Research on integrated scattering characteristics of extinctive materials for spaceborne telescopes
-
摘要
在散射理论的基础上,介绍了一种星载望远镜消光材料积分散射特性测试装置,实现对星载望远镜消光材料散射特性更为全面的测量。对积分散射理论、系统构造、系统性能进行了阐述。对系统进行建模仿真分析,得到结论:消光材料的散射特性在不同点位和入射角下存在明显差异,系统能够测量多种条件下消光材料的散射特性,并得到消光材料全面的散射特性分布。研究结果为根据消光材料特性进行针对性设计提供了更全面、更准确的散射特性分布,为杂散光的测量与抑制、高性能光学仪器的研制与装调以及计算光学等领域的研究提供了参考。为空间引力波探测星载望远镜系统的材料选型、特性研究、杂散光分析与抑制提供了基础。
Abstract
This paper presents a novel test device for evaluating the integral scattering characteristics of the extinction material in spaceborne telescopes. By employing the scattering theory, the device enables a more comprehensive measurement of the scattering characteristics, facilitating a better understanding of the material’s behavior. The paper discusses in detail the integral scattering theory, system construction, and system performance. The system is further modeled and simulated, leading to the conclusion that the scattering characteristics of the extinction material exhibit significant variations at different points and incident angles. Notably, the system is capable of measuring the scattering characteristics under various conditions, thereby providing a comprehensive distribution of the material's scattering behavior. This comprehensive and accurate scattering characteristic distribution serves as a valuable reference for targeted design, stray light measurement and suppression, development of high-performance optical instruments, and research in computational optics. Moreover, it establishes a solid foundation for material selection, characteristic investigation, stray light analysis, and suppression in spaceborne telescopes employed for the detection of gravitational waves.
-
Overview
Overview: Gravitational wave detection is a prominent and highly anticipated research area in modern science. With technological advancements and the development of scientific theories, our understanding of the techniques and methods for detecting gravitational waves has deepened. Gravitational waves are disturbances predicted by Einstein’s general theory of relativity, arising from the curvature of spacetime caused by mass and energy. The detection of gravitational waves holds significant importance in comprehending the evolution of the universe, black hole physics, and the origin of the cosmos, among other scientific inquiries. However, due to the extraordinarily weak intensity of gravitational waves, detection necessitates high-precision measurement devices and sophisticated technical means.
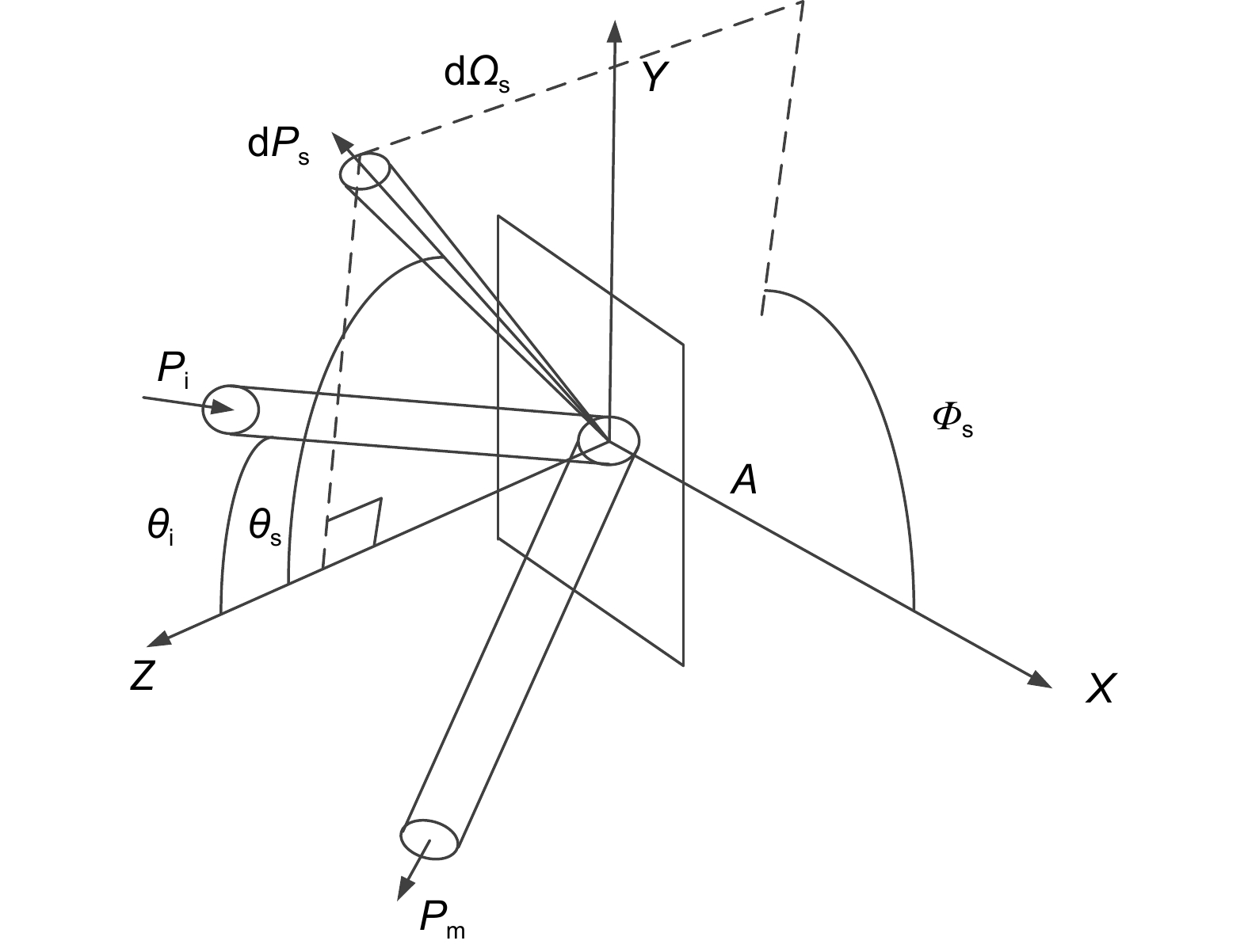
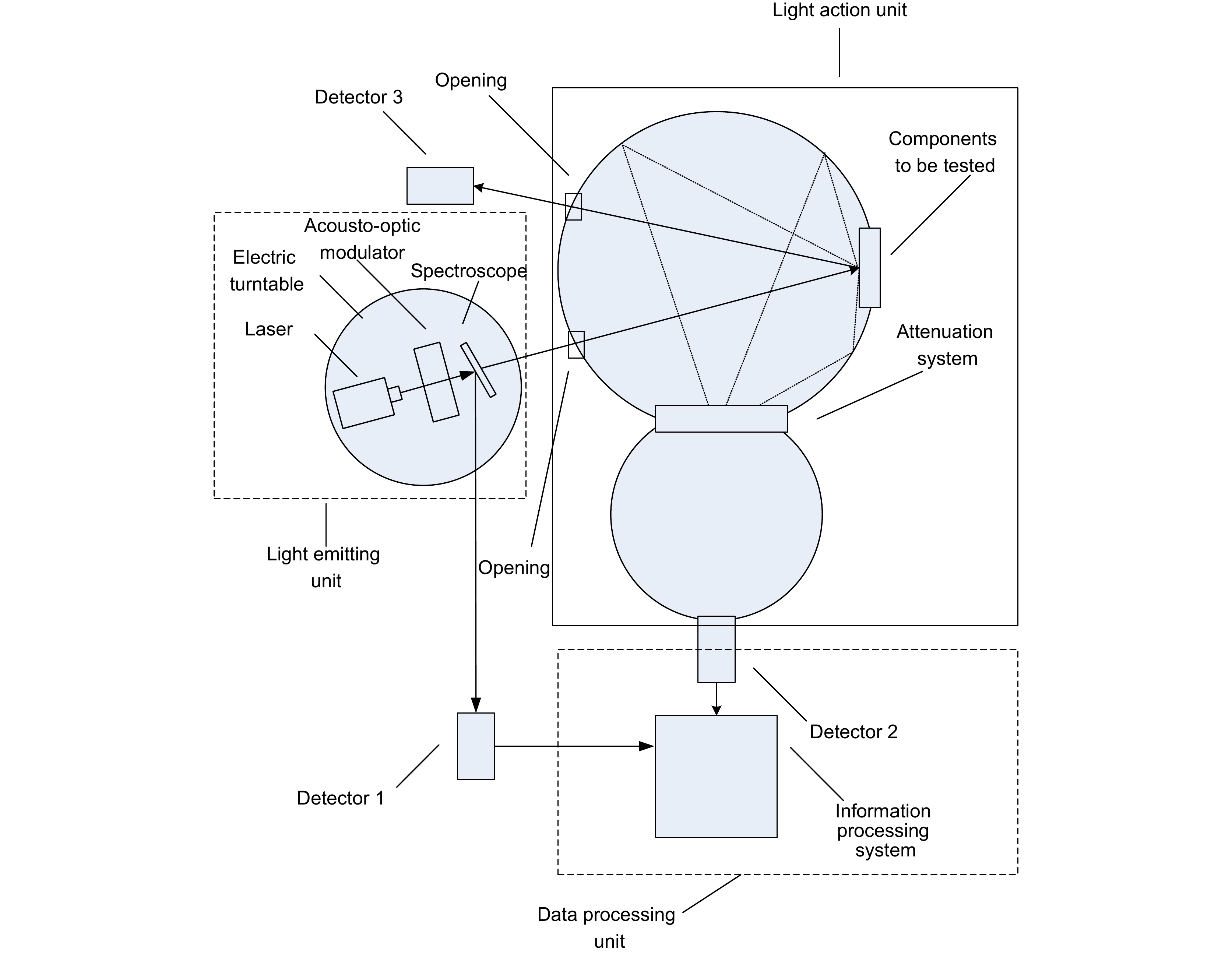
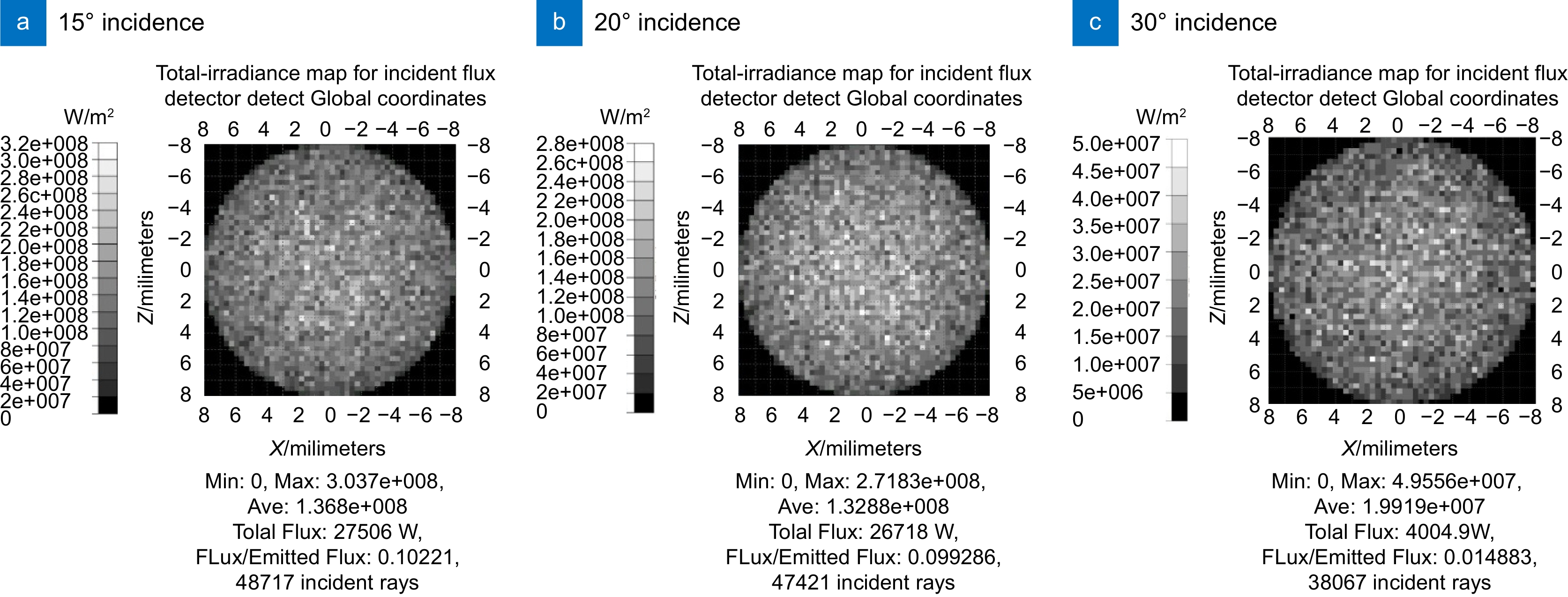
As one of the key tools for detecting gravitational waves, space-based telescopes offer advantages such as high precision, high resolution, and the ability to conduct long-duration observations. However, these telescopes encounter interference during observations, including cosmic background and scattered light generated by the telescope itself. To these interferences, extinguishing materials are used to reduce scattered light. These materials possess the ability to absorb or scatter light, effectively minimizing light reflection and scattering and thereby enhancing observation accuracy and signal-to-noise ratio of telescopes. In order to gain a better understanding of the scattering characteristics of extinguishing materials, this study analyzes and examines the design features of scattering light measurement systems both domestically and internationally, building upon the foundations of scattering theory. By combining practical detection challenges and experiences, a test device for assessing the integral scattering characteristics of extinguishing materials employed in space-based telescopes is devised, facilitating more comprehensive measurements of their scattering characteristics. Through simulation modeling and comparisons with actual measurements, it is concluded that the surface roughness of components and the incident angle of light impact the distribution of component scattering, especially in different materials where scattering characteristics demonstrate changes with increasing incident angles. Consequently, achieving precise measurements of the scattering characteristics distribution of components holds paramount importance in cutting-edge design endeavors. This research provides a more comprehensive and accurate understanding of the distribution of scattering characteristics based on the specific properties of extinguishing materials, serving as a valuable reference for stray light measurement and suppression, development and calibration of high-performance optical instruments, and research within the field of computational optics, among others. Ultimately, it establishes a foundation for material selection, characteristic exploration, stray light analysis, and suppression in the context of space-based gravitational wave detection telescopes.
-

-
Table 1. Changes in the number of rays with simulation results (SB-3)
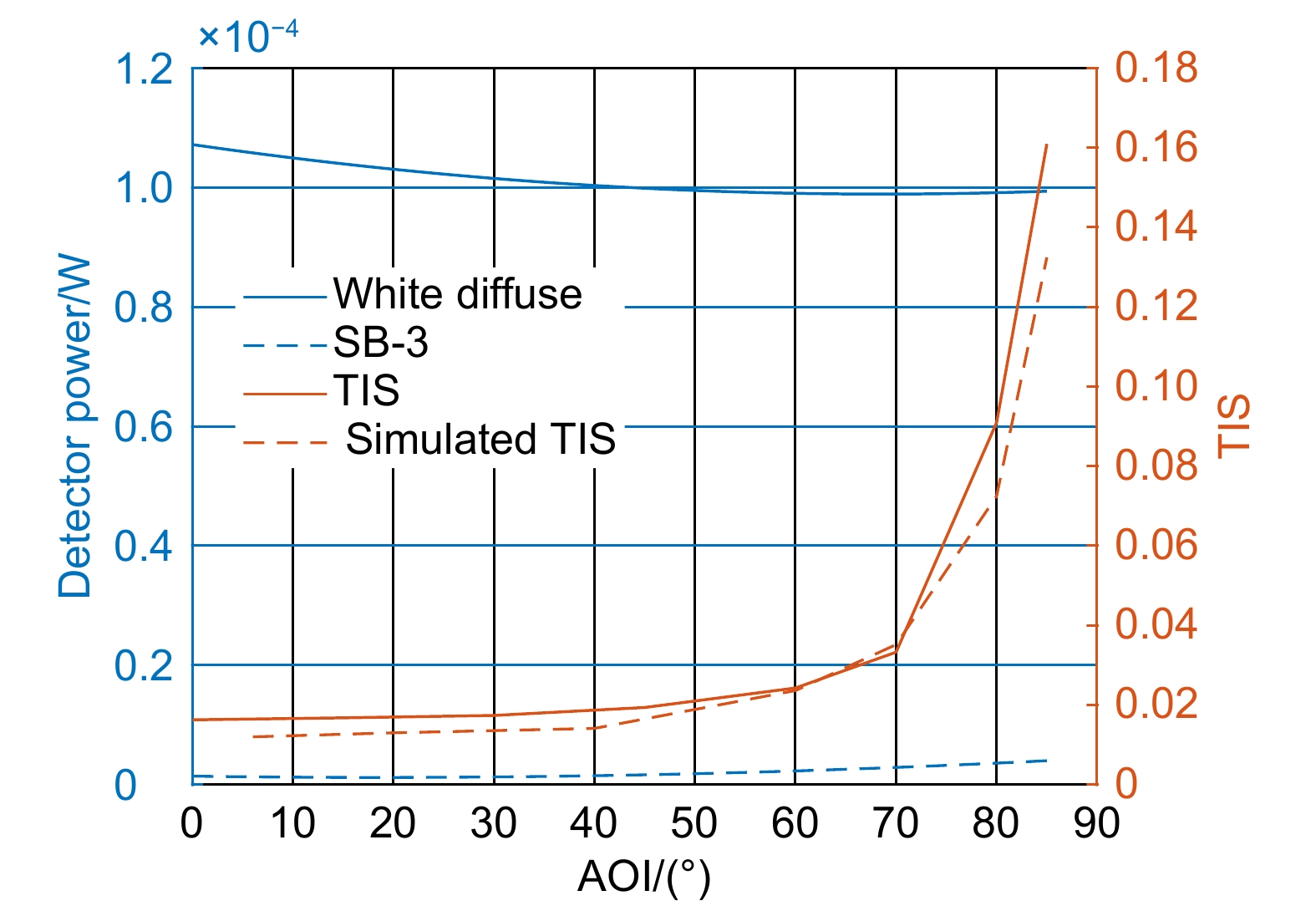
Number Number of light (rings) Detector response result 1 100 1.0908e-6 2 200 8.5724e-7 3 500 1.2615e-6 4 600 1.2585e-6 5 700 1.3414e-6 6 800 1.3944e-6 7 1000 1.2962e-6 8 1200 1.2357e-6 9 1500 1.2872e-6 Table 2. Simulation results of TIS characteristics of material surface
Incident angle Whiteboard SB-3 TIS 6° 1.0779e-4 1.2962e-6 0.01203 20° 9.8612e-5 1.2853e-6 0.01303 40° 1.0406e-4 1.4725e-6 0.01415 60° 9.7901e-5 2.317e-6 0.02366 -
参考文献
[1] Wang X Y, Bai S J, Zhang Q, et al. Research progress of telescopes for space-based gravitational wave missions[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(11): 230219. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230219
[2] Zhang Y H, Zhong Z Q, Zhang B. Analysis of surface scattering characteristics of ultra-smooth optical components in gravitational wave detection system[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(11): 230222. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230222
[3] Detrio J A, Miner S M. Standardized total integrated scatter measurements of optical surfaces[J]. Opt Eng, 1985, 24(3): 243419. doi: 10.1117/12.7973499
[4] Chen Y S. A method for measuring the total integrated scattering from laser mirrors[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 1984, 4(3): 285−288. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.1984.03.019
[5] Stover J C. Optical Scattering: Measurement and Analysis[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1990.
[6] Grochocki F, Fleming J. Stray light testing of the OLI telescope[J]. Proc SPIE, 2010, 7794: 77940W. doi: 10.1117/12.862225
[7] Liebe C C, Scherr L M. Sun-induced veiling glare in dusty camera optics[J]. Opt Eng, 2004, 43(2): 493−499. doi: 10.1117/1.1635835
[8] Peterson G L. Stray light test station for measuring point source transmission and thermal background of visible and infrared sensors[J]. Proc SPIE, 2008, 7069: 70690M. doi: 10.1117/12.794898
[9] Fest E C. Stray Light Analysis and Control[M]. Bellingham: SPIE, 2013.
[10] Liao Z B, Jiao W C, Fu R M. Veiling glare index calculation for refract optical system[J]. Acta Photonica Sin, 2011, 40(3): 424. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20114003.0424
[11] Coppens J, Franssen L, van den Berg T J T P. Reliability of the compensation comparison method for measuring retinal stray light studied using Monte-Carlo simulations[J]. J Biomed Opt, 2006, 11(5): 054010. doi: 10.1117/1.2357731
[12] Dittman M G, Donley E, Grochocki F. Deterministic sequential stray light analysis[J]. Proc SPIE, 2010, 7794: 77940T. doi: 10.1117/12.860861
[13] Ashikhmin M, Shirley P. An anisotropic phong BRDF model[J]. J Graphics Tools, 2000, 5(2): 25−32. doi: 10.1080/10867651.2000.10487522
[14] Schlick C. An inexpensive BRDF model for physically-based rendering[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 1994, 13(3): 233−246. doi: 10.1111/1467-8659.1330233
[15] Snyder W C, Wan Z M. BRDF models to predict spectral reflectance and emissivity in the thermal infrared[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens, 1998, 36(1): 214−225. doi: 10.1109/36.655331
[16] Lawrence J, Rusinkiewicz S, Ramamoorthi R. Efficient BRDF importance sampling using a factored representation[J]. ACM Trans Graphics, 2004, 23(3): 496−505. doi: 10.1145/1015706.1015751
[17] Boynton P A, Kelley E F. Stray light compensation in small area contrast measurements of projection displays[J]. Proc SPIE, 2002, 4657: 122−130. doi: 10.1117/12.463788
[18] Zhong X, Jia J Q. Stray light removing design and simulation of spaceborne camera[J]. Opt Precis Eng, 2009, 17(3): 621−625. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.2009.03.025
[19] Leviton D B, Gardner L D, Fineschi S, et al. White-light stray light test of the SOHO UVCS[J]. Proc SPIE, 1998, 3443: 50−60. doi: 10.1117/12.333613
[20] Fleming J, Grochocki F, Finch T, et al. New stray light test facility and initial results[J]. Proc SPIE, 2008, 7069: 70690O. doi: 10.1117/12.798920
[21] Blarre L, Mestreau A. Stray light characterization of optical systems[J]. Proc SPIE, 1996, 2775: 279−286. doi: 10.1117/12.246755
[22] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 光学系统杂(散)光测量方法: GB/T 10988–2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Veiling glare of optical systems-methods of measurement: GB/T 10988–2009[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009.
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: