-
摘要:
聚酰亚胺(PI)薄膜因具有优良的热稳定性、良好的机械强度等性能广泛应用于航空航天、微电子等领域,但应用在光学成像方向的报道极少。要将PI薄膜用于成像,对其本身的光学均匀性要求极为苛刻。本文实现了100 mm口径低热膨胀系数抗拉伸PI薄膜的光学均匀性满足瑞利判据,具有了成像领域应用的潜力。除了光学均匀性之外,该PI的拉伸强度为285 MPa,是PMDA-ODA型PI拉伸强度的~2.6倍;热膨胀系数约为3.2 ppm·K-1,可以与Novastrat®905相媲美,比商品化PI薄膜低一个数量级。这些优良的基础性能为进一步改进PI薄膜的空间适应性预留了更大的空间。PI光学均匀性的解决将为其在薄膜衍射光学元件中的应用奠定基础。
 Abstract:
Abstract:Polyimide (PI) film is widely used in aerospace, microelectronics, and other fields because of its excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength. However, there are very few reports about its application in the direction of optical imaging. To use PI film for imaging, the requirements for the optical homogeneity of the PI film are extremely demanding. The optical homogeneity of the stretch-resistant PI film proposed in this paper with 100 mm diameter and low thermal expansion coefficient meets the Rayleigh criterion, which has the potential for applications in the imaging field. In addition, the tensile strength of this PI is 285 MPa, which is ~2.6 times that of the PMDA-ODA type PI; the coefficient of thermal expansion is about 3.2 ppm·K-1, which is comparable to that of the Novastrat®905 type PI and is one order of magnitude lower than that of the commercial PI films. These excellent basic properties reserve more space to further improve the space adaptability of the PI film. The solution of the optical homogeneity of the PI film will lay the foundation for its application in thin film diffractive optical elements.
-
Key words:
- imaging /
- low thermal expansion coefficient /
- tensile strength /
- optical homogeneity
-

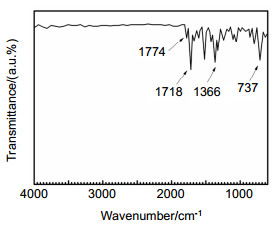
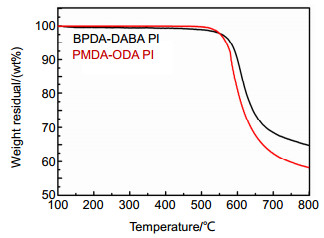
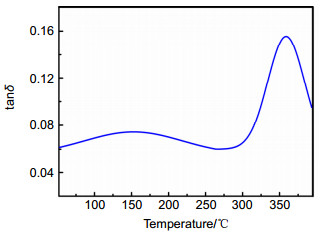
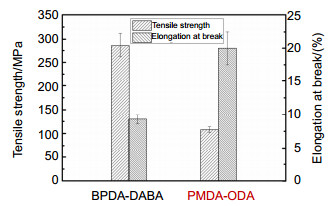
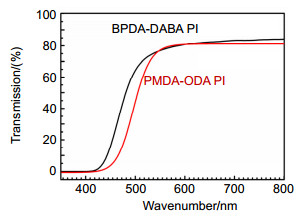
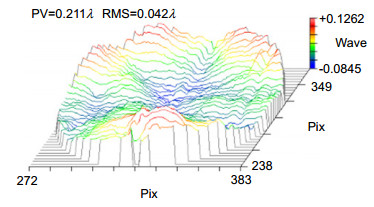
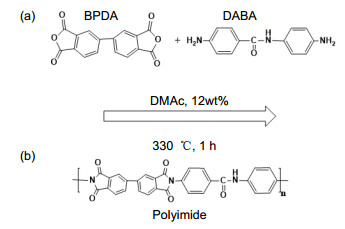
Overview: Diffractive optical element (DOE) is an important part of the large aperture spatial diffractive optical system. Materials of DOE with the characteristics of high optical transmittance, satisfactory optical homogeneity, and good dimensional stability are urgently required. As a kind of engineering polymer with high performance, polyimides (PIs) are widely used in the aerospace field, owing to their inherent good mechanical properties, resistance to chemicals, desirable dielectric permittivity, and high-temperature stability. However, the preparation of PI films on the market mostly adopts a biaxial stretching forming process, which is equivalent to pre-orienting the film and will introduce errors in beam control. In order to obtain PI with optical homogeneity, it is necessary to improve the existing preparation process. Nevertheless, there are few reports on the improvement of film forming process for optical imaging application. The forming process parameters of the optical imaging quality films: viscosity, rotation speed, spin coating time and precuring temperature are 105 p, 900 rpm, 120 s and 70 ℃, respectively. According to the film-forming process parameters, the optical homogeneity results of PI film with 100 mm aperture are obtained: PV≤1/4λ and RMS≤1/20λ. Moreover, the process has good stability, therefore, we can stably prepare PI film with large aperture (100 mm) which meet the Rayleigh criterion, which is the basis of the subsequent preparation of Fresnel film lens. The characteristic peak at 1366 cm-1 is due to the peak in amide bond. At 2900 cm-1~3200 cm-1, the broad absorption peaks of - COOH group and - NH group corresponding to the polyamic acid disappear, indicating that the polyimide film has been completely imidized. The temperature Td of 5% is 582 ℃. The carbon yield of the BPDA-DABA type PI at 800 ℃ is about 62.7%. The glass transition temperature Tg of BPDA-DABA PI is 359 ℃. The thermal expansion coefficient of PI film is about 3.2 ppm·K-1, which makes the deformation of PI film itself under the condition of temperature change have the lowest influence on the beam control. It can basically meet the requirements of optical PI for dimensional stability. The tensile strength of the BPDA-DABA type PI is ~285 MPa due to the hydrogen bond between molecular chains. The transparency of both the BPDA-DABA PI and PMDA-ODA PI films are more than 80% at 550 nm. In summary, BPDA-DABA PI has excellent mechanical strength and good thermal properties, and these basic indices can meet the design requirements of optical PI film. In this paper, the spin coating method is used to solve the problem that the low thermal expansion coefficient tensile PI film with 100 mm aperture meets Rayleigh criterion, which lays the foundation for solving the optical homogeneity of diffractive optical elements on the ground or in the synchronous orbit environment.
-

-
图 3 PI薄膜的TGA曲线 (注:PMDA-ODA PI的对比数据来自参考文献[18])
Figure 3. TGA curve of PI film
表 1 聚酰亚胺薄膜的热性能
Table 1. Thermal properties of polyimide films
Sample DMA TMA TGA tanδ a Tg/(℃) b CTE/(ppm·K-1) c Td in N2/(℃) d Carbon yield/(%) e PI 0.1591 359 3.2 582 62.7 表 2 聚酰亚胺薄膜的力学性能
Table 2. Mechanical properties of polyimide films
样品 拉伸强度/MPa 断裂伸长率/(%) PMDA-ODA 108±6 20±2.5 BPDA-DABA 285±25 9.3±0.7 -
[1] Hyde R A. Eyeglass. 1. Very large aperture diffractive telescopes[J]. Appl Opt, 1999, 38(19): 4198–4212. doi: 10.1364/AO.38.004198
[2] Barton I M, Britten J A, Dixit S N, et al. Fabrication of large-aperture lightweight diffractive lenses for use in space[J]. Appl Opt, 2001, 40(4): 447–541. doi: 10.1364/AO.40.000447
[3] Meinel A B, Meinel M P. Large membrane space optics: imagery and aberrations of diffractive and holographic achromatized optical elements of high diffraction order[J]. Opt Eng, 2002, 41(8): 1995–2007. doi: 10.1117/1.1487364
[4] Atcheson P D, Stewart C, Domber J, et al. MOIRE: initial demonstration of a transmissive diffractive membrane optic for large lightweight optical telescopes[J]. Proc SPIE, 2012, 8442: 844221. doi: 10.1117/12.925413
[5] Mao D, Lv G, Gao G H, et al. Fabrication of polyimide films with imaging quality using a spin-coating method for potential optical applications[J]. J Polym Eng, 2019, 39(10): 917–925. doi: 10.1515/polyeng-2019-0177
[6] 谭昭, 吴时彬, 杨伟, 等. 圆形薄膜预应力测量[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2020, 48(3): 109–114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2020.03.019
Tan Z, Wu S B, Yang W, et al. Measurement of circular membrane prestress[J]. Eng Plastics Appl, 2020, 48(3): 109–114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2020.03.019
[7] 罗倩, 吴时彬, 汪利华, 等. 拼接检测系统平面波前稀疏子孔径排列模型的优化[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(5): 170638. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170638
Luo Q, Wu S B, Wang L H, et al. Optimization of sparse subaperture array model for stitching detection of plane wavefront[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2018, 45(5): 170638. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170638
[8] 杨伟, 吴时彬, 汪利华, 等. 微结构薄膜望远镜研究进展分析[J]. 光电工程, 2017, 44(5): 475–482. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.05.001
Yang W, Wu S B, Wang L H, et al. Research advances and key technologies of macrostructure membrane telescope[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2017, 44(5): 475–482. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.05.001
[9] 刘盾, 杨伟, 吴时彬, 等. 主镜台阶数目对衍射成像系统传递函数的影响分析[J]. 光电工程, 2017, 44(8): 786–790. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.08.004
Liu D, Yang W, Wu S B, et al. Effect of the number of primary lens level on the MTF of diffractive imaging system[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2017, 44(8): 786–790. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.08.004
[10] Wang R Q, Zhang Z Y, Guo C, et al. Effects of fabrication errors on diffraction efficiency for a diffractive membrane[J]. Chin Opt Lett, 2016, 14(12): 120501. doi: 10.3788/COL201614.120501
[11] Zhang J, Li M J, Yin G H, et al. Low-cost method of fabricating large-aperture, high efficiency, Fresnel diffractive membrane optic using a modified moiré technique[J]. Chin Opt Lett, 2016, 14(10): 100501. doi: 10.3788/COL201614.100501
[12] Britten J A, Dixit S N, DeBruyckere M, et al. Large-aperture fast multilevel Fresnel zone lenses in glass and ultrathin polymer films for visible and near-infrared imaging applications[J]. Appl Opt, 2014, 53(11): 2312–2316. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.002312
[13] Wang S, Yang G J, Wu S B, et al. Preparation of solution-processable colorless polyamide-imides with extremely low thermal expansion coefficients through an in-situ silylation method for potential space optical applications[J]. e-Polymers, 2016, 16(5): 695–402. http://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/epoly-2016-0100/html
[14] Ni H J, Liu J G, Wang Z H, et al. A review on colorless and optically transparent polyimide films: Chemistry, process and engineering applications[J]. J Ind Eng Chem, 2015, 28: 16–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2015.03.013
[15] Meador M A B, Malow E J, Silva R, et al. Mechanically strong, flexible polyimide aerogels cross-linked with aromatic triamine[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2012, 4(2): 536–544. doi: 10.1021/am2014635
[16] Minton T K, Wright M E, Tomczak S J, et al. Atomic oxygen effects on POSS polyimides in low earth orbit[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2012, 4(2): 492–502. doi: 10.1021/am201509n
[17] Guo C L, Zhang Z Y, Xue D L, et al. High-performance etching of multilevel phase-type Fresnel zone plates with large apertures[J]. Opt Commun, 2018, 407: 227–233. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2017.09.006
[18] Lei X F, Chen Y, Zhang H P, et al. Space survivable polyimides with excellent optical transparency and self-healing properties derived from hyperbranched polysiloxane[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2013, 5(20): 10207–10220. doi: 10.1021/am402957s
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: