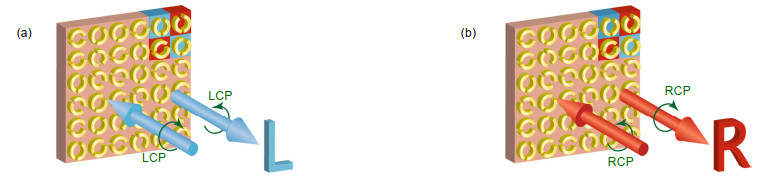-
摘要
全息术是一种三维成像技术,它已经被应用于多种实际场景。随着计算机科学与技术的迅猛发展,计算全息由于其方便和灵活的特性,已经成为一种广泛应用的全息成像方法。本文回顾了我们近期基于超表面的太赫兹计算全息研究进展。其中,作为全息板的超表面展示出了超越传统光学器件的独特性能。首先,利用超表面实现了对于全息板每个像素的相位振幅同时且独立的调控,进而实现了高质量全息成像。这种新的电磁波操控能力也带来了新的全息成像效果,如利用介质超表面实现了全息像沿传播方向上的连续变化。其次,对超表面在不同偏振态下的响应进行设计,分别实现了线偏振态与频率复用、圆偏振态复用、以及基于表面波的偏振复用超表面全息术。此外,本文提出了依赖于温度变化而主动可控的超表面全息术,为今后计算全息术的设计与实现提供了新的方案,也推动了超表面在实际应用方面的发展。
Abstract
Holography is a kind of technique enabling 3D imaging which has been applied in many practical fields. With the rapid development of computer science and technology, computer generated holography (CGH) has become a common holography design method due to its high convenience and flexibility. Herein, we present a review of our recent progress in metasurface-based terahertz CGH. In these demonstrations, the metasurfaces acting as the holograms have shown the novel capabilities beyond the conventional counterparts. We first present a meta-hologram with simultaneous and independent phase and amplitude control over each pixel, which enables high-quality holographic imaging. Such new characteristic also predicts new holographic imaging performances including holographic images transforming continuously along the propagation direction realized by dielectric metasurface. Then different responses under different incident polarization states are designed. A linear polarization and frequency multiplexed meta-hologram, a reflective circular polarization multiplexed meta-hologram, and a surface-wave-based polarization multiplexed meta-hologram have been achieved respectively. Furthermore, a thermally dependent dynamic meta-hologram which can change the holographic image actively is also given. The proposed method paves a novel way to the design and realization of CGH functional devices in the future and contributes to the development of metasurfaces towards practical applications.
-
Key words:
- terahertz /
- computer generated holography /
- metasurface /
- multiplexing
-
Overview

Overview: We review our recent progress in metasurface-based terahertz computer generated holography in which metasurfaces act as the holograms and show novel advantages.
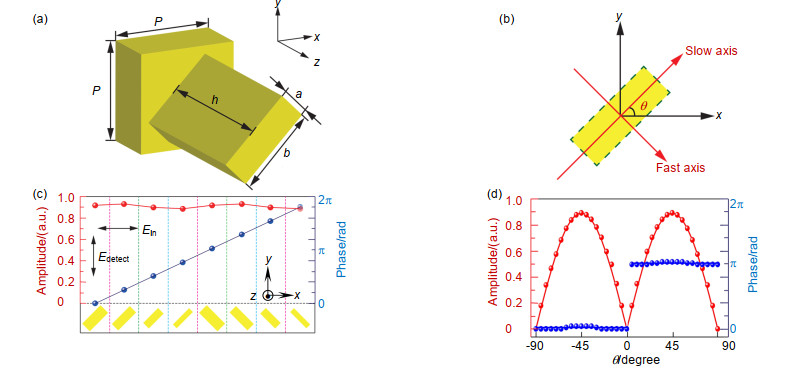
To get better quality of holographic image, the unit should modulate both amplitude and phase of incidence rather than just one of them. Based on the different resonance modes caused by parallel polarization incidence and perpendicular polarization incidence, a series of different C-shape split-ring resonators (CSRRs) are designed which have different modulating effects with each other in y-polarized transmittance and phase shift spectra under x-polarized normal incidence.
Although a fine hologram can be composed by CSRRs, its energy efficiency is low. To solve this problem, we resort to the all-dielectric metasurface. Its units are silicon pillar resonators which not only own the high energy efficiency but also can modulate both amplitude and phase of incidence like CSRRs.
To improve utilization efficiency of holograms, the multiplexed metasuface is one of the ideal solutions. The multiplexed holograms can increase information capacity of imaging system and make it more simplified. For these reasons, some multiplexed meta-holograms emerged in our works.
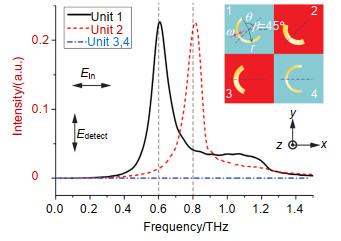
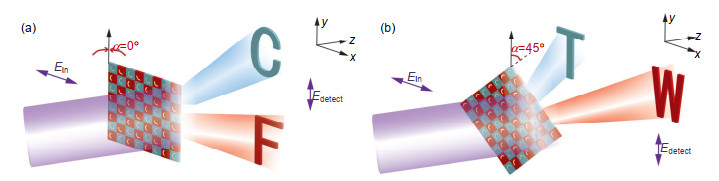
Firstly, a meta-hologram which is a linear polarization and frequency multiplexed one is designed. On the hologram, two sets of CSRRs which work at different frequencies are arranged and a pattern like checkerboard formed. Due to special design some CSRRs do not work when others do. Based on CSRRs working at different frequencies and the special arrangement, the linear polarization and frequency multiplexed hologram is achieved.
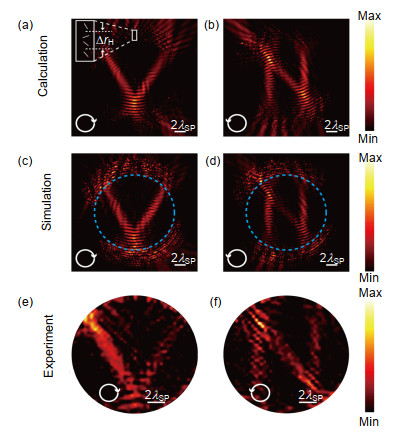
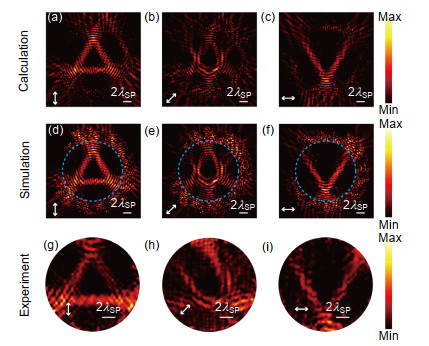
Secondly, a circular polarization multiplexed hologram is realized. There are two types of units on it which are L-type DSRRs (double-split ring resonators) and R-type DSRRs respectively and they response to the left-handed or right-handed circular polarization only. Based on the Pancharatnam-Berry phase and a modified Gerchberg-Saxton algorithm, the hologram shows different holographic images under left-handed and right-handed circular polarization incidence, respectively.
Thirdly, a surface plasmon holography which is polarization multiplexed is also achieved. On these holograms, slit-pair resonators act as the pixels. The holographic images are composed by a series of surface plasmon which excited by different pixels. The initial phase of surface plasmon from pixels is depended on the origin of the slit-pair resonator and the polarization of incidence.
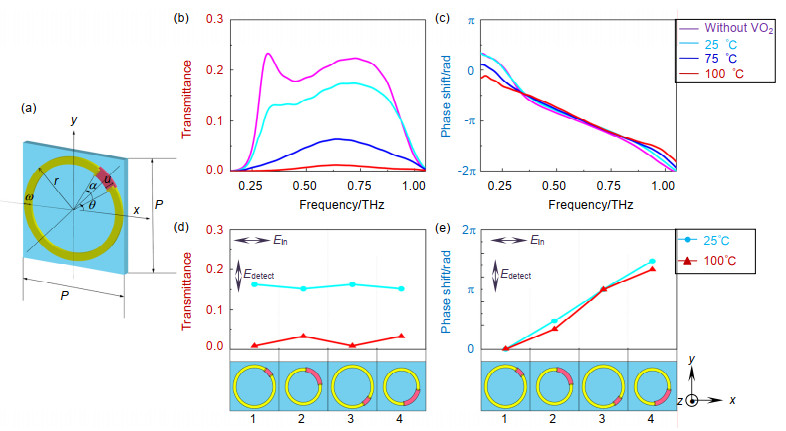
Finally, a thermally dependent active control meta-hologram is also designd and demonstrated in experiment. There are two sets of units on it which are passive units and active units. They are CSRRs and V-CSRRs (vanadium dioxide integrated CSRRs) which are CSRRs contained vanadium dioxide in their gaps. Based on the phase transition effect of vanadium dioxide andreasonable arrangement of passive and active units and destructive interference images showed by them, the hologram shows different holographic images in low and high temperatures, respectively.
-

-
-
参考文献
[1] Mittleman D. Sensing with Terahertz Radiation[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2003: 117-153.
[2] Siegel P H. Terahertz technology[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2002, 50(3): 910-928. doi: 10.1109/22.989974
[3] Pendry J B. Negative refraction makes a perfect lens[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2000, 85(18): 3966-3969. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.3966
[4] Shelby R A, Smith D R, Schultz S. Experimental verification of a negative index of refraction[J]. Science, 2001, 292(5514): 77-79. doi: 10.1126/science.1058847
[5] Zhang S, Park Y S, Li J S, et al. Negative refractive index in chiral metamaterials[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102(2): 023901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.023901
[6] Silveirinha M, Engheta N. Tunneling of electromagnetic energy through subwavelength channels and bends using ε-near-zero materials[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 97(15): 157403. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.157403
[7] Ergin T, Stenger N, Brenner P, et al. Three-dimensional invisibility cloak at optical wavelengths[J]. Science, 2010, 328(5976): 337-339. doi: 10.1126/science.1186351
[8] Liang D C, Gu J Q, Han J G, et al. Robust large dimension terahertz cloaking[J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(7): 916-921. doi: 10.1002/adma.201103890
[9] Valentine J, Li J, Zentgraf T, et al. An optical cloak made of dielectrics[J]. Nature Materials, 2009, 8(7): 568-571. doi: 10.1038/nmat2461
[10] Liu Z W, Lee H, Xiong Y, et al. Far-field optical hyperlens magnifying sub-diffraction-limited objects[J]. Science, 2007, 315(5819): 1686. doi: 10.1126/science.1137368
[11] Casse B D F, Lu W T, Huang Y J, et al. Super-resolution imaging using a three-dimensional metamaterials nanolens[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 96(2): 023114. doi: 10.1063/1.3291677
[12] Safavi-Naeini A H, Alegre T P M, Chan J, et al. Electromagnetically induced transparency and slow light with optomechanics[J]. Nature, 2011, 472(7341): 69-73. doi: 10.1038/nature09933
[13] Gu J Q, Singh R, Liu X J, et al. Active control of electromagnetically induced transparency analogue in terahertz metamaterials[J]. Nature Communications, 2012, 3: 1151. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2153
[14] Chen Y L, Analytis J G, Chu J H, et al. Experimental realization of a three-dimensional topological insulator, Bi2Te3[J]. Science, 2009, 325(5937): 178-181. doi: 10.1126/science.1173034
[15] Chang C Z, Zhang J S, Feng X, et al. Experimental observation of the quantum anomalous Hall effect in a magnetic topological insulator[J]. Science, 2013, 340(6129): 167-170. doi: 10.1126/science.1234414
[16] Ni X J, Kildishev A V, Shalaev V M. Metasurface holograms for visible light[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2807. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3807
[17] Zheng G X, Mühlenbernd H, Kenney M, et al. Metasurface holograms reaching 80% efficiency[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(4): 308-312. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.2
[18] Huang L L, Chen X Z, Mühlenbernd H, et al. Three-dimensional optical holography using a plasmonic metasurface[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2808. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3808
[19] Zheng J, Ye Z C, Sun N L, et al. Highly anisotropic metasurface: a polarized beam splitter and hologram[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6491.
[20] Genevet P, Capasso F. Holographic optical metasurfaces: a review of current progress[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2015, 78(2): 024401. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/78/2/024401
[21] Chen W T, Yang K Y, Wang C M, et al. High-efficiency broadband meta-hologram with polarization-controlled dual images[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(1): 225-230. doi: 10.1021/nl403811d
[22] Huang Y W, Chen W T, Tsai W Y, et al. Aluminum plasmonic multicolor meta-hologram[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(5): 3122-3127. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b00184
[23] Yifat Y, Eitan M, Iluz Z, et al. Highly efficient and broadband wide-angle holography using patch-dipole nanoantenna reflectarrays[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(5): 2485-2490. doi: 10.1021/nl5001696
[24] Aieta F, Genevet P, Kats M A, et al. Aberration-free ultrathin flat lenses and axicons at telecom wavelengths based on plasmonic metasurfaces[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(9): 4932-4936. doi: 10.1021/nl302516v
[25] Chen X Z, Huang L L, Mühlenbernd H, et al. Dual-polarity plasmonic metalens for visible light[J]. Nature Communications, 2012, 3: 1198. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2207
[26] Wang Q, Zhang X Q, Xu Y H, et al. A broadband metasurface‐based terahertz flat‐lens array[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2015, 3(6): 779-785. doi: 10.1002/adom.201400557
[27] Cong L Q, Xu N N, Gu J Q, et al. Highly flexible broadband terahertz metamaterial quarter‐wave plate[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2014, 8(4): 626-632.
[28] Yu N F, Aieta F, Genevet P, et al. A broadband, background-free quarter-wave plate based on plasmonic metasurfaces[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(12): 6328-6333. doi: 10.1021/nl303445u
[29] Gabor D. A new microscopic principle[J]. Nature, 1948, 161(4098): 777-778. doi: 10.1038/161777a0
[30] Leith E N, Upatnieks J. Reconstructed wavefronts and communication theory[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1962, 52(10): 1123-1130. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.52.001123
[31] Lohmann A W, Paris D P. Binary fraunhofer holograms, generated by computer[J]. Applied Optics, 1967, 6(10): 1739-1748. doi: 10.1364/AO.6.001739
[32] Zhang X Q, Tian Z, Yue W S, et al. Broadband terahertz wave deflection based on C‐shape complex metamaterials with phase discontinuities[J]. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(33): 4567-4572. doi: 10.1002/adma.201204850
[33] Arbabi A, Horie Y, Bagheri M, et al. Dielectric metasurfaces for complete control of phase and polarization with subwavelength spatial resolution and high transmission[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(11): 937-943. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.186
[34] Zhang H F, Zhang X Q, Xu Q, et al. High‐efficiency dielectric metasurfaces for polarization-dependent terahertz wavefront manipulation[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2018, 6(1): 1700773. doi: 10.1002/adom.201700773
[35] Xu Q, Zhang X Q, Wei M Q, et al. Efficient metacoupler for complex surface plasmon launching[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2018, 6(5): 1701117. doi: 10.1002/adom.201701117
[36] Devlin R C, Khorasaninejad M, Chen W T, et al. Broadband high-efficiency dielectric metasurfaces for the visible spectrum[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(38): 10473-10478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611740113
[37] Wang Q, Zhang X Q, Xu Y H, et al. Broadband metasurface holograms: toward complete phase and amplitude engineering[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 32867. doi: 10.1038/srep32867
[38] Deng Z L, Deng J H, Zhuang X, et al. Diatomic metasurface for vectorial holography[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 18(5): 2885-2892. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b00047
[39] Mueller J P B, Rubin N A, Devlin R C, et al. Metasurface polarization optics: independent phase control of arbitrary orthogonal states of polarization[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2017, 118(11): 113901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.113901
[40] Wen D D, Yue F Y, Li G X, et al. Helicity multiplexed broadband metasurface holograms[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 8241. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9241
[41] Wang Q, Plum E, Yang Q L, et al. Reflective chiral meta-holography: multiplexing holograms for circularly polarized waves[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2018, 7(1): 25.
[42] Ye W M, Zeuner F, Li X, et al. Spin and wavelength multiplexed nonlinear metasurface holography[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 11930. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11930
[43] Almeida E, Bitton O, Prior Y. Nonlinear metamaterials for holography[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 12533. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12533
[44] Wang Q, Xu Q, Zhang X Q, et al. All-dielectric meta-holograms with holographic images transforming longitudinally[J]. ACS Photonics, 2018, 5(2): 599-606. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b01173
[45] Wang Q, Zhang X Q, Plum E, et al. Polarization and frequency multiplexed terahertz meta‐holography[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2017, 5(14): 1700277. doi: 10.1002/adom.201700277
[46] Xu Q, Zhang X Q, Xu Y H, et al. Polarization‐controlled surface plasmon holography[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2017, 11(1): 1600212.
[47] Liu X B, Wang Q, Zhang X Q, et al. Thermally dependent dynamic meta‐holography using a vanadium dioxide integrated metasurface[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2019, 7(12): 1900175. doi: 10.1002/adom.201900175
[48] Wang B, Quan B G, He J W, et al. Wavelength de-multiplexing metasurface hologram[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 35657. doi: 10.1038/srep35657
[49] Gerchberg R W, Saxton W O. A practical algorithm for the determination of phase from image and diffraction plane pictures[J]. Optik, 1972, 35(2): 237-246.
[50] Guo J Y, Wang T, Zhao H, et al. Reconfigurable terahertz metasurface pure phase holograms[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2019, 7(10): 1801696. doi: 10.1002/adom.201801696
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: