Infrared intensity and polarization image mimicry fusion based on the combination of variable elements and matrix theory
-
摘要:
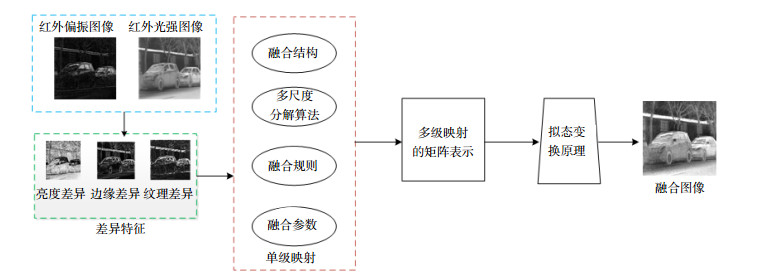
当前双模态红外图像融合在选取融合方法时,缺乏各要素之间的选取与组合的依据,且融合模型不能针对图像差异特征进行动态调整,造成融合效果不佳。针对上述问题,借鉴生物多拟态特性,提出了一种可变元素与矩阵相结合的双模态红外图像拟态融合算法。首先,将融合模型拆分成融合算法、融合规则、融合参数和融合结构相互独立的四部分,分别建立各部分与图像不同差异特征融合效果的单映射关系。其次,利用拟态变换思想,建立拟态变换融合方法,将融合过程所必要的四部分进行组合,从而派生出新的融合算法。最后,利用差异特征不同的源图像对所得拟态融合算法进行验证。实验结果表明,在图像差异特征不同时,利用该算法可以派生出更适合图像特征的融合方法,实现利用图像差异特征从而主动选择并动态调整融合算法的要求,使得所得到的融合图像中的差异特征可以有效融合,显著提高了原始图像视觉效果。
 Abstract:
Abstract:The current dual-mode infrared image lacks the selection and combination basis of each element when constructing the fusion method, and the fusion model cannot dynamically adjust for the image difference feature, resulting in poor fusion effect. Aiming at the above problems, referring to the multi-parameters of biological characters, this paper proposes infrared intensity and polarization image mimicry fusion based on the combination of variable elements and matrix theory. Firstly, the fusion model was divided into four parts: fusion algorithm, fusion rule, fusion parameter and fusion structure. The single mapping relationship between different parts and the difference of image feature fusion is established. Secondly, using the imaginary transformation idea, the imaginary transformation fusion method was established, and the necessary four parts of the fusion process are combined to derive a new fusion algorithm. Finally, it used the different source images with different features to verify the proposed mimetic fusion algorithm. Experimental results show that when the image difference features are different, the fusion method was more suitable for deriving image features, so as to achieve active selection and adjustment of the fusion algorithm. The different features in the fusion image can be effectively combined, and the visual effect of the original image is significantly improved.
-
Key words:
- image fusion /
- infrared imaging /
- matrix theory /
- dynamic reconstruction /
- multi-level mapping
-

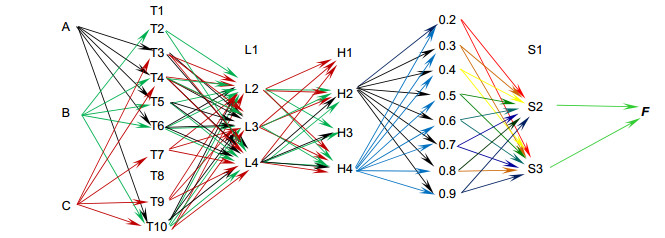
Overview: The infrared intensity image mainly reflects the shape, brightness, and position information of the target. The infrared polarization image mainly reflects the edge and details of the target. The fusion of the two can describe the target information more comprehensively, and plays an important role in the fields of space exploration, target identification, and security detection. Due to the increasingly complex scene information, the traditional fusion algorithm cannot meet the fusion requirements of the difference features between the two types of images, and cannot dynamically adjust the fusion method, resulting in poor fusion or even failure. Therefore, how to dynamically adjust the fusion algorithm based on different image difference features is necessary for dual-modality infrared image fusion. For the improvement of the fusion algorithm, researchers have done a series of studies, but in most cases either the fusion rules are improved or the fusion parameters are optimized, or a combination of multiple algorithms or changes in the fusion structure are performed for a single part. Those improvement cannot make active adjustments based on changes in the difference characteristics. The current dual-mode infrared image lacks the selection and combination basis of each element when constructing the fusion method, and the fusion model cannot dynamically adjust for the image difference feature, resulting in poor fusion effect. Aiming at the above problems, referring to the multi-parameters of biological characters, this paper proposes infrared intensity and polarization image mimicry fusion based on the combination of variable elements and matrix theory. Firstly, the fusion model was divided into four parts: fusion algorithm, fusion rule, fusion parameter and fusion structure. The single mapping relationship between different parts and the difference of image feature fusion is established. Secondly, using the imaginary transformation idea, the imaginary transformation fusion method was established, and the necessary four parts of the fusion process are combined to derive a new fusion algorithm. Finally, it used the different source images with different features to verify the proposed mimetic fusion algorithm. Experimental results show that when the image difference features are different, the fusion method was more suitable for deriving image features, so as to achieve the active selection and adjustment of the fusion algorithm. The fusion method dynamically adjusts the selection of each element in the fusion model using the idea of mimicry transformation, and provides a theoretical basis for its combination, so as to obtain an optimal fusion method. The proposed method gives full play to the advantages of each part and can significantly improve the fusion quality of image difference features, so that the main differences in the source images are well integrated.
-

-
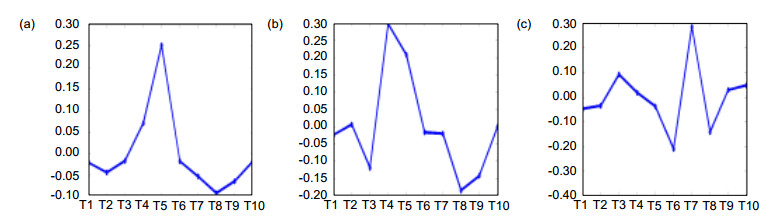
图 1 10种融合算法对不同图像特征的比较融合度。(a)融合算法针对边缘特征有效融合程度;(b)融合算法针对纹理特征有效融合程度;(c)融合算法针对亮度特征有效融合程度
Figure 1. Comparison of fusion algorithms for different image features. (a) The fusion degree of fusion algorithm for edge feature; (b) The fusion degree of fusion algorithm for texture features; (c) The fusion degree of fusion algorithm for brightness feature
图 2 4种低频融合规则对不同图像特征的比较融合度。(a)高频融合规则针对边缘特征融合程度;(b)高频融合规则针对纹理特征融合程度;(c)高频融合规则针对亮度特征融合程度
Figure 2. Comparison of four low - frequency fusion rules for different image features. (a) Fusion of high frequency fusion rules for edge feature; (b) High frequency fusion rules for texture feature fusion; (c) High frequency fusion rules for brightness feature fusion degree
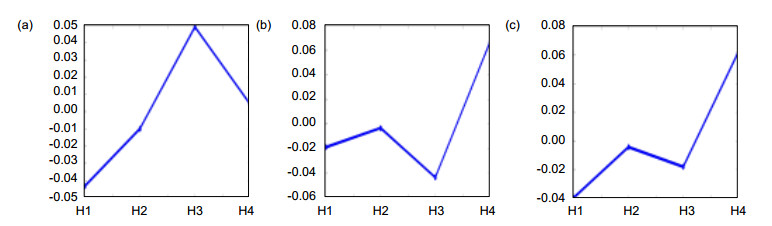
图 3 4种高频融合规则对不同图像特征的比较融合度。(a)低频融合规则针对边缘特征融合程度;(b)低频融合规则针对纹理特征融合程度;(c)低频融合规则针对亮度特征融合程度
Figure 3. Comparison of four kinds of high frequency fusion rules for different image features. (a) Low frequency fusion rule for edge feature fusion degree; (b) Low frequency fusion rules for texture feature fusion; (c) Low frequency fusion rule for brightness feature fusion degree
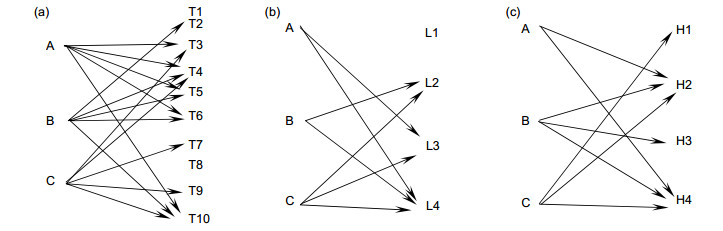
图 4 融合算法、(低频、高频)融合规则有效融合单映射图。(a)融合算法针对图像缘特征有效融合树形图;(b)低频融合规则针对图像特征有效融合树形图;(c)高频融合规则针对图像特征有效融合树形图
Figure 4. Fusion algorithm, (low frequency, high frequency) fusion rule effective fusion mapping. (a) The fusion algorithm is effective for the image edge feature; (b) The low frequency fusion rule is an effective fusion map for image features; (c) The high frequency fusion rule is an effective fusion map for image features
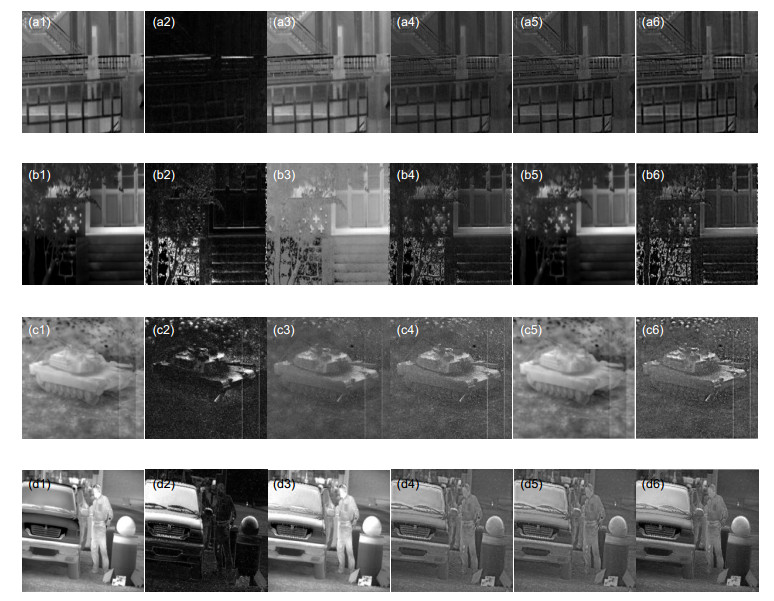
图 5 融合结构有效性实验结果。(a1)红外光强;(b1)红外偏振;(c1)串行;(d1)并行;(e1)嵌接;(a2)红外光强;(b2)红外偏振;(c2)串行;(d2)并行;(e2)嵌接
Figure 5. Experimental results of fusion structure validity. (a1) Infrared light intensity; (b1) Infrared polarization; (c1) Serial; (d1) Paralle; (e1) Embedded; (a2) Infrared light intensity; (b2) Infrared polarization; (c2) Serial; (d2) Parallel; (e2) Embedded
表 1 本文所选取10种常用融合方法
Table 1. This paper selected 10 fusion algorithms which were commonly used
符号表示 分解算法 T1 离散小波(DWT) T2 双树复小波(DTCWT) T3 顶帽分解(Top-hat) T4 非下采样剪切波(NSST) T5 非下采样轮廓波(NSCT) T6 曲线波分解(CT) T7 鲁棒主成分分析(RPCA) T8 稀疏矩阵(SR) T9 金字塔变换(LP) T10 引导滤波(GFF) 表 2 本文所选取8种典型融合规则
Table 2. Eight typical fusion rules were selected in this paper
频带 融合规则 符号表示 低频子带 加权平均 L1 邻域归一化梯度 L2 局部能量匹配 L3 区域标准差 L4 高频子带 绝对值取大 H1 局部特征匹配 H2 方向梯度算子 H3 边缘保持 H4 表 3 图 5第一组实验图像客观评价数据
Table 3. The first group of experimental images objective evaluation data of Fig. 5
串行式 并行式 内嵌式 信息熵 5.9839 6.4447 6.3264 标准差 22.3249 29.5242 28.4864 边缘强度 32.9473 44.3017 39.4146 平均梯度 3.1386 4.3687 3.8671 清晰度 3.3716 4.5031 4.1631 表 4 图 5第二组实验图像客观评价数据
Table 4. The second group of experimental images objective evaluation data of Fig. 5
串行式 并行式 内嵌式 信息熵 6.3279 6.5748 6.1010 标准差 24.9810 28.2811 23.0067 边缘强度 74.2576 85.5542 58.1074 平均梯度 7.3283 8.4076 5.8732 清晰度 8.5158 9.9143 6.5736 表 5 提取的差异特征结果
Table 5. The results of the extracted different features
标准差 粗糙度 Tamura 对比度 均值 空间频率 互信息 平均梯度 信息熵 (a1), (a2) 18.915 93.786 19.485 99.633 78.892 5.521 10.939 3.243 2.168 (b1), (b2) 1.378 107.65 4.5292 838.26 18.8577 26.0025 2.0156 7.163 0.4922 (c1), (c2) 3.5946 174.82 4.1135 504.96 84.2842 21.9329 6.1891 7.5285 0.4183 (d1), (d2) 16.612 117.21 5.4451 121.96 75.0349 4.8222 6.4946 1.3428 0.7690 表 6 归一化后的差异特征结果
Table 6. The results of the normalized different features
标准差 粗糙度 Tamura 对比度 均值 空间频率 互信息 平均梯度 信息熵 (a1), (a2) 0 -0.463 0 -0.881 -0.064 -0.788 0 -0.569 0 (b1), (b2) -0.927 -0.384 -0.768 0 -0.776 0 -0.818 -0.822 -0.773 (c1), (c2) -0.810 0 -0.789 -0.398 0 -0.156 -0.434 0 -0.807 (d1), (d2) -0.121 -0.329 -0.721 -0.885 -0.110 -0.815 -0.406 -0.049 -0.645 图 9(a) 图 9(b) (a3) (a4) (a5) (a6) 提高率/% (b3) (b4) (b5) (b6) 提高率/% 信息熵 6.9211 6.3210 6.8033 7.0297 1.57 7.1666 6.9668 7.2179 7.4122 2.69 标准差 29.8745 41.0471 27.5344 42.4889 3.51 51.2216 41.0466 51.1249 65.9690 28.97 边缘强度 64.0902 54.1903 69.0921 70.9012 2.62 109.893 95.3092 123.490 124.920 1.16 平均梯度 9.1023 6.8931 9.5870 9.6891 1.06 20.9031 18.3290 24.0912 24.8901 3.32 对比度 18.1619 18.3672 20.7563 22.4092 7.96 46.2368 45.0392 45.5714 41.9021 -9.38 图 9(c) 图 9(d) (c3) (c4) (c5) (c6) 提高率/% (d3) (d4) (d5) (d6) 提高率/% 信息熵 6.4939 6.3939 7.4952 7.5349 0.53 6.6595 6.7921 6.6012 7.0330 3.55 标准差 24.4735 55.5952 24.4569 55.0460 -0.99 28.4196 38.0187 27.3650 42.6571 12.20 边缘强度 48.0488 25.8891 46.1415 53.6570 -0.01 61.2338 22.5390 52.8918 60.4923 -1.21 平均梯度 4.7537 2.4337 4.8260 4.9316 2.19 5.9640 2.1784 5.2294 5.6973 -4.47 对比度 5.6069 5.6285 5.7833 5.8560 1.26 6.1640 4.0435 6.1783 6.7071 8.56 -
[1] 杨风暴, 蔺素珍, 王肖霞.红外物理与技术[M].北京:电子工业出版社, 2014: 257.
Yang F B, Lin S Z, Wang X X. Infrared Physics and Technology[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2014: 257.
[2] 姜会林, 江伦, 付强, 等.空间碎片偏振光谱成像探测技术研究[J].深空探测学报, 2015, 2(3): 272-277. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sktcxb201503014
Jiang H L, Jiang L, Fu Q, et al. Discussion of the polarization spectral imaging observations technology with space debris[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2015, 2(3): 272-277. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sktcxb201503014
[3] Moonon A U, Hu J W. Multi-focus image fusion based on NSCT and NSST[J]. Sensing and Imaging, 2015, 16(1): 4. doi: 10.1007/s11220-015-0106-3
[4] 李小明, 黄勤超.沙漠背景下红外偏振图像目标检测方法[J].红外技术, 2016, 38(9): 779-782. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwjs201609012
Li X M, Huang Q C. Target detection method for infrared polarization image in the background of desert[J]. Infrared Technology, 2016, 38(9): 779-782. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwjs201609012
[5] 王霞, 梁建安, 龙华宝, 等.典型背景和目标的长波红外偏振成像实验研究[J].红外与激光工程, 2016, 45(7): 0704002. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201607004
Wang X, Liang J A, Long H B, et al. Experimental study on long wave infrared polarization imaging of typical background and objectives[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2016, 45(7): 0704002. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201607004
[6] 岳振, 李范鸣.一种基于小波变换的红外偏振融合算法[J].应用光学, 2014, 35(2): 321-326. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx201402028
Yue Z, Li F M. Polarization image fusion algorithm based on wavelet transform[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2014, 35(2): 321-326. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx201402028
[7] Nencini F, Garzelli A, Baronti S, et al. Remote sensing image fusion using the curvelet transform[J]. Information Fusion, 2007, 8(2): 143-156. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2006.02.001
[8] Ma J Y, Chen C, Li C, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization[J]. Information Fusion, 2016, 31: 100-109. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2016.02.001
[9] Yang F B, Wei H. Fusion of infrared polarization and intensity images using support value transform and fuzzy combination rules[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2013, 60: 235-243. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=085c58d5b444546e549e65311bfc65a1
[10] Amolins K, Zhang Y, Dare P. Wavelet based image fusion techniques-an introduction, review and comparison[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2007, 62(4): 249-263. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2007.05.009
[11] 周强, 赵巨峰, 冯华君, 等.非下采样剪切波的红外偏振图像融合[J].浙江大学学报(工学版), 2014, 48(8): 1508-1516. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10335-1014269215.htm
Zhou Q, Zhao J F, Feng H J, et al. Infrared polarization image fusion with non-sampling shearlets[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2014, 48(8): 1508-1516. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10335-1014269215.htm
[12] Zhang L, Yang F B, Ji L N, et al. Multiple-algorithm parallel fusion of infrared polarization and intensity images based on algorithmic complementarity and synergy[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2018, 27(1): 013029. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2018JEI....27a3029Z
[13] Sappa A D, Carvajal J A, Aguilera C A, et al. Wavelet-based visible and infrared image fusion: a comparative study[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(6): 861. doi: 10.3390/s16060861
[14] 吕胜, 杨风暴, 吉琳娜.多尺度分解算法与融合规则优化组合的双模态红外图像融合[J].中国科技论文, 2017, 12(2): 161-167. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2017.02.008
Lv S, Yang F B, Ji L N. Dual-mode infrared image fusion based on the optimized combination of multi-scale decomposition and fusion rules[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2017, 12(2): 161-167. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2017.02.008
[15] Tomita M, Aoki S. Visual discrimination learning in the small octopus Octopus ocellatus[J]. Ethology, 2014, 120(9): 863-872. doi: 10.1111/eth.2014.120.issue-9
[16] Hanlon R T, Watson A C, Barbosa A. A "Mimic octopus" in the atlantic: flatfish mimicry and camouflage by Macrotritopus defilippi[J]. The Biological Bulletin, 2010, 218(1): 15-24. doi: 10.1086/BBLv218n1p15
[17] 邬江兴.拟态计算与拟态安全防御的原意和愿景[J].电信科学, 2014, 30(7): 2-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0801.2014.07.001
Wu J X. Meaning and vision of mimic computing and mimic security defense[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2014, 30(7): 2-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0801.2014.07.001
[18] 杨风暴.红外偏振与光强图像的拟态融合原理和模型研究[J].中北大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 38(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3193.2017.01.001
Yang F B. Research on theory and model of mimic fusion between infrared polarization and intensity images[J]. Journal of North University of China (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 38(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3193.2017.01.001
[19] Zhang L, Yang F B, Ji L N, et al. A categorization method of infrared polarization and intensity image fusion algorithm based on the transfer ability of difference features[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2016, 79: 91-100. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a96db848d0bb830d54bb043c2a3d2da5
[20] 陈木生.结合NSCT和压缩感知的红外与可见光图像融合[J].中国图像图形学报, 2016, 21(1): 39-44. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgtxtxxb-a201601005
Chen M S. Image fusion of visual and infrared image based on NSCT and compressed sensing[J]. Journal of image and Graphics, 2016, 21(1): 39-44. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgtxtxxb-a201601005
[21] 罗杰, 孔韦韦, 刘睿.基于NSST和区域生长的红外与可见光图像融合算法[J].中国科技论文, 2016, 11(14): 1673-1678. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2016.14.022
Luo J, Kong W W, Liu R. An infrared and visible image fusion method based on NSST and region growing algorithm[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2016, 11(14): 1673-1678. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2016.14.022
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: