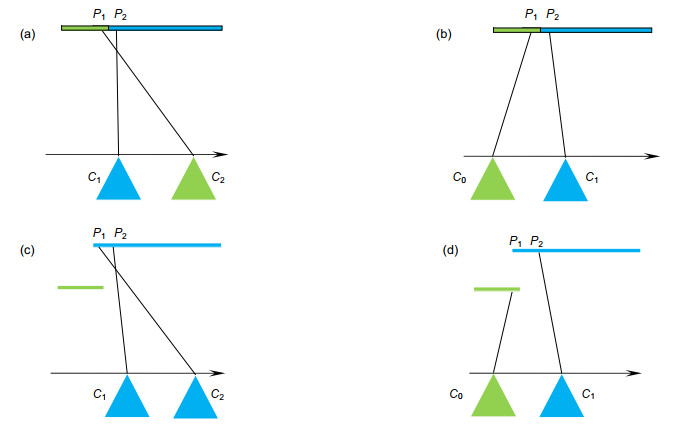
Overview: Depth estimation from multiple images is a central task in computer vision. Reliable depth information provides an effective source for visual tasks, such as target detection, image segmentation, and special effects for movies. As one of the new multi-view image acquisition devices, the light field camera makes it more convenient to acquire multiple images data. A light field camera can simultaneously sample a scene from multiple viewpoints with a single exposure, which has unique advantages in portability and depth accuracy over other depth sensors. Noise is a challenging issue for light field depth estimation. Especially for high-noise scenes containing occlusion, the simultaneous presence of occlusion and noise makes depth acquisition more difficult. For this problem, we present a light field depth estimation algorithm that is robust to occlusion and noise. The proposed method uses an inline occlusion handling framework. By integrating the occlusion handling into the anti-noise cost volume, the anti-occlusion ability of the proposed method is improved while maintaining the anti-noise performance. For the construction of the anti-noise cost volume, a focal stack matching measure based on the double-directions defocusing is proposed, which increases the defocus direction of the traditional focal stack and introduces more samples for a single match. More samples allow the algorithm to select the sample with the lowest matching cost, thereby improving the anti-noise performance. For occlusion handling, the occlusion mode in noisy scenes has greater computational difficulty. To eliminate the influence of occlusion on the focal stack and not be interfered by noise, the proposed algorithm designs view masks for different occlusion modes and constructs the cost volume respectively, and then adaptively selects the best volume according to the matching cost. After the cost volume is constructed, we use the filter-based algorithm to further smooth the cost volume. Because of the problem that traditional filtering methods cannot preserve the occlusion boundary, we design a multi-template filtering strategy. This strategy designs filters for occlusion in different directions and can better preserve the edge structure of the scene. Experiments are conducted on the HCI synthetic dataset and Stanford Lytro Illum dataset for real scenes. For quantitative evaluation, we use the percentage of bad pixels and the mean square error to measure the pros and cons of every algorithm. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves better performance than other state-of-the-art methods for scenes where occlusion and noise exist at the same time.
-

-
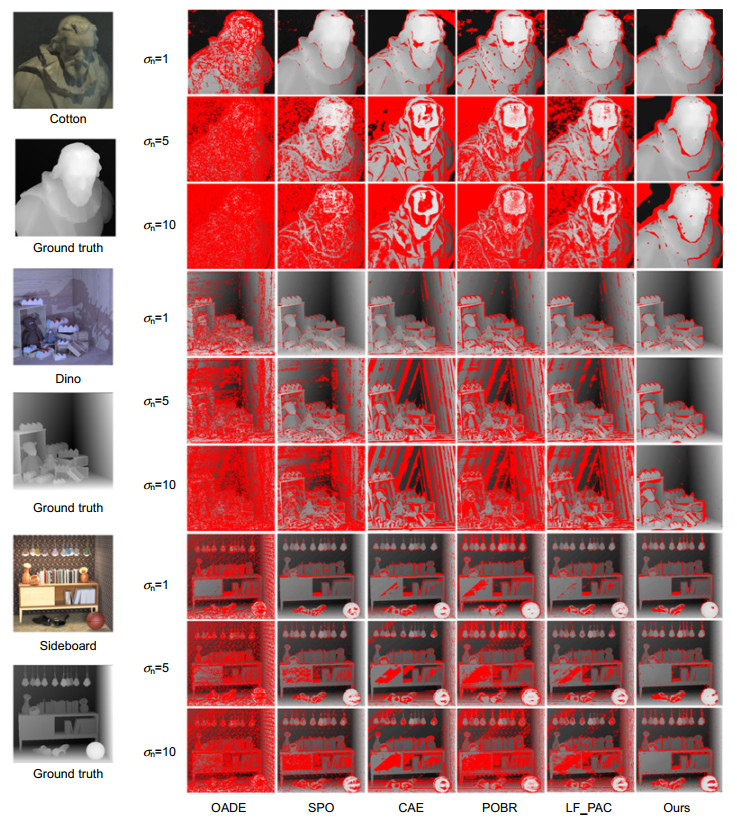
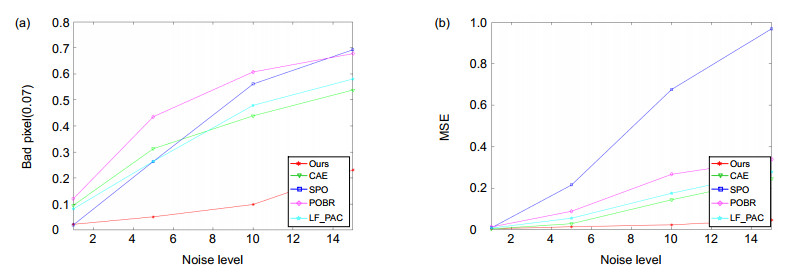
表 1 坏像素0.07评估
Table 1. BadPix(0.07)
名称 噪声等级 OADE SPO CAE POBR LF_PAC 本文方法 Cotton σn=1 22.39 3.46 11.02 16.92 9.13 5.92 σn=5 78.69 46.37 48.75 63.32 37.58 12.19 σn=10 88.37 78.02 65.75 76.54 64.34 20.54 Dino σn=1 13.11 3.06 9.23 13.24 9.78 4.62 σn=5 44.86 23.18 32.24 41.52 24.59 7.83 σn=10 69.27 59.44 44.38 64.20 46.58 11.07 Sideboard σn=1 27.41 7.48 11.40 22.82 10.34 8.67 σn=5 39.90 15.78 19.32 34.98 17.81 9.98 σn=10 50.98 29.31 28.85 46.35 33.07 14.97 Average 48.33 29.57 30.1 42.21 28.14 10.64 表 2 均方误差评估
Table 2. MSE×100
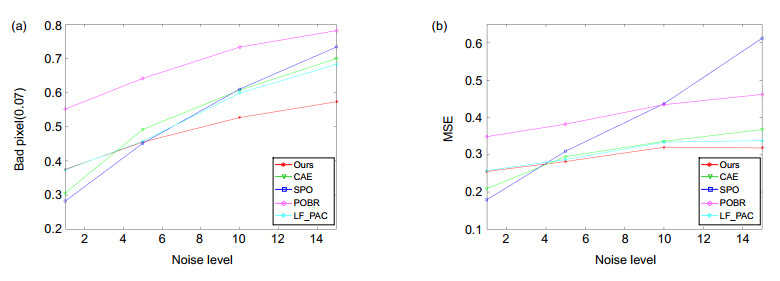
名称 噪声等级 OADE SPO CAE POBR LF_PAC 本文方法 Cotton σn=1 4.55 2.81 4.48 7.81 6.61 5.68 σn=5 41.25 55.76 14.14 34.37 20.07 9.64 σn=10 67.47 110.58 54.13 80.13 48.77 12.66 Dino σn=1 1.69 0.52 0.51 1.95 1.00 0.85 σn=5 5.92 8.89 1.41 2.81 1.52 1.29 σn=10 19.58 54.56 2.57 10.16 4.13 1.82 Sideboard σn=1 4.52 1.10 0.85 5.05 1.17 1.91 σn=5 5.58 6.38 1.18 6.11 1.50 1.98 σn=10 7.61 18.43 2.32 6.88 3.77 3.18 Average 17.57 28.78 9.07 17.25 9.84 4.33 表 3 坏像素0.07评估
Table 3. BadPix(0.07)
名称 噪声等级 非遮挡区域 遮挡区域 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Cotton σn=1 4.0 3.8 4.1 2.8 52.6 53.1 50.8 44.6 σn=5 7.8 7.4 7.7 7.6 55 56.4 56.1 55 σn=10 25.7 23.2 25.3 17.4 59.2 58.7 60.8 58.4 Dino σn=1 0.8 0.6 0.6 0.5 42.1 48.6 41.3 29.2 σn=5 2.2 1.9 1.8 2.0 47 46.3 46 43 σn=10 6.4 5.0 4.7 4.6 51.8 54.2 51.0 50.3 Sideboard σn=1 4.9 4.2 4.2 4.1 44.8 43.7 42.1 24.5 σn=5 5.2 4.9 5.0 4.3 46.8 44.6 44.6 29.7 σn=10 8.2 6.3 7.3 7.6 49.3 48.2 47.7 40.7 均值 7.3 6.4 6.7 5.6 49.9 50.4 48.9 41.7 名称 噪声等级 全局 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Cotton σn=1 7.49 7.83 7.57 5.9 σn=5 12.1 11.9 11.3 12.1 σn=10 25.9 25.8 27.4 20.5 Dino σn=1 8.59 8.2 6.35 4.6 σn=5 8.59 8.18 8.11 7.8 σn=10 12.1 11.9 11.2 11.0 Sideboard σn=1 14.2 13 12.6 8.6 σn=5 14.8 13.7 13.8 9.9 σn=10 16.9 15.6 15.2 14.9 均值 13.4 12.9 12.6 10.3 -
参考文献
[1] Ng R, Levoy M, Brédif M, et al. Light field photography with a hand-held plenoptic camera[R]. Computer Science Technical Report CSTR2, 2005: 1-11.
[2] Zhang S, Sheng H, Li C, et al. Robust depth estimation for light field via spinning parallelogram operator[J]. Comput Vis Image Underst, 2016, 145: 148-159. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2015.12.007
[3] Wanner S, Goldluecke B. Globally consistent depth labeling of 4D light fields[C]//2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2012.
[4] Chen J, Hou J H, Ni Y, et al. Accurate light field depth estimation with superpixel regularization over partially occluded regions[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2018, 27(10): 4889-4900. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2839524
[5] Jeon H G, Park J, Choe G, et al. Accurate depth map estimation from a lenslet light field camera[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2015.
[6] Williem, Park I K, Lee K M. Robust light field depth estimation using occlusion-noise aware data costs[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2018, 40(10): 2484-2497. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2746858
[7] Williem W, Park I K. Robust light field depth estimation for noisy scene with occlusion[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016.
[8] Tao M W, Hadap S, Malik J, et al. Depth from combining defocus and correspondence using light-field cameras[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2013.
[9] Wang T C, Efros A, Ramamoorthi R. Occlusion-aware depth estimation using light-field cameras[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2015.
[10] Sheng H, Zhao P, Zhang S, et al. Occlusion-aware depth estimation for light field using multi-orientation EPIs[J]. Pattern Recognit, 2018, 74: 587-599. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.09.010
[11] Guo Z H, Wu J L, Chen X F, et al. Accurate light field depth estimation using multi-orientation partial angular coherence[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 169123-169132. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2954892
[12] Strecke M, Goldluecke B. Sublabel-accurate convex relaxation with total generalized variation regularization[C]//German Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2018.
[13] Lin H T, Chen C, Kang S B, et al. Depth recovery from light field using focal stack symmetry[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2015.
[14] Sheng H, Zhang S, Cao X C, et al. Geometric occlusion analysis in depth estimation using integral guided filter for light-field image[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2017, 26(12): 5758-5771. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2745100
[15] Honauer K, Johannsen O, Kondermann D, et al. A dataset and evaluation methodology for depth estimation on 4d light fields[C]//Asian Conference on Computer Vision, 2016.
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: