-
摘要:
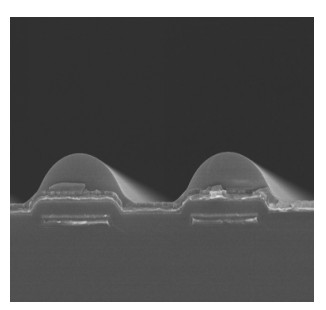
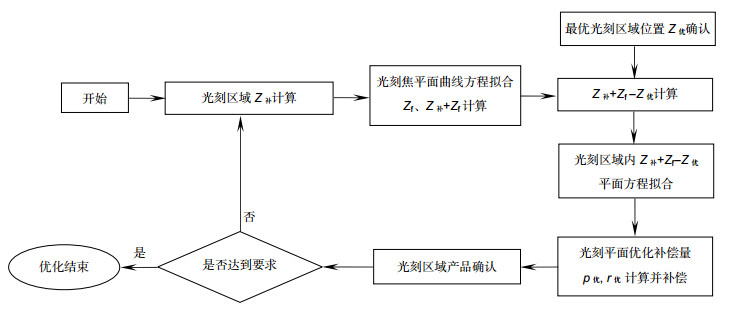
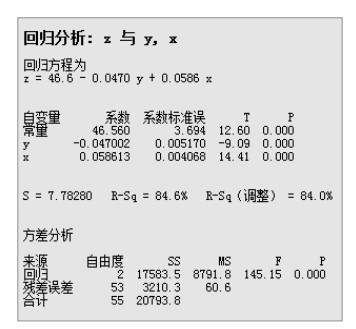
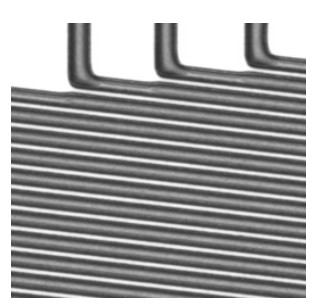
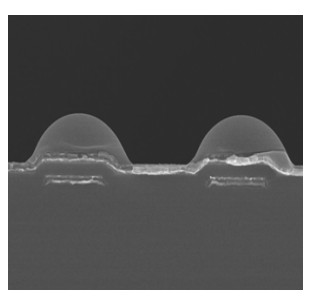
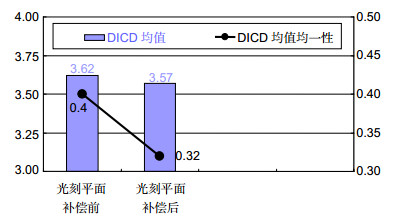
TFT线宽或线间距接近光刻机分辨率时,光刻图形容易产生光刻胶残留不良,为改善该问题,本文从光刻图形出发,以最佳光刻图形所在位置为基准,计算出光刻机光刻平面的优化补偿量,从而实现对光刻平面的补偿优化。首先,通过光刻机光刻平面的补偿量、基板载台平坦度及焦平面计算出光刻时光刻区域基板表面的高度值。然后,根据光刻区域内光刻图形状况找到最佳光刻区域位置,并以该位置为零点,计算出整个光刻区域相对于该位置的相对高度差值。其次,对光刻区域内的高度差值做平面拟合,计算出当拟合平面为垂直于Z轴的水平面时所需要的补偿量,该补偿量即为光刻区域内光刻平面的优化补偿量。最后,以该补偿量对光刻平面进行补偿,从而使得光刻区域内光刻平面均趋于同一最佳光刻面。结果表明:光刻平面优化补偿后,光刻区域内光刻图形均能形成清晰的图形,光刻胶残留不良得到改善,同时光刻DICD均值在目标值范围内减小了1.38%,DICD均一性提高了20%。
 Abstract:
Abstract:When the line width or line space of thin film transistor (TFT) is close to the resolution of the lithography machine, it is easy to appear the defect of photoresist remain in lithography pattern. In order to improve this problem, based on the position of the best lithography pattern, the optimal compensation amount of lithography plane of the lithography machine is calculated, so lithography plane is improved. Firstly, by the compensation of the lithography plane, the flatness of the plate stage and the focal plane, the value of the plate surface height is calculated in the lithography region. Then, according to the lithography pattern in the lithography region, the optimum position of the lithography region is found, and take this location as the zero point, the relative height difference between the total lithography region and the optimum position is calculated. Secondly, the fitting plane of the height difference in the lithography region is done, and the compensation is calculated when the fitting plane is the horizontal plane that is perpendicular to the Z axis, which is the optimal compensation of the lithography plane in the lithography region. Finally, the compensation is used to compensate the lithography plane, so that the lithography plane in the lithography region tends to the same optimal lithography plane. The results show that the lithography pattern can be clearly formed in the lithography region after the lithography plane is offset, the defect of the photoresist remain is improved, at the same time, the average value of the develop inspection critical dimension (DICD) is reduced by 1.38% in the target value range, and the uniformity of the DICD is increased by 20%.
-
Key words:
- thin film transistor /
- lithography plane /
- optimal compensation /
- plane fitting
-

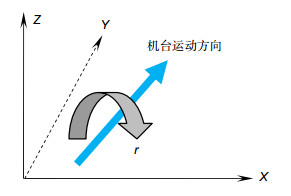
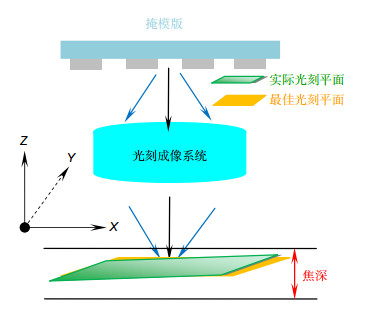
Overview: The traditional method of the thin film transistor (TFT) lithography plane compensation is realized by ensuring the flatness of photoresist plane and the photoresist plane is on the focal plane of the lithography machine, which is achieved by the compensation of flatness of the plate stage and the focus compensation of lithography machine. However, due to the existence of the compensation error, the quality of the actual lithography product picture is different from the ideal situation, when the TFT line width or line space is close to the minimum resolution of the lithography machine. The difference will lead to the defect of remaining photoresist, which seriously affects the yield of the lithography products. In order to solve the problem, based on the position of the best lithography pattern, the optimal compensation amount of lithography plane of the lithography machine is calculated. The difference of the result between the actual lithography product and the compensation of the lithography plane is reduced by the optimal compensation, which is compensated for the lithography machine. So, lithography plane is improved. Firstly, by the compensation of the lithography plane, the flatness of the plate stage and the focal plane, the value of the plate surface height is calculated in the lithography region. Then, according to the lithography pattern in the lithography region, the optimum position of the lithography region is found. Taking this location as the zero point, the relative height difference between the total lithography region and the optimum position is calculated. Secondly, the fitting plane of the height difference in the lithography region is done, and the compensation is calculated when the fitting plane is the horizontal plane that is perpendicular to the Z axis, which is the optimal compensation of the lithography plane in the lithography region. Finally, the compensation is used to compensate the lithography plane, so that the lithography plane in the lithography region tends to the same optimal lithography plane. The results show that, compared with no compensation, the lithography pattern can be clearly formed in the lithography region after the lithography plane is offset. The defect of the remaining photoresist is improved. At the same time, the average value of the DICD is reduced by 1.38% in the target value range, the uniformity of the DICD is increased by 20%, and the ability of small line lithography for the lithography machine at the minimum resolution has been significantly improved.
-

-
表 1 光刻区域基板载台平坦度
Table 1. The stage flatness of the lithography area
μm 机台y方向坐标/mm 机台x方向坐标/mm -730 -720 -600 -480 -360 -240 -120 0 905 14.62 15.93 21.46 26.70 31.74 32.03 28.74 27.92 810 23.08 23.26 26.39 31.83 35.13 35.12 30.14 29.19 708.75 32.74 33.22 37.75 38.04 37.76 38.29 36.12 32.25 607.5 40.86 41.47 46.04 45.25 39.95 42.40 38.43 36.11 506.25 47.73 48.09 49.50 52.04 47.81 48.49 40.67 38.38 405 56.53 57.93 58.79 59.20 55.62 55.68 47.96 44.06 303.75 68.09 68.21 71.23 66.00 60.35 62.15 57.52 51.90 表 2 光刻区域内Z补值
Table 2. The Z补 value of the lithography area
μm 机台y方向坐标/mm 机台x方向坐标/mm -730 -720 -600 -480 -360 -240 -120 0 905 14.62 16.46 28.36 26.52 51.37 58.02 61.10 66.65 810 21.43 22.15 31.64 43.45 53.11 59.46 60.86 66.27 708.75 29.34 30.35 41.25 47.90 53.98 60.89 65.08 67.57 607.5 35.71 36.85 47.78 53.36 54.43 63.24 65.63 69.68 506.25 40.82 41.71 49.49 58.40 60.53 67.57 66.12 70.20 405 47.87 49.80 57.03 63.80 66.58 73.01 71.66 74.13 303.75 57.67 58.33 67.71 68.84 69.57 77.73 79.46 80.21 表 3 光刻区域内光刻焦平面值
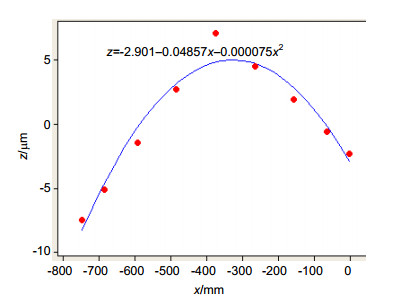
Table 3. The focus value of the lithography area
机台x方向坐标/mm -748 -685.5 -591.95 -485.1 -374 -262.9 -156.05 -62.5 0 Z/μm -7.50 -5.10 -1.50 2.70 7.10 4.50 1.90 -0.60 -2.30 表 4 光刻区域内Zf值
Table 4. The Zf value of the lithography area
μm 机台y方向坐标/mm 机台x方向坐标/mm -730 -720 -600 -480 -360 -240 -120 0 905 -7.41 -6.81 -0.76 3.13 4.86 4.44 1.85 -2.90 810 -7.41 -6.81 -0.76 3.13 4.86 4.44 1.85 -2.90 708.75 -7.41 -6.81 -0.76 3.13 4.86 4.44 1.85 -2.90 607.5 -7.41 -6.81 -0.76 3.13 4.86 4.44 1.85 -2.90 506.25 -7.41 -6.81 -0.76 3.13 4.86 4.44 1.85 -2.90 405 -7.41 -6.81 -0.76 3.13 4.86 4.44 1.85 -2.90 303.75 -7.41 -6.81 -0.76 3.13 4.86 4.44 1.85 -2.90 表 5 光刻区域内Zf+Z补值
Table 5. The Zf+Z补 value of the lithography area
μm 机台y方向坐标/mm 机台x方向坐标/mm -730 -720 -600 -480 -360 -240 -120 0 905 7.21 9.65 27.60 29.66 56.23 62.46 62.95 63.75 810 14.02 15.34 30.88 46.58 57.97 63.90 62.70 63.37 708.75 21.93 23.54 40.49 51.03 58.85 65.32 66.93 64.67 607.5 28.30 30.03 47.02 56.50 59.29 67.68 67.48 66.78 506.25 33.41 34.90 48.73 61.53 65.39 72.01 67.97 67.30 405 40.46 42.99 56.27 66.93 71.45 77.44 73.51 71.22 303.75 50.26 51.52 66.95 71.98 74.43 82.17 81.31 77.31 表 6 光刻区域内Z补+Zf-Z优值
Table 6. The Z补+Zf-Z优 value of the lithography area
μm 机台y方向坐标/mm 机台x方向坐标/mm -730 -720 -600 -480 -360 -240 -120 0 905 -52.08 -49.64 -31.69 -29.63 -3.06 3.16 3.66 4.46 810 -45.27 -43.95 -28.41 -12.71 -1.32 4.61 3.41 4.08 708.75 -37.37 -35.75 -18.80 -8.26 -0.44 6.03 7.64 5.38 607.5 -30.99 -29.26 -12.27 -2.80 0.00 8.39 8.19 7.49 506.25 -25.88 -24.39 -10.56 2.24 6.10 12.72 8.67 8.01 405 -18.84 -16.30 -3.02 7.64 12.16 18.15 14.22 11.93 303.75 -9.03 -7.78 7.66 12.68 15.14 22.88 22.02 18.02 -
[1] 王新久.液晶光学和液晶显示[M].北京:科学出版社, 2006: 230-251.
Wang X J. Liquid Crystal Optics & Liquid Cristal Display[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006: 230-251.
[2] 邵喜斌.液晶显示技术的最新进展[J].液晶与显示, 2000, 15(3): 163-170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2780.2000.03.001
Shao X B. Recent progress of liquid crystal display technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2000, 15(3): 163-170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2780.2000.03.001
[3] 车春城.广视角FFS技术CELL研究与设计[D].成都: 电子科技大学, 2007: 1-6.
Che C C. CELL research and design of FFS wide viewing angle technology[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2007: 1-6.
CNKI:CDMD:2.2007.100479 [4] 童林夙. 2012年后的平板显示世界[J].现代显示, 2007(7): 6-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6268.2007.07.002
Tong L S. Flat panel displays after 2012[J]. Advanced Display, 2007(7): 6-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6268.2007.07.002
[5] 黎午升, 惠官宝, 崔承镇, 等.在镜像投影曝光机上使用相移掩膜提高解像力的初步研究[J].液晶与显示, 2014, 29(4): 544-547. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjyxs201404012
Li W S, Hui G B, Cui C Z, et al. Preliminary study on improving resolution on mirror projection mask aligner with phase shift mask[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2014, 29(4): 544-547. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjyxs201404012
[6] 肖文俊.薄膜晶体管液晶显示器的串扰研究[D].北京: 北京交通大学, 2014: 1-4.
Xiao W J. A Research on crosstalk in TFT-LCDs[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2014: 1-4.
[7] Chun J Y, Kang C H, Ahn S J, et al. A-Si TFT-LCD mobile display with high pixel density using PenTile RGB WTM algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2006, 21(5): 474-477.
[8] 冯伯儒, 张锦, 侯德胜, 等.相移掩模和光学邻近效应校正光刻技术[J].光电工程, 2001, 28(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2001.01.001
Feng B R, Zhang J, Hou D S, et al. Optical microlithography with phase-shifting mask and optical proximity effect correction[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2001, 28(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2001.01.001
[9] 缪小运.先进光刻系统中焦平面测量与控制的研究[D].上海: 复旦大学, 2006: 5-9.
Miu X Y. Focal Plane Measure and Control Study[D]. Shanghai: Fudan University, 2006: 5-9.
10.7666/d.y1021731 [10] 黎午升, 惠官宝, 崔承镇, 等.相移掩膜应用于显示技术光刻细线化的初步研究[J].光电子技术, 2014, 34(4): 234-237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-488X.2014.04.005
Li W S, Hui G B, Cui C Z, et al. Preliminary study on improving photolithographic resolution of display technology with phase shift mask[J]. Optoelectronic Technology, 2014, 34(4): 234-237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-488X.2014.04.005
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: